Organs of the Body Quiz: Grade 4 Body Systems
Quick, kid-friendly human body system quiz. Instant results.
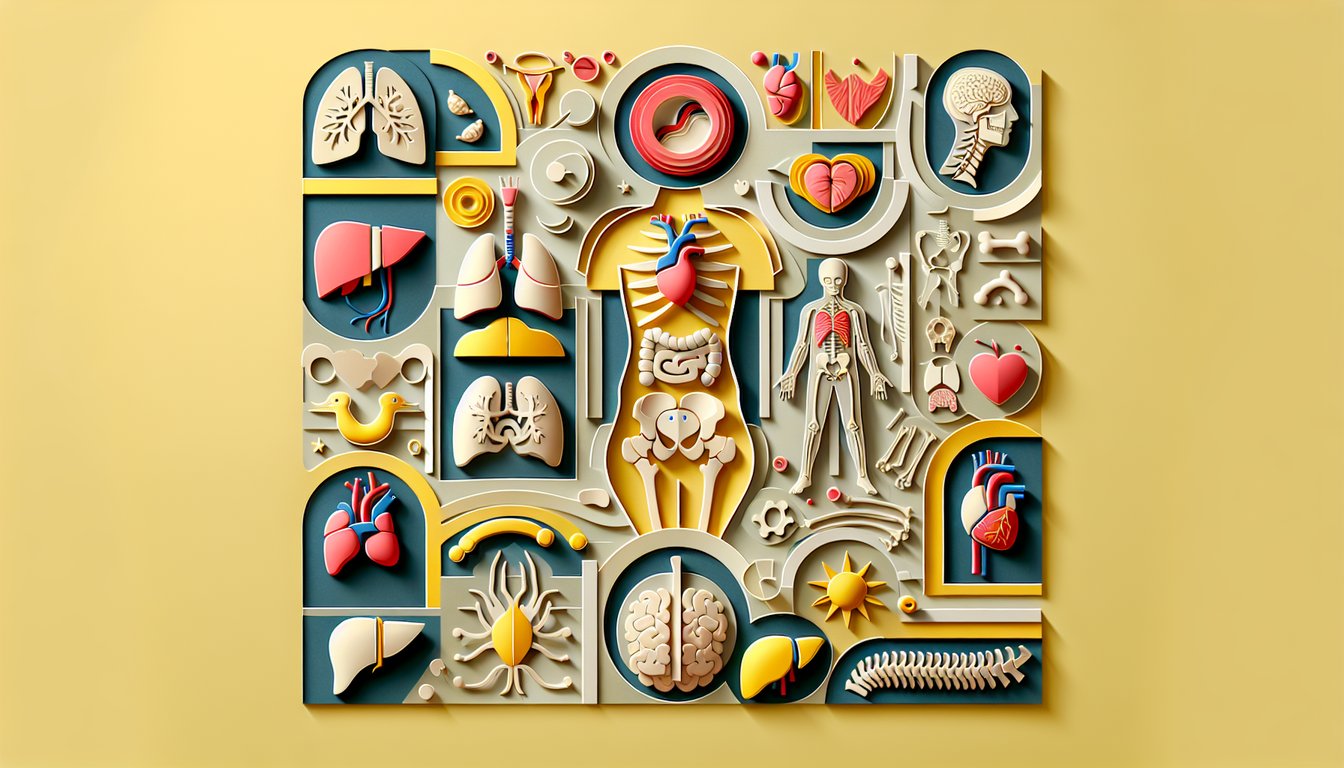
This organs of the body quiz helps fourth graders identify key organs and match each one to its body system. Practice questions cover the circulatory, respiratory, digestive, and nervous systems, with quick feedback to show what to review next. For more practice, see our human body system quiz and body systems test, or focus on the belly with this abdominal organs quiz.
Study Outcomes
- Understand Major Body Systems -
Learn to recognize and describe the primary human body systems covered in the Grade 4 anatomy quiz, including the circulatory, respiratory, digestive, and nervous systems.
- Identify Key Organs -
Be able to pinpoint and name essential organs such as the heart, lungs, stomach, and brain as you progress through the kids human body quiz.
- Explain Organ Functions -
Gain the ability to explain how each organ works within its system to keep the body healthy and functioning properly.
- Differentiate Between Systems -
Distinguish the roles and interactions of different body parts and organs by comparing and contrasting their functions.
- Apply Knowledge in Quiz Challenges -
Use your understanding to answer questions accurately in the elementary body systems test and improve your anatomy recall.
- Boost Confidence in Anatomy -
Develop greater confidence in your anatomical knowledge and prepare for more advanced science topics through this grade 4 anatomy quiz experience.
Cheat Sheet
- Overview of Major Body Systems -
The human body is organized into major systems like skeletal, circulatory, digestive, and nervous, each working together to keep you healthy. Reviewing how these systems interact is key to acing a human body systems quiz or elementary body systems test (Source: NIH). This big-picture approach sets you up for success on any grade 4 anatomy quiz!
- Skeletal System Basics -
Your skeleton gives your body shape, protects organs, and helps you move (Source: KidsHealth.org). Remember the mnemonic SOAP - Support, Organ protection, Assist movement, and Production of blood cells - to recall the five main functions. Knowing major bones like the femur and skull will boost your score on a body parts and organs quiz.
- Circulatory System Essentials -
The heart, blood, and vessels make up the circulatory system, delivering oxygen and nutrients everywhere (Source: American Heart Association). Use the phrase "ABO" to remember blood types - A, B, and O - and their compatibility rules. Understanding how your heart beats (about 70 beats per minute) can help on any kids human body quiz question about blood flow.
- Digestive System Pathway -
Food travels from Mouth to Esophagus to Stomach, then through the Small and Large Intestines (Source: Khan Academy). Try the fun phrase "My Eager Sister Sings Loudly" to remember Mouth, Esophagus, Stomach, Small intestine, Large intestine. Knowing this order helps you sail through digestive questions on a grade 4 anatomy quiz.
- Nervous System Connections -
Your brain, spinal cord, and nerves form the nervous system, sending electrical signals to control everything (Source: CDC). A quick trick: "NEBS" stands for Nerves, Electrical signals, Brain, Spinal cord to lock in the main parts. Mastering this gives you confidence in any elementary body systems test question on how we sense and react.