DES 2 ep 2
46) A 53-year-old Caucasian male is admitted to the hospital with a 2-week history of fatigue and decreased exercise tolerance. He says he can hardly climb two flights of stairs without getting dyspneic. He denies palpitations or chest pain. His past medical history is insignificant, and a routine check-up 6 months ago was normal. He admits two episodes of binge drinking during the last month, but says that he 'got it under control'. He is currently not taking any medications. His blood pressure is 150/90 mmHg and heart rate is 130/min, irregular. Lungs are clear on auscultation. ECG does not reveal P waves. Echocardiography shows significant left ventricular dilation with an ejection fraction of 35% and mitral regurgitation (1+). Which of the following intervention will most likely improve the left ventricular function in this patient?
. Preload optimization
. Decreasing afterload
. Inotropic support
. Rate or rhythm control
. Valve surgery
47) A 47-year-old Caucasian female presents with occasional episodes of nocturnal substernal chest pain that wakes her up during sleep. The pain episodes last 15-20 minutes and resolve spontaneously. She denies any illicit drug use. She leads a sedentary lifestyle but states that she can climb two flights of stairs without any discomfort. She has no history of hypertension or diabetes. Her pulse is 75/min and regular, blood pressure is 134/70 mmHg and respirations are 14/min. Extended ambulatory ECG monitoring reveals transient ST segment elevation in leads I, aVL, and V4-V6 during the episodes. Which of the following is the best treatment for this patient?
. Diltiazem
. Propranolol
. Aspirin
. Heparin
. Digoxin
48) A 55-year-old male presents to your office with a 6-month history of periodic substernal pressure. He experiences this pressure while walking uphill or climbing two flights of stairs. His past medical history is insignificant. He smokes 1 pack a day and consumes alcohol occasionally. His blood pressure is 160/90 mmHg and heart rate is 75/min. Resting ECG is normal. You suspect stable angina and order an ECG stress test that reveals horizontal ST segment depression in leads II, III, and aVF at submaximal heart rate. What is the best medication to treat this patient's condition?
. Thiazide
. Verapamil
. Amlodipine
. Metoprolol
. Enalapril
49) A 56-year-old white male presents to his primary care physician for follow-up evaluation of high blood pressure noted on each of three prior visits over a period of 6 months (systolic blood pressure ranging 140-145, diastolic blood pressure ranging 90-96 mmHg). He has smoked a pack of cigarettes per day for the past 20 years and takes 5-6 drinks of alcohol daily. He has no other medical problems and takes no medications. There is no family history of diabetes mellitus, coronary artery disease, hyperlipidemia or hypertension. On physical examination today, his blood pressure is 146/97 mmHg and pulse is 80/min. The remainder of the exam is unremarkable. Which of the following nonpharmacologic interventions would be expected to have the greatest impact on his high blood pressure?
. Smoking cessation
. Increased consumption of complex carbohydrates
. Increased calcium consumption
. Decreased alcohol intake
. Decreased consumption of animal protein
50) A 63-year-old female presents to your office for a routine check-up. She has no present complaints. Her past medical history includes OM, type 2, and hypertension. Her current medications include glyburide and atenolol. She does not smoke. She drinks 2-3 glasses of wine 1-2 times a week. Three consecutive BP measurements were in the range of 138-142/87-90 mmHg. Physical examination is within normal limits. Her recent fasting glucose level was 250 mg/dl. ECG recorded 1 month ago showed left ventricular hypertrophy. Which statement about the BP control in this patient is the most accurate?
. BP is within acceptable range
. BP is within optimal range
. It is better to keep systolic pressure less than 130 mmHg to slow end-organ damage
. Diastolic BP is within acceptable range, but systolic is not
. Systolic BP is within acceptable range, but diastolic is not
51) A 22-year-old white female is brought to your office by her mother because of the recurrent syncopal episodes. The first episode occurred about one year ago when her roommate committed suicide and then several similar episodes occurred usually provoked by a strong emotion. The episodes are preceded by light-headedness, weakness, and blurred vision and last about three minutes with rapid recovery of consciousness. Past medical history is insignificant. She is not taking any medications and denies drug abuse. Her blood pressure is 110/70 mmHg while supine and 108/70 mmHg while standing. Physical findings are within normal limits. EKG performed one month ago was normal. Which of the following is the next best step in the management of this patient?
. Echocardiography
. 24-hour (Holter) monitoring
. Invasive electrophysiologic testing
. Electroencephalogram
. Upright tilt table testing
52) A 59-year-old man presents to the emergency department (ED) complaining of new-onset chest pain that radiates to his left arm. He has a history of hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, and a 20-pack-year smoking history. His electrocardiogram (ECG) is remarkable for T-wave inversions in the lateral leads. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
. Give the patient two nitroglycerin tablets sublingually and observe if his chest pain resolves
. Place the patient on a cardiac monitor, administer oxygen, and give aspirin
. Call the cardiac catheterization laboratory for immediate percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI)
. Order a chest x-ray; administer aspirin, clopidogrel, and heparin
. Start a β-blocker immediately
53) A 63-year-old insurance agent is brought to the ED by paramedics for shortness of breath and an RR of 31 breaths per minute. The patient denies chest pain, fever, vomiting, or diarrhea. His wife says he ran out of his “water pill” 1 week ago. His BP is 185/90 mmHg, HR is 101 beats per minute, oxygen saturation is 90% on room air, and temperature is 98.9°F. There are crackles midway up both lung fields and 2+ pitting edema midway up his legs. An ECG shows sinus tachycardia. The patient is sitting up and able to speak to you. After placing the patient on a monitor and inserting an IV, which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
. Obtain blood cultures and complete blood cell (CBC) count, and begin empiric antibiotic therapy
. Order a statim (STAT) portable chest x-ray
. Administer oxygen via nasal cannula and have the patient chew an aspirin
Administer oxygen via non-rebreather, furosemide, nitroglycerin, and consider non-invasive respiratory therapy
. Rapid sequence endotracheal intubation
54) You have been asked to evaluate a 42-year-old white male smoker who presented to the emergency department with sudden onset of crushing substernal chest pain, nausea, diaphoresis and shortness of breath. His initial ECG revealed ST segment elevation in the anterior-septal leads. Cardiac enzymes were normal. The patient underwent emergent cardiac catheterization, which revealed only a 25% stenosis of the left anterior descending (LAD) artery. No percutaneous intervention was performed. Which of the following interventions would most likely reduce his risk of similar episodes in the future?
. Placement of a percutaneous drug-eluting coronary artery stent
. Placement of a percutaneous non-drug-eluting coronary artery stent
. Beginning therapy with a beta-blocker
. Beginning therapy with an ACE inhibitor
Beginning therapy with a calcium-channel blocker
55) Two weeks after hospital discharge for documented myocardial infarction, a 65-year-old returns to your office concerned about low-grade fever and pleuritic chest pain. There is no associated shortness of breath. Lungs are clear to auscultation and the heart is free of murmur, gallop, or rub. ECG is unchanged from the last one in the hospital. Which therapy is most likely to be effective?
. Antibiotics
Anticoagulation with warfarin (Coumadin)
. An anti-inflammatory agent
. An increase in antianginal medication
. An increase in antianginal medication
56) A 55-year-old patient presents to you after a 3-day hospital stay for gradually increasing shortness of breath and leg swelling while away on a business trip. He was told that he had congestive heart failure, but is asymptomatic now, with normal vital signs and physical examination. An echocardiogram shows an estimated ejection fraction of 38%. The patient likes to keep medications to a minimum. He is currently on aspirin and simvastatin. Which would be the most appropriate additional treatment?
. Begin an ACE inhibitor and then add a beta-blocker on a scheduled basis
. Begin digoxin plus furosemide on a scheduled basis
Begin spironolactone on a scheduled basis
. Begin furosemide plus nitroglycerin
. Given his preferences, no other medication is needed unless shortness of breath and swelling recur
57) An active 78-year-old female with history of hypertension presents with the new onset of left hemiparesis. Cardiac monitoring reveals atrial fibrillation. She had been in sinus rhythm on check-up 3 months earlier. Optimal management at discharge includes a review of antihypertensive therapy, a ventricular rate control agent, and which of the following?
. Automated implanted cardioverter-defibrillator (AICD)/permanent pacemaker to avoid the need for anticoagulation
Immediate direct-current cardioversion
. Antiplatelet therapy such as aspirin, without warfarin
. Antiplatelet therapy plus warfarin with a target INR of 1.5
. Warfarin with a target INR of 2.0 to 3.0.
58) A 72-year-old male with a history of poorly controlled hypertension develops a viral upper respiratory infection. On his second day of symptoms he experiences palpitations and presents to the emergency room. His blood pressure is 118/78 mmHg. The following rhythm strip is obtained. What is the best next step in the management of this patient?

. Administration of intravenous metoprolol
. Administration of intravenous adenosine
. Administration of intravenous amiodarone
. Emergent electrical cardioversion
. Initiation of chest compressions and preparation for semielective intubation
59) An otherwise asymptomatic 65-year-old man with diabetes presents to the ER with a sports-related right shoulder injury. His heart rate is noted to be irregular, and this ECG is obtained. Which of the following is the best immediate therapy?
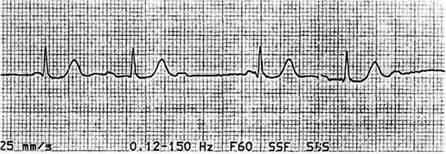
j

. Atropine
. Isoproterenol
. Pacemaker placement
. Electrical cardioversion
. Observation
60) A patient has been in the coronary care unit for the past 24 hours with an acute anterior myocardial infarction. He develops the abnormal rhythm shown below, although blood pressure remains stable at 110/68 mmHg. Which of the following is the best next step in therapy?
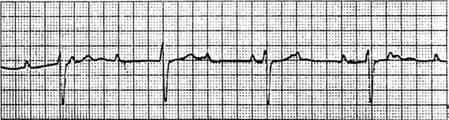

. Perform cardioversion.
. Arrange for pacemaker placement.
. Give digoxin.
. Give propranolol.
. Give lidocaine.
61) A 70-year-old male with a history of coronary artery disease presents to the emergency department with 2 hours of substernal chest pressure, diaphoresis, and nausea. He reports difficulty “catching his breath.” An electrocardiogram shows septal T-wave inversion. The patient is given 325-mg aspirin and sublingual nitroglycerin while awaiting the results of his blood work. His troponin I is 0.65 ng/mL (normal < 0.04 ng/mL). The physician in the emergency department starts the patient on low-molecular-weight heparin. His pain is 3/10. Blood pressure is currently 154/78 mmHg and heart rate is 72. You are asked to assume care of this patient. What is the best next step in management?
. Arrange for emergent cardiac catheterization
. Begin intravenous thrombolytic therapy
. Admit the patient to a monitored cardiac bed and repeat cardiac enzymes and ECG in 6 hours
. Begin intravenous beta-blocker therapy
. Begin clopidogrel 300 mg po each day
62) You are volunteering with a dental colleague in a community indigent clinic. A nurse has prepared a list of patients who are scheduled for a dental procedure and may need antibiotic prophylaxis beforehand. Of the patients listed below, who would be most likely to benefit from antibiotic prophylaxis to prevent infective endocarditis?
. 17-year-old male with coarctation of the aorta
. 26-year-old female with a ventricular septal defect repaired in childhood
. 42-year-old female with mitral valve prolapse
. 65-year-old male with prosthetic aortic valve
. 72-year-old female with aortic stenosis
63) An 80-year-old woman was admitted to your service for dizziness. Cardiac monitoring initially revealed atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response. Her ventricular rate was controlled with beta-blocker. An echocardiogram revealed an enlarged left atrium and an ejection fraction of 50%. No evidence of diastolic heart dysfunction was noted. She is now asymptomatic, with blood pressure 130/80 mmHg, heart rhythm irregularly irregular, and heart rate around 80/minute. Which of the following is the best management strategy of this patient’s arrhythmia?
. Electrical cardioversion plus prolonged anticoagulation
. Electrical cardioversion without anticoagulation
. Chemical cardioversion plus prolonged anticoagulation
. Chemical cardioversion without anticoagulation
. Continued rate control plus prolonged anticoagulation
64) You are seeing a 45-year-old female patient of your partner for the first time in your clinic. A quick review of the patient’s medical record shows that her systolic blood pressure was greater than 140 mmHg at both of her last clinic appointments. Her medical history is otherwise significant only for diabetes mellitus. Her blood pressure today is 164/92 mmHg. What is the best next step in her blood pressure management?
. Ask the patient to keep a written record of her blood pressure and bring with her to a return appointment
Advise the patient to begin a heart healthy, low sodium diet and refer to a nutritionist
. Prescribe an ACE inhibitor in addition to heart healthy diet
. Prescribe a dihydropyridine calcium-channel blocker in addition to a heart healthy diet
. Arrange for echocardiogram to assess for end-organ damage
65) A 68-year-old male complains of pain in his calves while walking. He notes bilateral foot pain, which awakens him at night. His blood pressure is 117/68 mmHg. Physical examination reveals diminished bilateral lower extremity pulses. An ankle:brachial index measures 0.6. The patient’s current medications include aspirin and hydrochlorothiazide. Which of the following is the best initial management plan for this patient’s complaint?
. Smoking cessation therapy, warfarin
. Smoking cessation therapy, warfarin
Smoking cessation therapy, schedule an arteriogram
. Smoking cessation therapy, warfarin, peripherally acting calcium-channel blocker
. Smoking cessation therapy, consultation with a vascular surgeon
66) An 82-year-old woman is brought to the ED by her daughter for worsening fatigue, dizziness, and light-headedness. The patient denies chest pain or shortness of breath. She has not started any new medications. Her BP is 140/70 mmHg, HR is 37 beats per minute, and RR is 15 breaths per minute. An IV is started and blood is drawn. An ECG is seen below. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
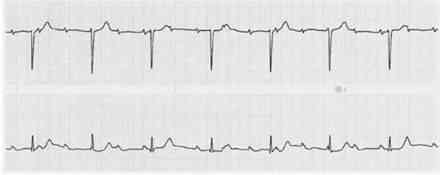

. Bed rest for the next 48 hours and follow-up with her primary-care physician
. Administer aspirin, order a set of cardiac enzymes, and admit to the cardiac care unit (CCU)
. Admit for Holter monitoring and echocardiogram
. Place a magnet on her chest to turn off her pacemaker
. Place on a cardiac monitor, place external pacing pads on the patient, and admit to the CCU
67) A 52-year-old man presents to his primary care physician’s office for routine care. He has hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, and type 2 diabetes mellitus, and has smoked one pack of cigarettes per day for the past 30 years. Medications include hydrochlorothiazide, atorvastatin, and glipizide. There is a family history of myocardial infarction in the maternal grandfather at age 60. The patient has undergone screening for colon and prostate cancer. Physical examination reveals a pleasant, obese man who is 175 cm (5′9″) tall and weighs 108 kg (238 lb). His blood pressure is 155/81 mmHg, heart rate is 78/min, respiratory rate is 14/min, and temperature is 36.8°C (98.3°F). What one action would most reduce the patient’s stroke risk?
Blood glucose reduction
Blood pressure reduction
Moking cessation
Serum cholesterol reduction
Weight loss
68) A 29-year-old tall, thin man presents to the ED after feeling short of breath for 2 days. In the ED, he is in no acute distress. His BP is 115/70 mmHg, HR is 81 beats per minute, RR is 16 breaths per minute, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. Cardiac, lung, and abdominal examinations are normal. An ECG reveals sinus rhythm at a rate of 79. A chest radiograph shows a small right-sided (< 10% of the hemithorax) spontaneous pneumothorax. A repeat chest x-ray 6 hours later reveals a decreased pneumothorax. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
. Discharge the patient with follow-up in 24 hours
. Perform needle decompression in the second intercostal space, midclavicular line
. Observe for another 6 hours
. Insert a 20F chest tube into right hemithorax
Admit for pleurodesis
69) A 47-year-old man with a history of hypertension presents to the ED complaining of continuous left-sided chest pain that began while snorting cocaine 1 hour ago. The patient states he never experienced chest pain in the past when using cocaine. His BP is 170/90 mmHg, HR is 101 beats per minute, RR is 18 breaths per minute, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. The patient states that the only medication he takes is alprazolam to “calm his nerves.” Which of the following medications is contraindicated in this patient?
. Metoprolol
. Diltiazem
. Lorazepam
. Aspirin
. Nitroglycerin
70) A 60-year-old man with coronary artery disease, peptic ulcer disease, and gout presents to the emergency department with a 24-hour history of abdominal pain. The pain, which is most intense in the upper abdomen, was sudden in onset and has become progressively more severe. Free air in the abdomen is detected on x-ray films. The patient is in an agitated state. His extremities are cool and capillary refill time is 3 seconds. His blood pressure is 80/40 mmHg and heart rate is 130/min. The neck veins are flat and the lungs are clear to auscultation. His hemoglobin is 13.8 g/dL. A urinary catheter is inserted and 10 mL of urine is drained. What is the most appropriate treatment for this patient at this time?
Broad-spectrum antibiotics for presumed sepsis
Infusion of isotonic fluid
Inotropic support with dopamine, vasopressin, or dobutamine
Infusion of norepinephrine
Transfuse with 1 unit packed RBCs
71) A 19-year-old man complains of chest pain while playing basketball on his high school team. Paramedics are called and he is rushed to the hospital. Physical examination reveals moderate mitral regurgitation and a crescendodecrescendo systolic ejection murmur that gets louder with Valsalva maneuver. Echocardiography reveals thickened left ventricular walls and dynamic left ventricular outflow tract obstruction. What is the best first step in management?
β-Blockers
Calcium channel blockers
Warfarin
Partial excision of the interventricular septum
Digoxin
72) A 57-year-old man presents to the emergency department with worsening substernal chest pain occurring over the past 20 minutes. He has a medical history significant for a 2-packper- day smoking history, gout, obesity, hypercholesterolemia, hypertension, osteoarthritis of both knees, inflammatory bowel disease, and recently diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus that is well controlled on oral antiglycemics (haemoglobin A1c of 7.8%). On physical examination he is in moderate distress, diaphoretic, and nauseous. His temperature is 37.5°C (99.5°F), pulse is 112/min, blood pressure is 142/85 mmHg, and respiratory rate is 22/min. He tests positive for MI by serial cardiac enzymes. He is started on the appropriate therapy and is ready for discharge the following evening. What is the number one preventive measure this patient can take to decrease his immediate risk for a second MI?
Decrease the amount of cholesterol in his diet
Exercise three times a week
Lower his blood pressure to the 120/80 mm Hg range
Lower his blood sugar levels to achieve a hemoglobin A1c level <7%
Quit smoking
73) A 31-year-old kindergarten teacher presents to the ED complaining of acute-onset substernal chest pain that is sharp in nature and radiates to her back. The pain is worse when she is lying down on the stretcher and improves when she sits up. She smokes cigarettes occasionally and was told she has borderline diabetes. She denies any recent surgeries or long travel. Her BP is 145/85 mmHg, HR is 99 beats per minute, RR is 18 breaths per minute, and temperature is 100.6°F. Examination of her chest reveals clear lungs and a friction rub. Her abdomen is soft and nontender to palpation. Her legs are not swollen. Chest radiography and echocardiography are unremarkable. Her ECG is shown below. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?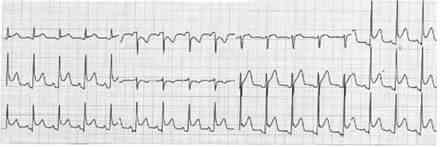

. Anticoagulate and CT scan to evaluate for a PE
. Prescribe a NSAID and discharge the patient
. Aspirin, heparin, clopidogrel, and admit for ACS
. Administer thrombolytics if the pain persists
. Prescribe antibiotics and discharge the patient
74) A 51-year-old woman presents to the ED after 5 consecutive days of crushing substernal chest pressure that woke her up from sleep in the morning. The pain resolves spontaneously after 20 to 30 minutes. She is an avid rock climber and jogs 5 miles daily. She has never smoked cigarettes and has no family history of coronary disease. In the ED, she experiences another episode of chest pain. An ECG reveals ST-segment elevations and cardiac biomarkers are negative. The pain is relieved with sublingual nitroglycerin. She is admitted to the hospital and diagnostic testing reveals minimal coronary atherosclerotic disease. Which of the following is the most appropriate medication to treat this patient’s condition?
Aspirin
. Calcium channel blocker (CCB)
β-Blocker
. H2-Blocker
. Antidepressant
75) While discussing a case presentation with a medical student, a nearby patient who just returned from getting an ankle radiograph done yells out in pain. You walk over to him and ask what is wrong. He states that since returning from the radiology suite, his automatic implantable cardioverter defibrillator (AICD) is discharging. You hook him up to the monitor and note that his rhythm is sinus. You observe a third shock while the patient is in sinus rhythm. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
. Send the patient back to the radiology suite for another radiograph to desensitize his AICD
. Administer pain medication and wait until the device representative arrives at the hospital to power off the AICD
. Admit the patient to the telemetry unit to monitor his rhythm and find the cause of his AICD discharge
. Place a magnet over the AICD generator to inactivate it and thereby prevent further shocks
. Make a small incision over his chest wall and remove the AICD generator and leads
76) A 22-year-old primagravida woman develops hypertension at 28 weeks. She is asymptomatic and the examination is normal except for 1+ pedal edema. Her complete blood count, liver enzymes, and electrolytes are normal. The urinalysis is positive for proteinuria. Which of the following is true for this type of hypertension?
Improves in the third trimester
Leads to large-birth-weight babies
Should be controlled with medications
Spares the placenta
Spares maternal kidney function
77) A 61-year-old man has a non-ST-elevation MI and is admitted to the coronary care unit. The following day, he develops bradycardia but no symptoms. His blood pressure is 126/84 mmHg, pulse 50/min, and on examination, the heart sounds are normal, with no extra sounds or rubs. His ECG has changed. Which of the following ECG findings is the best indication for this patient to receive a pacemaker?
Persistent bradycardia
Second-degree AV block Mobitz type I
First-degree AV block
New right bundle branch block
Left bundle branch block (LBBB) and second-degree AV block Mobitz type II
78) A 63-year-old woman on digitalis for chronic atrial fibrillation experiences fatigue, nausea, and anorexia. Her pulse is regular at 50 beats/min, and the heart sounds, chest, and abdominal examinations are normal. On the ECG, no P waves are visible and the QRS complexes are narrow and regular. Which of the following is the most appropriate management step?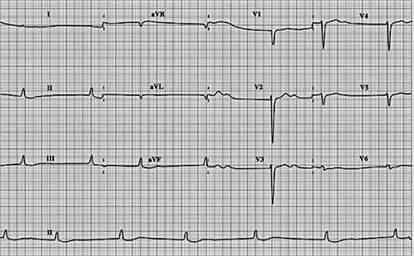

An increase in digitalis dose
Complete cessation of digitalis
Addition of a beta-blocker
Withdrawal of digitalis for one dose
Addition of a calcium channel blocker
79) A 26-year-old white nonsmoking woman returns for a follow-up appointment with her primary care provider. At a routine health maintenance visit 8 months earlier, her blood pressure was 179/97 mmHg. Since then she has adhered to a low-fat diet and exercises regularly. On repeat measurement 1 month later, her blood pressure was still elevated, despite her compliance with the prescribed hydrochlorothiazide and lisinopril. She has no complaints and denies headaches, chest pain, or mental status changes. On physical examination she is a slender woman in no apparent distress. An abdominal bruit that lateralizes to the left is heard. Her blood pressure is 178/99 mmHg in her left arm and 181/95 mmHg in her right arm. A basic metabolic panel and complete blood count are within normal range. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in patient care?
Add a statin to the patient’s current drug regimen to decrease fatty arterial plaques
Admit patient to the hospital and start intravenous nitroprusside
Increase the dosage of her antihypertensive regimen
Order duplex imaging of the renal arteries and proceed to percutaneous transluminal angioplasty if renal artery stenosis is found
Order duplex imaging of the renal arteries and proceed to surgical revascularization if renal artery stenosis is found
80) A 58-year-old man is admitted to the coronary care unit for telemetric monitoring after an episode of bradycardia. While in the unit, he suddenly loses consciousness. His pulse is undetectable and his blood pressure drops to 40 mmHg. His airway is clear and patent, and he is still breathing on his own. An ECG shows electrical activity. Chest compressions are started and he is quickly given a bolus of intravenous sodium bicarbonate and atropine. When his tracing does not improve, the boluses are repeated twice, and finally his tracing returns to normal sinus rhythm. Moments later, when he regains consciousness, he complains of a dry mouth, blurred vision, and feeling flushed. What is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient?
This patient has atropine toxicity and requires urgent administration of a cholinergic agonist
This patient has atropine toxicity and requires urgent administration of a muscarinic agonist
This patient has bicarbonate toxicity and requires urgent administration of calcium citrate
This patient is experiencing transient adverse effects of atropine and requires only supportive measures
This patient is experiencing transient adverse effects of atropine and requires only supportive measures
81) A 2-year-old girl is referred to the hospital for evaluation of her inability to gain weight. She is well fed by her parents, but appears to tire during feedings and has been losing weight despite frequent high-calorie meals. There is no family history of developmental delay or short stature. She is well dressed, her hair is brushed, and she is playful but tires quickly. Her temperature is 36.5°C (97.7°F), pulse is 110/min, blood pressure is 90/50 mmHg, and respiratory rate is 24/min. She has a harsh 2/6 holosystolic murmur that is best heard at the left sternal border, which is unchanged and has been present since birth. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Continue to monitor the patient for increased weight loss and increased shunting
PH probe for gastroesophageal refl ux disease
Refer for evaluation and possible closure of ventricular septal defect
Skeletal survey
Stool culture
82) A 31-year-old man who works for a moving company presents to the ED because he thinks he was having a heart attack. He does not smoke, and jogs 3 days a week. His father died of a heart attack in his sixties. He describes a gradual onset of chest pain that is worse with activity and resolves when he is at rest. His HR is 68 beats per minute, BP is 120/70 mmHg, and RR is 14 breaths per minute. On examination, his lungs are clear and there is no cardiac murmur. You palpate tenderness over the left sternal border at the third and fourth ribs. An ECG reveals sinus rhythm at a rate of 65. A chest radiograph shows no infiltrates or pneumothorax. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
82) A 31-year-old man who works for a moving company presents to the ED because he thinks he was having a heart attack. He does not smoke, and jogs 3 days a week. His father died of a heart attack in his sixties. He describes a gradual onset of chest pain that is worse with activity and resolves when he is at rest. His HR is 68 beats per minute, BP is 120/70 mmHg, and RR is 14 breaths per minute. On examination, his lungs are clear and there is no cardiac murmur. You palpate tenderness over the left sternal border at the third and fourth ribs. An ECG reveals sinus rhythm at a rate of 65. A chest radiograph shows no infiltrates or pneumothorax. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Administer aspirin, clopidogrel, and heparin, and admit for acute coronary syndrome (ACS)
Administer ibuprofen and reassure the patient that he is not having a heart attack
Inject corticosteroid into the costochondral joint to reduce inflammation
Observe the patient for 6 hours
83) A 27-year-old man who is otherwise healthy presents to the ED with a laceration on his thumb that he sustained while cutting a bagel. You irrigate and repair the wound and are about to discharge the patient when he asks you if he can receive an ECG. It is not busy in the ED so you perform the ECG, as seen below. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?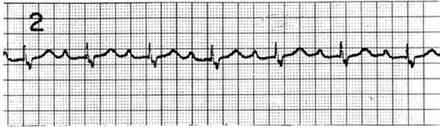

Admit the patient for placement of a pacemaker
Admit the patient for a 24-hour observation period
Administer aspirin and send cardiac biomarkers
Repeat the ECG because of incorrect lead placement
Discharge the patient home
84) A 56-year-old woman was recently started on medication for high blood pressure. At her next office visit her hypertension is under good control, but she now complains of “feeling strange” since she started the medication. On further questioning, she reports feeling chest tightness several times over the past 2 weeks, and has also noticed pain in her elbows and knees. Her blood pressure is 124/78 mmHg (146/82 mmHg on last visit), heart rate is 102/min, and respiratory rate is 14/min. Her examination is notable for several erythematous plaques on the malar distribution of the face, arms, and upper torso. What medication was she most likely started on during her last visit?
Captopril
Furosemide
Metoprolol
Hydralazine
Verapamil
85) A 34-year-old woman presents to your office complaining of several months of chest pain. She says that the pain is left-sided, does not change with deep inspiration, and typically lasts several hours. The pain has no relation to physical activity, but worsens with emotional stress. The patient has no significant family history, and does not use tobacco, alcohol or drugs. She takes no medications and has no drug allergies. On exam, her blood pressure is 110/70 mmHg and her heart rate is 78/min. ECG is normal. Which of the following is the best next step in her management?
Reassurance
Stress ECG testing
Lower extremity venous ultrasonography
Transthoracic echocardiography
Chest X-ray
86) A 60-year-old male patient is receiving aspirin, an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor, nitrates, and a beta-blocker for chronic stable angina. He presents to the ER with an episode of more severe and long-lasting angina chest pain each day over the past 3 days. His ECG and cardiac enzymes are normal. Which of the following is the best course of action?
Admit the patient and add intravenous digoxin
Admit the patient for thrombolytic therapy
Admit the patient and begin low-molecular-weight heparin
Admit the patient for observation with no change in medication
Increase the doses of current medications and follow closely as an outpatient
87) A 42-year-old man presents to the clinic for routine evaluation. His medical history is signified cant for gallstones. The patient denies smoking and drinks alcohol occasionally. His mother had a heart attack at the age of 63 years. His blood pressure is 134/77 mmHg. The patient is overweight with well-healed laparoscopic cholecystectomy scars. Fasting laboratory tests show: Aspartate aminotransferase: 37 U/L, Alanine aminotransferase: 28 U/L, Alkaline phosphatase: 88 U/L, Total cholesterol: 268 mg/dL, LDL cholesterol: 183 mg/dL, HDL cholesterol: 46 mg/dL, Triglycerides: 166 mg/dL. What is the most appropriate next step in management?
A trial of lifestyle modification alone (diet, exercise, and weight loss)
A trial of lifestyle modification combined with statin and niacin therapy
A trial of lifestyle modification combined with statin therapy
Niacin therapy
Statin therapy
88) A 60-year-old man with a history of congestive heart failure presents to his physician. He has a 5-year history of excessive daytime sleepiness and snoring. He also admits to three drinks of alcohol per day. His temperature is 36.6°C (98.0°F), pulse is 85/min, blood pressure is 138/82 mmHg, respiratory rate is 14/min, and oxygen saturation is 99% on room air. His body mass index is 31 kg/m2. Physical examination is significant for macroglossia and a short neck. Polysomnography is performed and is significant for multiple nocturnal episodes of airflow cessation at the nose and mouth, despite evidence of continuing respiratory effort. Which of the following is the most effective management for this patient?
Avoidance of alcohol
Avoidance of supine posture
Nasal continuous positive airway pressure
Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty
Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty
89) During a screening physical examination for participating in high school sports, a 14-yearold girl is found to have a late apical systolic murmur preceded by a click. The rest of the examination is unremarkable. Echocardiography shows superior displacement of the mitral leaflets of > 2 mm during systole into the left atrium, with a thickness of at least 8 mm. In addition, she states that her father also has some type of heart “murmur,” but she knows nothing else about it. Which of the following is the most appropriate management at this time?
Digoxin
Instruct the patient to avoid all forms of strenuous activity
Metoprolol
Mitral valve replacement
Prophylactic antibiotics for dental procedures
90) A 27-year-old man complains of chest palpitations and light-headedness for the past hour. He has no past medical history and is not taking any medications. He drinks a beer occasionally on the weekend and does not smoke cigarettes. His HR is 180 beats per minute, BP is 110/65 mmHg, and oxygen saturation is 99% on room air. An ECG reveals an HR of 180 beats per minute with a QRS complex of 90 milliseconds with a regular rhythm. There are no discernable P waves. Which of the following is the most appropriate medication to treat this dysrhythmia?
Digoxin
Lidocaine
Amiodarone
Adenosine
Bretylium
91) A 70-year-old female has been healthy except for hypertension treated with a thiazide diuretic. She presents with sudden onset of a severe, tearing chest pain, which radiates to the back and is associated with dyspnea and diaphoresis. Blood pressure is 210/94 mmHg. Lung auscultation reveals bilateral basilar rales. A faint murmur of aortic insufficiency is heard. The BNP level is elevated at 550 pg/mL (Normal < 100). ECG shows nonspecific ST-T changes. Chest x-ray suggests a widened mediastinum. Which of the following choices represents the best initial management?
91) A 70-year-old female has been healthy except for hypertension treated with a thiazide diuretic. She presents with sudden onset of a severe, tearing chest pain, which radiates to the back and is associated with dyspnea and diaphoresis. Blood pressure is 210/94 mmHg. Lung auscultation reveals bilateral basilar rales. A faint murmur of aortic insufficiency is heard. The BNP level is elevated at 550 pg/mL (Normal < 100). ECG shows nonspecific ST-T changes. Chest x-ray suggests a widened mediastinum. Which of the following choices represents the best initial management?
Percutaneous coronary intervention with consideration of angioplasty and/or stenting
Blood cultures and rapid initiation of vancomycin plus gentamicin, followed by echocardiography
IV beta-blocker to control heart rate, IV nitroprusside to control blood pressure, transesophageal echocardiogram
IV heparin followed by CT pulmonary angiography
92) A 67-year-old homeless male presents 24 hours after the onset of substernal chest pain and is diagnosed with an anterior wall myocardial infarction. There is no history of previous chest pain, dyspnea, palpitations, syncope or leg swelling. He has no hypertension or diabetes mellitus. He does acknowledge a 40 pack-year smoking history. Upon discharge, echocardiography shows normal left ventricular size, left ventricular anterior wall hypokinesis and an ejection fraction of 50%. Two years later, the patient is found dead in the street. Autopsy reveals a dilated left ventricle with a globular shape and thinned walls along with a scar on the anterior wall. Which of the following would have most likely prevented this patient's pathologic findings?
. Aspirin
. Isosorbide dinitrate
. Enalapril
. Amlodipine
. Digoxin
{"name":"DES 2 ep 2", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"46) A 53-year-old Caucasian male is admitted to the hospital with a 2-week history of fatigue and decreased exercise tolerance. He says he can hardly climb two flights of stairs without getting dyspneic. He denies palpitations or chest pain. His past medical history is insignificant, and a routine check-up 6 months ago was normal. He admits two episodes of binge drinking during the last month, but says that he 'got it under control'. He is currently not taking any medications. His blood pressure is 150\/90 mmHg and heart rate is 130\/min, irregular. Lungs are clear on auscultation. ECG does not reveal P waves. Echocardiography shows significant left ventricular dilation with an ejection fraction of 35% and mitral regurgitation (1+). Which of the following intervention will most likely improve the left ventricular function in this patient?, 47) A 47-year-old Caucasian female presents with occasional episodes of nocturnal substernal chest pain that wakes her up during sleep. The pain episodes last 15-20 minutes and resolve spontaneously. She denies any illicit drug use. She leads a sedentary lifestyle but states that she can climb two flights of stairs without any discomfort. She has no history of hypertension or diabetes. Her pulse is 75\/min and regular, blood pressure is 134\/70 mmHg and respirations are 14\/min. Extended ambulatory ECG monitoring reveals transient ST segment elevation in leads I, aVL, and V4-V6 during the episodes. Which of the following is the best treatment for this patient?, 48) A 55-year-old male presents to your office with a 6-month history of periodic substernal pressure. He experiences this pressure while walking uphill or climbing two flights of stairs. His past medical history is insignificant. He smokes 1 pack a day and consumes alcohol occasionally. His blood pressure is 160\/90 mmHg and heart rate is 75\/min. Resting ECG is normal. You suspect stable angina and order an ECG stress test that reveals horizontal ST segment depression in leads II, III, and aVF at submaximal heart rate. What is the best medication to treat this patient's condition?","img":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/3012/images/ogquiz.png"}
More Quizzes
Explore the Wonders of Habitats Quiz
9421
Me conhece?
14713
Driving License 1 - part 3
1050
SWIFT Test
11614
Free Wastewater Treatment Operator Certification
201030878
Conflict Management: Test Your Resolution Skills
201036173
Ace Your Surgical Prep: Chapter 11 Practice Test
201044193
Discover Your Sailor Starlight Persona - Free
201028545
Free Business Process Management
201025169
What Are the Kindly Ones in Percy Jackson? Free
201066666
Can You Convert English to Italian Sentences? Take the!
201041824
Which Bird Are You? Free Bird Personality
201029824