Shoulder ligaments quiz: test your shoulder joint anatomy
Quick, free shoulder anatomy quiz. Instant results.
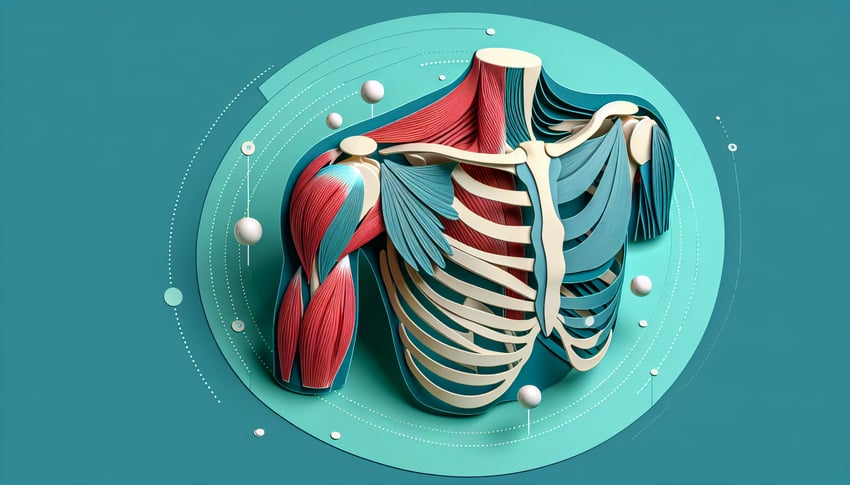
Use this shoulder joint quiz to check your understanding of ligaments, stabilizers, and key movements. Build confidence before an exam with quick feedback, then expand your review with the shoulder anatomy quiz and the shoulder girdle anatomy quiz . If you need to sharpen landmarks, try the bone markings quiz .
Study Outcomes
- Identify Key Shoulder Muscles -
Pinpoint and name the primary muscles involved in shoulder movement, including the deltoid and rotator cuff group.
- Describe Muscle Origins and Insertions -
Outline the specific bony attachment points for each muscle, clarifying how origins and insertions dictate shoulder mechanics.
- Analyze Shoulder Joint Movements -
Examine how different muscles coordinate to produce actions like abduction, rotation, flexion, and extension of the shoulder.
- Apply Clinical Implication Knowledge -
Connect anatomical details to common clinical conditions such as impingement syndrome and rotator cuff tears for better diagnosis and treatment understanding.
- Differentiate Intrinsic vs Extrinsic Muscles -
Distinguish between muscles that originate within the shoulder girdle and those that act upon the shoulder from the torso or arm.
- Recall Key Anatomical Landmarks -
Memorize and locate important structures like the acromion, glenoid cavity, and humeral head to enhance spatial orientation.
Cheat Sheet
- Rotator Cuff Muscle Origins & Insertions -
Recall the SITS mnemonic (Supraspinatus, Infraspinatus, Teres minor, Subscapularis) to memorize origins on the scapula and insertions on the humeral head. For instance, supraspinatus originates in the supraspinous fossa and inserts on the greater tubercle, as noted in Gray's Anatomy (2020). This foundation is essential for nailing your shoulder joint anatomy quiz with confidence.
- Glenohumeral Joint Stability Mechanics -
Understand the static stabilizers (glenoid labrum, joint capsule, ligaments) and dynamic stabilizers (rotator cuff muscles) that work together to maintain joint congruency. According to the Journal of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery (2019), the labrum deepens the socket by about 50%, boosting stability. Visualizing these forces helps you tackle shoulder anatomy questions realistically.
- Scapulohumeral Rhythm & Movement Ratios -
Use the 2:1 ratio mnemonic: for every 2° of glenohumeral abduction, there's 1° of scapulothoracic upward rotation (AAOS, 2021). This synergy between scapula and humerus maximizes range of motion and reduces impingement risk. Practicing with movement diagrams will sharpen your test shoulder anatomy skills.
- Clinical Implications: Impingement & Labral Tears -
Learn Neer's stages of impingement (I - III) and the SLAP tear classification (Type I - IV) as described in the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Recognizing pain patterns in abduction or external rotation can guide your diagnosis approach. Applying these clinical scenarios makes your shoulder joint muscles quiz answers pop with practical insight.
- Neurovascular Structures Around the Shoulder -
Map the course of the axillary nerve around the surgical neck of the humerus and the posterior circumflex humeral artery, per Netter's Atlas (2018). A simple tip: "Army over Navy" reminds you the artery (Army) runs above the nerve (Navy) through the quadrangular space. This trick ensures you won't miss critical shoulder clinical implications on exam day.