P 495 TO 512 *Q 1 TO 50*
1) A 31-year-old, HIV-infected man from New York presents to the ER with anorexia, malaise, night sweats, fever, and weight loss of 6.8kg (15 lb) over the past one month. He also has a cough productive of yellow sputum. He was diagnosed with HIV two years ago. When last checked two months ago, his CD4 count was 220/microL. He is not taking any medications. His temperature is 39.2°C (102.2°F), pulse is 96/min, and blood pressure is 120/80 mm Hg. Physical examination reveals rales in his right upper chest. Laboratory studies show: Hematocrit 30%, WBC count 3,400/microL, Neutrophils 86%, Bands 2%, Lymphocytes 4%, Monocytes 8%. PPD test shows 3 mm induration. Chest x-ray reveals a right upper lobe cavitation. Sputum examination shows partially acid-fast, filamentous, branching rods. Based on these findings, which of the following organism is the most likely cause of this patient's pulmonary disease?
. Pneumocystis jiroveci
. Mycobacterium tuberculosis
. Coccidioides species
. Nocardia species
. Streptococcus pneumonia
.2) A 45-year-old man comes to the office and complains of intermittent, bloody diarrhea and abdominal pain for the past month. During this time period, he has lost six pounds. He was diagnosed with HIV infection in the past, but has refused antiretroviral therapy. Laboratory results show a CD4 count of 50cells/μL. The stool examination is negative. Colonoscopy with biopsy shows multiple colonic ulcerations and mucosal erosions. The biopsy shows large cells containing eosinophilic intranuclear and basophilic intracytoplasmic inclusions. What is the most likely cause of this patient's diarrhea?
. Cryptosporidium
. Cytomegalovirus
. Entamoeba
. Kaposi sarcoma
. Mycobacterium avium complex
.3) A 73-year-old diabetic man presents with low-grade fever, facial pain over his right maxilla, and bloody nasal discharge for the last three days. For the last day, he has had diplopia. He was diagnosed with diabetes mellitus 10 years ago. For the last year, he has been on insulin. His most recent hemoglobinA1C was 12.0. His temperature is 39.0°C (102.2°F), pulse is 88/min, and blood pressure is 130/76mm Hg. Examination shows right-sided nasal congestion and necrosis of the right nasal turbinate with tenderness over the right maxillary sinus. There is chemosis and proptosis of his right eye. CT scan shows opacification of the right maxillary sinus. Which of the following is the most likely causative organism?
. Rhizopus species
. Staphylococcus aureus
. Pseudomonas aeruginosa
. Haemophilus influenzae
. Moraxella catarrhalis
.4) A 43-year-old HIV-positive male presents to your office with several exophytic purple skin masses on his lower abdomen. Physical examination reveals tender hepatomegaly and an abdominal CT scan shows nodular, contrast-enhanced intrahepatic lesions of variable size. Liver biopsy is attempted but severe hemorrhage results. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
. Mycobacteria
. Spirochetes
. Bartonella
. Clostridia
. Brucella
.5) A 23-year-old, HIV-infected female presents with a five-day history of fever and productive cough. She is on antiretroviral therapy, and her CD4 count is 300/mm3. Her temperature is 39.0°C (102.5°F), pulse is 95/min, respirations are 22/min, and blood pressure is 115/76 mm Hg. Physical exam reveals dullness to percussion and bronchial breath sounds in the right lung base. Chest x-ray is shown below. What is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
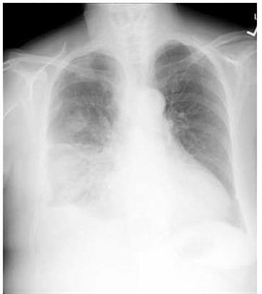
Share

. Streptococcus pneumonia
. Mycobacterium tuberculosis
. Disseminated coccidioidomycosis
. Pneumocystis jiroveci (P. jiroveclj)
. Pseudomonas aeruginosa
.6) A 75-year-old female nursing home resident complains of cough and fever. Her past medical history is significant for hypertension, myocardial infarction (experienced two years ago), and a traumatic right foot amputation. Her current medications are atenolol, hydrochlorothiazide, and aspirin. Her temperature is 39.4°C (103°F), pulse is 110/min, respirations are 22/min, and blood pressure is 110/76 mmHg. Crackles are present at right lung base. Chest x-ray reveals a right lower lobe infiltrate. Which of the following pathogens is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
. Staphylococcus aureus
. Streptococcus pneumoniae
. Haemophilus influenzae
. Anaerobic bacteria
. Gram-negative rods
.7) A 45-year-old man presents to the emergency room with a two-day history of fever, dyspnea, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. He has no chest pain, but complains of dry cough. His past medical history is significant for bone marrow transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia (AML) three months ago. His temperature is 39°C (102.2°F), blood pressure is 122/80 mm Hg, pulse is 98/min, and respirations are 22/min. Exam of the oropharynx reveals thrush. Lungs exam demonstrates bilateral diffuse rales. Heart sounds are regular. Nonspecific abdominal tenderness is present. The chest radiograph shows multifocal, diffuse patchy infiltrates. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's current condition?
. Mycoplasma pneumoniae
. Pneumocysfis jiroveci
. Graft-versus-host disease
. Cytomegalovirus
. Aspergillus fumigatus
.8) A 55-year-old woman presents with a three-week history of low-grade fever, weight loss of 4.5kg (10 lb), and malaise. She is known to have mitral valve prolapse, but is otherwise healthy. She underwent a tooth extraction one month ago. She denies alcohol, tobacco, and illicit drug use. Her temperature is 38.5°C (101.3°F), pulse is 90/min, respirations are 18/min, and blood pressure is 145/76 mm Hg. Her chest is clear to auscultation and percussion. Cardiac examination reveals a III/IV holosystolic murmur at the apex that radiates to the axilla. Chest x-ray is normal. Urinalysis is unremarkable. Blood cultures are drawn and empiric antibiotics are started. Echocardiogram shows mitral regurgitation with vegetation on the mitral valve. Which of the following organisms is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
. Staphylococcus aureus
. Staphylococcus epidermidis
. Staphylococcus saprophyticus
. Viridans group streptococci
. Enterococcus species
.9) A 50-year-old man presents to the office with fatigue, malaise, and disabling joint pain in his fingers, wrists, shoulder, hips, knees, and ankles. His pain is severe and associated with a mild degree of morning stiffness for 10-15 minutes. He occasionally takes acetaminophen and ibuprofen for this pain. He has a 10-pack-year smoking history. He does not drink alcohol. Family history includes an uncle who died of liver cancer. On examination, there is grayish skin pigmentation, most prominent on the exposed parts. Abdominal examination is significant for liver enlargement 2 cm below the costal margin. Laboratory studies reveal the following: Hemoglobin 13.0 g/L, Leukocyte count 5,500/mm3, Serum creatinine 0.8 mg/dl, Blood glucose 218mg/dl, Aspartate aminotransferase (SGOT) 128 U/L, Alanine aminotransferase (SGPT) 155 U/L, Alkaline phosphatase 120 U/L , Serum iron 450 mol/L (50-170g/dL), Transferrin saturation of iron 62% (22-47%), Serum Ferritin 3000ng/L (15-200 ng/ml, males). X-ray of the joints shows narrowing of joint spaces and diffuses demineralization. This patient's condition makes him more vulnerable to which of the following infections?
. Listeria monocytogenes
. Streptococcus pneumoniae
. Escherichia coli
. Chlamydia psittaci
. Epstein Barr virus
.10) A 19-year-old white male presents with nausea, vomiting, and abdominal cramps. He has had four episodes of vomiting over the last two hours. He has not had diarrhea or fever. Four hours ago, he ate a salad from a local restaurant. His pulse is 82/min, blood pressure is 120/80 mm Hg, and temperature is 37.2°C (99°F). Abdominal and rectal examinations are unremarkable. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
. Staphylococcus aureus
. Bacillus cereus
. Clostridium perfringens
. Clostridium difficile
. Enterotoxigenic E coli
.11) A 72-year-old male presents with a two-day history of intense pain in his right ear, along with ear discharge. The pain is so severe that he is unable to sleep. It radiates to his temporomandibular joint and is aggravated by chewing. His disease has worsened despite the use of topical antibiotics. He takes metformin and enalapril. On physical examination, granulation tissue is noted in the lower part of his external auditory canal. Cranial nerves are intact. Oropharynx is clear without exudate. Which of the following is the most likely causative organism of this patient's ear condition?
. Staphylococcus aureus
. Bacillus cereus
. Clostridium perfringens
. Clostridium difficile
. Enterotoxigenic E coli
.12) A 26-year-old male presents to your office with periodic flank pain. He also noticed that his urine was red during the last several days. He is known to be HIV-positive. One month ago, he presented with thrush. At that time, he was found to have a CD4 count of 100, and was started on anti-retroviral therapy. His current CD4 count is 250. Physical examination reveals no oral cavity lesions. The lungs are clear on auscultation. The serum creatinine level is 2.2 mg/dl. Urinalysis shows hematuria and needle-shaped crystals in the sediment. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's current condition?
. Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NRTI)
. Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI)
. Protease inhibitor
. Viral infection
. Neoplastic process
.13) A 12-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department because of severe pain near his left knee. He has sickle cell disease, and has been hospitalized previously for sickle cell crisis. Vital signs are notable for mild fever. Examination of the left lower extremity reveals a normal knee joint with marked tenderness and swelling over the proximal tibia. Labs show leukocytosis and elevated ESR. He is subsequently diagnosed with osteomyelitis. Which of the following organisms is the most likely cause of his condition?
. Escherichia coli
. Pseudomonas species
. Salmonella species
. Staphylococcus aureus
. Group B streptococcus
.14) A 67-year-old man presents to his primary care provider in January with fever and a productive cough. The patient had been seen ten days earlier with complaints of fever to 102°F (39.0°C), myalgias, rhinorrhea, and dry cough. At that time, his lung exam revealed occasional crackles. He was given a medication and told to follow up if his symptoms worsened. The symptoms did remit over the first five days, but he began to feel worse again two days ago. He smokes a half-pack of cigarettes per day and drinks alcohol several times a week. On exam today, his temperature is 102.3°F (39.3°C), and lung exam reveals increased tactile fremitus in the left lower lobe. What is the most likely pathogen responsible for his current condition?
. Pneumocystis jiroveci
. Klebsiella pneumoniae
. Pseudomonas aeruginosa
. Mycoplasma pneumoniae
. Staphylococcus aureus
.15) A 33-year-old man presents with low-grade fever, abdominal cramps, and diarrhea for the past six hours. He has had eight episodes of loose, watery stool containing blood and mucus over this time period. Last night, he ate shrimp and crab meat at a local restaurant. His current pulse is 85/min, blood pressure is 110/80 mm Hg, and temperature is 37.7°C (99.9°F). There are no significant findings on abdominal or rectal examinations. Stool examination shows numerous red blood cells and leukocytes Which of the following is the most likely causative organism of this patient's condition?
. Shigella species
. Enterohemorrhagic E coli
. Vibrio parahaemolytious
. Yersinia enterocolitica
. Campylobacter jejuni
.16) A 46-year-old farmer comes to the physician because of pain and swelling of his right heel. He accidentally stepped on a rusty nail while working 2 weeks ago. Although he applied over the-counter antibiotic cream locally and took acetaminophen orally, he continued to have pain at the site of the injury. He has no other medical problems and takes no medication. He has no known drug allergies. He smokes 2-3 cigarettes a day and drinks alcohol occasionally. His temperature is 38.3°C (101°F), blood pressure is 140/90 mm Hg, pulse is 84/min and respirations are 14/min. On examination, the right heel is swollen, red, and warm and tender to touch. A small puncture wound is visible. Laboratory reports show mild leukocytosis. X-ray of the right foot shows features suggestive of osteomyelitis. The most likely cause of the patient's symptoms is infection with which of the following?
. Beta-hemolytic streptococci
. Staphylococcus epidermidis
. Clostridium tetani
. Pseudomonas aeruginosa
. Escherichia coli
.17) A 31-year-old, HIV-infected man from New York presents to the ER with anorexia, malaise, night sweats, fever, and weight loss of 6.8kg (151b) over the past one month. He also has a cough productive of yellow sputum. He was diagnosed with HIV two years ago. When last checked two months ago, his CD4 count was 220/microL. He is not taking any medications. His temperature is 39.2°C (102.2°F), pulse is 96/min, and blood pressure is 120/80mm Hg. Physical examination reveals rales in his right upper chest. Laboratory studies show: Hematocrit 30%, WBC count 3,400/microL, Neutrophils 86%, Bands 2%, Lymphocytes 4%, Monocytes 8%. PPD test shows 3 mm induration. Chest x-ray reveals a right upper lobe cavitation. Sputum examination shows partially acid-fast, filamentous, branching rods. Based on these findings, which of the following organism is the most likely cause of this patient's pulmonary disease?
. Pneumocystis jiroveci
. Mycobacterium tuberculosis
. Coccidioides species
. Nocardia species
. Streptococcus pneumonia
.18) A 26-year-old man comes to his physician with a two-week history of fatigue, fever, muscle aches, and arthralgias. He denies any weight loss. His temperature is 37.7°C (99.9°F), blood pressure is 115/75 mm Hg, respirations are 14/min, and pulse is 75/min. Physical examination is unremarkable, except for splenomegaly. Laboratory studies show: Hemoglobin 13 gm/dL, WBC count 12,000/microL, Neutrophils 22%, Lymphocytes 70%, Monocytes 5%, Basophils 1%, Eosinophils 2%, Platelet count 220,000/microL. Peripheral blood smear shows large basophilic lymphocytes with a vacuolated appearance. Heterophile antibody test is negative. What is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
. Chronic fatigue syndrome
. Cytomegalovirus infection
. Acute toxoplasmosis
. Mycobacterial infection
. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia
.19) A 27-year-old man presents with symptoms of fever, chills, malaise, and joint discomfort in his hands and knees. He looks unwell, his temperature is 39.4°C, blood pressure 115/70 mm Hg, pulse 110/min, head and neck is normal, and his jugular venous pressure (JVP) has a prominent c-v wave. There is also a 3/6 pan-systolic murmur heard at the right sternal border that increases with respiration. His lungs are clear, abdomen is soft, and hand joints are normal. He has multiple puncture sites on his forearms from injection drug use. Which of the following is the most likely causative organism?
Staphylococcus aureus
Staphylococcus epidermidis
Streptococcus viridans
Enterococci
Candida
.20) A 73-year-old man from a nursing home develops headache, fever, cough, sore throat, malaise, and severe myalgia during a community outbreak affecting numerous other residents at the home. The symptoms gradually resolve after 3 days, and he starts feeling better but then there is a reappearance of his fever, with cough and yellow sputum production. On examination, his temperature is 38.5°C, pulse 100/min, respiration 24/min, oxygen saturation 88% and crackles in the right lower lung base, bronchial breath sounds and dullness on percussion. CXR reveals a new infiltrate in the right lower lobe. Which of the following is the most likely causative organism?
Primary viral pneumonia
An autoimmune reaction
Mycoplasma pneumoniae
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Neisseria catarrhalis
.21) A 56-year-old man is having intermittent fevers and malaise for the past 2 weeks. He has no other localizing symptoms. Two months ago, he had valve replacement surgery for a bicuspid aortic valve. A mechanical valve was inserted and his postoperative course was uncomplicated. On examination, his temperature is 38°C, blood pressure 124/80 mm Hg, pulse 72/min, and head and neck are normal. There is a 3/6 systolic ejection murmur, the second heart sound is mechanical, and a 2/6 early diastolic murmur is heard. The lungs are clear and the skin examination is normal. Three sets of blood cultures are drawn and an urgent echocardiogram is ordered. Which of the following is the most likely causative organism?
Staphylococcus aureus
S. epidermidis
S. viridans
Enterococci
Candida
22) A 25-year-old woman is admitted with fever and hypotension. She has a 3-day history of feeling feverish. She has no history of chronic disease, but she uses tampons for heavy menses. She is acutely ill and, on physical examination, found to have a diffuse erythematous rash extending to palms and soles. She is confused. Initial blood tests are as follows: White blood cell count: 22,000/μL, Na+: 125 mEq/L, K+: 3.0 mEq/L, Ca++: 8.0 mEq/mL, Activated partial thromboplastin time (PTT): 65 (normal 21 to 36), Prothrombin time (PT): 12s (normal < 15s), Aspartate aminotransferase: 240 U/L (normal < 40), Creatinine: 3.0 mg/dL, Antinuclear antibodies: negative, Anti-DNA antibodies: negative, Serologic tests for RMSF, leptospirosis, measles: negative. Which of the following best describes the pathophysiology of the disease process?
. Acute bacteremia
. Toxin-mediated inflammatory response syndrome
. Exacerbation of connective tissue disease
. Tick-borne rickettsial disease
. Allergic reaction
.23) A 21-year-old woman visits her physician because of 3 weeks of a flu-like‖ illness. She reports symptoms of malaise, fever, fatigue, and a sore throat. There is no weight loss or night sweats, and she has not traveled out of country. Her past medical history is not significant and she is not taking any medications. Physical examination is normal except for enlarged cervical lymph nodes. Laboratory data show hemoglobin 13.2 g/dL; hematocrit 42%; platelets 380,000/mL; WBC 8500/mL, with 35% segmented neutrophils, 1% eosinophils, and 64% lymphocytes, of which 36% were atypical. A heterophil antibody (sheep cell agglutination) test is negative. Which of the following is the most likely causative organism?
Herpes simplex
Echovirus
CMV
Coxsackievirus
Reovirus
.24) A 4-year-old boy is sent to the emergency room because of clinical suspicion of meningitis. He has been ill for 2 days with fever and lethargy. On examination, he is febrile, the neck is stiff, and papilledema is present. There is no rash, the lungs are clear, and heart sounds normal. Which of the following is the most likely causative organism?
Neisseria meningitidis
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Haemophilus influenzae
Staphylococcus
Listeria species
.25) A 24-year-old woman presents with chills and rigors. She looks unwell, and her temperature is 39.4°C, blood pressure 100/60 mm Hg, pulse 110/min, and oxygen saturation 95%. There is a 3/6 pansystolic murmur at the right sternal border, which increases with inspiration. Her arms have multiple tattoos and needle marks from injection drug use. Blood cultures (2/2 sets) are positive for S. aureus, and she is started on appropriate antibiotics. Her renal function is mildly impaired and her urinalysis is positive for protein, and microscopy reveals red cell casts. Which of the following mechanisms is the most likely explanation for her renal abnormalities?
Septic emboli
Cardiac failure with prerenal azotemia
A high level of circulating immune complexes
Fungal disease
Inevitable progression to renal failure
.26) A recent outbreak of severe diarrhea is currently being investigated. Several adolescents developed bloody diarrhea, and one remains hospitalized with acute renal failure. A preliminary investigation has determined that all the affected ate at the same restaurant. The food they consumed was most likely to be which of the following?
. Pork chops
. Hamburger
. Gefilte fish
. Sushi
. Soft-boiled eggs
.27) A 23-year-old woman presents with a painless chronic vulvar ulcer. She recently arrived to study in the United States from Southern India. The lesion began as a papule and then ulcerated. It has persisted for several months. Currently, physical examination reveals a painless elevated area of beefy red, friable granulation tissue. She has been sexually active for several years. Which of the following is the most likely causative organism?
Spirochete
Gram-positive coccus
Intracellular Gram-negative bacteria
Chronic viral infection
Fungus
.28) An 18-year-old man develops fever, neck stiffness, and headache. On examination, his blood pressure is 105/80 mm Hg, pulse 100/min, temperature 38.7°C, and neck flexion is very painful. The ears, throat, and sinuses are normal; there are no focal neurologic signs, and the remaining examination is normal. His is the second case of meningitis in his university dormitory building. Which of the following is the most likely causative organism?
Neisseria meningitidis
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Haemophilus influenzae
Staphylococcus
Listeria species
.29) A 19-year-old woman was traveling in a rural area of South America. She returned 3 weeks ago and, over the past few days, has gradually developed lower abdominal pain and diarrhea. Now the symptoms are much worse with 10 stools a day consisting mostly of mucus and blood. She is afebrile, the abdomen is tender in left lower quadrant, and the remaining examination is normal. Her stool is mostly comprised of blood and mucus. Which of the following is the most likely causative organism?
Escherichia coli infection
Salmonella infection
Shigella infection
Vibrio parahaemolyticus infection
E. Histolytica infection
.30) An 18-year-old man develops fever, neck stiff- ness, and headache. On examination, his blood pressure is 110/80 mm Hg, pulse 100/min, temperature 38.7°C, and neck flexion is very painful. The ears, throat, and sinuses are normal; there are no focal neurologic signs; and the remaining examination is normal. There are no reported similar cases in the community. Which of the following is the most likely causative organism?
Neisseria meningitides
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Haemophilus influenzae
Staphylococcus
Listeria species
.31) A previously well 28-year-old female has developed gradual onset of fever and malaise over 2–3 weeks. She also complains of arthralgias and myalgias. Repeated measurement of her temperature reveals a low grade fever between 38°C and 39°C. Physical examination reveals an oval retinal hemorrhage with a clear, pale center; a pansystolic cardiac murmur heard best at the apex; and small, tender nodules on her fingertips. Which of the following is the most likely causative organism?
Staphylococcus aureus
S. epidermidis
Viridans streptococci
Enterococcus
Candida
.32) A 70-year-old patient with long-standing type 2 diabetes mellitus presents with complaints of pain in the left ear with purulent drainage. On physical examination, the patient is afebrile. The pinna of the left ear is tender, and the external auditory canal is swollen and edematous. The white blood cell count is normal. Which of the following organisms is most likely to grow from the purulent drainage?
. Pseudomonas aeruginosa
. Streptococcus pneumoniae
. Candida albicans
. Haemophilus influenzae
. Moraxella catarrhalis
.33) Three hours after a church social, eight people develop severe diarrhea. Other symptoms included nausea, vomiting, and abdominal cramps. Food served included chicken salad and cream-filled pastries. All affected individuals had the chicken salad. Which of the fol- lowing is the most likely causative organism?
Staphylococcal enterotoxin
Clostridium perfringens
Salmonella species
Ptomaine poisoning
.34) A 9-year-old boy has a severe sore throat with fever and dysphagia. On examination, there are grayish-white papulovesicular lesions on an erythematous base that ulcerate. They are located on the soft palate, anterior pillars of the tonsils and uvula. There are no lesions on the gingiva, tongue, or lips. A clinical diagnosis of herpangina is made. Which of the following is the most likely causative organism?
Measles (Morbillivirus)
Rubella (rubivirus)
Coxsackievirus A
HSV-1
HSV-2
.35) A 10-year-old boy presents with fever, headache, photophobia, and neck discomfort in the middle of summer. He is alert and oriented, but has neck pain with flexion and extension of the head. His fundi are normal, and there are no focal neurologic findings or skin changes. A lumbar puncture reveals normal protein and glucose with a cell count of 240/mL (90% lymphocytes). Which of the following is the most likely causative organism?
Enterovirus (coxsackievirus or echovirus)
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Neisseria meningitides
Listeria monocytogenes
HSV-1
.36) A 60-year-old man presents with fever and malaise 6 weeks after mitral valve replacement. On examination, his temperature is 38°C, blood pressure 130/80 mm Hg, pulse 80/min, and a loud pansystolic murmur at the apex, which radiates to the axilla. He has no skin or neurologic findings. Which of the following is the most likely causative organism?
Staphylococcus saprophyticus
Pneumococcus
Staphylococcus epidermidis
Staphylococcus aureus
A fungus
.37) A previously healthy 25-year-old music teacher develops fever and a rash over her face and chest. The rash is itchy and, on examination, involves multiple papules and vesicles in varying stages of development. One week later, she complains of cough and is found to have an infiltrate on x-ray. Which of the following is the most likely etiology of the infection?
. Streptococcus pneumoniae
. Mycoplasma pneumoniae
. Histoplasma capsulatum
. Varicella-zoster virus
. Gonococcus pneumoniae
.38) A 19-year-old male has a history of athlete’s foot but is otherwise healthy when he develops sudden onset of fever and pain in the right foot and leg. On physical examination, the foot and leg are fiery red with a welldefined indurated margin that appears to be rapidly advancing. There is tender inguinal lymphadenopathy. The most likely organism to cause this infection is which of the following?
. Staphylococcus epidermidis
. Tinea pedis
. Streptococcus pyogenes
. Mixed anaerobic infection
. Alpha-hemolytic streptococci
.39) A 60-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 3-month history of worsening fatigue and back pain. She has had diabetes mellitus for the past three years, and hypertension for the past ten years. Laboratory studies show: Hb 9.0 mg/dL, Serum calcium 11.2 mg/dL, Serum phosphorus 3.5 mg/dL, BUN 38 mg/dL, Serum creatinine 2.0 mg/dL. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's renal failure?
. Hypertension
. Diabetes mellitus
. Para protein
. Primary hyperparathyroidism
. Renal artery stenosis
.40) A 70-year-old man comes to the physician due to a 4-6 month history of "almost continuous urinary dribbling." This symptom is present both day and night, and is progressively getting worse. He denies dysuria and hematuria. He has a 20-year history of diabetes mellitus-type 2, hypertension, alcoholic hepatitis and coronary artery disease. He had a gastric emptying study done a few weeks ago because of continuous nausea and early satiety. He had laser photocoagulation of both eyes for diabetic retinopathy. He has smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for 50 years, and drinks 4 to 6 beers daily. He takes NPH insulin, regular insulin, metformin, aspirin, metoprolol, lisinopril and metoclopramide. His vital signs are stable. Physical examination shows a well-appearing man. Pertinent physical findings are a normal sized prostate, decreased sensation in both legs below the knees, and absent Achilles tendon and knee reflexes bilaterally. Fecal occult blood test is negative. Postvoid residual volume is 550 ml. Urinalysis shows: Specific gravity 1.020, Blood trace, Glucose positive, Ketones negative, Protein moderate, Leukocyte esterase negative, Nitrites negative, WBC 1-2/hpf, RBC 3-4/hpf. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's incontinence?
. Multiinfarct dementia
. Overflow incontinence due to detrusor weakness
. Overflow incontinence from bladder outlet obstruction
. Urinary tract infection
. Overflow incontinence due to medication
.41) A 46-year-old man complains of right flank discomfort. He describes decreased urination over the last week with occasional episodes of high urine output and weakness. He is otherwise healthy. There is no family history of renal disease. On physical examination, his blood pressure is 140/90 mmHg and his heart rate is 80/min. The serum creatinine level is 2.1 mg/dl. Urinalysis shows few red blood cells, white blood cells, trace protein, and no casts. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his complaints?
. Hematologic malignancy
. Renal artery stenosis
. Inherited renal disease
. Interstitial nephritis
. Urinary outflow obstruction
.42) A 17-year-old man comes to the emergency department and complains of intensive left flank pain that radiates to the groin. He refers to his symptom as "stone passage," which he has experienced "for so many times since childhood." His uncle has the same problem. Urinalysis shows hexagonal crystals. The urinary cyanide nitroprusside test is positive. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
. Amino acid transport abnormality
. Parathyroid adenoma
. Abnormality of uric acid metabolism
. Excessive intestinal reabsorption of oxalate
. Infection
.43) A 12-year-old girl comes to the physician because of a 2-day history of periorbital edema and abdominal distention. She has no other complaints. She has never been diagnosed with hypertension. Her father died at the age of 40, with renal failure. Her temperature is 37.1°C (98.9°F), blood pressure is 125/75 mm Hg, pulse is 80/min, and respirations are 14/min. Examination shows facial puffiness, shifting dullness, and 1+ bilateral pitting pedal edema. Urinalysis shows 3+ proteinuria and lipid laden casts. 24-hour urinary protein excretion is 5 g/day, total serum protein is 4.5 g/dl and serum albumin is 2.3 g/dl. Which of the following is this patient at increased risk of developing?
. Macrocytic normochromic anemia
. Accelerated atherogenesis
. Hypergammaglobulinemia
. Hypercalcemia
. Hypoparathyroidism
.44) A 20-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by his mother because of a one-day history of fever, headache, and altered mental status. He has no history of medical illness. Herpes simplex encephalitis is suspected after cerebral spinal fluid analysis shows lymphocytic pleocytosis, elevated protein level, and normal glucose level; in addition, CT scan shows contrast enhancement in the temporoparietal area. High-dose intravenous acyclovir therapy is started. Two days after the beginning of the therapy, the neurologic status improves, but the patient develops oliguria. Laboratory studies show: Serum sodium 140 mEq/L, Serum potassium 4.5 mEq/L, Serum creatinine 2.8 mg/dl, BUN 25 mg/dl. Which of the following is the most likely cause of renal damage in this patient?
. Prerenal azotemia
. Renal tubular obstruction
. Glomerular injury
. Interstitial nephritis
. Bladder neck obstruction
.45) A 65-year-old male has been having a non-productive, hacking cough for over a week. He takes an over-the-counter medication containing guaifenesin and diphenhydramine in an effort to improve his symptoms. The next day, he complains of lower abdominal discomfort and difficulty voiding. Which of the following most likely accounts for this patient's new complaint?
. Detrusor inactivity
. Urethral obstruction
. Detrusor-sphincter dyssynergia
. Overactive bladder
. Abdominal muscle weakness
.46) A 12-year-old girl is brought to the clinic due to a 2-month history of headaches. Her headaches last 1-2 hours and have no fixed time of occurrence. She denies nausea, vomiting, chills or fevers. She has no other medical problems and takes no medication. Her family history is significant for hypertension and diabetes. Her blood pressure is 156/90 mm Hg, pulse is 80/min, and respirations are 14/min. Examination shows an alert child in no distress. There is a soft to-and-fro bruit heard at the right costovertebral angle. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her hypertension?
. Coarctation of aorta
. Renal artery atherosclerosis
. Pheochromocytoma
. Fibromuscular dysplasia
. Conn's syndrome
.47) A 59-year-old man comes to the physician because of dysuria, urinary urgency, and frequency. He also complains of hematuria, nocturia, decreased force of stream, and a feeling of incomplete voiding. These symptoms have been present for more than a month. For the past few days he has been experiencing dull, non-radiating suprapubic pain. He has also been having low-grade fever and malaise for the past couple of days. He has been taking analgesics for osteoarthritis of his right knee for more than 10 years. He has a 40-pack-years history of cigarette smoking and does not use alcohol or drugs. Rectal examination shows a smooth, firm enlargement of the prostate without induration or asymmetry. Neurological examination shows no abnormalities. Urinalysis shows hematuria with isomorphic red blood cells. Laboratory studies show a serum creatinine of 1.5 mg/dl, and a PSA of 2 ng/ml. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for this patient's symptoms?
. Benign prostatic hyperplasia
. Carcinoma of bladder
. Carcinoma of prostate
. Urethral stricture
. Neurogenic bladder
48) An 80-year-old female is brought from a nursing home with a two day history of poor oral intake and lethargy. Her past medical history is significant for hypertension, diabetes mellitus, coronary artery disease with coronary stenting two years ago and Alzheimer's disease. She was hospitalized six months ago with pneumonia. Her current medications are aspirin, lisinopril, metoprolol, hydrochlorothia zide, metformin and memantine. Her blood pressure is 95/60 mmHg and heart rate is 90/min. Physical examination reveals fine crackles at the right lung base. Her mucous membranes are dry. Her laboratory findings are significant for WBC of 15,000/mm3, creatinine of 2.1 and BUN of 61 mg/dl. Her creatinine was 0.9 mg/dl during the last admission. Which of the following is the best explanation for the abnormal laboratory findings in this patient?
. Age-related renal function decline
. Renal inflammatory infiltration
. Renal tubular dysfunction
. Renal vasoconstriction
. Obstructive uropathy
49) A 60-year-old man comes to the physician because of worsening fatigue and nausea. He had a carotid angiogram for the evaluation of symptomatic carotid artery stenosis 15 days ago, and was discharged home three days after the procedure. His medical problems are hypercholesterolemia, coronary artery disease, intermittent claudication, hypertension for 18 years, and diabetes mellitus for 15 years. Physical examination shows painless, reddish-blue mottling of the skin of the extremities. Laboratory studies show: Hb 10.5 g/dl, WBC 10,000/cmm with 12% eosinophils, BUN 46 mg/dl, Serum creatinine 3.0 mg/dl, Serum C3 level Decreased. Urinalysis:pH Normal,Esterase Negative, Nitrite Negative, Protein 1+, WBC Many eosinophils, RBC 1-2/HPF. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's findings?
. Contrast nephropathy
. Cholesterol embolism
. Diabetic nephropathy
. Post streptococcal glomerulonephritis
. Acute allergic interstitial nephropathy
50) A 40-year-old man comes to the physician because of a two-week history of fatigue, lower extremity edema and dark urine. He has no history of serious illnesses. He takes no medications. He does not use tobacco, alcohol, or drugs. His blood pressure is 130/80 mm Hg and pulse is 80/min. Physical examination shows symmetric pitting edema of lower extremities. Laboratory studies show a serum creatinine level of 1.1 mg/dl. Urinalysis shows 4+ proteinuria and microhematuria. Light microscopy of the specimen obtained from kidney biopsy shows dense deposits within glomerular basement membrane that stain for C3, not immunoglobulins. Which of the following is the most likely pathophysiologic mechanism that explains this patient's condition?
. Anti-GBM antibodies
. Circulating immune complexes
. Persistent activation of the alternative complement pathway
. Cell-mediated injury
. Non-immunologic damage
{"name":"P 495 TO 512 *Q 1 TO 50*", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"1) A 31-year-old, HIV-infected man from New York presents to the ER with anorexia, malaise, night sweats, fever, and weight loss of 6.8kg (15 lb) over the past one month. He also has a cough productive of yellow sputum. He was diagnosed with HIV two years ago. When last checked two months ago, his CD4 count was 220\/microL. He is not taking any medications. His temperature is 39.2°C (102.2°F), pulse is 96\/min, and blood pressure is 120\/80 mm Hg. Physical examination reveals rales in his right upper chest. Laboratory studies show: Hematocrit 30%, WBC count 3,400\/microL, Neutrophils 86%, Bands 2%, Lymphocytes 4%, Monocytes 8%. PPD test shows 3 mm induration. Chest x-ray reveals a right upper lobe cavitation. Sputum examination shows partially acid-fast, filamentous, branching rods. Based on these findings, which of the following organism is the most likely cause of this patient's pulmonary disease?, .2) A 45-year-old man comes to the office and complains of intermittent, bloody diarrhea and abdominal pain for the past month. During this time period, he has lost six pounds. He was diagnosed with HIV infection in the past, but has refused antiretroviral therapy. Laboratory results show a CD4 count of 50cells\/μL. The stool examination is negative. Colonoscopy with biopsy shows multiple colonic ulcerations and mucosal erosions. The biopsy shows large cells containing eosinophilic intranuclear and basophilic intracytoplasmic inclusions. What is the most likely cause of this patient's diarrhea?, .3) A 73-year-old diabetic man presents with low-grade fever, facial pain over his right maxilla, and bloody nasal discharge for the last three days. For the last day, he has had diplopia. He was diagnosed with diabetes mellitus 10 years ago. For the last year, he has been on insulin. His most recent hemoglobinA1C was 12.0. His temperature is 39.0°C (102.2°F), pulse is 88\/min, and blood pressure is 130\/76mm Hg. Examination shows right-sided nasal congestion and necrosis of the right nasal turbinate with tenderness over the right maxillary sinus. There is chemosis and proptosis of his right eye. CT scan shows opacification of the right maxillary sinus. Which of the following is the most likely causative organism?","img":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/3012/images/ogquiz.png"}
More Quizzes
MMBC Vancouver Quiz
1360
Koniambo Nickel - Quiz Niveau 1
5218
Polynesian social credit test
1589
Health Survey/Poll
520
What Christian Denomination Am I? Find Out Now!
201031714
Ultimate Ballet Terminology: Test Your Ballet Terms
201042039
Free Golf Rules Knowledge
201021680
Is She Flirting With Me? Decode Her Signals Now!
201029553
Toledo Rockets Football: Tavares Bolden Challenge
201023935
Topics in International Business
15821380
Medication Dosage: Test Your Calculation Skills Now!
201023935
Free ER Airway Practice
201021834