BIOL 230 LAB Quiz Review for 11/21/2017

BIOL 230 Lab Quiz Review
Test your knowledge on sterilization, disinfectants, and microbial actions with our comprehensive BIOL 230 Lab Quiz Review. This quiz covers essential topics to reinforce your understanding of microbiology practices.
You'll learn about:
- Different methods of killing microorganisms
- The impact of solutions on cell membranes
- Antimicrobial agents and their effects
The process of destroying all living organisms (including endospores) and viruses.
Sanitation
Sterilization
Disinfection
Decontamination
Treatment of an object or surface to make it safe to handle and lessen the number of microorganisms.
Disinfection
Sterilization
Sanitation
Decontamination
The elimination of microorganisms, but not necessarily endospores, from inanimate objects or surfaces.
Disinfection
Sterilization
Decontamination
Sanitation
______________ heat is generally more effective than __________ heat at killing microorganisms.
Moist;Dry
Dry;Moist
Moist heat kills microorganisms by denaturing their DNA and melting the lipids in the cytoplasmic (plasma) membrane.
True
False
What are the two methods of applying moist heat?
Boiling water (90°C)
Boiling water (100°C)
Autoclave
Incineration
What are the two methods of applying dry heat?
Autoclave
Incineration
UV light
Oven
Hot Air Sterilization
Refrigeration and freezing kills microorganisms by lowering temperature to stop growth by stopping microbial metabolism.
True
False
If a cell was dropped into a solution and the cell shrinks then the solution is _______?
Isotonic
Hypotonic
Hypertonic
If the net movement of solvent (H2O) was towards the cell then the solution is ___________?
Isotonic
Hypotonic
Hypertonic
If a cell with no cell wall was dropped into an hypotonic environment then the environment is ___________?
Static
Cidal
Hypotonic solutions Results in shrinkage of the cytoplasmic (plasma) membrane also called "Plasmolysis".
True
False
Prolonged exposure to UV rays can be lethal to cells because Thymine dimers form in the DNA.
True
False
The cidal activity of UV light depends on the length of exposure and the wavelength; Longer exposures and a wavelength of 260 - 270 nm have greater cidal activities.
True
False
The filters contain pores small enough to prevent the passage of microbes by large enough to allow the organism-free fluid to pass through.
True
False
Why are filters preferred over autoclaving for materials such as vaccines, antibiotic solutions, sera and enzyme solutions.?
Heat Sensative
Denature
An agent used to eliminate vegetative microorganisms inanimate objects or surfaces but is generally too toxic to use on human tissues.
Antiseptic
Disinfectant
Sanitizer
An agent that kills or inhibits growth of microorganisms and is safe to use on human tissue.
Disinfectant
Sanitizer
Antiseptic
Chemical agents are usually unreliable for sterilization because they work slowly and dry out before sterilization.
True
False
Broad-spectrum drugs/antibiotics are effective against a variety of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria while Narrow-spectrum drugs/antibiotics are effective against just gram-positive or gram-negative or only a few species.
Broad-spectrum drugs/antibiotics are effective against a variety of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria while Narrow-spectrum drugs/antibiotics are effective against just gram-positive or gram-negative or only a few species.
Antibiotics vs Synthetic Drugs:
Synthetic drugs are man made and are usually created in a lab while antibiotics are chemicals products created by other microorganisms that are static or cidal to other microorganisms.
Antibiotics vs Synthetic Drugs:
Synthetic drugs are man made and are usually created in a lab while antibiotics are chemicals products created by other microorganisms that are static or cidal to other microorganisms.
The factors that may influence antimicrobial action of disinfectants, antiseptics, and sanitizers are The concentration of the chemical agent; The temperature at which the agent is being used
The kinds of microorganisms present; The number of microorganisms present and
The nature of the material bearing the microorganism.
The factors that may influence antimicrobial action of disinfectants, antiseptics, and sanitizers are The concentration of the chemical agent; The temperature at which the agent is being used
The kinds of microorganisms present; The number of microorganisms present and
The nature of the material bearing the microorganism.
There are 2 common antimicrobial modes of action for disinfectants, antiseptics and sanitizers:
1) Damage the lipids and/or proteins of the cytoplasmic (plasma) membrane
2) Denature microbial enzymes
There are 2 common antimicrobial modes of action for disinfectants, antiseptics and sanitizers:
1) Damage the lipids and/or proteins of the cytoplasmic (plasma) membrane
2) Denature microbial enzymes
An in vitro test is done under artificial, controlled, laboratory conditions while an in vivo test is one done under the conditions of normal use. The reason why chemicals in vitro agents many not necessarily apply to in vivo is because of the nature the drugs are taken (ingested). One problem would be how to reach the affected area or if the chemical can withstand the body's differing environments (Stomach higher pH).
An in vitro test is done under artificial, controlled, laboratory conditions while an in vivo test is one done under the conditions of normal use. The reason why chemicals in vitro agents many not necessarily apply to in vivo is because of the nature the drugs are taken (ingested). One problem would be how to reach the affected area or if the chemical can withstand the body's differing environments (Stomach higher pH).
Transient microbiota are temporary and resident microbiota are permanent. It is easier to remove transient microbiota because they have not evolved to acquire characteristics/features that allow them to cling to the body. Thus when washing hands most likely all the transient microbiota are removed while only some of the resident microbiota are removed. Effectively reducing the number of microorganisms in the hands.
Transient microbiota are temporary and resident microbiota are permanent. It is easier to remove transient microbiota because they have not evolved to acquire characteristics/features that allow them to cling to the body. Thus when washing hands most likely all the transient microbiota are removed while only some of the resident microbiota are removed. Effectively reducing the number of microorganisms in the hands.
Antimicrobial chemotherapy is the use of chemicals to inhibit or kill microorganisms in or on the host. This is based on selective toxicity, which means the agent used must inhibit or kill the microorganism without seriously harming the host.
Antimicrobial chemotherapy is the use of chemicals to inhibit or kill microorganisms in or on the host. This is based on selective toxicity, which means the agent used must inhibit or kill the microorganism without seriously harming the host.
The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) is the lowest concentration of a chemotherapeutic agent capable of preventing growth of the test organism. To lower the cost. Chance of toxicity and the chance of side effects and hypersensitivity in a host.
The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) is the lowest concentration of a chemotherapeutic agent capable of preventing growth of the test organism. To lower the cost. Chance of toxicity and the chance of side effects and hypersensitivity in a host.
The vegetative form of a protozoa (motile, feeding, reproducing form) is called a cyst and their protective form called a trophozoite.
True
False
Parasitic Protozoa include:
Amoeba- No general shape; look like spilled liquid with tentacles
Flagllates - Have flagella for movement and some with undulating membrane (Trypanasoma)
Ciliates- Covered in cilia and are motile
Sporozoa- Non motile/moving nasties
Parasitic Protozoa include:
Amoeba- No general shape; look like spilled liquid with tentacles
Flagllates - Have flagella for movement and some with undulating membrane (Trypanasoma)
Ciliates- Covered in cilia and are motile
Sporozoa- Non motile/moving nasties
The classes of helminths (worms):
Nematodes - Roundworms
Trematodes- Flukes (Bacon Strips)
Cestodes - Tapeworms/Flatworms/ Segmented worms
The classes of helminths (worms):
Nematodes - Roundworms
Trematodes- Flukes (Bacon Strips)
Cestodes - Tapeworms/Flatworms/ Segmented worms
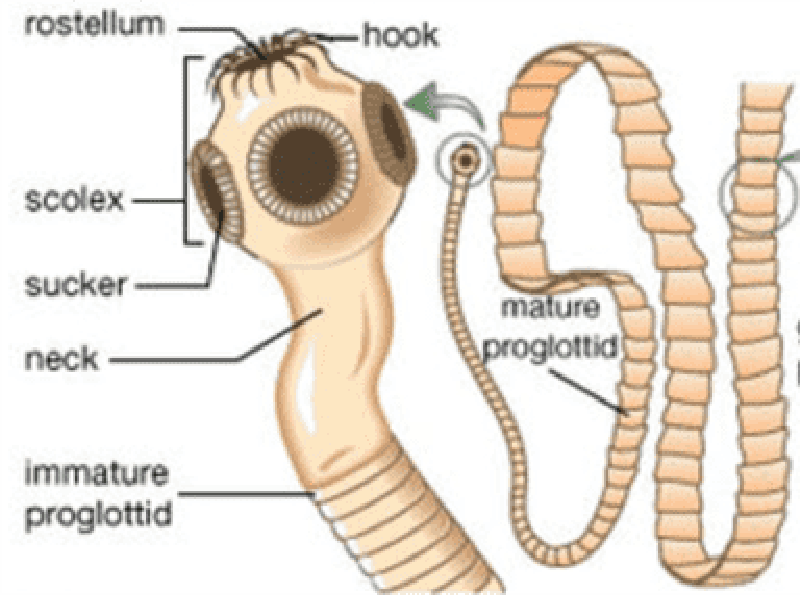
In a tapeworm the scolex is the head and a proglottid is a segment that contains a uterus and thousands of ova (EGGS).
In a tapeworm the scolex is the head and a proglottid is a segment that contains a uterus and thousands of ova (EGGS).
{"name":"BIOL 230 LAB Quiz Review for 11\/21\/2017", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Test your knowledge on sterilization, disinfectants, and microbial actions with our comprehensive BIOL 230 Lab Quiz Review. This quiz covers essential topics to reinforce your understanding of microbiology practices.You'll learn about:Different methods of killing microorganismsThe impact of solutions on cell membranesAntimicrobial agents and their effects","img":"https:/images/course1.png"}
More Quizzes
Microbiology
1368
Stains for microscopy
10511
Welcome to Uusi puu - New wood quiz!
10514
Who Would Do That?
1059
Do I Want Another Baby? - Free Readiness Check
201018440
SECNAVINST 5216.5 Correspondence Manual - Free
201022817
Tall Nicknames - Find Your Perfect Match
201018787
British Open Trivia - Test Your Championship Knowledge
201021701
Blue Eye Samurai Character - Which Are You?
201020267
Life Satisfaction - Are You Happy? Free Online
201019740
What Is a Juggalette? Juggalo Culture - Free
201020489
Am I Attractive?: Do Guys Notice You
201020952
