Back Muscles Quiz: Label the Major Muscle Groups
Quick, free back anatomy quiz to test your knowledge. Instant results.
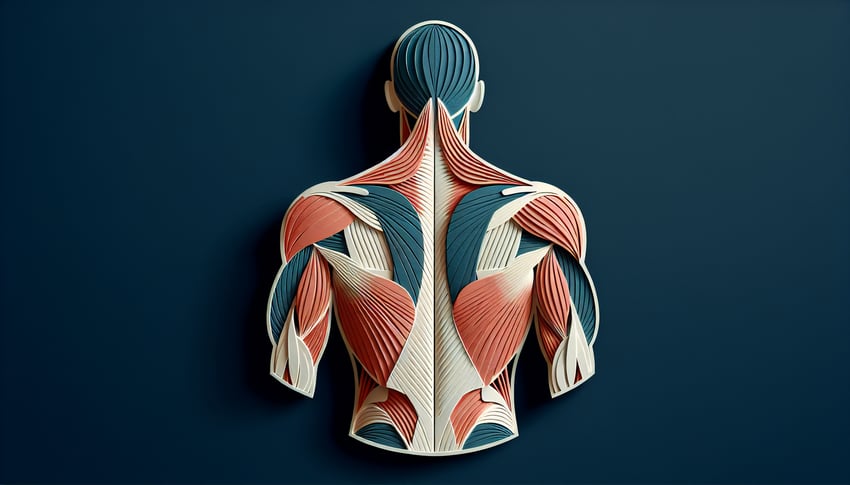
This back muscles quiz helps you label the trapezius, latissimus dorsi, rhomboids, and more on clear diagrams. Check your knowledge fast, then explore related areas with a scapula labeling quiz , a vertebrae labeling quiz , or an axial muscles quiz . Get instant feedback and keep practicing.
Study Outcomes
- Identify Major Back Muscles -
Learn to identify the trapezius, latissimus dorsi, rhomboids, and other key back muscles by name and position.
- Label Superficial vs Deep Layers -
Distinguish between superficial and deep muscle layers on diagrams to enhance your understanding of back muscle anatomy.
- Recall Anatomical Origins and Insertions -
Memorize the origins and insertions of each back muscle group to support accurate labeling and functional understanding.
- Differentiate Muscle Functions -
Understand and explain the primary actions of each muscle, such as extension, rotation, and stabilization of the spine and shoulders.
- Apply Knowledge in Practical Quizzes -
Test your anatomy skills through interactive labeling exercises, reinforcing your retention of back muscle names and functions.
Cheat Sheet
- Trapezius Anatomy & Function -
In the back muscles quiz, you'll need to identify the trapezius's triangular shape spanning from the occiput to T12 and recognize its three fiber segments for scapular elevation, retraction, and depression. Use the mnemonic "Up, Back, Down" to remember upper, middle, and lower fiber actions. (Source: Gray's Anatomy, 41st ed.)
- Latissimus Dorsi Origins & Actions -
The latissimus dorsi originates along the thoracolumbar fascia, iliac crest, and lower ribs and inserts into the intertubercular groove of the humerus to power shoulder extension, adduction, and internal rotation. Often called the "swimmer's muscle," it's essential in any back muscle quiz for its broad, fan-like appearance. (Source: Netter's Atlas of Human Anatomy, 7th ed.)
- Erector Spinae Group Breakdown -
The erector spinae consists of iliocostalis, longissimus, and spinalis columns, critical for spinal extension and posture maintenance in back muscles labeling exercises. Remember "I Love Spaghetti" to sequence them from lateral to medial. (Source: Tortora & Nielsen, Principles of Anatomy and Physiology.)
- Rhomboids & Levator Scapulae Roles -
Rhomboid major and minor retract and downwardly rotate the scapula, while levator scapulae elevates it, making these key when labeling back muscles on any musculoskeletal chart. A quick self-check: pull shoulders back to feel rhomboid engagement and shrug slightly for levator activation. (Source: American Journal of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation.)
- Deep Intrinsic Stabilizers -
Multifidus, interspinales, and rotatores sit closest to vertebrae, providing fine-tuned proprioception and segmental stability; multifidus is especially prominent in the lumbar region. Use "MRI" (Multifidus, Rotatores, Interspinales) to ace the muscles of the back quiz on deep layer identification. (Source: Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy.)