Pediatrie
1) An infant is born to a woman who has received very little prenatal care. The mother is anxious, complains of heat intolerance and fatigue, and reports that she has not gained much weight despite having an increased appetite. On examination the mother is tachycardic, has a tremor, and has fullness in her neck and in her eyes. The infant is most likely at risk for development of which of the following?
. Thrombocytosis
. Constipation
. Heart failure
. Macrocephaly
. Third-degree heart block
2) An otherwise healthy 7-year-old girl is brought to your office by her father because she has some acne, breast development, and fine pubic hair. Which of the following is the most likely etiology for her condition?
. Early onset of “normal” puberty (constitutional)
. A feminizing ovarian tumor
. A gonadotropin-producing tumor
. A lesion of the central nervous system (CNS)
. Exogenous estrogens
3) A primiparous woman whose blood type is O positive gives birth at term to an infant who has A- positive blood and a hematocrit of 55%. A total serum bilirubin level obtained at 36 hours of age is 12 mg/dL. Which of the following additional laboratory findings would be characteristic of ABO hemolytic disease in this infant?
. Petechiae
. A normal reticulocyte count
. A positive direct Coombs test
. Crescent-shaped red blood cells in the blood smear
. Elevated hemoglobin
4) A 14-year-old girl presents to clinic for an annual check up. Her parents are concerned that the child is not meeting normal milestones of adolescent growth. The patient reports no recent illnesses. She is up- to-date on her vaccines, and is not having any trouble in school. She denies drug use and is active in sports. On examination, her vital signs are stable. Her lungs are clear and heart is regular in rate and rhythm. Breast and areolar enlargement is noted with no contour separation of the areola. Pubic hair is noted to be dark. The patient also reports that she started menstruating 8 months ago. Which of the following is the most likely Tanner stage of development in this patient?
. Stage V
. Stage I
. Stage II
. Stage III
. Stage IV
5) A 7-year-old boy presents to the physician's office with a 3-week history of left-sided anterior cervical lymph node enlargement. The enlarged nodes are not tender to palpation. A few papules developed on the left forearm at the onset of lymphadenopathy. The boy has a kitten at home. Which of the following is the most likely organism causing lymphadenopathy in this child?
. Staphylococcus aureus
. Actinomyces israelii
. Bartonella henselae
. Francisella tularensis
. Mycobacterium tuberculosis
6) A 10-year-old boy comes to the office with fever and chills for 5 days and myalgia. He has recently returned from a 2-week vacation to New England with his family. On physical examination he has mild splenomegaly. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his symptoms?
Psittacosis
Kawasaki disease
Pneumococcus
Babesiosis
Leptospirosis
7) A female infant develops cyanosis. She was delivery vaginally at 43 weeks' gestation, and the amniotic fluid had a greenish color. She has dry, peeling skin, emaciated extremities and long fingernails. Tachypnea, nasal flaring, and sub- and intercostal retractions are observed. Auscultation reveals rales and rhonchi. The chest radiograph reveals flattening of the diaphragm, hyperinflation of the lungs, and patchy opacities diffusely distributed over both lung fields. Arterial blood gases reveal hypoxia and hypercarbia. What is most likely impairing the normal respiratory function of this newborn?
. Meconium
. Fetal lung fluid
. Poor alveolar compliance
. Paralysis of the diaphragm
. Fibrosis of the lungs
8) A 5-month-old boy is brought in for a routine check-up. He was born at 37 weeks' gestation and has had persistent wheezing since shortly after birth despite inhaled bronchodilator and oral corticosteroid therapy. His diet consists of 32 ounces of iron-fortified cow's milk-based formula daily. On physical examination, the child appears well-nourished and happy. You note moderate relief of his wheezing with neck extension. Which of the following is the most likely mechanism of this infant's wheezing?
. Asthma
. Allergic reaction to cow's milk
. Aspiration of a foreign body
. Compression of the airway by a vascular ring
. Chronic upper respiratory tract infection
9) A mother delivers a neonate with meconium staining and Apgar scores of 3 at 1 and 5 minutes of life. She had no prenatal care and the delivery was by emergency cesarean section for what the obstetricians report as “severe fetal bradycardia.”Which of the following sequelae could be expected to develop in this intubated neonate with respiratory distress?
. Thrombocytosis
. Sustained rise in pulmonary arterial pressure
. Hyperactive bowel sounds
. Microcephaly with micrognathia
. Cataracts
10) . A neonate is noted to have an abnormally shaped face with a very small jaw. Several hours after birth, the baby develops convulsions and tetany. Serum chemistries show the following: Sodium 1 40 mEq/L, Potassium 4 mEq/L, Chloride 100 mEq/L, Bicarbonate 24 mEq/L, Magnesium 2 mEq/L, Calcium 5 mg/dL, Glucose 100 mg/dL. This child's disorder is associated with aplasia or hypoplasia of which of the following organs?
Thyroid
Ovaries
Pancreas
Pituitary
Thymus
11) A 1-year-old boy is brought to the physician by his parents for evaluation of bruising and blood in his stool. The child has had multiple episodes of otitis media and has been hospitalized twice with pneumonia, but has never had bleeding or easy bruising in the past. He has been eating and drinking well with no vomiting or diarrhea. He is afebrile with a heart rate of 150/min and a blood pressure of 80/40 mmHg. On examination, he is well-developed, well-nourished, and has a fair complexion. There are dry, scaly patches on his cheeks and lower extremities. He also has bruising and purpura on his lower extremities. His diaper contains a small amount of occult blood positive stool, but no fissures are seen on rectal examination. The remainder of the physical examination is unremarkable. Laboratory studies show: Complete blood count: Hemoglobin 11 .5 g/dL, Platelet count 20,000/mm3, Leukocyte count 6,500/mm3, Neutrophils 76%, Eosinophils 1%, Lymphocytes 13%, Monocytes 10%. A peripheral smear reveals a low number of platelets, and the platelets that are seen are small. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his bleeding?
. Impaired platelet production
. Bone marrow infiltration
. Platelet antibodies
. Nutritional deficiency
. Platelet activation and consumption
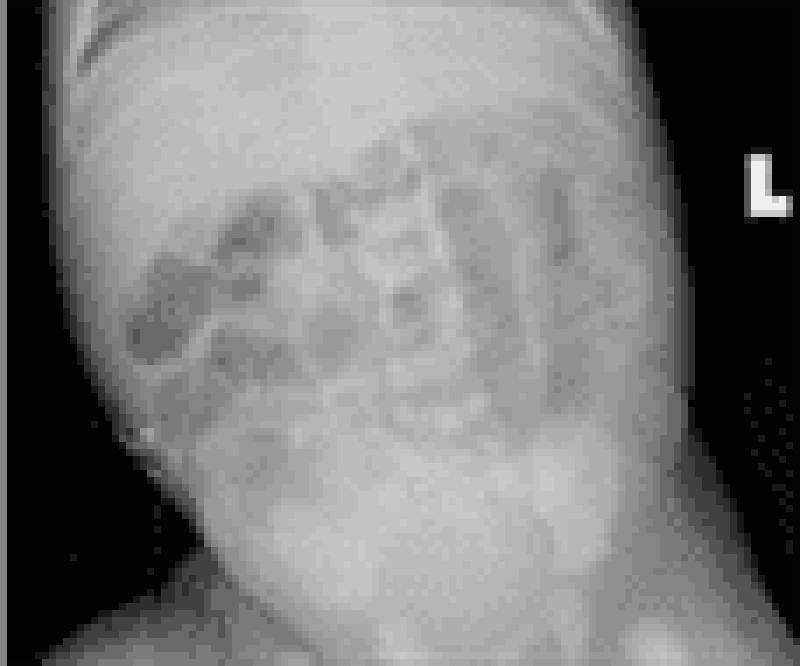
12) A 2-day-old boy in the newborn nursery was born at 39 weeks gestation to a 38-year-old woman by vaginal delivery. The mother received epidural fentanyl for severe painful contractions during labor, but the delivery was uncomplicated. Since birth, the boy has shown little interest in breast or bottle feeding. He spit up the last feed but has not vomited. He has not yet passed meconium. Physical examination shows a newborn with generalized hypotonia, a flat facial profile, low-set folded earlobes, and a single transverse crease on each palm. His abdomen is firm and distended. Digital rectal examination is notable for a tight anal canal and relieves an expulsion of gas and stool. Abdominal x-ray shows markedly distended loops of bowel with no gas in the rectum. What is the mostly likely mechanism for his findings?
. Invagination of a part of the intestine into itself
. Constipation from decreased levels of thyroxine
. Failure of neural crest cell migration during fetal intestinal development
. Intestinal ileus from exposure to maternal epidural analgesia
. Intestinal obstruction from inspissated meconium
13) Otitis media occurring during the first 8 weeks of life deserves special consideration, because the bacteria responsible for infections during this time may be different from those that affect older infants and children. Which of the following organisms is the most likely to cause otitis media in these infants?
Toxoplasma gondii
Chlamydia trachomatis
E. coli
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Treponema pallidum
14) A 3-month-old girl is brought to the pediatrician for a scheduled visit. She has been meeting all development milestones but has been vomiting after each feeding. The infant weighed 3 kg (6 lb 10 oz) at birth and now weighs 6 kg (13 lb 3 oz). She does not have diarrhea and is afebrile. The remainder of the physical examination is unremarkable. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's vomiting?
Pyloric stenosis
Adrenogenital syndrome
Child abuse
Inborn error of metabolism
Overfeeding
15) A 16-year-old Asian boy presents with a two-day history of fever, malaise, and painful enlargement of his parotid glands. He has no significant past medical history. He was born in India, and has not received any childhood vaccinations. He recently returned from a one-week vacation in India. His vital signs are stable, except for a mild fever. Examination shows bilateral parotid enlargement. The rest of the examination is unremarkable. Which of the following organs is most likely to be affected by this patient's illness?
. Spleen
. Testes
. Pancreas
. Liver
. Kidney
16) A pregnant woman has premature rupture of membranes. Her baby is born 3 days later, at 37 weeks' gestation. The 5-minute APGAR score is 4. Lung sounds are reduced, and the infant appears to be in respiratory distress. Peripheral blood smear with differential counts demonstrates a neutrophil count of 30,000/mL, with toxic granules evident in many neutrophils. Gram stain of buffy coat demonstrates small gram-positive cocci in chains. Which of the following is the most likely causative organism?
Neisseria meningitides
Group A Streptococcus
Group B Streptococcus
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Staphylococcus aureus
Methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus
17) A 14-year-old boy is evaluated for short stature. He has no significant past medical history and is considered otherwise healthy by his parents. He eats a normal diet and has regular meals. His height and weight have been consistently at the 5th percentile since early childhood. His physical examination is normal, with genitalia at Tanner stage 3. Which of the following is the most likely laboratory finding for this boy?
. Increased serum creatinine concentration
. Bone age that is equivalent to chronologic age
. Decreased complement C3 level
. Decreased serum albumin concentration
. Decreased thyroid stimulating hormone
18) The recent suicide of a well-known high school cheerleader in your community has generated an enormous amount of community concern and media coverage. A girl who was close friends with the deceased makes an appointment and comes in to your office to discuss the event with you. You ask, and she denies suicidal ideation, but she has many questions about suicide. Correct statements about adolescent suicide include which of the following?
. Those who are successful have a history of a prior attempt or prior serious suicidal ideation
. Girls tend to use more lethal means
. The number of attempted suicides is much higher among boys
. Inquiry by pediatricians, high school teachers, parents, or friends about suicidal thoughts typically precipitates the act
. The number of suicides in adolescents 10 to 19 years of age has decreased significantly since the 1950s
19) A 2-month-old male is brought to the emergency department for evaluation of cyanosis, which occurred earlier in the day while the infant was taking his bottle. Initially, he became fussy and sweaty, then his mother noticed that his lips turned blue. He became intermittently tachypneic and continued to cry. As the crying continued, the cyanosis worsened. His temperature is 37C (98.6 F), blood pressure is 80/50 mmHg, pulse is 150/min, and respiratory rate is 45/min. On examination, the child is alert, cyanotic, and tachypneic. Cardiac auscultation reveals a normal S 1 followed by a systolic ejection click. A grade 2/6 crescendo-decrescendo systolic ejection murmur is heard at the left upper sternal border. The patient is immediately placed in a knee-chest position. This maneuver will improve this patient's condition by which of the following mechanisms?
Increased right to left shunting
. Increased systemic venous return
. Decreased pulmonary blood flow
. Increased systemic vascular resistance
. Increased respiratory drive .
20) You are called to the ER to see one of your patients. The father of this 14-year-old mildly retarded child says that he found the child about 20 minutes ago in the neighbor’s garden shed with an unknown substance in his mouth. The child first had a headache, but then became agitated and confused; while you are talking to the father in the ER the child begins to have a seizure and dysrhythmia on the cardiac monitor. The blood gas demonstrates a severe metabolic acidosis. Which of the following agents is most likely the culprit?
. Paraquat
. Organophosphate
. Chlorophenothane (DDT)
. Sodium cyanide
. Warfarin
21) A 17-year-old sexually active girl comes to your office complaining of acne that is unresponsive to the usual treatment regimen. Physical examination reveals severe nodulocystic acne of her face, upper chest, and back. You consider prescribing isotretinoin (Accutane), but you are concerned about side effects. Reviewing the literature, you find which of the following to be true about isotretinoin?
. Significant decrease in serum triglyceride levels are noted in 25% of patients
. Its efficacy can be profound and permanent
. It is not known to be a teratogen
. Most patients experience excessive tearing and salivation
. Severe arthritis necessitating cessation of the drug occurs in about 15% of patients
22) The parents of a 1-month-old infant bring him to the emergency center in your local hospital for emesis and listlessness. Both of his parents wanted a natural birth, so he was born at home and has not yet been to see a physician. On examination, you find a dehydrated, listless, and irritable infant. Although you don’t have a birth weight, the parents do not feel that he has gained much weight. He has significant jaundice. His abdominal examination is significant for both hepatomegaly and splenomegaly. Laboratory values include a total bilirubin of 15.8 mg/dL and a direct bilirubin of 5.5 mg/dL. His liver function tests are elevated and his serum glucose is 38 mg/dL. Serum ammonia is normal. A urinalysis is negative for glucose, but it has a “mouse-like” odor. These findings are consistent with which of the following conditions?
. Phenylketonuria
. Homocystinuria
. Maple syrup urine disease .
Galactosemia .
Ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency
23) After an uneventful labor and delivery, an infant is born at 32 weeks’ gestation weighing 1500 g (3 lb, 5 oz). Respiratory difficulty develops immediately after birth and increases in intensity thereafter. At 6 hours of age, the child’s respiratory rate is 60 breaths per minute. Examination reveals grunting, intercostal retraction, nasal flaring, and marked cyanosis in room air. Auscultation reveals poor air movement. Physiologic abnormalities compatible with these data include which of the following?
. Decreased lung compliance, reduced lung volume, right-to-left shunt of blood
. Decreased lung compliance, increased lung volume, left-to-right shunt of blood
. Normal lung compliance, reduced lung volume, left-to-right shunt of blood
. Normal lung compliance, increased lung volume, right-to-left shunt of blood
. Decreased lung compliance, reduced lung volume, left-to-right shunt of blood
24) A 15-year-old girl is seen in your clinic with a sprained ankle, which occurred the previous day while she was exercising in her room. You realize that you have not seen her for quite some time, and begin to expand your examination beyond the ankle. You find relatively minimal swelling on her right ankle. She has dental decay, especially of anterior teeth and a swollen, reddened, irritated uvula. She seems to be somewhat hirsute on her arms and legs, but has thinning of her hair of the head. She has a resting heart rate of 60 beats per minute, and her oral temperature is 35.5°C (96°F). Further questioning suggests that she has developed secondary amenorrhea. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in the management of this girl?
. Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) testing
. Pregnancy testing
. Thyroid function panel
. Comparison of current and past weights
. Radiograph of ankle
25) You have been recently named as the medical director of the normal newborn nursery in your community hospital and have been asked to write standardized admission orders for all pediatricians to follow. Which of the following vaccines will you include on these orders?
. Haemophilus influenza B vaccine
. Hepatitis A vaccine
. Hepatitis B vaccine
. Combination diphtheria, tetanus, and acellular pertussis vaccine
. Inactivated polio virus
26) A small-for-gestational-age infant is born at 30 weeks’ gestation. At 1 hour of age, his serum glucose is noted to be 20 mg/dL (normally greater than 40 mg/dL). Which of the following is the most likely explanation for hypoglycemia in this infant?
. Glucagondeficiency
. Inadequate stores of nutrients
. Adrenal immaturity
. Pituitary immaturity
. Insulin excess
27) Your sister who lives in another state sends via e-mail photographs of her 6-month-old infant. You note the child has a white reflection from one of his eyes. You hastily assist in arranging an urgent pediatric ophthalmologic evaluation. Your sister immediately accesses the Internet and begins to ask questions of you. Which of the following statements found by your sister is correct?
. Most cases of retinoblastoma are unilateral and hereditary
. Cure rates for retinoblastoma treated in the United States exceed 90%
. Biopsy is usually performed to confirm the diagnosis
. Intraocular calcifications are an unusual finding and suggest worse prognosis
. Patients with the hereditary form of retinoblastoma are at significantly increased risk of leukemia in later years
28) A 2950-g (6.5-lb) black baby boy is born at home at term. On arrival at the hospital, he appears pale, but the physical examination is otherwise normal. Laboratory studies reveal the following: mother’s blood type A, Rh-positive; baby’s blood type O, Rh-positive; hematocrit 38%; and reticulocyte count 5%. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the anemia?
. Sickle-cell anemia
. Fetomaternal transfusion
. ABO incompatibility
. Physiologic anemia of the newborn
. Iron-deficiency anemia
29) A 1-week-old male newborn is seen in the office for "noisy breathing." The mother says that the "noisy breathing" is more prominent when the infant is lying on his back, and improves when he is in a prone position with his chin up. The newborn is afebrile and has no cough, vomiting, or cyanosis. There are no inspiratory retractions or wheezes. On direct laryngoscopy, the epiglottis is rolled in from side to side. Which of the following statements is true about the child's condition?
. The child should be held in an upright position for 30 minutes after feeding and never fed while lying down
. The child requires immediate tracheostomy
. The child should be treated with intravenous ceftriaxone
. The child's condition is likely to deteriorate as the age advances
. In this condition the stridor improves when the child cries
30) A 2-month-old infant comes to the emergency center with fever for 2 days, emesis, a petechial rash, and increasing lethargy. In the ambulance he had a 3-minute generalized tonic/clonic seizure that was aborted with lorazepam. He does not respond when blood is drawn or when an IV is placed, but he continues to ooze blood from the skin puncture sites. On examination, his anterior fontanelle is open and bulging. His CBC shows a WBC of 30,000 cells/μL with 20% band forms. Which of the infant’s problems listed below is a contraindication to lumbar puncture?
. Significantly elevated WBC count consistent with bacteremia
. Uncorrected bleeding diathesis
. Bulging fontanelle
. Dehydration
. History of recent seizure
31) A 3-day-old infant, born at 32 weeks’ gestation and weighing 1700 g (3 lb, 12 oz), has three episodes of apnea, each lasting 20 to 25 seconds and occurring after a feeding. During these episodes, the heart rate drops from 140 to 100 beats per minute, and the child remains motionless; between episodes, however, the child displays normal activity. Blood sugar is 50 mg/dL and serum calcium is normal. Which of the following is most likely true regarding the child’s apneic periods?
. They are due to an immature respiratory center
. They are evidence of underlying pulmonary disease
. They are a part of periodic breathing
. They are secondary to hypoglycemia
. They are manifestations of seizures
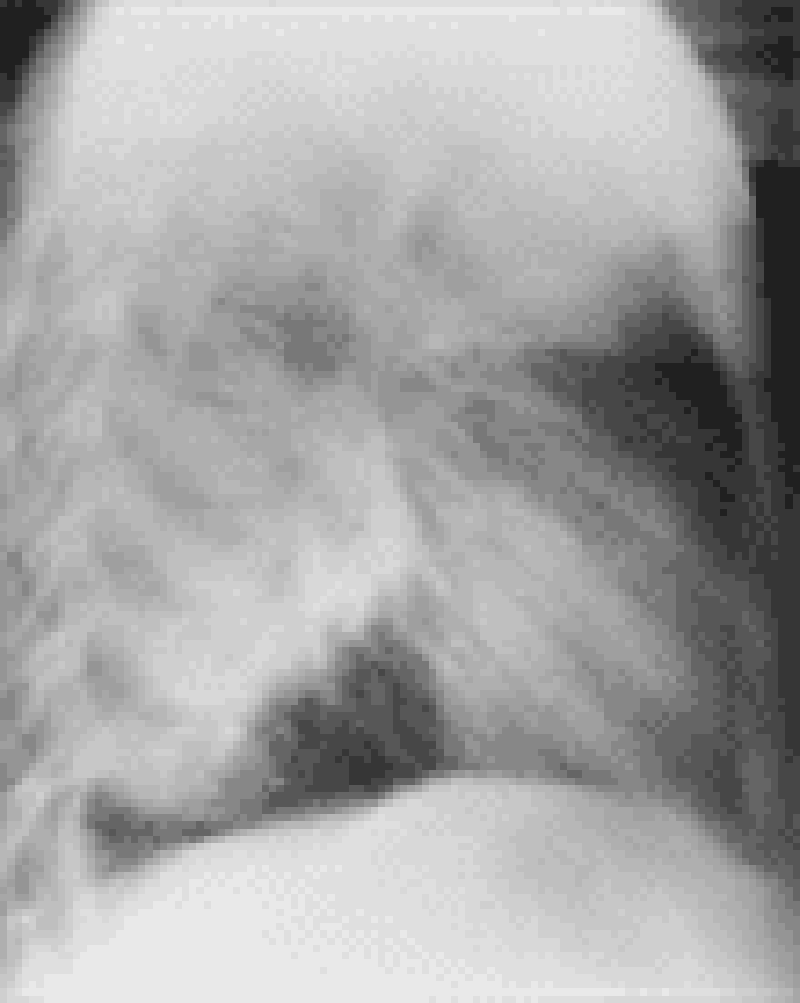
32) A 10-year-old boy presents with a 1-day history of fever, cough, and chest pain. He has not been eating and has been listless. He does not have any previous history of health problems. On physical examination, his temperature is 40°C, and he is tachypneic. He looks ill. He has rales on his left posterior lower lung fields. You order a chest x-ray. Which of the following organisms is most likely responsible for his pneumonia?
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Haemophilus influenzae
Mycoplasma pneumoniae
Pneumocystis carinii
Staphylococcus aureus
33) A patient has the sudden onset of fretfulness and pain. He curls up with his legs drawn in to his abdomen. Over the next few hours he continued to have episodes of pain and cries with tears, but between these times he acts normally. The patient's mother fears something is terribly wrong and brings him to the hospital. His past medical history was unremarkable. The previous week he had had a cold with a runny nose. His stools had been normal that day. On examination he is quiet and his abdomen is surprisingly soft and normal. In the emergency room there is a semi-soft stool with some blood mixed with mucus. This classic presentation of intussusception is most likely to occur in which of the following age groups?
. Late adolescence
. Birth to 4 weeks of age
. 6 to 12 months of age
. 3 to 5 years of age
. Early adolescence
34) A 10-year-old girl has bullous target lesions and mucosal erythema, which developed after her third dose of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole for a urinary tract infection. Which of the following is a likely associated clinical finding?
Nausea
Diarrhea
Fever
Lymphadenopathy
Vomiting
35) A 16-year-old boy is brought into the emergency department by his friends. He is semicomatose, with a pulse of 60/min and respirations of 6-8/min. His pupils are constricted. Which of the following will most likely be revealed on a urine toxicology screen?
. Tricyclic antidepressant intoxication
. Amphetamine intoxication
. Cocaine intoxication
. Ethanol intoxication .
Opiate intoxication
36) An 8-month-old female infant is brought to the clinic for a well-baby examination. She was born prematurely at 35 weeks gestation. She weighs 2.3kg (5 Ib). She cannot sit unsupported. Physical examination reveals mild facial hypoplasia, epicanthal folds, micrognathia, long nasal philtrum, thin upper lip and short palpebral fissures. Auscultation of the heart reveals an III/ IV harsh holosystolic murmur over the precordium. Her karyotype is normal. What is the most likely cause of these findings?
Maternal hyperglycemia Infection with rubella during pregnancy
Maternal age
Moderate or excessive intake of alcohol during pregnancy
Treatment with lithium for manic disorder
Infection with rubella during pregnancy
37) A 12-year-old boy is brought to the clinic by his parents because "he cannot walk anymore." Yesterday, he became irritable, uneasy, and complained of tingling and weakness in both his legs. This morning, he couldn't stand up or move his legs, and complained of pain in his leg and thigh muscles. He denies any headaches, nausea or vomiting. He had an episode of febrile diarrhea 10 days ago. His family history is unremarkable. Physical examination reveals symmetric flaccid paralysis of both legs, absent deep tendon reflexes, and decreased superficial touch and vibratory sense. There is no nuchal rigidity. What structure is most likely affected in this patient's condition?
Medial lemniscus
Cerebral cortex
Corticospinal tract
Peripheral nerves
Gracile fasciculus
38) A 5-year-old boy suffers from a condition characterized by recurrent fungal and viral infections, thymic hypoplasia, tetany, and abnormal facies. Serum levels of immunoglobulins are mildly depressed, and lymph node biopsy shows lymphocyte depletion of T-dependent areas. Which of the following is the underlying pathogenetic mechanism?
. Developmental defect of the third/fourth pharyngeal pouches
. In utero infection by human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
. Mutations of an autosomal gene encoding adenosine deaminase
. Mutations of an X-linked gene coding for a cytokine receptor subunit
. Mutations of an X-linked gene coding for a tyrosine kinase
39) While working in the newborn nursery, you have the chance to counsel a first time mother. She had a healthy pregnancy and good prenatal care. The infant was delivered via normal spontaneous vaginal delivery and is doing well. You are counseling the mother on the benefits of breastfeeding, and she asks you what the differences are between human milk and formula. Which of the following is a true statement?
Human milk has more calcium and phosphorus than formula
Human milk provides adequate amounts of vitamin D
Human milk contains only trace amounts of immunoglobulin A
Human milk protein absorbs better and improves gastric emptying
The main advantage of formula is it decreases colic
40) A newborn is diagnosed with congenital heart disease. You counsel the family that the incidence of heart disease in future children is which of the following?
25% to 30%
1%
2% to 6%
8% to 10%
15% to 20%
41) An otherwise healthy 13-year-old boy has seasonal allergic rhinitis. He complains of excessive rhinorrhea, frequent sneezing, and nasal congestion. He has a nasal voice and breathes with his mouth. He derives some relief from keeping windows closed at home and spending as litde time as possible outdoors in periods of high pollen concentration. However, he is excessively bothered by nasal congestion. Which of the following drugs would be most effective in relieving nasal congestion?
Alpha-adrenergic agents such as phenylephrine
Antihistamines such as chlorpheniramine
Antihistamines such as loratadine
Cromoglycate or similar mast cell stabilizers
Ipratropium bromide
42) A 7 -year-old Caucasian boy is brought to the emergency room with a severe headache, vomiting, and altered mental status of acute onset. His temperature is 36.7 C (98 F), blood pressure is 130/70 mm Hg, pulse is 60/min, and respirations are 18/min. Neurologic examination reveals nuchal rigidity, but no focal neurologic signs. A CT scan shows blood in the subarachnoid space. Which of the following is the most probable additional finding in this patient?
Trauma
History of seizures
Mental retardation
Congenital heart disease
Coagulation abnormalities
43) A 3-year-old boy is brought to the office by his parents for the evaluation of dry eyes and photophobia. He has some difficulty in adapting to darkness. He is a very poor eater, and his diet consists mainly of canned foods, and very rarely, fresh vegetables or milk. Examination reveals dry, scaly skin, follicular hyperkeratosis in the extensor surfaces of the extremities, and dry, silver-gray plaques on the bulbar conjunctiva. What is the most likely diagnosis of this patient?
. Hypervitaminosis A
. Vitamin A deficiency
. Thiamine deficiency
. Ariboflavinosis
. Scurvy
44) An infant is due for her first dose of polio vaccine. Her parents have heard that there are two different types of vaccine for polio. They want to know why their daughter needs to get another shot rather than just taking the oral form of the vaccine. You tell the parents the major advantage of the injectable vaccine is which of the following?
boosting her immunity through secondary transmission
Lower cost
Increased mucosal immunity
Better efficacy
Avoidance of vaccine-associated paralytic poliomyelitis
45) An infant can regard his parent’s face, follow to the midline, lift his head from the examining table, smile spontaneously, and respond to a bell. He does not yet regard his own hand, follow past the midline, nor lift his head to a 45° angle off the examining table. Which of the following is the most likely age of the infant?
12 months
1 month
3 months
6 months
9 months
46) A child is brought to your clinic for a routine examination. She can put on a T-shirt but requires a bit of help dressing otherwise. She can copy a circle well but has difficulty in copying a square. Her speech is understandable and she knows four colors. She balances proudly on each foot for 2 seconds but is unable to hold the stance for 5 seconds. Which of the following is the most likely age of this child?
5 years
1 year
2 years
3 years
4 years
47) A 16-year-old boy with a history of ulcerative colitis presents to the physician complaining of diarrhea and a rash. He states that his appetite has been decreased recently, and also complains of nausea and abdominal pain in addition to watery diarrhea. He has an erythematous rash on his distal arms and legs that "burns". His mother reports that he has had poor concentration and has been irritable lately. Vital signs are stable. Examination reveals a beefy red tongue that appears swollen. Abdominal examination is normal. The rash resembles a sunburn and is located on his distal arms and legs. It is symmetrical and tender to palpation. Neurological examination is normal. This patient's symptoms are most likely due to a deficiency of which of the following vitamins?
. Cyanocobalamin
. Thiamine
. Riboflavin
. Niacin
. Pyridoxine
48) A full-term infant is brought to the office on her 6th day of life because her mother noted that she looked "yellow". The mother states that the infant is strictly breast-fed and has been eating every 2-3 hours. On examination, she is noted to be jaundiced over her trunk and face. There is no scleral icterus. She is otherwise healthy. Both the mother and baby are Rh positive. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this infant's jaundice?
. Rh incompatibility
. Breast-feeding jaundice
. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency
. Hypothyroidism
. Physiologic jaundice
49) A 5-year-old pedestrian is hit by a car in a mall parking lot and he is brought to the emergency department. There was loss of consciousness for less than 1 minute. On evaluation, the child has no neurologic deficits and a CT scan of the head reveals no intracranial abnormalities and no obvious skull fractures. The parents want to know what possible long-term problems there might be. You remember that problems after head trauma may include the development of seizures and that the risk of developing posttraumatic epilepsy is increased by which of the following?
A brief loss of consciousness
An acute intracranial hemorrhage
Retrograde amnesia
Posttraumatic vomiting
A small linear skull fracture
50) A one-year-old girl is brought to the office for the evaluation of sickle cell anemia. Both her parents have sickle cell trait, and her elder sister has sickle cell anemia. Her vital signs are stable. Her height and weight are appropriate for age. On examination, she appears healthy and normal. Her birth and past medical histories are insignificant. Hemoglobin electrophoresis reveals 40% hemoglobin S. What is the most common presentation of this condition?
Frequent UTI
Acute painful episodes
Painless hematuria
Splenic infarction
Dactylitis
51) A boy is brought to the office by his parents for a routine visit. During the physical examination, he can obey two-step commands, use two- to three-word phrases, and can build a tower of six blocks. According to his mother, he can walk up and down the stairs without help. What is the most likely age of this child?
4 years
15 months
18 months
2 years
3 years
52) A 12-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department because of severe pain near his left knee. He has sickle cell disease and has been hospitalized previously for sickle cell crisis. Vital signs are notable for persistent fever. Examination of the left lower extremity reveals a normal knee joint with marked tenderness and swelling over the proximal tibia. Laboratory studies show leukocytosis and elevated ESR. Imaging studies confirm the diagnosis of osteomyelitis. Which of the following organisms is the most likely cause of his condition?
. Group B streptococcus
. Escherichia coli
. Pseudomonasspecies
. Salmonella species
. Streptococcus pneumoniae
53) A child is brought to the physician for a routine visit. On examination, the child can name multiple items in the examination room, and can also combine 2 words into a short sentence. His mother estimates that he knows about 200 words. When his mother tries to help him onto the examination table, he says "me do it." Although his mother seems to understand most of what he says, you can only understand about half of his speech. Which of the following is the most likely age of this child?
. 36 months
. 12 months
. 15 months
. 18 months
. 24 months
54) A 2-year-old boy is brought to the office by his mother because he has not started to walk yet. His birth history is significant for prolonged labor, and his APGAR scores at 1 and 5 minutes were 3 and 5, respectively. His older brother is 4 years old, and has a normal developmental history. On examination, the child has hypotonia, learning disabilities and hyperactive deep tendon reflexes. What is the most likely cause for the child's delayed milestones?
Infantile spinal muscular atrophy
Cerebral anoxia
Congenital infection
Congenital muscular dystrophy
Friedreich's ataxia
55) A 2-year-old boy is brought to the office by his parents due to severe diarrhea since yesterday. He has had approximately 20 episodes of non-bloody, non-mucoid stool passage in the last twenty hours, and one episode of bilious vomiting. He is also feeding less than usual. He is febrile, tachycardic and moderately dehydrated. What is the most likely cause of his presentation?
Rotavirus
Norwalk virus
E.coli
Campylobacter jejuni
Shigella
56) Routine examination of an otherwise healthy kindergarten child with a history of asthma reveals a BP of 140/90 mmHg. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the hypertension?
obesity
Theophylline toxicity
Chronic lung disease
Renal disease
Coarctation of the aorta
57) A 6-year-old boy is seen in the office for evaluation of polyuria. Further questioning reveals several months of headache with occasional emesis. Your physical examination reveals a child who is less than 5% for weight. He has mild papilledema. His glucose is normal, and his first urine void specific gravity after a night without liquids is 1.005 g/mL. Which of the following might also be expected to be seen in this patient?
. Bitemporal hemianopsia
. Sixth nerve palsy
. Unilateral cerebellar ataxia
. Unilateral pupillary dilatation
. Unilateral anosmia
58) A 2-year-old girl is brought to the clinic due to fever, irritability and lethargy for the past two weeks. Over the past two months, she has complained of intermittent abdominal discomfort and has lost weight. Abdominal palpation reveals a firm nodular mass in the right flank. No bruits are heard. Abdominal x-ray reveals multiple calcifications in the renal area. Urine examination reveals increased levels of homovanillic acid and vanillylmandelic acid. Which embryonic structure has this mass most likely arisen from?
Lymphoid stem cells
Metanephros
Mesonephron
Paramesonephron
Neural crest cells
59) A 9-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department due to an episode of seizures during class. His teacher says that the seizure started suddenly, and he fell to the ground with sustained flexion of the arms and extension of the legs, followed by clonic movements of the whole body. He has also been irritable lately, and his school performance has declined. His parents arrive shortly and say that they recently noticed he was lethargic and frequently complained of headaches, especially in the morning. His medical history is unremarkable. Physical examination reveals decreased muscle strength of the left side of the body, with brisk deep tendon reflexes in the left arm and leg. MRI of the head reveals a space-occupying lesion in the right parietal lobe. What tumor is most likely responsible for this patient's symptoms?
Craniopharyngioma
Benign astrocytoma
Medulloblastoma
Glioblastoma multiforme
Pinealoma
60) A 2-year-old boy is brought to the pediatrician for a routine well-child visit. He has been growing and developing normally. He is starting to put words together into 2-word phrases. The boy eats a variety of foods including meats, vegetables, and fruits, and drinks 24-28 ounces (700ml) of whole milk each day. Past medical history is unremarkable. His mother has no concerns at today's visit. His physical examination is within normal limits. Laboratory results are as follows: Complete blood count: Hemoglobin 9.4 g/dl, Hematocrit 28%, Mean corpuscular volume 64 fl, Red cell distribution width 14% (normal 11.5%-16.0%), Reticulocytes 3.0%, Platelets 240,000/μL, Leukocytes 7,500/μL, Blood, plasma, and serum, Ferritin 100 ng/ml (7-140 ng/ml), Iron-binding capacity 300 μg/dl (240-450 μg/dl). Which of the following is the most likely cause for this child's anemia?
. Reduced production of globin chains
. Abnormal utilization of iron
. Cobalamin deficiency
. Iron deficiency
. Red blood cell membrane instability
{"name":"Pediatrie", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"1) An infant is born to a woman who has received very little prenatal care. The mother is anxious, complains of heat intolerance and fatigue, and reports that she has not gained much weight despite having an increased appetite. On examination the mother is tachycardic, has a tremor, and has fullness in her neck and in her eyes. The infant is most likely at risk for development of which of the following?, 2) An otherwise healthy 7-year-old girl is brought to your office by her father because she has some acne, breast development, and fine pubic hair. Which of the following is the most likely etiology for her condition?, 3) A primiparous woman whose blood type is O positive gives birth at term to an infant who has A- positive blood and a hematocrit of 55%. A total serum bilirubin level obtained at 36 hours of age is 12 mg\/dL. Which of the following additional laboratory findings would be characteristic of ABO hemolytic disease in this infant?","img":"https://cdn.poll-maker.com/11-514592/123.png?sz=1200"}
More Quizzes
Quizz Ortográfico
1470
HAPPY BIRTHDAY TO OCHI
1266
Spanish- possessive adjectives
630
El Adroconcurso
520
Dutch Bros - Test Your Coffee Menu Knowledge
201018479
Am I Charismatic? Free with Instant Results
201021637
Am I a Princess or a Queen? - Find Your Royal Type
201021381
The Weeknd - Test Your Fan Knowledge
201029473
Guess the Person - Identify Celebrities from Photos
201020211
Psych Season 2 Trivia - Are You a True Fan?
201018479
CCNA Wireless - Which Two Devices Affect Networks?
201020892
What Is My Wolf Name? Find Out with a Free
201019892