Modules 4 – 7
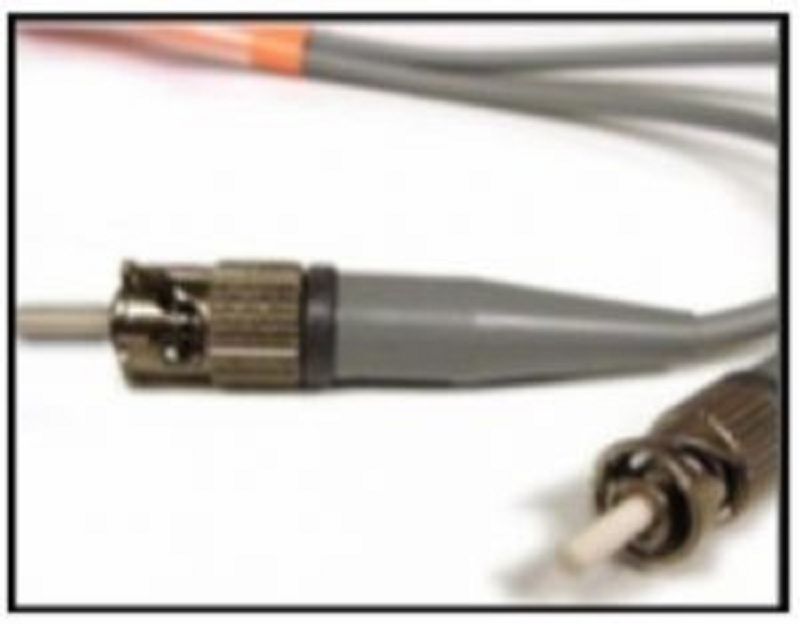
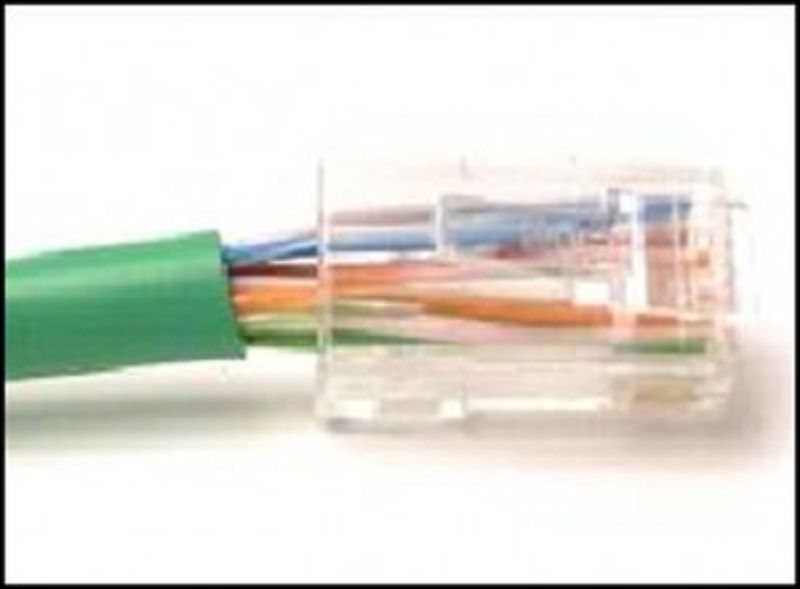

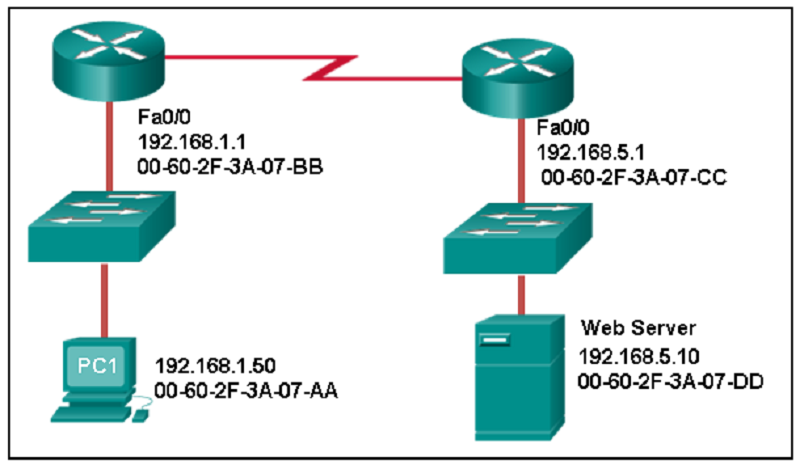

Explanation: Issuing the command ipconfig /all from the PC0 command prompt displays the IPv4 address and MAC address. When the IPv4 address 10.1.1.5 is pinged from PC0, the switch stores the source MAC address (from PC0) along with the port to which PC0 is connected. When the destination reply is received, the switch takes the destination MAC address and compares to MAC addresses stored in the MAC address table. Issuing the show mac-address-table on the PC0 Terminal application displays two dynamic MAC address entries. The MAC address and port entry that does not belong to PC0 must be the MAC address and port of the destination with the IPv4 address 10.1.1.5.
Which port does Switch0 use to send frames to the host with the IPv4 address 10.1.1.5?