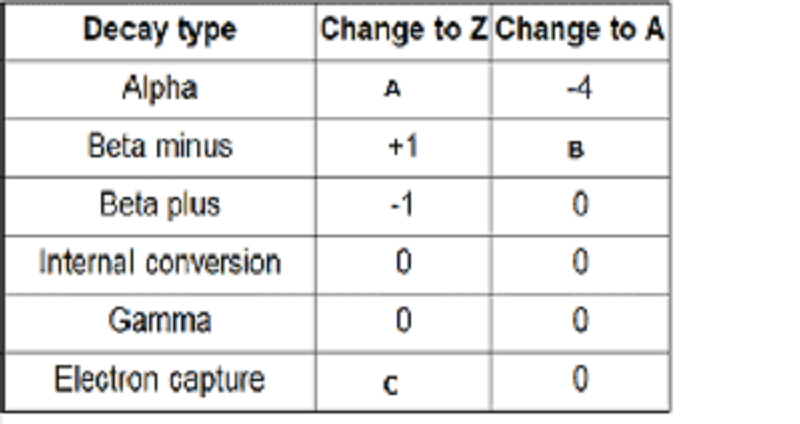
Radioactivity
{"name":"Radioactivity", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Test your knowledge on radioactivity with our comprehensive quiz designed for enthusiasts and students alike. Dive deep into topics like decay processes, particles involved, and the principles governing radioactivity.17 Engaging QuestionsMultiple Choice FormatScore and Learn as You Go!","img":"https:/images/course6.png"}
More Quizzes
Introduction to nuclear engineering ch2 quiz
261365
QM by A.K.
1586
REPRESENTANTES JUVENILES
6316
20100
Test Your PSSA Training Skills - Free Online Practice
201045895
Am I in Love with My Boyfriend? Take the Now!
201027623
Dive into Swimming Trivia: Ultimate Freestyle Challenge
201024691
Biomedical Instrumentation Lab
15830829
Free Wobble Base Pairing
201026301
Baseball Trivia for Kids: Fun to Test Their Skills
201028498
Months of the Year in Spanish - Test Your Skills
201068793
Are You Computer Literate? Free Computer Literacy Test
201036120