Part 45
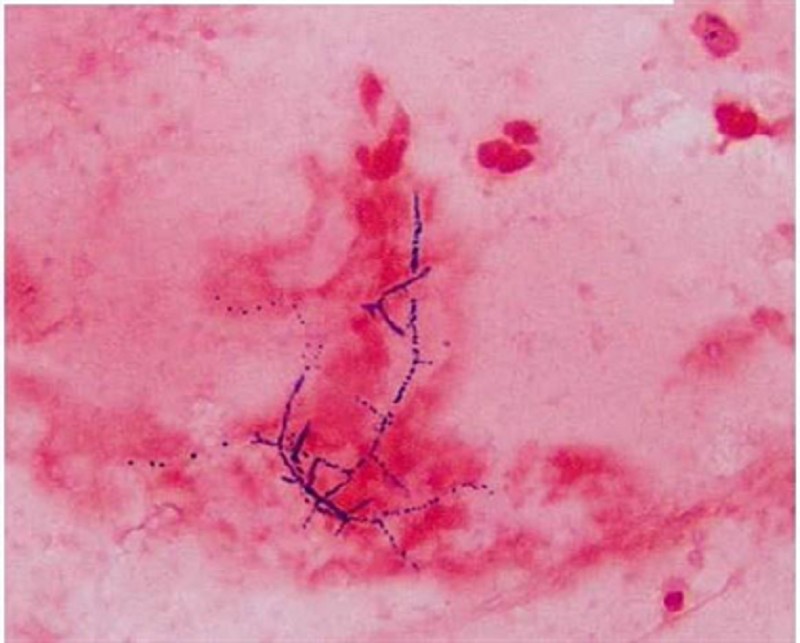
53) A 40-year -old man who underwent a renal transplant six months ago comes to the clinic with fever, chills, and a productive cough. His temperature is 39.4°C (103°F), pulse is 110/min, respirations are 22/min, and blood pressure is 110/65 mmHg. Chest x-ray shows a right lower lobe nodule with a cavity. Sputum gram stain is shown below. What is the most appropriate treatment of this patient's condition?
. Penicillin
. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
. Vancomycin
. Gentamycin
. Metronidazole
54) A 36-year-old woman who lives in the suburbs of a large city comes to your office for a tuberculin skin test. She will be volunteering in her daughter's school cafeteria and the school district requires tuberculin testing. You inject a small amount of Mycobacterium tuberculosis purified protein derivative (PPD) in the skin and 2 days later she returns for a reading. You measure 12 mm of induration. She reports no history of tuberculosis exposure and no underlying medical conditions. She has never before been tested for tuberculosis. She was born in the United States, is not a healthcare worker, and has never spent time in prison. What is the best next step in her management?
. Chest X-ray
. Observation
. Isoniazid for 6 months
. Isoniazid with pyridoxine for 9 months
. Isoniazid, rifampin and pyrazinamide for 8 weeks
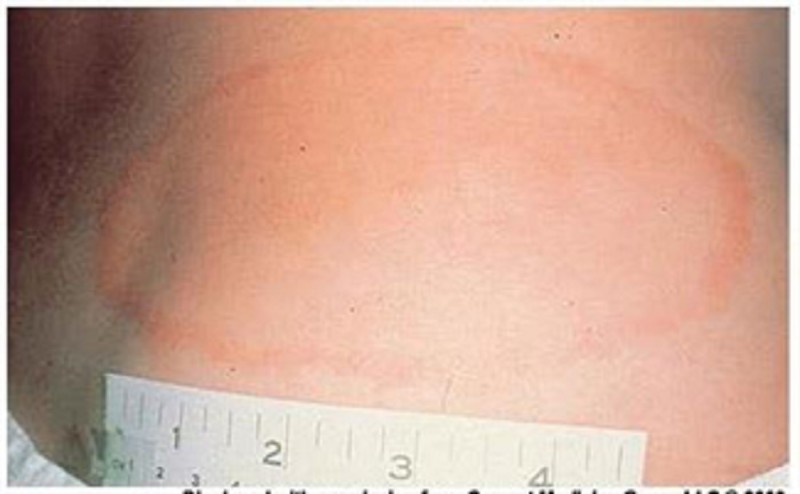
55) A 22-year-old female presents to the office with a three-day history of rash, fever, and malaise. There is no burning or itching associated with the rash. Two weeks ago, she had been camping in northern Massachusetts, and noted a tick bite after walking through the woods. She is twelve weeks pregnant. The rash is shown below. The examination is otherwise unremarkable. What is the most appropriate treatment for this patient?
. Doxycycline
. Amoxicillin
. Azithromycin
. Ceftriaxone
. Penicillin G
56) A 5-year-old Hispanic girl is brought to the emergency department (ED) due to a cat bite on her right upper extremity. She was bitten after rambunctiously playing for several minutes with the cat, which had just been given to her as a birthday gift. Her most recent booster tetanus vaccine was one year ago. Her temperature is 36.7°C (98°F), blood pressure is 108/70 mm Hg, pulse is 107/min, and respirations are 21/min. Physical examination reveals a deep puncture wound on the volar aspect of her right forearm. Before going to the ED, her mother cleaned the wound with hydrogen peroxide. There is no visible debris in the wound, and little bleeding is evident. Neurovascular function is intact. Her wound is cleaned in the ED with Betadine and lavaged with saline solution. What is the best next step in managing this girl's care?
. Bandage with dry gauze and discharge home
. Prescribe amoxicillin
. Prescribe amoxicillin/clavulanate
. Prescribe erythromycin
. Prescribe levofloxacin
57) A 57-year-old male comes to your office in the middle of January. He complains of a 4-day history of a nonproductive cough and coryza. He also has vague muscle aches and a mild headache. He denies any shortness of breath or chest pain. His past medical history is significant for hyperlipidemia and impaired glucose tolerance. He takes aspirin and simvastatin 40 mg at bedtime. He has no known drug allergies. His medical records show that he did not show up for his scheduled annual influenza vaccine this year. His temperature is 38.5°C (101.3°F), blood pressure is 135/80 mm Hg, and pulse is 88/min. Physical examination shows conjunctival redness and an erythematous oropharynx. The tympanic membranes are clear. The heart sounds are audible with no added murmurs, rubs or gallops. His breath sounds are vesicular in quality and equal bilaterally. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
. Administer influenza vaccination now
. Write a prescription for amantidine
. Write a prescription for oseltamivir
. Advise bed rest and symptomatic treatment with acetaminophen
. Empiric trial of oral antibiotics
58) A 60-year-old Caucasian woman undergoes elective coronary artery bypass surgery and aortic valve replacement. Her postoperative course is complicated by acute renal failure, atrial fibrillation, and pulmonary edema. On the third postoperative day, extubation is attempted but not tolerated, thus warranting reintubation. On the fifth postoperative day, she develops a fever to 38.9°C (102°F). Her pulse is 110-120/min and irregular, respirations are 36/min, and blood pressure is 110/65 mmHg. Her chest x-ray shows right middle and lower lobe infiltrates. WBC count is elevated with bandemia. Gram stain of her sputum shows gram-negative rods. She is given intravenous ceftriaxone; however, she deteriorates over the next 24 hours. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient?
. Stop ceftriaxone and start piperacillin-tazobactam
. Continue ceftriaxone and add vancomycin
. Stop ceftriaxone and start clindamycin
. Continue ceftriaxone and add ceftazidime
. Continue ceftriaxone and add amphotericin
59) A 34-year-old man is traveling in Southeast Asia on business. He is staying in Western-style hotels and eating food in large restaurants. He has not eaten from street vendors. One week after arrival, he develops symptoms of anorexia, nausea, and abdominal cramps followed by the sudden onset of watery diarrhea. He has no fever or chills and there is no blood or pus in the stools. Which of the following is the most appropriate therapy for his condition?
Amoxicillin
Symptomatic therapy with loperamide
Doxycycline
Oral rehydration only
Specific antitoxin
60) A 45-year-old woman is undergoing chemotherapy for breast cancer. She presents 10 days after her last chemotherapy with fever (temperature > 38.5°C), but no other symptoms except a sore throat and mouth. On examination, she looks well, there is oral mucositis, ears are normal, lungs are clear, and the central line site is clean. The CXR, urinalysis, and biochemistry are normal. Her WBC is 800/mL and the absolute neutrophil count is low ( < 500). Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Start empiric bacterial antibiotics
Start empiric antifungal and bacterial antibiotics
Acetaminophen alone until culture results are available
Start antiviral medications for HSV-1
Start antiviral and bacterial antibiotics
61) A 74-year-old man residing in a nursing home develops symptoms of high fever, diarrhea, chest pain, and nonproductive cough. His temperature is 40°C, blood pressure 120/80 mm Hg, respiration 24/min, and oxygen saturation 90%. He has bibasilar crackles, normal heart sounds, and a soft nontender abdomen. His CXR reveals bilateral lower lobe infiltrates. He is not able to provide any sputum, and the urine is positive for legionella antigen. Which of the following is the most appropriate antibiotic choice?
Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
Azithromycin
Ceftriaxone
Cefuroxime
Gentamicin
62) A 28-year-old female presents to her internist with a 2-day history of low-grade fever and lower abdominal pain. She denies nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea. On physical examination, there is temperature of 38.3°C (100.9°F) and bilateral lower quadrant tenderness, without point or rebound tenderness. Bowel sounds are normal. On pelvic examination, an exudate is present and there is tenderness on motion of the cervix. Her white blood cell count is 15,000/μL and urinalysis shows no red or white blood cells. Serum β-hCG is undetectable. Which of the following is the best next step in management?
. Treatment with ceftriaxone and doxycycline
. Endometrial biopsy
. Surgical exploration
. Dilation and curettage
. Aztreonam
63) Two students from a university dormitory building have contracted meningitis due to Neisseria meningitides. Which of the following students in the dormitory are most likely to benefit from chemoprophylaxis?
Everybody in the dormitory, with oral amoxicillin
Close contacts only, with oral amoxicillin
Everybody in the dormitory, with oral rifampin
Close contacts only, with oral rifampin
Everybody in the dormitory, with meningococcal vaccine
64) You are a physician in charge of patients who reside in a nursing home. Several of the patients have developed influenza-like symptoms, and the community is in the midst of influenza A outbreak. None of the nursing home residents have received the influenza vaccine. Which course of action is most appropriate?
. Give the influenza vaccine to all residents who do not have a contraindication to the vaccine (ie, allergy to eggs)
. Give the influenza vaccine to all residents who do not have a contraindication to the vaccine; also give oseltamivir for 2 weeks to all residents
. Give amantadine alone to all residents
. Give azithromycin to all residents to prevent influenza-associated pneumonia
. Do not give any prophylactic regimen
65) A 22-year-old university student complains of fatigue and malaise for the past 2 weeks. She also reports feeling feverish, and recently had a sore throat. Physical examination reveals enlarged tonsils and palpable cervical lymph nodes. There is also tenderness in the right upper quadrant on deep palpation, and minimal splenomegaly. Laboratory data show hemoglobin 13 g/dL; hematocrit 40%; platelets 340,000/mL; WBC 9400/mL, with 35% segmented neutrophils, 1% eosinophils, and 64% lymphocytes, of which 36% were atypical. A heterophil antibody (sheep cell agglutination) test is positive. Which of the following is the most appropriate initial treatment for this condition?
Gamma-globulin
Adequate rest
Chlorambucil
Chloramphenicol
Radiation therapy
66) A 44-year-old renal transplant patient develops severe cough and shortness of breath on exertion. On examination, he appears dyspneic, respirations 24/min, pulse 110/min, and oxygen saturation 88%. His lungs are clear on auscultation and heart sounds are normal. CXR shows bilateral diffuse perihilar infiltrates. Bronchoscopy and bronchial brushings show clusters of cysts that stain with methenamine silver. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Amphotericin B
Cephalosporins
Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
Aminoglycosides
Penicillins
67) A businesswoman needs to make frequent trips to South America, but every time she is there, she develops traveler’s diarrhea, which requires her to change her business schedule. To prevent future episodes during business trips, she is inquiring about prophylaxis methods. Which of the following is the most helpful advice for her?
Take loperamide for symptoms
Take trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole every day
Take azithromycin every day
Take doxycycline every day
Take ciprofloxacin only if moderate or severe symptoms develop
68) A 30-year-old male patient complains of fever and sore throat for several days. The patient presents to you today with additional complaints of hoarseness, difficulty breathing, and drooling. On examination, the patient is febrile and has inspiratory stridor. Which of the following is the best course of action?
. Begin outpatient treatment with ampicillin
. Culture throat for β-hemolytic streptococci
. Admit to intensive care unit and obtain otolaryngology consultation
. Schedule for chest x-ray
. Obtain Epstein-Barr serology
69) A 35-year-old previously healthy male develops cough with purulent sputum over several days. On presentation to the emergency room, he is lethargic. Temperature is 39°C, pulse 110, and blood pressure 100/70. He has rales and dullness to percussion at the left base. There is no rash. Flexion of the patient’s neck when supine results in spontaneous flexion of hip and knee. Neurologic examination is otherwise normal. There is no papilledema. A lumbar puncture is performed in the emergency room. The cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) shows 8000 leukocytes/μL, 90% of which are polys. Glucose is 30 mg/dL with a peripheral glucose of 80 mg/dL. CSF protein is elevated to 200 mg/dL. A CSF Gram stain shows gram-positive diplococci. Which of the following is the correct treatment option?
. Begin acyclovir for herpes simplex encephalitis
. Obtain emergency MRI scan before beginning treatment
. Begin ceftriaxone and vancomycin for pneumococcal meningitis
. Begin ceftriaxone, vancomycin, and ampicillin to cover both pneumococci and Listeria
. Begin high-dose penicillin for meningococcal meningitis
70) A young man has recently been bitten by a stray dog. He has a penetrating wound to the right forearm. The dog is nowhere to be found. In the emergency room, the wound is cleaned with water and povidone-iodine solution. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Start postexposure prophylaxis
Contact the local public health professional for further advice
Treat with oral doxycycline
Treat with IV ceftriaxone
Start IV acyclovir
71) A 22-year-old male, recently incarcerated and now homeless, has received one week of clarithromycin for low-grade fever and left upper-lobe pneumonia. He has not improved on antibiotics, with persistent cough productive of purulent sputum and flecks of blood. Repeat chest x-ray suggests a small cavity in the left upper lobe. Which of the following statements is correct?
. The patient has anaerobic infection and needs outpatient clindamycin therapy
. The patient requires sputum smear and culture for acid fast bacilli
. The patient requires glove and gown contact precautions
. Isoniazid prophylaxis should be started if PPD is positive
. Drug resistant pneumococci may be causing this infection
72) A 23-year-old woman visits your office because of headache, malaise, anorexia, pain in both sides of her jaw, and discomfort in both lower abdominal quadrants. Physical examination reveals enlarged parotid glands; bilateral lower quadrant abdominal tenderness; a temperature of 38.7°C; and a pulse rate of 92/min. Serologic testing (IgM) confirms the diagnosis of mumps. Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment for this condition?
Symptomatic
Immunization
Broad-spectrum antibiotics
Sulfonamides
Steroids
73) A 25-year-old woman complains of dysuria, frequency, and suprapubic pain. She has not had previous symptoms of dysuria and is not on antibiotics. She is sexually active and on birth control pills. She has no fever, vaginal discharge or history of herpes infection. She denies back pain, nausea, or vomiting. On physical examination she appears well and has no costovertebral angle tenderness. A urinalysis shows 20 white blood cells per high power field. Which of the following statements is correct?
. A 3-day regimen of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole is adequate therapy
Uantitative urine culture with antimicrobial sensitivity testing is mandatory
. Obstruction resulting from renal stone should be ruled out by ultrasound
. Low-dose antibiotic therapy should be prescribed while the patient remains sexually active
. The etiologic agent is more likely to be sensitive to trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole than to fluoroquinolones
74) A 40-year-old woman cut her finger while cooking in her kitchen. Two days later she became rapidly ill with fever and shaking chills. Her hand became painful and mildly erythematous. Later that evening her condition deteriorated as the erythema progressed and the hand became a dusky red. Bullae and decreased sensation to touch developed over the involved hand. What is the most important next step in the management of this patient?
. Surgical consultation and exploration of the wound
. Treatment with clindamycin for mixed aerobic-anaerobic infection
. Treatment with penicillin for clostridia infection
. Vancomycin to cover community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus
. Evaluation for acute osteomyelitis
75) A 60-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 2-week history of worsening fatigue. He has chronic renal insufficiency, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, hypercholesterolemia, hypothyroidism, polymyalgia rheumatica and depression. He was started on lisinopril for the prevention of proteinuria from diabetic nephropathy. Physical examination shows a few basal crackles. He is being considered for dialysis. Laboratory studies show hyperkalemia with serum K + of 6.0 mEq/L. EKG shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the best treatment to remove K+ from his body?
Sodium bicarbonate
Beta agonists
Calcium gluconate
Kayexalate
Insulin plus glucose
76) A 45-year-old man with advanced chronic renal failure comes to the physician because of edema of his feet. His temperature is 37°C (99°F), blood pressure is 150/100mm Hg, pulse is 78/min, and respirations are 15/min. Examination shows bilateral ankle edema. Laboratory studies show BUN of 62 mg/dl, serum creatinine of4.2 mg/dl, serum potassium of 5.6 meq/l, serum sodium of 146 meq/l, and total plasma cholesterol of 260 mg/dl. Which of the following is most likely to improve the prognosis of his disease?
. Captopril
. Simvastatin
. Protein restriction
. Salt restriction
. Potassium restriction

77) A 68-year-old male presents to the emergency room with cough. Chest x-ray is clear of infiltrates but reveals a right upper lobe lung lesion incidentally. A chest CT scan with IV contrast is performed in the emergency department and reveals a 1 cm x 2cm round lesion in the right upper lobe. The patient is admitted to the hospital, and by day 3 of his hospitalization, he has developed acute renal failure. The patient's past medical history is significant for hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes and coronary artery disease. His medications include aspirin, hydrochlorothiazide, clopidogrel, metoprolol, atorvastatin and lisinopril, all of which he has been taking for several years. He has no known drug allergies. He is a former smoker and does not use alcohol or drugs. His baseline blood pressure is 140/90 mm Hg and has remained in the 140s/90s throughout this admission. Physical examination is otherwise unremarkable. The patient's laboratory values from the time of admission to present are given below. Over the course of the next week, the patient's renal function returns to normal. Which of the following would most likely have prevented his renal failure?
. Prednisone
Intravenous hydration
. Furosemide
. Stopping clopidogrel
. 100% oxygen mask
78) A 23-year-old male hospitalized for confusion and seizures is treated with intravenous high-dose acyclovir. On the third day of hospitalization, his serum creatinine level increases to 3.4 mg/dl from a baseline of 0.9 mg/dl at admission. The observed finding could have been potentially prevented by which of the following?
. Careful allergy history taking
. Monitoring the blood drug levels
. Pre-treatment with allopurinol
. Pre-treatment with prednisone
. Aggressive intravenous hydration
79) A 27-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 1-day history of fever and joint pains. He is being treated with cephalexin for a skin infection. His urine has turned darker. His temperature is 38.5°C (101.3°F), blood pressure is 125/70 mm Hg, pulse is 90/min, and respirations are 15/min. Examination shows a skin rash; examination otherwise shows no abnormalities. Urinalysis shows: 8 RBCs/HPF, 12 WBCs/HPF with white cell casts, eosinophiluria, and a mild degree of proteinuria. Laboratory studies show a BUN of 40 mg/dl and serum creatinine of 2.2 mg/dl. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
. Discontinue cephalexin
. Start ampicillin and gentamicin
. Start oral ciprofloxacin
. Start intravenous steroids
. Start oral steroids
80) A 30-year-old man is admitted to the hospital with a diagnosis of acute renal failure secondary to poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis. On his fifth hospital day, he develops retrosternal, non-radiating chest pain which is relieved by leaning forward. He denies the use of tobacco or drugs. He drinks alcohol occasionally. He has no past history of any serious illness. His temperature is 37.6°C (99.8°F), blood pressure is 145/95 mm Hg, pulse is 80/min, and respirations are 20/min. A pericardial friction rub is heard on chest auscultation. The rest of the examination shows no abnormalities. EKG shows ST segment elevation in all leads, with elevation of the PR segment in lead aVR. The chest x-ray is normal. Urinalysis shows hematuria, red cell casts and mild proteinuria. Laboratory studies show a BUN level of 60 mg/dl and a serum creatinine level of 3 8 mg/dl. What is the most appropriate next step in management?
. Broad spectrum antibiotics
. Intravenous steroids
. Hemodialysis
. Thrombolytic therapy
. NSAIDs
81) A 47-year-old diabetic woman comes to the physician due to the recent onset of tremors. She has undergone combined pancreatic and kidney transplantation secondary to end stage renal disease and diabetes. She takes multiple medications, including immunosuppressants. Her temperature is 36.1° C (97°F), blood pressure is 152/90 mm Hg, pulse is 78/min, and respirations are 16/min. Examination shows gum hypertrophy. Laboratory studies show: Hb 13.0 g/dl, WBC 8,000/cmm, Serum Na 135 mEq/L, Serum K 5.3 mEq/L, BUN 26 mg/dl, Serum Creatinine 1.7 mg/dl. Which of the following immunosuppressants is most likely responsible for her presentation?
. Tacrolimus
. Cyclosporine
. Azathioprine
. Mycophenolate
. Diuretic
82) A 45-year-old male patient comes to the physician's office for a routine check-up. He denies any symptoms and says he feels "perfectly healthy." He was diagnosed with hypertension and mixed hypercholesterolemia a year ago. He is currently taking hydrochlorothiazide, amiloride and simvastatin daily. He does not use tobacco, alcohol or drugs. His blood pressure today is 135/85 mm Hg. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. Routine blood results reveal the following: CBC: Hb 14.2g/dL, Ht 42%, MCV 86 fl, Platelet count 260,000/cmm, Leukocyte count 8,500/cmm, Neutrophils 70%, Eosinophils 1%, Lymphocytes 24%, Monocytes 5%. Serum: Serum Na 140 mEq/L, Serum K 5.7 mEq/L, Chloride 100 mEq/L, Bicarbonate 24 mEq/L, BUN 10 mg/dL, Serum Creatinine 1.1 mg/dL, Calcium 9.0 mg/dL, Blood Glucose 118 mg/dL, Total cholesterol 220 mg/dL, LDL cholesterol 130 mg/dL. The blood sample is checked and is not hemolysed. The EKG shows normal sinus rhythm. What is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient?
Intravenous calcium gluconate
Intravenous dextrose + insulin
Stop amiloride and recheck lab results in 1 week
Stop HCTZ and recheck lab results in 1 week
Start patient on a low potassium diet
83) A 50-year-old man comes to the emergency department due to a sudden onset of severe, colicky pain in the right flank. He was admitted twice in the past for similar complaints; he was managed conservatively and sent home on both occasions. He has no other medical problems. He does not use tobacco, alcohol or drugs. His vital signs are stable. He is given IV fluids and narcotics. Laboratory studies show: Hb 14.5 g/dL, WBC 13,000/cmm; no bands, Platelets 300,000/cmm, BUN 16 mg/dl, Serum Creatinine 0.8 mg/dl. CT scan of the abdomen without contrast shows renal calculi. Which of the following is the best advice for the prevention of future stones in this patient?
Decrease dietary calcium intake
Mega doses of Vitamin C
Decrease dietary protein and oxalate
Restrict fluid intake
Increase sodium intake
84) A 64-year-old male with a past medical history of hypertension, diabetes and chronic renal insufficiency presents with gross hematuria. His baseline serum creatinine is 1.6-1.7 mg/dl. The patient's medications include aspirin, hydrochlorothiazide, enalapril, and simvastatin. He has no known environmental, medication, or contrast allergies. On physical examination, the patient has a blood pressure of 130/80 mm Hg. The examination is otherwise unremarkable. Contrast CT scan of the abdomen is planned to evaluate his condition. Which of the following interventions would be most helpful in preventing contrast-induced kidney damage?
. Prednisone
. Non-ionic contrast agent
. Furosemide
. 100% oxygen mask
. Stopping simvastatin
85) A 26-year-old man comes to the emergency department because of a sudden onset of severe right-sided flank pain. The pain is colicky and radiates from the flank to the scrotum. He also has nausea, vomiting and dark-colored urine. He has never had these symptoms before. His temperature is 37°C (98.6°F), blood pressure is 126/70 mm Hg, pulse is 90/min, and respirations are 18/min. Examination shows no abnormalities. He is given adequate analgesia. Non-contrast helical CT shows a 4 mm radiopaque stone in the right upper ureter. Laboratory studies show serum calcium of 9.8 mg/dl, serum creatinine of 0.9 mg/dl, and BUN of 15mg/dl. Urinalysis shows hematuria but no casts. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
. 24 hr urine collection for metabolic evaluation
. Reassurance
. Fluid intake greater than 2L/day
. Intake of potassium citrate
. Restriction of dietary oxalate
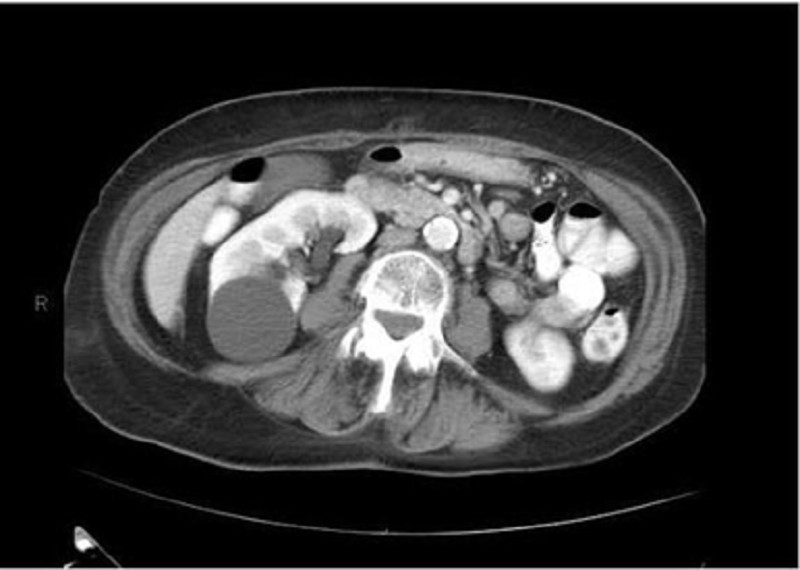
86) A healthy 54-year-old man comes to the physician for a routine health maintenance examination. He has no complaints, but he is requesting for a CT scan of the abdomen. His father died at the age of 60 due to the sudden rupture of an undiagnosed abdominal aortic aneurysm. He has a history of hypertension and gouty arthritis. His social history is not significant. His vital signs are stable. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. ACT scan of the abdomen is shown below. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
. Reassurance
. Surgery
. CT guided biopsy
. Antibiotics
. Repeat CT scan in 3 months
87) A 72-year-old woman with poorly controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus presents to your clinic one week after being discharged from the hospital. She had been admitted with pyelonephritis secondary to a multi-drug resistant organism, and received several days of intravenous antibiotics. Her serum creatinine on admission had been 2.1 mg/dl. Today it is found to be 4.9 mg/dl. Urinalysis reveals rare epithelial casts and no white blood cells. FENa is greater than 2%. What antibiotic did she most likely receive during her hospitalization?
. Nafcillin
. Vancomycin
. Levofloxacin
. Amikacin
. Doxycycline
88) A 58-year-old man comes to the physician and complains of "problems with erection." He has recurrent and persistently painful erections. His other medical problems include ulcerative colitis, kidney stones, insomnia, depression, hypertension, drug-induced diabetes, obesity and hypercholesterolemia. He does not use tobacco, alcohol, or drugs. He takes prednisone, mesalamine, insulin, 6-mercaptopurine, simvastatin, glyburide, enalapril, trazodone, and fluoxetine. He has no known drug allergies. His vital signs are stable. The general physical examination is unremarkable. Avoidance of which of the following medications could have prevented his condition?
. Fluoxetine
. Trazodone
. Enalapril
. Glyburide
. Simvastatin
89) A 30-year-old woman comes to the physician due to the recent onset of occipital headaches. She has taken acetaminophen several times, but the pain returns. She has no fever or visual problems. She has not had similar episodes in the past. She has no history of serious illness. Her temperature is 36.1°C (98°F), blood pressure is 160/90 mm Hg, pulse is 88/min, and respirations are 16/min. Physical examination shows a rightsided renal bruit Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment for this patient's condition?
. ACE inhibitors
. Furosemide
. Angioplasty with stent placement
. Surgery
. Oral prednisone
90) A 45-year-old man with known cirrhosis due to hepatitis C is admitted to the hospital for abdominal discomfort and confusion. Physical examination reveals a distended abdomen, leg edema, and deep yellow discoloration of the skin and sclerae. Bibasilar crackles are heard on chest auscultation. His serum sodium level is 127 mEq/L, potassium level is 2.9 mEq/L, and creatinine level is 1.3 mg/dl. On day 3 of his hospitalization, the serum creatinine is 4.2mg/dl. A urinalysis reveals: Protein negative, Glucose negative, WBC 4-5/hpf, RBC 0-1/hpf. Renal ultrasound is normal and the post-void residual urinary volume is less than 50 ml. He is given 2 L of normal saline intravenously with no change in his serum creatinine concentration. This patient's kidney dysfunction can be best corrected by which of the following?
. High-dose spironolactone
. ACE inhibitors
. Liver transplantation
. Broad spectrum antibiotics
. Pegylated interferon
91) A 56-year-old man develops oliguria three days after having a kidney transplantation. His postoperative course was uncomplicated. His blood pressure is 160/100 mm Hg and heart rate is 90/min. Palpation of the transplant reveals mild tenderness. Laboratory studies show: Serum sodium 145 mEq/L, Serum potassium 5.5 mEq/L, Serum calcium 8.6 mg/dl, Serum creatinine 3.2 mg/dl, BUN 30 mg/dl. His serum cyclosporine level is normal. Renal ultrasonography does not detect dilatation of the calyces. Biopsy of the transplant shows heavy lymphocyte infiltration and vascular involvement with swelling of the intima. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
. Decrease the dose of cyclosporine
. Give IV steroids
. Order ureterography
. Administer IV diuretics
. Prepare for surgery
92) A 25-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 3-day history of burning micturition and increased urinary frequency. She has suprapubic discomfort. She denies having unusual vaginal discharge. She has been sexually active and monogamous for the past 4 years with her husband. Her temperature is 37.1°C (98.9°F), blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg, pulse is 68/min, and respirations are 15/min. Examination shows suprapubic tenderness without flank tenderness. The rest of the examination is normal. Urinalysis shows: Specific gravity 1.020, Blood Trace, Glucose Negative, Ketones Negative, Leukocyte esterase Positive, Nitrites Positive, WBC 40-50/hpf, RBC 6-10/hpf, Bacteria 50+. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
. Urine culture
. Oral trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
. Oral ciprofloxacin
. Oral nitrofurantoin
. Intravenous trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
93) A 34-year-old man is being evaluated for possible end-stage renal disease. He has a long history of diabetes, type 1. He previously developed chronic renal insufficiency despite being on enalapril and insulin. His renal function is getting worse day by day. A nephrologist is currently managing his renal condition. Which of the following long-term treatments would give the best survival rate for this patient?
. Hemodialysis
. Peritoneal dialysis
. Renal transplantation from a cadaver
. Renal transplantation from a living related donor
. Renal transplantation from a living unrelated donor
94) A 50-year-old diabetic woman presents for follow-up of her hypertension. Her blood pressure is 152/96 in the office today and she brings in readings from home that are consistently in the same range over the past month. Her current medications are amlodipine 5 mg daily and hydrochlorothiazide 25 mg daily. The diuretic was added when she developed peripheral edema on the amlodipine; now she has only trace peripheral edema. A spot urine specimen shows 280 μg of albumin per mg creatinine (microalbuminuria is present if this value is between 30 and 300 μg/mg). What would be the best next therapeutic step in this patient?
. Add clonidine
. Add a beta-blocker
. Increase the thiazide diuretic dose
. Add an alpha-blocker
. Add angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blocker
95) A 64-year-old woman develops severe diarrhea 2 weeks after finishing antibiotics for pneumonia. She has also noticed decreased urine output despite drinking lots of fluids. On examination, she has a postural drop in her blood pressure, the JVP is low, and the abdomen is soft but diffusely tender. Despite giving 4 L of normal saline, her urine output remains low. The urinalysis is positive for heme-granular casts and the urine sodium is 42mEq/L. Which of the following medications should be held during the recovery phase of this woman’s ARF?
Acetaminophen
Digoxin
Lorazepam
Enalapril
Simvastatin
96) A 67-year-old man with a history of gout presents with intense pain in his right great toe. He has a complex past medical history, including hypertension, coronary artery disease, congestive heart failure, myelodysplasia, and chronic kidney disease with a baseline creatinine of 3.2 mg/dL and a uric acid level of 10 mg/dL. His medications include aspirin, simvastatin, clopidogrel, furosemide, amlodipine, and metoprolol. What is the best therapy in this situation?
. Colchicine 1.2 mg po initially, followed by 0.6 mg 1 hour later
. Allopurinol 100 mg po daily and titrate to uric acid less than 6 mg/dL
. Prednisone 40 mg po daily
. Naproxen 750 mg po once followed by 250 mg po tid
. Probenecid 250 mg po bid
97) A 60-year-old diabetic woman develops angina and will need a coronary angiogram for evaluation of coronary artery disease. She has a creatinine of 2.2. Which of the following is the most effective in reducing the risk of contrast induced nephropathy?
. Administer mannitol immediately after the contrast is given
. Perform prophylactic hemodialysis after the procedure
. Give IV hydration with normal saline or sodium bicarbonate prior to and following the procedure
. Indomethacin 25 mg the morning of the procedure
. Dopamine infusion before and after the procedure
98) A 56-year-old man presents with hypertension and peripheral edema. He is otherwise healthy and takes no medications. Family history reveals that his father and a brother have kidney disease. His father was on hemo-dialysis before his death at age 68 of a stroke. Physical examination reveals BP 174/96 mm Hg and AV nicking on funduscopic examination. He has a soft S4 gallop. Bilateral flank masses measuring 16 cm in length are palpable. Urinalysis shows 15 to 20 RBC/hpf and trace protein but is otherwise normal; his serum creatinine is 2.4 mg/dL. Which is the most likely long-term complication of his condition?
. End-stage renal disease requiring dialysis or transplantation
. Malignancy
. Ruptured cerebral aneurysm
. Biliary obstruction owing to cystic disease of the pancreas
. Dementia
99) A 63-year-old woman has Type II diabetes mellitus, which is well-controlled. Her physical examination is positive for peripheral neuropathy in the feet and nonproliferative retinopathy. A urinalysis is positive for proteinuria. Which of the following treatments is most likely to attenuate the course of renal disease?
Calcium channel blockers
ACE inhibitors
Hepatic hydroxymethylglutaryl- coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) inhibitors
Dietary carbohydrate restriction
Weight reduction
100) A 60-year-old man is brought in by ambulance and is unable to speak. The EMS personnel tell you that a neighbor informed them he has had a stroke in the past. There are no family members present. His serum sodium is 118 mEq/L. Which of the following is the most helpful first step in the assessment of this patient’s hyponatremia?
. Order a chest x-ray
. Place a Foley catheter to measure 24-hour urine protein
. Clinical assessment of extracellular fluid volume status
. CT scan of head
. Serum AVP (arginine vasopressin) level
101) A 39-year-old woman is admitted to the gynecology service for hysterectomy for symptomatic uterine fibroids. Postoperatively the patient develops an ileus accompanied by severe nausea and vomiting; ondansetron is piggybacked into an IV of D5 ½ normal saline running at 125 cc/h. On the second postoperative day the patient becomes drowsy and displays a few myoclonic jerks. Stat labs reveal Na 118, K 3.2, Cl 88, HCO3 22, BUN 3, and creatinine 0.9. Urine studies for Na and osmolality are sent to the lab. What is the most appropriate next step?
. Change the IV fluid to 0.9% (normal) saline and restrict free-water intake to 600 cc/d
. Change the ondansetron to promethazine, change the IV fluid to lactated Ringer solution, and recheck the Na in 4 hours
. Start 3% (hypertonic) saline, make the patient NPO, and transfer to the ICU
. Change the IV fluid to normal saline and give furosemide 40 mg IV stat
. Make the patient NPO and send for stat CT scan of the head to look for cerebral edema
102) You evaluate a 48-year-old man for chronic renal insufficiency. He has a history of hypertension, osteoarthritis, and gout. He currently has no complaints. His medical regimen includes lisinopril 40 mg daily, hydro-chlorothiazide 25 mg daily, allopurinol 300 mg daily, and acetaminophen for his joint pains. He does not smoke but drinks 8 oz of wine on a daily basis. Examination shows BP 146/86 mm Hg, pulse 76, a soft S4 gallop, and mild peripheral edema. There is no abdominal bruit. His UA reveals 1+ proteinuria and no cellular elements. Serum creatinine is 2.2 mg/dL and his estimated GFR from the MDRD formula is 42 mL/minute. What is the most important element is preventing progression of his renal disease?
. Discontinuing all alcohol consumption
. Discontinuing acetaminophen
. Adding a calcium channel blocker to improve blood pressure control
. Obtaining a CT renal arteriogram to exclude renal artery stenosis
. Changing the lisinopril to losartan
103) A 45-year-old woman with cirrhosis secondary to autoimmune hepatitis is seeing her hepatologist for routine follow-up. She reports that she has been feeling relatively well lately, and complains only of mild fatigue. Her medical history is otherwise unremarkable. Her medications include lactulose, spironolactone, propranolol and furosemide. Her vital signs are stable and the remainder of her physical exam is consistent with compensated cirrhosis. Her laboratory values are given below: Sodium 132 mEq/L, Potassium 4.1 mEq/L, Chloride 100 mEq/L, Bicarbonate 24 mEq/L, Glucose 102 mg/dl, Creatinine 0.9 mg/dl, Calcium 7.4 mg/dl, Total protein 6.1 g/dl, Albumin 2.5 g/dl, Total bilirubin 2.1 mg/dl, AST 80 units/L, ALT 102 units/L. What is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient's hypocalcemia?
. Calcium gluconate infusion
. Measurement of vitamin D levels
. Replace furosemide with hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ)
. Initiate oral calcium and vitamin D replacement
. No intervention is required
104) A 43-year-old female with history of hepatitis C, alcohol use and cirrhosis is admitted to the hospital for severe vomiting for the last 2 days. Her temperature is 36.7°C (98.2°F), pulse is 90/min, respirations are 14/min and blood pressure is 100/70 mmHg supine. Her lungs are clear to auscultation. She has mild epigastric tenderness, but there is no abdominal distention. Extremities have no edema. Her laboratory profile shows: Blood PH 7.49, PaO2 100 mmHg, PaCO2 41 mm Hg, HCO3- 30 mEq/L, Sodium 138 mEq/L, Potassium 3.0 mEq/L, Chloride 95 mEq/L. Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment for the patient's alkalosis?
. Intravenous ammonium chloride and potassium
. Intravenous hydrochloric acid and potassium
. Intravenous mannitol
. Intravenous normal saline and potassium
. Dialysis
105) A 21-year-old woman complains of progressive weakness and loss of energy. She nearly collapsed yesterday while performing one of her routine 3 hour workouts. Additionally, she has been performing badly in college despite persistent attempts to improve her grades. Physical exam reveals a blood pressure of 102/58 mmHg, heart rate of 113/min, fine hair covering her face, and normal heart and lungs. Laboratory studies show the following findings: Sodium 140 mEq/L, Potassium 24 mEq/L, Calcium 10.1 mg/dL, Chloride 90 mEq/L, Bicarbonate 40 mEq/L, Urine chloride 14 mEq/L. Which of the following is most likely to correct the laboratory abnormalities in this patient?
Calcium gluconate infusion
Normal saline infusion
Sodium bicarbonate solution infusion
. Loop diuretics
. Hyperventilation
106) A 52-year-old man with Burkitt lymphoma is admitted to the hospital for chemotherapy. He is started on chemotherapy without incident. Two days into his hospitalization, he develops new peaked T-waves on his ECG. Laboratory analysis reveals a serum potassium concentration of 6.2 mEq/L, and the patient is given one ampule of calcium gluconate emergently. His renal function is within normal limits. Which of the following additional interventions will most rapidly correct his hyperkalemia?
. Hemodialysis
. Sodium polystyrene sulfonate
. Furosemide
. Insulin and glucose
. High-dose inhaled β2 agonist
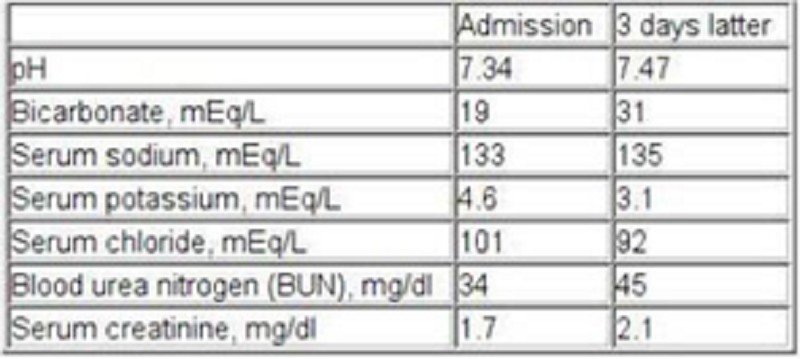
107) A 58-year-old alcoholic is admitted with diagnosis of decompensated liver cirrhosis. The lab panel is shown below on the day of admission and 3 days later. Which of the following best explains the acid-base status change in this patient?
Acute renal failure
Bowel ischemia
Loop diuretic therapy
Opioid medication use
Right lower lobe atelectasis
108) A 58-year-old man is admitted to the intensive care unit with an exacerbation of his chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and respiratory failure. After several hours on noninvasive ventilation the patient develops worsening respiratory distress and requires endotracheal intubation. Which of the following is a contraindication to the use of succinylcholine for rapid-sequence intubation?
. Hyperkalemia
. COPD exacerbation
Hepatic failure
. Hypokalemia
. Hypercalcemia
109) A 66-year-old white male comes to the physician's office for the first time because of generalized muscle weakness. His review of systems is otherwise negative. He has a past medical history of hypertension, type- 2 diabetes, hyperlipidemia, chronic renal insufficiency and ischemic cardiomyopathy. Neurological examination shows mild weakness of the lower limbs, depressed reflexes and normal sensation. Laboratory studies show: Serum sodium 134 mEq/L, Serum potassium 6.0 mEq/L, Bicarbonate 24 mEq/L, Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) 38 mg/dl, Serum creatinine 2.8 mg/dl, Calcium 8.2 mg/dl, Blood glucose 298 mg/dl. A dose of sodium polystyrene sulfonate is given. Which of the following additional interventions is most important in this patient's management?
. Review all his current medications
. Measure serum renin and aldosterone levels
. Obtain electromyography
. Obtain acetylcholine receptor antibodies
. Start oral prednisone therapy
110) A 79-year-old female presents to your office with a three-day history of nausea, diarrhea, poor oral intake and weakness. Her past medical history is significant for hypertension treated with enalapril and diltia zem. Her serum chemistry shows the following: Sodium 139 mEq/L, Potassium 7.8 mEq/L, Bicarbonate 14 mEq/L, Chloride 95 mEq/L, Glucose 155 mg/dl, BUN 80 mg/dl, Creatinine 3.1 mg/dl. EKG reveals QRS prolongation and prominent T wave peaking in precordial leads. Which of the following pharmacologic therapies plays a role in treating this patient's electrolyte condition?
. Stimulating alpha 1-adrenoreceptors
. Stimulating beta 1-adrenoreceptors
. Stimulating beta2-adrenoreceptors
. Blocking alpha 1-adrenoreceptors
. Blocking beta 1-adrenoreceptors
111) A 42-year-old male is brought to the emergency department immediately after having a prolonged seizure episode. His family describes a past medical history of grand mal seizures. He has been on phenytoin for the past 10 years, but stopped taking the drug six months ago because he had not had any seizures in the last nine years. He is otherwise healthy and had been doing well until this seizure episode. He does not use tobacco, alcohol or drugs. He is afebrile. His blood pressure is 136/88 mm Hg, respirations are 18/min and pulse is 96/min. He appears confused and lethargic. Chest auscultation is unremarkable, and his abdomen is soft and nontender. A limited neurologic examination is non-focal. His laboratory report shows: Serum sodium 140 mEq/L, Serum potassium 4.0 mEq/L, Chloride 103 mEq/L, Bicarbonate 17 mEq/L, Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) 20 mg/dl, Serum creatinine 0.8 mg/dl, Blood glucose 98 mg/dl. Chest x-ray and urinalysis are within normal limits, and a CT scan of the head is unremarkable. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient's metabolic acidosis?
. Give intravenous bicarbonate
. Check serum ketones
. Check serum lipase
. Observe and repeat the labs after 2 hours
. Start dopamine
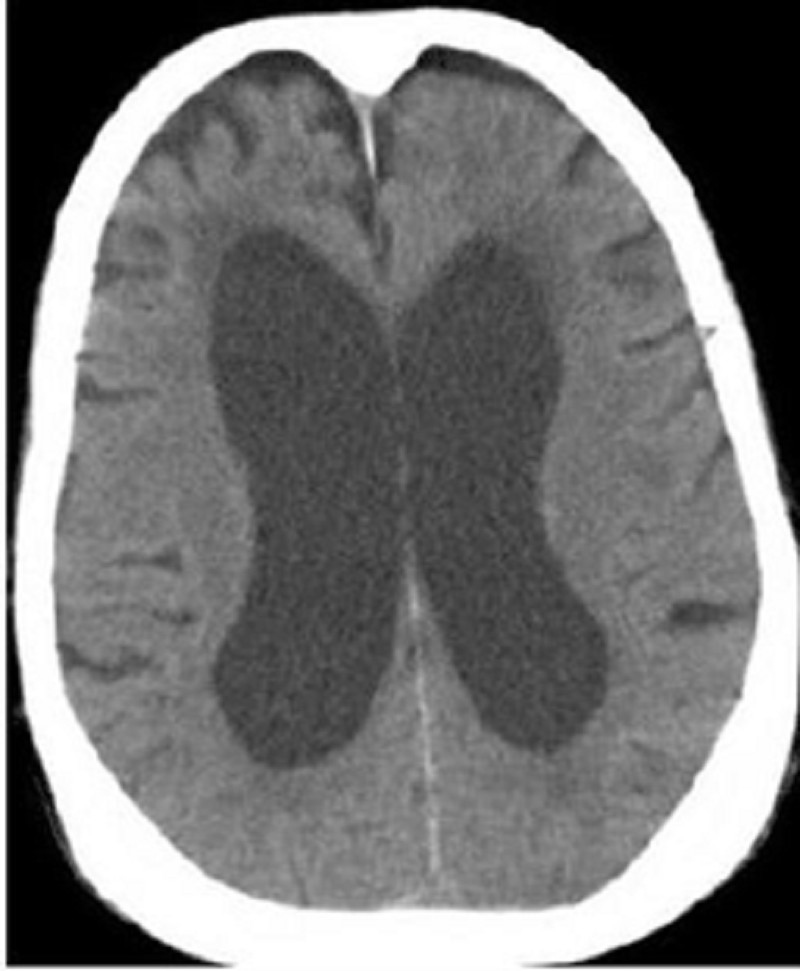
112) A 79-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician complaining of memory loss. She reports increasing difficulty balancing her check book and remembering the names of new acquaintances over the last several months. Her only other complaint is occasional urinary incontinence, which she attributes to old age. She denies headache, vision changes, rash, nausea, or vomiting. Her past medical history is significant for hypertension controlled with felodipine. On exam her vital signs are within normal limits. The heart and lung exams are also unremarkable. The cranial nerves are intact, fundoscopic exam is normal, and no tremor is observed. Her gait is slow and shuffling, there is no dysmetria, and her Folstein mini-mental status score is 24/30. CT scan of her brain is shown below. Which of the following interventions is most likely to relieve her symptoms?
. Ventriculoperitoneal shunt
. Hematoma evacuation
. Levodopa/carbidopa
. Vitamin B12 replacement
. High-dose penicillin
113) A 50-year-old male patient comes to the office because he is concerned about the marked tremors of his hands. His tremors disappear with voluntary activity and worsen with emotional stress. He finds it mild difficult to initiate movements. He does not have a family history of tremors. Physical examination reveals tremors that occur at a frequency of 3-4 cycles/sec. There is rigidity of his limb musculature. His gait and posture is minimally disturbed. His higher mental functions are intact. Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment for this patient?
. Benztropine
. Amantadine
. Selegiline
. Clozapine
. Propranolol
114) A 67-year-old male presents with a six-month history of rigidity, gait problems, tremor and slowness of movements. His condition has progressively worsened over the last few months, and he is now unable to perform his routine daily activities due to the slowness of his movements. He is not taking any medications. On examination, he is alert and conscious. His face is without expression. There is a resting tremor of his hands. He has a stooped posture and shuffling gate. There is rigidity of his limb muscles. Which of the following is the most appropriate initial treatment for this patient?
. L-dopa
. Amantadine
. Selegiline
. Clozapine
. Benztropine
115) A 58-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with severe headache and agitation. She describes her pain as right-sided and retro-orbital, and also reports blurred vision, constipation, and vomiting. Her medical history is significant for Parkinson's disease, hypothyroidism, hypertension and chronic hepatitis C. Work-up reveals that her current condition is medication-induced. Which of the following agents is most likely responsible?
. Levodopa
. Selegiline
. Bromocriptine
. Trihexyphenidyl
. Propranolol
116) A 67-year-old male comes to the office for a routine physical exam. He retired this year and wants "a clean bill of health." He has no complaints. He stopped smoking 10 years ago, but smoked for 40 years prior to that. He only takes a "water pill" for hypertension. His vital signs are normal. The physical examination reveals a bruit in his neck. His chest x-ray, EKG, and blood work have normal results. Duplex ultrasonography of his neck reveals a 70% irregular lesion at the right common carotid artery bifurcation. The left common carotid artery has a 40% lesion. What is the best next step in the management of this patient?
. Left carotid surgery
. Right carotid surgery
. Long term ASA therapy
. Temporal artery biopsy
. Heparin
117) A middle-aged woman is found wandering the streets with an abnormal gait. Police officers bring her to the hospital. She mumbles when asked for her name and age. She is not oriented to time or place. Her blood pressure is 160/100 mmHg and her heart rate is 100/min. She is afebrile. Mucous membranes are moist and the pupils are dilated and reactive to light. She moves all of her extremities, and her deep tendon reflexes are symmetric. Which of the following is the best initial treatment for this patient?
. Naloxone
. Flumazenil
. Thiamine
. Haloperidol
. Clonidine
{"name":"Part 45", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"53) A 40-year -old man who underwent a renal transplant six months ago comes to the clinic with fever, chills, and a productive cough. His temperature is 39.4°C (103°F), pulse is 110\/min, respirations are 22\/min, and blood pressure is 110\/65 mmHg. Chest x-ray shows a right lower lobe nodule with a cavity. Sputum gram stain is shown below. What is the most appropriate treatment of this patient's condition?, 54) A 36-year-old woman who lives in the suburbs of a large city comes to your office for a tuberculin skin test. She will be volunteering in her daughter's school cafeteria and the school district requires tuberculin testing. You inject a small amount of Mycobacterium tuberculosis purified protein derivative (PPD) in the skin and 2 days later she returns for a reading. You measure 12 mm of induration. She reports no history of tuberculosis exposure and no underlying medical conditions. She has never before been tested for tuberculosis. She was born in the United States, is not a healthcare worker, and has never spent time in prison. What is the best next step in her management?, 55) A 22-year-old female presents to the office with a three-day history of rash, fever, and malaise. There is no burning or itching associated with the rash. Two weeks ago, she had been camping in northern Massachusetts, and noted a tick bite after walking through the woods. She is twelve weeks pregnant. The rash is shown below. The examination is otherwise unremarkable. What is the most appropriate treatment for this patient?","img":"https://cdn.poll-maker.com/11-485967/for-student-des-2016-2017-last-pdf---adobe-reader.bmp?sz=1200"}
More Quizzes
How well do you remember England's 2016 World T20 campaign?
1050
Security Quiz
9413
M/F
221134
EU kérdések
63320
Ultimate Spanish Pronoun Practice - Test Your Skills
201031491
Free English Usage Assessment
201021737
Guess the Movie by Actors' Names - Test Your Film IQ!
201097605
Free Python Basics Knowledge Test
201024012
M&M Game Questions: Ultimate Chocolate Trivia Challenge
201024213
ALAT Certification Practice: Test Your Knowledge
201078809
Which Lemonade Mouth Character Are You? Free Personality
201024842
How Obsessed Are You with Scarlett Johansson? Take the
201028725