DES C_Management (2) Prepared : CHILLY
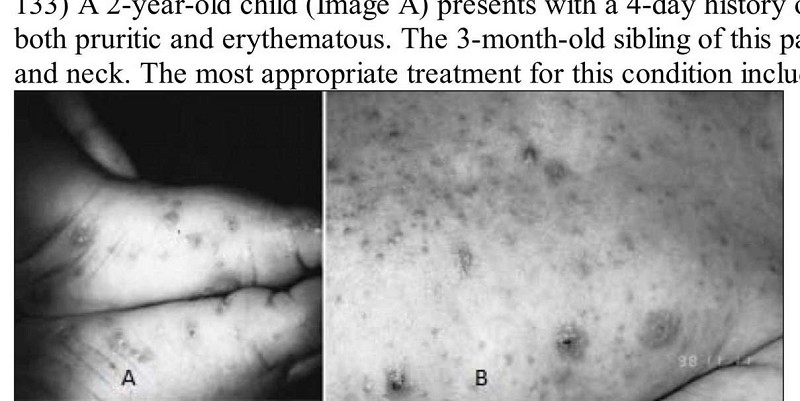
A 2-year-old child (Image A) presents with a 4-day history of a rash limited to the feet and ankles. The papular rash is both pruritic and erythematous. The 3-month-old sibling of this patient (Image B) has similar lesions also involving the head and neck. The most appropriate treatment for this condition includes which of the following?
Coal-tar soap
Emollients
Topical antifungal cream
Permethrin
Hydrocortisone cream
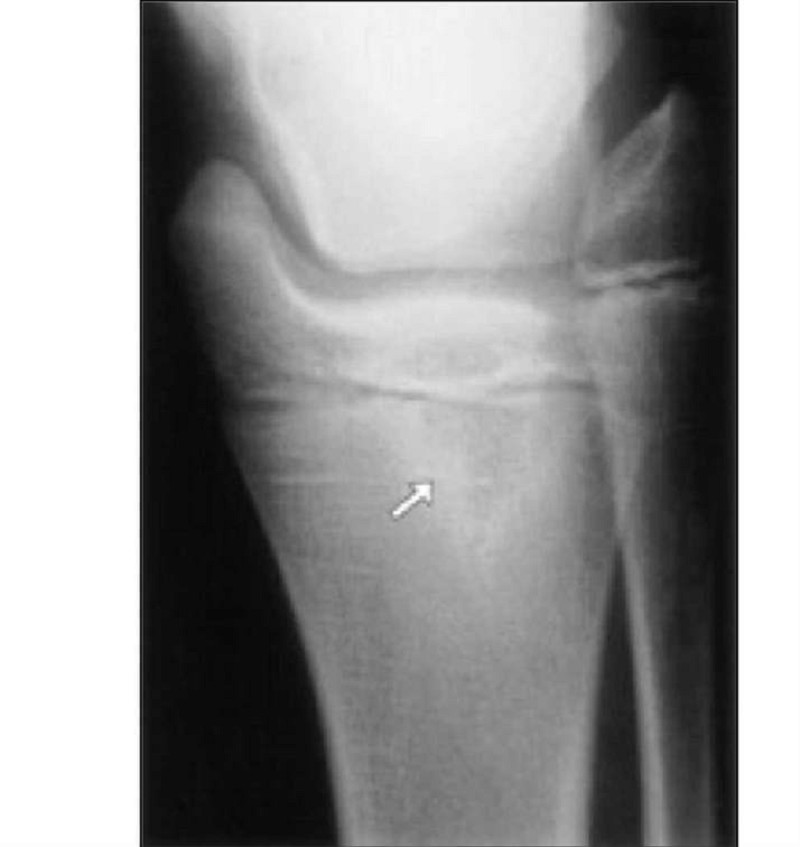
A 2-year-old child is seen in the emergency center with a 10-day complaint of fever and a limp. The child has an elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and the radiograph shown below. Which of the following statements about this child’s condition is correct?
It is most commonly caused by Streptococcus pyogenes
Usually results in tenderness in the region of infection that is diffuse, notlocalized
It causes diagnostic radiographic changes on plain films within 48 hours of the beginning of symptoms
It can arise following development of deep cellulitis
It requires antibiotic therapy usually for 10 to 14 days
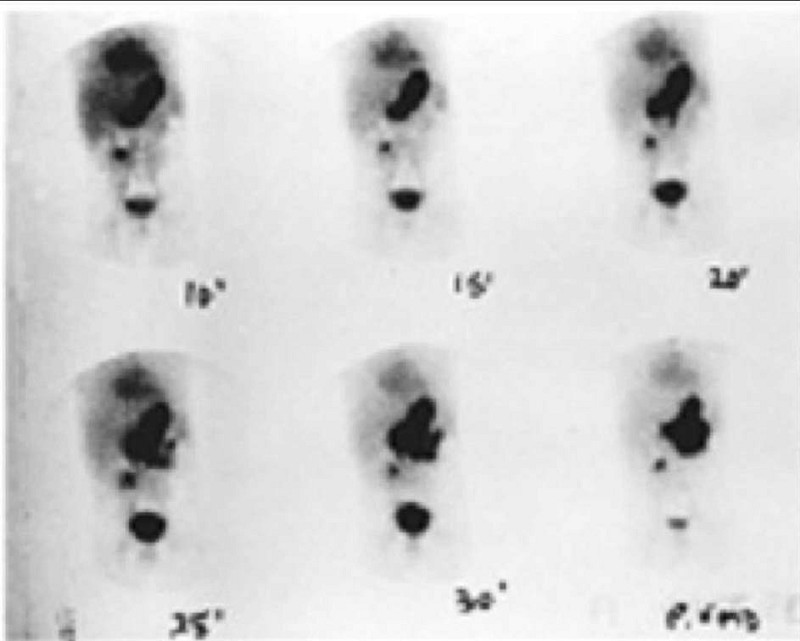
A 2-year-old child presents with a 2-day history of painless rectal bleeding. On examination, the child is pale with tachycardia. The abdomen is nondistended and nontender. There is dark blood on rectal examination. The child has the following imaging study (see Figure 6-2). Which of the following is the most appropriate management?
Aggressive resuscitation followed by surgical exploration
Acid suppression therapy
IV steroids
Colonoscopy
Surgical exploration
A 20-year-old female college student is brought to the emergency department by police at 2:30 am after she was caught attempting to enter the White House. She is highly agitated and is pacing around the examination room. Upon further questioning, she states that she just flew in from Texas to meet with the president because she has a "foolproof plan for eliminating terrorism worldwide in just seven days." She adds that she has barely slept for the past ten nights because she has been working intensively on this plan. She speaks very quickly, but periodically stops to angrily shout, "I'm going to sue all of you for interfering with my right to meet with the president." The evaluation has to be stopped because she demands that she be allowed to leave. Family history is significant for major depression in her mother. Vital signs are temperature 37.0°C (98.6°F), blood pressure 148/84 mmHg, pulse 98/min, and respiratory rate 22/min. Which of the following medications should be administered to this patient immediately?
Fluoxetine
Desipramine
Mirtazapine
Haloperidol
Lithium carbonate
A 20-year-old female comes to the physician because she has never had a period. She has no medical problems, has never had surgery, and takes no medications. Examination shows that she is a tall female with long extremities. She has normal size breasts, although the areolas are pale. She has little axillary hair. Pelvic examination is significant for scant pubic hair and a short, blind-ended vaginal pouch. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient?
Bilateral gonadectomy
Unilateral mastectomy
Bilateral mastectomy
Unilateral gonadectomy
No intervention is necessary
A 20-year-old female is brought to the Emergency Room by her college roommate who states that the patient vomited all night. The patient complains of a sore throat and says she has not eaten for the last two days. She admits to a "sugar problem" and quit taking her medication because she has not been eating. Examination reveals an ill-appearing woman. Her temperature is 37.9 C (100.2 F), blood pressure is 118/78 mm Hg, pulse is 160/min, and respirations are 30/min. The patient's lips and mucous membranes are dry. There is a fruity odor noted to the patient's breath. The lung and cardiac examination are unremarkable except for mild tachypnea and tachycardia. Laboratory analysis shows: Sodium 130 mEq/L, Potassium 6.1 mEq/L, Chloride 100 mEq/L, Bicarbonate 8 mEq/L, Urea nitrogen 10 mg/dL, Creatinine 1.0 mg/dL, Glucose 680 mg/dL, pH 7.15, pCO2: 30 mm Hg, pO2: 85 mm Hg, Urinalysis is positive for ketones. Which of the following is the most appropriate initial step in management?
IV fluid bolus with normal saline and potassium
Mannitol
Immediate intubation
Intramuscular ceftriaxone
Intravenous insulin
A 20-year-old G1 at 38 weeks gestation presents with regular painful contractions every 3 to 4 minutes lasting 60 seconds. On pelvic examination, she is 3 cm dilated and 90% effaced; an amniotomy is performed and clear fluid is noted. The patient receives epidural analgesia for pain management. The fetal heart rate tracing is reactive. One hour later on repeat examination, her cervix is 5 cm dilated and 100% effaced. Which of the following is the best next step in her management?
Stop epidural infusion to enhance contractions and cervical change
Perform cesarean delivery for inadequate cervical effacement
No intervention; labor is progressing normally
Initiate Pitocin augmentation for protracted labor
Begin pushing
A 20-year-old G1 at 41 weeks has been pushing for 21/2 hours. The fetal head is at the introitus and beginning to crown. It is necessary to cut an episiotomy. The tear extends through the sphincter of the rectum, but the rectal mucosa is intact. How should you classify this type of episiotomy?
First-degree
Mediolateral episiotomy
Third-degree
Fourth-degree
Second-degree
A 20-year-old G1P0 at 30 weeks gestation with a known placenta previa is delivered by cesarean section under general anesthesia for vaginal bleeding and nonreassuring fetal heart rate tracing. The baby is easily delivered, but the placenta is adherent to the uterus and cannot be completely removed, and heavy uterine bleeding is noted. Which of the following is the best next step in the management of this patient?
Close the uterine incision and perform curettage
Administer prostaglandin F2α (Hemabate) intramuscularly
Perform hysterectomy
Administer misoprostol (Cytotec) suppositories per rectum
Administer methylergonovine (Methergine) intramuscularly
A 20-year-old G1P0 presents to your clinic for follow-up for a suction dilation and curettage for an incomplete abortion. She is asymptomatic without any vaginal bleeding, fever, or chills. Her examination is normal. The pathology report reveals trophoblastic proliferation and hydropic degeneration with the absence of vasculature; no fetal tissue is identified. A chest x-ray is negative for any evidence of metastatic disease. Which of the following is the best next step in her management?
Hysterectomy
Radiation therapy
Combination chemotherapy
Single-agent chemotherapy
Weekly human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) titers
A 20-year-old G1P1 is postpartum day 2 after an uncomplicated vaginal delivery of a 6-lb 10-oz baby boy. She is trying to decide whether to have you perform a circumcision on her newborn. The boy is in the wellbaby nursery and is doing very well. In counseling this patient, you tell her which of the following recommendations from the American Pediatric Association?
Circumcisions should be performed routinely because they decrease the incidence of male urinary tract infections
Circumcisions should be performed routinely because they decrease the incidence of penile cancer
Circumcisions should be performed routinely because they decrease the incidence of sexually transmitted diseases
Circumcisions should not be performed routinely because of insufficient data regarding risks and benefits
Circumcisions should not be performed routinely because it is a risky procedure and complications such as bleeding and infection are common.
A 20-year-old woman complains of skin problems and is noted to have erythematous papules on her face with blackheads (open comedones) and whiteheads (closed comedones). She has also had cystic lesions. She is prescribed topical tretinoin, but without a totally acceptable result. You are considering oral antibiotics, but the patient requests oral isotretinoin, which several of her college classmates have used with benefit. Which of the following statements is correct?
Intralesional triamcinolone should be avoided due to its systemic effects
Systemically administered isotretinoin therapy cannot be considered unless concomitant contraceptive therapy is provided
The patient will not benefit from topical antibiotics since she did not respond to topical retinoids
The teratogenic effects of isotretinoin are its only clinically important side effects
Antimicrobial therapy is of no value since bacteria are not part of the pathogenesis of the process
A 20-year-old woman has developed low-grade fever, a malar rash, and arthralgias of the hands over several months. High titers of anti-DNA antibodies are noted, and complement levels are low. The patient’s white blood cell count is 3000/µL, and platelet count is 90,000/µL. The patient is on no medications and has no signs of active infection. Which of the following statements is correct?
If glomerulonephritis, severe thrombocytopenia, or hemolytic anemia develops, high-dose glucocorticoid therapy would be indicated
The disease process described is an absolute contraindication to pregnancy
Joint deformities will likely occur
The patient can be expected to develop Raynaud phenomenon when exposed to cold
Central nervous system symptoms will occur within 10 years
A 20-year-old woman presents with complaints of vaginal discharge and vulvar pruritus. She has no other medical problems. Physical examination reveals a thin, malodorous vaginal discharge and erythema of the vulva and vaginal mucosa. No other exam abnormalities are noted. Wet-mount preparation of the discharge shows motile pear-shaped organisms. Which of the following management options is most appropriate?
Oral metronidazole for the patient only
Reassurance
Topical metronidazole cream for the patient only
Oral metronidazole for both the patient and her sexual partner
Doxycycline for both the patient and her sexual partner
A 20-year-old woman with a family history of von Willebrand disease is found to have an activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) of 78 (normal = 32) on routine testing prior to cholecystectomy. Further investigation reveals a prothrombin time (PT) of 13 (normal = 12), a platelet count of 350,000/mm3, and an abnormal bleeding time. Which of the following should be administered in the perioperative period?
Factor VIII
Desmopressin (DDAVP)
Aminocaproic acid
Vitamin K
Platelets
A 20-year-old, gravida 1, para 0, at 10 weeks gestation is brought to the emergency department because of moderate vaginal bleeding. She has a colicky suprapubic pain radiating to the back and denies the passage of tissue through her introitus. She does not use tobacco, alcohol or drugs. She has no history of trauma or serious illness. Her temperature is 37.0C (98.7 F), blood pressure is 100/65 mm of Hg, pulse is 90/min and respirations are 17/min. Physical examination shows a dilated cervix and the products of conception can be seen through it. Her blood type is AB Rh negative and her antibody titer is 1:2. Ultrasonogram shows a ruptured gestational sac with no fetal heart motion. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Administration of a dilute infusion of oxytocin to induce labor
IV fluids, suction curettage and RhoGAM administration
Serial beta-hCG monitoring
Reassurance, administration of RhoGAM and follow up
Hospitalization, analgesics and observation
A 21-year-old college student undergoes surgery to remove a small cyst in his palm at the base of his third digit. He receives an axillary regional block prior to die procedure but still has discomfort post-operatively. Injection of anesmetic in which of the following sites may be used to treat his pain?
Posterior to the elbow, between the olecranon and the medial epicondyle
Posterior to the brachioradialis muscle
Near the spiral groove of the humerus
Into die anatomic snuff box
Between the palmaris longus and flexor digitorum tendons
A 21-year-old female military recruit presented to the physician's office because of pain in her right foot. The pain started a few weeks ago and initially only occurred with activity, but now the pain is present even at rest. She has no history of obvious trauma. Examination shows swelling and warmth in the foot and point tenderness over the second metatarsal. Plain films of the foot show a hairline fracture of the shaft of the second metatarsal. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Bone scan
Surgical intervention
Plaster cast
Rest and analgesics
MRI of the foot
A 21-year-old female presents with an annular pruritic rash on her neck. She explains that the rash has been present for the past 3 weeks and that her roommate had a similar rash not long ago. Physical examination is remarkable for a 20-mm scaling, erythematous plaque with a serpiginous border. Which of the following is the most appropriate initial treatment for this condition?
Oral cephalexin
Hydrocortisone cream
Griseofulvin
Topical ketoconazole
Topical mupirocin ointment
A 21-year-old female, G1P0, who recently emigrated from Zimbabwe presents for prenatal counselling in her 34th week of pregnancy. She received no prenatal care. Ultrasound evaluation reveals lower-than-normal fetal length and markedly reduced fetal head size. Which of the following could have prevented this condition?
Smoking cessation
Folic acid supplementation
Malaria prophylaxis
Zidovudine treatment
MMR vaccination
A 21-year-old G2P1 at 25 weeks gestation presents to the emergency room complaining of shortness of breath. She reports a history of asthma and states her peak expiratory flow rate (PEFR) with good control is usually around 400. During speaking the patient has to stop to catch her breath between words; her PEFR is 210. An arterial blood gas is drawn and oxygen therapy is initiated. She is afebrile and on physical examination expiratory wheezes are heard in all lung fields. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in her management?
Antibiotics
Theophylline
Intravenous corticosteroids
Chest x-ray
Inhaled β-agonist
A 21-year-old G2P2 calls her physician 7 days postpartum because she is concerned that she is still bleeding from the vagina. She describes the bleeding as light pink to bright red and less heavy than the first few days postdelivery. She denies fever or any cramping pain. On examination she is afebrile and has an appropriately sized, nontender uterus. The vagina contains about 10 cc of old, dark blood. The cervix is closed. Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment?
Suction dilation and curettage for retained placenta
Reassurance
High-dose oral estrogen for placental subinvolution
Oxytocin for uterine atony
Antibiotics for endometritis
A 21-year-old male is admitted to the intensive care unit after attempting to commit suicide by overdosing on some pills he found in the medicine cabinet at home. A psychiatry consult is ordered. While interviewing the patient, the psychiatrist observes that the patient has a "blank" expression on his face and is minimally responsive. He refuses to make eye contact and speaks in monosyllables. An attempt is made to obtain a more detailed history from the patient's father. He describes his son as very aloof, having avoided the other children in the neighborhood and participated in few activities as a child. His son dropped out of school in ninth grade and has not been able to maintain jobs throughout the years because of his social difficulties. He adds that his son has been increasingly isolated this past year and that he has complained his deceased mother frequently asks him to "join her in heaven." Which of the following medications would provide the greatest benefit to this patient?
Fluphenazine injections
Thioridazine
Chlorpromazine
Haloperidol
Risperidone
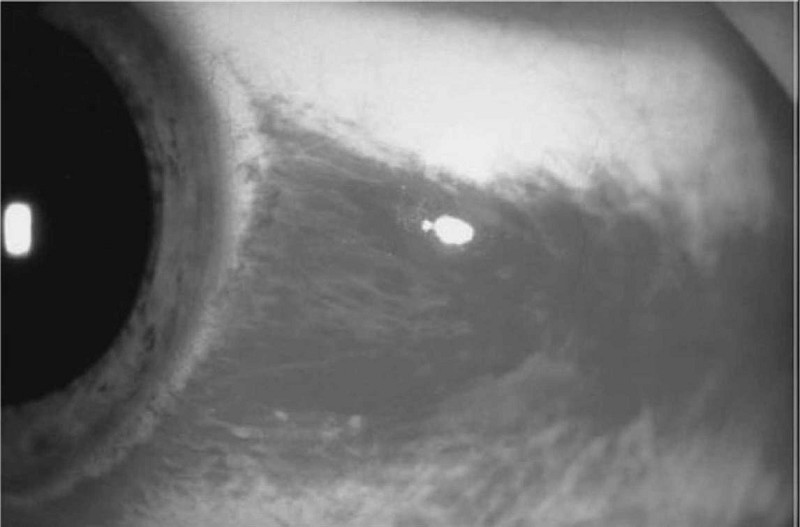
A 21-year-old man presents to the ED with a red eye. The patient complains of rhinorrhea and a nonproductive cough but has no eye pain or discharge. He also has no associated ecchymosis, bony tenderness of the orbit, or pain on extraocular eye movement. His vision is normal, extraocular movements are intact, and intraocular pressure (IOP) is 12. A picture of his eye is shown below. What is the most appropriate management of this condition?
Call ophthalmology immediately
Elevate patient’s head
Administer ophthalmic timolol
Administer 1% atropine
Reassurance only
A 21-year-old man with type 1 diabetes mellitus presents to the emergency department with complaints of abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting. His temperature is 36.0°C (97.0°F), pulse is 110/min, blood pressure is 102/60 mmHg, and respirations are 26/min. Lungs are clear to auscultation. Abdomen is soft, non-tender and non-distended. Chemistry panel shows: Sodium 130 mEq/L, Potassium 5.2 mEq/L, Chloride 90 mEq/L, Bicarbonate 10 mEq/L, Blood glucose 450 mg/dl. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Normal saline and NPH insulin
Sodium bicarbonate
0.45% saline and regular insulin
Normal saline and regular insulin
5% dextrose and NPH insulin
A 21-year-old previously healthy man presents to your office for a routine check-up. He has no current complaints. He does not smoke or consume alcohol. His family history is significant for cystic fibrosis in his older brother. He is sexually active with one partner and uses condoms regularly. He visits a dentist twice per year. His temperature is 36.6°C (97.9°F), pulse is 78/min, respirations are 14/min, and blood pressure is 120/76 mmHg. Physical examination reveals several non-tender, rubbery cervical lymph nodes, each measuring approximately 1 cm in diameter. There is no hepatosplenomegaly. Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient?
Lymph node biopsy
Erythromycin
Observation
Dicloxacillin
Prednisone
A 21-year-old primigravid woman at 39 weeks' gestation comes to the labor and delivery ward with painful contractions every three minutes. Her prenatal course was unremarkable. Examination shows her cervix to be 3 centimeters dilated and 90% effaced. The fetal heart rate tracing is in the 150s and reactive. 5 hours later cervical examination reveals that the patient is 9 centimeters dilated and at -1 station. The fetal heart rate tracing shows moderate variable decelerations with each contraction and decreased variability. Fetal scalp sampling is performed that yields fetal scalp pH of 7.04, 7.05, and 7.06. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Forceps-assisted vaginal delivery
Cesarean delivery
Vacuum-assisted vaginal delivery
Expectant management
Episiotomy
A 21-year-old woman asks you to evaluate a small painless lump in the midline of her neck that moves with swallowing. You make the clinical diagnosis of thyroglossal duct cyst. Which of the following is the most appropriate management of this patient?
Excision of the cyst, the central portion of the hyoid bone, and the tract to the base of the tongue, with sampling of central cervical lymph nodes
Excision of the cyst, the central portion of the hyoid bone, and the tract to the base of the tongue, with biopsy of the thyroid gland
Excision of the cyst, the central portion of the hyoid bone, and the tract to the base of the tongue
Excision of the cyst and the central portion of the hyoid bone
Excision of the cyst
A 21-year-old woman at 36 weeks gestation is admitted for delivery. She has severe preeclampsia. Her blood pressure is 190/110 mmHg, pulse is 80/min and respirations are 16/min. Physical examination shows 3+ pitting edema of the legs and brisk deep tendon reflexes. Fundoscopic examination shows no abnormalities. Laboratory studies show elevated BUN, serum creatinine and serum transaminases. Urinalysis shows 4+ proteinuria. Intravenous hydralazine and magnesium sulfate was initiated on admission. After stabilization, intravenous oxytocin and artificial rupture of membranes (AROM) was administered for induction of labor. Two hours later, her blood pressure is 150/90 mmHg, pulse is 78/min and respirations are 9/min. Repeat examination shows hyporeflexia and a completely effaced cervix that is 5 cm dilated. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Continue current treatment and proceed with delivery
Stop intravenous oxytocin and intubate the patient
Stop hydralazine and monitor serum cyanide level
Stop magnesium sulfate and give calcium gluconate
Stop hydralazine and do an emergency caesarian section
A 21-year-old woman comes to the physician because of "bumps" on her vulva that she has just recently noticed. These bumps do not cause her symptoms, but she wants to know what they are and wants them removed. She has no medical problems, takes no medications, and has no allergies to medications. She smokes one-half pack of cigarettes per day. She is sexually active with 3 partners. Examination shows 3 cauliflower-like lesions on the right labia majora. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Acyclovir
Cryotherapy
Penicillin
Cone biopsy
Vulvectom
A 21-year-old woman complains of progressive weakness and loss of energy. She nearly collapsed yesterday while performing one of her routine 3 hour workouts. Additionally, she has been performing badly in college despite persistent attempts to improve her grades. Physical exam reveals a blood pressure of 102/58 mmHg, heart rate of 113/min, fine hair covering her face, and normal heart and lungs. Laboratory studies show the following findings: Sodium 140 mEq/L, Potassium 24 mEq/L, Calcium 10.1 mg/dL, Chloride 90 mEq/L, Bicarbonate 40 mEq/L, Urine chloride 14 mEq/L. Which of the following is most likely to correct the laboratory abnormalities in this patient?
Sodium bicarbonate solution infusion
Loop diuretics
Hyperventilation
Calcium gluconate infusion
Normal saline infusion
A 21-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, at 22 weeks' gestation comes to the physician because of a malodorous vaginal discharge. She states that she first noticed the discharge 2 days ago and since then it has become more profuse and malodorous. Her prenatal course has been unremarkable during this pregnancy. Her prior pregnancy was complicated by preterm labor and delivery at 31 weeks' gestation. Examination shows a grayish vaginal discharge. A strong amine odor is released when KOH is applied to a sample of the discharge. Examination of a normal saline ("wet") preparation reveals numerous "clue" cells. Which of the following is the most appropriate pharmacotherapy?
Oral penicillin
No treatment is needed
IV penicillin
Intramuscular penicillin
Oral metronidazole
A 21-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, at 28 weeks' gestation comes to the physician because of spotting after intercourse and a foul-smelling vaginal discharge. Her prenatal course has, up to now, been uncomplicated, and she has no medical problems. Speculum examination shows inflammation of the cervix with a mucopurulent cervical discharge. A gonorrhea and Chlamydia test is performed which comes back positive for chlamydia. Which of the following is the most appropriate pharmacotherapy?
Azithromycin
Levofloxacin
Penicillin
Streptomycin
Doxycycline
A 22-year-old Caucasian male is evaluated for an episode of syncope that occurred while playing soccer. It lasted only 2 minutes without any post-syncopal confusion, sleepiness or weakness. He had prior episodes of dizziness while playing active sports as well as vague chest discomfort. His uncle died suddenly at a young age. Auscultation of his precordium reveals a III/IV systolic murmur along the left sternal border. The patient is most likely to benefit from which of the following medications?
Nitrates
Disopyramide
Amlodipine
Digitalis
Beta-blockers
A 22-year-old college student calls his psychiatrist because for the past week, after cramming hard for finals, his thoughts have been racing and he is irritable. The psychiatrist notes that the patient’s speech is pressured as well. The patient has been stable for the past 6 months on 500 mg of valproate twice a day. Which of the following is the most appropriate first step in the management of this patient’s symptoms?
Tell the patient to begin psychotherapy one time per week
Increase the valproate by 500 mg/day
Start haloperidol 5 mg qd
Prescribe clonazepam 1 mg qhs
Hospitalize the patient
A 22-year-old convenience store clerk is shot once with a .38 caliber revolver. The entry wound is in the left midclavicular line, 2 inches below the nipple. There is no exit wound. He is hemodynamically stable. A chest x-ray film shows a small pneumothorax on the left, and demonstrates the bullet to be lodged in the left paraspinal muscles. In addition to the appropriate treatment for the pneumothorax, which of the following will this patient most likely need?
Extraction of the bullet via left thoracotomy
Exploratory laparotomy
Extraction of the bullet via local back exploration
Barium swallow
Bronchoscopy
A 22-year-old female comes to the physician complaining of pain during sexual activity. She is unable to have intercourse because her vagina becomes tense, resulting in intense pain upon penetration. She is living with her boyfriend and this is her first sexual relationship. She now avoids intercourse because of her fear of the pain. She has no history of serious illness. Speculum examination is not possible due to tense perineal musculature. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Laparoscopy to visualize endometriosis
Kegel exercises and gradual dilatation
Advise self-stimulation techniques
Refer to a sex therapist
Prescribe vaginal lubricants
A 22-year-old female presents with complaints of heat intolerance, sweating and palpitations. She also reports menstrual irregularities, increased appetite and diarrhea. Her pulse is 102/min and regular, blood pressure is 116/80 mmHg, temperature is 37.2°C (99°F), and respirations are 14/min. Physical examination reveals a diffusely enlarged, nontender thyroid gland. TSH level is 0.05 mU/L. Free T4 and T3 levels are elevated. Radioactive iodine uptake at 24 hours is 50 percent. Thyroid stimulating immunoglobulins are present. She is started on propylthiouracil 300 mg daily in three divided doses. After two weeks, she returns and complains of a sore throat. Her pulse is 98/min and regular, temperature is 38.6°C (101.5°F), blood pressure is 115/76 mmHg, and respirations are 15/min. The soft palate, pharynx, and tonsils are red and swollen. What is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient?
Increase propylthiouracil dose
Throat culture
Oral penicillin
Add propranolol
Stop propylthiouracil
A 22-year-old G1P1 who is postpartum day 2 and is bottle-feeding complains that her breasts are very engorged and tender. She wants you to give her something to make the engorgement go away. Which of the following is recommended to relieve her symptoms?
Bromocriptine
Use oral antibiotics
Pump her breasts
Estrogen-containing contraceptive pills
Breast binder
A 22-year-old G3P0030 obese female comes to your office for a routine gynecologic examination. She is single, but is currently sexually active. She has a history of five sexual partners in the past, and became sexually active at age 15. She has had three first-trimester voluntary pregnancy terminations. She uses Depo-Provera for birth control, and reports occasionally using condoms as well. She has a history of genital warts, but denies any prior history of abnormal Pap smears. The patient denies use of any illicit drugs, but admits to smoking about one pack of cigarettes a day. Her physical examination is normal. However, 3 weeks later you receive the results of her Pap smear, which shows a high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HGSIL). Which of the following factors in this patient’s history does not increase her risk for cervical dysplasia?
Multiple sexual partners
Use of Depo-Provera
Smoking
History of genital warts
Young age at initiation of sexual activity
A 22-year-old male, recently incarcerated and now homeless, has received one week of clarithromycin for low-grade fever and left upper-lobe pneumonia. He has not improved on antibiotics, with persistent cough productive of purulent sputum and flecks of blood. Repeat chest x-ray suggests a small cavity in the left upper lobe. Which of the following statements is correct?
Drug resistant pneumococci may be causing this infection
Isoniazid prophylaxis should be started if PPD is positive
The patient requires glove and gown contact precautions
The patient requires sputum smear and culture for acid fast bacilli
The patient has anaerobic infection and needs outpatient clindamycin therapy
A 22-year-old man is brought to the emergency department after falling from a motorbike. He has right wrist pain. His temperature is 37.1C (98.6F), blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg, pulse is 80/min, and respirations are 17/min. He is well oriented and cooperative. His pupils are bilaterally reactive. Physical examination shows no signs of trauma except for marked tenderness in the right anatomical snuff box. An x-ray film of the wrist joint shows a radiolucent line across the waist of the right scaphoid bone. Which of the following is the most next step management?
Advise rest, ice, compression and elevation for wrist joint
Cast immobilization for 6-12 weeks
Send the patient home with analgesics and repeat X ray after 15 days
Percutaneous fixation of scaphoid bone
Open reduction and internal fixation of scaphoid bone
A 22-year-old man is examined following a motor vehicle accident. He has a right knee dislocation which is reduced in the emergency room. He has palpable pedal pulses and is neurologically intact. Which of the following is an appropriate next step in his workup and management?
Observation with serial pulse checks
Surgical exploration of the right popliteal artery
Prophylactic below-knee 4-compartment fasciotomies
Angiography of the right lower extremity
Measurement of ankle-brachial indices
A 22-year-old man is stabbed in the right chest with a 5-cm-long knife blade. On arrival at the emergency department, he is wide awake and alert. He is speaking with a normal tone of voice but complaining of shortness of breath. The right hemithorax is hyperresonant to percussion and has no breath sounds; the rest of the initial survey is negative. His blood pressure is 110/75 mm Hg, pulse is 86/min, and venous pressure is 3cm H2O. Pulse oximetry shows a saturation of 85%. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in patient care?
Sonographically guided evacuation of the pericardial sac
Chest x-ray and insertion of a chest tube
Immediate insertion of a needle into the right pleural space
Securing an airway by orotracheal intubation
Infusion of 2 L Ringer's lactate
A 22-year-old man presents to the ED complaining of dysuria for 3 days. He states that he has never had this feeling before. He is currently sexually active and uses a condom most of the time. He denies hematuria but notes a yellowish discharge from his urethra. His BP is 120/75 mm Hg, HR is 60 beats per minute, and temperature is 98.9°F. You send a clean catch urinalysis to the laboratory that returns positive for leukocyte esterase and 15 white blood cells per high power field (WBCs/hpf). Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Have him follow-up immediately with a urologist to evaluate for testicular cancer
Order a CT scan to evaluate for a kidney stone
Discharge the patient with strict instructions to return if his symptoms worsen
Send urine for culture and administer SMX/TMP orally
Send a urethral swab for culture and administer 125 mg ceftriaxone intramuscularly and 1 g azithromycin orally
A 22-year-old man undergoes an exploratory laparotomy after a gunshot wound to the abdomen. The patient has multiple injuries, including a significant liver laceration, multiple small-bowel and colon injuries, and an injury to the infrahepatic vena cava. The patient receives 35 units of packed RBCs, 15 L of crystalloid, 12 units of fresh-frozen plasma (FFP), and 12 packs of platelets. The patient’s abdomen is packed closed and he is taken to the intensive care unit for further resuscitation. Which of the following warrants a decompressive laparotomy?
Increased cerebral perfusion pressure
Decreased plasma renin and aldosterone
Decreased systemic vascular resistance
Increased peak airway pressure
Increased cardiac output
A 22-year-old nulliparous woman comes to the physician with lower abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. She is unable to keep anything down. She is sexually active and uses oral contraceptive pills. The patient's last menstrual period was 15 days ago. Her temperature is 39C (102.2F), blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg, and pulse is 110/min. Physical examination shows dry mucous membranes, soft and symmetrical abdomen, and diffuse tenderness over the lower quadrants. External genitalia show no abnormalities; speculum examination shows purulent discharge from the cervical os. The uterus is normal in size but is tender to palpation and motion. The adnexae are markedly tender but no palpable mass is noted. Cervical cultures are pending. Urine pregnancy test is negative. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management of this patient?
Outpatient treatment with oral amoxicillin and clavulanic acid
Outpatient treatment with metronidazole and ampicillin
Outpatient treatment with ceftriaxone and doxycycline
Inpatient treatment with cefotetan and doxycycline
Admit the patient and wait for culture results
A 22-year-old primagravida woman develops hypertension at 28 weeks. She is asymptomatic and the examination is normal except for 1+ pedal edema. Her complete blood count, liver enzymes, and electrolytes are normal. The urinalysis is positive for proteinuria. Which of the following is true for this type of hypertension?
improves in the third trimester
Leads to large-birth-weight babies
Spares the placenta
Should be controlled with medications
Spares maternal kidney function
A 22-year-old primigravid woman at 8 weeks' gestation comes to the physician for her first prenatal visit. She has had some nausea but no other complaints. She has had no bleeding per vagina or abdominal pain. She had an ovarian cystectomy at age 18 but no other medical or surgical problems. She takes no medications and has no known drug allergies. Examination is unremarkable except for an 8-week-sized non-tender uterus. The patient wants information on vitamin supplementation during pregnancy. Which of the following represents the correct amount of vitamin A supplementation this patient should take daily?
Vitamin A supplementation during pregnancy is not recommended
10,000 IU
5,000 IU
50,000 IU
100,000 IU
A 22-year-old primigravid woman at term comes to the labor and delivery ward because of painful contractions every 2 minutes. She has had no gush of fluid and no bleeding from the vagina. Her prenatal course was unremarkable. She takes no medications and has no allergies to medications. Examination shows that her cervix is 6 cm dilated and 100% effaced; the fetus is at 0 station. The fetal heart rate has a baseline in the 150s and is reactive. The patient desires an epidural for pain relief. Which of the following should be given orally shortly before the epidural is placed?
Antacid
Regular "house" meal
Antibiotic
Aspirin
Clear liquid meal
A 22-year-old primigravid woman comes for her initial prenatal visit at 6 weeks gestation. She has no complaints except mild nausea. She quit tobacco and alcohol use after she learned that she was pregnant. Vital signs are within normal limits. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. The screening VDRL test returns positive, as does the confirmatory FTA-ABS test. The patient has a history of an allergic reaction to penicillin. Which of the following is the best treatment for this patient?
Doxycycline
Penicillin desensitization
Erythromycin
Tetracycline
Ciprofloxacin
A 22-year-old primigravid woman comes to the labor and delivery ward at term with regular, painful contractions. Her prenatal course was unremarkable. She has a past medical history significant for mitral valve prolapse with regurgitation demonstrated on echocardiography. She takes no medications and has no allergies to medications. Examination shows that her cervix is 4 centimeters dilated and the fetus is in vertex presentation. The fetal heart rate is reassuring. Which of the following is the most appropriate management of this patient?
Antibiotic prophylaxis is not necessary
Administer intravenous antibiotics six hours after the delivery
Administer intravenous antibiotics after the cord is clamped
Administer intravenous antibiotics 30 minutes prior to the delivery
Administer intravenous antibiotics throughout labor
A 22-year-old primigravida presents to your office for a routine OB visit at 34 weeks gestational age. She voices concern because she has noticed an increasing number of spidery veins appearing on her face, upper chest, and arms. She is upset with the unsightly appearance of these veins and wants to know what you recommend to get rid of them. Which of the following is the best advice to give this patient?
Tell her that this is a condition which requires evaluation by a vascular surgeon
Recommend that she wear an abdominal support
Tell her that the appearance of these blood vessels is a normal occurrence with pregnancy
Refer her to a dermatologist for further workup and evaluation
Tell her that you are concerned that she may have serious liver disease and order liver function tests
A 22-year-old primiparous woman is in premature labor at 30 weeks’ gestation. Despite administration of tocolytic agents, it seems she will deliver soon. Pulmonary maturity might be enhanced by the administration of which of the following drugs?
Hydroxyprogesterone
Magnesium sulfate
Betamethasone
Chloroprocaine
Digitalis
A 22-year-old professional basketball player falls on his outstretched hand during a scrimmage game. He has mild swelling at the wrist and tenderness to palpation in the anatomic snuffbox. No fracture is visible on multiple radiographs of the wrist and hand. Which of the following is the most appropriate management of this patient?
Presumptive diagnosis of a scaphoid fracture, with application of a wrist splint, and repeat x-rays in 10–14 days
Presumptive diagnosis of a scaphoid fracture, with application of a short-arm cast including the thumb
Presumptive diagnosis of a scaphoid fracture, application of a short-arm cast including the thumb, and removal of the cast, with repeat x-rays in 10–14 days
Anti-inflammatory medication and application of ice
Elastic wrist support, analgesics, and restricted activity for 1–2 weeks
A 22-year-old university student complains of fatigue and malaise for the past 2 weeks. She also reports feeling feverish, and recently had a sore throat. Physical examination reveals enlarged tonsils and palpable cervical lymph nodes. There is also tenderness in the right upper quadrant on deep palpation, and minimal splenomegaly. Laboratory data show hemoglobin 13 g/dL; hematocrit 40%; platelets 340,000/mL; WBC 9400/mL, with 35% segmented neutrophils, 1% eosinophils, and 64% lymphocytes, of which 36% were atypical. A heterophil antibody (sheep cell agglutination) test is positive. Which of the following is the most appropriate initial treatment for this condition?
Gamma-globulin
Adequate rest
Chlorambucil
Chloramphenicol
Radiation therapy
A 22-year-old white female is brought to your office by her mother because of the recurrent syncopal episodes. The first episode occurred about one year ago when her roommate committed suicide and then several similar episodes occurred usually provoked by a strong emotion. The episodes are preceded by light-headedness, weakness, and blurred vision and last about three minutes with rapid recovery of consciousness. Past medical history is insignificant. She is not taking any medications and denies drug abuse. Her blood pressure is 110/70 mmHg while supine and 108/70 mmHg while standing. Physical findings are within normal limits. EKG performed one month ago was normal. Which of the following is the next best step in the management of this patient?
Electroencephalogram
Upright tilt table testing
Invasive electrophysiologic testing
Echocardiography
24-hour (Holter) monitoring
A 22-year-old white male presented to the emergency room (ER) with the sudden onset of acute right upper quadrant pain. The ultrasound showed cholelithiasis. Initial evaluation revealed hemoglobin of 9 gm/dl with an MCV of 90 fl and a total reticulocyte count of 1000 cells per microliter. Peripheral smear revealed polychromatophilia and spherocytes. Liver fun
His condition is classically transmitted as autosomal recessive disorder
The patient's mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC) is likely to be very low
Vaccination against parvovirus has shown to decrease morbidity and mortality
This patient should be placed on folic acid supplementation
He will probably depend on transfusions
A 22-year-old white obese female presents with headache for the last few weeks. Headache is worse at night and wakes her from sleep. Headache is pulsating in quality and is also associated with nausea and vomiting. She denies any weakness, sensory abnormalities or visual problems. She denies any history of trauma. She does not take any medication. Neurological examination is unremarkable. Fundoscopy shows papilledema. CT scan of head does not show any abnormality. Lumbar puncture is performed and CSF examination is normal except increased CSF pressure. Weight loss fails to control her symptoms. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient?
Treatment with acetazolamide
Treatment with mannitol
Treatment with corticosteroids
Repeated lumbar punctures
Surgery
A 22-year-old woman comes to the office for the evaluation of a breast mass which she discovered while taking a shower 2 months ago. She experiences severe pain in this mass during her menses. She looks very anxious because her 45-year-old friend was diagnosed with breast cancer last year, and who "now has all sorts of medicines that have made her lose her hair." She has no other problems. She has never been pregnant. She is an occasional smoker, and drinks 3-4 beers a week. There is no family history of breast cancer. Her vital signs are stable. Physical examination reveals a 4 x 5 x 6 cm firm, moveable, rubbery mass in her left breast. Ultrasound shows a cystic mass. Needle aspiration yields clear fluid, after which the mass disappears. What is the best approach in the management of this patient?
Order a mammogram to look for other lesions
Breath CT scan
Send the fluid for cytology
Observe for 4 weeks
Perform a core biopsy
A 22-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a missed menstrual period. She has a complex past medical history. She has hypothyroidism, for which she takes thyroxine, she has an artificial heart valve, for which she takes Coumadin, and she recently started tetracycline for acne. She does not think that she is pregnant because she is currently on the oral contraceptive pill, but, if pregnant, she would keep the pregnancy. Physical examination, including pelvic examination, is unremarkable. Urine human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is positive. Which of the following medications should the patient continue to take during the pregnancy?
Coumadin
Discontinue all medications
Tetracycline
Thyroxine
Oral contraceptive pill (OCP)
A 22-year-old woman comes to the physician for an annual examination. She has been sexually active since the age of 15 and has not had regular Pap smears or examinations. She is currently sexually active with multiple partners and intermittently uses condoms. She has no medical problems and takes no medications. Her examination is unremarkable. Her Pap smear is described as satisfactory but limited by the absence of endocervical cells. It is otherwise within normal limits. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Perform laparoscopy with laparoscopically directed biopsies
Perform exploratory laparotomy
Perform colposcopy with colposcopically directed biopsies
Repeat the endocervical portion of the Pap test as soon as possible
Repeat the Pap smear in 1 year
A 22-year-old woman comes to the physician seeking advice. Last night, while she was having sexual intercourse, the condom broke. She is very concerned that she may become pregnant and wants to know whether she can do anything at this point. She has no medical problems and has never had surgery. She takes ibuprofen for dysmenorrhea. She is allergic to sulfa drugs. On physical examination, she is anxious and intermittently sobbing. Her temperature is 37 C (98.6 F), blood pressure is 140/90 mm Hg, pulse is 98/min, and respirations are 24/min. The remainder of her physical examination is unremarkable. A urine pregnancy test is negative. Which of the following is the most appropriate pharmacotherapy?
Clomiphene
Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
Norgestrel/ethinyl estradiol
Gentamicin
Gentamicin Labetalol
A 22-year-old woman comes to the physician with her husband because of vaginal irritation and a malodorous vaginal discharge. Her symptoms started 4 days ago. She also notes pain with intercourse and dysuria. Pelvic examination reveals vaginal and cervical erythema and a copious greenish, frothy discharge. The pH of this discharge is 6.0. A wet preparation is done with normal saline, which shows numerous flagellated organisms that are slightly larger than the surrounding white blood cells. Which of the following is the most appropriate management?
Do not treat the patient or her partner
Treat the patient and her partner with penicillin
Treat only die patient with penicillin
Treat the patient and her partner with metronidazole
Treat only the patient with metronidazole
A 22-year-old woman consults you for treatment of hirsutism. She is obese and has facial acne and hirsutism on her face and periareolar regions and a male escutcheon. Serum LH level is 35 mIU/mL and FSH is 9 mIU/mL. Androstenedione and testosterone levels are mildly elevated, but serum DHAS is normal. The patient does not wish to conceive at this time. Which of the following single agents is the most appropriate treatment of her condition?
Oral contraceptives
Parlodel
Wedge resection
Corticosteroids
GnRH
A 22-year-old woman has a known family history of breast cancer in her first-degree relatives. She undergoes genetic testing and is found to be a BRCA1 mutation carrier. She does not currently desire bilateral prophylactic mastectomy. Which of the following is the next best option to manage her risk for breast cancer?
Mammography every 12 months starting at age 35
Tamoxifen for chemoprevention
Mammography every 12 months starting at age 25
Mammography every 6 months starting at age 35
Mammography every 6 months starting at age 25
A 22-year-old woman has been seeing you for treatment of recurrent urinary tract infections over the past 6 months. She married 6 months ago and became sexually active at that time. She seems to become symptomatic shortly after having sexual intercourse. Which of the following is the most appropriate recommendation for this patient to help her with her problem?
Recommend use of condoms to prevent recurrence of the UTIs
Prescribe prophylactic urinary antispasmodic
Prescribe suppression with an antibiotic
Refer her to a urologist
Schedule an IVP
A 22-year-old woman in labor progresses to 7 cm dilation, and then has no further progress. She therefore undergoes a primary cesarean section. Examination 2 days after the section shows a temperature of 39.1 C (102.4 F), blood pressure of 110/70 mm Hg, pulse of 90/min, and respirations of 14/min. Lungs are clear to auscultation bilaterally. Her abdomen is moderately tender. The incision is clean, dry, and intact, with no evidence of erythema. Pelvic examination demonstrates uterine tenderness. Which of the following is the most appropriate pharmacotherapy?
Ampicillin-gentamicin
Clindamycin-metronidazole
Metronidazole
Clindamycin-gentamicin
Ampicillin
A 22-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department by her father because she is demonstrating "strange, disorganized behavior." Earlier that day, she had insisted that the television news anchorman was talking directly to her about the risks of "poison rays" from the moon. She was also apparently attempting to re-organize her bedroom closet when her father found her mumbling incoherently and counting the same pair of socks over and over. She is agitated when examined in the emergency department and the decision is made to admit her to the psychiatric ward. There, after a detailed interview, the diagnosis of schizophrenia is made. She is stabilized with antipsychotics and then discharged home. Her father asks what can be done to ease her return to everyday life and to decrease the likelihood of re-hospitalization. Which of the following measures would be most helpful in this regard?
Strongly encourage the patient to make new friends
Keep family stresses and conflicts to a minimum
Encourage the patient to return to work
Minimize the patient's social interaction with others
Restrict the patient to home as much as possible
A 22-year-old woman is seen in a surgery clinic for a bulge in the right groin. She denies pain and is able to make the bulge disappear by lying down and putting steady pressure on the bulge. She has never experienced nausea or vomiting. On examination she has a reducible hernia below the inguinal ligament. Which of the following is the most appropriate management of this patient?
Emergent surgical repair of hernia with exploratory laparotomy to evaluate the small bowel
Elective surgical repair of hernia
Emergent surgical repair of hernia
Observation for now and follow-up in surgery clinic if she develops further symptoms
Observation for now and follow-up in surgery clinic in 6 months
A 22-year-old woman presents to the emergency department after she is bitten on her right arm by her neighbor's dog. She provoked the dog while it was eating. The dog is not immunized against rabies, but does not show any signs of rabies. Her right forearm shows a deep bite wound. Her last tetanus booster was 3 years ago. Her wound is cleaned with soap, water, and povidone-iodine solution. What is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient?
Active and passive immunization for rabies
Observe the dog for 10 days
Passive immunization for rabies
Active immunization for rabies
Kill the dog and do brain biopsy
A 22-year-old woman presents to the emergency department in an agitated state, certain that she is "about to die." Fifteen minutes ago, she developed heart palpitations and a severe "viselike" tightness in her chest. She experienced a similar episode last week, which resolved in twenty minutes. She denies using any drugs and her medical history is unremarkable. Her father has a history of heart disease and her mother has diabetes mellitus. She takes no medications. Vital signs are temperature 37.0°C (98.6°F), blood pressure 132/74 mmHg, pulse 118/min, and respiratory rate 30/min. She is sweating profusely. EKG reveals sinus tachycardia. The most appropriate next step is administration of which of the following?
Alprazolam
Buspirone
Fluoxetine
Imipramine
Aspirin
A 22-year-old woman who is 4 months pregnant presents after a motor vehicle collision complaining of abdominal pain and right leg pain. She has an obvious deformity of her right femur. She is hemodynamically stable. Which of the following is the best next step in her management?
MRI of the abdomen
Focused assessment with sonography for trauma (FAST) examination of the abdomen
Plain film of the abdomen with a lead apron as a shield
Observation with serial abdominal exams
Diagnostic peritoneal lavage
A 22-year-old woman with cystic fibrosis is engaged to be married and asks you about childbearing. How should you advise her?
She should use nasal oxygen throughout pregnancy to minimize fetal hypoxemia
Pregnancy and delivery are usually successful with special care and precautions
Pregnancy is contraindicated because maternal mortality is significantly increased
An amniocentesis should be done to detect fetal cystic fibrosis
Her children have a 25% chance of having cystic fibrosis
A 22-year-old woman with mild persistent asthma comes to the primary care clinic after an emergency department visit 2 days ago for an acute asthma exacerbation. She notes an increase in frequency of wheezing and shortness of breath for the past 4 months, with daily symptoms, and has been symptomatic for at least 2 nights per week. She has also had three emergency department visits during the same period. Her current asthma medications include montelukast (leukotriene inhibitor) daily and an albuterol inhaler as needed. The patient’s peak flow is 75% of predicted. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Add a long-acting inhaled β-adrenergic agonist and low-dose inhaled steroid to the regimen
Discontinue the leukotriene inhibitor and change the regimen to daily low-dose inhaled steroids
Admit to the hospital for further pulmonary work-up
Add systemic steroids to the regimen
Start cromolyn sodium
A 22-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, comes to the physician for her first prenatal visit She had a previous full-term, normal vaginal delivery 2 years ago. She has no medical problems and has never had surgery. She takes no medications and has no known drug allergies. Pelvic examination reveals a mucopurulent cervical discharge, no cervical motion tenderness, and an 8-week-sized, non-tender uterus. A cervical swab is performed. Two days later, the laboratory calls to notify the physician that the patient is positive for Chlamydia trachomatis. Which of the following is the most appropriate pharmacotherapy?
Ceftriaxone
Metronidazole
Penicillin
Tetracycline
Erythromycin
A 22-year-old woman, gravida 3, para 2, at 22 weeks' gestation comes to the physician because of an ulcer near her vagina. She noted this a few days ago and it has not improved. The ulcer is painless. The patient has no history of medical problems and takes no medications. She is allergic to penicillin. Examination is significant for a 22 week-sized uterus and a 1 cm, raised, nontender lesion on the distal portion of the vagina. A rapid plasma reagin (RPR) test is sent; the result is positive. A microhemagglutination assay for Treponema pallidum (MHA-TP) is also read as positive. Which of the following is the most appropriate management for this patient?
Desensitize the patient and then administer penicillin
Administer erythromycin
Administer tetracycline
Administer metronidazole
Administer levofloxacin
A 23-year-old female comes to your office to review her daily prescription medications. She had a positive pregnancy test three days ago despite strict contraception. Her last menstrual period was 5 weeks ago. She is on albuterol and beclomethasone inhalers for bronchial asthma, isotretinoin for acne, and lithium for bipolar disorder. Her bipolar disorder has been stable for the past several years. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or drugs. Physical examination shows no abnormalities; vital signs are stable. Which of the following is the most appropriate advice for this patient?
Ask her to stop all 4 medications
Ask her to continue all 4 medications
Ask her to stop isotretinoin and wean lithium
Ask her to stop beclomethasone, isotretinoin and lithium
Ask her to stop beclomethasone and lithium
A 23-year-old G1 at 38 weeks gestation presents in active labor at 6 cm dilated with ruptured membranes. On cervical examination the fetal nose, eyes, and lips can be palpated. The fetal heart rate tracing is 140 beats per minute with accelerations and no decelerations. The patient’s pelvis is adequate. Which of the following is the most appropriate management for this patient?
Perform forceps rotation in the second stage of labor to convert mentum posterior to mentum anterior and to allow vaginal delivery
Allow patient to labor spontaneously until complete cervical dilation is achieved and then perform an internal podalic version with breech extraction
Attempt manual conversion of the face to vertex in the second stage of labor
Allow spontaneous labor with vaginal delivery
Perform immediate cesarean section without labor
A 23-year-old G1P0 reports to your office for a routine OB visit at 28 weeks gestational age. Labs drawn at her prenatal visit 2 weeks ago reveal a 1-hour glucose test of 128, hemoglobin of 10.8, and a platelet count of 80,000. All her other labs were within normal limits. During the present visit, the patient has a blood pressure of 120/70 mm Hg. Her urine dip is negative for protein, glucose, and blood. The patient denies any complaints. The only medication she is currently taking is a prenatal vitamin. She does report a history of epistaxis on occasion, but no other bleeding. Which of the following medical treatments should you recommend to treat the thrombocytopenia?
Stop prenatal vitamins
Splenectomy
Intravenous immune globulin
Oral corticosteroid therapy
No treatment is necessary
A 23-year-old G2P2 requires a cesarean delivery for arrest of active phase. During labor she develops chorioamnionitis and is started on ampicillin and gentamicin. The antibiotics are continued after the cesarean delivery. On postoperative day 3, the patient remains febrile and symptomatic with uterine fundal tenderness. No masses are appreciated by pelvic examination. She is successfully breast-feeding and her breast examination is normal. Which antibiotic should be initiated to provide better coverage?
Cephalothin
Vancomycin
Clindamycin
Polymixin
Levofloxacin
A 23-year-old G3P2002 presents for a routine obstetric (OB) visit at 34 weeks. She reports a history of genital herpes for 5 years. She reports that she has had only two outbreaks during the pregnancy, but is very concerned about the possibility of transmitting this infection to her baby. Which of the following statements is accurate regarding how this patient should be counseled?
There is no risk of neonatal infection during a vaginal delivery if no lesions are present at the time the patient goes into labor
The patient should be scheduled for an elective cesarean section at 39 weeks of gestation to avoid neonatal infection
Starting at 36 weeks, weekly genital herpes cultures should be done
The herpes virus is commonly transmitted across the placenta in a patient with a history of herpes
Suppressive antiviral therapy can be started at 36 weeks to help prevent an outbreak from occurring at the time of delivery
A 23-year-old G3POA2 female presents to your clinic at an estimated 12 weeks of gestational age. She is a new patient and has come to your clinic to seek an elective abortion. She has had two elective abortions in the past because of unplanned pregnancy. She has no past medical history and takes no medications. Her physical examination is within normal limits and a limited ultrasound examination was able to detect fetal heart tones. You and your partners have a strict policy against performing abortions because some members of the group object to the procedure. You decide it would be best to stick to this policy; however, the patient becomes angry and tells you that she will sue you if you do not perform the procedure. What is the best response to this patient?
"If we keep doing abortions, then your uterus can get scarred and you may not be able to become pregnant again
"I can refer you to another physician who will perform the procedure"
"I don't think any physician will perform an abortion at this gestational age."
"If you wanted to have an abortion why did you not come earlier?"
"You can do what you want. I cannot do the abortion because of our group policy"
A 23-year-old gravida 3, para 2 is admitted to the hospital at 31 weeks' gestation with painful uterine contractions. Her cervix is initially 3 cm dilated. Magnesium sulfate is started. Over the next 5 hours she progresses to full dilation. After a 1-hour second stage, she delivers a 2013-g (4-lb, 7-oz) newborn. In the neonatal intensive care unit, the infant develops respiratory distress and pneumonia. Over the following days the infant develops septicemia. Preliminary blood cultures demonstrate gram-positive cocci in chains. Treatment with which of the following would most likely have prevented this neonatal outcome?
Folic acid
Naloxone
Oxytocin
Penicillin
Gentamicin
A 23-year-old male hospitalized for confusion and seizures is treated with intravenous high-dose acyclovir. On the third day of hospitalization, his serum creatinine level increases to 3.4 mg/dl from a baseline of 0.9 mg/dl at admission. The observed finding could have been potentially prevented by which of the following?
Pre-treatment with allopurinol
Aggressive intravenous hydration
Pre-treatment with prednisone
Careful allergy history taking
Monitoring the blood drug levels
A 23-year-old male is brought to the emergency department from the scene of a motor vehicle accident. He appears distressed and complains of severe abdominal pain and distention. Urgent laparotomy reveals splenic laceration, and splenectomy is performed. There are no post-operative complications. The patient has no significant past medical history. He drinks alcohol occasionally but denies smoking cigarettes or using illicit drugs. He works as a computer programmer in a small office. Which of the following vaccines is recommended in this patient?
Hepatitis A
Meningococcal
Pertussis
Salmonella
Hepatitis B
A 23-year-old man comes to the emergency department (ED) at 2:00 am due to severe pain all over his body for the past few hours. He was diagnosed with sickle cell anemia at 6 months of age, and has had previous episodes of unbearable pain in his chest, abdomen, thighs and lower back. He was hospitalized six times in the past twelve months. He does not have regular follow-up visits up with his physician, and comes to see him "only if required." His blood pressure is 110/80 mmHg, pulse is 80/min, respirations are 16/min and temperature is 37 C (98F). Adequate hydration and analgesics are administered in the ED. What is the best intervention to prevent his painful episodes?
Prophylactic antibiotics
Hydroxyurea
Erythropoietin
Periodic blood transfusions
Folic acid supplements
A 23-year-old man is admitted to the hospital after being struck by a motor vehicle. The patient sustained a compound fracture of his left femur in the accident and has had moderate blood loss. He was admitted to the hospital, has been stabilized over the past few days, and is now preparing for physical therapy. His hematocrit is 24%. The man feels weak and fatigued and easily gets short of breath with mild exertion. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Transfuse whole blood to a goal hematocrit of 30%
Transfuse packed red blood cells to a hematocrit goal of 30%
Transfuse fresh frozen plasma to a hematocrit goal of 30%
Discontinue physical therapy until the patient recovers more of his strength
Continue with physical therapy; no transfusion is indicated
A 23-year-old man is brought to the emergency department after being hit in the neck with a dull instrument. He has neck pain and stiffness. Vital signs are stable. Neurological examination shows no abnormalities. An astute medicine resident decides to order an angiogram of the neck vessels to rule out carotid artery injury. Diagnostic angiography shows an intimal flap in the left internal carotid artery just above the carotid bifurcation. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Neck exploration and repair
Aspirin
Ligation of carotid artery
Observation
Heparin
A 23-year-old man is brought to the emergency department in an obtunded state following a gun-shot wound to the right upper quadrant of the abdomen. His systolic blood pressure is 60 mm Hg and unable to obtain diastolic blood pressure. His pulse is 136/min. Chest auscultation shows clear heart and breath sounds. The abdomen appears distended, and there is an obvious gun-shot wound on the right upper quadrant. The bowel sounds are decreased. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Diagnostic peritoneal lavage
Angiography
Focused ultrasonography
Laparoscopy
Laparotomy
A 23-year-old man is seen in the emergency department for sudden onset, right-sided pleuritic chest pain that developed 30 minutes ago while he was watching television. The patient also complains of difficulty breathing. He has no prior medical history, denies smoking and intravenous drug use, and does not take any medications. His temperature is 37.3°C (99.1°F), blood pressure is 130/82 mm Hg, pulse is 92/ min and regular, respiratory rate is 20/min and shallow, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. His body mass index is 18 kg/m². Diminished breath sounds, hyperresonance, and decreased tactile fremitus are prominent in the right lung field. The trachea is midline. X-ray of the chest shows a 10% pneumothorax on the right. Which of the following is the most appropriate initial management?
Tube thoracostomy with doxycycline pleurodesis
Thoracoscopy with stapling of blebs
Open thoracotomy with oversewing of the pleural blebs and scarification of the pleura
Needle decompression
Observation with supplemental oxygen
A 23-year-old man presents to the emergency department with a soft-tissue injury to the left lower extremity. The injury was sustained 8 hours earlier in a motorcycle accident on a gravel road. On examination, the patient has a 7-cm deep laceration to the calf, with visible road debris. He had full tetanus immunization as a child and a tetanus booster immunization at age 15. Appropriate management of this injury would include which of the following?
Tetanus toxoid and IV antibiotics
Irrigation and debridement of the wound; IV antibiotics
Irrigation and debridement of the wound; tetanus toxoid
Irrigation and debridement of the wound; tetanus toxoid and tetanus immune globulin
Irrigation and debridement of the wound
A 23-year-old married woman consults you because she and her husband have never consummated their marriage because she has severe pain with attempts at vaginal penetration. Her pelvic examination is normal except for involuntary tightening of her vaginal muscles when you attempt to insert a speculum. Which of the following conditions would best be treated with the use of vaginal dilators?
Primary dysmenorrhea
Vulvar vestibulitis
Anorgasmia
Deep-thrust dyspareunia
Vaginismus
A 23-year-old primigravid female at 38 weeks' gestation was admitted to the delivery room for management of labor. She was in active labor for 4-hours during which her cervical dilation progressed from 3cm to 8cm, and descent progressed from - 1 to +1 station. Examination 6-hours later showed the same degree of dilation and descent. The fetal head is in the Left Occipita Anterior (LOA) position. An external tocometer is placed and reveals contractions 3 min apart, lasting 50 seconds each. Internal pelvic assessment shows prominent ischial spines. FetaI heart monitoring shows a baseline of 140 bpm with frequent accelerations. Prenatal ultrasound at 37-weeks showed a fetus of average size. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Forceps application
Administer IV Oxytocin
Zavanelli maneuver
Close observation for 2 more hours
Low-transverse C section
A 23-year-old primigravid woman at 9 weeks gestation presents to the emergency room because of generalized weakness and lightheadedness. For the past 4 weeks she has not been able to keep anything down and over the past week her nausea and vomiting have worsened. She has no fever, abdominal pain, diarrhea, headache, dysuria, polyuria, tremor, or heat intolerance. She does not use tobacco, alcohol or illicit drugs. Her temperature is 37.2 C (98.9 F); orthostatic vitals are as follows: BP 136/86 mm Hg and pulse 98/min supine, and 110/70 mm Hg and 115/min standing. Physical examination shows dry mucus membranes. The remainder of the examination is unremarkable. Laboratory studies show: Hematocrit: 50%, Platelets: 200,000/mm3, Serum sodium: 130 mEq/L, Serum potassium: 2.8 mEq/L, Chloride: 86 mEq/L, Bicarbonate: 30 mEq/L, Blood urea nitrogen (BUN): 30mEq/L, Serum creatinine: 1.6 mg/dl, Blood glucose: 98 mg/dl. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
CT scan of the head
Quantitative beta HCG levels
Right upper quadrant ultrasonogram
Upper GI endoscopy
Pelvic ultrasonogram
A 23-year-old primigravid woman comes to your office for her first prenatal visit. She is working as an aerobics instructor and is concerned about the effect her exercise schedule might have on the pregnancy. She teaches 30 minutes daily in the morning and does not feel fatigued. She does not use tobacco, alcohol or drugs. Vital signs are normal and physical examination is unremarkable. Which of the following is the best advice to give this patient?
"You can even intensify your training efforts if you want"
"You may have prolonged labor during delivery"
"You should continue your current aerobic exercise schedule"
"You need to reduce the intensity of exercise"
"You need to reduce the duration of exercise time to 15 minutes per day"
A 23-year-old white female presents with an acute onset of headache for the last eight hours. Her headache is severe, unilateral, pulsating in quality, associated with photophobia, worsens with physical activity, and does not respond to acetaminophen or ibuprofen. This is her 6th episode of similar headache over the last 2 months, and it is her first time to seek medical attention. Her neurological examination is unremarkable. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient?
Propranolol
Rizatriptan
Prochlorperazine
Verapamil
Ergotamine
A 23-year-old woman comes to the physician because she thinks that she may be pregnant. She missed her last two periods and feels "different." A urine pregnancy test is positive and an ultrasound reveals a 12-week fetus. The patient is very concerned because she received the measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine four months ago and was told to wait 3 months before attempting conception. The pregnancy is desired. The patient asks if she should have a termination of pregnancy because she was vaccinated shortly before becoming pregnant. Which of the following is the most appropriate response?
The vaccine risk is high and termination should be strongly considered
The vaccine risk is moderate and termination should be considered
The vaccine risk is low and is not in itself a reason to terminate
There is no vaccine risk and termination is completely inappropriate
The vaccine risk is high and termination is mandated
A 23-year-old woman develops painful vulvar vesicles that contain intranuclear inclusions on cytologic examination. She is 22 weeks’ pregnant. Which of the following statements about genital herpes is correct?
Acyclovir should be prescribed from 36 gestational weeks until after delivery in women with primary herpes anytime during pregnancy
Herpes cultures from the cervix should be obtained weekly beginning at 36 weeks’ gestation
Intrauterine infection with herpes is common after 20 weeks in women with primary herpes
An active genital herpetic lesion any time after 20 weeks’ gestation requires a cesarean section
Pitocin induction of labor should be started within 4 hours after ruptured amniotic membranes in a woman at term with active genital herpes
A 23-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department because of severe respiratory distress. She was stung by a bee one hour ago. Her temperature is 37.1C (98.8F), blood pressure is 80/50 mm Hg, pulse is 98/min and respirations are 20/min. Examination shows a conscious woman in severe respiratory distress with audible wheezing. Her skin is warm to palpation. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Look for the stinger and carefully remove it
Give her oral steroids
Give her intravenous anti-histamines
Giver her subcutaneous epinephrine
Give her intravenous steroids
A 23-year-old woman presents for evaluation of a 7-month history of amenorrhea. Examination discloses bilateral galactorrhea and normal breast and pelvic examinations. Pregnancy test is negative. Which of the following classes of medication is a possible cause of her condition?
Antiestrogens
Prostaglandins
GnRH analogues
Gonadotropins
Phenothiazines
A 23-year-old woman presents for evaluation of infertility. For the past 12 months she has been having sexual intercourse without contraception but has not been able to conceive. Her history is significant for irregular periods for the past 2 years. She reports exercising intensely six days per week and acknowledges having a lot of stress at work. She smokes one pack of cigarettes daily. On physical examination, her vital signs are within normal limits. Her BMI is 18 kg/m2. Urine pregnancy test is negative. Laboratory studies show: Serum FSH: low, Serum LH: low, Serum prolactin: normal, Serum TSH: normal. Which of the following therapies would be most helpful for this patient's infertility?
Continuous GnRH therapy
In vitro fertilization
Anti-androgen agent
Pulsatile GnRH therapy
Dopamine agonist
A 23-year-old woman seeks help for exquisite pain with defecation and blood streaks on the outside of her stools, which she has been having for several weeks. Because of the pain, she has avoided having bowel movements, and when she finally did the stools were hard and even more painful. When seen, she has no fever or leukocytosis. Physical examination has to be done under spinal anesthesia, because the patient was so afraid of the pain that she initially refused even inspection of the area. The examination confirms the suspected diagnosis, and she is placed on stool softeners and appropriate topical agents, but without success. She is willing to undergo more aggressive treatment. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step?
Fistulotomy
Rubber band ligation
Lateral internal sphincterotomy
Incision and drainage
Excision of the lesion
A 23-year-old woman visits your office because of headache, malaise, anorexia, pain in both sides of her jaw, and discomfort in both lower abdominal quadrants. Physical examination reveals enlarged parotid glands; bilateral lower quadrant abdominal tenderness; a temperature of 38.7°C; and a pulse rate of 92/min. Serologic testing (IgM) confirms the diagnosis of mumps. Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment for this condition?
Steroids
Symptomatic
Immunization
Broad-spectrum antibiotics
Sulfonamides
A 23-year-old woman was diagnosed with schizophrenia after a single episode of psychosis (hallucinations and delusions) that lasted 7 months. She was started on a small dose of olanzapine at the time of diagnosis, which resulted in the disappearance of all her psychotic symptoms. She has now been symptom free for the past 3 years. Which of the following treatment changes should be made first?
Her olanzapine should be maintained at a constant level, but she can stretch out the time between her appointments with the psychiatrist
Her olanzapine should be switched to a long-acting depot antipsychotic medication such as haloperidol decanoate
Her olanzapine should be decreased, but not stopped
Her olanzapine should be decreased and then stopped if she remains symptom free
Her diagnosis should be reexamined as she is likely not schizophrenic at all
A 23-year-old woman who is 10 weeks pregnant with her first pregnancy is referred to you for smoking cessation. She has been smoking since the age of 21 and has never tried to quit. However, now that she is pregnant she would really like to quit. She has no symptoms of depression. Her past medical history is significant for asthma. She uses an inhaler occasionally for her asthma and takes no other medications. She has never had surgery and has no known drug allergies. Physical examination is normal for a patient at 10 weeks’ gestation. Which of the following is the most appropriate management for this patient?
Refer for smoking cessation counseling
Prescribe bupropion
Prescribe the nicotine patch
Prescribe fluoxetine
Address smoking cessation after delivery
A 23-year-old woman with an 18-year history of insulin-dependent diabetes is brought to the emergency department by her date, who became alarmed by her acute mental confusion and sudden-onset bizarre behavior. He explains that they spent the day at the beach, where she had been very active, playing volley ball and swimming, and that they missed lunch but were on their way to eat dinner when this sudden change in behavior occurred. He states over and over again that they had not been using drugs or drinking alcohol. The triage nurse notes perspiration, increased salivation, restlessness, and tachycardia. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient?
Order arterial blood gases (ABGs) analysis
Order an immediate drug screen
Order an immediate blood glucose analysis
Order serum electrolytes analysis
Order a complete blood count (CBC)
A 23-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1 at 26 weeks' gestation, comes to the physician because of fevers and pain in the middle of the back on the right side. Her fevers started 2 days ago, and the back pain began yesterday. Her temperature is 38.3 C (101 F), blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg, pulse is 110/min, and respirations are 16/min. She has left costovertebral angle tenderness. Her abdomen is benign and gravid. Her laboratory values show leukocytes of 18,000/mm3. Urinalysis reveals white blood cells that are too numerous to count per high powered field. Which of the following is the most appropriate pharmacotherapy for this patient?
Acyclovir
Levofloxacin
Metronidazole
Tetracycline
Cefazolin
A 23-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, at 6 weeks' gestation comes to the emergency department because of lower abdominal pain and fevers. She states that her symptoms began 2 days ago and have steadily worsened since. Past medical history is significant for 2 episodes of gonorrhea and 1 episode of chlamydia. Temperature is 38.9 C (102.1 F), blood pressure is 110/76 mm Hg, pulse is 102/min, and respirations are 12/minute. Abdominal examination demonstrates significant lower abdominal tenderness. Pelvic examination shows a mucopurulent cervical discharge and bimanual examination reveals cervical motion tenderness and adnexal tenderness. Complete blood count shows leukocytes 18,000/mm3. Pelvic ultrasound shows a 6-week intrauterine gestation with no adnexal findings. Which of the following is the most appropriate management?
Intravenous clindamycin and gentamicin and hospital admission
Laparoscopy
Intravenous cefotetan and doxycycline and hospital admission
Intramuscular ceftriaxone, oral doxycycline, and discharge home
No treatment is necessary
A 23-year-old, gravida 2, para 1 woman at 30 weeks gestation comes to the ER after she noticed a sudden gush of clear fluid coming from her vagina. She has had no uterine contractions or vaginal bleeding. Her pregnancy has been uncomplicated; she has had consistent prenatal care. Vital signs are normal. Sterile speculum examination shows the cervix is minimally effaced and 2cm dilated; there is pooling of clear fluid in the vaginal fornix, and when pressure is applied to the fundus, clear fluid comes out of the cervix. Emergency ultrasound shows a fetus of average size in the vertex presentation and an Amniotic Fluid Index (AFI) of 15. Nonstress test shows a baseline of 120 bpm and frequent accelerations. Amniotic fluid analysis shows lecithin/sphingomyelin ratio of 1.0. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Immediate vaginal delivery
Repair of ruptured membranes
Amnioinfusion
Cesarean section
Betamethasone
A 23-year-old, previously healthy man presents to the ER after sustaining a single gunshot wound to the left chest. The entrance wound is 3 cm inferior to the nipple and the exit wound is just below the scapula. A chest tube is placed that drains 400 mL of blood and continues to drain 50 to 75 mL/h during the initial resuscitation. Initial blood pressure of 70/0 mm Hg has responded to 2L crystalloid and is now 100/70 mm Hg. Abdominal examination is unremarkable. Chest x-ray reveals a reexpanded lung and no free air under the diaphragm. Which of the following is the best next step in his management?
Peritoneal lavage
Local wound exploration
Admission and observation
Exploratory celiotomy
Exploratory thoracotomy
A 24-year old woman comes to the physician because of burning with urination. She states that every time she urinates there is pain and that she has a feeling that she constantly needs to urinate even though only a little comes out. She has never had any similar symptoms before. She has no medical problems and no known drug allergies. Examination is unremarkable. Urinalysis demonstrates that the urine is positive for leukocyte esterase and nitrites. Which of the following is the most appropriate pharmacotherapy?
Wait for the culture results to institute therapy
Oral trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole for 3 days
Intramuscular ceftriaxone
Oral levofloxacin for 7 days
Intravenous levofloxacin
A 24-year-old African American female presents in the 35th week of an uncomplicated pregnancy with numbness and burning in her right palm. She says the sensation is so uncomfortable that it frequently makes it difficult to sleep Which of the following is the best initial treatment for this patient?
Indomethacin
Oral corticosteroids
Decompression surgery
Wrist splinting
Local corticosteroid injection
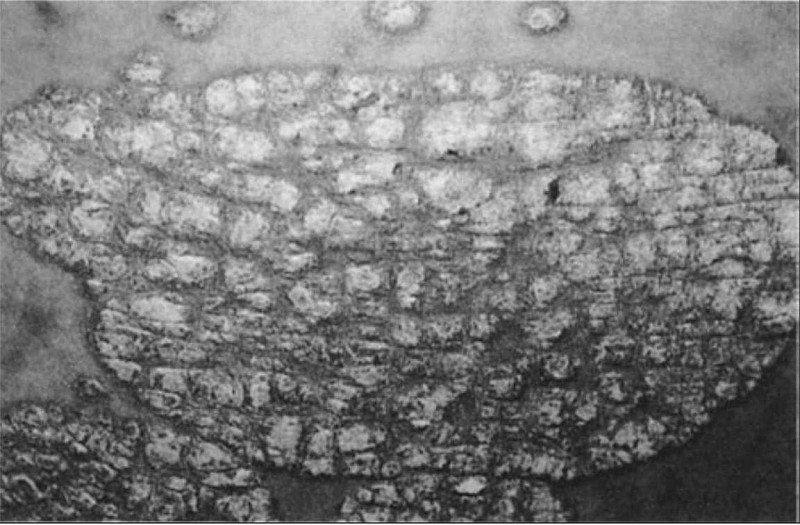
A 22-year-old male presents with a 6-month history of a red, nonpruritic rash over the trunk, scalp, elbows, and knees. These eruptions are more likely to occur during stressful periods and have occurred at sites of skin injury. The patient has tried topical hydrocortisone without benefit. On examination, sharply demarcated plaques are seen with a thick scale. Pitting of the fingernails is present. There is no evidence of synovitis. What is the best first step in the therapy of this patient’s skin disease?
Photochemotherapy (PUVA)
Topical fluticasone
Oral cyclosporine
Topical calcipotriene
Oral methotrexate
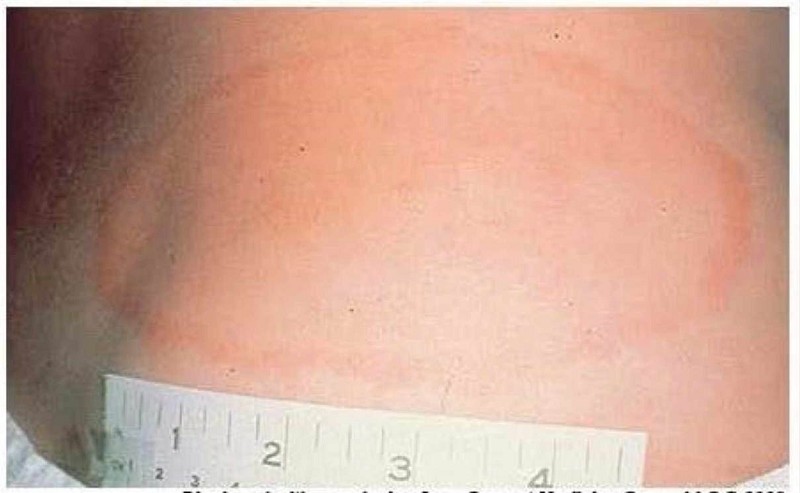
A 22-year-old female presents to the office with a three-day history of rash, fever, and malaise. There is no burning or itching associated with the rash. Two weeks ago, she had been camping in northern Massachusetts, and noted a tick bite after walking through the woods. She is twelve weeks pregnant. The rash is shown below. The examination is otherwise unremarkable. What is the most appropriate treatment for this patient?
Doxycycline
Azithromycin
Ceftriaxone
Penicillin G
Amoxicillin
{"name":"DES C_Management (2) Prepared : CHILLY", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"A 19-year-old woman, gravida 1, para 1, is immediately status post a normal spontaneous vaginal delivery and normal third stage when she develops brisk bright red bleeding from the vagina. Her prenatal course was unremarkable. She has asthma, which worsened during the pregnancy. Ten years ago, she had a tonsillectomy. She takes a steroid and albuterol inhaler. She has no known drug allergies. Her temperature is 37 C (98.6 F), blood pressure is 100\/70 mm Hg, pulse is 115\/min, and respirations are 16\/min. Her abdomen is soft and non-tender. Her uterus is soft and \"boggy\" to palpation. Pelvic examination reveals no evidence of a laceration. Which of the following treatments should be avoided in managing this patient's postpartum hemorrhage? Acetaminophen IV hydration Methylergonovine Oxytocin 15-methyl-prostaglandin F2ct (PGF2a), A 19-year-oldgangmemberisshotintheabdomenwith a .38 caliber revolver. The entry wound is in the epigastrium, to the left of the midline. The bullet is lodged in the psoas muscle on the right. He is hemodynamically stable, and the abdomen is moderately tender. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in diagnosis? Close clinical observation Emergency ultrasound CT scan of the abdomen Diagnostic peritoneal lavage Exploratory laparotomy, A 2-month-old child of an HIV-positive mother is followed in your pediatric practice. Which of the following therapies should be considered for this child? . Monthly evaluation for Kaposi sarcoma . Prophylaxis against Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia (Pneumocystis carinii) . Vitamin C supplementation . Oral polio virus vaccine . Bone marrow transplantation","img":"https://cdn.poll-maker.com/20-797345/image.jpeg?sz=1200"}
More Quizzes
Water Quiz
940
Dsad
100
Basketball terminology(Pick the right answer)
5218
Dislocation and Fracture
10510
Free Advanced C# Programming
201021696
Free Home Health Authorization
201021696
Free OCD Awareness: 15 Questions
201022008
Nickname Generator for Girls: Find Your Perfect Alias
201025220
Free Integrated Healthcare Knowledge
201023570
Free Psychological Assessment Fundamentals
201023761
Free Icelandic Language Proficiency
201028035
Ultimate on Famous Hamlet Quotes - Test Your Wit
201023957