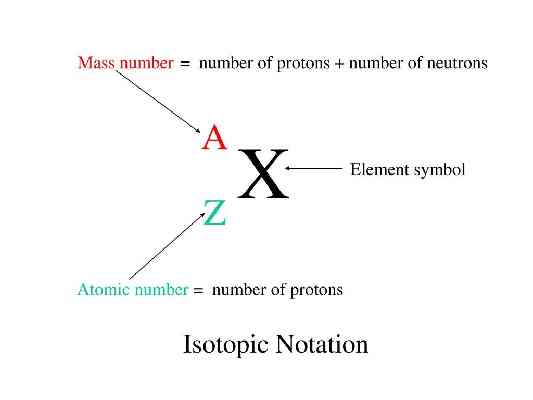
Nuclear Chemistry Review
{"name":"Nuclear Chemistry Review", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Test your knowledge of nuclear chemistry in this engaging quiz designed for students, teachers, and enthusiasts alike. With 12 comprehensive questions, you'll explore topics such as radioactivity, particle behavior, and historic discoveries in nuclear science.Covers key concepts and terminologySuitable for various knowledge levelsFun and educational way to review material","img":"https:/images/course2.png"}
More Quizzes
Nuclear principles in engineering ch5
26130
STEM CHEM TEST CHAPTER 24/25
261322
Daily Learning
11643
Future Insights Quiz
10512
Free Riddle Trivia for Logic Lovers
201024064
Think You're an HR Pro? Take the Ultimate HR Test Now!
201030100
Ocean Trivia: Test Your Knowledge of Currents
201023867
Free Cloud Computing Services Assessment
201024681
Free Community Fundraising Trivia
201021629
Free Local Knowledge Trivia
201024471
Quiz: Can You Spot Machu Picchu & Other Disney Landmarks?
201023867
World Cup Football: Are You a Trivia Champion?
201031563