G.O. Diagnosis
1) A 16-year-old girl presents to the emergency department complaining of fever, chills, abdominal pain, and vaginal bleeding. She gives a history of unprotected sexual activity with her 17-year-old boyfriend over the past several months. Her last menstrual period was 8 weeks ago. She reports having a dilatation and curettage procedure at an unlicensed abortion clinic recently to try to abort the pregnancy. Her temperature is 38.7C (101.7F), heart rate is 120/min, and blood pressure is 100/70 mmHg. Pelvic examination reveals cervical motion tenderness, tissue in the internal os, and foul-smelling vaginal discharge. Urine is positive for β-human chorionic gonadotropin. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Ectopic pregnancy
Pelvic abscess
Septic abortion
Threatened abortion
Vaginal laceration
2) A 19-year-old G0 woman presents to her family physician complaining of dysmenorrhea for the past year. She reports severe right-sided pain that coincides with days 1–5 of her menstrual cycle. Her menses occur regularly every 28 days, and she requires three to four pads per day for the first 2 days of her bleeding and one to two pads per day for the remainder. She has never had surgery. She is not sexually active and does not smoke. Her last menstrual period was 1 week ago. Her temperature is 36.7C (98.1F), blood pressure is 121/74 mmHg, heart rate is 80/min, and respiratory rate is 14/min. Physical examination reveals a thin, healthy-appearing young woman. Pelvic examination reveals a normal sized uterus and no cervical motion tenderness. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Ectopic pregnancy
Endometriosis
Leiomyoma
Pelvic inflammatory disease
Polycystic ovarian syndrome
3) After an appropriate diagnostic evaluation, a 59-year-old woman with postmenopausal bleeding had a total abdominal hysterectomy and bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy (TAH-BSO). The pathologic diagnosis is adenocarcinoma of the endometrium. An endometrial adenocarcinoma that is confined to the uterus and extends more than 50% through the myometrium is at which stage?
IC
IIA
IIB
IIIA
IVA
4) A 39-year-old woman at 16 weeks’ gestation complains of headaches, blurred vision, and epigastric pain. Her blood pressure is now 156/104 mmHg. Her uterine fundus is palpable 22 cm above her symphysis pubis. Fetal heart tones could not be heard with a handheld Doppler. She has 3+proteinuria. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Anencephaly
Twin gestation
Maternal renal disease
Hydatidiform mole
Gestational diabetes mellitus
5) A 39-year-old G3P3 complains of severe, progressive secondary dysmenorrhea and menorrhagia. Pelvic examination demonstrates a tender, diffusely enlarged uterus with no adnexal tenderness. Results of endometrial biopsy are normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Endometriosis
. Endometritis
. Adenomyosis
. Uterine sarcoma
. Leiomyoma
6) A 28-year-old G3P0 has a history of severe menstrual cramps, prolonged, heavy periods, chronic pelvic pain, and painful intercourse. All of her pregnancies were spontaneous abortions in the first trimester. A hysterosalpingogram (HSG) she just had as part of the evaluation for recurrent abortion showed a large uterine septum. You have recommended surgical repair of the uterus. Of the patient’s symptoms, which is most likely to be corrected by resection of the uterine septum?
. Habitual abortion
. Dysmenorrhea
. Menometrorrhagia
. Dyspareunia
. Chronic pelvic pain
7) A 22-year-old woman presents with mouth sores, sore throat, vaginal discharge, fever, and myalgia. She has no other medical problems. She takes oral contraceptive pills. She is in a monogamous relationship and states that her partner occasionally uses barrier contraception. Physical examination reveals a temperature of 38.3 C (101 F), cervical and inguinal lymphadenopathy, exudative pharyngitis, and multiple ulcers on the oral mucosa, the labia, and cervix. The vaginal discharge is profuse, and Gram stain indicates many neutrophils. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Chancroid
Condyloma acuminatum
Herpes simplex virus
Lymphogranuloma venereum
Syphilis
8) A 14-year-old Caucasian female presents to clinic for a routine check-up. She complains that her menstrual cycles are irregular and that her menses last seven to ten days. She underwent menarche one year ago and her last menstrual period was two weeks ago. She eats a balanced diet and works out in a gym on weekends. Her past medical history is insignificant and her BMI is 25 kg/m2. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's complaints?
. Endometrial stimulation by progesterone
. Complex atypical hyperplasia of the endometrium
. Absent ovulation
. Increased FSH secretion
. Endometrial atrophy
9) A 32-year-old female with a history of amenorrhea develops white nipple discharge. She eats a balanced diet and exercises regularly. She is not sexually active. Her family history is significant for her mother dying of breast cancer at age 50. The most likely diagnosis in this patient is:
. Fibrocystic breast disease
. Fibroadenoma
. Intraductal papilloma
. Lobular breast carcinoma
. Pituitary adenoma
10) A 37-year-old female presents to your clinic complaining of lower abdominal discomfort. On bimanual examination the uterus is enlarged. Biopsy reveals normal appearing endometrial glands within the myometrium. The most likely diagnosis is:
. Leiomyoma
. Endometrial carcinoma
. Adenomyosis
. Endometriosis
. Ectopic pregnancy
11) A 75-year-old woman presents with a pruritic vulvar lesion. Physical examination reveals an irregular white, rough area involving her vulva. Biopsies from this area reveal a combination of squamous hyperplasia of the epidermis (acanthosis) with hyperkeratosis and mild dermal inflammation. No atrophy or dysplasia of the epidermis is seen. What is the best diagnosis?
. Balanitis xerotica obliterans
. Bowen disease
. Lichen sclerosus
. Lichen simplex chronicus
. Paget disease
12) A 65-year-old woman presents with a pruritic red, crusted, sharply demarcated map-like lesion involving a large portion of her labia majora. Histologic sections from this lesion reveal individual anaplastic tumor cells infiltrating the epidermis. Distinctive clear spaces are noted between these anaplastic cells and the surrounding normal epithelial cells. These malignant cells stain positively for mucin and negatively with S100. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Clear cell adenocarcinoma
. Malignant melanoma
. Extramammary Paget disease
. Sarcoma botryoides
. Squamous cell carcinoma
13) A 39-year-old woman presents with severe menorrhagia and colicky dysmenorrhea. A hysterectomy including resection of the fallopian tubes and ovaries is performed. Examination by the pathologist finds a right adnexal cyst measuring approximately 2.3 cm in diameter and filled with clotted blood. Microscopic examination reveals the presence in the wall of the cyst of endometrial glands, stroma, and hemosiderin pigment. What is the best diagnosis?
. Adenomyosis
. Endometriosis
. Hydatid cyst
. Hydatidiform mole
. Luteal cyst
14) A 23-year-old woman presents with urinary frequency and abnormal uterine bleeding. A careful medical history finds that her abnormal menstrual bleeding is characterized by excessive bleeding at irregular intervals. A pelvic examination finds a single mass in the anterior wall of the uterus, this being confirmed by ultrasonography. Which one of the following clinical terms best describes the abnormal uterine bleeding in this woman?
. Amenorrhea
. Dysmenorrhea
. Menometrorrhagia
. Oligomenorrhea
. Polymenorrhea
15) A 25-year-old woman presents with lower abdominal pain, fever, and a vaginal discharge. Pelvic examination reveals bilateral adnexal (ovarian) tenderness and pain when the cervix is manipulated. Cultures taken from the vaginal discharge grow Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient’s adnexal pain?
. Adenomatoid tumor
. Ectopic pregnancy
. Endometriosis
. Luteoma of pregnancy
. Pelvic inflammatory disease
16) A 28-year-old primigravid woman at 34 weeks gestation is brought to the emergency department following a motor vehicle accident. She had intense abdominal pain and became agitated and restless in the ambulance. She has mild vaginal bleeding and diffuse abdominal pain. She is on continuous fetal heart monitoring. Her prenatal course, prenatal tests and fetal growth have been normal. Prenatal ultrasound at the 16th week showed no abnormalities and an intrauterine gestation consistent with dates. Her blood pressure is 110/60mmHg, pulse is 110/min and respirations are 32/min. Physical examination shows hyperventilation, cold extremities and a distended abdomen with irregular contours. Fetal heart monitoring shows repetitive late decelerations and a long-term variability of 2 cycles/min. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Abruptio placenta
. Placenta previa
. Vasa previa
. Uterine rupture
. Rupture of ectopic pregnancy
17) A 22-year-old, gravida 1, para 0, at 13 weeks gestation is brought to the emergency department because of vaginal discharge and lower abdominal discomfort. She has had no passage of tissue from her vagina. She does not use tobacco, alcohol or drugs. She has no history of trauma. Her temperature is 37.0C (98.7F), blood pressure is 128/80 mmHg, pulse is 76/min and respirations are 14/min. Physical examination shows a closed cervix, a slightly tender uterus with a size consistent with gestational age, free adnexae and scant bright red bleeding from the introitus. Ultrasonogram in the emergency department shows normal fetal heart motion. She is anxious and concerned about her baby. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Incomplete abortion
. Threatened abortion
. Completed abortion
. Inevitable abortion
. Ectopic pregnancy
18) A 32-year-old woman, gravida 3, para 2, at 38 weeks gestation is admitted to the hospital for labor pains. Her prenatal course, prenatal tests and fetal growth have been normal. Prenatal ultrasound at the 16th week showed no abnormalities and an intrauterine gestation consistent with dates. In her second pregnancy, she had to undergo cesarean section. The woman is admitted to the delivery room and fetal heart and uterine contraction monitoring is started. Her blood pressure is 100/60mmHg, pulse is 115/min and respirations are 26/min. Pelvic examination shows the cervix is 60% effaced and 6cm dilated. Uterine contractions are regular and occurring every 4 minutes. Fetal heart tracing shows no abnormalities. Suddenly, the patient starts complaining of an intense lower abdominal pain. She is restless and vaginal bleeding is noted. Fetal heart monitoring shows variable decelerations, and the fetus has shifted to the ‘-2' station from '0' station Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Placental abruption
. Vasa previa
. Uterine rupture
. Endometritis
. Bladder distention
19) A 25-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, at 32 weeks gestation is brought to the emergency department because of acute onset severe uterine contractions and moderate vaginal bleeding. Her first pregnancy was uncomplicated. She has a history of cocaine addiction but she is now participating in a drug rehabilitation program. Ultrasonogram performed at the 16th week showed no abnormalities and an intrauterine gestation consistent with dates. Her temperature is 37.0 C (98.7F), blood pressure is 130/80 mmHg, pulse is 90/min and respirations are 15/min. Physical examination shows uterine tenderness, hyperactivity, and increased uterine tone. Fetal heart tracing shows 140/min with good long-term and beat-to-beat variability. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Abruptio placenta
. Placenta previa
. Vasa previa
. Uterine rupture
. Normal labor
20) During the evaluation of infertility in a 25-year-old female, a hysterosalpingogram showed evidence of Asherman syndrome. Which one of the following symptoms would you expect this patient to have?
. Hypomenorrhea
. Oligomenorrhea
. Menorrhagia
. Metrorrhagia
. Dysmenorrhea
21) A 29-year-old woman presents with complaints of a vaginal discharge. She has had two sexual partners over the past 4 weeks, and she reports that she uses oral contraceptives and that her partners were not using condoms. Examination shows she is afebrile, with no lymphadenopathy. Pelvic examination shows no ulcers, but a thick white discharge is noted at the cervical os on speculum examination. A Gram stain of the discharge reveals gram negative diplococci. A sample of the discharge is also sent out for culture. The patient is appropriately treated and returns unhappily 3 weeks later with identical symptoms. A Gram stain of the discharge is again done, and this time reveals no organisms. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her symptoms?
Noncompliance with antibiotic therapy
Reinfection due to an occult urethral source
Reinfection from an untreated sexual partner
A resistant strain of the original organisms
An undetected, underlying immunosuppression
22) An 18-year-old woman presents with amenorrhea and is found to have normal secondary sex characteristics and normal-appearing external genitalia. Her first menstrual period was at age 13, and her cycle has been unremarkable until now. She states that her last menstrual period was 8 weeks prior to this visit. A urine test for hCG is positive. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Ectopic pregnancy
. Intrauterine pregnancy
. Stein-Leventhal syndrome
. Turner syndrome
. Weight loss syndrome
23) A 24-year-old woman delivers a normal 8-lb baby boy at 40 weeks of gestation. She has no history of drug abuse, and her pregnancy was unre-markable. Examination had revealed the placenta to be located normally, but following delivery the woman fails to deliver the placenta and subsequently develops massive postpartum hemorrhage and shock. Emergency surgery is performed to stop the bleeding. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her postpartum bleeding?
. An abruptio placenta
. A placenta previa
. A placenta accreta
. A hydatidiform mole
. An invasive mole
24) A 26-year-old woman develops acute lower abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding. While in the bathroom she passes a cast of tissue composed of clot material and then collapses. She is brought to the hospital, where a physical examination reveals a soft, tender mass in right adnexa and pouch of Douglas. Histologic examination of the tissue passed in the bathroom reveals blood clots and decidualized tissue. No chorionic villi or trophoblastic tissue are present. Which of the following conditions is most likely present in this individual?
. Aborted intrauterine pregnancy
. Complete hydatidiform mole
. Ectopic pregnancy
. Endometrial hyperplasia
. Partial hydatidiform mole
25) A 26-year-old woman in the third trimester of her first pregnancy develops persistent headaches and swelling of her legs and face. Early during her pregnancy, a physical examination was unremarkable; however, now her blood pressure is 170/105 mmHg and urinalysis reveals slight proteinuria. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Eclampsia
. Gestational trophoblastic disease
. Nephritic syndrome
. Nephrotic syndrome
. Preeclampsia
26) A 22-year-old nulliparous woman has recently become sexually active. She consults you because of painful coitus, with the pain located at the vaginal introitus. It is accompanied by painful involuntary contraction of the pelvic muscles. Other than confirmation of these findings, the pelvic examination is normal. Which of the following is the most common cause of this condition?
. Endometriosis
. Psychogenic causes
. Bartholin gland abscess
. Vulvar atrophy
. Ovarian cyst
27) A 35-year-old African-American marathon runner presents to the gynecologist complaining of secondary amenorrhea that developed three months ago. Her cycles are normally 28 days long, and her menses last three to five days with moderate flow. One year ago, the woman adopted a vigorous exercise regimen that lasted between three and five hours every day. Since then, her BMI has declined from 23.4 to 16.5. She has been winning many local races and is considering increasing the difficulty of her exercise regimen, but would like to address the issue of her amenorrhea first. Physical examination reveals a thin woman with well-defined musculature but is otherwise unremarkable. Pregnancy test is negative. What is the most likely etiology of her amenorrhea?
. Kwashiorkor
. Testosterone deficiency
. Estrogen deficiency
. Progesterone deficiency
. Prolactin excess
28) A 38-year-old Caucasian female presents to the office complaining of lethargy, weight gain and fatigue. She denies headaches, pruritus or urine discoloration. She just gave birth 2 months ago via vaginal delivery; her baby is in good health and receives formula nutrition. Her delivery was complicated by vaginal bleeding that required blood transfusion, and postpartum endometritis that rapidly responded to antibiotics. She has not had any menstrual periods following delivery. Physical examination shows sparse pubic hair, dry skin and delayed tendon reflexes. Urinalysis shows no glucose or ketones. Which of the following is most likely to be responsible for this patient's condition?
. Infiltrative disorder
. Autoimmune tissue destruction
. Ischemic necrosis
. Drug effect
. Neoplasia
29) A 24-year-old gravida 2, para 1, African American woman at 12 weeks gestation comes for her first prenatal visit. Except for early morning mild headaches and nausea she has no other symptoms. Physical examination shows mild bilateral ankle edema. Blood pressure is measured twice 15 minutes apart and is 150/96 mmHg on both occasions. Blood is drawn for laboratory tests and the patient is sent home with a follow-up appointment 3 days later. She returns 3 days later and repeat blood pressure is the same. Laboratory studies show: Urinalysis: Protein: negative; Blood: negative; Glucose: negative; Ketones: negative; Leukocyte esterase: negative; Nitrites: negative; WBC:1-2/hpf; RBC: 1-2/hpf. Chemistry panel: Serum sodium: 150 mEq/L; Serum potassium: 2.5 mEq/L; Chloride: 100 mEq/L; Bicarbonate: 23 mEq/L; Blood urea nitrogen (BUN): 14 mg/dL; Serum creatinine: 0.8 mg/dL. Ultrasonogram reveals intrauterine gestation consistent with dates; no abnormalities noted. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Preeclampsia
. Chronic hypertension
. Molar pregnancy
. Transient hypertension of pregnancy
. Normal pregnancy
30) A 27-year-old female at 30 weeks gestation complains of difficulty hearing, especially on the right side. She denies any ear pain or discharge. Her pregnancy was complicated by acute pyelonephritis at 22 weeks gestation, which was treated with antibiotics. She does not smoke or consume alcohol, and she eats a balanced diet. She has no preexisting medical problems and takes no medications aside from a multivitamin. Her blood pressure is 160/100 mmHg and heart rate is 75/min. Cardiac and pulmonary examinations are unremarkable. No focal abnormalities are found on neurologic examination. When a tuning fork is placed on the right mastoid process, she appreciates the tone louder than when it is held near the external auditory meatus. Audiometry shows right low-frequency hearing loss. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's complaints?
. Antibiotic treatment
. Hypertension of pregnancy
. Meniere's disease
. Otosclerosis
. Chronic otitis media
31) You are asked to consult on a 31-year-old woman who is at 26 weeks’ gestation and who has had fever for 2 days. She states that she starting feeling fevers and chills approximately 3 days ago. These symptoms have worsened since that time and she has also experienced myalgias, back pain, malaise, and upper respiratory complaints. She was initially diagnosed with the flu, but her condition seems to be worsening. Her prenatal course has been otherwise uncomplicated. She has no past medical or surgical history. Her past obstetric history is significant for a normal spontaneous vaginal delivery 3 years ago. She takes no medications and is allergic to sulfa drugs. Her physical examination is significant for a temperature of 38.3 C (101.0 F) and mild abdominal tenderness. Her urine culture is negative. Her obstetrician performed an amniocentesis yesterday that demonstrated gram-positive rods. Which of the following is the most likely causative organism?
. Clostridium difficile
. Escherichia coli
. Lactobacillus bulgaricus
. Listeria monocytogenes
. Neisseria gonorrhoeae
32) A 54-year-old woman comes to the physician for an annual examination. She has no complaints. For the past year, she has been taking tamoxifen for the prevention of breast cancer. She was started on this drug after her physician determined her to be at high risk on the basis of her strong family history, nulliparity, and early age at menarche. She takes no other medications. Examination is within normal limits. Which of the following is this patient most likely to develop while taking tamoxifen?
. Breast cancer
. Elevated LDL cholesterol
. Endometrial changes
. Myocardial infarction
. Osteoporosis
33) A 24-year-old woman comes to the physician because of right lower quadrant abdominal pain. She has had the pain off and on for the past month, but it is now increasing. She has no other symptoms and no medical problems. Examination reveals a mildly tender, right adnexal mass. Pelvic ultrasound shows a 7 cm right adnexal complex cyst. Urine hCG is negative. The patient is taken to the operating room for laparotomy and right ovarian cystectomy. Microscopically the cyst has cartilage, adipose tissue, intestinal glands, hair, and a calcification that appears to be a tooth. There is also a large amount of thyroid tissue. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Corpus luteum
. Ectopic pregnancy
. Gastric carcinoma
. Struma ovarii
. Thyroid carcinoma
34) A 60-year-old woman comes to the physician for an annual examination. She has no complaints. She had her last menstrual period at age 55 and has had no vaginal bleeding since. She has no medical problems and has never had surgery. She takes no medications and has no allergies to medications. The physical examination is unremarkable. She is concerned about cancer and wants to know which type is the major cause of cancer death in women. Which of the following is the correct response?
. Breast cancer
. Cervical cancer
. Endometrial cancer
. Lung cancer
. Ovarian cancer
35) A 36-year-old primigravid woman at 36 weeks' gestation comes to the physician for a prenatal visit. She is experiencing good fetal movement and has had no loss of fluid, bleeding from the vagina, or contractions. She has no complaints. Her past medical history is significant for mitral stenosis, which she developed after an episode of rheumatic fever as a child. She also has asthma for which she uses an albuterol inhaler daily. She has herpes outbreaks approximately once a year. At her last visit she was found to be positive for Group B Streptococcus colonization. For which of the following disease processes would this patient benefit by having a forceps-assisted vaginal delivery at the time of delivery?
. Asthma
. Group B Streptococcus (GBS) colonization
. Herpes
. Mitral stenosis
. This patient would not benefit from a forceps-assisted vaginal delivery
36) A 14-year-old girl comes to the office for a health maintenance evaluation. She is concerned that she has not yet started her menstrual cycle. Her height has increased by 3 inches since her last visit 1 year ago, and her weight is up by 10 pounds. On physical examination, the physician notes a general enlargement of her breasts and areola. Examination of her genital area reveals pubic hair that is coarse and dark and extends past the medial border of the labia. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Constitutional delay
. Dysfunctional uterine bleeding
. Dysmenorrhea
. Primary amenorrhea
. Secondary amenorrhea
37) A 27-year-old primigravid woman at 10 weeks gestation is brought to the emergency department because of vaginal bleeding and cramping lower abdominal pain. She continues to have cramping in the ER. Her temperature is 37.0 C (98.7 F), blood pressure is 100/76 mmHg, pulse is 84/min and respirations are 14/min. Physical examination shows an effaced and dilated cervix. Gestational tissue is visualized through the internal cervical os. Bimanual examination shows the uterus is soft and enlarged, and vaginal bleeding is seen. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Inevitable abortion
. Threatened abortion
. Molar pregnancy
. Complete abortion
. Missed abortion
38) A 30-year-old G2P2 woman comes to the physician with fatigue, mood swings, irritability, breast tenderness, abdominal bloating, and headaches that occur monthly. The symptoms are worse just before her menses and resolve by the third day of her menstrual cycle. The symptoms interfere with her daily activities, including her proficiency at work. The patient's only current medication is a multivitamin. She uses spermicidal foam and condoms for birth control. Her menses are regular. Her sister was diagnosed with hypothyroidism and takes levothyroxine. Examination shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her symptoms?
. Menopausal transition
. Migraine
. Normal menstrual cycle
. Premenstrual syndrome
. Somatization
39) At a follow-up routine prenatal visit, the uterine fundus of a healthy 23-year-old pregnant woman is palpated halfway between her symphysis pubis and umbilicus. Which of the following is the most appropriate test to order at this stage of her pregnancy?
Serum human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) titer
Glucose tolerance test
Amniocentesis
Maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein (MSAFP)
Cervical culture for group B Streptoccus (GBS)
40) A 25-year-old woman in her 15th week of pregnancy presents with uterine bleeding and passage of a small amount of watery fluid and tissue. She is found to have a uterus that is much larger than estimated by her gestational dates. Her uterus is found to be filled with cystic, avascular, grapelike structures that do not penetrate the uterine wall. No fetal parts are found. Immunostaining for p57 was negative in the cytotrophoblasts and villi mesenchyme. Which of the following is the best diagnosis?
. Partial hydatidiform mole
. Complete hydatidiform mole
. Invasive mole
. Placental site trophoblastic tumor
. Choriocarcinoma
41) A 24-year-old woman delivered a healthy baby by vaginal delivery at 36 weeks gestation. She had a prolonged premature rupture of the membranes, and mid forceps application was required during delivery. On the second postpartum day she complained of fever and chills. She cannot breast-feed because her "nipples are tender". Her temperature is 38.5C (101.3F), blood pressure is 120/55 mmHg and pulse is 92/min. Bimanual examination shows tender uterus and foul-smelling lochia. Her nipples are cracked but without surrounding erythema or warmth. Physical examination otherwise shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Normal postpartum
. Puerperal mastitis
. Endometritis
. Deep venous thrombosis
. Aspiration pneumonia
42) A 20-year-old, G1 PO, woman at 35 weeks gestation comes to the hospital because of regular uterine contractions. She noticed a passage of clear fluid per vagina for the past 24 hours. She has no other symptoms. Her pregnancy thus far has been uncomplicated. Her temperature is 38.2 C (100.7 F), blood pressure is 120/68 mmHg, pulse is 110/min and respirations are 17/min. Speculum examination shows a closed cervix and clear fluid pooling in the vaginal fornix. The pH of the fluid is 7.5. Fetal heart monitoring shows a rate of 165/min and uterine contractions occurring every 3-4 minutes. Initial laboratory studies show: Hemoglobin: 10.2 g/L; Platelets: 198,000/mm3; Leukocyte count: 18,500/mm3; Neutrophils: 86%; Lymphocytes: 14%. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Abruptio placenta
. Intraamniotic infection
. Urinary tract infection
. Trichomonas vaginitis
. Normal labor
43) A 37-year-old woman comes to the physician for evaluation of infertility. She and her 39-year-old husband have not been able to conceive after 13 months of unprotected and frequent intercourse. She has 28-day regular menstrual cycles. The patient had a pregnancy with her husband at age 31. She has no other genitourinary complaints such as menorrhagia, dyspareunia or pelvic pain. She has no previous history of sexually transmitted diseases or abdominal surgery. The patient does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. She is an aerobics instructor and teaches 230-minute classes daily. Her blood pressure is 130/80 mm Hg and pulse is 84/min. Her body mass index is 23 kg/m2. Complete physical examination is unremarkable. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her condition?
. Adrenal hyperplasia
. Decreased ovarian reserve
. Intense exercise
. Premature ovarian failure
. Uterine leiomyomas
44) A 20-year-old, G1PO, woman at 35 weeks gestation comes to the hospital because of regular uterine contractions and passage of clear fluid per vagina. She has no other symptoms. Her pregnancy thus far has been uncomplicated. Her temperature is 38.2 C (100.7 F), blood pressure is 120/68 mmHg, pulse is 110/min and respirations are 17/min. Speculum examination shows a closed cervix and clear fluid pooling in the vaginal fornix. The pH of the fluid is 7.5. Fetal heart monitoring shows a rate of 165/min and uterine contractions occurring every 3-4 minutes. Initial laboratory studies show: Hemoglobin 10.2 g/L; Platelets 198,000/mm3; Leukocyte count 18,500/mm3; Neutrophils 86%; Lymphocytes 14%. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Abruptio placenta
. Intraamniotic infection
. Urinary tract infection
. Trichomonas vaginitis
. Normal labor
45) A 40-year-old G3P3 comes to your office for a routine annual GYN examination. She tells you that she gets up several times during the night to void. On further questioning, she admits to you that during the day she sometimes gets the urge to void, but sometimes cannot quite make it to the bathroom. She attributes this to getting older and is not extremely concerned, although she often wears a pad when she goes out in case she loses some urine. This patient is very healthy otherwise and does not take any medication on a regular basis. She still has regular, monthly menstrual periods. She has had three normal spontaneous vaginal deliveries of infants weighing between 7 and 8 lb. An office dipstick of her urine does not indicate any blood, bacteria, WBCs, or protein. Her urine culture is negative. Based on her office presentation and history, which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Urinary stress incontinence
. Urinary tract infection
. Overflow incontinence
. Bladder dyssynergia
. Vesicovaginal fistula
46) An 18-year-old G0 comes to see you complaining of a 3-day history of urinary frequency, urgency, and dysuria. She panicked this morning when she noticed the presence of bright red blood in her urine. She also reports some midline lower abdominal discomfort. She had intercourse for the first time 5 days ago and reports that she used condoms. On physical examination, there are no lacerations of the external genitalia, there is no discharge from the cervix or in the vagina, and the cervix appears normal. Bimanual examination is normal except for mild suprapubic tenderness. There is no flank tenderness, and the patient’s temperature is normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Chlamydia cervicitis
. Pyelonephritis
. Acute cystitis
. Acute appendicitis
. Monilial vaginitis
47) A 17-year-old teenage girl presents to your office with a 10-month history of lower abdominal pain that radiates to the upper thighs and back. The pain is colicky in nature and usually starts a few hours prior to menses, lasting 3-4 days. Menses have occurred at regular 28-day intervals over the past 2 years. She has no inter-menstrual bleeding. She became sexually active 6-months ago and does not use contraception. Physical examination shows healthy external genitalia and well-developed secondary sexual characteristics; the uterus is normal in size and freely mobile. Examination shows no other abnormalities. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her pelvic pathology?
. Ureteric stone
. Pelvic infection
. Abnormal myometrial growth
. Increased prostaglandins
. Ectopic endometrial implants
48) You have diagnosed a healthy, sexually active 24-year-old female patient with an uncomplicated acute urinary tract infection. Which of the following is the likely organism responsible for this patient’s infection?
. Chlamydia
. Pseudomonas
. Klebsiella
. Escherichia coli
. Candida albicans
49) A 15-year-old girl is being evaluated for primary amenorrhea. She has no other symptoms. She has not been sexually active. She has no other medical problems and does take any medication. Her family history is unremarkable. On examination, you note fully developed breasts and absent axillary and pubic hair. External genitalia have a normal appearance, but the vagina is abnormally short and blind ended. Initial work-up reveals no uterus on ultrasound, a testosterone level of 400 ng/dl (Normal is 20-80 for a female), and a 46 XY karyotype. Which of the following events is most likely to have caused the absence of in utero development of the internal reproductive organs?
. Absence of mullerian inhibiting factor
. Presence of mullerian inhibiting factor
. Agenesis of Wolffian ducts
. Agenesis of mullerian ducts
. Testosterone surge
50) A previously healthy 50-year-old gravida 5, para 4, Caucasian woman comes to the physician complaining of passing small amounts of urine while sneezing or coughing for the past five months. She denies any episodes of weakness, numbness or fecal incontinence. There is no history of dysuria, increased frequency of urination, or hematuria. Her symptoms are progressively getting worse. Her other medical problems include diabetes mellitus type 2 diagnosed 3 years ago, treated with glyburide 2.5mg/day. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or drugs, and has no known drug allergies. She mentions that she is an avid jogger, but her problem causes her significant embarrassment. She now has to wear absorbent pads while jogging. Her vital signs are within normal limits. On examination, the abdomen is soft. Neurological examination is within normal limits. Pelvic examination shows a cystocele. The patient's labs reveal: Urine: Specific gravity: 1.020, Blood: negative, Glucose: negative, Leukocyte esterase: negative, Nitrites: negative, WBC: 5-10/hpf, Bacteria: none. Random blood sugar is 120 mg/dl. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her symptoms?
. Detrusor instability
. Interstitial cystitis
. Overflow incontinence due to detrusor weakness
. Overflow incontinence due to medication
. Pelvic floor muscle weakness
51) A 34-year-old primigravida develops severe postpartum bleeding requiring aggressive volume resuscitation and transfusion of 5 units of packed red blood cells. Her pregnancy was complicated by mild hypertension and trace proteinuria that was treated with low-dose methyldopa. Her mother suffered from premature menopause and severe osteoporosis. Seven days after giving birth, she has failed to lactate. Her urinalysis is insignificant and her blood pressure has ranged from 95 to110 mmHg systolic and 69 to 75 mmHg diastolic. Fundoscopy shows no retinal changes. Which of the following is most likely deficient in this patient?
. Inhibin
. Progesterone
. Aldosterone
. Prolactin
. Oxytocin
52) A 35-year-old African-American marathon runner presents to the gynecologist complaining of secondary amenorrhea that developed three months ago. Her cycles are normally 28 days long, and her menses last three to five days with moderate flow. One year ago, the woman adopted a vigorous exercise regimen that lasted between three and five hours every day. Since then, her BMI has declined from 23.4 to 16.5 Kg/m2. She has been winning many local races and is considering increasing the difficulty of her exercise regimen, but would like to address the issue of her amenorrhea first. Physical examination reveals a thin woman with well-defined musculature but is otherwise unremarkable. Pregnancy test is negative. What is the most likely etiology of her amenorrhea?
. Kwashiorkor
. Testosterone deficiency
. Estrogen deficiency
. Progesterone deficiency
. Prolactin excess
53) A 26-year-old primigravid woman at 32 weeks gestation comes to the physician because of swelling of her hands and feet. Her previous prenatal check-up was normal. Blood pressure is 150/95 mmHg, and five minutes later following lateral rest her blood pressure is 140/95 mmHg. Physical examination shows 2+ pitting edema of the legs and a macular eruption on the cheekbones. Optic fundi show no abnormalities. Laboratory studies are as follows: Urinalysis: 4+ protein, RBC casts, Urine protein: 8 g/24hr, Uric acid: 5 mg/dl, BUN: 28 mg/dl, Serum creatinine: 2.1 mg/dl, Serum electrolytes, liver function tests and coagulation studies are within normal limits. A serum antinuclear antibody (ANA) test is positive in high titers Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Pregnancy induced hypertension
. Chronic hypertension with superimposed pre-eclampsia
. Glomerulonephritis
. Hemolytic uremic syndrome
. HELLP syndrome
54) A 28-year-old G1P0 presents to your office at 18 weeks gestational age for an unscheduled visit secondary to right-sided groin pain. She describes the pain as sharp and occurring with movement and exercise. She denies any change in urinary or bowel habits. She also denies any fever or chills. The application of a heating pad helps alleviate the discomfort. As her obstetrician, what should you tell this patient is the most likely etiology of this pain?
. Round ligament pain
. Appendicitis
. Preterm labor
. Kidney stone
. Urinary tract infection
55) A 30-year-old G2P1001 patient comes to see you in the office at 37 weeks gestational age for her routine OB visit. Her first pregnancy resulted in a vaginal delivery of a 9-lb 8-oz baby boy after 30 minutes of pushing. On doing Leopold maneuvers during this office visit, you determine that the fetus is breech. Vaginal examination demonstrates that the cervix is 50% effaced and 1 to 2 cm dilated. The presenting breech is high out of the pelvis. The estimated fetal weight is about 7 lb. The patient denies having any contractions. You send the patient for a sonogram, which confirms a fetus with a double footling breech presentation. There is a normal amount of amniotic fluid present and the head is hyperextended in the “stargazer” position. Which of the following is the best next step in the management of this patient?
. Allow the patient to undergo a vaginal breech delivery whenever she goes into labor.
. Send the patient to labor and delivery immediately for an emergent cesarean section.
. Schedule a cesarean section at or after 41 weeks gestational age.
. Schedule an external cephalic version in the next few days.
. Allow the patient to go into labor and do an external cephalic version at that time if the fetus is still in the double footling breech presentation.
56) A 33-year-old woman presents to the physician because of a malodorous vaginal discharge that has been present for the past 3 days. She has no vaginal or vulvar irritation, and has no urinary complaints. Pelvic examination demonstrates a copious, gray discharge with a pH of 5.0. When 1 drop of potassium hydroxide (KOH) is added to a sample of the discharge there is an intense amine odor. A normal saline wet preparation is performed that demonstrates epithelial cells whose borders and nuclei are obscured by the presence of bacteria. Which of the following is the most likely pathogen?
Candida albicans
Chlamydia trachomatis
Gardnerella vaginalis
Lactobacillus species
Trichomonas vaginalis
57) A 32-year-old woman is brought to the operating room for diagnostic laparoscopy because of chronic pelvic pain and chronic right upper quadrant pain. She has had these pains for the past 2 years. Her bowel and bladder function are normal. Past medical history is significant for two episodes of gonorrhea. She drinks one beer per day. Laboratory studies show: Urine hCG: negative, Haematocrit: 39%, leukocyte count: 8,000/mm3, platelet count: 200,000/mm3, AST: 12U/L, ALT:14U/L. Intraoperatively, the patient is noted to have dense adhesions involving her fallopian tubes, ovaries, and uterus. The fallopian tubes themselves appear clubbed and occluded. A survey of her upper abdomen is remarkable for perihepatic adhesions extending from the liver surface to the diaphragm. The liver otherwise appears unremarkable. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis for her right upper quadrant pain?
Alcoholic cirrhosis
Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome
Hepatitis
Hepatocellular carcinoma
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome
58) A 22-year-old primigravid woman at 10 weeks gestation is brought to the emergency department because of vaginal bleeding and lower abdominal pain. She was cleaning the house when she suddenly started feeling colicky pain in the suprapubic area. The pain did not subside after resting, and a few minutes later a tissue-like substance passed through her vagina along with moderate bleeding. The pain subsequently ceased, but she still has mild discomfort. Her temperature is 37.0 C (98.7 F), blood pressure is 120/70 mmHg, pulse is 90/min and respirations are 16/min. Physical examination shows a closed cervix and blood pooled in the vaginal vault. Ultrasonogram shows a vacant uterine cavity and free adnexae. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Incomplete abortion
. Molar pregnancy
. Inevitable abortion
. Ectopic pregnancy
. Complete abortion
59) A 26-year-old Caucasian female calls your office with a question about levothyroxine dosage during pregnancy. She is contemplating her first pregnancy very soon. You have been following her for primary hypothyroidism for several years. Her thyroid functions have been stable on a daily levothyroxine dose of 100μg. Her TSH level three months ago was 2.0 μU/ml (0.35 - 5.0 μU/ml is normal). What would be the most appropriate answer to this patient's question?
. Ask her to increase her levothyroxine dose before becoming pregnant
. She is most likely to increase her levothyroxine dose during pregnancy
. Her levothyroxine dose will not change after she becomes pregnant
. She is most likely to decrease her levothyroxine dose during pregnancy
. Levothyroxine is contraindicated in pregnancy and she has to switch to liothyronine (T3)
60) A 50-year-old woman presents to your office complaining of severe insomnia, hot flashes, and mood swings. She also states that her mother had a hip fracture at 65 years of age. She is afraid of developing osteoporosis and having a similar incident. Her last menstrual period was six months ago. Her past medical history is significant for hypothyroidism diagnosed seven years ago. She takes L-thyroxine and the dose of the hormone has been stable for the last several years. Her blood pressure is 120/70 mmHg and her heart rate is 75/min. Serum TSH level is normal. You consider estrogen replacement therapy for this patient. Which of the following is most likely concerning estrogen replacement therapy in this patient?
. The level of total thyroid hormones would decrease
. The metabolism of thyroid hormones would decrease
. The requiren1ent for L-thyroxine would increase
. The volume of distribution of thyroxine would decrease
. The level of TSH would decrease
61) A previously healthy 50-year-old gravida 5, para 4, Caucasian woman comes to the physician complaining of passing small amounts of urine while sneezing or coughing for the past five months. She denies any episodes of weakness, numbness or fecal incontinence. There is no history of dysuria, increased frequency of urination, or hematuria. Her symptoms are progressively getting worse. Her other medical problems include diabetes mellitus type 2 diagnosed 3 years ago, treated with glyburide 2.5mg/day. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or drugs, and has no known drug allergies. She mentions that she is an avid jogger, but her problem causes her significant embarrassment. She now has to wear absorbent pads while jogging. Her vital signs are within normal limits. On examination, the abdomen is soft. Neurological examination is within normal limits. Pelvic examination shows a cystocele. The patient's labs reveal: Urine Specific gravity: 1.020, Blood: negative, Glucose: negative, Leukocyte esterase: negative, Nitrites: negative, WBC: 5-10/hpf, Bacteria: none. Random blood sugar is 120 mg/dl. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her symptoms?
. Detrusor instability
. Bladder irritation from a neoplasm
. Interstitial cystitis
. Overflow incontinence due to detrusor weakness
. Pelvic floor muscle weakness
62) A 28-year-old, G2 P1 woman presented to the hospital at 34weeks gestation because of midepigastric and right upper quadrant pain associated with nausea and vomiting. She has been closely followed for mild hypertension and mild proteinuria (250 mg/24hr) on an outpatient basis since the 28th week of gestation. Her previous pregnancy was without incident. Her temperature is 37.2 C (98.9 F), blood pressure is 160/94 mmHg and pulse is 80/min. Physical examination shows epigastric and right upper quadrant tenderness; her bowel sounds are slightly reduced. The extremities have 2+ edema. Fetal heart sounds are audible on Doppler. Laboratory studies show: Hb: 8.2g/dl, Platelets: 96,000/mm3, Prothrombin time: 12.4 sec, Partial thromboplastin time: 23.6 sec, Serum creatinine: 1.1 mg/dl, Total bilirubin: 2.6 mg/dl, Direct bilirubin: 0.8 mg/dl, Alkaline phosphatase: 120 U/L, Aspartate aminotransferase: 308 U/L, Alanine aminotransferase: 265 U/L, Lipase: 53 U/L. Peripheral blood smear shows numerous red blood cell fragments. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. HELLP syndrome
. Acute fatty liver of pregnancy
. Hemolytic uremic syndrome
. Viral hepatitis
. Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura
63) A 36-year-old woman, gravida 3, para 2, comes to the physician for a prenatal checkup. According to the last menstrual period and an ultrasonography performed at 16 weeks gestation, she is at 30 weeks gestation. She missed two antenatal appointments. She does not use tobacco, alcohol or drugs. Examination shows a fundal height of 26cm (9.8in). Fetal heart tones are heard by Doppler. Repeat ultrasonogram shows a biparietal diameter consistent with dates and an abdominal circumference below the 10th percentile. Which of the following could most likely be responsible for the observed fetal findings?
. Chromosomal abnormalities
. Intrauterine infection
. Hypertension
. Gross fetal anomalies
. Inaccurate dates
64) While you are on call at the hospital covering labor and delivery, a 32-year-old G3P2002, who is 35 weeks of gestation, presents complaining of lower back pain. The patient informs you that she had been lifting some heavy boxes while fixing up the baby’s nursery. The patient’s pregnancy has been complicated by diet-controlled gestational diabetes. The patient denies any regular uterine contractions, rupture of membranes, vaginal bleeding, or dysuria. She denies any fever, chills, nausea, or emesis. She reports that the baby has been moving normally. She is afebrile and her blood pressure is normal. On physical examination, you note that the patient is obese. Her abdomen is soft and nontender with no palpable uterine contractions. No costovertebral angle tenderness can be elicited. On pelvic examination her cervix is long and closed. The external fetal monitor indicates a reactive fetal heart rate strip; there are rare irregular uterine contractions demonstrated on the tocometer. The patient’s urinalysis comes back with trace glucose, but is otherwise negative. The patient’s most likely diagnosis is which of the following?
. Labor
. Musculoskeletal pain
. Urinary tract infection
. Chorioamnionitis
. Round ligament pain
65) A 29-year-old G3P2 presents to the emergency center with complaints of abdominal discomfort for 2 weeks. Her vital signs are: blood pressure 120/70 mm Hg, pulse 90 beats per minute, temperature 36.94C, respiratory rate 18 breaths per minute. A pregnancy test is positive and an ultrasound of the abdomen and pelvis reveals a viable 16-week gestation located behind a normal-appearing 10×6×5.5 cm uterus. Both ovaries appear normal. No free fluid is noted. Which of the following is the most likely cause of these findings?
. Ectopic ovarian tissue
. Fistula between the peritoneum and uterine cavity
. Primary peritoneal implantation of the fertilized ovum
. Tubal abortion
. Uterine rupture of prior cesarean section scar
66) A 32-year-old G2P1 at 28 weeks gestation presents to labor and delivery with the complaint of vaginal bleeding. Her vital signs are: blood pressure 115/67 mm Hg, pulse 87 beats per minute, temperature 37.0C, respiratory rate 18 breaths per minute. She denies any contraction and states that the baby is moving normally. On ultrasound the placenta is anteriorly located and completely covers the internal cervical os. Which of the following would most increase her risk for hysterectomy?
. Desire for sterilization
. Development of disseminated intravascular coagulopathy (DIC)
. Placenta accreta
. Prior vaginal delivery
. Smoking
67) A 29-year-old woman comes to the emergency department because of constant, severe lower abdominal pain. She also complains of fever and chills. Three weeks ago she had an intrauterine device (IUD) placed for contraception. Her temperature is 38.3 C (101 F), blood pressure is 110/76 mm Hg, pulse is 110/min, and respirations are 16/min. She has bilateral lower quadrant abdominal tenderness. On pelvic examination, she has cervical motion tenderness and bilateral adnexal tenderness. A urinalysis is negative. A pelvic ultrasound is negative, with normal uterus and adnexae and no free fluid. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Appendicitis
Hemorrhagic ovarian cyst
Ovarian torsion
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
Pyelonephritis
68) A 32-year-old G5P1 presents for her first prenatal visit. A complete obstetrical, gynecological, and medical history and physical examination is done. Which of the following would be an indication for elective cerclage placement?
. Three spontaneous first-trimester abortions
. Twin pregnancy
. Three second-trimester pregnancy losses without evidence of labor or abruption
. History of loop electrosurgical excision procedure for cervical dysplasia
. Cervical length of 35 mm by ultrasound at 18 weeks
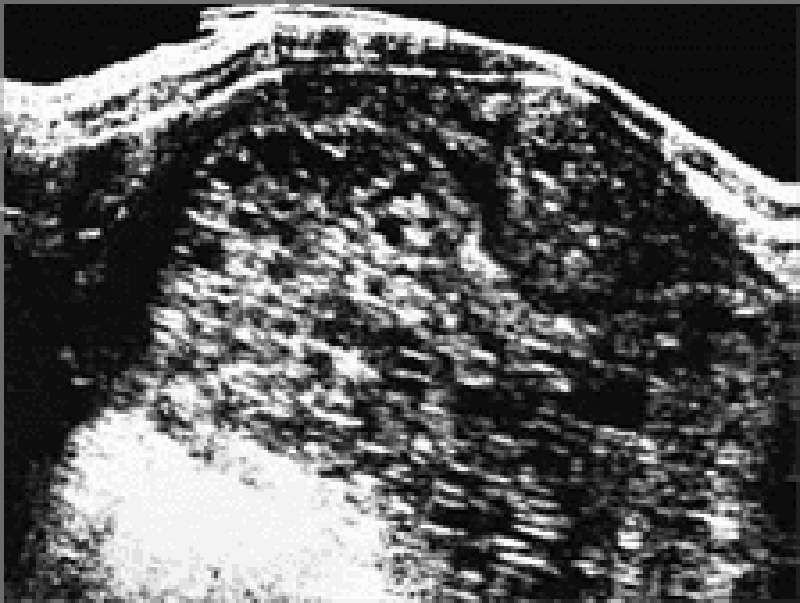
69) A 19-year-old primigravida is expecting her first child; she is 12 weeks pregnant by dates. She has vaginal bleeding and an enlarged-for-dates uterus. In addition, no fetal heart sounds are heard. The ultrasound shown below is obtained. Which of the following is true regarding the patient’s diagnosis?
. The most common chromosomal makeup of a partial or incomplete mole is 46XX, of paternal origin
. Older maternal age is not a risk factor for hydatidiform mole
. Partial or incomplete hydatidiform mole has a higher risk of developing into choriocarcinoma than complete mole
. Vaginal bleeding is a common symptom of hydatidiform mole
. Hysterectomy is contraindicated as primary therapy for molar pregnancy in women who have completed childbearing
70) A 32-year-old female presents to the emergency department with abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding. Her last menstrual period was 8 weeks ago and her pregnancy test is positive. On examination she is tachycardic and hypotensive and her abdominal examination findings reveal peritoneal signs, a bedside abdominal ultrasound shows free fluid within the abdominal cavity. The decision is made to take the patient to the operating room for emergency exploratory laparotomy. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Ruptured ectopic pregnancy
. Hydatidiform mole
. Incomplete abortion
. Missed abortion
. Torsed ovarian corpus luteal cyst
71) A 19-year-old woman comes to the emergency department and reports that she fainted at work earlier in the day. She has mild vaginal bleeding. Her abdomen is diffusely tender and distended. In addition, she complains of shoulder and abdominal pain. Her temperature is 37.2C, pulse rate is 120 beats per minute, and blood pressure is 80/42 mm Hg. Which of the following is the best diagnostic procedure to quickly confirm your diagnosis?
. Computed tomography of the abdomen and pelvis
. Culdocentesis
. Dilation and curettage
. Posterior colpotomy
. Quantitative β-human chorionic gonadotropin (β-hCG)
72) A 22-year-old G1P0 woman who is 10 weeks pregnant with twins presents to the emergency department because of vomiting and dizziness. She has had “morning sickness” for the past month and would vomit once or twice a day. However, over the past week, she has been vomiting multiple times a day, and she has been unsuccessful at “keeping anything down” for the past 2 days. She denies fever or change in her bowel movements; her last bowel movement was that morning and was well formed. She has otherwise been healthy. Physical examination reveals a tired-appearing, pale woman with poor skin turgor; otherwise her examination is unremarkable. Her blood pressure is 110/75 mm Hg lying down and 90/45 mmHg sitting up. Her pulse is 80/min lying down and 115/min sitting up. Her respiratory rate is 24/min, and her temperature is 37.2C (99.0F). Her original blood work results are: WBC count: 14,000/mm3, Platelet count: 350,000/mm3, Na+: 150 mEq/L, K+: 4 mEq/L, Cl-: 88 mEq/L, HCO3-: 26 mEq/L, Hemoglobin: 15 g/dL, Hematocrit: 40%, Aspartate aminotransferase: 80 U/L, Alanine aminotransferase: 85 U/L. What is this woman’s most likely diagnosis?
Acute viral hepatitis A
Food poisoning with Salmonella
Hyperemesis gravidarum
Preeclampsia
Viral gastroenteritis
73) A 58-year-old woman with stage II epithelial ovarian cancer undergoes successful surgical debulking followed by chemotherapy with carboplatin and radiation therapy. Subsequently, she develops non-pitting edema of both legs and pain and numbness in her legs. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her pain and numbness?
Nerve damage caused by the pelvic lymphadenectomy
Lymphedema
Carboplatin therapy
Radiation therapy
Recurrent ovarian cancer
74) A 26-year-old black gravida 2, para 1, at 32 weeks' gestation presents to the physician for a prenatal visit. Her prenatal course has been remarkable for hyperemesis gravidarum in the first trimester. She also had a urine culture in the first trimester that grew out Group B Streptococcus. She has had type 1 diabetes for the past 2 years and has had good control of her blood glucose levels during this pregnancy. Her first pregnancy resulted in a low transverse cesarean section for dystocia. Other than insulin, she takes no medicines and has no known drug allergies. After a routine prenatal visit, the physician sends her to the antepartum fetal testing unit to undergo a non-stress test (NST). Which of the following characteristics makes this patient a good candidate for antepartum fetal testing with an NST?
Black race
Diabetes mellitus
Group B Streptococcus urine culture
History of cesarean section
Hyperemesis gravidarum
75) A 39-year-old Caucasian female presents to your office with a palpable nodularity in the right breast. Pathologically, the lesion is composed of ducts distended by pleomorphic cells with prominent central necrosis. The lesion does not extend beyond the ductal basal membrane. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
. Paget disease
. Comedocarcinoma
. Medullary carcinoma
. Sclerosing adenosis
. Mammary duct ectasia
76) A 32-year-old female presents to your office complaining of a small amount of vaginal discharge. Wet mount preparation of the discharge shows few leukocytes. Application of KOH solution to the discharge yields a strong fishy odor. The most likely diagnosis is:
. Gonorrhea infection
. Chlamydia infection
. Bacterial vaginosis
. Fungal infection
. Trichomonas infection
77) A 50-year-old woman presents with fatigue, insomnia, hot flashes, night sweats, and absence of menses for the last 5 months (secondary amenorrhea). Her urine hCG test is negative. Laboratory tests reveal decreased serum estrogen and increased serum FSH and LH levels. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this individual’s clinical signs and symptoms?
. 17-hydroxylase deficiency of the adrenal cortex
. Prolactin-secreting tumor of the anterior pituitary
. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone–secreting tumor of the hypothalamus
. Menopause
. Menarche
78) A 39-year-old woman presents with new onset of a bloody discharge from her right nipple. Physical examination reveals a 1-cm freely movable mass that is located directly beneath the nipple. Sections from this mass reveal multiple fibrovascular cores lined by several layers of epithelial cells. Atypia is minimal. The lesion is completely contained within the duct and no invasion into underlying tissue is seen. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Benign phyllodes tumor
. Ductal papilloma
. Intraductal carcinoma
. Paget disease
. Papillary carcinoma
79) A 48-year-old woman presents with a 1.5-cm firm mass in the upper outer quadrant of her left breast. A biopsy from this mass reveals many of the ducts to be filled with atypical cells. In the center of these ducts there is extensive necrosis. No invasion into the surrounding fibrous tissue is seen. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Colloid carcinoma
. Comedocarcinoma
. Infiltrating ductal carcinoma
. Infiltrating lobular carcinoma
. Lobular carcinoma in situ
80) A 51-year-old woman presents with an ill-defined, slightly firm area in the upper outer quadrant of her right breast. The clinician thinks this area is consistent with fibrocystic change, but a biopsy from this area has a focus of lobular carcinoma in situ. Which of the following histologic features is most characteristic of this lesion?
. Expansion of lobules by monotonous proliferation of small cells
. Large cells with clear cytoplasm within the epidermis
. Large syncytium-like sheets of pleomorphic cells surrounded by aggregates of lymphocytes
. Small individual malignant cells dispersed within extracellular pools of mucin
. Small tumor cells with little cytoplasm infiltrating in a single-file pattern
81) A 46-year-old woman presents with a 4-month history of a discharge from the nipple. An excisional biopsy of the nipple area reveals infiltration of the nipple by large cells with clear cytoplasm. These cells are found both singly and in small clusters in the epidermis and are PAS-positive and diastase resistant. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Ductal papilloma
. Eczematous inflammation
. Mammary duct ectasia
. Paget disease
. Phyllodes tumor, malignant
82) A 59-year-old woman who had been diagnosed with infiltrating ductal carcinoma 2years prior presents with pain of her right breast. The breast is swollen, tender on palpation, and is diffusely indurated with a “peau d’orange” appearance. Multiple axillary lymph nodes are palpable in the lower axilla. A skin biopsy from her breast reveals extensive invasion of dermal lymphatics. What is the best diagnosis?
. Angiosarcoma
. Comedocarcinoma
. Duct ectasia
. Inflammatory carcinoma
. Sclerosing adenosis
83) A 26-year-old woman comes to the physician's office for evaluation of a vulvar ulcer that she noticed two days ago. Initially she had a small painless papule that later became ulcerated. Upon further questioning she reluctantly admits to using sex to obtain drugs. She also reports using oral contraceptives to prevent pregnancy. On vulvar examination there is a 2-cm ulcer with a non-exudative base and a raised, indurated margin. Painless bilateral inguinal lymphadenopathy is present. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Syphilis
. Chancroid
. Herpes genitalis
. Granuloma inguinale
. Basal cell carcinoma
84) A 23-year-old woman who is 26 weeks pregnant presents to the emergency department with sudden onset severe shortness of breath and inability to lie flat. She recently emigrated from Eastern Europe. Her medical history is significant for recurrent sore throats requiring tonsillectomy as a child. Presently, her blood pressure is 110/60 mmHg and her heart rate is 120/min. An EKG rhythm strip suggests atrial fibrillation. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
. Constrictive pericarditis
. Mitral stenosis
. Myocardial infarction
. Aortic insufficiency
85) A 47-year-old woman presents to your office with complaints of lower abdominal pain, nocturia, urinary urgency and frequency relieved with urination. She states the symptoms have been worsening this past month and she recently experienced dyspareunia. She is sexually active with her husband, but this is causing her a great amount of pain. She has four children and had uncomplicated pregnancies. She denies fevers or chills. On examination, she has diffuse lower abdominal pain with no rebound or guarding. Her external genitalia appear normal. On bimanual examination, palpation of the anterior vaginal wall elicits extreme pain. No cervical motion tenderness is present. No other abnormalities are noted. A urinalysis is negative. The most likely diagnosis is:
. Urinary tract infection
. Stress incontinence
. Cystocele
. Interstitial cystitis
. Pelvic inflammatory disease
86) A 22-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, at 39 weeks gestation is admitted to the hospital for delivery. She has had regular and painful uterine contractions occurring every 3 minutes for the past 10 hours. Her pregnancy has been uncomplicated. She had a normal vaginal delivery for her first pregnancy and required an episiotomy. A recent ultrasound at 37 weeks gestation showed a fetus in a cephalic presentation with an estimated fetal weight of 3,400 g (7.5 lb). Examination shows the cervix is soft, 50% effaced and 2 cm dilated. She is given epidural anesthesia per her request. Eight hours later, her cervix has not significantly changed, and uterine contractions are occurring every 5 minutes. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her current condition?
. Cephalopelvic disproportion
. Early anesthesia
. Cervical dysfunction
. Perineal scar
. False labor
87) A 24-year-old gravida 2, para 1, African American woman at 12 weeks gestation comes for her first prenatal visit. Except for early morning mild headaches and nausea she has no other symptoms. Physical examination shows mild bilateral ankle edema. Blood pressure is measured twice 15 minutes apart and is 150/96 mmHg on both occasions. Blood is drawn for laboratory tests and the patient is sent home with a follow-up appointment 3 days later. She returns 3 days later and repeat blood pressure is the same. Laboratory studies show: Urinalysis: Protein: negative, Blood: negative, Glucose: trace, Ketones: negative, Leukocyte esterase: negative, Nitrites: negative, WBC: 1-2/hpf, RBC: 1-2/hpf. Chemistry panel: Serum sodium: 150 mEq/L, Serum potassium: 2.5 mEq/L, Chloride: 100 mEq/L, Bicarbonate: 23 mEq/L, Blood urea nitrogen (BUN): 14 mg/dL, Serum creatinine: 0.8 mg/dL. Ultrasonogram reveals intrauterine gestation consistent with dates; no abnormalities noted. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Preeclampsia
. Chronic hypertension
. Molar pregnancy
. Transient hypertension of pregnancy
. Normal pregnancy
88) A 27-year-old primigravid woman at 30 weeks’ gestation comes to the emergency department complaining of abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Earlier in the day she began to experience severe epigastric and later right upper quadrant pain. Until now her pregnancy has been uneventful and she has had regular prenatal care. Her past medical history and review of symptoms are unremarkable. On examination she is a pregnant woman in moderate distress, lying still on the hospital bed. Vital signs are: temperature 38.9 C (102.0 F), blood pressure 105/68 mm Hg, and pulse 108/min. Her abdomen is extremely tender to palpation in the right upper quadrant with guarding. There is no vaginal bleeding or discharge. Laboratory studies show: Hematocrit: 36%, Leukocytes: 15,000/mm3 (88% neutrophils), Platelets: 158,000/mm3. Liver function tests, including transaminases, are normal. Prothrombin time is within normal limits. Urinalysis is unremarkable except for a few red blood cells on microscopy. X-ray is deferred out of concern for the fetus. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient’s symptoms?
. Acute fatty infiltration of the liver
. Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy
. Luminal obstruction of the appendix from lymphoid hyperplasia or fecalith
. Pregnancy outside the uterine endometrium
. Premature separation of a normally implanted placenta
89) A 29-year-old woman comes to your office because she has been feeling depressed. She states that at times over the past several years she has regular occurrences of depression, anxiety, tearfulness, anger, and difficulty with work and social relationships. These occurrences have been increasing over the past several months. She doesn’t remember when her symptoms start or end. “It’s all a blur,” she says. She has had several urinary tract infections in her life, but otherwise has no medical problems. She takes no medications and has no drug allergies. Physical examination is normal. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in caring for this patient?
. Have her keep a symptom calendar
. Schedule an MRI of the brain
. Schedule a pelvic ultrasound
. Start the patient on a benzodiazepine
. Start the patient on a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor
90) You examine a 28-year-old woman who is 2 days status post-cesarean delivery for a nonreassuring fetal heart rate tracing in labor. Her prenatal course was complicated by her developing acute tuberculosis in the days immediately before her delivery. When you diagnosed her with tuberculosis, she decided to hold off on therapy until after the baby was born. She was also found to be Group B Streptococcus–positive on a 36-week vaginal culture. She has a past medical history significant for chronic hepatitis B. Her past surgical history is significant for a breast reduction 4 years ago. Postpartum she is doing well, with no complaints, normal vital signs, and a normal postpartum physical examination. She wants to know if she is able to breast feed her infant. Which of the following conditions precludes this patient from breastfeeding?
. Chronic hepatitis B
. Group B Streptococcus colonization
. Status-post breast reduction
. Status-post cesarean delivery
. Untreated tuberculosis
91) A 36-year-old woman, gravida 3, para 2, at 33 weeks' gestation comes to the physician for a prenatal visit. She has some fatigue but no other complaints. Her current pregnancy has been complicated by a Group B Streptococcus urine infection at 16 weeks. Her past obstetric history is significant for a primary, classic cesarean delivery 5 years ago for a non-reassuring fetal tracing. Two years ago, she had a repeat cesarean delivery. Past surgical history is significant for an appendectomy 10 years ago. Which of the following is the major contraindication to a vaginal birth after cesarean (VBAC) in this patient?
. Classic uterine scar
. Group B Streptococcus urine infection
. Previous appendectomy
. Prior cesarean delivery for non-reassuring fetal tracing
. Two prior cesarean deliveries
92) A 59-year-old G4P4 presents to your office complaining of losing urine when she coughs, sneezes, or engages in certain types of strenuous physical activity. The problem has gotten increasingly worse over the past few years, to the point where the patient finds her activities of daily living compromised secondary to fear of embarrassment. She denies any other urinary symptoms such as urgency, frequency, or hematuria. In addition, she denies any problems with her bowel movements. Her prior surgeries include tonsillectomy and appendectomy. She has adult-onset diabetes and her blood sugars are well controlled with oral Metformin. The patient has no history of any gynecologic problems in the past. She has four children who were all delivered vaginally. Their weights ranged from 8 to 9 lb. Her last delivery was forceps assisted. She had a third-degree laceration with that birth. She is currently sexually active with her partner of 25 years. She has been menopausal for 4 years and has never taken any hormone replacement therapy. Her height is 5 ft 6 in, and she weighs 190 lb. Her blood pressure is 130/80 mmHg. Based on the patient’s history, which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Overflow incontinence
. Stress incontinence
. Urinary tract infection
. Detrusor instability
. Vesicovaginal fistula
93) A 49-year-old G4P4 presents to your office complaining of a 2-month history of leakage of urine every time she exercises. She has had to limit her physical activities because of the loss of urine. She has had burning with urination and some blood in her urine for the past few days. Which of the following is the best next step in the evaluation and management of this patient?
. Physical examination
. Placement of a pessary
. Urinalysis with urine culture
. Cystoscopy
. Office cystometrics
94) An obese 46-year-old G6P1051 with type 1 diabetes since age 12 presents to your office complaining of urinary incontinence. She has been menopausal since age 44. Her diabetes has been poorly controlled for years because of her noncompliance with insulin therapy. She often cannot tell when her bladder is full, and she will urinate on herself without warning. Which of the following factors in this patient’s history has contributed the most to the development of her urinary incontinence?
. Menopause
. Obesity
. Obstetric history
. Age
. Diabetic status
95) A 76-year-old woman presents for evaluation of urinary incontinence. She had a hysterectomy for fibroid tumors of the uterus at age 48. After complete evaluation, you determine that the patient has genuine stress urinary incontinence. On physical examination, she has a hypermobile urethra, but there is no cystocele or rectocele. There is no vaginal vault prolapse. Office cystometrics confirms genuine stress urinary incontinence. Which of the following surgical procedures should you recommend to this patient?
. Kelly plication
. Anterior and posterior colporrhaphy
. Burch procedure
. Abdominal sacral colpopexy
. Le Fort colpocleisis
96) A patient presents to your office approximately 2 weeks after having a total vaginal hysterectomy with anterior colporrhaphy and Burch procedure for uterine prolapse and stress urinary incontinence. She complains of a constant loss of urine throughout the day. She denies any urgency or dysuria. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for this complaint?
. Failure of the procedure
. Urinary tract infection
. Vesicovaginal fistula
. Detrusor instability
. Diabetic neuropathy
97) A 90-year-old G5P5 with multiple medical problems is brought into your gynecology clinic accompanied by her granddaughter. The patient has hypertension, chronic anemia, coronary artery disease, and osteoporosis. She is mentally alert and oriented and lives in an assisted living facility. She takes numerous medications, but is very functional at the current time. She is a widow and not sexually active. Her chief complaint is a sensation of heaviness and pressure in the vagina. She denies any significant urinary or bowel problems. On performance of a physical examination, you note that the cervix is just inside the level of the introitus. Based on the physical examination, which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Normal examination
. First-degree uterine prolapse
. Second-degree uterine prolapse
. Third-degree uterine prolapse
. Complete procidentia
98) A 52-year-old woman comes to the physician because of hot flashes. Her last menstrual period was 1 year ago. Over the past year, she has noted a persistence of her hot flashes, which come several times each day and are associated with a feeling of heat and flushing. They also awaken her at night and interfere with her sleep. She has no medical problems, takes no medications, and has no known drug allergies. She has a family history of cardiovascular disease and she does not smoke. Physical examination is unremarkable. She is started on estrogen and medroxyprogesterone acetate (Provera). The addition of a progestin is most likely to decrease her risk of which of the following?
. Breast cancer
. Breast pain
. Endometrial cancer
. Mood changes
. Weight gain
99) A previously healthy 21-year-old woman has a profuse, malodorous vaginal discharge. Examination shows a greenish gray "frothy" discharge with a "fishy" odor and petechial lesions on the cervix. There is no cervical motion tenderness. Her temperature is 37.5 C (99.4 F), blood pressure is 120/80 mm Hg, pulse is 60/min, and respirations are 16/min. Microscopic evaluation of the discharge is most likely to show which of the following?
. "Clue cells"
. Gram-negative diplococci
. Gram-positive diplococci
. Motile, flagellated organisms
. Pseudohyphae or hyphae
100) A 26-year-old nulligravid woman comes to the emergency department because of severe right lower quadrant pain. She states that the pain started last night. This morning she was awakened from sleep with severe pain in the same area. During the episode of pain, she also had nausea, vomiting, and diaphoresis. On admission to the emergency department she required 5 mg of morphine to control her pain. Examination is significant for right lower quadrant tenderness and a tender right adnexal mass on pelvic examination. Urine hCG is negative. Urinalysis is negative. Transvaginal ultrasound reveals an 8 cm right ovarian mass. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Appendicitis
. Ectopic pregnancy
. Nephrolithiasis
. Ovarian torsion
. Pelvic inflammatory disease
101) A 21-year-old woman comes to the physician because of abdominal pain. She states that the pain is in her right lower quadrant and has been getting worse over the past 3 months. She has no other symptoms and a normal appetite. Examination demonstrates mild right lower quadrant abdominal tenderness. Pelvic examination reveals mild right adnexal enlargement and tenderness. Urine human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is negative. A pelvic ultrasound is obtained that shows a 4-centimeter, heterogeneous hyperechoic lesion in the right adnexa with cystic areas. On transvaginal ultrasound, hair and calcifications are demonstrated within the cystic areas. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Appendicitis
. Benign cystic teratoma (dermoid)
. Corpus luteum cyst
. Ectopic pregnancy
. Tubo-ovarian abscess
102) A 27-year-old has just had an ectopic pregnancy. Which of the following events would be most likely to predispose to ectopic pregnancy?
. Previous cervical conization
. Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
. Use of a contraceptive uterine device (IUD)
. Induction of ovulation
. Exposure in utero to diethylstilbestrol (DES)
103) A healthy 42-year-old G2P1001 presents to labor and delivery at 30 weeks gestation complaining of a small amount of bright red blood per vagina which occurred shortly after intercourse. It started off as spotting and then progressed to a light bleeding. By the time the patient arrived at labor and delivery, the bleeding had completely resolved. The patient denies any regular uterine contractions, but admits to occasional abdominal cramping. She reports no pregnancy complications and a normal ultrasound done at 14 weeks of gestation. Her obstetrical history is significant for a previous low transverse cesarean section at term. Which of the following can be ruled out as a cause for her vaginal bleeding?
. Cervicitis
. Preterm labor
. Placental abruption
. Placenta previa
. Subserous pedunculated uterine fibroid
104) A 23-year-old G3P1011 at 6 weeks presents for routine prenatal care. She had a cesarean delivery 3 years ago for breech presentation after a failed external cephalic version. Her daughter is Rh-negative. She also had an elective termination of pregnancy 1 year ago. She is Rh-negative and is found to have a positive anti-D titer of 1:8 on routine prenatal labs. Failure to administer RhoGAM at which time is the most likely cause of her sensitization?
. After elective termination
. At the time of cesarean delivery
. At the time of external cephalic version
. Within 3 days of delivering a Rh-negative fetus
. At 28 weeks in the pregnancy for which she had a cesarean delivery
105) A 39-year-old G1P0 at 39 weeks gestational age is sent to labor and delivery from her obstetrician’s office because of a blood pressure reading of 150/100 mm Hg obtained during a routine OB visit. Her baseline blood pressures during the pregnancy were 100 to 120/60 to 70. On arrival to labor and delivery, the patient denies any headache, visual changes, nausea, vomiting, or abdominal pain. The heart rate strip is reactive and the tocodynamometer indicates irregular uterine contractions. The patient’s cervix is 3 cm dilated. Her repeat blood pressure is 160/90 mm Hg. Hematocrit is 34.0, platelets are 160,000, SGOT is 22, SGPT is 15, and urinalysis is negative for protein. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Preeclampsia
. Chronic hypertension
. Chronic hypertension with superimposed preeclampsia
. Eclampsia
. Gestational hypertension
106) A 21-year-old woman presents to the clinic in tears. She states that she recently found out she was pregnant at 10 weeks’ gestation. She is a recovering alcoholic but recently relapsed, consuming several drinks a day. She is nervous about the effects of her drinking on her fetus. For which of the following is the patient at greatest risk?
Eclampsia
Hypoplastic lung
Macrosomia
Microcephaly
Polyhydramnios
107) A 24-year-old G2P2 woman presents to the emergency department complaining of vaginal bleeding and abdominal cramping. She is sexually active in a monogamous relationship with her husband. Her last menstrual period was 6 weeks ago. The patient is afebrile, and vital signs are within normal limits. Pelvic examination is notable for a dilated cervix, fetal tissue in the vaginal vault, and no cervical motion tenderness. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient’s abortion?
Acute maternal infection
Chromosomal abnormality
Maternal exposure to environmental chemicals
Maternal smoking
Trauma
108) A 31-year-old woman with systemic lupus erythematosus who is 4 weeks pregnant presents to her obstetrician for her first prenatal visit. She is very concerned that the lupus will affect her baby. She was diagnosed with systemic lupus erythematosus 5 years ago and her symptoms have been well controlled with low-dose prednisone. She has baseline renal insufficiency, with a creatinine level of 1.3 mg/dL that has been stable for the past 6 months. This is her first pregnancy. For which of the following is the baby at increased risk?
Acute renal failure
Chorioretinitis
Complete heart block
Ebstein’s anomaly
Rash
109) A 30-year-old G0 woman with a past medical history of dysmenorrhea presents to an infertility clinic with her husband for a follow-up visit. The couple has been trying to get pregnant for the past 3 years with no success. Their infertility work-up thus far has included a semen analysis, hysterosalpingogram, and estrogen, progesterone, and follicle-stimulating hormone blood levels, all of which were normal. Currently the woman feels well; her only complaint is frustration regarding her inability to conceive. A pelvic ultrasound done last week demonstrated a 3-cm well-circumscribed mass on the patient’s left ovary. Her last menstrual period was 3 weeks ago. The ovarian mass most likely represents which of the following?
Corpus luteum cyst
Ectopic pregnancy
Endometrioma
Leiomyoma
Tubo-ovarian abscess
110) At 38 weeks’ gestation, a 4030-g (8.9-lb) boy is delivered by spontaneous vaginal delivery. During the first minute of life he is limp, cyanotic, lacks respiratory effort, has a heart rate of 95/min, flexes his extremities, and grimaces to nasal suctioning. By 5 minutes, he continues to grimace to nasal suctioning, has a weak cry, is well perfused with a heart rate of 160/min, and is kicking both legs. Based on his Apgar scores, when will the child need to be resuscitated?
Indicated at 1 and 5 minutes
Indicated at 1 minute and not at 5 minutes
Indicated at 5 minutes and not at 1 minute
Not enough information to determine
Not indicated at 1 or 5 minutes
111) A 23-year-old G1P0 woman at 28 weeks’ gestation presents to her obstetrician for a prenatal examination. She has received poor prenatal care up to this point, but is confident about dating the pregnancy. She denies use of alcohol and illicit drugs but has continued to smoke during the pregnancy. The mother has gained only 9 kg (20 lb) during the course of the pregnancy. The mother’s temperature is 36.8C (98.2F), pulse is 94/min, blood pressure is 138/84 mm Hg, and respiratory rate is 12/min. The fundal height is 23 cm above the pubic symphysis. Further examination with ultrasound reveals the fetus is <10% of the expected weight for the gestational age with symmetric growth anomalies. What is the most likely cause for the intrauterine growth restriction of this fetus?
In utero infection
Inadequate maternal weight gain during pregnancy
Maternal hypertension
Maternal smoking
Singleton pregnancy
112) A 22-year-old obese woman presents to the obstetrics-gynecology clinic complaining of mild abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding. The patient states that she is sexually active with her boyfriend and uses condoms “basically all the time.” She states that her last menstrual period was 7 weeks ago and insists that her periods have always been irregular, occurring every 3 to 4 months. She denies any past medical history but states that she used to have a problem with excess facial hair prior to starting low-dose oral contraceptive pills. Which of the following is the best next step in diagnosis?
Endometrial biopsy
Measure prothrombin time/partial thromboplastin time
Measure thyroid-stimulating hormone level
Measure urine β-human chorionic gonadotropin level
Progesterone challenge
113) A full-term 2200-g (4.9-lb) boy was born to a 30-year-old G4P3 woman whose pregnancy was complicated by a seizure disorder for which she inconsistently took carbamazepine. The pregnancy was also notable for an abnormal triple screen for which an amniocentesis was declined. His Apgar scores are 7 and 9 at 1 and 5 minutes, respectively. His temperature is 37.0C (98.6F), blood pressure is 65/45 mm Hg, heart rate is 110/min, and respiratory rate is 30/min. His head circumference is <5th percentile. There is a small fleshy sac protruding from the sacral spine. His reflexes are 2+ throughout, and his strength is 5/5 in all extremities. His fingernails are very small. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Anoxia due to maternal seizing
Fetal alcohol syndrome
Perinatal exposure to carbamazepine
Trisomy 18
Trisomy 21
114) A 28-year-old woman and her husband present to her obstetrician. They have been married for 7 years and have been trying to become pregnant for the past 2 years. Prior to this the woman used an intrauterine device for contraception, which she had in place for 5 years. Both are healthy without any medical problems, and both deny a history of sexually transmitted diseases. The woman states that her menstrual cycles have always been regular (every 28 days, lasting for 5 days) since she was 14 years old. She also denies menorrhagia and dysmenorrhea. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this couple’s infertility?
Endometriosis
Low sperm concentration
Pelvic inflammatory disease
Premature ovarian failure
Prior placement of an intrauterine device
115) A 28-year-old teacher presents to the clinic complaining of 5 months of polyuria, polydipsia, and weight loss. Additionally, her menses, which have always been irregular, have stopped altogether. She is concerned because both her mother and maternal aunt suffer from noninsulin-dependent diabetes, and they told her they had similar symptoms before they were diagnosed. Upon questioning she reveals that she is in a committed relationship and has no desire to have children, so she uses barrier protection during intercourse. Physical examination reveals an obese woman with hirsutism currently in no acute distress. Testing for β-human chorionic gonadotropin level, random blood sugar level, cholesterol panel, and a luteinizing hormone/follicle-stimulating hormone ratio suggests the patient has polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS). Although no one in her family has had cancer, she is concerned that her symptoms are a harbinger of cancer or that she might be likely to suffer from cancer in the future. This diagnosis would most raise her risk for which kind of cancer?
Cervical cancer
Colon cancer
Endometrial cancer
Lung cancer
Ovarian cancer
116) A 26-year-old primigravid woman at 32 weeks gestation comes to the physician because of swelling of her hands and feet. Her previous prenatal check-up was normal. Blood pressure is 150/95 mmHg, and five minutes later following lateral rest her blood pressure is 140/95 mmHg. Physical examination shows 2+ pitting edema of the legs and a macular eruption on the cheekbones. Optic fundi show no abnormalities. Laboratory studies are as follows: Urinalysis: 4+ protein, RBC casts, Urine protein: 8 g/24hr, Uric acid: 5 mg/dl, BUN: 28 mg/dl, Serum creatinine: 2.1 mg/dl, Serum electrolytes, liver function tests and coagulation studies are within normal limits. A serum antinuclear antibody (ANA) test is positive in high titers. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Pregnancy induced hypertension
. Chronic hypertension with superimposed pre-eclampsia
. Glomerulonephritis
. Hemolytic uremic syndrome
. HELLP syndrome
117) A 23-year-old woman complains of breast pain two days after delivering her first child. The delivery was complicated by mild postpartum bleeding. On exam, both breasts are tense, warm, and tender to touch. Her blood pressure is 130/70 mmHg, heart rate is 100/min, and temperature is 99.4 F (37.4 C). What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Mastitis
. Breast abscess
. Breast engorgement
. Plugged ducts
. Superficial vein thrombosis
118) A 32-year-old woman comes to your office for re-evaluation of her birth control method. She wants her intrauterine device (IUD) removed because it is causing her pelvic pain. She wants to be placed on oral contraceptive pills (OCPs). She has had hypertension for the past five years controlled with hydrochlorothiazide and atenolol. She has a family history of diabetes mellitus and ovarian carcinoma. Her body mass index (BMI) is 34 kg/m2. Physical examination is unremarkable. If she starts taking oral contraceptive pills, which of the following statement is most correct?
. She is at risk of endometrial cancer
. Her hypertension may worsen
. She will develop benign breast disease
. She will become diabetic
. She is at risk of ovarian cancer
119) A 28-year-old G1A1 woman presents to a gynecology clinic with a chief complaint of reduced menstrual flow for the past 6 months, especially last month. She denies any pain with menstruation or irregularity in her cycle. She says that she had an elective termination by dilation and curettage approximately 9 months ago. She is sexually active with one partner and always uses condoms. Review of her records indicates a past history of abnormal Papanicolaou (Pap) smears, but she has not been followed recently. She denies any history of irregular menses, and says that age of menarche was 13 years. She takes no medications. Physical examination reveals a normally developed 68-kg (150lb) woman who is 183 cm (6') tall. She is in no acute distress. A β-human chorionic gonadotropin test from her original visit 1 week ago is negative. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Asherman’s syndrome
Cervical stenosis
Endometrial cancer
Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism
Kallmann’s syndrome
120) An 18-year-old female college student presents to student health services with a complaint of a burning sensation while urinating and abdominal pain. She denies urinary urgency or increased frequency. She has no significant past medical history. She is currently sexually active with a new partner. She does not use barrier contraception. She denies any previous history of sexually transmitted diseases. On examination she is afebrile, heart rate is 70/min, and blood pressure is 120/60 mm Hg. Examination reveals no peritoneal signs but there is tenderness to palpation over the suprapubic region. On pelvic examination the cervix appears edematous and friable with a small amount of discharge from the os. A urine sample reveals numerous WBCs but no organisms on Gram stain. A cervical swab is sent for Gram stain and culture. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for these findings?
Infection with Chlamydia trachomatis
Infection with Escherichia coli
Infection with Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Infection with Proteus mirabilis
Interstitial cystitis
121) A 13-year-old girl had growth of breast buds at 11 years, followed by the appearance of pubic hair between the ages of 11.5 and 12 years. Which pubertal event is most likely to occur next?
Beginning of accelerated growth
Menarche
Tanner stage 5 breast development
Maximal growth rate
Tanner stage 5 pubic hair
122) A 17-year-old G1P1001 is now 5 weeks postpartum after a routine vaginal delivery. She calls your office to report a 3-week history of difficulty sleeping and “feeling blue.” On further questioning, she reports difficulty concentrating, very poor appetite, occasional wishes that she had never become pregnant, and feelings of guilt about those wishes. She has not left her home in more than a week because she “just can’t find the energy to go anywhere.” This patient’s symptoms are most consistent with:
Postpartum blues
Normal adolescent adjustment to motherhood
Postpartum depression
Hypothyroidism
Postpartum psychosis
123) A 48-year-old woman with five children complains of urinary incontinence with coughing and stair climbing. She likely has genuine stress urinary incontinence if which of the following is true?
Loss of urine is secondary to involuntary bladder contractions.
Loss of urine is associated with a strong desire to void immediately.
Loss of urine occurs in relation to anxiety or depression.
Loss of urine occurs when intravesical pressure exceeds maximal urethral pressure.
Loss of urine is due to increased intravesical pressure associated with bladder distention.
124) An 18-year-old nullipara has suddenly stopped menstruating. She recently lost 8.6 kg when she started long-distance running. The laboratory test most consistent with her cause of secondary amenorrhea is which of the following?
A serum prolactin level of 86 ng/mL (normal <20)
A serum LH level of 48 mIU/mL (normal 6–35)
A serum estradiol level of 128 pg/mL (normal 40–300)
A serum FSH level of 3 mIU/mL (normal 5–18)
A serum testosterone level of 156 ng/dL (normal 40–110)
125) On the first pelvic examination of an 18-yearold nulligravida, a soft, fluctuant mass is found in the superior aspect of the right labia majora. This is asymptomatic. She tells you it has been present for several years and seems to be enlarging slightly. There is no defect in the inguinal ring. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Vulvar varicosities
Inguinal hernia
Femoral hernia
Cyst of the canal of Nuck
Granuloma inguinale
126) Your patient has just had twins and wonders if there is any way to determine whether the twins are identical. You correctly tell her which of the following?
Close examination of the placenta can often provide this answer
There is no way to tell unless one is a girl and one a boy
Only matching of human lymphocyte antigens could determine this with certainty
Identical twins occur only once in about 80 births of twins
It is unlikely because the birth weights differed by more than 200 g
127) A 42-year-old woman comes to the physician because of vaginal itch and discharge, dysuria, and dyspareunia. These symptoms have been steadily worsening over the past 3 days. Pelvic examination reveals an erythematous vagina and a thin, green, frothy vaginal discharge with a pH of 6. Microscopic examination of the discharge demonstrates the presence of a pear-shaped, motile organism. Which of the following is the most likely pathogen?
Candida albicans
Gardnerella vaginalis
Herpes simplex virus
Treponema pallidum
Trichomonas vaginalis
128) A 22-year-old professional tennis player presents to your office with a 5-month history of amenorrhea. She describes an intense schedule of regular exercise, and says that she eats a balanced diet but avoids fatty foods. She does not smoke or consume alcohol. Her mother suffers from long-standing hypertension. The patient's BMI is 22.5 kg/mm2. Pregnancy test is negative. The patient is at greatest risk for which of the following?
. Decreased thyroid function
. Decreased bone mineral density
. Atypical endometrial hyperplasia
. Poor glucose tolerance
. Cholesterol precipitation in the gallbladder
129) A 24-year-old woman delivered a healthy baby by vaginal delivery at 36 weeks gestation. She had a prolonged premature rupture of the membranes, and mid forceps application was required during delivery. On the second postpartum day she complained of fever and chills. She cannot breast-feed because her "nipples are tender''. Her temperature is 38.5 C (101.3 F), blood pressure is 120/55 mmHg and pulse is 92/min. Bimanual examination shows tender uterus and foul-smelling lochia. Her nipples are cracked but without surrounding erythema or warmth. Physical examination otherwise shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Normal postpartum
. Puerperal mastitis
. Endometritis
. Deep venous thrombosis
. Aspiration pneumonia
130) A seven-year-old girl is brought to the physician's office because of a sudden onset of growth spurt, pubic hair development, and breast enlargement. Her family history is not significant. She has no other medical problems. On examination, there is no hirsutism or acne. Her weight is 70th percentile and her height is 98th percentile. Examination showed a pelvic mass. Pelvic ultrasonogram showed a right ovarian mass. Initial evaluation showed elevated estrogen levels. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Dysgerminoma
. Sertoli-Leydig cell tumor
. Granulosa cell tumor
. Mature teratoma
. Serous cystadenoma
131) A 36-year-old woman, gravida 3, para 2, comes to the physician for a prenatal checkup. According to her last menstrual period and an ultrasonography performed at 16 weeks gestation, she is at 30 weeks gestation. She missed two antenatal appointments. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or drugs. Examination shows a fundal height of 26 cm (9.8 in). Fetal heart tones are heard by Doppler. Repeat ultrasound shows a fetal biparietal diameter consistent with 30 weeks and an abdominal circumference below the 10th percentile. Which of the following could most likely be responsible for the observed fetal findings?
. Chromosomal abnormalities
. Intrauterine infection
. Hypertension
. Fetal anomalies
. Inaccurate dates
132) A 19-year-old primigravid woman at 34 weeks gestation comes to the physician because of diffuse headache, right upper quadrant pain and visual disturbances. During her last visit two weeks ago she was found to have an elevated blood pressure and 1+ proteinuria. She was advised to follow-up closely and sent home on bed rest. Her blood pressure today is 176/120 mm Hg and pulse is 86/min. Physical examination shows 2+ pitting edema in both legs and right upper quadrant tenderness. Fetal heart tones are audible by Doppler. Urinalysis shows 3+ proteinuria. Serum aspartate aminotransferase (AST) is 88 U/L and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) is 80 U/L. Serum creatinine now is 1.4 mg/dl. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her right upper quadrant pain?
. Common bile duct obstruction
. Cystic duct obstruction
. Peptic ulcer disease
. Rupture of hepatic adenoma
. Distention of liver capsule
133) A 26-year-old woman presents to her physician because of pain in her breast. She gave birth 3 months ago and is breast-feeding. Soon after she began lactating she developed cracks in the nipples, and for the past 5 days her left breast has become progressively more tender. On physical examination, her affected breast is red, hot, swollen, and painful to palpation. Her temperature is 38.3 C (101 F), and her white cell count is 13,000/mm3. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Breast abscess
Breast cancer
Intraductal papilloma
Mastalgia
Traumatic hematoma
134) A 32-year-old G3P2 woman at 38 weeks gestation is admitted to the hospital for labor pains. Her prenatal course, prenatal tests, and fetal growth have been normal. Ultrasound at the 16th week showed no abnormalities and an intrauterine gestation consistent with dates. In her second pregnancy, she underwent a cesarean section. The woman is admitted to the delivery room and fetal heart and uterine contraction monitoring is started. Her blood pressure is 100/60 mm Hg, pulse is 115/min, and respirations are 26/min. Pelvic examination shows that the cervix is 60% effaced and 6 cm dilated. Uterine contractions are regular and occur every 4 minutes. Fetal heart tracing shows no abnormalities. The patient suddenly complains of intense lower abdominal pain. She is restless and vaginal bleeding is noted. Fetal heart monitoring shows repetitive variable decelerations, and the fetus has shifted from 0 to -2 station. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Placental abruption
. Vasa previa
. Uterine rupture
. Endometritis
. Normal delivery
135) A 16-year-old female presents to the ER complaining of left lower quadrant abdominal pain that started suddenly 24 hours ago. The pain does not radiate and is 5/10 in severity. She denies having fevers, vomiting, dysuria, diarrhea or vaginal bleeding. Her last menstrual period was two weeks ago. She takes no medications. On physical examination, her temperature is 37.2 C (98.9 F), blood pressure is 110/65 mmHg, pulse is 80/min and respirations are 14/min. There is mild left lower quadrant tenderness without rebound or rigidity, and the remainder of the examination is unremarkable. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Ectopic pregnancy
. Leiomyoma
. Midcycle pain
. Ovarian torsion
. Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome
136) A 53-year-old obese, menopausal woman comes to the physician for a routine annual examination. Her last menstrual period was one year ago. Upon further questioning, she says that she sometimes experiences hot flashes of mild intensity. She is sexually active and denies vaginal dryness or dyspareunia. Her medical problems include mild hypertension managed with hydrochlorothiazide and a salt-reduced diet. Her obstetrical history is significant for an elective termination of pregnancy at 35 years of age because of an abnormal maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein. Physical examination is normal. Which of the following is a possible cause of the comparatively milder nature of the symptoms the patient is having compared to many other menopausal women with more severe symptoms?
. Peripheral adipose tissue production of estrogens
. Compensatory adrenal production of estrogens
. Conversion of adrenal androgens to estrogens by adipose tissue
. Conversion of adrenal androgens to estrogens by the liver
. Increased levels of FSH
137) A 39-year-old G5P5 woman delivered a 4.1-kg (9-lb) healthy male infant 20 minutes ago. She is now experiencing heavy vaginal bleeding, with the passage of large blood clots. She had an uncomplicated pregnancy, with a 15.9-kg (35-lb) weight gain. The patient had spontaneous onset of labor and spontaneous rupture of the membranes at 5 cm dilation. Labor lasted 3 hours, including 10 minutes of pushing. She did not have an episiotomy. The placenta delivered spontaneously 5 minutes after the infant, was normal in appearance, and was intact with a 3-vessel cord. The patient's previous 4 pregnancies and deliveries were normal. Her blood pressure is 110/60 mm Hg, pulse is 106/min, and respirations are 20/min. The uterine fundus is soft and at the level of the umbilicus. The patient's peri-pad is saturated with blood, and there are clots extruding from the vagina. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
. Cervical/vaginal laceration
. Clotting disorder
. Inverted uterus
. Retained placental tissue
. Uterine atony
138) A 28-year-old woman is admitted for delivery. She began experiencing regular, painful uterine contractions three hours ago and her water broke en route to the hospital. The cervix is 5 cm dilated and 80% effaced. The fetal presentation is vertex and the baby's head is at -1 station. After placing a fetal heart monitor and external tocometer, repetitive decreases in fetal heart rate are noted which begin at the same time as the contractions and end before the contractions have ceased. Which of the following is most likely responsible for the fetal heart pattern?
. Periods of fetal sleep
. Umbilical cord compression
. Fetal head compression
. Uteroplacental insufficiency
. Intrauterine infection
139) A 37-year-old woman presents for evaluation of infertility. She and her 39-year-old husband have not been able to conceive after 9 months of unprotected and frequent intercourse. She had one pregnancy with her husband when she was 31. She has 28-day regular menstrual cycles and enjoys frequent sexual intercourse. She has no other complaints. She denies any previous history of sexually transmitted diseases or abdominal surgery. She does not use tobacco, alcohol or drugs. She has been working as an aerobic teacher and teaches two 30 minute classes every day. Her blood pressure is 130/80 mmHg and her pulse is 84/min. Her BMI is 23 Kg/m2. Complete physical examination is unremarkable. Which of the following is most likely cause of her condition?
. Intense exercise
. Hypothyroidism
. Premature ovarian failure
. Adrenal hyperplasia
. Oocyte aging
140) A 32-year-old woman, gravida 1, is in active labor. Lumbar epidural anesthesia is being used for pain control. She is having contractions every two to three minutes. The cervix is 4cm dilated. Fetal heart rate is reassuring. Her blood pressure is 90/55 mmHg and heart rate is 120/min. What is the most probable cause of her hypotension?
. Depressed myocardial contractility
. Intravascular fluid loss
. Blood venous pooling
. Blood redistribution to the upper trunk
. CNS involvement
141) A 23-year-old woman complains of breast pain two days after delivering her first child. The delivery was complicated by mild postpartum bleeding. On exam, both breasts are tense, warm, and tender to touch. Her blood pressure is 130/70 mmHg, heart rate is 100/min, and temperature is 994 0F (37,4 0C). What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Mastitis
. Breast abscess
. Breast engorgement
. Plugged ducts
. Superficial vein thrombosis
142) An 18-year-old woman arrives in your clinic with primary amenorrhea, sexual infantilism, and clitoromegaly. She has a history of ambiguous external genitalia noted at birth. Reviewing her records, you see that laparotomy performed at 17 months of age revealed normal internal female genitalia and ovarian biopsy performed at that time revealed normal-appearing primordial follicles. Laboratory studies today reveal a normal female karyotype and high serum testosterone and androstenedione concentrations. Estradiol and estrone are undetectable in the serum. Serum FSH and LH concentrations are high. Pelvic imaging shows multiple ovarian cysts. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia
. Aromatase deficiency
. McCune-Albright syndrome
. Kallmann's syndrome
. Galactosemia
143) A 26-year-old G0P0 comes to your office with a chief complaint of being too hairy. She reports that her menses started at age 13 and have always been very irregular. She has menses every 2 to 6 months. She also complains of acne and is currently seeing a dermatologist for the skin condition. She denies any medical problems. Her only surgery was an appendectomy at age 8. Her height is 5ft 5 in., her weight is 180 lb, and her blood pressure is 100/60 mm Hg. On physical examination, there is sparse hair around the nipples, chin, and upper lip. No galactorrhea, thyromegaly, or temporal balding is noted. Pelvic examination is normal and there is no evidence of clitoromegaly. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for this patient’s problem?
. Idiopathic hirsutism
. Polycystic ovarian syndrome
. Late-onset congenital adrenal hyperplasia
. Sertoli-Leydig cell tumor of the ovary
. Adrenal tumor
144) A 29-year-old woman comes to the office for a periodic health maintenance examination. She has no complaints. Her past medical history is significant for irritable bowel syndrome. She has never had any surgery. She has been taking the oral contraceptive pill for the past 12 years, ever since she became sexually active. She has no known drug allergies. Physical examination, including pelvic examination, is unremarkable. By taking the oral contraceptive pill, this patient is decreasing her risk most significantly for which of the following?
. Breast cancer
. Cerebrovascular disease
. Cervical cancer
. Liver cancer
. Ovarian cancer
145) A 36-year-old woman comes to your office because of back pain. She states that the pain started around the time of her cesarean delivery 8 weeks ago. The pain is located in the lower back and does not radiate. It improves with rest and worsens with prolonged standing. She cannot stand for more than 30 minutes without what she describes as debilitating pain. She has no significant past medical history. She had a cesarean delivery 8 weeks ago for arrest of dilation during labor. She had epidural anesthesia for labor and surgery. Otherwise she has never had surgery. She takes ibuprofen for the pain. She is allergic to sulfa drugs. Physical examination is within normal limits, including a normal neurologic examination. The patient is most interested in knowing what caused her to start having this back pain. Which of the following is the most appropriate response?
. “Epidurals have not been shown to be associated with back pain.”
. “Your back pain is most likely caused by breastfeeding.”
. “Your back pain was likely caused by the arrest of dilation.”
. “Your back pain was likely caused by the cesarean delivery.”
. “Your back pain is normal in the postpartum period.”
146) A 65-year-old woman comes to the physician because of bleeding from the vagina. She states that her last menstrual period was at age 50 and that she has had no bleeding since. She has no medical problems and takes no medications. She is not sexually active. Examination is unremarkable, including a normal pelvic examination. After informed consent is obtained, an endometrial biopsy is performed. The patient complains of discomfort during and after the procedure but feels well enough to go home. Later that night, with her abdominal pain worsening, the patient comes to the emergency department. An ultrasound is performed that shows a normal uterus and adnexae but a complex fluid collection posterior to the uterus. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Bowel perforation
. Endometritis
. Endometrial cancer
. Tubo-ovarian abscess
. Uterine perforation
147) A 23-year-old female comes to the physician because of a swelling in her vagina. She states that the swelling started about 3 days ago and has been growing larger since. The swelling is not painful, but it is uncomfortable when she jogs. She has asthma for which she uses an albuterol inhaler, but no other medical problems. Examination shows a cystic mass 4 cm in diameter near the hymen by the patient's left labia minora. The mass is nontender and there is no associated erythema. The mass is freely mobile. The rest of the pelvic examination is unremarkable. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Bartholin's cyst
. Condyloma lata
. Granuloma inguinale
. Hematocolpos
. Vulvar cancer
148) A 32-year-old morbidly obese diabetic woman presents to your office complaining of prolonged vaginal bleeding. She has never been pregnant. Her periods were regular, monthly, and light until 2 years ago. At that time, she started having periods every 3 to 6 months. Her last normal period was 5 months ago. She started having vaginal bleeding again 3 weeks ago, light at first. For the past week she has been bleeding heavily and passing large clots. On pelvic examination, the external genitalia is normal. The vagina is filled with large clots. A large clot is seen protruding through the cervix. The uterus is in the upper limit of normal size. The ovaries are normal to palpation. Her urine pregnancy test is negative. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Uterine fibroids
. Cervical polyp
. Incomplete abortion
. Chronic anovulation
. Coagulation defect
149) A 25-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 2 is 4days status post cesarean section and develops a temperature to 100.7 F (38.2 C). She had her cesarean section when she went into unstoppable preterm labor with a breech fetus. She had an uncomplicated postoperative course until this temperature elevation. Her pulse is 100/min, blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg, and respirations are 16/min. There is discoloration and cyanosis around the incision. The area around the incision is completely numb. There is no uterine tenderness on bimanual exam. Which of the following is of the most concern in this patient?
. Endometritis
. Mastitis
. Necrotizing fasciitis
. Preeclampsia
. Wound infection
150) A 27-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 2, comes to the physician to have her staples removed after an elective repeat cesarean delivery. Her pregnancy course was uncomplicated. She states that she is doing well except that since the delivery she has noticed some episodes of sadness and tearfulness. She is eating and sleeping normally and has no strange thoughts or thoughts of hurting herself or others. Physical examination is within normal limits for a patient who is status post cesarean delivery. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Maternity blues
. Postpartum depression
. Postpartum mania
. Postpartum psychosis
. Poststerilization depression
151) A 26-year-old primigravid woman at 42 weeks' gestation comes to the labor and delivery ward for induction of labor. The prenatal course was significant for a positive group B Streptococcus culture performed at 35 weeks. Antenatal testing over the past 2 weeks has been unremarkable. The patient is started on lactated Ringer's IV solution. Sterile vaginal examination shows that the patient's cervix is long, thick, and closed. Prostaglandin (PGE2) gel is placed into the vagina, and electronic fetal heart rate monitoring is continued. In approximately 60 minutes, the fetal heart rate falls to the 90s, as the tocodynamometer shows the uterus to be contracting every 1 minute with essentially no rest in between contractions. Which of the following was most likely the cause of the uterine hyperstimulation?
. Infection
. IV fluids
. Postdates pregnancy
. Prostaglandin (PGE2) gel
. Vaginal examination
152) A 16-year-old female comes to the physician because of an increased vaginal discharge. She developed this symptom 2 days ago. She also complains of dysuria. She is sexually active with one partner and uses condoms intermittently. Examination reveals some erythema of the cervix but is otherwise unremarkable. A urine culture is sent which comes back negative. Sexually transmitted disease testing is performed and the patient is found to have gonorrhea. While treating this patient's gonorrhea infection, treatment must also be given for which of the following?
. Bacterial vaginosis
. Chlamydia
. Herpes
. Syphilis
. Trichomoniasis
153) A 12-year-old female comes to the physician because of a vaginal discharge. The discharge started about 2 months ago and is whitish in color. There is no odor. The patient has no complaints of itching, burning, or pain. The patient started breast development at 9 years of age and her pubertal development has proceeded normally to this point. She has not had her first menses and she is not sexually active. She has no medical problems. Examination is normal for a 12-year-old female. Microscopic examination of the discharge shows no evidence of pseudohyphae, clue cells, or trichomonads. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Bacterial vaginosis
. Candida vulvovaginitis
. Physiologic leukorrhea
. Syphilis
. Trichomoniasis
154) A 50-year-old woman complains of leakage of urine. After genuine stress urinary incontinence, which of the following is the most common cause of urinary leakage?
. Detrusor dyssynergia
. Unstable bladder
. Unstable urethra
. Urethral diverticulum
. Overflow incontinence
155) A 65-year-old woman complains of leakage of urine. Which of the following is the most common cause of this condition in such patients?
. Anatomic stress urinary incontinence
. Urethral diverticulum
. Overflow incontinence
. Unstable bladder
. Fistula
156) A healthy 59-year-old woman with no history of urinary incontinence undergoes vaginal hysterectomy and anteroposterior repair for uterine prolapse, large cystocele, and rectocele. Two weeks postoperatively, she presents to your office with a new complaint of intermittent leakage of urine. What is the most likely cause of this complaint following her surgery?
. Detrusor instability
. Overflow incontinence
. Rectovaginal fistula
. Stress urinary incontinence
. Vesicovaginal fistula
157) A postmenopausal woman is undergoing evaluation for fecal incontinence. She has no other diagnosed medical problems. She lives by herself and is self-sufficient, oriented, and an excellent historian. Physical examination is completely normal. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient’s condition?
. Rectal prolapse
. Diabetes
. Obstetric trauma
. Senility
. Excessive caffeine intake
158) A 30-year-old G3P3 is being evaluated for urinary urgency, urinary frequency, and dysuria. She also complains of pain with insertion when attempting intercourse. She frequently dribbles a few drops of urine after she finishes voiding. She has had three full-term spontaneous vaginal deliveries. Her last baby weighed more than 9 lb. She had multiple sutures placed in the vaginal area after delivery of that child. She also has a history of multiple urinary tract infections since she was a teenager. On pelvic examination, she has a 1-cm tender suburethral mass. With palpation of the mass, a small amount of blood-tinged pus is expressed from the urethra. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient’s problem?
. Urethral polyp
. Urethral fistula
. Urethral stricture
. Urethral eversion
. Urethral diverticulum
159) A 22-year-old woman, gravida 4, para 3, at 38 weeks' gestation comes to the labor and delivery ward with a gush of fluid. Sterile speculum examination reveals a pool of fluid that is nitrazine positive and forms ferns when viewed under the microscope. The fetal heart rate is in the 150s and reactive. An ultrasound demonstrates that the fetus is in the breech position. A cesarean delivery is performed. During the operation, the physician, who has received no recent immunizations, is stuck with a needle that had been used on the patient. Which of the following is this physician at greatest risk of contracting?
. HIV
. Hepatitis B
. Hepatitis C
. Scabies
. Syphilis
160) A 67-year-old woman comes to the physician because of pain with urination and frequent urination. She has hypertension for which she takes a beta-blocker, but no other medical problems. She states that she is not sexually active. She does not smoke and drinks cranberry juice daily. Examination shows mild suprapubic tenderness and genital atrophy but is otherwise unremarkable. Urinalysis shows 50 to 100 leukocytes/high powered field (hpf) and 5 to 10 erythrocytes/hpf. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the infection?
. Cardiac disease
. Cranberry juice ingestion
. Hypoestrogenism
. Nephrolithiasis
. Sexual intercourse
161) A 39-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, at 30-weeks gestation comes to the physician for a prenatal visit. The patient's due date was determined by a 7-week ultrasound. Her prenatal course has been unremarkable. She has no complaints of contractions, loss of fluid, or bleeding from the vagina, and her baby is moving well. Examination demonstrates a fetal heart rate of 150 and a fundal height of 27 centimeters, which is the same measurement as that determined 4 weeks ago. This patient's fundal height measurement is most suggestive of which of the following?
. Inaccurate estimated date of delivery (due date)
. Intrauterine growth restriction
. Premature labor
. Twin gestation
. Uterine cancer
162) A 19-year-old female comes to the physician because she has not had a menstrual period. She experienced normal breast development through puberty but has yet to have a period. She has no other complaints. She has no medical problems. Examination shows the patient to be tall with long arms and big hands. The breasts are normal-appearing except that the nipples are immature and the areolae are pale. Pelvic examination shows scant pubic hair with a blind-ended vaginal pouch. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Asherman syndrome
. Kallmann syndrome
. Polycystic ovarian syndrome
. Testicular feminization syndrome
. Turner syndrome
163) A 53-year-old woman comes to the physician because of concerns regarding menopause. She has a period almost every month, but her cycle is lengthening. She is worried because her mother, her two older sisters, and practically all her aunts have osteoporosis. She does not want to be on estrogen because she is concerned about cancer and thrombosis. Physical examination is within normal limits. The patient is started on raloxifene. On this medication, which of the following is this patient most likely to develop?
. Breast cancer
. Elevated cholesterol
. Endometrial hyperplasia
. Hot flashes
. Osteoporosis
164) A 24-year-old woman comes to the physician for an initial prenatal visit. Her last menstrual period was 7 weeks ago and a home urine pregnancy test was positive. She has had no bleeding or abdominal pain. She does complain of increased fatigue lately and some mild nausea and vomiting. Examination is significant for both a systolic and a diastolic cardiac murmur. The uterus is 8 weeks' sized and nontender. Which of the following findings is most suggestive of structural heart disease in this woman?
. Diastolic murmur
. Enlarged uterus
. Fatigue
. Nausea and vomiting
. Systolic murmur
165) A 75-year-old woman comes to the physician because of abdominal distension. She states that she always feels bloated and that she gets full quickly when eating. She has hypertension, for which she takes an angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor, and no other medical problems. Examination shows abdominal distension and a positive fluid wave. Pelvic examination reveals a large, nontender right adnexal mass. Abdominal CT scan demonstrates masses on both ovaries, ascites, and omental caking. CA-125 level is significantly elevated. Serum alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) are negative. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Choriocarcinoma
. Cystic teratoma (dermoid)
. Embryonal carcinoma
. Epithelial ovarian cancer
. Sertoli stromal cell tumor
166) A 20-year-old woman presents to her gynecologist complaining of several days of vaginal itching and increased vaginal secretions that have an unpleasant odor. She denies any recent fever, back pain, hematuria, or vaginal bleeding. She has been sexually active with multiple sexual partners and rarely uses protection. On examination she has a moderate amount of frothy green discharge. Amine “whiff” test of the discharge is negative, and the pH of the discharge is 6. Multiflagellated organisms are seen on microscopy. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Bacterial vaginosis
Neisseria gonorrhoeae infection
Syphilis
Trichomoniasis
Vaginal candidiasis
167) A 20-year-old primigravid woman at 32 weeks gestation comes to the physician because of swelling in her hands and ankles. She has no headache, visual disturbances or epigastric pain. She has no previous medical problems. She does not use tobacco, alcohol or illicit drugs. Her previous prenatal check-up at 28 weeks gestation was normal. Her medical records show no preexisting hypertension or proteinuria. Her blood pressure is 156/100 mmHg, and after 15 minutes of lateral rest, a repeat reading is 154/98 mmHg. Physical examination shows 2+ pitting edema in both legs and hands. Deep tendon reflexes are normal. Fundoscopic examination shows no abnormalities. Fetal heart tones are audible by Doppler. Laboratory studies show: Hb: 13.0 g/dl, Hct: 50%, Platelets: 300,000/mm3, Creatinine: 1.1 mg/dl. 24-hours urine protein excretion is 1gm, which is new. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Mild preeclampsia
. Severe preeclampsia
. Chronic hypertension
. Transient hypertension of pregnancy
. Eclampsia
168) A 29-year-old G3P2 black woman in the thirty-third week of gestation is admitted to the emergency room because of acute abdominal pain that has been increasing during the past 24 hours. The pain is severe and is radiating from the epigastrium to the back. The patient has vomited a few times and has not eaten or had a bowel movement since the pain started. On examination, you observe an acutely ill patient lying on the bed with her knees drawn up. Her blood pressure is 100/70 mm Hg, her pulse is 110 beats per minute, and her temperature is 38.8C (101.8F). On palpation, the abdomen is somewhat distended and tender, mainly in the epigastric area, and the uterine fundus reaches 31 cm above the symphysis. Hypotonic bowel sounds are noted. Fetal monitoring reveals a normal pattern of fetal heart rate (FHR) without uterine contractions. On ultrasonography, the fetus is in vertex presentation and appropriate in size for gestational age; fetal breathing and trunk movements are noted, and the volume of amniotic fluid is normal. The placenta is located on the anterior uterine wall and no previa is seen. Laboratory values show mild leukocytosis (12,000 cells per mL); a hematocrit of 43; mildly elevated serum glutamicoxaloacetic transaminase (SGOT), serum glutamic-pyruvic transaminase (SGPT), and bilirubin; and serum amylase of 180 U/dL. Urinalysis is normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Acute degeneration of uterine leiomyoma
. Acute cholecystitis
. Acute pancreatitis
. Acute appendicitis
. Severe preeclamptic toxemia
169) A 38-year-old G1P0 presents to the obstetrician’s office at 37 weeks gestational age complaining of a rash on her abdomen that is becoming increasingly pruritic. The rash started on her abdomen, and the patient notes that it is starting to spread downward to her thighs. The patient reports no previous history of any skin disorders or problems. She denies any malaise or fever. On physical examination, she is afebrile and her physician notes that her abdomen, and most notably her stretch marks, is covered with red papules and plaques. No excoriations or bullae are present. The patient’s face, arms, and legs are unaffected by the rash. Which of the following is this patient’s most likely diagnosis?
. Herpes gestationis
. Pruritic urticarial papules and plaques of pregnancy
. Prurigo gravidarum
. Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy
. Impetigo herpetiformis
170) A 28-year-old G1 presents to your office at 8 weeks gestation. She has a history of diabetes since the age of 14. She uses insulin and denies any complications related to her diabetes. Which of the following is the most common birth defect associated with diabetes?
. Anencephaly
. Encephalocele
. Meningomyelocele
. Sacral agenesis
. Ventricular septal defect
171) A 32-year-old G1 at 10 weeks gestation presents for her routine OB visit. She is worried about her pregnancy because she has a history of insulin-requiring diabetes since the age of 18. Prior to becoming pregnant, her endocrinologist diagnosed her with microalbuminuria. She has had photo laser ablation of retinopathy in the past. Which diabetic complication is most likely to be worsened by pregnancy?
. Benign retinopathy
. Gastroparesis
. Nephropathy
. Neuropathy
. Proliferative retinopathy
172) A 40-year-old G3P2 obese patient at 37 weeks presents for her routine OB visit. She has gestational diabetes that is controlled with diet. She reports that her fasting and postprandial sugars have all been within the normal range. Her fetus has an estimated fetal weight of 6.5 lb by Leopold maneuvers. Which of the following is the best next step in her management?
. Administration of insulin to prevent macrosomia
. Cesarean delivery at 39 weeks to prevent shoulder dystocia
. Induction of labor at 38 weeks
. Kick counts and routine return OB visit in 1 week
. Weekly biophysical profile
173) A 36-year-old G1P0 at 35 weeks gestation presents to labor and delivery complaining of a several-day history of generalized malaise, anorexia, nausea, and emesis. She denies any headache or visual changes. Her fetal movement has been good, and she denies any regular uterine contractions, vaginal bleeding, or rupture of membranes. On physical examination, you notice that she is mildly jaundiced and appears to be a little confused. Her vital signs indicate a temperature of 37.7C (99.9F), pulse of 70 beats per minute, and blood pressure of 100/62 mm Hg. Blood is drawn and the following results are obtained: WBC = 25,000, Hct = 42.0, platelets = 51,000, SGOT/PT= 287/350, glucose = 43, creatinine = 2.0, fibrinogen = 135, PT/PTT = 16/50 s, serum ammonia level = 90 mmol/L (nl = 11-35). Urinalysis is positive for 3+ protein and large ketones. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Hepatitis B
. Acute fatty liver of pregnancy
. Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy
. Severe preeclampsia
. Hyperemesis gravidarum
174) A 32-year-old G1P0 reports to your office for a routine OB visit at 14 weeks gestational age. Labs drawn at her first prenatal visit 4 weeks ago reveal a platelet count of 60,000, a normal PT, PTT and bleeding time. All her other labs were within normal limits. During the present visit, the patient has a blood pressure of 120/70 mm Hg. Her urine dip reveals the presence of trace protein. The patient denies any complaints. The only medication she is currently taking is a prenatal vitamin. On taking a more in-depth history you learn that, prior to pregnancy, your patient had a history of occasional nose and gum bleeds, but no serious bleeding episodes. She has considered herself to be a person who just bruises easily. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Alloimmune thrombocytopenia
. Gestational thrombocytopenia
. Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura
. HELLP syndrome
. Pregnancy-induced hypertension
175) A 20-year-old G1 patient delivers a live-born infant with cutaneous lesions, limb defects, cerebral cortical atrophy, and chorioretinitis. Her pregnancy was complicated by pneumonia at 18 weeks. What is the most likely causative agent?
. Cytomegalovirus
. Group B streptococcus
. Rubella virus
. Treponemal pallidum
. Varicella zoster
176) A 34-year-old G2 at 36 weeks delivers a growth-restricted infant with cataracts, anemia, patent ductus arteriosus, and sensorineural deafness. She has a history of chronic hypertension, which was well controlled with methyldopa during pregnancy. She had a viral syndrome with rash in early pregnancy. What is the most likely causative agent?
. Parvovirus
. Rubella virus
. Rubeola
. Toxoplasma gondii
. T. pallidum
177) A 25-year-old G3 at 39 weeks delivers a small-for-gestational-age infant with chorioretinitis, intracranial calcifications, jaundice, hepatosplenomegaly, and anemia. The infant displays poor feeding and tone in the nursery. The patient denies eating any raw or undercooked meat and does not have any cats living at home with her. She works as a nurse in the pediatric intensive care unit at the local hospital. What is the most likely causative agent?
. Cytomegalovirus
. Group B streptococcus
. Hepatitis B
. Parvovirus
. T. gondii
178) A 23-year-old G1 with a history of a flulike illness, fever, myalgias, and lymphadenopathy during her early third trimester delivers a growth-restricted infant with seizures, intracranial calcifications, hepatosplenomegaly, jaundice, and anemia. What is the most likely causative agent?
. Cytomegalovirus
. Hepatitis B
. Influenza A
. Parvovirus
. T. gondii
179) A 32-year-old G5 delivers a stillborn fetus at 34 weeks. The placenta is noted to be much larger than normal. The fetus appeared hydropic and had petechiae over much of the skin. What is the most likely causative agent?
. Herpes simplex
. Parvovirus
. Rubella virus
. T. pallidum
. Varicella zoster
180) A 38-year-woman at 39 weeks delivers a 7-lb infant female without complications. At 2 weeks of life, the infant develops fulminant liver failure and dies. What is the most likely causative virus?
. Cytomegalovirus
. Hepatitis B
. Herpes simplex
. Parvovirus
. Rubeola
181) A 20-year-old woman who works as a kindergarten teacher presents for her routine visit at 32 weeks. Her fundal height measures 40 cm. An ultrasound reveals polyhydramnios, an appropriately grown fetus with ascites and scalp edema. The patient denies any recent illnesses, but some of the children at her school have been sick recently. What is the most likely cause of the fetal findings?
. Cytomegalovirus
. Hepatitis B
. Influenza A
. Parvovirus
. Toxoplasmosis gondii
182) A 25-year-old female in her first pregnancy delivers a 6-lb male infant at 38 weeks. The infant develops fever, vesicular rash, poor feeding, and listlessness at 1 week of age. What is the most likely cause of the infant’s signs and symptoms?
. Cytomegalovirus
. Group B streptococcus
. Hepatitis B
. Herpes simplex
. Listeria monocytogenes
183) A 22-year-old woman delivers a 7-lb male infant at 40 weeks without any complications. On day 3 of life, the infant develops respiratory distress, hypotension, tachycardia, listlessness, and oliguria. What is the most likely cause of the infant’s illness?
. Cytomegalovirus
. Group B streptococcus
. Hepatitis B
. Herpes simplex
. L. monocytogenes
184) A 29-year-old G2P1 at 40 weeks is in active labor. Her cervix is 5 cm dilated, completely effaced, and the vertex is at 0 station. She is on oxytocin to augment her labor and she has just received an epidural for pain management. The nurse calls you to the room because the fetal heart rate has been in the 70s for the past 3 minutes. The contraction pattern is noted to be every 3 minutes, each lasting 60 seconds, with return to normal tone in between contractions. The patient’s vital signs are blood pressure 90/40 mm Hg, pulse 105 beats per minute, respiratory rate 18 breaths per minute, and temperature 36.1C (97.6F). On repeat cervical examination, the vertex is well applied to the cervix and the patient remains 5 cm dilated and at 0 station, and no vaginal bleeding is noted. Which of the following is the most likely cause for the deceleration?
. Cord prolapse
. Epidural analgesia
. Pitocin
. Placental abruption
. Uterine hyperstimulation
185) You are delivering a 33-year-old G3P2 and encounter a shoulder dystocia. After performing the appropriate maneuvers, the baby finally delivers, and the pediatricians attending the delivery note that the right arm is hanging limply to the baby’s side with the forearm extended and internally rotated. Which of the following is the baby’s most likely diagnosis?
. Erb palsy
. Klumpke paralysis
. Humeral fracture
. Clavicular fracture
. Paralysis from intraventricular bleed
186) A 25-year-old G1 at 37 weeks presents to labor and delivery with gross rupture of membranes. The fluid is noted to be clear and the patient is noted to have regular painful contractions every 2 to 3 minutes lasting for 60 seconds each. The fetal heart rate tracing is reactive. On cervical examination she is noted to be 4 cm dilated, 90% effaced with the presenting part a −3 station. The presenting part is soft and felt to be the fetal buttock. A quick bedside ultrasound reveals a breech presentation with both hips flexed and knees extended. What type of breech presentation is described?
. Frank
. Incomplete, single footling
. Complete
. Double footling
. Cephalic presentation
187) A 34-year-old G3P2 delivers a baby by spontaneous vaginal delivery. She had scant prenatal care and no ultrasound, so she is anxious to know the sex of the baby. At first glance you notice female genitalia, but on closer examination the genitalia are ambiguous. Which of the following is the best next step in the evaluation of this infant?
. Chromosomal analysis
. Evaluation at 1 month of age
. Pelvic ultrasound
. Thorough physical examination
. Laparotomy for gonadectomy
188) A 24-year-old primigravid woman, who is intent on breast-feeding, decides on a home delivery. Immediately after the birth of a 4.1-kg (9-lb) infant, the patient bleeds massively from extensive vaginal and cervical lacerations. She is brought to the nearest hospital in shock. Over 2 hours, 9 units of blood are transfused, and the patient’s blood pressure returns to a reasonable level. A hemoglobin value the next day is 7.5 g/dL, and 3 units of packed red blood cells are given. The most likely late sequela to consider in this woman is which of the following?
. Hemochromatosis
. Stein-Leventhal syndrome
. Sheehan syndrome
. Simmonds syndrome
. Cushing syndrome
189) A 27-year-old G4P3 at 37 weeks presents to the hospital with heavy vaginal bleeding and painful uterine contractions. Quick bedside ultrasound reveals a fundal placenta. The patient’s vital signs are blood pressure 140/92 mmHg, pulse 118 beats per minute, respiratory rate 20 breaths per minute, and temperature 37C (98.6F). The fetal heart rate tracing reveals tachycardia with decreased variability and a few late decelerations. An emergency cesarean section delivers a male infant with Apgar scores of 4 and 9. With delivery of the placenta, a large retroplacental clot is noted. The patient becomes hypotensive, and bleeding is noted from the wound edges and her IV catheter sites. She requires 12 units of packed red blood cells and fresh frozen plasma for resuscitation. After a short stay in the intensive care unit the patient recovers. When can long-term complications related to sequela of postpartum hemorrhage first be noted?
. 6 hours postpartum
. 1 week postpartum
. 1 month postpartum
. 6 month postpartum
. 1 year postpartum
190) On postoperative day 3 after an uncomplicated repeat cesarean delivery, the patient develops a fever of 38.2C (100.8F). She has no complaints except for some fullness in her breasts. On examination she appears in no distress; lung and cardiac examinations are normal. Her breast examination reveals full, firm breasts bilaterally slightly tender with no erythema or masses. She is not breast-feeding. The abdomen is soft with firm, nontender fundus at the umbilicus. The lochia appears normal and is nonodorous. Urinalysis and white blood cell count are normal. Which of the following is a characteristic of the cause of her puerperal fever?
. Appears in less than 5% of postpartum women
. Appears 3 to 4 days after the development of lacteal secretion
. Is almost always painless
. Fever rarely exceeds 37.8C (99.8F)
. Is less severe and less common if lactation is suppressed
191) A 22-year-old G1 at 34 weeks is tested for tuberculosis because her father, with whom she lives, was recently diagnosed with tuberculosis. Her skin test is positive and her chest x-ray reveals a granuloma in the upper left lobe. Which of the following is true concerning infants born to mothers with active tuberculosis?
. The risk of active disease during the first year of life may approach 90% without prophylaxis.
. Bacille Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccination of the newborn infant without evidence of active disease is not appropriate.
. Future ability for tuberculin skin testing is lost after BCG administration to the newborn.
. Neonatal infection is most likely acquired by aspiration of infected amniotic fluid.
. Congenital infection is common despite therapy
192) A 21-year-old G1 at 40 weeks, who underwent induction of labor for severe preeclampsia, delivered a 3900-g male infant via vaginal delivery after pushing for 21/2 hours. A second-degree midline laceration and sidewall laceration were repaired in the usual fashion under local analgesia. The estimated blood loss was 450 cc. Magnesium sulfate is continued postpartum for the seizure prophylaxis. Six hours after the delivery, the patient has difficulty voiding. Which is the most likely cause of her problem?
. Preeclampsia
. Infusion of magnesium sulfate
. Vulvar hematoma
. Ureteral injury
. Use of local analgesia for repair
193) Three days ago you delivered a 40-year-old G1P1 by cesarean section following arrest of descent after 2 hours of pushing. Labor was also significant for prolonged rupture of membranes. The patient had an epidural, which was removed the day following delivery. The nurse pages you to come to see the patient on the postpartum floor because she has a fever of 38.8C (102F) and is experiencing shaking chills. Her blood pressure is 120/70 mm Hg and her pulse is 120 beats per minute. She has been eating a regular diet without difficulty and had a normal bowel movement this morning. She is attempting to breast-feed, but says her milk has not come in yet. On physical examination, her breasts are mildly engorged and tender bilaterally. Her lungs are clear. Her abdomen is tender over the fundus, but no rebound is present. Her incision has some serous drainage at the right apex, but no erythema is noted. Her pelvic examination reveals uterine tenderness but no masses. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Pelvic abscess
. Septic pelvic thrombophlebitis
. Wound infection
. Endometritis
. Atelectasis
194) A 34-year-old G1P1 who delivered her first baby 5 weeks ago calls your office and asks to speak with you. She tells you that she is feeling very overwhelmed and anxious. She feels that she cannot do anything right and feels sad throughout the day. She tells you that she finds herself crying all the time and is unable to sleep at night. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Postpartum depression
. Maternity blues
. Postpartum psychosis
. Bipolar disease
. Postpartum blues
195) A 40-year-old G4P5 at 39 weeks gestation has progressed rapidly in labor with a reassuring fetal heart rate pattern. She has had an uncomplicated pregnancy with normal prenatal labs, including an amniocentesis for advanced maternal age. The patient begins the second stage of labor and after 15 minutes of pushing starts to demonstrate deep variable heart rate accelerations. You suspect that she may have a fetus with a nuchal cord. You expediently deliver the baby by low-outlet forceps and hand the baby over to the neonatologists called to attend the delivery. As soon as the baby is handed off to the pediatric team, it lets out a strong spontaneous cry. The infant is pink with slightly blue extremities that are actively moving and kicking. The heart rate is noted to be 110 on auscultation. What Apgar score should the pediatricians assign to this baby at 1 minute of life?
. 10
. 9
. 8
. 7
. 6
196) A 32-year-old G2P1 at 41 weeks is undergoing an induction of oligohydramnios. During the course of her labor, the fetal heart rate tracing demonstrates severe variable decelerations that do not respond to oxygen, fluid, or amnioinfusion. The patient’s cervix is dilated to 4 cm. A low-transverse cesarean delivery is performed for nonreassuring fetal heart tones. After delivery of the fetus you send a cord gas, which comes back with the following arterial blood values: pH 7.29, Pco2: 50, and Po2: 20. What condition does the cord blood gas indicate?
. Normal fetal status
. Fetal acidemia
. Fetal hypoxia
. Fetal asphyxia
. Fetal metabolic acidosis
197) A 25-year-old G1P1 comes to see you 6 weeks after an uncomplicated vaginal delivery for a routine postpartum examination. She denies any problems and has been breast-feeding her newborn without any difficulties since leaving the hospital. During the bimanual examination, you note that her uterus is irregular, firm, nontender, and about a 15-week size. Which of the following is the most likely etiology for this enlarged uterus?
. Subinvolution of the uterus
. The uterus is appropriate size for 6 weeks postpartum
. Fibroid uterus
. Adenomyosis
. Endometritis
198) A 74-year-old woman presents to your office for well-woman examination. Her last Pap smear and mammogram were 3 years ago. She has hypertension, high cholesterol, and osteoarthritis. She stopped smoking 15 years ago, and denies alcohol use. Based on this patient’s history which of the following medical conditions should be this patient’s biggest concern?
. Alzheimer disease
. Breast cancer
. Cerebrovascular disease
. Heart disease
. Lung cancer
199) A 16-year-old G0 female presents to your office for a routine annual gynecologic examination. She reports that she has previously been sexually active, but currently is not dating anyone. She has had three sexual partners in the past and says she diligently used condoms. She is a senior in high school and is doing well academically and has many friends. She lives at home with her parents and a younger sibling. She denies any family history of medical problems, but says her 80-year-old grandmother was recently diagnosed with breast cancer. She denies any other family history of cancer. She says she is healthy and has no history of medical problems or surgeries. She reports having had chicken pox. She smokes tobacco and drinks beer occasionally, but denies any illicit drug use. She had her first Pap smear and gynecologic examination last year with another doctor and reports that everything was normal. Her menses started at age 13 and are regular and light. She denies any dysmenorrhea. Her blood pressure is 90/60 mm Hg. Her height is 5ft 6 in and she weighs 130 lb. Based on this patient’s history, what would be the most likely cause of death if she were to die at age 16?
. Suicide
. Homicide
. Motor vehicle accidents
. Cancer
. Heart disease
200) A married 41-year-old G5P3114 presents to your office for a routine examination. She reports being healthy except for a history of migraine headaches. All her Pap smears have been normal. She developed gestational diabetes in her last pregnancy. She drinks alcohol socially, and admits to smoking occasionally. Her grandmother was diagnosed with ovarian cancer when she was in her fifties. Her blood pressure is 140/90 mm Hg; height is 5ft 5 in; weight is 150 lb. Which of the following is the most common cause of death in women of this patient’s age?
. HIV
. Cardiac disease
. Accidents
. Suicide
. Cancer
201) A 34-year-old woman comes to the physician for evaluation of vulvar lesions. Examination reveals multiple small teardrop shaped growths at the vestibule of the vulva. Application of trichloroacetic acid results incomplete resolution of the lesions. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her lesions?
. Secondary syphilis
. Human papilloma virus
. Carcinoma of vulva
. Lichen sclerosis
. Lichen planus
202) A 36-year-old G2P2 presents for her well-woman examination. She has had two spontaneous vaginal deliveries without complications. Her largest child weighed 3500 g at birth. She uses oral contraceptive pills and denies any history of an abnormal Pap smear. She does not smoke, but drinks about four times per week. Her weight is 70 kg. Her vital signs are normal. After placement of the speculum, you note a clear cyst approximately 2.5 cm in size on the lateral wall of the vagina on the right side. The cyst is nontender and does not cause the patient any dyspareunia or discomfort. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis of this mass?
. Bartholin duct cyst
. Gartner duct cyst
. Lipoma
. Hematoma
. Inclusion cyst
203) A 24-year-old nullipara is being evaluated for infertility. On pelvic examination, she has a single cervix. A diagnostic laparoscopy shows a double uterine fundus. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis of her uterine anomaly?
Septate uterus
Unicornuate uterus
Bicornuate uterus
Didelphic uterus
A diethylstilbestrol (DES) exposed uterus
204) A 58-year-old G6P4Ab2 diabetic woman who weighs 122.6 kg (270 lb) has her first episode of vaginal bleeding in 5 years. Her physician performs an outpatient operative hysteroscopy and dilatation and curettage (D&C). Which of the following is an indication for the procedure and the most likely diagnosis?
Endometrial cancer because of her high parity
Endometrial cancer because of her obesity
Cervical cancer because of her age
Cervical cancer because of her diabetes
Ovarian cancer because of her obesity
205) A 53-year-old obese, postmenopausal woman presents to your office for a routine annual examination. Her last menstrual period was one year ago. Upon further questioning, she says that she sometimes experiences hot flashes of mild intensity. She is sexually active and denies vaginal dryness or dyspareunia. She has mild hypertension managed with hydrochlorothiazide and a salt-reduced diet. Her obstetrical history is significant for an elective termination of pregnancy at 35 years of age because of an abnormal MSAFP. Physical examination is normal. What is the most likely cause of the mild nature of the symptoms the patient is having?
. Peripheral fat tissue production of estrogens
. Compensatory adrenal production of estrogens
. Conversion of adrenal androgens to estrogens by fat tissue
. Conversion of adrenal androgens to estrogens by liver
. Increased levels of FSH
206) A 26-year-old woman comes to the physician’s office for evaluation of a vulvar ulcer that she noticed two days ago. Initially she had a small painless papule that later became ulcerated. Upon further questioning she reluctantly admits to using sex to obtain drugs. She also reports using oral contraceptives to prevent pregnancy. On vulvar examination there is a 2cm ulcer with a non-exudative base and a raised, indurated margin. Painless bilateral inguinal lymphadenopathy is present. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Syphilis
. Chancroid
. Herpes genitalis
. Granuloma inguinale
. Basal cell carcinoma
207) A 19-year-old primigravid woman at 39 weeks’ gestation is in active labor, and her cervix is 4 cm dilated, 90% effaced. Her amniotic membranes have been ruptured for 4 hours. Contractions are strong at 2- to 3-minute intervals and of 60- to 70-second duration. For the past 30 minutes, repetitive variable decelerations of the fetal heart rate have occurred. They have lasted 60–90 seconds, and the fetal heart rate has dropped as low as 60 beat per minute (BPM). You explain that there is a risk that the baby will become hypoxic and recommend a cesarean section. She refuses. Which of the following is the most appropriate course of action?
Obtain permission for the cesarean section from her mother
Perform a cesarean section as an emergency
Obtain a court order permitting a cesarean section
Counsel her carefully about the fetal risks but accede to her wishes
Assign her care to another obstetrician
208) A 24-year-old woman has a MSAFP of 0.5 MOM (multiples of the median) at 17 weeks’ gestation. Which of the following fetal abnormalities is most likely to occur with this MSAFP?
Spina bifida
Omphalocele
Gastroschisis
Bladder exstrophy
Trisomy 21
209) A 69-year-old woman with diabetes mellitus complains of urinary incontinence. Her diabetes is well controlled with oral hypoglycemic agents. She has no complaints other than the wetness. Which of the following tests is most likely to demonstrate the cause?
Urinalysis
Urine culture and sensitivity
Intravesical instillation of methylene blue
The Q-tip test
Measurement of residual urine volume
210) A 48-year-old G5P5 woman has genuine stress incontinence (GSI). Kegel exercises have not helped, and her incontinence is gradually worsening. Her urethrovesical junction (UVJ) is prolapsed into the vagina, and her urethral closure pressure is normal. Which of the following procedures will most likely cure her incontinence?
Retropubic urethropexy
Anterior colporrhaphy
Suburethral sling procedure
Needle suspension of paraurethral tissue
Paraurethral collagen injections
211) A 51-year-old woman comes to your office for a routine health maintenance examination. She says that she has been having irregular menses and occasional hot flashes for the past eight months. She has a very stressful job and drinks two to three cups of coffee every morning. She does not smoke, but drinks two to three ounces of alcohol daily. She eats a pure vegetarian diet and walks two miles on a treadmill each day. Her vital signs are within normal limits. Her BMI is 31 kg/m2 Physical examination is unremarkable. You inform her that she is probably reaching menopause, and that she will be at an increased risk of developing osteoporosis. Which of the following is the most significant risk factor for the development of osteoporosis in this patient?
. Caffeine use
. Obesity
. Excess alcohol use
. Vegetarian diet
. Excess walking
212) A 16-year-old female presents to the ER complaining of left lower quadrant abdominal pain that started suddenly 24 hours ago. The pain does not radiate and is 5/ 10 in severity. She denies having fevers, vomiting, dysuria, diarrhea or vaginal bleeding. Her last menstrual period was two weeks ago. She takes no medications. On physical examination, her temperature is 37.20C (98.9.F), blood pressure is 11 0/65 mmHg, pulse is 80/min and respirations are 14/min. There is mild left lower quadrant tenderness without rebound or rigidity, and the remainder of the examination is unremarkable. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Ectopic pregnancy
. Leiomyoma
. Midcycle pain
. Acute appendicitis
. Pelvic inflammatory disease
213) A 30-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 10-month history of dysmenorrhea associated with a dull pelvic sensation. She has heavy periods but denies inter-menstrual bleeding. She is sexually active with her husband and does not use contraception because they have been trying to become pregnant for one year. She has no pain during intercourse. Physical examination shows normal external genitalia and an enlarged uterus, but is otherwise normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Pelvic inflammatory disease
. Endometriosis
. Fibroid uterus
. Pelvic congestion syndrome
. Primary dysmenorrhea
214) A 26-year-old woman complains of a vaginal discharge causing burning and itching of the perineum. The pH of the discharge is 4.5. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her discharge?
Monilial vaginitis
Trichomonas vaginitis
Chlamydial cervicitis
Gonococcal cervicitis
Bacterial vaginosis
215) A 45-year-old woman has bilateral breast pain that is most severe premenstrually. On palpation, there is excessive nodularity, tenderness, and cystic areas that diminish in size after menses. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Fibrocystic disease
Fibroadenomas
Intraductal papilloma
Breast cancer
Engorgement attributable to increased prolactin
216) A 19-year-old nulligravid woman at 38 weeks' gestation comes to her physician because she has passed bloody mucus discharge. Her prenatal course was unremarkable including a normal 19-week ultrasound. On speculum examination, there are no vaginal or cervical lesions. On vaginal examination, the cervix is 2 cm dilated and 100% effaced, and the fetus is at +1 station. The fetal heart rate has a baseline of 140 and is reactive. She has painful contractions every 2 minutes. One hour later the patient's cervix is 3 cm dilated, and a small amount of bloody mucus is noted on the examining glove. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Early labor
Placental abruption
Placenta previa
Urinary tract infection
Vasa previa
217) A 33-year-old, white woman, gravida 3, para 2, at 37 weeks' gestation comes to the emergency department because of painful uterine contractions and heavy vaginal bleeding that started after she used intranasal cocaine. The patient's prenatal course was significant because she conceived while on the oral contraceptive pill, she occasionally used cocaine and heroin during the pregnancy, and she was found to be positive for group B Streptococcus colonization at 35 weeks. Fetal monitoring is not reassuring. The patient undergoes cesarean section, at which the uterus has a bluish hue. On inspection, the placenta is noted to have an adherent, retroplacental clot on 50% of its surface. Which of the following is the most likely initiating factor for this patient's presentation?
Cocaine
Gestational age
Group B Streptococcus colonization
Oral contraceptive pill use
White race
218) A 64-year-old woman comes to the physician because she is "leaking" urine. She states that, over the past 3 years, she has had incontinence several times daily. She describes these episodes as small squirts of urine that come out whenever she laughs, coughs, sneezes, or engages in physical activity. Physical examination shows mild uterine prolapse and a moderate cystocele. Urine culture is negative. Postvoid residual is 25 ml (normal <50 mL) Cystometrogram is normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Detrusor instability (DI)
Genuine stress urinary incontinence (GSUI)
Neurogenic bladder
Pyelonephritis
Urinary tract infection
219) A 50-year-old woman is diagnosed with cervical cancer. Which lymph node group would be the first involved in metastatic spread of this disease beyond the cervix and uterus?
. Common iliac nodes
. Parametrial nodes
. External iliac nodes
. Paracervical or ureteral nodes
. Para-aortic nodes
220) A 51-year-old woman is diagnosed with invasive cervical carcinoma by cone biopsy. Pelvic examination and rectal-vaginal examination reveal the parametrium to be free of disease, but the upper portion of the vagina is involved with tumor. Intravenous pyelography (IVP) and sigmoidoscopy are negative, but a computed tomography (CT) scan of the abdomen and pelvis shows grossly enlarged pelvic and periaortic nodes. This patient is classified at which of the following stages?
. IIa
. IIb
. IIIa
. IIIb
. IV
221) A 70-year-old woman presents for evaluation of a pruritic lesion on the vulva. Examination shows a white, friable lesion on the right labia majora that is 3 cm in diameter. No other suspicious areas are noted. Biopsy of the lesion confirms squamous cell carcinoma. In this patient, lymphatic drainage characteristically would be first to which of the following nodes?
. External iliac lymph nodes
. Superficial inguinal lymph nodes
. Deep femoral lymph nodes
. Periaortic nodes
. Internal iliac nodes
222) A postmenopausal woman presents with pruritic white lesions on the vulva. Punch biopsy of a representative area is obtained. Which of the following histologic findings is consistent with the diagnosis of lichen sclerosus?
. Blunting or loss of rete pegs
. Presence of thickened keratin layer
. Acute inflammatory infiltration
. Increase in the number of cellular layers in the epidermis
. Presence of mitotic figures
223) At the time of annual examination, a patient expresses concern regarding possible exposure to sexually transmitted diseases. During your pelvic examination, a single, indurated, nontender ulcer is noted on the vulva. Venereal Disease Research Laboratory (VDRL) and fluorescent treponemal antibody (FTA) tests are positive. Without treatment, the next stage of this disease is clinically characterized by which of the following?
. Optic nerve atrophy and generalized paresis
. Tabes dorsalis
. Gummas
. Macular rash over the hands and feet
. Aortic aneurysm
224) A 7-year-old girl is brought to your office by her parents after they noticed the development of axillary and pubic hair 3 months ago. The girl has also experienced a significant growth spurt over the past year. There has been no change in her behavior or school performance. The girl denies headaches, vomiting or visual disturbances. Her personal and family medical histories are unremarkable. On examination, you note the presence of axillary hair, pubic hair at Tanner stage 2, and breast development at Tanner stage 3. Abdominal, genital and neurologic examinations reveal nothing abnormal. Her bone age is more than two standard deviations above normal. Serum FSH and LH levels are elevated. MRI of the brain is normal. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her symptoms?
. Excess peripheral conversion of testosterone to estrogen
. Estrogen-producing ovarian cysts
. Polycystic ovarian syndrome
. Late onset congenital adrenal hyperplasia
. Early activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis
225) A 16-year-old girl presents for evaluation of acne, which has been getting progressively worse over the past 2 weeks. Her medical history is significant for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) for which she has been taking prednisone for a recent exacerbation. Hydroxychloroquine is her only other medicine. She does not use tobacco, alcohol or drugs and her menstrual cycle is regular. On physical examination, her blood pressure is 110/76 mmHg and her pulse is 72/min. Her BMI is 22 kg/m2. Distributed over the face, arms and trunk are monomorphous erythematous papules. There are no open or closed comedones. The remainder of the physical examination is unremarkable. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her acne?
. Adolescent acne
. Androgen abuse
. Polycystic ovarian disease
. Medication side effect
. Systemic lupus erythematosus
226) A 22-year-old, gravida 1, para 0, at 13 weeks gestation is brought to the emergency department because of vaginal discharge and lower abdominal discomfort. She has had no passage of tissue from her vagina. She does not use tobacco, alcohol or drugs. She has no history of trauma. Her temperature is 37.0C (98.7F), blood pressure is 128/80 mmHg, pulse is 76/min and respirations are 14/min. Physical examination shows a closed cervix, a slightly tender uterus with a size consistent with gestational age, free adnexa and scant bright red bleeding from the introitus. Ultrasonogram in the emergency department shows normal fetal heart motion. She is anxious and concerned about her baby. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Incomplete abortion
. Threatened abortion
. Completed abortion
. Inevitable abortion
. Ectopic pregnancy
227) A 28-year-old woman at 39 weeks gestation is admitted to the hospital. She has regular uterine contractions. Her blood pressure is 120/70mmHg, pulse is 80/min and respirations are 18/min. Fetal heart monitoring is placed and shows a baseline rate of 130 beats/min, without any associated abnormalities. Pelvic examination shows the cervix is 50% effaced and 3cm dilated. Amniotomy is performed and a bloody show is noted. Immediately after the rupture of membranes, the baseline fetal heart rate increases to 160 beats/min and then drops to 70 beats/min. As labor progresses, repetitive late decelerations are noted, as well as an increase in vaginal bleeding. Repeat vital signs of the patient shows a blood pressure of 130/70mmHg, pulse of 80/min and respirations of 18/min. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the current condition?
. Premature separation of the placenta
. Abnormal placental implantation
. Abnormal umbilical vessels
. Excessive amniotic fluid
. Tear in uterine musculature
228) A 20-year-old woman, gravida 1, para 0, at 36 weeks gestation comes to the physician because of diffuse headache, blurry vision and epigastric pain. She has no previous history of hypertension, renal disease or neurologic disease. Her mother has a history of migraine headaches. Her temperature is 37.2 C (98.9 F), blood pressure is 200/126 mmHg and pulse is 80/min. Physical examination shows bilateral lower extremity edema. Deep tendon reflexes are exaggerated. Laboratory studies show: Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) 23 mg/dl, Serum creatinine 1.6 mg/dl, Blood glucose 98 mg/dl. Urinalysis: Protein: 4+, Blood: negative, Glucose: negative, WBC: 1-2/hpf, RBC: 1-2/hpf, Casts: none. Fetal heart tones are heard by Doppler. While evaluating her, she suddenly develops generalized tonic-clonic convulsions. Which of the following is the most accurate diagnosis of this new event?
. Hypertensive encephalopathy
. Uremic encephalopathy
. Viral encephalitis
. Eclamptic seizures
. Brain abscess
229) A 29-year-old woman, gravida 3, para 2, at 35 weeks gestation is brought to the emergency department because of vaginal bleeding. She has had no uterine contractions. Her prenatal course, prenatal tests and fetal growth have been normal. Prenatal ultrasound at the 12th week showed an intrauterine gestation consistent with dates. Four years ago, she had a low transverse cesarean section in her second pregnancy. Physical examination shows bright red vaginal bleeding. Her temperature is 37.0 C (98.7 F), blood pressure is 100/70 mm Hg, pulse is 90/min and respirations are 16/min. Fetal heart monitoring is reassuring. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Abruptio placenta
. Placenta previa
. Vasa previa
. Uterine rupture
. Normal labor
230) A 23-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, at 38 weeks' gestation was admitted to the delivery room for management of labor. On admission 6-hours ago, the patient was in the active phase of labor and the cervix was 4cm dilated. She was then placed under external tocometer and epidural anesthesia. Contractions were regular, occurring 2-3 minutes apart and lasting 40-60 seconds. She progressed well to 7cm. However, she has remained at 7cm the past 4 hours. The fetus is in the Left Occipita Anterior (LOA) position and at +1 station. Internal pelvic assessment shows prominent ischial spines. Electronic fetal heart monitoring shows 140 bpm with normal beat-to-beat and long term variability. Prenatal ultrasound at 37-weeks showed no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's anomaly of labor?
. Inlet dystocia
. Midpelvis contraction
. Macrosomic baby
. Hypotonic uterine contractions
. Injudicious analgesia
231) A 24-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, at 36 weeks' gestation is brought to the emergency department after passing out. She is drowsy and moaning, complaining of abdominal pain. Her husband accompanies her. He states that she has not experienced any trauma, but that she experienced the sudden onset of severe abdominal pain before she passed out. She has no significant past medical history. Her pregnancy has been uncomplicated thus far. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or drugs. She takes supplemental vitamins, but no other medications. Her temperature is 36.9 C (98.4F), blood pressure is 90/60 mm of Hg, and pulse is 130/min. Physical examination shows a cold and diaphoretic female. Examination shows a uterus consistent in size with a 36-week gestation; the cervical os is closed and no vaginal bleeding is noted. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Placenta previa
. Abruptio placentae
. Preeclampsia
. Amniotic fluid embolism
. Septic shock
232) A 28-year-old male comes for evaluation of infertility. He has been healthy and otherwise has no complaints. He says the he eats a high protein diet and exercises daily in order to be muscular. He weighs 85 kg (187 1b) and is 175cm (70 in) tall. His temperature is 37.2 C (98.9 F), and his blood pressure is 130/82 mmHg. Physical examination shows small testes. The remainder of the examination is unremarkable. Initial laboratory studies show: Hemoglobin: 16.0 g/L, Platelets: 200,000/mm3, Leukocyte count: 4,500/mm3, Serum creatinine: 1.4 mg/dl, Serum LH: low, Serum testosterone: low. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his infertility?
. Klinefelter syndrome
. Mumps orchitis
. Exogenous steroid use
. Myotonic dystrophy
. Varicocele
233) A 14-year-old female is brought to the physician's office for evaluation of excessive menstrual bleeding. She experienced menarche at age 13, and since then her menses have been irregular and unpredictable. Her last menstrual period was 6 weeks ago and for the past week she has been having heavy menstrual bleeding. She has never been sexually active. Vital signs are stable. Her external genitalia are normal. She refused pelvic examination, and a pregnancy test is negative. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her symptoms?
. Bleeding disorder
. Anovulation
. Cervical polyp
. Endometrial carcinoma
. Uterine fibroids
234) A 25-year-old female presents to the physician's office for evaluation of infertility. Her menstrual periods are regular. She has mild chronic pelvic pain. Her husband's semen analysis is within normal limits. She has no history of sexually transmitted diseases in the past. Her temperature is 37.2 C (98.9 F), and her blood pressure is 120/72 mmHg. Physical examination shows a normal sized uterus and enlarged left adnexae. Ultrasonography shows a homogeneous mass on the left ovary, but is otherwise normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Endometriosis
. Ovarian malignancy
. Chronic pelvic inflammatory disease
. Adenomyosis
. Pelvic congestion syndrome
235) A 30-year-old woman in her second pregnancy presents to your office at 36 weeks gestation complaining of dull, low back pain. The pain is minimal in the morning, but increases at the end of the day. She also noticed ankle edema that appears at the end of the day. Her past medical history is insignificant. Her temperature is 36.7C (98F), blood pressure is 120/80 mmHg, pulse is 90/min, and respirations are 18/min. Urinalysis is normal. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's complaints?
. Multiple myeloma
. Compression fracture of the vertebrae
. Herniated disk
. Metastatic or primary tumor
. Increased lumbar lordosis
236) A 22-year-old woman presents to office with a 3-week history of scant vaginal discharge. She has no other complaints. She is sexually active and uses oral contraceptives. She has regular 26-day menstrual cycles and her last menstrual period was ten days ago. She does not smoke or consume alcohol. Her temperature is 36.7C (98 F), blood pressure is 120/80 mmHg, pulse is 80/min, and respirations are 14/min. On examination, the abdomen is non tender. Yellow mucopurulent discharge is seen at the cervical os. Which of the following organisms is the most probable cause of this patient's problem?
. Chlamydia trachomatis
. Neisseria gonorrhoeae
. Herpes simplex
. Trichomonas vaginalis
. Candida albicans
237) A 24-year-old female and her husband come to the physician's office for evaluation of infertility. They have not been able to conceive after 12 months of frequent intercourse without contraception. She has no other medical problems and takes no medication. Physical examination shows an obese woman with excess thick hair over her chin and along the linea alba of the lower abdomen. There is no increase in muscles mass. When asked about the excess hair, she states that she has had it for a long time. Serum testosterone levels are elevated. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her infertility?
. Abnormal cervical mucus
. Luteal phase defect
. Impaired oocyte transport
. Impaired zygote implantation
. Anovulation
238) A 41-year-old woman, gravida 3, para 3, comes to the physician because of a 2-year history of dysmenorrhea and menorrhagia that has been increasing in intensity. She has no dyspareunia or any other symptoms. She has a history of chronic hypertension. She had a cesarean section in her 3rd pregnancy followed by surgical sterilization. Vital signs are normal. Bimanual examination shows a symmetrically enlarged and tender uterus with soft consistency and free adnexae. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Adenomyosis
. Endometriosis
. Leiomyomata
. Endometrial carcinoma
. Endometritis
239) A 24-year-old G0 presents to your office complaining of vulvar discomfort. More specifically, she has been experiencing intense burning and pain with intercourse. The discomfort occurs at the vaginal introitus primarily with penile insertion into the vagina. The patient also experiences the same pain with tampon insertion and when the speculum is inserted during a gynecologic examination. The problem has become so severe that she can no longer have sex, which is causing problems in her marriage. She is otherwise healthy and denies any medical problems. She is experiencing regular menses and denies any dysmenorrhea. On physical examination, the region of the vulva around the vaginal vestibule has several punctate, erythematous areas of epithelium measuring 3 to 8 mm in diameter. Most of the lesions are located on the skin between the two Bartholin glands. Each inflamed lesion is tender to touch with a cotton swab. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis? Obstetric gynecology pretest 12th 319?
. Vulvar vestibulitis
. Atrophic vaginitis
. Contact dermatitis
. Lichen sclerosus
. Vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia
240) A 29-year-old G0 comes to your office complaining of a vaginal discharge for the past 2 weeks. The patient describes the discharge as thin in consistency and of a grayish white color. She has also noticed a slight fishy vaginal odor that seems to have started with the appearance of the discharge. She denies any vaginal or vulvar pruritus or burning. She admits to being sexually active in the past, but has not had intercourse during the past year. She denies a history of any sexually transmitted diseases. She is currently on no medications with the exception of her birth control pills. Last month she took a course of amoxicillin for treatment of a sinusitis. On physical examination, the vulva appears normal. There is a discharge present at the introitus. A copious, thin, whitish discharge is in the vaginal vault and adherent to the vaginal walls. The vaginal pH is 5.5. The cervix is not inflamed and there is no cervical discharge. Wet smear of the discharge indicates the presence of clue cells. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Candidiasis
. Bacterial vaginosis
. Trichomoniasis
. Physiologic discharge
. Chlamydia
241) A 20-year-old G2P0020 with an LMP 5 days ago presents to the emergency room complaining of a 24-hour history of increasing pelvic pain. This morning she experienced chills and a fever, although she did not take her temperature. She reports no changes in her urine or bowel habits. She has had no nausea or vomiting. She is hungry. She denies any medical problems. Her only surgery was a laparoscopy performed last year for an ectopic pregnancy. She reports regular menses and denies dysmenorrhea. She is currently sexually active. She has a new sexual partner and had sexual intercourse with him just prior to her last menstrual period. She denies a history of any abnormal Pap smears or sexually transmitted diseases. Urine pregnancy test is negative. Urinalysis is completely normal. WBC is 18,000. Temperature is 38.8C (102F). On physical examination, her abdomen is diffusely tender in the lower quadrants with rebound and voluntary guarding. Bowel sounds are present but diminished. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Ovarian torsion
. Endometriosis
. Pelvic inflammatory disease
. Kidney stone
. Ruptured ovarian cyst
242) A 43-year-old G2P2 comes to your office complaining of an intermittent right nipple discharge that is bloody. She reports that the discharge is spontaneous and not associated with any nipple pruritus, burning, or discomfort. On physical examination, you do not detect any dominant breast masses or adenopathy. There are no skin changes noted. Which of the following conditions is the most likely cause of this patient’s problem?
. Breast cancer
. Duct ectasia
. Intraductal papilloma
. Fibrocystic breast disease
. Pituitary adenoma
243) A 20-year-old G0, LMP 1 week ago, presents to your gynecology clinic complaining of a mass in her left breast that she discovered during routine breast self-examination in the shower. When you perform a breast examination on her, you palpate a 2-cm firm, nontender mass in the upper inner quadrant of the left breast that is smooth, well-circumscribed, and mobile. You do not detect any skin changes, nipple discharge, or axillary lymphadenopathy. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Fibrocystic breast change
. Fibroadenoma
. Breast carcinoma
. Fat necrosis
. Cystosarcoma phyllodes
244) A mother brings her 12-year-old daughter in to your office for consultation. She is concerned because most of the other girls in her daughter’s class have already started their period. She thinks her daughter hasn’t shown any evidence of going into puberty yet. Knowing the usual first sign of the onset of puberty, you should ask the mother which of the following questions?
. Has her daughter started to develop breasts?
. Has her daughter had any acne?
. Does her daughter have any axillary or pubic hair?
. Has her daughter started her growth spurt?
. Has her daughter had any vaginal spotting?
245) A 9-year-old girl presents for evaluation of regular vaginal bleeding. History reveals thelarche at age 7 and adrenarche at age 8. Which of the following is the most common cause of this condition in girls?
. Idiopathic
. Gonadal tumors
. McCune-Albright syndrome
. Hypothyroidism
. Tumors of the central nervous system
246) A 55-year-old woman presents to your office for consultation regarding her symptoms of menopause. She stopped having periods 8 months ago and is having severe hot flushes. The hot flushes are causing her considerable stress. What should you tell her regarding the psychological symptoms of the climacteric?
. They are not related to her changing levels of estrogen and progesterone.
. They commonly include insomnia, irritability, frustration, and malaise.
. They are related to a drop in gonadotropin levels.
. They are not affected by environmental factors.
. They are primarily a reaction to the cessation of menstrual flow.
247) An 18-year-old patient presents to you for evaluation because she has not yet started her period. On physical examination, she is 5ft 7 in tall. She has minimal breast development and no axillary or pubic hair. On pelvic examination, she has a normally developed vagina. A cervix is visible. The uterus is palpable, as are normal ovaries. Which of the following is the best next step in the evaluation of this patient?
. Draw her blood for a karyotype.
. Test her sense of smell.
. Draw her blood for TSH, FSH, and LH levels.
. Order an MRI of the brain to evaluate the pituitary gland.
. Prescribe a progesterone challenge to see if she will have a withdrawal bleed.
248) A mother brings her daughter in to see you for consultation. The daughter is 17 years old and has not started her period. She is 4ft 10 in tall. She has no breast budding. On pelvic examination, she has no pubic hair. By digital examination, the patient has a cervix and uterus. The ovaries are not palpable. As part of the workup, serum FSH and LH levels are drawn and both are high. Which of the following is the most likely reason for delayed puberty and sexual infantilism in this patient?
. Adrenogenital syndrome (testicular feminization)
. McCune-Albright syndrome
. Kallmann syndrome
. Gonadal dysgenesis
. Müllerian agenesis
249) A 30-year-old female comes to your office for her first prenatal visit. She has been married for 3-years and has been trying to conceive for the past year. She had been unsuccessful; however, she now has a 2-month history of amenorrhea. She has been experiencing morning sickness and has had abdominal distension and breast fullness over the past two weeks. She states that her home urine pregnancy test is positive. She seems happy and excited about this long awaited pregnancy. She has no previous medical problems. She has been taking prenatal vitamins for the past 3 weeks after she first missed her period. Physical examination shows a tympanic abdomen. Ultrasonogram shows a normal endometrial stripe. Pregnancy testing in the office is negative. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Missed abortion
. Fetal demise
. Ectopic pregnancy
. Molar pregnancy
. Pseudocyesis
250) A 15-year-old girl is being evaluated for primary amenorrhea. She has no other symptoms. She has not been sexually active. She has no other medical problems and does not take any medication. Her family history is unremarkable. On examination, you note fully developed breasts and absent axillary and pubic hair. External genitalia have a normal appearance, but the vagina is abnormally short and blind ended. Initial work-up reveals no uterus on ultrasound, a testosterone level of 400 ng/dl (Normal is 20-80 for a female), and a 46 XY karyotype. Which of the following events is most likely to have caused the absence of in utero development of the internal reproductive organs?
. Absence of mullerian inhibiting factor
. Presence of mullerian inhibiting factor
. Agenesis of Wolffian ducts
. Agenesis of mullerian ducts
. Testosterone surge
251) A 30-year-old female delivers a term male infant with signs of thyrotoxicosis. Prior to the pregnancy, she was surgically treated for Graves’ disease and was prescribed hormone replacement therapy in the form of levothyroxine 0.25 mg daily. Levothyroxine was maintained during pregnancy and thyroid hormone levels were monitored and maintained within the reference range. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the neonate's condition?
. Levothyroxine therapy
. Active thyroid tissue in the mother secreting thyroid hormone
. Persistence of thyroid stimulating immunoglobulin in the mother
. Inadequate surgery with persistence of thyroid tissue post-operatively
. Delivery hemorrhage
252) Select the most likely diagnosis. A. Child abuse B. Foreign body C. Trichomonas vaginitis D. Bacterial vaginosis E. Candidiasis A 25-year-old woman presents to the physician's office for evaluation of foul-smelling vaginal discharge. She has been sexually active with a new partner for the past month. Physical examination reveals a thin, whitish-gray vaginal discharge. There is no discharge from the cervical os, and there is no adnexal or cervical motion tenderness. The remainder of the examination is normal. The pH of the vaginal fluid is 5.0. When KOH is added to vaginal discharge on a slide, an amine-like ("fishy") odor is perceived. A wet mount of the fluid reveals many epithelial cells with adherent bacteria. No polymorphonuclear cells are seen.
. A
. B
. C
. D
. E
253) A 24-year-old woman comes to the physician for her third prenatal check-up at 12 weeks gestation. She has been feeling well for the last 4 weeks because she no longer has nausea and vomiting. She had a small dark brown discharge 4 weeks ago, but it stopped spontaneously. Physical examination shows the cervix is closed and fetal heart tones are not heard. Real-time ultrasonogram shows a collapsed gestational sac with absent fetal heart motion. Urine pregnancy test is positive. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Hydatiform mole
. Threatened abortion
. Complete abortion
. Inevitable abortion
. Missed abortion
254) A 21-year-old G0 presents to your office because her menses is 2 weeks late. She states that she is taking her birth control pills correctly; she may have missed a day at the beginning of the pack, but took it as soon at she remembered. She denies any medical problems, but 3 or 4 weeks ago she had a “viral stomach flu” and missed 2 days of work for nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Her cycles are usually regular even without contraceptive pills. She has been on the pill for 5 years and recently developed some midcycle bleeding, which usually lasts about 2 days. She has been sexually active with the same partner for the past 3 months and has a history of chlamydia 3 years ago. She has had a total of 10 sexual partners. A urine pregnancy test is positive. Which of the following is the major cause of unplanned pregnancies in women using oral contraceptives?
. Breakthrough ovulation at midcycle
. High frequency of intercourse
. Incorrect use of oral contraceptives
. Gastrointestinal malabsorption
. Development of antibodies
255) A 15-year-old girl is being evaluated for primary amenorrhea. She is otherwise healthy and has no previous medical problems. Vital signs are within normal limits. Physical examination reveals normal breast development, normal pubic and axillary hair, and a blind vagina; the uterus and adnexae could not be appreciated. Pelvic ultrasonography reveals 2 ovaries and no uterus is seen. The karyotype is 46 XX. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Mullerian agenesis
. Androgen insensitivity
. 5-alpha-reductase deficiency
. Imperforate hymen
. Turner's syndrome
256) A 23-year-old woman presents to your office with the complaint of a red splotchy rash on her chest that occurs during intercourse. It is nonpuritic and painless. She states that it usually resolves within a few minutes to a few hours after intercourse. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the rash?
. Allergic reaction to her partner’s pheromones
. Decreased systolic blood pressure during the plateau phase
. Increased estrogen during the excitement phase
. Vasocongestion during the excitement phase
. Vasocongestion during the orgasmic phase
257) A 62-year-old woman presents for annual examination. Her last spontaneous menstrual period was 9 years ago, and she has been reluctant to use postmenopausal hormone replacement because of a strong family history of breast cancer. She now complains of diminished interest in sexual activity. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her complaint?
. Decreased vaginal length
. Decreased ovarian function
. Alienation from her partner
. Untreatable sexual dysfunction
. Physiologic anorgasmia
258) A 28-year-old primigravid woman comes to the physician for a follow-up prenatal visit. According to prenatal records, ultrasound at 16 weeks gestation showed an intrauterine gestation consistent with dates and showed no abnormalities. She is now at 40 weeks gestation. Examination shows a fundal height consistent with dates and the cervix is not favorable. Fetal heart tracing is reassuring. She wishes to continue the pregnancy for two more weeks rather than undergoing induction. She should be closely monitored for which of the following?
. Polyhydramnios
. Oligohydramnios
. Abruptio placentae
. Placenta previa
. Preeclampsia
259) A 34-year-old sexually active female comes to your office because of urinary frequency and dysuria for two days. She has had two such episodes in the past, each treated with oral antibiotics. Physical examination reveals suprapubic tenderness and her urinalysis is positive for nitrite, leukocyte esterase, many WBC, and a moderate amount of bacteria. Which of the following is the most common reason for the higher incidence of urinary tract infections in females than in males?
. Closer proximity of the urethral meatus to the anus in females
. Frequent use of spermicide and diaphragms in females
. Shorter urethral length in females
. Higher post-void urine residual in females
. Hormonal fluctuation of females
260) A 31-year-old woman comes to the physician because she has not had a menstrual period for 7 months. She previously had normal cycles. She also states that over the past year she has felt increasingly weak and tired. She notes that she always feels cold and that her hair has been thinning over the course of the year. She also complains of constipation, weight gain, and depression. Her temperature is 36.7 C (98 F), blood pressure is 100/60 mmHg, pulse is 56/minute, and respirations are 10/minute. Examination is significant for brittle hair and delayed deep tendon reflexes. Urine human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is negative. Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) is 20 μU/mL. Prolactin is normal. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's amenorrhea?
. Hyperprolactinemia
. Hypothyroidism
. Kallmann syndrome
. Polycystic ovarian syndrome
. Pregnancy
261) A 17-year-old female comes to the physician because she has not yet had a menstrual period. She also complains of a lack of breast development. Past medical history is significant for anosmia and color blindness. Past surgical history is significant for a cleft palate that was repaired in childhood. She takes no medications and has no allergies to medications. Examination is significant for absent breast development, and a hypoestrogenic vulva and vagina. Urine hCG is negative. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Anorexia nervosa
. Kallmann syndrome
. Polycystic ovarian syndrome
. Pregnancy
. Testicular feminization syndrome
262) A 38-year-old woman comes to the physician because of burning with urination. She states that the burning started about 2 days ago and has been growing worse since. She has no frequency or urgency. She had one episode of pyelonephritis in the past but no other medical problems. On examination there is no costovertebral angle or abdominal tenderness. The examination is significant for a thick, white vaginal discharge with erythema and excoriations of the labia. Urinalysis is negative. KOH/Normal saline smear demonstrates pseudohyphae. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Candida vaginitis
. Hemorrhagic ovarian cyst
. Pelvic inflammatory disease
. Pyelonephritis
. Urinary tract infection
263) A 25-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 2, comes to the physician to discuss birth control options. She and her partner have tried to use condoms; however, they find it difficult to use them consistently and she would like to try another form of contraception. She has no medical problems, takes no medications, and has no family history of cancer. Her examination is within normal limits. After a discussion with the physician, she chooses to take the oral contraceptive pill (OCP). She stays on the pill for the next three years. She now has most significantly decreased her risk of developing which of the following malignancies?
. Bone cancer
. Breast cancer
. Cervical cancer
. Endometrial cancer
. Liver cancer
264) A 25-year-old woman comes to the physician because of pain and burning with urination. She states that the symptoms started two days ago and have worsened since. She has no fever or chills and has never had these symptoms before. She has hypothyroidism for which she takes thyroid hormone replacement. Otherwise she has no medical problems. Her temperature is 37 C (98.6 F). Examination is unremarkable including a normal pelvic examination. A KOH and normal saline "wet prep" is performed on her vaginal discharge and is negative. Urinalysis reveals numerous white blood cells. Which of the following is the most likely pathogen?
. Escherichia coli
. Neisseria gonorrhoeae
. Pseudomonas species
. Staphylococcus saprophyticus
. Trichomonas vaginalis
{"name":"G.O. Diagnosis", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"1) A 16-year-old girl presents to the emergency department complaining of fever, chills, abdominal pain, and vaginal bleeding. She gives a history of unprotected sexual activity with her 17-year-old boyfriend over the past several months. Her last menstrual period was 8 weeks ago. She reports having a dilatation and curettage procedure at an unlicensed abortion clinic recently to try to abort the pregnancy. Her temperature is 38.7C (101.7F), heart rate is 120\/min, and blood pressure is 100\/70 mmHg. Pelvic examination reveals cervical motion tenderness, tissue in the internal os, and foul-smelling vaginal discharge. Urine is positive for β-human chorionic gonadotropin. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?, 2) A 19-year-old G0 woman presents to her family physician complaining of dysmenorrhea for the past year. She reports severe right-sided pain that coincides with days 1–5 of her menstrual cycle. Her menses occur regularly every 28 days, and she requires three to four pads per day for the first 2 days of her bleeding and one to two pads per day for the remainder. She has never had surgery. She is not sexually active and does not smoke. Her last menstrual period was 1 week ago. Her temperature is 36.7C (98.1F), blood pressure is 121\/74 mmHg, heart rate is 80\/min, and respiratory rate is 14\/min. Physical examination reveals a thin, healthy-appearing young woman. Pelvic examination reveals a normal sized uterus and no cervical motion tenderness. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?, 3) After an appropriate diagnostic evaluation, a 59-year-old woman with postmenopausal bleeding had a total abdominal hysterectomy and bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy (TAH-BSO). The pathologic diagnosis is adenocarcinoma of the endometrium. An endometrial adenocarcinoma that is confined to the uterus and extends more than 50% through the myometrium is at which stage?","img":"https://cdn.poll-maker.com/22-854062/-.png?sz=1200"}
More Quizzes
Quiz - 1 Aug 2020
1166
إختبر معلوماتك حول كأس العالم
630
How well do you know me?
740
Iconic TV
1680
Can You Spot Indirect Disease Transmission? Free
201033056
Test Your JWST Knowledge: James Webb Space Telescope
201084643
Quiz Journey: How Well Do You Know the Band Journey?
201092286
Ecosystem Questions: Test Your 3rd Grade Science Skills
201040782
Topics in Sociology
15821413
Laura Pergolizzi: Test Your LP Knowledge Now!
201025949
Which Greek God Are You? Discover Your Divine Parent
201032630
Free Acronym Knowledge
201027228