Skin Layers Quiz: Label and Test Your Knowledge
Quick, free layers of the skin quiz with instant results and helpful feedback.
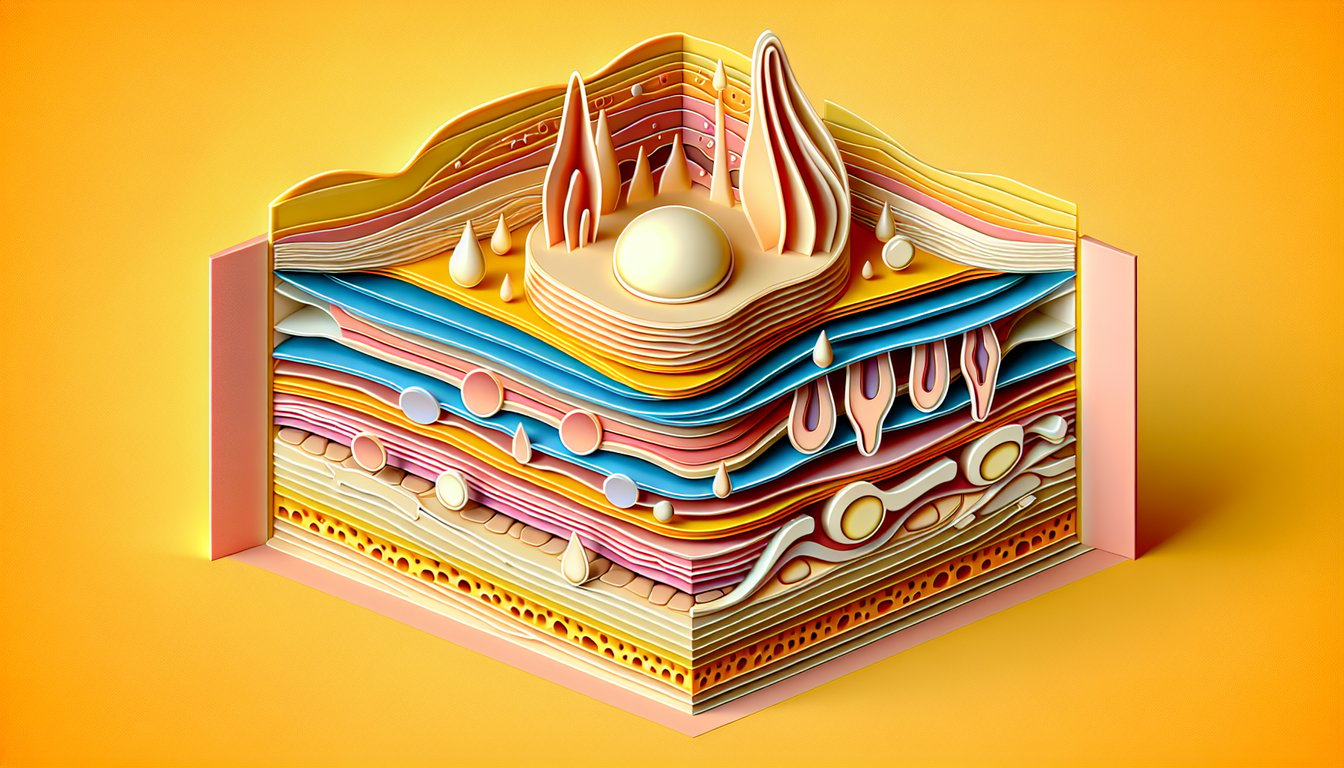
This skin layers quiz helps you label the epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis, spot glands and hair follicles, and check what you know with instant feedback. If you want to review related tissue types, try our epithelial tissue identification quiz and connective tissue quiz, or keep going with a broader anatomy and physiology quiz.
Study Outcomes
- Identify Skin Layers -
Recognize and name the epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis to build a solid foundation in integumentary system anatomy.
- Label Key Structures -
Accurately place labels on a skin diagram, marking features like hair follicles, sweat glands, and sensory receptors.
- Distinguish True/False Statements -
Evaluate quiz statements such as "blood vessels are only found in the dermis" to reinforce factual understanding.
- Analyze Vascular Distribution -
Examine how blood vessels traverse different skin layers and understand their role in nutrient delivery and thermoregulation.
- Compare Layer Functions -
Contrast the protective, sensory, and regulatory roles of each skin layer to appreciate their integrated functions.
- Apply Knowledge to Real-World Scenarios -
Use quiz feedback to improve practical skills in fields like dermatology, cosmetology, and healthcare education.
Cheat Sheet
- Layered Epidermal Architecture -
When tackling the layers of the skin quiz, remember the five strata of the epidermis: stratum corneum, lucidum, granulosum, spinosum, and basale. Use the mnemonic "Come, Let's Get Sun Burned" to lock in the order from outermost to deepest. These layers average 0.05 - 1.5 mm in thickness and house keratinocytes responsible for barrier function (University of Michigan Histology).
- Dermal Zones and Functions -
In an integumentary labeling quiz, distinguish the papillary dermis (loose collagen, dermal papillae) from the reticular dermis (dense collagen, elastin fibers). The papillary layer's capillary loops nourish the epidermis, while the reticular layer provides tensile strength with Type I collagen. Visualize a cross-section diagram from Gray's Anatomy to master their appearance.
- Hypodermis/Subcutaneous Insights -
Although often omitted in a skin diagram quiz, the hypodermis (subcutaneous tissue) contains adipocytes that insulate and store energy. Its thickness varies by region - think "love handles" versus eyelids - so practice labeling areas with thicker versus thinner hypodermis. This layer also anchors skin to underlying fascia per Mayo Clinic guidelines.
- Vascular Distribution Reality Check -
True or false: "Blood vessels are only found in the dermis." False! While the dermis houses the primary vascular plexus, vessels also extend into the hypodermis to supply adipose tissue. Remember, the avascular epidermis relies on diffusion from dermal capillaries (American Journal of Anatomy).
- Diagram Labeling Best Practices -
For a skin diagram quiz, study high-resolution cross-sections from resources like Netter's and label at least ten structures: epidermal layers, papillae, sweat glands, follicles, and nerve endings. Test yourself by covering the labels and redrawing key features; repetition builds recall. Consider flashcards pairing images with names to boost retention.