new Part 4 (765-865) (765-1019) NR 2

Mental Health Diagnosis Quiz
Test your knowledge and understanding of various mental health diagnoses with our comprehensive quiz. This assessment covers a range of scenarios and patient presentations, challenging you to identify the most likely diagnosis based on the given information.
Perfect for healthcare professionals, students, or anyone interested in psychology, this quiz includes:
- Multiple-choice questions
- Real-life case scenarios
- Detailed feedback on answers
A 20-year-old woman is brought to the emergency room by her family because they have been unable to get her to eat or drink anything for the past 2 days. The patient, although awake, is completely unresponsive both vocally and nonverbally. She actively resists any attempt to be moved. Her family reports that during the previous 7 months she became increasingly withdrawn, socially isolated, and bizarre; often speaking to people no one else could see. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Catatonia
Schizoaffective disorder
Delusional disorder
Schizophreniform disorder
PCP intoxication
A 21-year-old man is brought to the emergency room by his parents because he has not slept, bathed, or eaten in the past 3 days. The parents report that for the past 6 months their son has been acting strangely and “not himself.” They state that he has been locking himself in his room, talking to himself, and writing on the walls. Six weeks prior to the emergency room visit, their son became convinced that a fellow student was stealing his thoughts and making him unable to learn his school material. In the past 2 weeks, they have noticed that their son has become depressed and has stopped taking care of himself, including bathing, eating, and getting dressed. On examination, the patient is dirty, disheveled, and crying. He complains of not being able to concentrate, a low energy level, and feeling suicidal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis for this patient?
Schizoaffective disorder
Schizophrenia
Bipolar I disorder
Schizoid personality disorder
Delusional disorder
A 47-year-old woman is brought to the emergency room after she jumped off an overpass in a suicide attempt. In the emergency room she states that she wanted to kill herself because the devil had been tormenting her for many years. After stabilization of her fractures, she is admitted to the psychiatric unit, where she is treated with risperidone and sertraline. After 2 weeks she is no longer suicidal and her mood is euthymic. However, she still believes that the devil is recruiting people to try to persecute her. In the past 10 years, the patient has had three similar episodes prior to this one. Throughout this time, she has never stopped believing that the devil is persecuting her. Which of the following is the most appropriate diagnosis for this patient?
Schizoaffective disorder
Delusional disorder
Schizophrenia, paranoid type
Schizophreniform disorder
Major depression with psychotic features
A 40-year-old woman is arrested by the police after she is found crawling through the window of a movie star’s home. She states that the movie star invited her into his home because the two are secretly married and “it just wouldn’t be good for his career if everyone knew.” The movie star denies the two have ever met, but notes that the woman has sent him hundreds of letters over the past 2 years. The woman has never been in trouble before and lives an otherwise isolated and unremarkable life. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Delusional disorder
Schizoaffective disorder
Bipolar I disorder
Cyclothymia
Schizophreniform disorder
A 26-year-old woman is brought to the emergency room by her husband after she begins screaming that her children are calling to her and becomes hysterical. The husband states that 2 weeks previously, the couple’s two children were killed in a car accident, and since that time the patient has been agitated, disorganized, and incoherent. He states that she will not eat because she believes he has been poisoning her food, and she has not slept for the past 2 days. The patient believes that the nurses in the emergency room are going to cause her harm as well. The patient is sedated and later sent home. One week later, all her symptoms remit spontaneously. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis for this patient?
Brief psychotic disorder
Delirium
Schizophreniform disorder
Major depression with psychotic features
Posttraumatic stress disorder
A 25-year-old woman is diagnosed with schizophrenia when, after the sudden death of her mother, she begins complaining about hearing the voice of the devil and is suddenly afraid that other people are out to hurt her. Her history indicates that she has also experienced a 3-year period of slowly worsening social withdrawal, apathy, and bizarre behavior. Her family history includes major depression in her father. Which of the following details of her history leads the physician to suspect that her outcome may be poor?
She had an insidious onset of her illness
She is female
She was age 25 at diagnosis
She had an acute precipitating factor before she began hearing voices
There is a history of affective disorder in her family
A 22-year-old man is brought to the emergency room after he became exceedingly anxious in his college dormitory room, stating that he was sure the college administration was sending a “hit squad” to kill him. He also notes that he can see “visions” of men dressed in black who are carrying guns and stalking him. His thought process is relatively intact, without thought blocking or loose associations. His urine toxicology screen is positive for one of the following drugs. Which drug is the most likely cause of these symptoms?
Amphetamines
Barbiturates
Heroin
Benzodiazepines
MDMA (Ecstasy)
A 72-year-old woman is brought to the emergency room by her daughter after she found her mother rummaging in the garbage cans outside her home. The daughter states that the patient has never had any behavior like this previously. On interview, the patient states she sees “martians hiding around her home, and on occasion, hears them too.” She also demonstrates a constructional apraxia, with difficulty drawing a clock and intersecting pentagons. All of these symptoms point to a medical cause for this patient’s behavior except one. Which symptom is common in patients with a psychiatric cause for their behavior (ie, not a medical cause)?
Auditory hallucinations
Patient’s age
No previous history of this behavior
Visual hallucinations
Constructional apraxia
A 62-year-old man with chronic schizophrenia is brought to the emergency room after he is found wandering around his halfway house, confused and disoriented. His serum sodium concentration is 123 meq/L and urine sodium concentration is 5 meq/L. The patient has been treated with risperidone 4 mg/day for the past 3 years with good symptom control. His roommate reports that the patient often complains of feeling thirsty. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient’s symptoms?
Psychogenic polydipsia
Renal failure
Inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (ADH) secretion
Addison disease
Nephrotic syndrome
A 75-year-old man is being cared for in a hospice setting. He has widely spread prostatic carcinoma and is considered terminal. Which of the following psychiatric symptoms are seen in 90% of all terminal patients?
Delusions
Hallucinations
Flight of ideas
Anxiety
Depression
A 52-year-old man is seen by a psychiatrist in the emergency room because he is complaining about hearing and seeing miniature people who tell him to kill everyone in sight. He states that these symptoms developed suddenly during the past 48 hours, but that he has had them “on and off” for years. He states that he has never previously sought treatment for the symptoms, but that this episode is particularly bad. He denies the use of any illicit substances. The patient is alert and oriented to person, place, and time. His mental status examination is normal except for his auditory and visual hallucinations. His thought process is normal. His drug toxicology screen is positive for marijuana. He is quite insistent that he needs to be “put away” in the hospital for the symptoms he is experiencing. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Malingering
Substance-induced psychosis
Schizophrenia
Schizoaffective disorder
Schizophreniform disorder
A 25-year-old man is brought to the physician after complaining about a visual hallucination of a transparent phantom of his own body. Which of the following specific syndromes is this patient most likely to be displaying?
Autoscopic psychosis
Capgras syndrome
Lycanthropy
Cotard syndrome
Folie á deux
A 26-year-old man comes to the physician with the chief complaint of a depressed mood for the past 5 weeks. He has been feeling down, with decreased concentration, energy, and interest in his usual hobbies. Six weeks prior to this office visit, he had been to the emergency room for an acute asthma attack and was started on prednisone. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Substance-induced mood disorder
Mood disorder secondary to a general medical condition
Major depression
Adjustment disorder
Dysthymia
A 24-year-old woman, 5 days after delivery of a normal, full-term infant, is brought to the obstetrician because she is so tearful. She states that her mood is quite labile, often changing within minutes. She has trouble sleeping, both falling asleep and awakening early. She notes anhedonia, stating she doesn’t enjoy “much of anything” right now. Which of this patient’s symptoms point preferentially to a postpartum depression?
Anhedonia
Time that is, 5 days post-delivery
Tearfulness
Labile mood
Insomnia
A 28-year-old woman sees her physician with the chief complaint of a depressed mood. She also notes that she is sleeping more than usual––up to 14 hours per night––but does not feel rested and that she feels tired and fatigued all the time. She has gained 14 lb in the last month, something that she is very unhappy about, but she says that she seems to have such a craving for sweets that the weight gain seemed inevitable. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Seasonal affective disorder
Mood disorder secondary to a general medical condition
Substance-induced mood disorder
Cyclothymia
Dysthymic disorder
A 27-year-old woman has been feeling blue for the past 2 weeks. She has little energy and has trouble concentrating. She states that 6 weeks ago she had been feeling very good, with lots of energy and no need for sleep. She says that this pattern has been occurring for at least the past 3 years, though the episodes have never been so severe that she couldn’t work. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Cyclothymic disorder
Borderline personality disorder
Seasonal affective disorder
Major depression, recurrent
Bipolar disorder, depressed
A 19-year-old woman comes to the psychiatrist for a history of anger and irritability, which occurs on monthly on an average. During this time the patient also reports feeling anxious and “about to explode,” which alternates rapidly with crying spells and angry outbursts. The patient notes during this time she can’t concentrate and sleeps much more than she usually needs to do. During the several days these symptoms last, the patient must skip most of her classes because she cannot function. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Premenstrual dysphoric disorder
Adjustment disorder with depressed mood
Major depression
Dysthymic disorder
Depressive personality disorder
A 64-year-old man is admitted to the psychiatric unit after an unsuccessful suicide attempt. Following admission, he attempts to cut his wrists three times in the next 24 hours and refuses to eat or drink anything. He is scheduled to have electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) because he is so severely depressed that an antidepressant is deemed too slow acting. Which of the following side effects should the patient be informed is most common after ECT?
Headache
Palpitations
Deep venous thromboses
Interictal confusion
Worsening of the suicidal ideation
A 14-year-old boy is brought to the psychiatrist because for the past 15 months he has been irritable and depressed almost constantly. The boy notes that he has difficulty concentrating, and he has lost 5 lb during that time period without trying. He states that he feels as if he has always been depressed, and he feels hopeless about ever feeling better. He denies suicidal ideation or hallucinations. He is sleeping well and doing well in school, though his teachers have noticed that he does not seem to be able to concentrate as well as he had previously. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Dysthymic disorder
Major depression
Mood disorder secondary to a general medical condition
Normal adolescence
Cyclothymia
A 45-year-old woman comes to her physician for help with her insomnia. She states “ever since my husband died, I just can’t sleep.” The patient states her 57-year-old husband died suddenly of a heart attack 9 weeks ago. Since that time, the patient has had a very depressed mood, had been crying, has lost interest in activities, is fatigued, and has insomnia. Which of the following symptoms, if present, should make the physician think this patient has a major depression instead of bereavement?
The patient has marked functional impairment
The patient feels that she would be better off dead
The patient has lots of guilt about not recognizing that the chest pain her husband was having was the start of a heart attack
The patient has mild psychomotor retardation
The patient reports hearing the voice of her dead husband calling her name twice
A 32-year-old man is being treated for a severe major depression. Which of the following symptoms, if present, is one of the most accurate indicators of long-term suicidal risk?
Hopelessness
Revenge fantasies
Presence of rage in the patient
Presence of guilt
The patient has a need for punishment
A 44-year-old white male presents with a long history of joint pains in several joints. He has seen a physician before but no diagnosis was made. He has been taking ibuprofen with partial relief. He has now developed fever, diarrhea and weight loss. He denies any genitourinary or eye symptoms. He does not use tobacco, alcohol or drugs. He is a farmer. On examination, he has generalized lymphadenopathy and non-deforming arthritis. Small intestinal biopsy reveals periodic Acid-Schiff (PAS)-positive macrophages. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Whipple's disease
Reactive arthritis
Sarcoidosis
Inflammatory bowel disease
Celiac disease
A 33-year-old tennis player comes to you with a complaint of pain in his right shoulder. He says that the pain is absent at rest but present when he lifts his arm over his head. The pain is compromising his play. On examination, active motion at right shoulder is limited due to pain. Pain is most severe on passive internal rotation and flexion at the right shoulder. No atrophy of the shoulder muscle is seen. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
Subacromial bursitis
Tear of long head of bicep tendon
Tennis elbow
Anterior dislocation of shoulder
Axillary nerve palsy
A 75-year-old white male comes to the physician's office for his routine health maintenance examination. He has no symptoms. He has a past medical history significant for hypertension and hyperlipidemia. He takes aspirin, hydrochlorothiazide and simvastatin. He does not smoke and consumes 1-2 beers on weekends. He walks 2 miles every morning and eats a balanced diet. His vital signs are within normal limits. His chest is clear to auscultation, and his abdomen is soft and nontender. Rectal examination shows a diffusely enlarged, firm prostate without nodules. Stool for occult blood is negative. The distal interphalangeal joints are enlarged, and his gait is normal. His labs are as follows: Total bilirubin 1.0 mg/dl, Alkaline phosphatase 420 U/L, Aspartate aminotransferase (SGOT) 20 U/L, Alanine aminotransferase (SGPT) 25 U/L, Serum creatinine 0.8 mg/dl, Calcium 8.8 mg/dl, Serum PSA 2.1 ng/ml. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the elevated alkaline phosphatase in this patient?
Paget's disease of bone
Metastatic bone disease
Plasma cell neoplasia
Simvastatin
Alcohol use
A 21-year-old Caucasian female presents with a one-week history of low-grade fever and joint pain. She describes symmetric swelling of the small hand joints. Her rheumatoid factor tests positive, and antinuclear antibodies are weakly positive at a 1:40 dilution. She is treated with NSAIDs. Four weeks later, the patient reports not taking the prescribed drugs since she feels no pain. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Viral arthritis
Septic arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis
Crystalline arthritis
Systemic lupus erythematosus
A 64-year-old male comes to the physician's office because of increasing pain in his right groin for the past several months. The pain increases with activity and is relieved with rest. He also has difficulty moving after a period of rest. He denies any trauma or falls. He has no fever, weight loss or loss of appetite. He has had lumbar disk herniation in the past but denies any current back pain. He has no other active medical problems. His vital signs are within normal limits. He weighs 95 kg (210 lb) and is 168 cm (66 in) tall. Examination shows pain on passive internal rotation of right hip joint. Direct pressure over the groin did not increase the pain. His reflexes are 2+, and there are no sensory deficits. Muscle bulk, tone and power are within normal limits. Pulses are 2+ in both legs. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his hip pain?
Degenerative joint disease
Cutaneous nerve compression
Inflammation of the trochanteric bursa
Disruption of bone vasculature
Referred pain from the lumbosacral area
A 36-year-old female who is currently having regular menstrual periods comes to the emergency room because of malaise and a high-grade fever with chills. She also complains of pain in multiple joints. She always uses highly absorbent tampons during her menses. She uses intravenous heroin and cocaine and works as a prostitute. Her temperature is 39.3°C (103.4°F), pulse is 102/min, blood pressure is 120/80mmHg and respirations are 14/min. Examination shows multiple pustules on the extensor surfaces of her forearms. Joint examination does not show redness, swelling or tenderness. Three sets of blood cultures are negative Based on these findings, which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
Disseminated gonococcal infection
Infective endocarditis
Toxic shock syndrome
Acute HIV infection
Secondary syphilis
A 54-year-old retired schoolteacher comes to the physician's office because of worsening low back pain. The pain started three weeks ago. It is continuous and is worse at night. He has had little relief with over-the-counter nonsteroidal analgesics. He has no other symptoms. He had a surgical resection of a lung tumor one year ago for non-small cell carcinoma of the lung. Preoperative positron emission tomography (PET) scanning did not reveal any evidence of metastasis. His vital signs are within normal limits. Examination shows local spinal tenderness at the L4-L5 level. What is the most likely cause of his back pain?
Metastatic disease
Lumbar strain
Central spinal canal stenosis
Disc herniation
Vertebral compression fracture
A 60-year-old man presents to the emergency department after being awoken from sleep by severe pain in his right great toe. He reports that his toe is suddenly swollen and very tender to touch. On review of systems, the patient also describes occasional headaches and pruritus that can be "unbearable" after a hot bath. He does not smoke or drink alcohol. On physical examination, his lungs are normal. The liver span is 10 cm and the spleen is palpable 2 cm below the costal margin. Aspiration of the affected toe joint reveals negatively birefringent crystals. Which of the following is most likely responsible for this patient's symptoms?
Myeloproliferative disorder
Chronic kidney disease
Hemochromatosis
Inherited enzyme deficiency
Hyperparathyroidism
A 29-year-old woman presents to your office complaining of easy fatigability over the last several months. She tires easily after walking short distances. She also has difficulties combing her hair due to an inability to hold her hands over her head for a long time. She reports a weight loss of two or three pounds over the last two months. She denies fever or loss of appetite. She does not smoke or consume alcohol. On family history, her father died of a stroke when he was 54 years old and her mother has diabetes mellitus. On examination, she is afebrile with a pulse of 105/min. Cardiac exam reveals regular rhythm with no murmur. Her gait is normal but, when asked to sit down slowly, she drops into the chair. A fine finger tremor is evident when she extends her arms. Her muscles are non-tender to palpation. She appears to have decreased muscle mass in her shoulders. Deep tendon reflexes are normal. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
Thyroid disease
Upper motor neuron disease
Polyneuropathy
Inflammatory muscle disease
Cerebellar dysfunction
A 62-year-old male treated for hypertension and hyperlipidemia complains of nagging right knee pain that is worse in the evening. The pain has been present for several months and it seems to limit his physical activities. His blood pressure is 160/100 mmHg and his heart rate is 70/min. His BMI is 32 kg/m2, and palpation of the knee reveals a cool joint with bony tenderness. His blood cholesterol level is 200 mg/dl and his serum uric acid level is 9.0 mg/dl. Which of the following additional findings is likely on further examination of the right knee?
Bony crepitus
Soft tissue swelling
Painful tibial tuberosity
Palpable popliteal mass
Subcutaneous nodules
A 34-year-old man complains of back tightness and persistent low back pain. The pain has a dull and aching quality. It is worse during the night and in the morning but improves gradually during the day. He has no significant past medical history. He does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. He is married and lives with his wife. His pulse is 80/min, respirations are 14/min, and blood pressure is 120/76 mmHg. Which of the following most likely accounts for this patient's symptoms?
Apophyseal joint arthritis
Ligamentous sprain
Lumbar disk degeneration
Nerve root demyelinization
Abnormal bone mineralization
A 34-year-old woman with a skin rash, joint pains, and oral ulcers is diagnosed with systemic lupus erythematosus. She has no renal or central nervous system involvement, and her past medical history and review of systems are otherwise negative. Therapy with hydroxychloroquine is started. Which of the following screening tests is most important in this patient?
Eye examination
Complete blood count
Liver function panel
Urinalysis
Audiometry
A 68-year-old man with hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and diabetes is hospitalized for an acute myocardial infarction. It is complicated by pulmonary edema and he undergoes angiography of the left anterior descending artery. On post-operative day 3, he complains of abdominal pain and discoloration of his toes. His vital signs are stable. Examination shows bluish discoloration of his right great toe and of all the toes on his left foot. The skin over the toes is cold and clammy. Bilateral pedal pulses are present and full. His abdomen is soft and mildly tender at the center. Chest auscultation is clear. Laboratory studies show a rise in creatinine to 2.3 g/dl from his baseline of 1.2 g/dl. An EKG shows sinus rhythm and Q waves in anterior leads. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his toe discoloration?
Cholesterol embolism
Ketoacidosis
Vasospasm
Right to left shunt
Autoimmune vasculitis
A 32-year-old man presents to the clinic with one week of escalating lower back pain. He describes the pain as dull and aching. It increases with motion and it is not completely relieved by rest. He has no significant past medical history. He smokes one pack of cigarettes per day and consumes alcohol occasionally. He admits to being "under a lot of stress" and has recently used injectable drugs. His family history is significant for prostate cancer in his father. His temperature is 36.7°C (98°F), pulse is 90/min, respirations are 16/min, and blood pressure is 120/80 mmHg. Gentle percussion over the lumbar vertebrae elicits pain. A full neurologic exam including straight leg raise is normal. Laboratory results are shown below: Complete blood count: Leukocyte count 6,500/mm3, Hematocrit 46%, Platelets 400,000/mm3. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Vertebral osteomyelitis
Ankylosing spondylitis
Lumbar disk herniation
Lumbar spinal stenosis
Vertebral compression fracture
A 35-year-old African-American woman comes to the physician's office complaining of blurred vision, cough and shortness of breath. For the past few days she has had mild fevers, malaise and easy fatigability. She has never had these symptoms before and is anxious to uncover a diagnosis. She was recently incarcerated for two months. She practices unprotected sex with her new boyfriend. Her temperature is 37.2°C (98.9°F) and her blood pressure is 116/80 mmHg. On exam, her right eye is red and slit lamp examination shows leukocytes in the anterior chamber. Lungs have patchy rales. Chest x-ray shows bilateral reticulonodular infiltrates and hilar adenopathy. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
Sarcoidosis
Acute HIV infection
Disseminated tuberculosis
Histoplasmosis
Ankylosing spondylitis
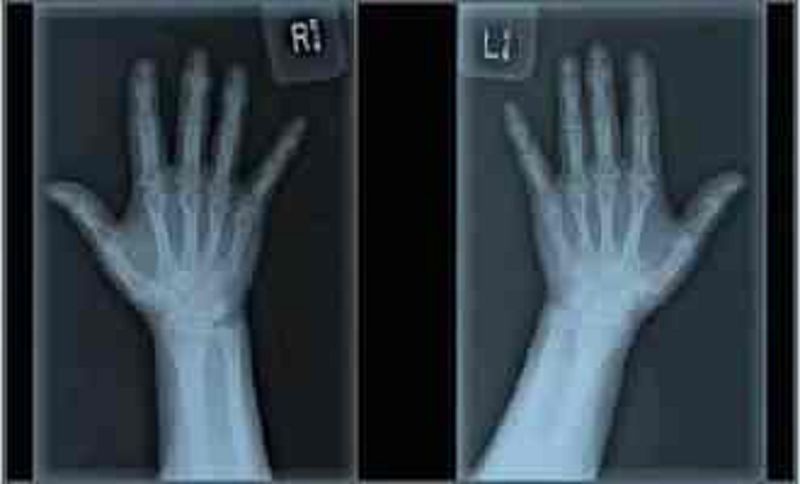
A 60-year-old Caucasian woman comes to the physician because of joint pains in both hands. Her other medical problems include obesity and gastroesophageal reflux disease. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or drugs. Family history is not significant. Her medications include omeprazole and acetaminophen. Her vital signs are within limits. X-ray of the joints is shown below. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Osteoarthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Reactive arthritis
Gouty arthritis
A 67-year-old male hospitalized after elective hernia repair complains of severe right knee pain. Physical examination reveals redness and swelling of the right knee with limited motion due to pain. His temperature is 38.9°C (102°F), blood pressure is 160/110 mm Hg, pulse is 80/min, and respirations are 16/min. Synovial fluid analysis reveals the following findings: WBC count 30,000mm3, Neutrophils 90%, Crystals rhomboid-shaped, positively birefringent, Gram stain negative. Which of the following is most likely associated with this patient's current condition?
Chondrocalcinosis
Tophi
Transient bacteremia
Rheumatoid factor
Heberden nodes
A 43-year-old Caucasian female presents to your office complaining of joint pain and swelling in her hand. On history, she endorses easy fatigability and loss of energy that has been worsening insidiously. It is especially difficult for her to do daily activities in the morning due to prolonged stiffness. She also describes frequent knee pain accompanied by a low-grade fever. She takes ibuprofen and naproxen to relieve her symptoms. Her hematocrit is 33%. The patient is at the greatest risk of which of the following?
Osteoporosis
Osteitis fibrosis cystica
Osteitis deformans
Avascular bone necrosis
Osteomalacia
A 32-year-old Caucasian male complains of inability to grip his cup of coffee and hold a pen in the morning. He says that he is 'fully functional' in the afternoon. His ESR is 45 mml hr. Which of the following is most likely to be affected by this patient's disease?
Cervical spine
Sacral spine
Sacroiliac joints
Lumbar spine
Thoracic spine
A 21-year-old woman presents with 4 months of slowly progressive low back pain. Her back pain is associated with early morning stiffness that improves as the day progresses. She has no fever or gastrointestinal complains. She denies any recent illness. On examination, there is limited range of motion of her back. Other examination is unremarkable. Plain X-ray films show bilateral sacroiliitis. Which of the following conditions is this patient at greatest risk of developing?
Anterior uveitis
Aortic coarctation
Thoracic aortic aneurysm
Renal failure
Oral ulcers
A 30-year-old female comes to your office with a complaint of pain over the lateral side of her wrist for the last four days. She is two months postpartum and notes that her pain is most severe when she lifts her infant from a crib. On examination, there is tenderness over the radial side of wrist and first dorsal compartment. Passive stretching of the thumb tendons over the radial styloid while the thumb is held in flexion aggravates the pain. She denies any recent trauma over the tender area. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
De Quervain tenosynovitis
Osteoarthritis of first metacarpophalangeal joint
Trigger thumb
Scaphoid fracture
Flexor carpi radialis tenosynovitis
A 44-year-old female complains of generalized weakness, low-grade fever and joint pain. Her daily activities are limited due to joint stiffness, especially in the morning. Her hand joints are swollen symmetrically. The inferior pole of the spleen is palpable on physical examination. Her hematocrit is 34%. Liver and renal function tests are normal. Two months after the initial visit, the patient develops painful oral ulcers. Her laboratory values are: Hematocrit 33%, AST 120 U/L, ALT 90 U/L, Alkaline phosphatase 90 U/L, Bilirubin 1.1 mg/dl, Creatinine 0.8 mg/dl, BUN 16 mg/dl. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's current complaints?
Antimetabolite agent
Viral hepatitis
Felty syndrome
Lymphoid cell proliferation
Corticosteroid treatment
A 35-year-old woman presents with complaints of aching pain and stiffness over her entire body for the past 3 months. She also reports, easy fatigability, poor sleep and frequent headaches. She has been using over the counter pain medications with no relief. While examining her, she complains of extreme pain to gentle palpation over her neck, shoulders and back. Her vital signs are stable. What is your diagnosis?
Fibromyalgia.
Chronic fatigue syndrome
Polymyalgia rheumatica
Rheumatoid arthritis
Polymyositis.
A 25-year-old immigrant from Eastern Europe is being evaluated for right shoulder pain and swelling. He also complains of heel pain while walking. Palpation over the heels, iliac crests and tibial tuberosities elicits tenderness. Which of the following additional findings is most likely in this patient?
Limited spine mobility
Positive rheumatoid factor
Proteinuria
Subcutaneous nodules
Hand joint deformities
A 9-year-old Caucasian male complains of fever, sore throat and difficulty swallowing. Small tender lymph nodes are palpated in the cervical region. The symptoms subside quickly on penicillin therapy. Ten days later, the patient presents again with fever, skin rash and fleeting joint pain in the lower extremities. Physical examination reveals scattered urticaria and palpable lymph nodes in the cervical, axillary and inguinal regions. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's current complaints?
Drug-induced reaction
Rheumatic fever
Lymphoproliferative disorder
Henoch-Schonlein purpura
Infective endocarditis
A 66-year-old man comes to the physician's office complaining of progressive lower back pain. Over-the-counter ibuprofen has provided him with moderate relief. The back pain is associated with bilateral leg pain that is precipitated by walking. The pain improves upon lying down or sitting. He has no pain at night, and no problems with bowel and bladder function. He underwent coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) 6 years ago for a 3-vessel coronary artery disease. His medications include aspirin, enalapril, atenolol, and lovastatin. Physical examination shows normal strength, reflexes and sensation in his legs. A straight leg raise test fails to reproduce pain. His femoral, popliteal and pedal pulses are full bilaterally and he has no bruits. Plain films of the lumbosacral spine show degenerative changes of the vertebrae. Ankle brachial index measurement is within normal limits. Which of the following is most likely responsible for his current condition?
Spinal canal narrowing
Atherosclerosis
Bulging disc
Vertebral metastasis
Spinal cord compression
A 35-year-old female presents with a complaint of oral ulcers that are extremely painful. She had a similar presentation three months ago and the ulcers healed without any scarring. Her medical history includes a recent visit to the ophthalmologist with complaints of blurred vision and she is now being treated for anterior uveitis. She has also had recurrent painful ulcers in her genital area for which she has regular follow-up with her gynecologist. On examination, you notice many hyper-pigmented areas over her extremities and few painful, nodular lesions. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Behcet's syndrome
Sarcoidosis
Reiter's Syndrome
Herpes simplex infection
Systemic lupus erythematosus
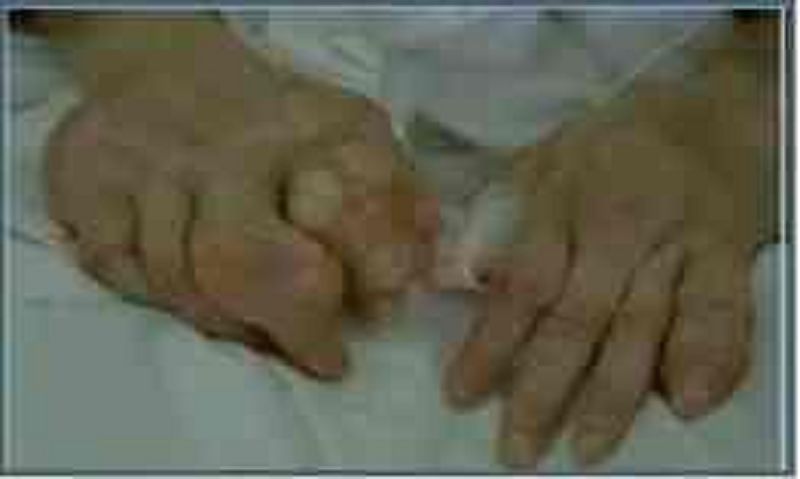
A 71-year-old female is brought to your clinic by her daughter with a complaint of severe pain in her fingers. Her daughter says, "Mom has horrible problems with her joints and she has never tried to get help". The patient adds that her fingers have been swollen and painful for a few weeks. She claims that she had a similar condition in her foot last year. She was given a pain pill, but it was ineffective. She takes a water pill for her blood pressure. What is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
Gouty arthritis
Rheumatoid nodules
Severe osteoarthritis
Bone tumor
Severe psoriatic arthritis
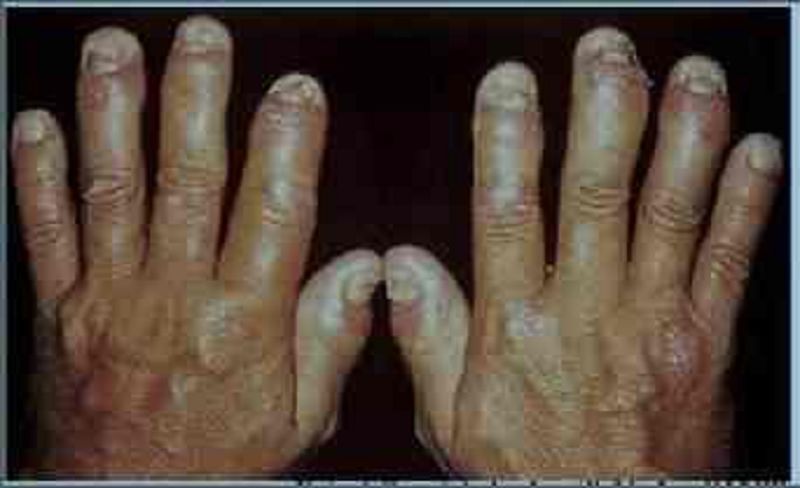
A 52-year-old male presents with a long history of joint pain. He describes pain and stiffness of the small joints of his hand that is worse in the morning and can last several hours. He also complains of occasional digit swelling. A picture of the patient's hands is shown on the slide below. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Psoriatic arthritis
Enteropathic arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis
Crystalline arthritis
Sarcoidosis
A 30-year-old white male presented to your office with low back pain and stiffness. His pain is worse in the morning and is improved with activity. He has also been having bloody diarrhea for the past few days. On examination, he has painful erythematous nodules over his shins. Pain and stiffness is present in his lower back. Plain radiographs show sacroiliac joint inflammation. Stool cultures are negative. Laboratory studies show anemia and thrombocytosis. P-ANCA is positive in high titers. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his symptoms?
Inflammatory bowel disease
Reactive arthritis from diarrhea
Infection with T ropheryma whippelii
Gluten-sensitive enteropathy
Infection with Giardia Iamblia
A 42-year-old male presents to your office complaining of back pain that started two days ago after carrying heavy packages. He denies any weakness or sensory changes in his legs. His past medical history is insignificant. He is not taking any medications and denies drug abuse. His temperature is 36.7°C (98°F), blood pressure is 120/76 mmHg, pulse is 80/min, and respirations are 16/min. Physical examination reveals paravertebral tenderness. Lower extremity power is 5/5 and the deep tendon reflexes are 2+. Babinski's sign is negative. Straight-leg raising test is negative at 90 degrees. What is the most probable diagnosis in this patient?
Lumbosacral strain
Multiple myeloma
Ankylosing spondylitis
Compression fracture of the vertebrae
Herniated disk
A 30-year-old obese woman comes to the emergency department complaining of four days of progressive pain, swelling and redness of her right leg. She has no obvious trauma or insect bites. She does not use tobacco, alcohol or illicit drugs. Her temperature is 38.7°C (103.0°F), pulse is 106/min, and blood pressure is 130/80 mmHg. Her right calf is swollen, erythematous, and extremely tender and warm to the touch over a 6 x 3 cm region. There is a tender, palpable mass in her right groin. There is no overlying crepitus and no bullae are seen. The toe webs are fissured and macerated. Laboratory studies show: Complete blood count: Hemoglobin 14.0 g/L, Platelets 222,000/mm3, Leukocyte count 14,500/mm3, Neutrophils 86%, Lymphocytes 14%, Which of the following is the most likely cause of her current leg condition?
Cellulitis
Arterial thrombosis
Deep venous thrombosis
Necrotizing fascitis
Ruptured Baker's cyst
A 27-year-old African-American woman presents with several complaints. She has had pain and swelling of her hands and wrists for the past few days. She also complains of easy fatigability and frequent mouth ulcers. She has no significant past medical history and does not take any medications. Her temperature is 37.1°C (98.9°F), blood pressure is 140/90mmHg, and pulse is 76/min. Examination reveals swollen, tender metacarpophalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joints. There are superficial ulcers on her buccal mucosa. X-ray of hands and wrists shows no bony erosions. Laboratory studies show: Hemoglobin 11.0 g/L, Platelets 90,000/mm3, Leukocyte count 4,500/mm3. Urinalysis shows 2+ protein and red blood cell casts. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her joint pains?
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Dermatomyositis
Sarcoidosis
Neuropathic joint disease
Systemic iron overload
A 63-year-old painter presents with pain in his right shoulder for the past few weeks. He experiences pain when he tries to reach for objects and he is unable to lift his arm above his head. He denies trauma to the shoulder, fevers, chills and weight loss. Vital signs are within normal limits. On exam, the physician raises the patient's arm while asking him to relax the shoulder. At 60 degrees, the patient begins to shrug his shoulder and complain of pain. In spite of the pain, his range of motion is normal. A lidocaine injection into the shoulder leads to a significant decrease in pain upon lifting the arm. Which of the following is most likely responsible for his current condition?
Rotator cuff impingement
Rotator cuff tear
Adhesive capsulitis
Crystal arthritis
Bacterial infection
A 22-year-old Caucasian female comes to your office complaining of difficulty swallowing. She says that solid food sticks in the middle of her chest, and that's why she prefers liquids. She has lost 10 pounds over the last 3 months. She also complains of recent severe heartburn that does not respond well to over-the-counter antacids. On review of systems, she denies cough, shortness of breath and palpitations. She has noticed occasional swelling and pain in her small finger joints. Her fingers turn blue upon cold exposure, and she always wears gloves to keep them warm. She does not smoke or drink alcohol. She denies illegal drug use. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
CREST syndrome
Esophageal neoplasm
Achalasia
Diffuse esophageal spasm
Rheumatoid arthritis
A 28-year-old woman presents to her physician's office because of pain in her left knee joint. She reports having mild discomfort and pain in right wrist 4 days ago and left ankle pain two days ago. She denies any recent respiratory illness, diarrhea, or urinary symptoms. She has no vaginal discharge. She has no previous medical problems and does not take any medications. She drinks half a pint of vodka daily but denies intravenous drug abuse. She is single and sexually active. Her last menstrual period was one week ago. Her temperature is 38.5°C (101.3°F), blood pressure is 120/80 mmHg, pulse is 98/min, and respirations are 15/min. Examination of the knee reveals warmth, tenderness, decreased range of motion, and an effusion. No skin lesions are present and her pelvic examination is unremarkable. Synovial fluid analysis shows a white blood cell count of 75,000/microl. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her symptoms?
Gonococcal septic arthritis
Non-gonococcal septic arthritis
Acute rheumatic fever
Acute HIV infection
Crystal induced arthritis
A 45-year-old tennis player comes to your office with a complaint of pain over the lateral side of the right elbow. He has been a professional tennis player for 15 years but has never had this kind of pain before. Range of motion at both elbows is normal. There is point tenderness over the lateral side of the distal end of right humerus. Pain is exacerbated by extension of wrist against resistance. The rest of the physical examination is normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
Lateral epicondylitis
Rotator cuff injury
Radial tunnel syndrome
Rupture of long head of biceps tendon
Posterior interosseous nerve entrapment
A 65-year-old man complains of periodic back pain radiating to his thigh and buttock. The pain is related to walking or climbing the stairs but is promptly relieved by leaning forward. He also has noticed tingling and numbness in both lower extremities. He has a history of hypertension and takes hydrochlorothiazide. He does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. His pulse is 76/min, respirations are 14/min, and blood pressure is 140/80 mmHg. Lumbar extension reproduces the pain and tingling, while lumbar flexion relieves the symptoms. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
Degenerative central canal stenosis
Iliac artery atherosclerosis
Abdominal aortic aneurysm
Lumbar disk herniation
Spina bifida occulta
A 51-year-old Caucasian female complains of low-back pain radiating to the buttocks. She also complains of persistent muscle pain that gets worse with exercise. Physical examination reveals normal muscle strength. Her joints are not swollen, but palpation over the outer upper quadrants of the buttocks and the medial aspect of the knees elicits tenderness. Her ESR is 12mm/hr. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Fibromyalgia
Seronegative spondyloarthropathy
Polymyalgia rheumatica
Polymyositis
Rheumatoid arthritis
A 27-year-old male presents to the physician's office because of pain on the medial side of the tibia just below the knee. The pain does not radiate and is continuous. He relates the onset of his pain to falling on the ground while playing football two weeks ago. He denies fever, malaise and weight loss. His past medical history is not significant. On examination, a well-defined area of tenderness is present on the upper tibia below the medial knee joint. There is no redness, warmth or swelling. His gait is normal. A valgus stress test has no effect on his pain. X-ray of the knee and tibia shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his current symptoms?
Anserine bursitis
Prepatellar bursitis
Medial collateral ligament strain
Patellofemoral syndrome
Medial compartment osteoarthritis
A 16-year-old boy presents with a seven-month history of intermittent right knee pain and swelling. He states that his discomfort first began after a baseball injury. This injury was associated with pain, swelling, and restriction of movement in his right knee. He has had three subsequent episodes of pain and swelling in his right knee, not precipitated by trauma. The last episode occurred three days ago. He denies history of fevers or chills. There is no history of recent travel, other than a camping trip with his friends to Long Island, New York a few months ago. On physical examination, he has a marked effusion of his right knee and is unable to fully flex or extend his leg. X-ray reveals no bony abnormalities. What is the most probable diagnosis?
Lyme arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis
Septic arthritis
Reactive arthritis
Osteomyelitis
A 75-year-old female comes to the emergency room with acute onset of severe back pain. The pain started while lifting a turkey from the freezer. She had no obvious trauma preceding the pain. She denies weakness or sensory loss in the legs. Her past medical history is significant for temporal arteritis diagnosed several months ago and has been taking prednisone. She does not smoke or consume alcohol. Her temperature is 36.7°C (98°F), blood pressure is 140/70 mmHg, pulse is 80/min, and respirations are 16/min. Physical examination reveals local tenderness of the lumbar spine area. Bilateral ankle reflex is absent. Knee reflex is 2+ in both legs. Babinski's sign is absent bilaterally. Muscle power is 5/5 in both legs. Bilateral straight-leg raising to 90 degrees does not increase the pain What is the most probable diagnosis in this patient?
Compression fracture of the vertebrae
Multiple myeloma
Ankylosing spondylitis
Lumbosacral strain
Herniated disk
A 66-year-old man complains of a 1-year history of low-back and buttock pain that worsens with walking and is relieved by sitting or bending forward. He has hypertension and takes hydrochlorothiazide but has otherwise been healthy. There is no history of back trauma, fever, or weight loss. On examination, the patient has a slightly stooped posture, pain on lumbar extension, and has a slightly wide base gait. Pedal pulses are normal and there are no femoral bruits. Examination of peripheral joints and skin is normal. What is the most likely cause for this patient’s back and buttock pain?
Lumbar spinal stenosis
Herniated nucleus pulposus
Atherosclerotic peripheral vascular disease
Facet joint arthritis
Prostate cancer
A 22-year-old man develops the insidious onset of low-back pain improved with exercise and worsened by rest. There is no history of diarrhea, conjunctivitis, urethritis, rash, or nail changes. On examination, the patient has loss of mobility with respect to lumbar flexion and extension. He has a kyphotic posture. A plain film of the spine shows sclerosis of the sacroiliac joints. Calcification is noted in the anterior spinal ligament. Which of the following best characterizes this patient’s disease process?
The patient has a spondyloarthropathy, most likely ankylosing spondylitis
He is most likely to have acute lumbosacral back strain and requires bed rest
The patient is likely to die from pulmonary fibrosis and extrathoracic restrictive lung disease
A rheumatoid factor is likely to be positive
A colonoscopy is likely to show Crohn disease
A 20-year-old man complains of arthritis and eye irritation. He has a history of burning on urination. On examination, there is a joint effusion of the right knee and a rash of the glans penis. Which of the following is correct?
An infectious process of the GI tract may precipitate this disease
Neisseria gonorrhoeae is likely to be cultured from the glans penis
The patient is likely to be rheumatoid factor—positive
An ANA is very likely to be positive
CPK will be elevated
Last week a 20-year-old college student developed acute wrist pain and swelling. This resolved in four days. Yesterday, he developed pain and swelling in his left knee. Two months ago he went on a backpacking trip in Rhode Island. A week or so later he developed an enlarging circular red spot that persisted for 2 weeks and then resolved. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Lyme disease
Acute rheumatoid arthritis
Parvovirus infection
Psoriatic arthritis
Inflammatory bowel disease
A 38-year-old man has pain and stiffness of his right knee. This began 2-weeks ago after he fell while skiing. On two occasions he had the sense that his knee was locked in a semiflexed position for a few seconds. He has noted a popping sensation when he bends his knee. On examination there is tenderness over the medial joint line of the knee. Marked flexion and extension of the knee are painful. The Lachman test (anterior displacement of the lower leg with the knee at 20°of flexion) and the anterior drawer test are negative. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Medial meniscus tear
Osteoarthritis
Anterior cruciate ligament tear
Chondromalacia patella
Lumbosacral radiculopathy
A 63-year-old painter complains of severe right shoulder pain. The pain is located posteriorly over the scapula. These symptoms began after he fell from a ladder 2 weeks ago. The pain is especially bad at night and makes it difficult for him to sleep. In addition, he has had some pain in the right upper arm. Treatment with acetaminophen and ibuprofen has been unsuccessful in controlling his pain. On examination the patient appears uncomfortable. The right shoulder has full range of motion. Movement of the shoulder is not painful. There is no tenderness to palpation of the scapula. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Cervical radiculopathy
Subdeltoid bursitis
Rotator cuff tendonitis
Adhesive capsulitis
Osteoarthritis
A 50-year-old woman with rheumatoid arthritis has been treated with meloxicam (Mobic). You add hydroxychloroquine. Six weeks later her arthritis is mildly improved. The same joints are still involved but she now reports only 1-hour morning stiffness. She has, however, developed epigastric burning and melena for the past 3 days. Stool is strongly positive for occult blood. Which of the following is the most likely cause for the melena in this case?
NSAID gastropathy
Emotional stress over her illness resulting in acid peptic disease
Hydroxychloroquine-induced acid peptic disease
Gastric lymphoma associated with autoimmune disease
Meckel diverticulum
A 55-year-old woman with long-standing rheumatoid arthritis is on prednisone 5 mg daily and etanercept (Enbrel) 50 mg subcutaneously once a week. Her arthritis is well-controlled. However, she complains of a 2-day history of headaches, chills, and spiking fevers to 39.4°C (103°F). You suspect which of the following?
A serious infection
An allergic febrile reaction to etanercept
Fever related to her underlying autoimmune disease
A viral syndrome
An occult malignancy
A 32-year-old Japanese woman has a long history of recurrent aphthous oral ulcers. In the last 2 months she has had recurrent genital ulcers. She now presents with a red painful eye that was diagnosed as anterior uveitis. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Behçet disease
Herpes simplex
HIV infection
Diabetes mellitus
Systemic lupus erythematosus
A 53-year-old man presents with arthritis and bloody nasal discharge. Urinalysis reveals 4+proteinuria, RBCs, and RBC casts. ANCA is positive in a cytoplasmic pattern. Antiproteinase 3 (PR3) antibodies are present, but antimyeloperoxidase (MPO) antibodies are absent. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Wegener granulomatosis
Behçet syndrome
Sarcoidosis
Henoch-Schönlein purpura
Classic polyarteritis nodosa
A 35-year-old right-handed construction worker presents with complaints of nocturnal numbness and pain involving the right hand. Symptoms wake him and are then relieved by shaking his hand. There is some atrophy of the thenar eminence. Tinel sign is positive. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Carpal tunnel syndrome
De Quervain tenosynovitis
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Rheumatoid arthritis of the wrist joint
Guillain-Barré syndrome
A 50-year-old white woman presents with aching and stiffness in the trunk, hip, and shoulders. There is widespread muscle pain after mild exertion. Symptoms are worse in the morning and improve during the day. They are also worsened by stress. The patient is always tired and exhausted. She has trouble sleeping at night. On examination, joints are normal. ESR is normal, and Lyme antibody and HIV test are negative. A diagnosis is best made by which of the following?
Demonstration of 11 tender points
Trial of glucocorticoid
Muscle biopsy
Psychiatric evaluation
Trial of an NSAID
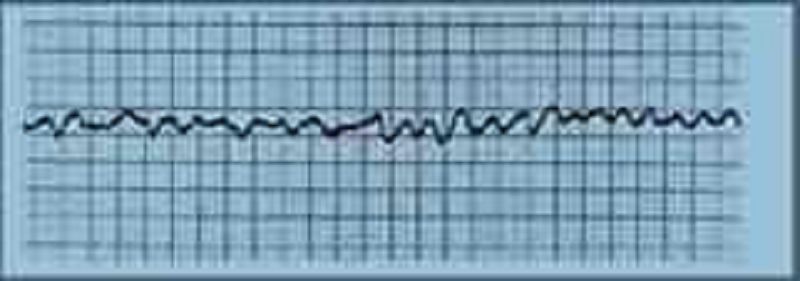
A 72-year-old female is admitted to the ICU with severe chest pain. The initial set of cardiac enzymes is positive and her EKG reveals an anterior wall myocardial infarction. She receives treatment with aspirin clopidogrel, metoprolol nitroglycerine drip, and morphine. Two hours later, her telemetry monitor displays the following rhythm. Which of the following is the best next step in managing this patient?
Defibrillation
Lidocaine
Digoxin
Amiodarone
Immediate echocardiogram
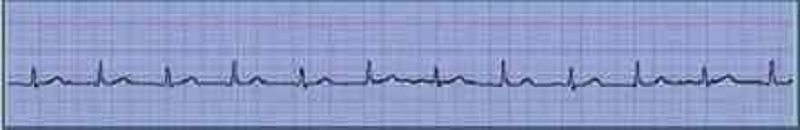
A 46-year-old man collapsed while getting out of his bed. He has been feeling weak over the last several days and has complained of vague chest discomfort. He ascribed the symptoms to a recent respiratory infection and did not visit a doctor. His mother died of a stroke and his father suffered from recurrent myocardial infarctions. He eats a balanced diet and takes a multivitamin daily. His most recent blood cholesterol level was 200 mg/dl. An ECG strip taken by EMS is shown below. Which of the following is the best initial management of this patient?
Pericardiocentesis
Procainamide
Synchronized DC cardioversion
Thrombolytic therapy
Beta-blockers and aspirin
A 67-year-old Caucasian male is hospitalized in the intensive care unit (ICU) with an episode of prolonged hypotension and shortness of breath. His skin is cold and clammy. Intra-arterial blood pressure monitoring is established, and pulmonary artery catheterization is performed to control basic hemodynamic parameters. His blood pressure is 70/40 mmHg, and heart rate is 100/min. Cardiac output (CO) measured by thermodilution method is 2.3 L/min. Pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP) is estimated to be 22 mmHg. Systemic vascular resistance (SVR) calculated using data on mean arterial pressure, right atrial pressure and cardiac output is 2000 dynes*s/cm5 (N= 700 -1200 dynes*s/cm5). Which of the following is the most likely underlying problem in this patient?
Cardiogenic shock
Volume depletion
Septic shock
Volume overload
Right ventricular infarction
A 59-year-old man comes to visit his friend in the hospital and collapses in the parking lot. He had been feeling unwell all day due to vague chest discomfort. A bystander witnesses his collapse, finds no pulse, and immediately calls for help. Which of the following is the most important factor for survival in this patient?
Time to defibrillation
Time to chest compressions
Time to endotracheal intubation
Time to epinephrine injection
Time to cardiac catheterization lab
A 59-year-old male presents to the ER with sudden onset severe chest pain associated with vomiting and diaphoresis. The pain radiates to the left shoulder and is not relieved by sublingual nitroglycerine. His past medical history is significant for diabetes mellitus for seven years and hypercholesterolemia for six years. His medications include metformin, glipizide and simvastatin. On physical examination, his blood pressure is 150/98 mmHg and pulse is 86/min. An EKG obtained in the ER shows ST segment elevations in leads aVL and I. Cardiac troponin and CK-MB are elevated. Which of the following medications should be avoided in this patient at this time?
Nifedipine
Heparin
Captopril
Metoprolol
Aspirin
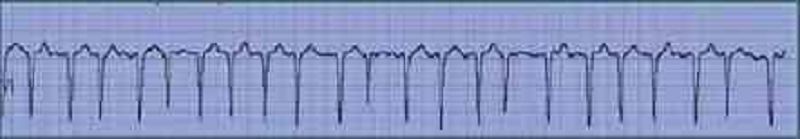
A 69-year-old male undergoes coronary artery bypass and aortic valve replacement surgery. The procedure goes well, and he is extubated and discharged to the step-down unit on postoperative day 2. That night, he complains of weakness, chest tightness and shortness of breath. His blood pressure is 70/30 mmHg, respiratory rate is 26/min, and heart rate is 148 beats per minute. Lung auscultation reveals bibasilar crackles. An EKG rhythm strip is obtained. Which of the following is the best next step in the management of this patient?
DC cardioversion
Amiodarone
Transcutaneous pacing
Lidocaine
Digoxin
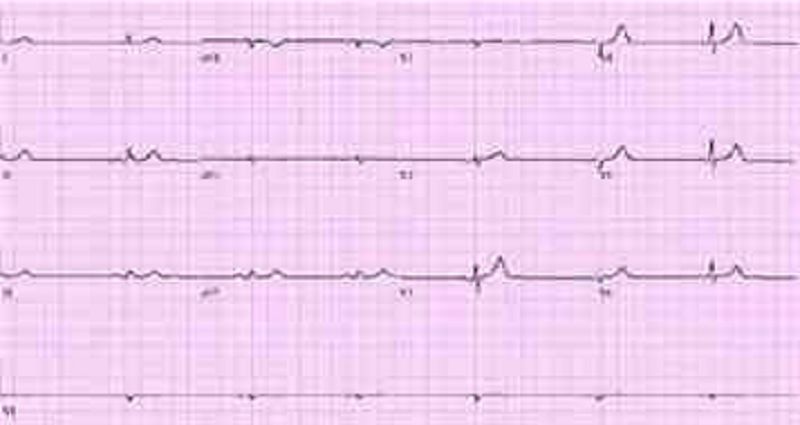
A 66-year-old male is rushed to the emergency department because he feels dizzy and light-headed. He denies chest pain or palpitations. He has a history of hypertension and diabetes. His blood pressure is 116/62 mmHg and his pulse is 35-40/min. He is alert, awake, and fully oriented. He is breathing comfortably and does not appear to be in any distress. His extremities are slightly cold and capillary refill is 3 seconds. His EKG is shown below. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Intravenous atropine
Intravenous epinephrine
Intravenous adenosine push
Intravenous amiodarone
Transcutaneous pacing
A 68-year-old male was intubated in the emergency room because of pulmonary edema. Stat echocardiogram reveals an ejection fraction of 45% and severe mitral regurgitation. In spite of aggressive diuresis with furosemide, the patient continues to require mechanical ventilation secondary to pulmonary edema. What is the best next step in treating this patient?
Begin intravenous enalapril
Arrange for mitral valve replacement surgery
Place an intra-aortic balloon pump
Begin metoprolol
Begin a second loop diuretic
A 45-year-old male is brought to the ER with sudden onset palpitations and chest tightness. His past medical history is significant for hypertension, gout and diabetes mellitus. Cardiac monitoring shows atrial fibrillation at a rate of 120-140/min. As the nurse is attempting to establish IV access, the patient becomes unresponsive. There is no palpable pulse over the carotids or femoral arteries. The cardiac monitor still shows atrial fibrillation at the same rate. What is the best next step in management?
Chest compressions
Synchronized cardioversion
Defibrillation
.IV lidocaine
Arterial blood gas analysis
A 64-year-old male presents to the emergency department with chest pain. An ECG reveals ST elevations in leads II, III, and aVF. Thrombolytic therapy and heparin are administered, and the pain resolves. Eight hours after admission, the patient develops hypotension. He denies recurrence of chest pain. His temperature is 37.5°C (99.6°F), blood pressure is 84/55 mm Hg, pulse is 90/min, and respirations are 15/min. His medications include a nitroglycerin drip, beta-blocker, aspirin, heparin, and simvastatin. Examination reveals an elevated jugular venous pressure of 14 cm, cold clammy extremities, and clear lung fields. Based on this information, what is the next best step in this patient's management?
Administer normal saline bolus and stop nitroglycerin
Start dopamine
Administer intravenous furosemide
Initiate temporary cardiac pacing
Stop nitroglycerin and start dobutamine drip
Neighbors find a 65-year-old male unconscious in his garden and immediately call EMS. The man is intubated at the scene. In the ER, he develops sustained ventricular tachycardia and requires cardioversion. He is started on an antiarrhythmic agent and, once recovered, is discharged to home. Three months later he returns to his physician complaining of dyspnea on exertion. Chest x-ray reveals bilateral lung fibrosis. All cultures are negative and lung biopsy reveals lipoid pneumonitis. Which of the following medications is most likely responsible for his current condition?
Amiodarone
Procainamide
Lidocaine
Quinidine
Digoxin
A 36-year-old female presents to the emergency room complaining of chest pain that started suddenly while she was shopping at the mall. She also reports shortness of breath, palpitations and diaphoresis. The pain is retrosternal and radiates to the left arm. There are no aggravating or relieving factors. On review of systems, the patient reports having had a runny nose, sore throat and dry cough for the past 3 days. Her past medical history is significant for panic attacks, for which she takes paroxetine, and dysfunctional uterine bleeding, for which she takes estrogen. Her family history is significant for the sudden death of her father at age 44 from a heart attack. Social history reveals that she has smoked one pack of cigarettes per day for the past 15 years. Which of the following is the most appropriate initial therapy for this patient?
Aspirin
Lorazepam
Heparin
Ibuprofen
Acetaminophen
A 21-year-old man comes to the ER with palpitations and dizziness that began suddenly one hour ago. He notes having similar past episodes provoked by fatigue or strong emotions. He says he can usually stop the episodes by putting his head into cold water or squatting and taking a deep breath. However, these techniques are not working this time. Presently, his blood pressure is 60/30 mmHg and his heart rate is 240/min. He is diaphoretic with cold extremities. An EKG rhythm strip shows a regular, narrow complex tachycardia. Which of the following is the best next step in managing his condition?
DC cardioversion
Adenosine
Procainamide
Verapamil
Digoxin
A 64-year-old Caucasian male presents to the Emergency Room with a sharp, left-sided chest pain. He says that the pain is worse when he takes deep breaths, but he gets relief with leaning forward. He had an acute non-ST elevation myocardial infarction six months ago and had undergone angioplasty for the right coronary artery. His other medical problems include: diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, peripheral neuropathy, diabetic retinopathy, paroxysmal atrial fibrillation, hypothyroidism, and chronic renal insufficiency. His vital signs are BP 142/86 mmHg, PR 78/min, RR 16/min, and T 36.1°C (97°F). On examination, you find a pericardial rub. EKG shows diffuse ST elevation. Lab results are: Hb 9.0 g/dl, WBC 8,000/cmm, Platelets 210,000/cmm, Blood Glucose 248 mg/dl, Serum Na 135 mEq/L, Serum K 5.8 mEq/L, Bicarbonate 17 mEq/L, BUN 86 mg/dl, Serum Creatinine 4.4 mg/dl. Which of the following is the most appropriate management of this patient?
Hemodialysis
NSAIDs
Corticosteroids
Pericardiocentesis
Echocardiography
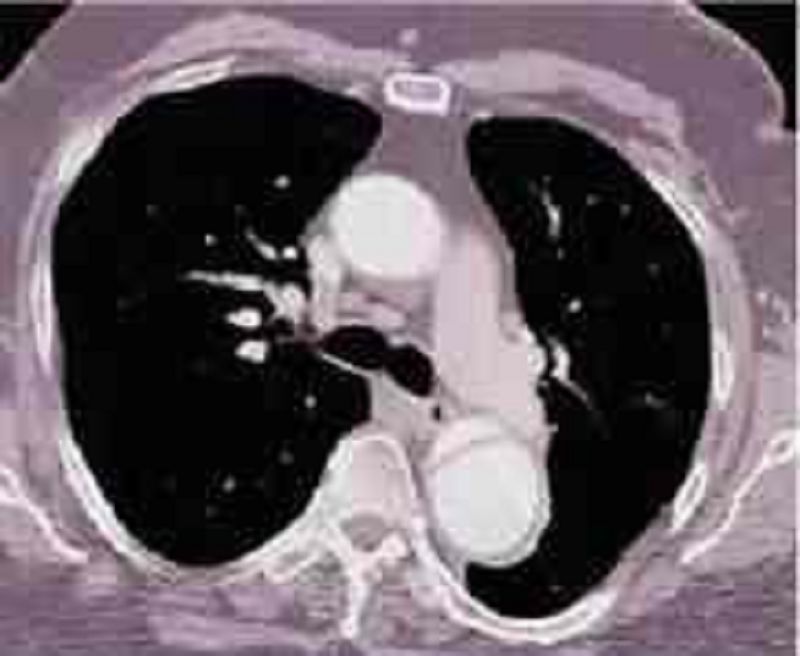
A 48-year-old African American man presents to the emergency room with severe retrosternal chest pain. His temperature is 36.7°C (98°F), blood pressure is 190/ 100 mmHg, pulse is 100/min, and respirations are 16/min. On physical examination, his lungs are clear to auscultation and his heart sounds are normal. EKG shows evidence of left ventricular hypertrophy. A CT image of his chest is shown below. Which of the following is the most appropriate immediate pharmacotherapy for this patient?
Labetalol
Nifedipine
Heparin
Hydrochlorothiazide
Hydralazine
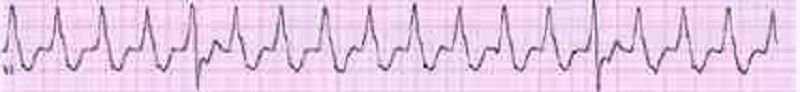
A 64-year-old male is admitted in ICU for acute myocardial infarction. He is on metoprolol, lisinopril, aspirin, furosemide, and potassium supplements. All of a sudden, the nurse mentions that the patient has a change in his tele monitoring. His blood pressure is 120/60 mmHg. His potassium level is 4.2. He is alert, awake and oriented time, place and person. Examination shows scattered bilateral crackles, peripheral pedal edema and elevated JVI. Which of the following is the next best step in the management of this patient?
IV amiodarone
IV digoxin
Cardioversion
IV diltiazem
Carotid massage
A 56-year-old man presents to the emergency department with dyspnea. He describes waking up during the night with difficulty breathing and chest pain that kept him from falling back to sleep. He has never had these symptoms before. His past medical history is significant for long-standing hypertension and non-compliance with his antihypertensive therapy. He has smoked a pack of cigarettes per day for the past 30 years. On physical examination, his blood pressure is 170/100 mmHg and his heart rate is 120/min and regular. Lung auscultation reveals bibasilar rales and scattered wheezes. Which of the following is most likely to relieve this patient's dyspnea?
Nitroglycerin
Metoprolol
Hydralazine
Dopamine
Amiodarone
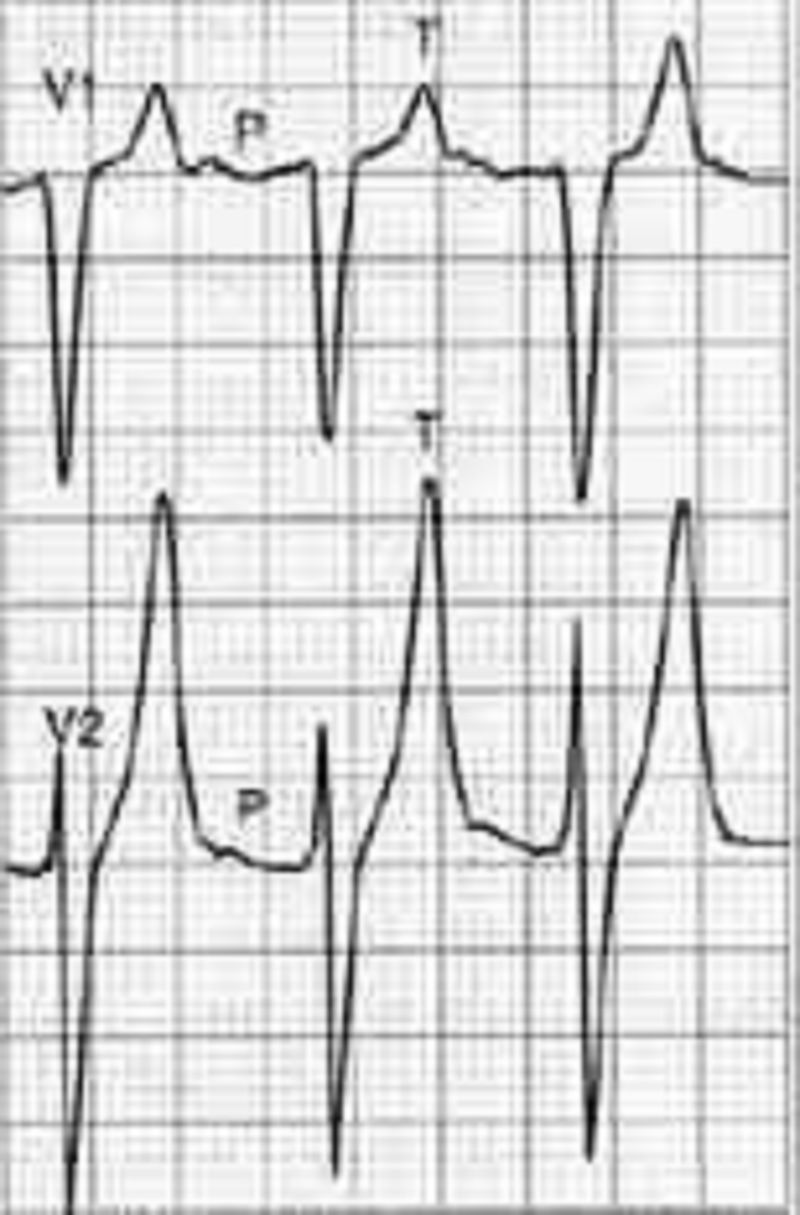
A 70-year-old male with a history of mild chronic kidney disease, diabetes mellitus, and CHF is admitted to your inpatient service with decreased urine output, weakness, and shortness of breath. He takes several medications but cannot remember their names. Labs are pending; his ECG is shown below. Based on the information available, what is the best initial step in management?
Administration of intravenous calcium gluconate
Administration of intravenous insulin
Administration of intravenous sodium bicarbonate
Administration of intravenous 3% hypertonic saline
Administration of oral sodium polystyrene sulfonate
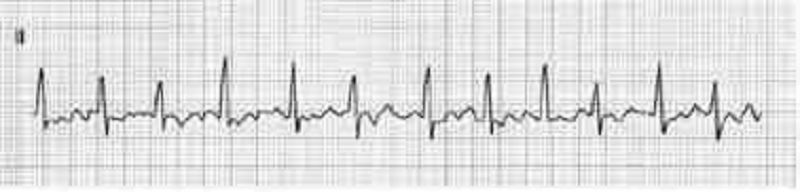
A 51-year-old man with a long history of hypertension presents to the ED complaining of intermittent chest palpitations lasting for a week. He denies chest pain, shortness of breath, nausea, and vomiting. He recalls feeling similar episodes of palpitations a few months ago but they resolved. His blood pressure (BP) is 130/75 mmHg, heart rate (HR) is 130 beats per minute, respiratory rate (RR) is 16 breaths per minute, and oxygen saturation is 99% on room air. An ECG is seen below. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Administer diltiazem
Sedate patient for immediate synchronized cardioversion with 100 J
Prepare patient for the cardiac catheterization laboratory
Administer warfarin
Administer amiodarone
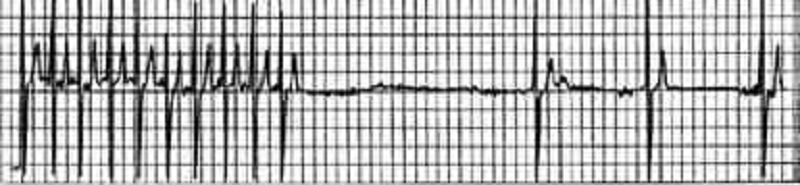
An 82-year-old white female is admitted to the hospital for observation after presenting to the emergency department with dizziness. After being placed on a cardiac monitor in the ER, the rhythm strip below was recorded. There is no past history of cardiac disease, diabetes, or hypertension. With prompting, the patient discloses several prior episodes of transient dizziness and one episode of brief syncope in the past. Physical examination is unremarkable. Which of the following is the best plan of care?
Arrange placement of a permanent pacemaker
Reassurance. This is a benign condition, and no direct therapy is needed
Reassurance. The patient may not drive until she is symptom free, but otherwise no direct therapy is needed
Nuclear cardiac stress testing; treatment depending on results
Begin therapy with aspirin
A 48-year-old man presents to the emergency department complaining of crushing substernal chest pain. He is diaphoretic, anxious, and dyspneic. His pulse is 110/min, blood pressure is 175/112 mmHg, respiratory rate is 30/min, and oxygen saturation is 94%. Aspirin, oxygen, sublingual nitroglycerin, and morphine are given, but they do not relieve his pain. ECG shows ST-segment elevation in leads V2 to V4. The duration of symptoms is now approximately 30 minutes. What is the most appropriate treatment for this patient at this time?
Tissue plasminogen activator
Calcium channel blocker
Intravenous angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor
Intravenous β-blocker
Magnesium sulfate
A 70-year-old woman presents to the emergency department complaining of dizziness. She is disoriented to the date and her location and it is difficult to gather an accurate history. Her pulse is 48/min, blood pressure is 84/60 mmHg, and respiratory rate is 12/min. On examination her extremities are cool and clammy. Her capillary refill time is 5 seconds. What is the most appropriate therapy?
Atropine
Adenosine
Amiodarone
Isoproterenol
Metoprolol
A 64-year-old man in the surgical intensive care unit goes into rapid atrial fibrillation on postoperative day one after a decortication for a loculated pulmonary empyema. He is given an appropriate loading dose of digoxin, but 4 hours after his second dose, the patient complains of increased palpitations and dizziness. The patient is conscious and hemodynamically stable. STAT serum blood tests show a potassium level of 5.0 mEq/L; all other electrolytes, including divalents, are in the normal range. The digitalis level is above the therapeutic range at 4 ng/mL (therapeutic range 0.5-2 ng/mL). Results of cardiac telemetry are shown in the image. Which of the following should be administered immediately?
Magnesium
Calcium
Furosemide
Potassium
Sodium polystyrene sulfonate
A 49-year-old man presents to the clinic for a health maintenance visit. He has no complaints, but he requests a prescription for his “pressure pills,” as he lost his original prescription. On physical examination his blood pressure is 220/130 mmHg. Physical examination is otherwise within normal limits. Laboratory tests show: Na+: 142 mEq/L, K+: 3.8 mEq/L, Cl−: 105 mEq/L, Carbon dioxide: 25 mEq/L, Blood urea nitrogen: 20 mg/dL, Creatinine: 1.0 mg/dL, Glucose: 133 mg/dL. Urinalysis is within normal limits, and his ECG is normal. Which of the following is the most effective management?
Administer oral metoprolol for management of hypertensive urgency
Administer intravenous nitroprusside for management of hypertensive emergency
Administer intravenous nitroprusside for management of hypertensive urgency
Administer oral furosemide for management of hypertensive emergency
Administer sublingual nifedipine for management of hypertensive emergency
A 65-year-old man presents to the emergency department following the acute onset of palpitations. His wife states that he was eating dinner when he noticed the palpitations, lightheadedness, and shortness of breath. The patient has a history of treated hypertension, but no other medical history. The patient is not able to relate any meaningful history. Blood pressure is 80/40 mmHg, heart rate is 126/ min, respiratory rate is 20/min, and oxygen saturation is 99% on room air; he is afebrile. His heart rate is irregularly irregular with no murmurs, clicks, or rubs. Respiratory examination is unremarkable. X-ray of the chest shows no acute disease. ECG shows no discernible P waves and an irregularly spaced QRS response. Which of the following is the best first step in management?
Cardioversion to sinus rhythm
Administration of adenosine
Cardiac catheterization and stent placement
Carotid massage
Placement of dual lead pacemaker
{"name":"new Part 4 (765-865) (765-1019) NR 2", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Test your knowledge and understanding of various mental health diagnoses with our comprehensive quiz. This assessment covers a range of scenarios and patient presentations, challenging you to identify the most likely diagnosis based on the given information.Perfect for healthcare professionals, students, or anyone interested in psychology, this quiz includes:Multiple-choice questionsReal-life case scenariosDetailed feedback on answers","img":"https:/images/course5.png"}
More Quizzes
Psychiatrie
115580
Chat 2 Exam 3 part 2
33160
20100
¿A qué escuela económica perteneces?
11610
Bradley Effect Definition (AP Gov): Ch. 6 Demographics
201018813
Introduction to Applied Statistics - Free Practice
15816862
What Rodent Are You? Free Personality
201017833
Logical Fallacies Practice - Identify the Fallacy
201015976
What Breathing Style Am I? Find Your Demon Slayer Style
201017106
Best Swimsuits for Body Type - Free Fit Finder
201018343
Iterative Statement Definition - Which Is True?
201017426
What Zootopia Animal Am I? Free Personality
201017903