Practice spotter 11/12
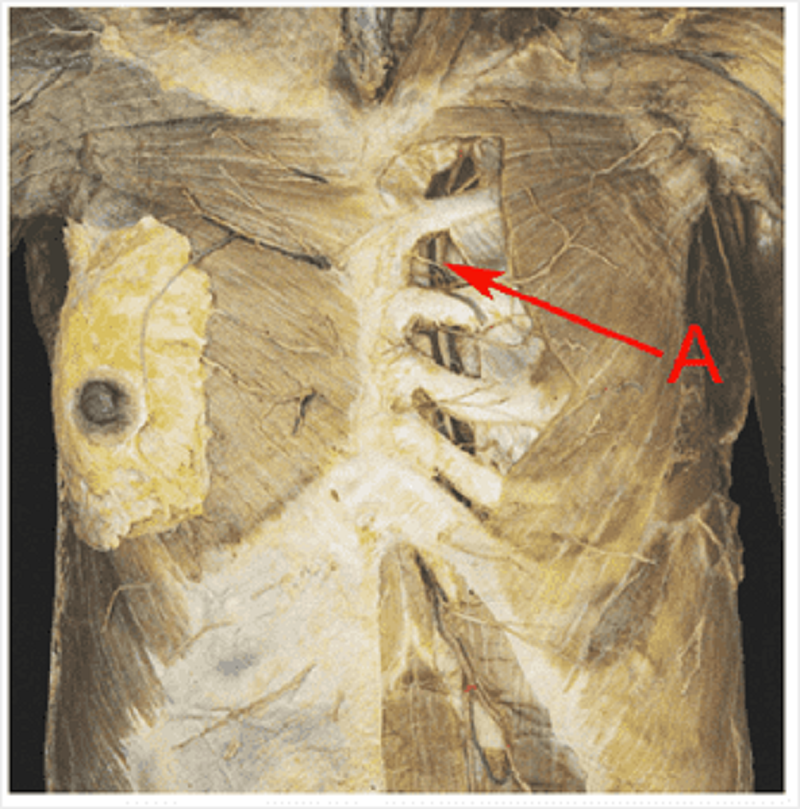
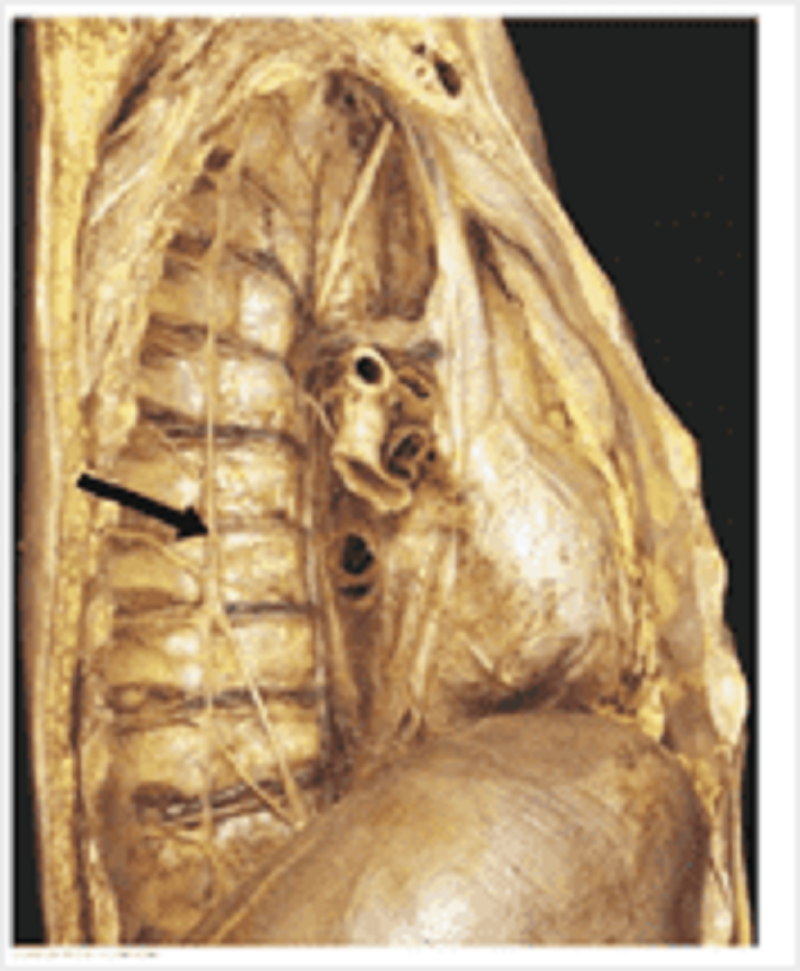
Prosection of deep surface of anterior thoracic wall. Identify A.
Internal thoracic artery
Costal artery
Sternal artery
Mediastinal artery
Anterior intercostal artery
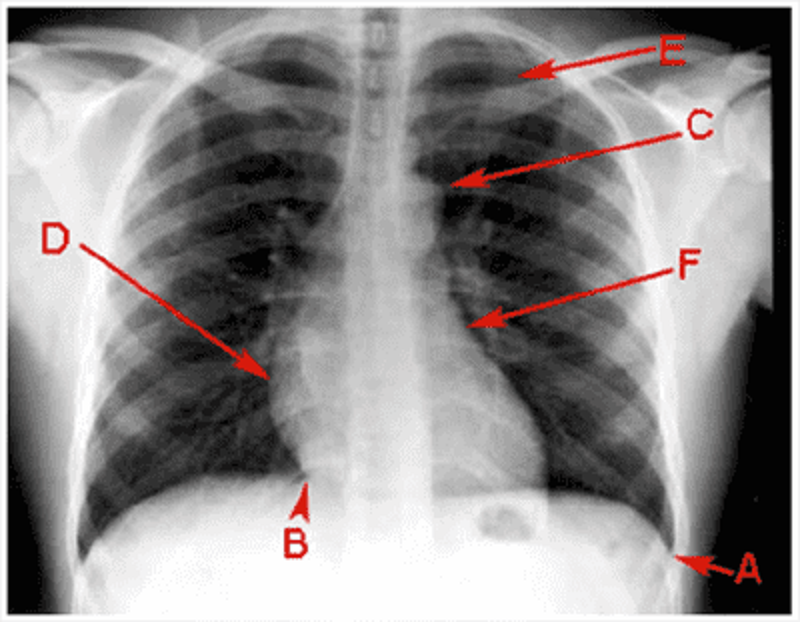
A (PA chest film)
Costophrenic angle
Cardiophrenic angle
Aortic knuckle
Right atrium
Right ventricle
Left ventricle
Left atrium
1st rib
2nd rib
Pulmonary hilum
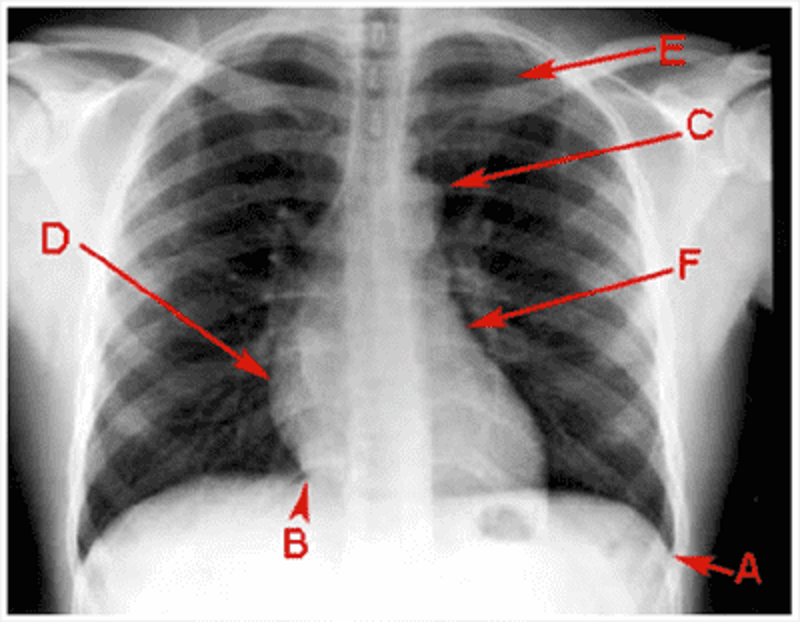
B
Costophrenic angle
Cardiophrenic angle
Aortic knuckle
Right atrium
Right ventricle
Left ventricle
Left atrium
1st rib
2nd rib
Pulmonary hilum
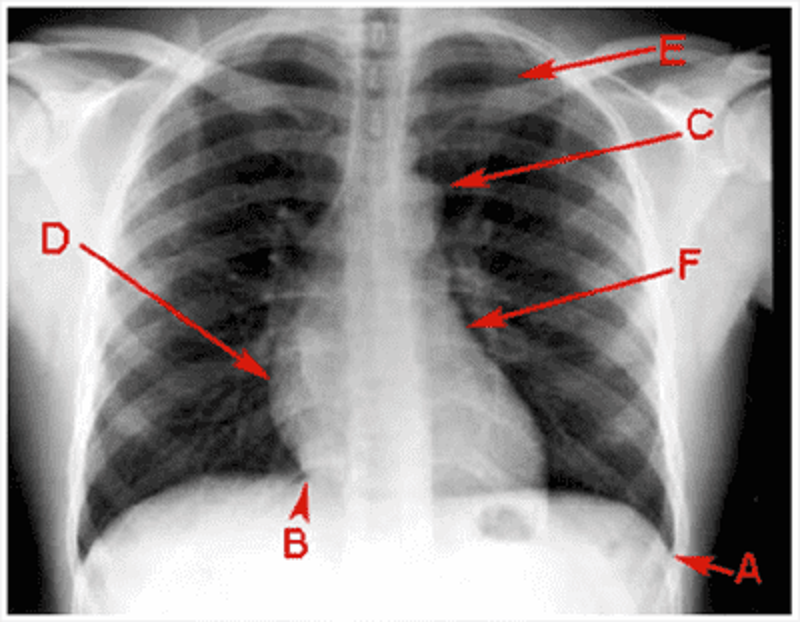
C
Costophrenic angle
Cardiophrenic angle
Aortic knuckle
Right atrium
Right ventricle
Left ventricle
Left atrium
1st rib
2nd rib
Pulmonary hilum
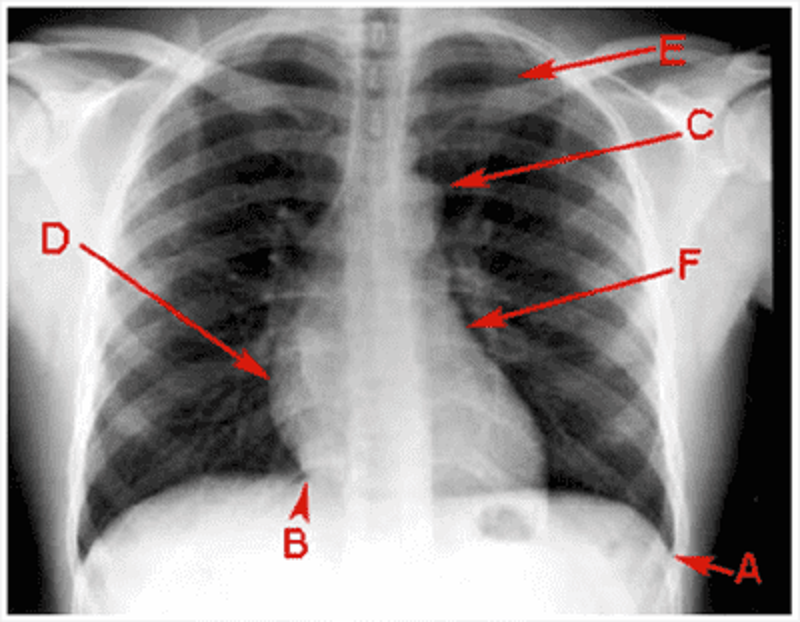
D
Costophrenic angle
Cardiophrenic angle
Aortic knuckle
Right atrium
Right ventricle
Left ventricle
Left atrium
1st rib
2nd rib
Pulmonary hilum
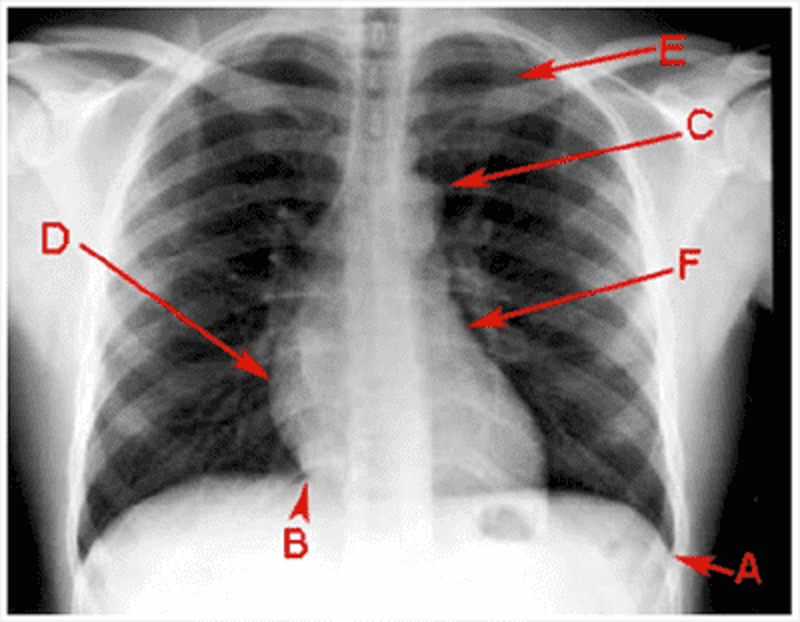
E
Costophrenic angle
Cardiophrenic angle
Aortic knuckle
Right atrium
Right ventricle
Left ventricle
Left atrium
1st rib
2nd rib
Pulmonary hilum
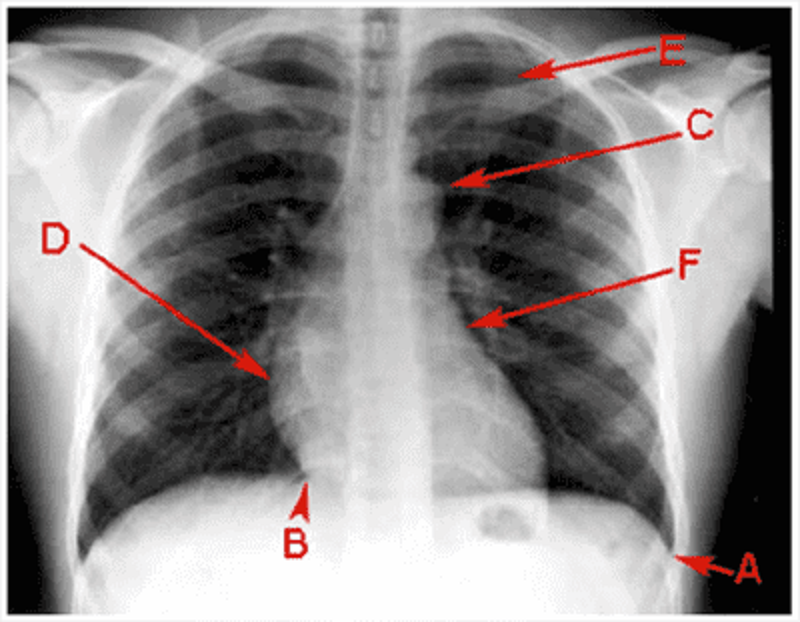
F
Costophrenic angle
Cardiophrenic angle
Aortic knuckle
Right atrium
Right ventricle
Left ventricle
Left atrium
1st rib
2nd rib
Pulmonary hilum
Left atrium: what is the name of structure A?
Left atrium
Right atrium
Right ventricle
Left ventricle
Right auricle
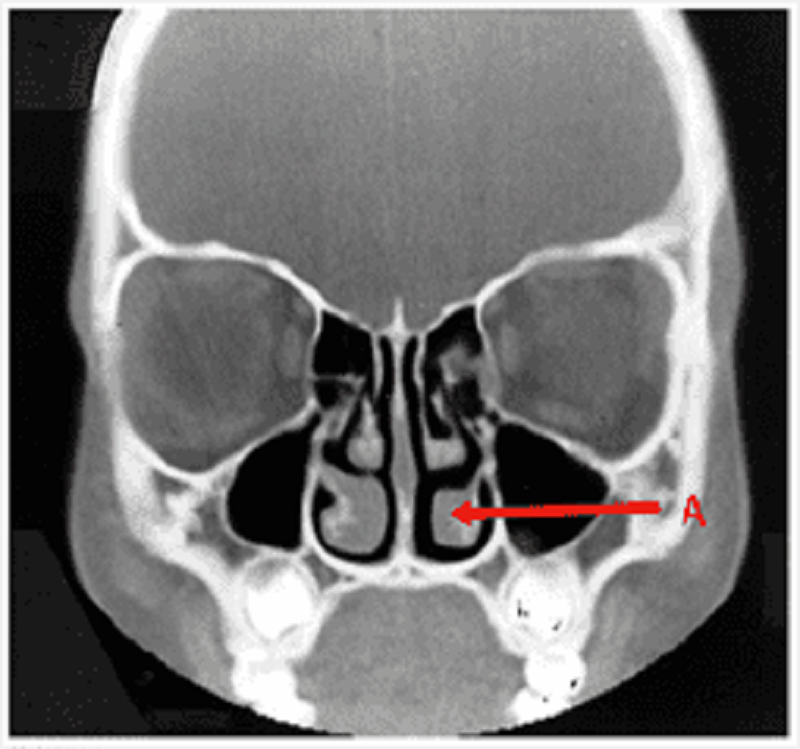
Pharynx: name structure A
Inferior meatus
Middle meatus
Inferior conchae
Nasal septum
Middle conchae
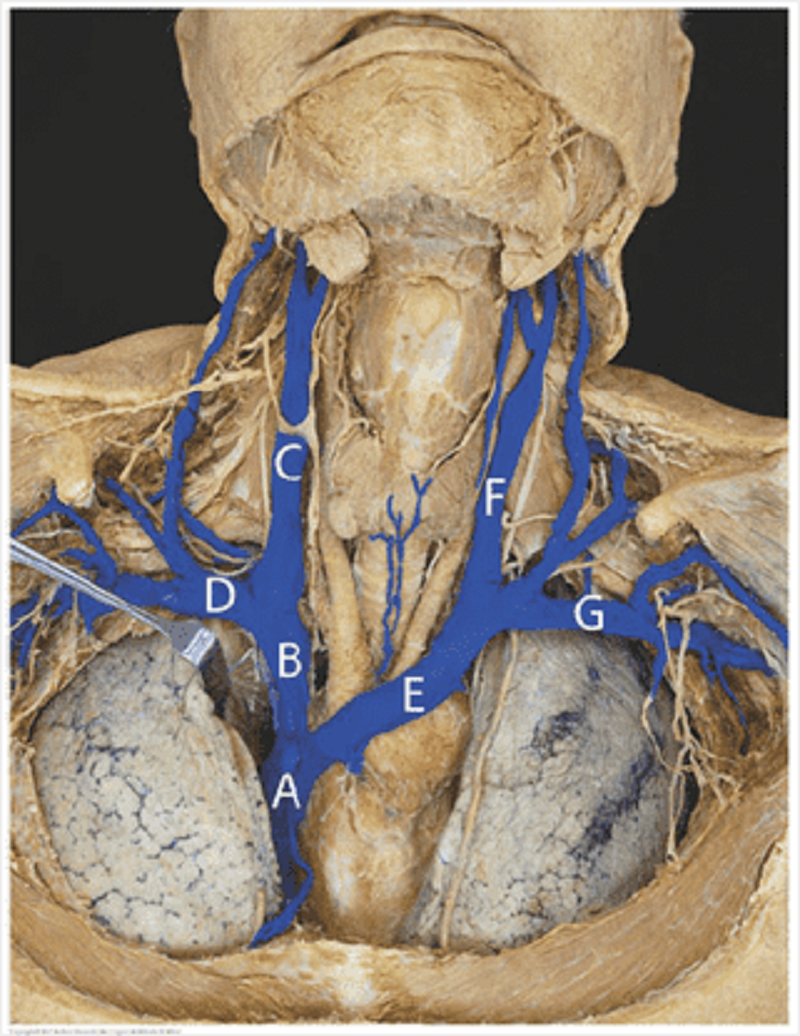
Major vessels (veins): match the letters of the major veins to their names? Superior vena cava
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
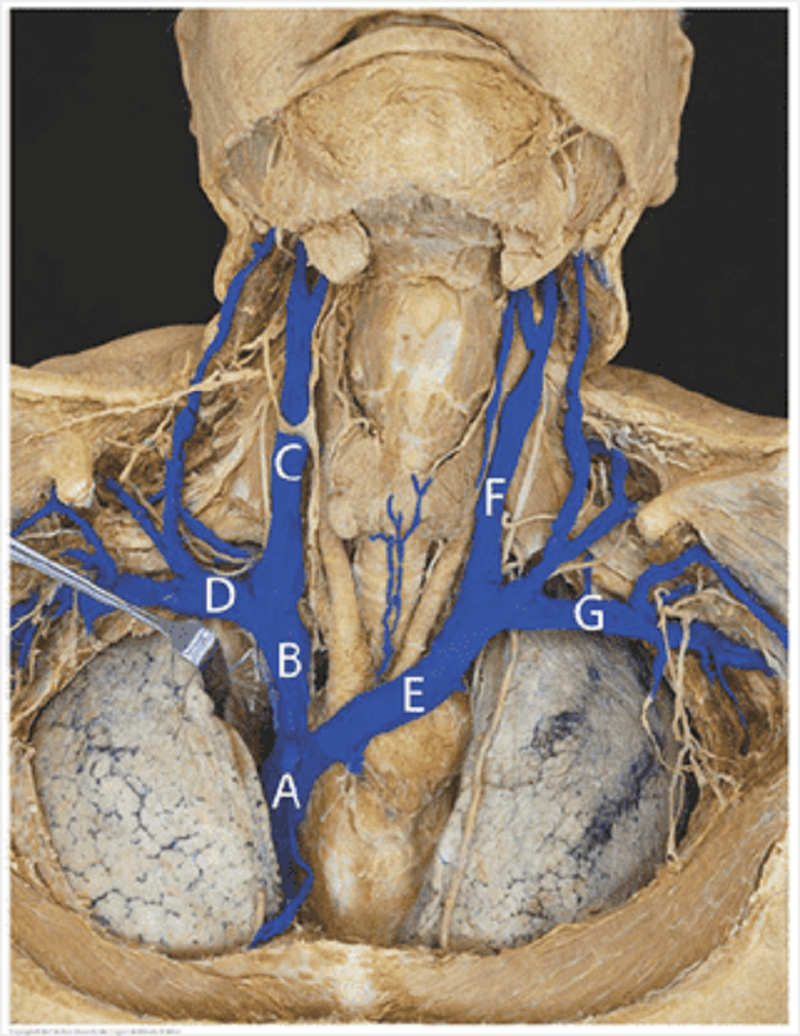
Left brachiocephalic vein
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
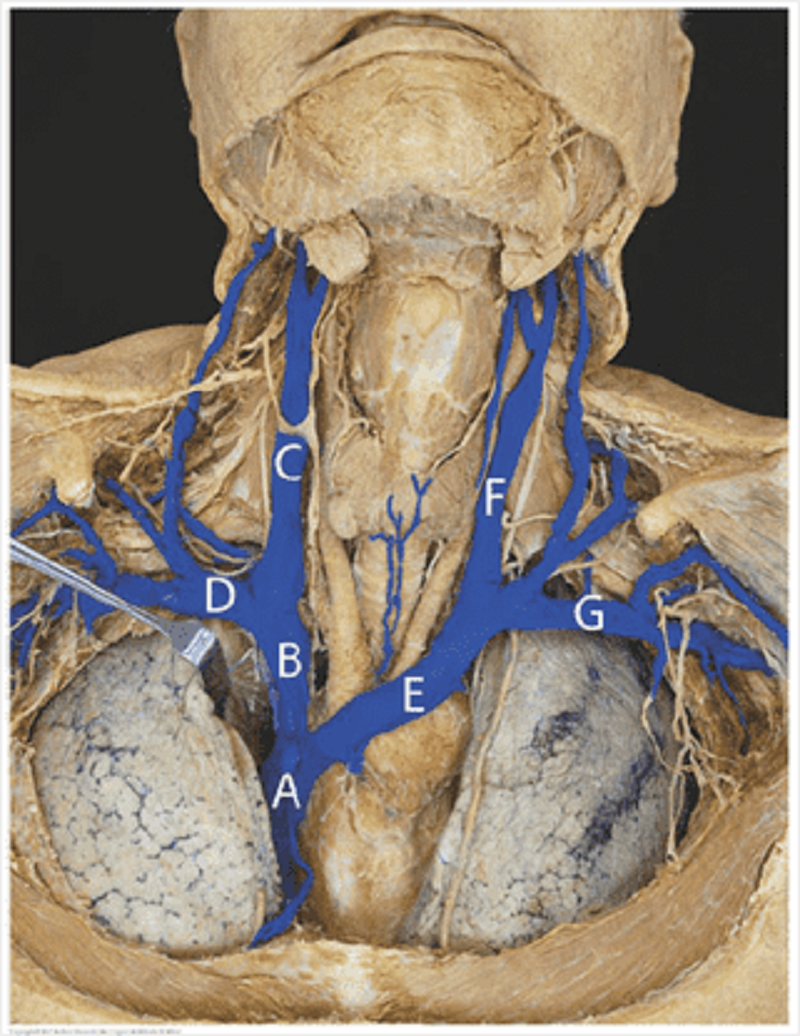
Right subclavian vein
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
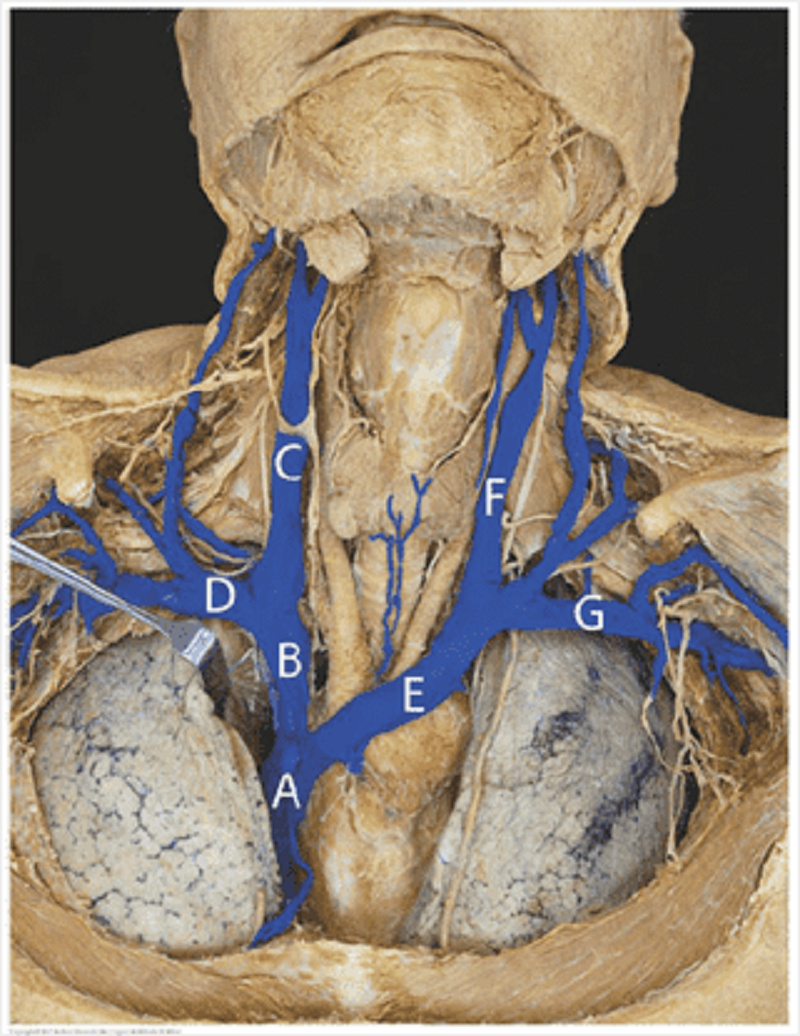
Right internal jugular vein
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
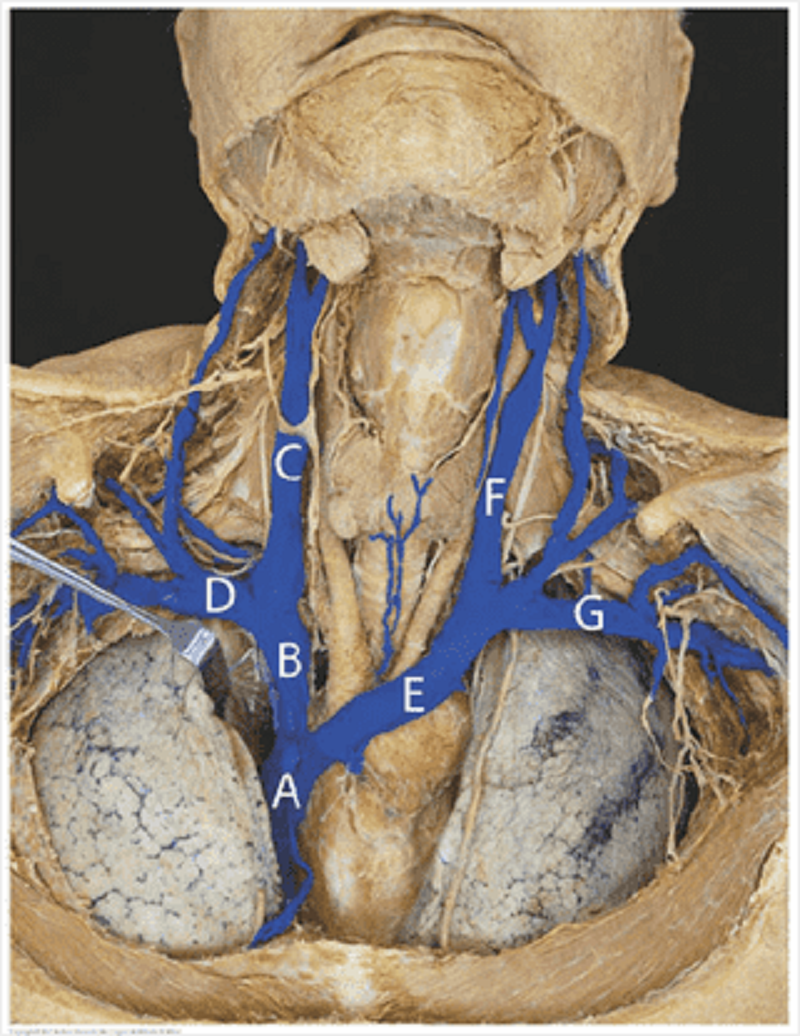
Left subclavian vein
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
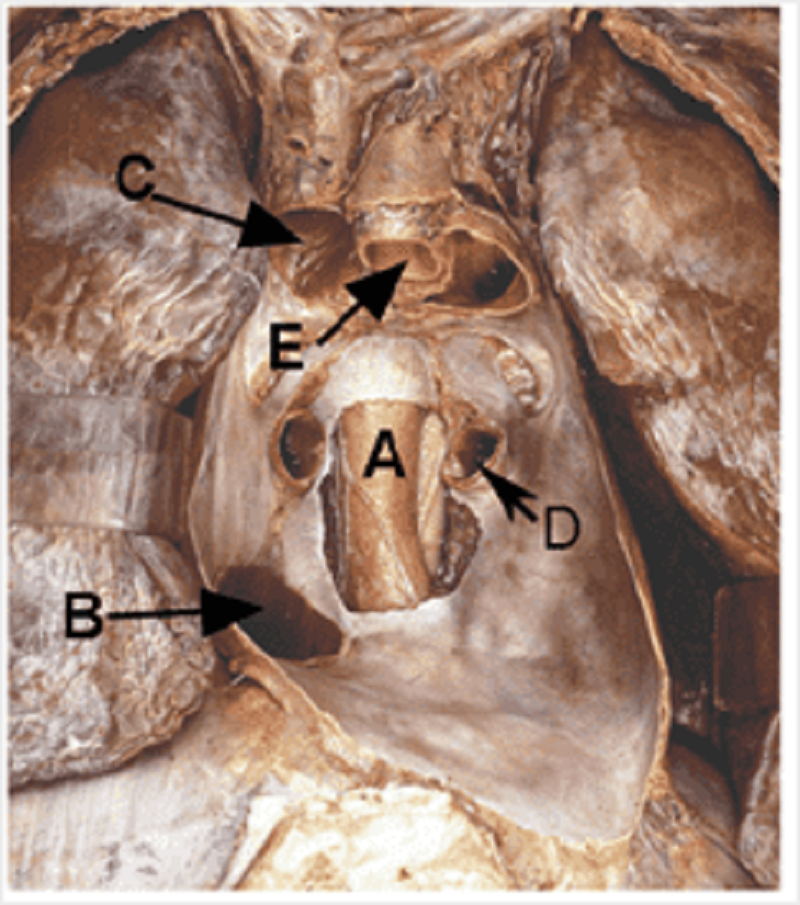
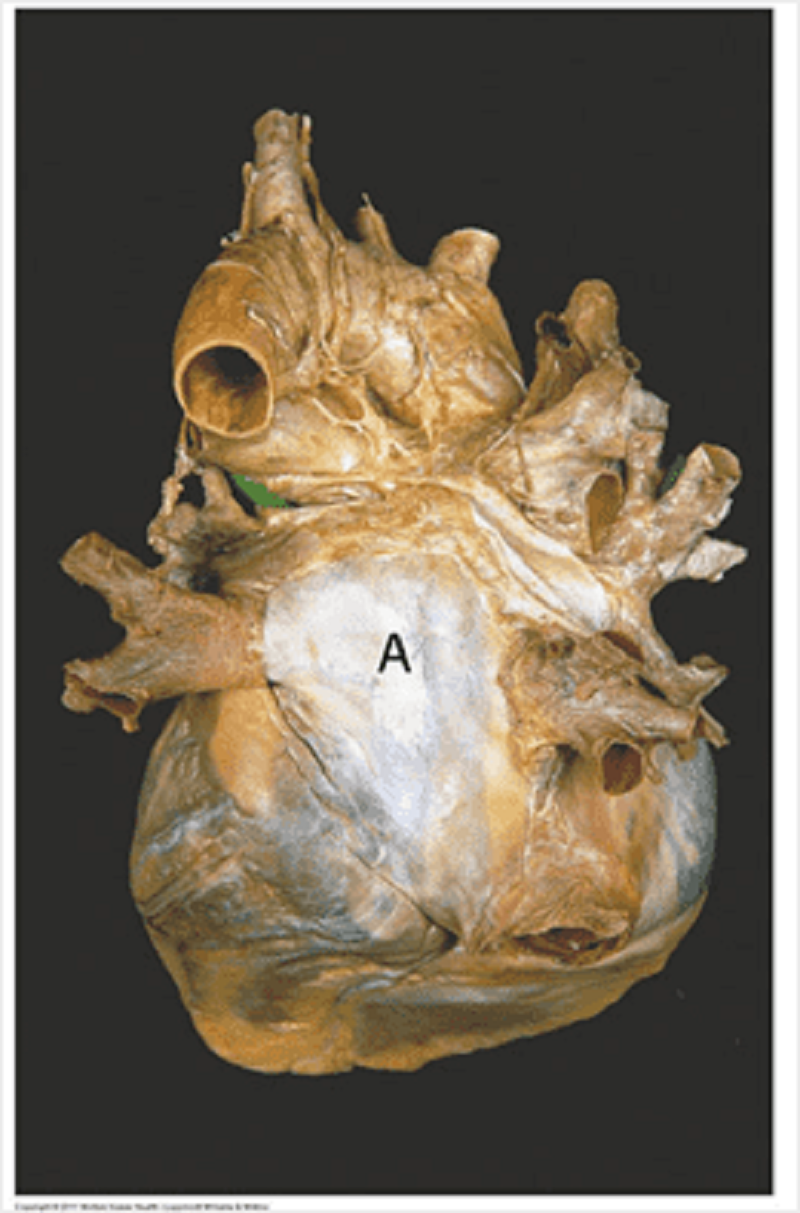
This is the posterior pericardium with the heart removed. Identify the labelled structures in the picture. A.
Oesophagus
Inferior vena cava
Superior vena cava
Pulmonary vein
Aorta
Pulmonary trunk
Trachea
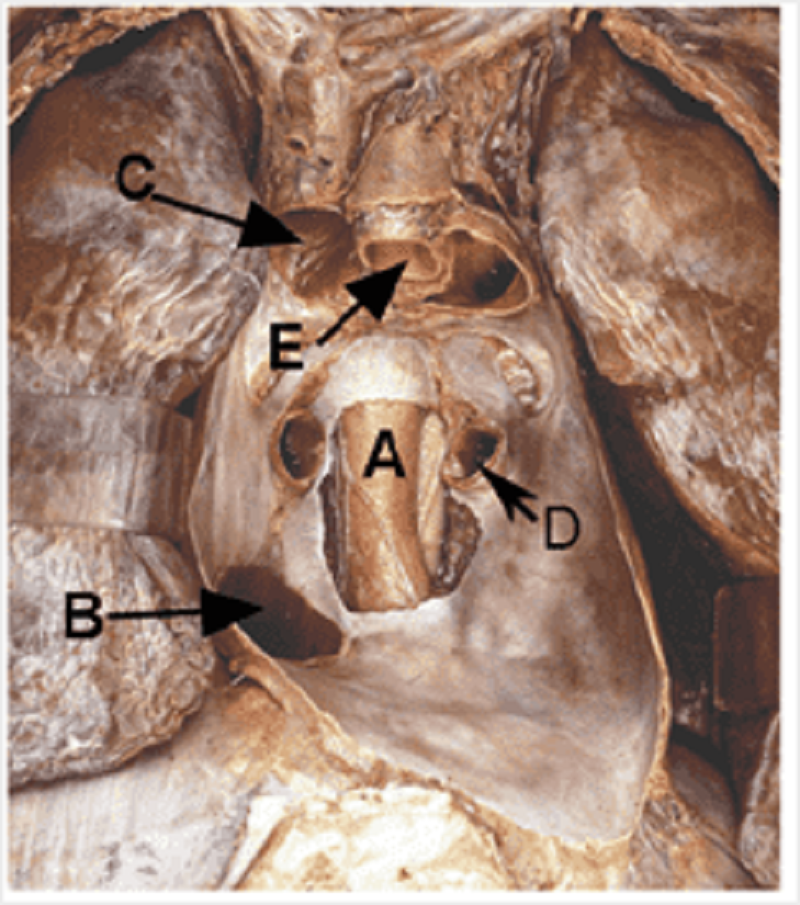
B
Oesophagus
Inferior vena cava
Superior vena cava
Pulmonary vein
Aorta
Pulmonary trunk
Trachea
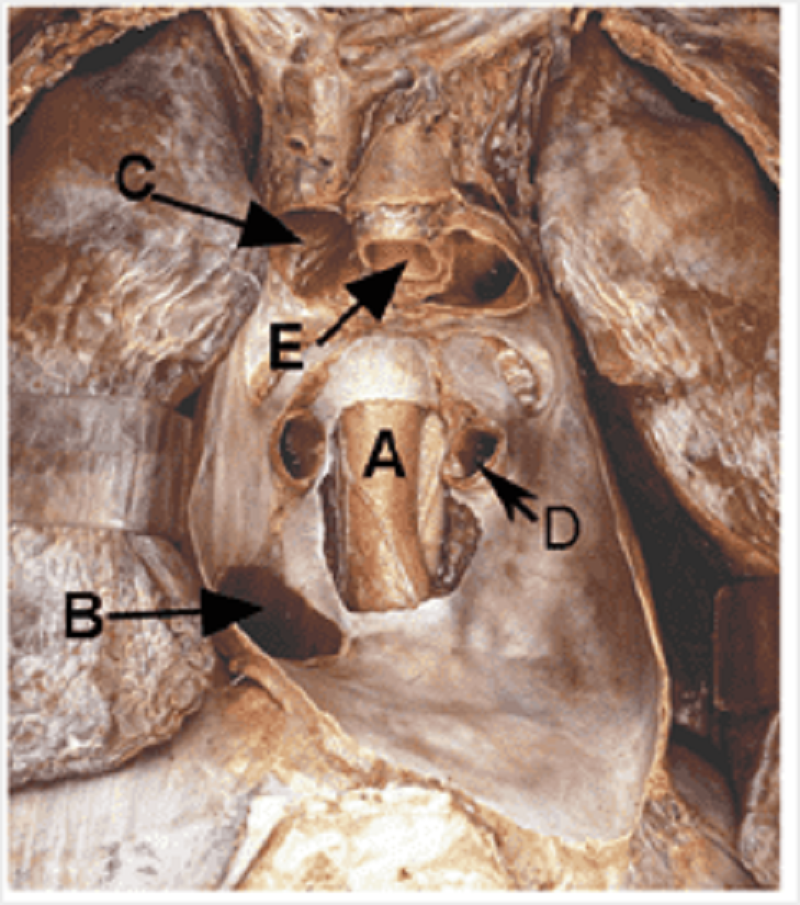
C
Oesophagus
Inferior vena cava
Superior vena cava
Pulmonary vein
Aorta
Pulmonary trunk
Trachea
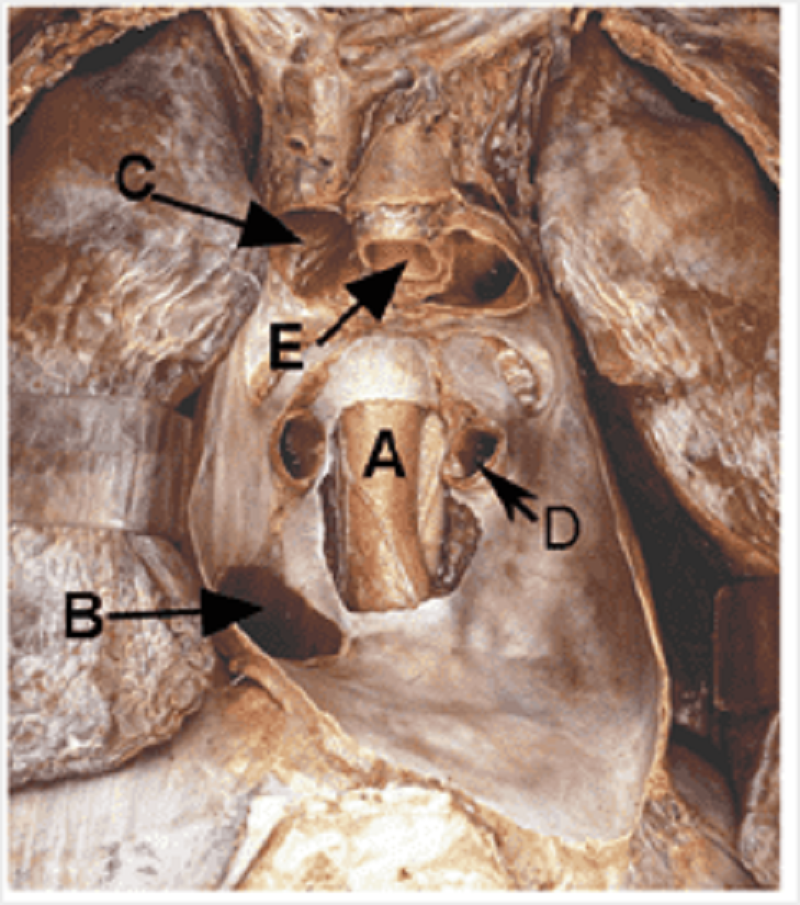
D
Oesophagus
Inferior vena cava
Superior vena cava
Pulmonary vein
Aorta
Pulmonary trunk
Trachea
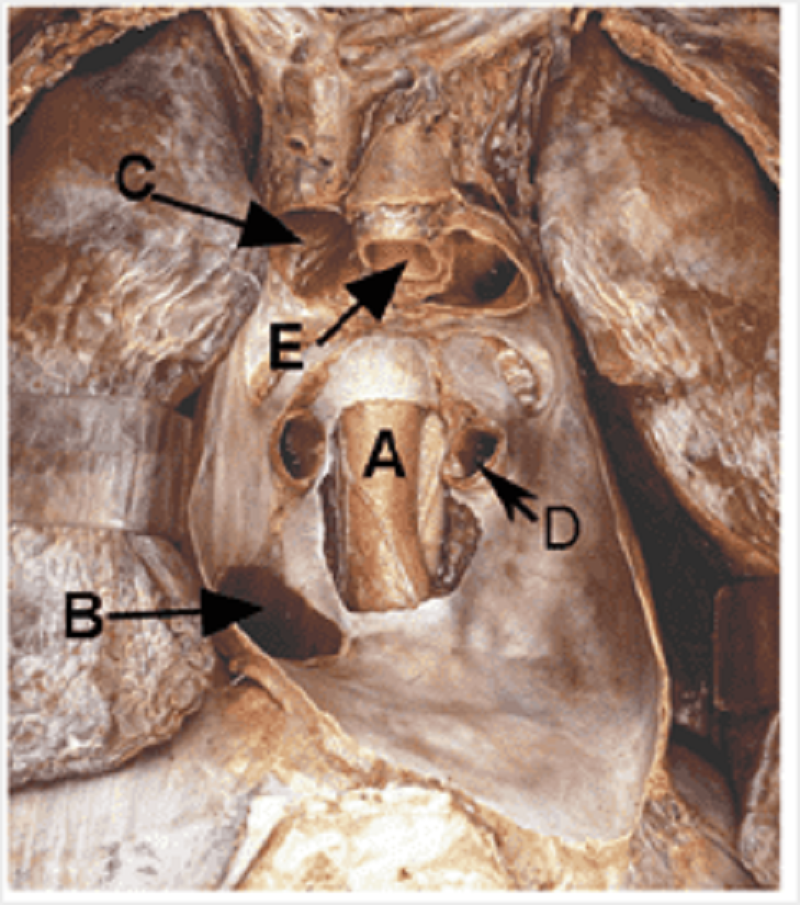
E
Oesophagus
Inferior vena cava
Superior vena cava
Pulmonary vein
Aorta
Pulmonary trunk
Trachea
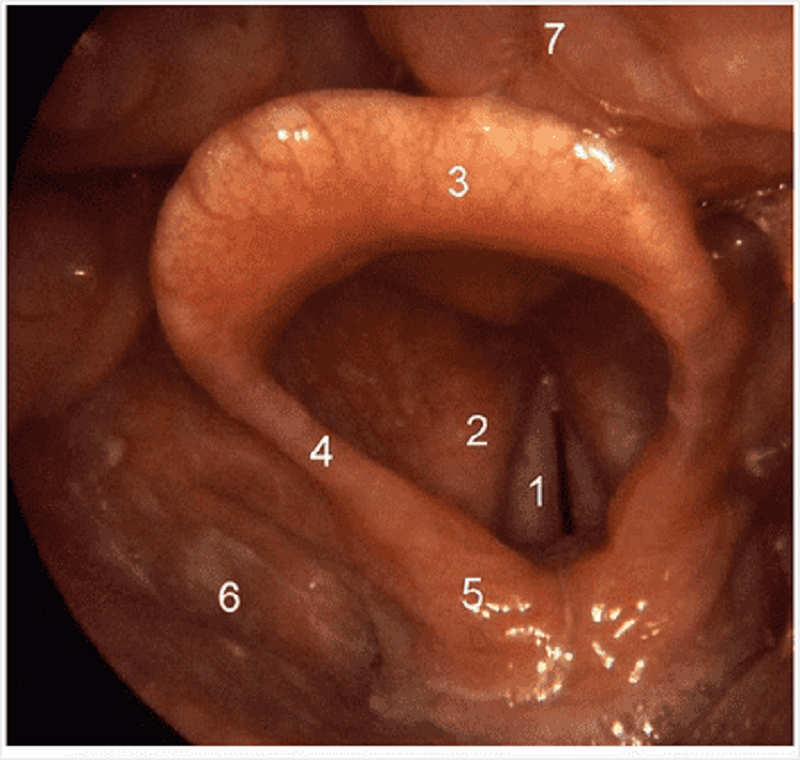
Name structure 3 on this superior view of the larynx.
Epiglottis
Vocal folds
Vestibular fold
Tongue
Cuneiform and corniculate cartilage
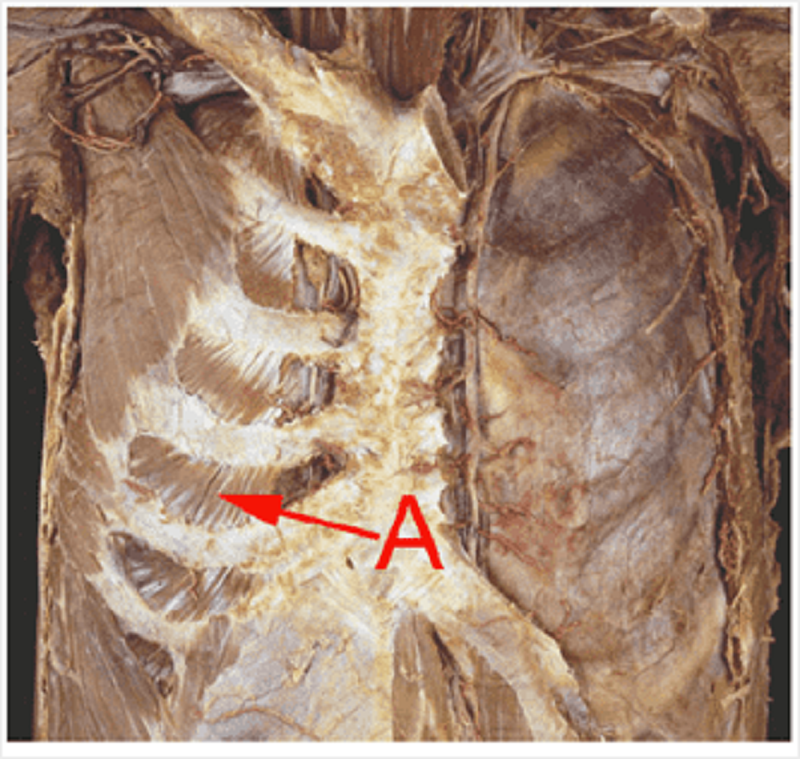
Thorax muscles: what structure(s) run immediately posterior to the structure labelled A?
Internal intercostal muscle
Neurovascular bundle
Innermost intercostal muscle
Internal oblique muscle
External intercostal muscle
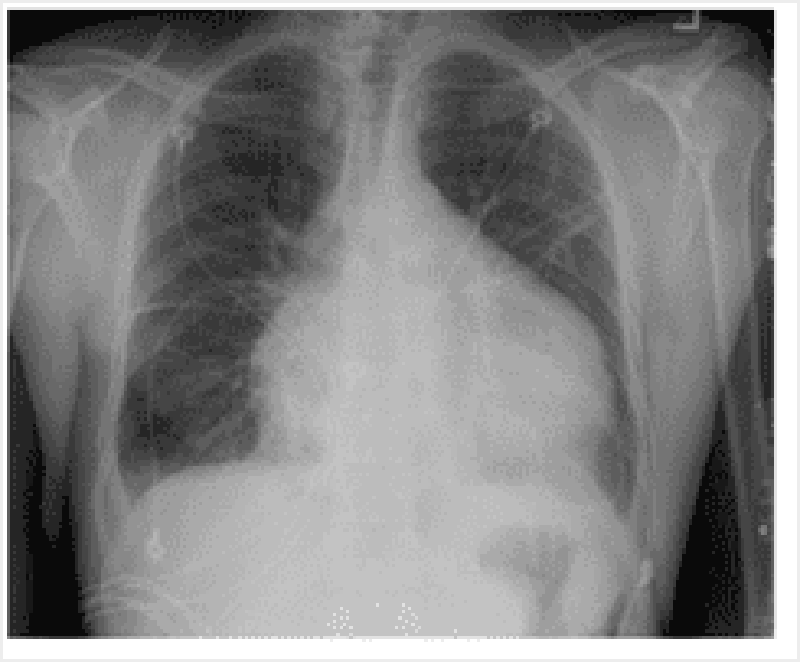
Cardiac tamponade: A 33 year old male was brought into A and E barely conscious after being stabbed with a kitchen knife in his anterior chest. His wound is in the fifth intercostal space, immediately left of the sternum. The veins of his face and neck are enlarged. His chest X ray shows a massive enlargement of the cardiac silhouette. Which of the following structures has been damaged by the knife causing the cardiac tamponade?
Right ventricle
Left ventricle
Right atrium
Left atrium
Aortic arch
Superior vena cava
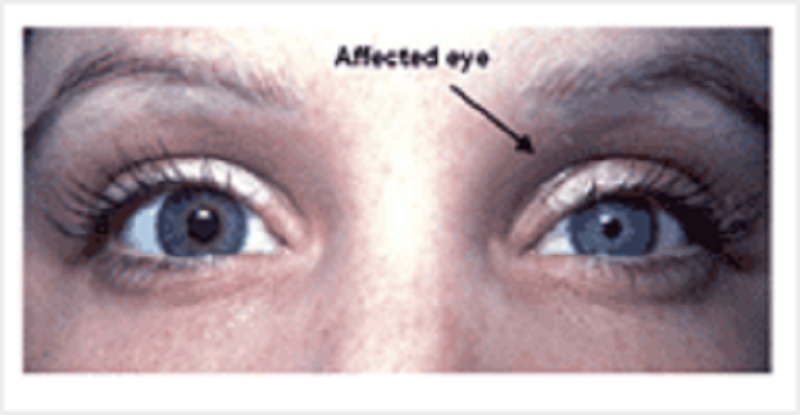
Horner's syndrome: A 34 year old female presents with Horner's syndrome. She has left sided myosis, ptosis and anhydrosis. An MRI reveals a Pancoast's tumour in the apex of the left lung. What structure is most likely compromised by the tumour?
Cervical spinal nerves
Thoracic spinal nerves
White ramus communicans T1 to T3
Left vagus nerve
Cervical plexus
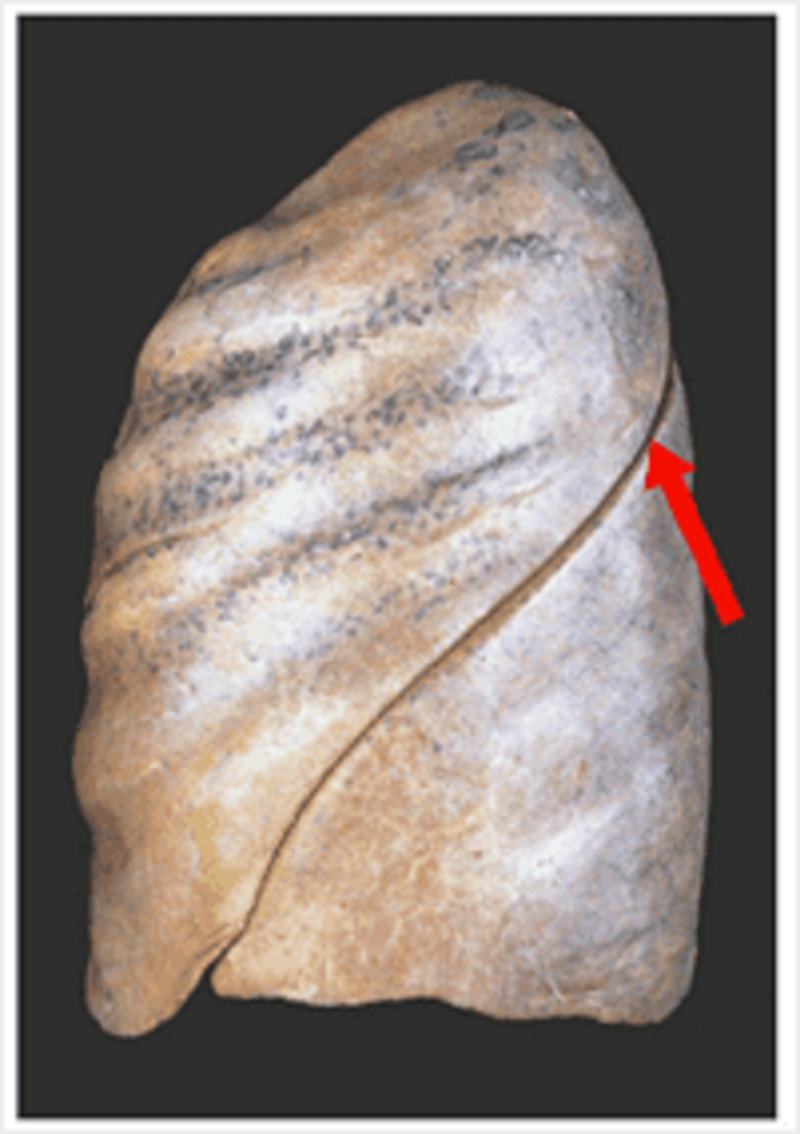
Lung oblique: what is the anatomical landmark of the highest point of this fissure posteriorly?
C5-C6
C7-T1
T2-T3
T5-T6
T7-T8
Sympathetic nervous system: what is the consequence of activation of the structure indicated on the cardiorespiratory system?
Increased heart rate, coronary vasodilation, bronchodilation
Increased heart rate, secretomotor to alveolar glands, bronchodilation
Increased heart rate, coronary vasodilation, bronchoconstriction
Decreased heart rate, secretomotor to alveolar glands, bronchodilation
Decreased heart rate, coronary vasodilation, bronchoconstriction
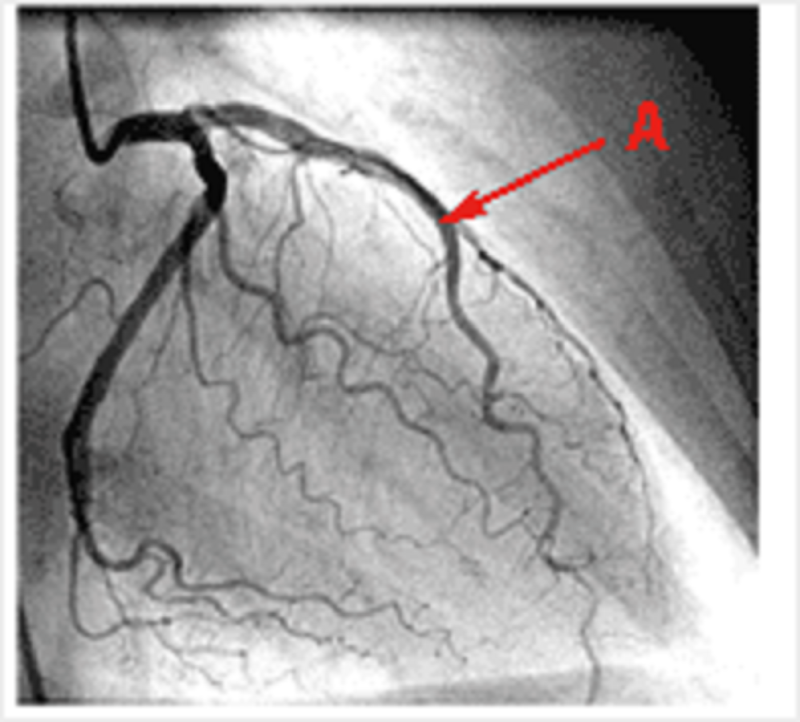
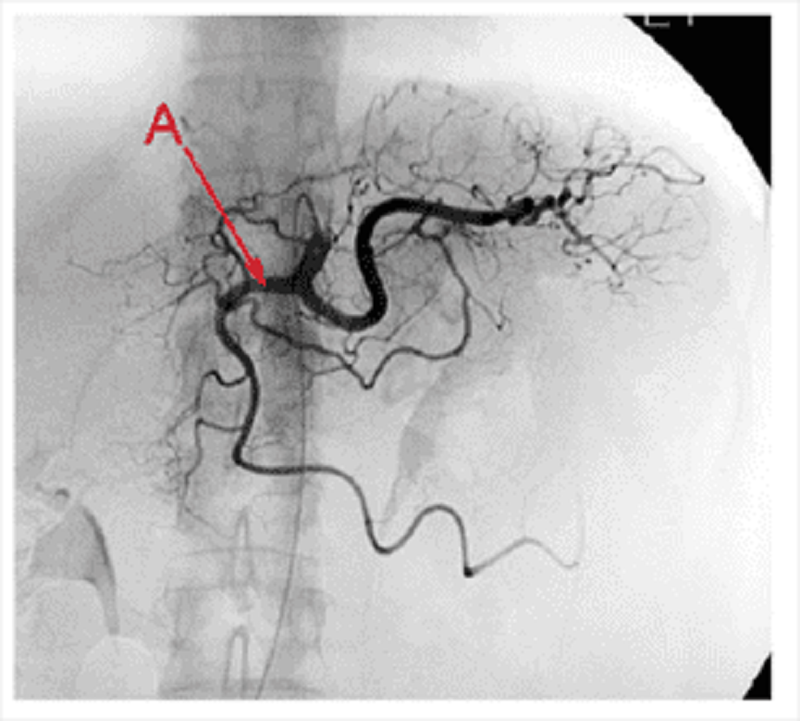
Coronary vessels angiogram: what region of the heart does this vessel typically supply?
Anterior interventricular septum
Left atrium
Right atrium
SA node
AV node
Posterior interventricular septum
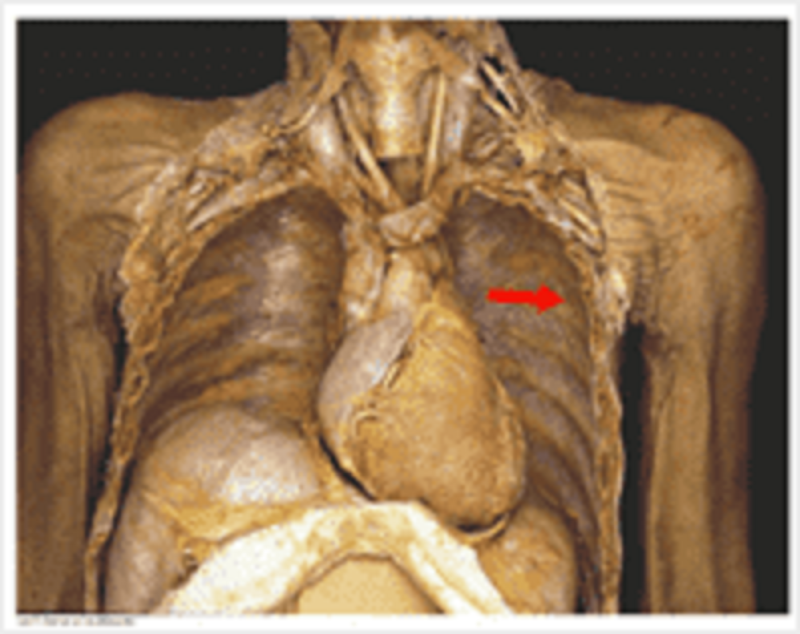
Pleura: which nerve fibres carry the information for the sensation of the parietal pleura labelled?
Intercostal nerve
Vasomotor autonomic nerve
Phrenic nerve
Vagus nerve
Recurrent laryngeal nerve
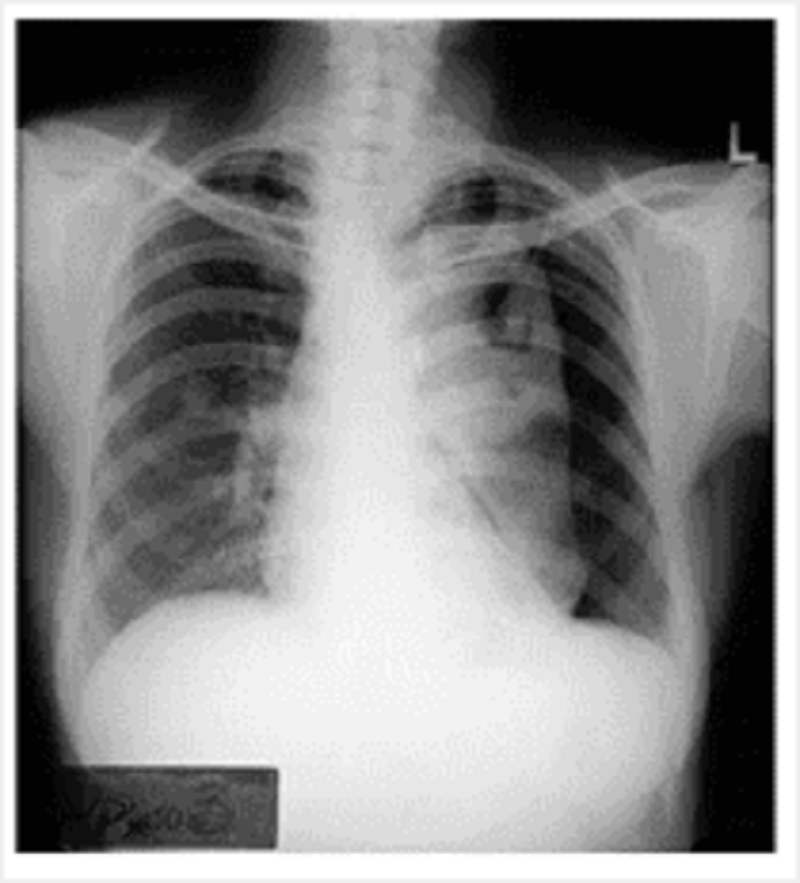
What abnormality is clearly seen in this chest X ray?
Pneumothorax
Emphysema
Tuberculosis
Cystic fibrosis
Pneumonia
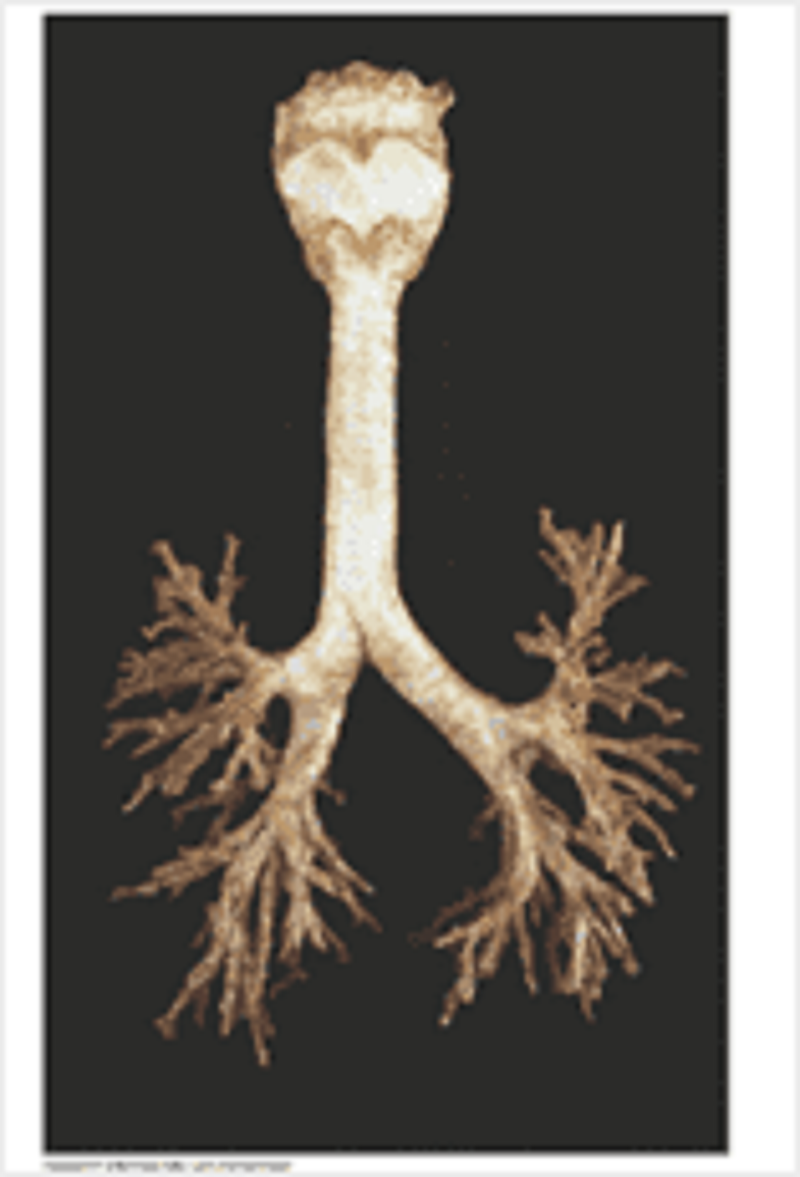
Of the structures forming the air passage, which cartilage is enclosing it completely?
Cricoid cartilage
Thyroid cartilage
First cartilage of trachea
Second cartilage of trachea
Epiglottis
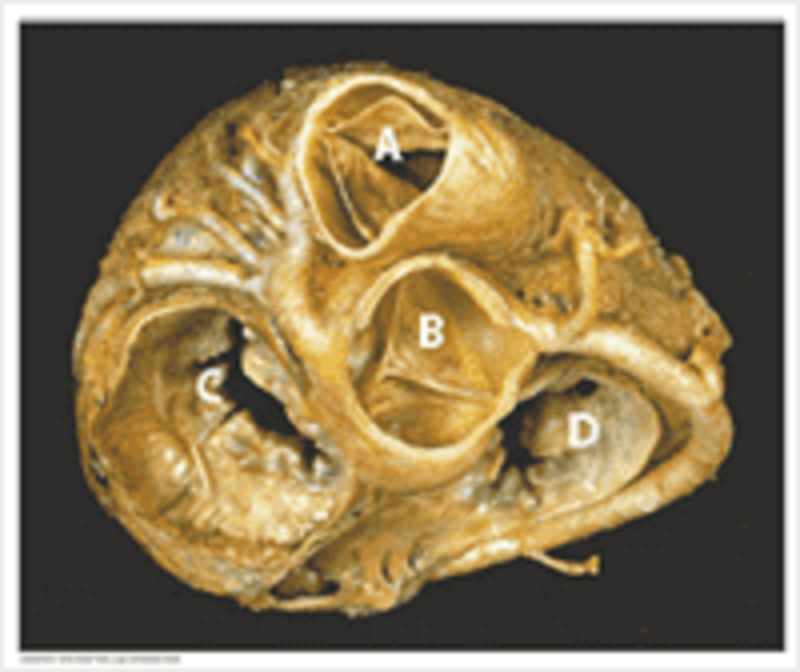
Valves: match the letters to the appropriate structures. A
Pulmonary valve
Aortic valve
Mitral valve
Tricuspid valve
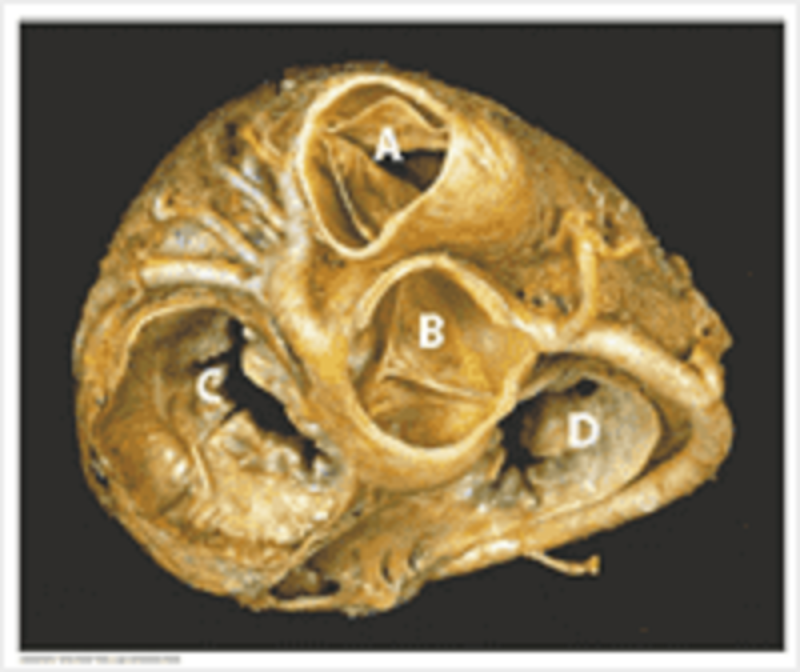
B
Pulmonary valve
Aortic valve
Mitral valve
Tricuspid valve
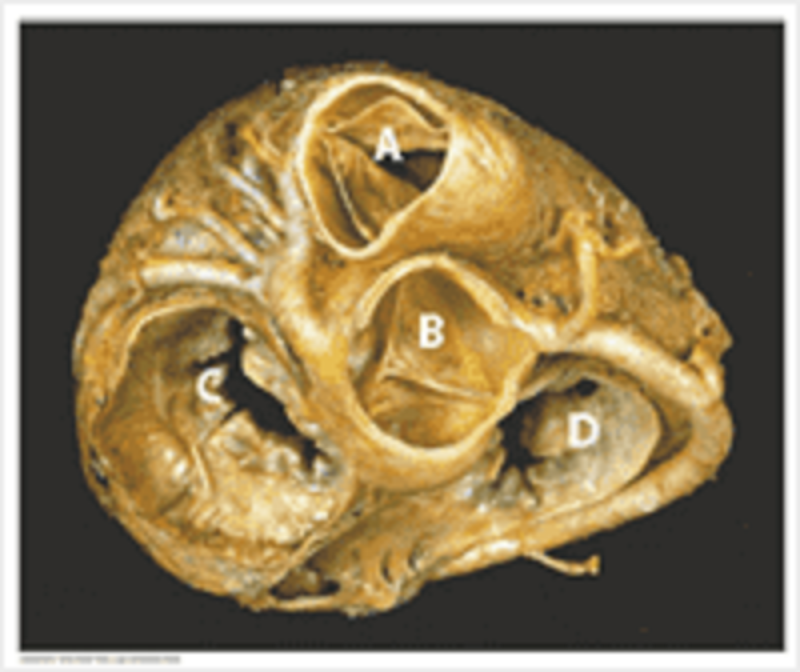
C
Pulmonary valve
Aortic valve
Mitral valve
Tricuspid valve
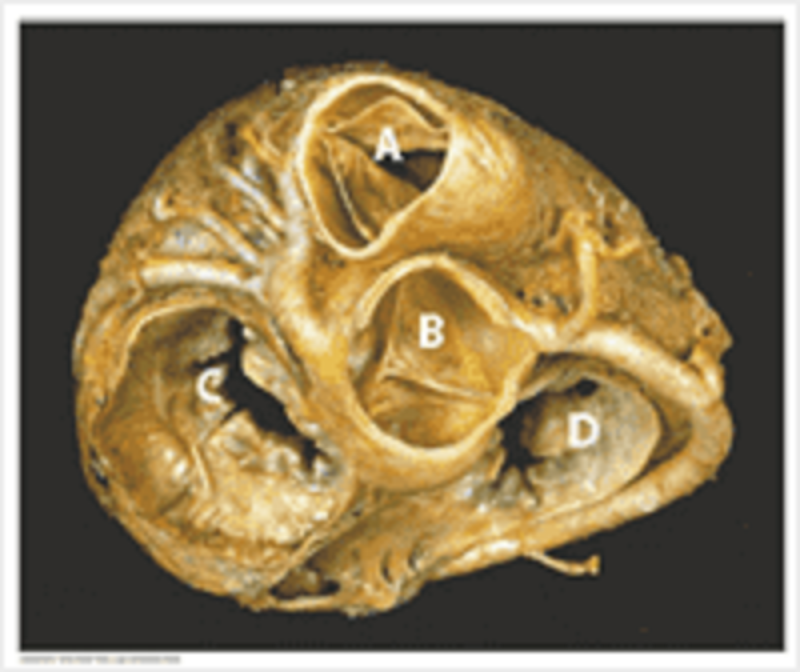
D
Pulmonary valve
Aortic valve
Mitral valve
Tricuspid valve
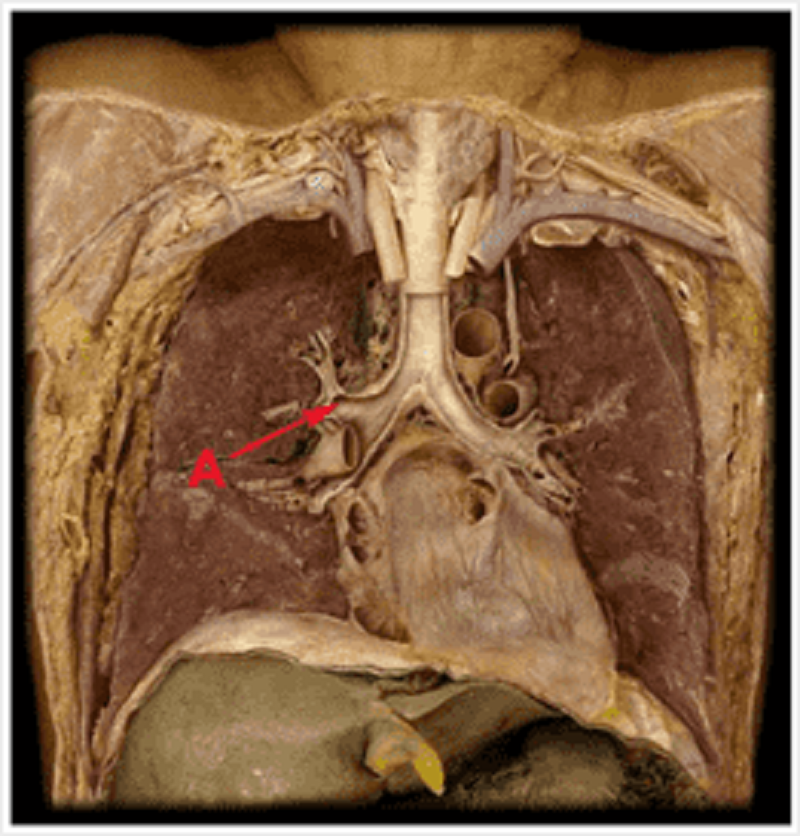
Anatomy of the bronchial tree: identify A
Right inferior lobar bronchus
Right middle lobar bronchus
Bronchus intermedialis
Right main bronchus
Right superior lobar bronchus
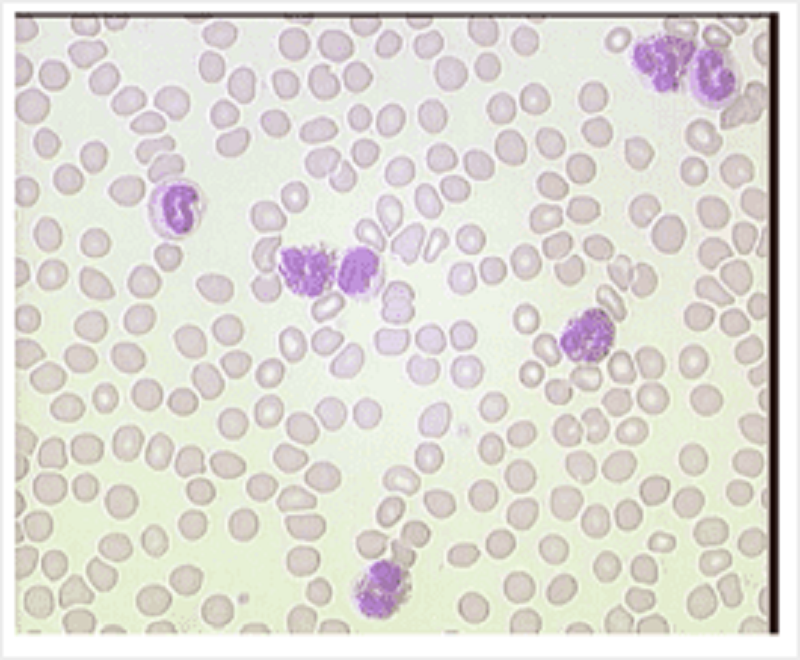
Blood: A 30 year old man who has recently arrived from Africa has come to your surgery complaining of tiredness. His blood film is here. His Hb is 12g/dl (normal range 13.5-17.5g/dl); MCV 75fl (normal range 80-96fl). From the blood film you can tell he has:
Basophilia
Lymphocytosis
Eosinophilia
Neutropenia
Monocytosis
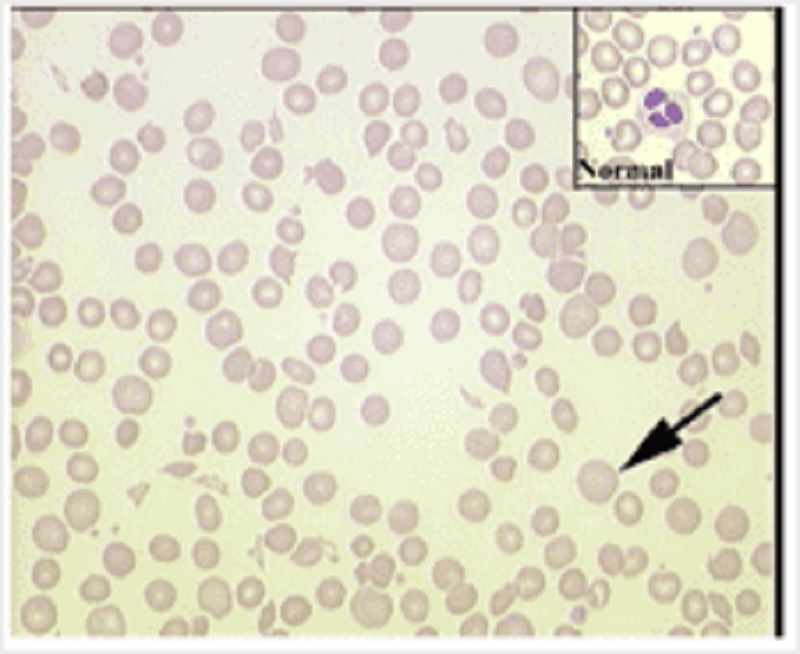
Blood: the cell indicated in this blood film is a
Target cell
Reticulocyte
Lymphocyte
Neutrophil
Sickle cell
Nucleated erythrocyte
Mature erythrocyte
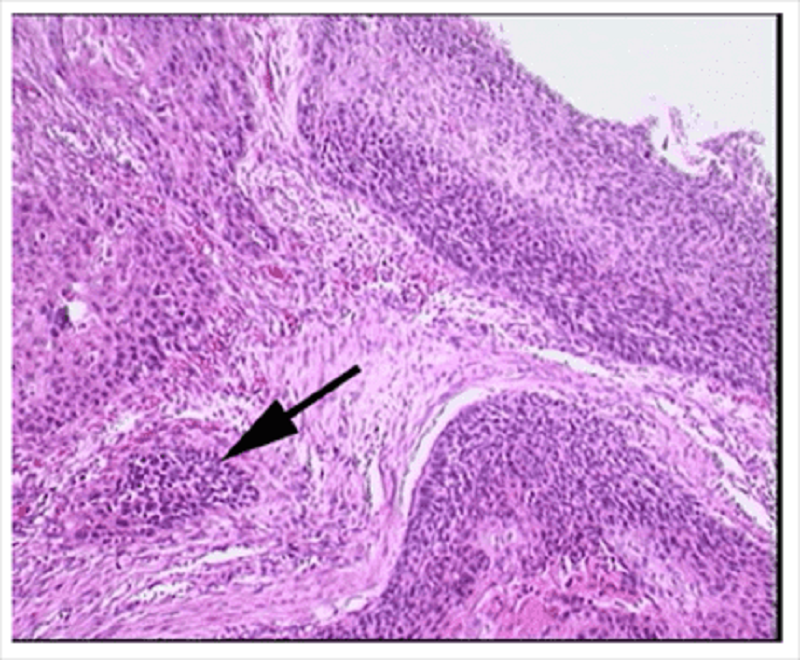
Histology of a tumour removed from the lung is shown. The arrow indicates
Lymphocytes
Squamous cells
Mucoserous gland
Hyaline cartilage
Fibrocollagenous tissue
Smooth muscle
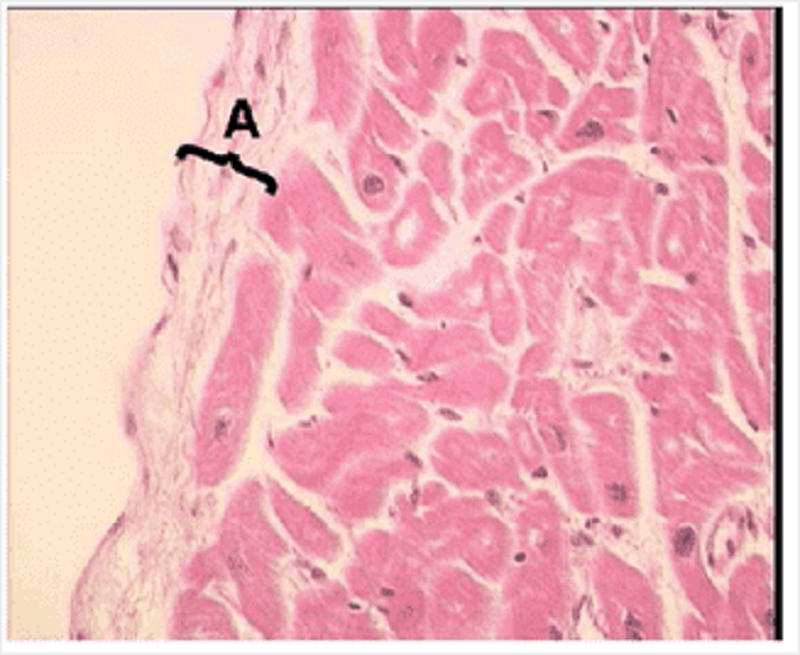
Blood would normally be in the space to the left. What is labelled A?
Endocardium
Myocardium
Tunica intima of the artery
Stratified squamous epithelium
Epicardium
Tunica adventitia of the artery
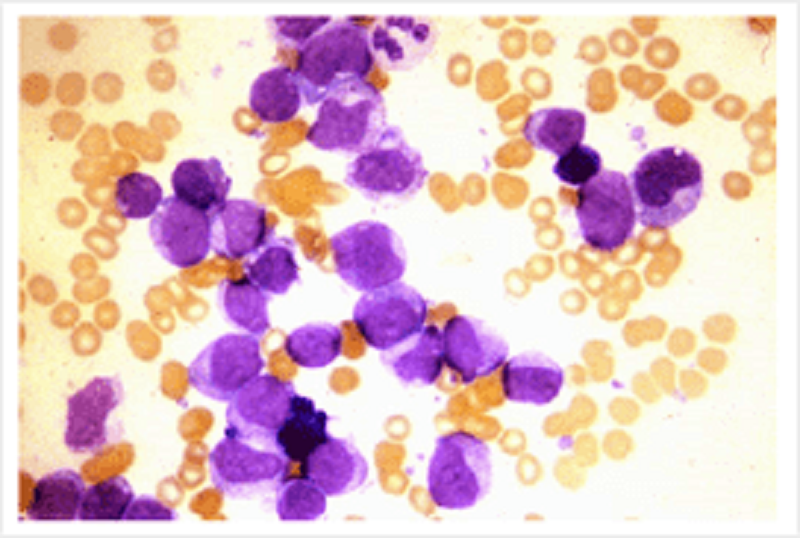
Blood: A 65 year old woman presented with increasing breathlessness, spontaneous bleeding from her gums and easy bruising. Blood count: Hb 5.6 (11.5-15.5g/dl); MCV 102 (80-96)fl; WBC 80 (4-11x10'9/l); PLT 10 (150-400x10'9/l). Leukocyte differential: Blasts 98%; Neutrophils 0.8 (2-7.5); Lymphocytes 0.8 (1.5-4). What is the likely diagnosis?
Acute myeloid leukaemia
Chronic myeloid leukaemia
Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia
Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia
Infectious mononucleosis
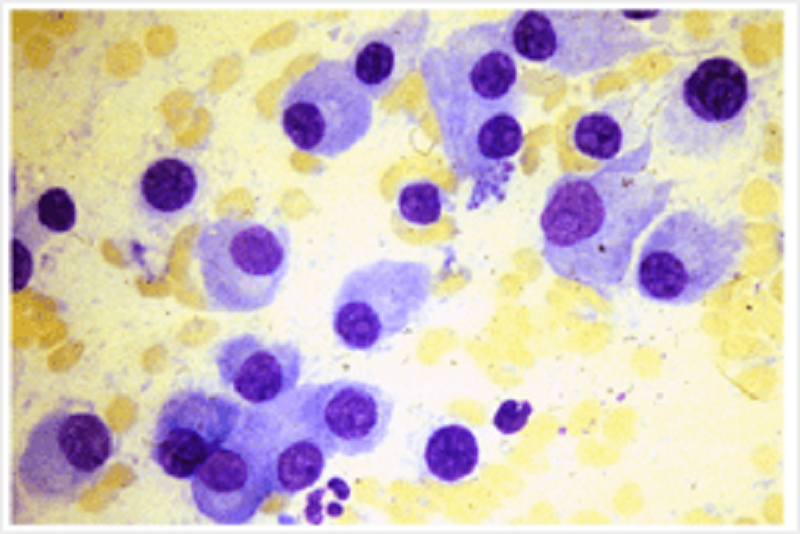
A 60 year old woman presented with severe back pain. An X ray of her back demonstrated a collapsed fourth lumbar vertebra. Her haemoglobin was 8g/dl (normal 11.5-15.5) and MCV 100fl (normal 80-96). WBC and platelet count were normal. Blood film exhibited marked rouleaux formation. A bone marrow aspirate is below. What is the diagnosis?
Multiple myeloma
Osteoporosis
Liver disease
Vitamin B12 deficiency
Carcinoma of the breast
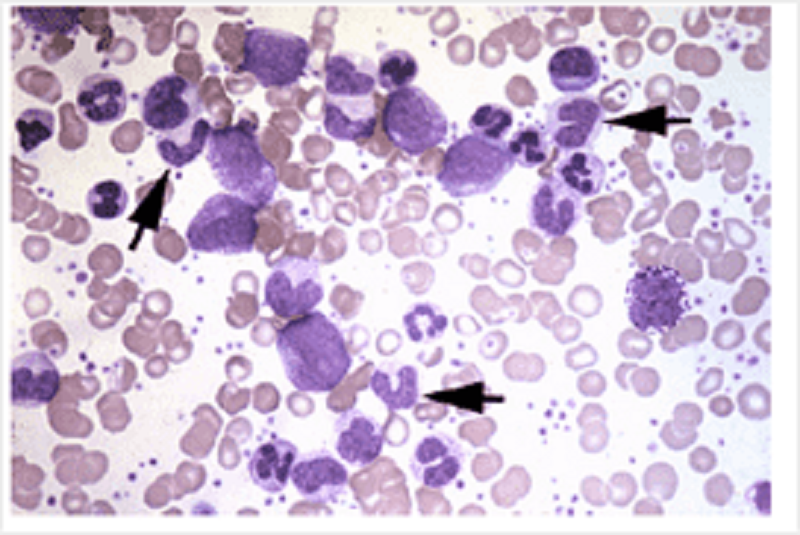
A blood film from a patient is shown. The cells indicated by the arrows are:
Granulocyte precursors
Lymphocyte precursors
Mature eosinophils
Mature neutrophils
Mature monocytes
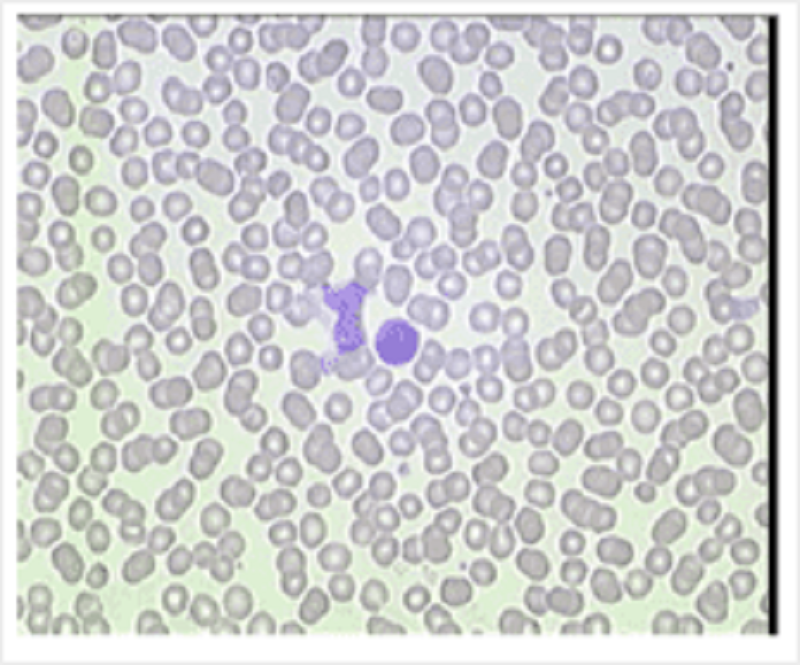
A 23 year old man presented to his GP complaining of tiredness and sore throat. He had cervical lymphadenopathy and a temperature of 38.8 degrees. His blood count was: Hb 12.7; MCV 86; WBC 15.5 (normal 4-11); PLT 203. Leukocyte differential: neutrophils 2.3; lymphocytes 13 (normal 1.5-4); monocytes 0.8. His blood film is here. What condition is suspected?
Viral infection
Bacterial infection
Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia
Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia
Parasitic infection
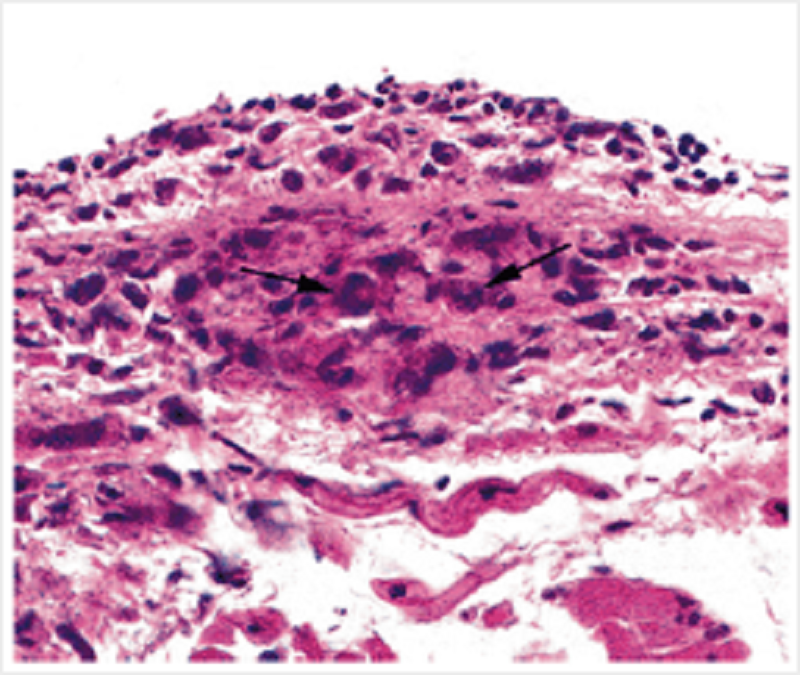
A man with a 6 week history of flitting joint pains, fever and tachycardia died from cardiac complications of his condition. This is a photomicrograph of a characteristic lesion found in his myocardium. What are the cells indicated by the arrows?
Macrophages
Lymphocytes
Fibroblasts
Cardiac myocytes
Neutrophils
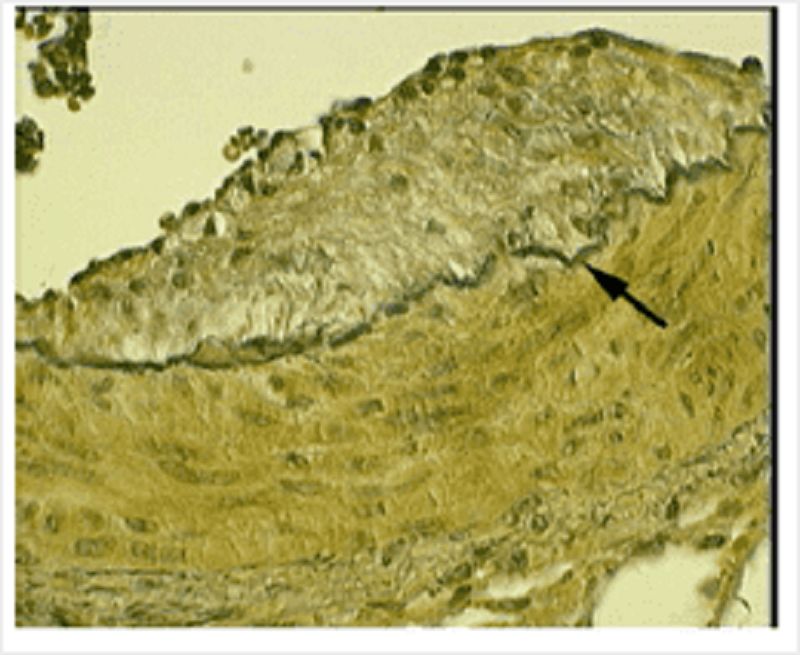
A coronary artery is specially stained to highlight a particular constituent of it. What is indicated by the arrow?
Internal elastic lamina
External elastic lamina
Basement membrane
Endothelium
Tunica adventitia
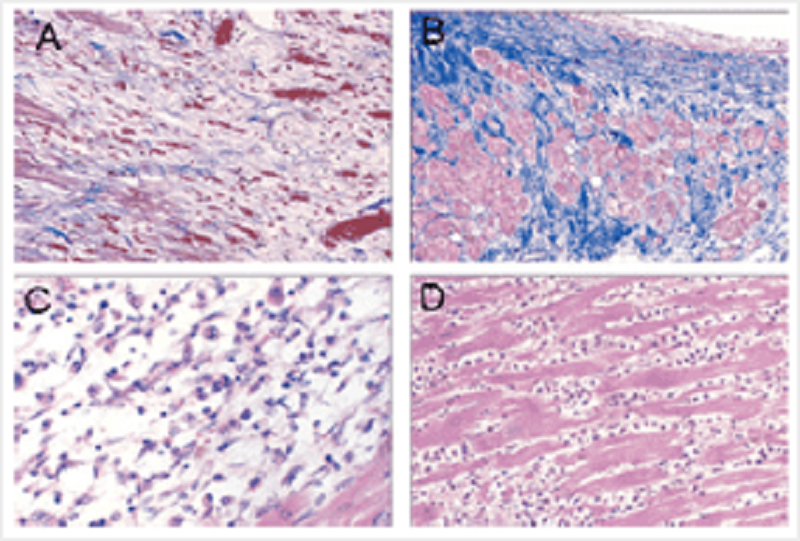
The photomicrographs show 4 different stages of myocardial infarct repair. Collagen is stained blue. Order them from earliest stage to most advanced stage.
D; C; A; B
C; D; A; B
D; C; B; A
C; D; B; A
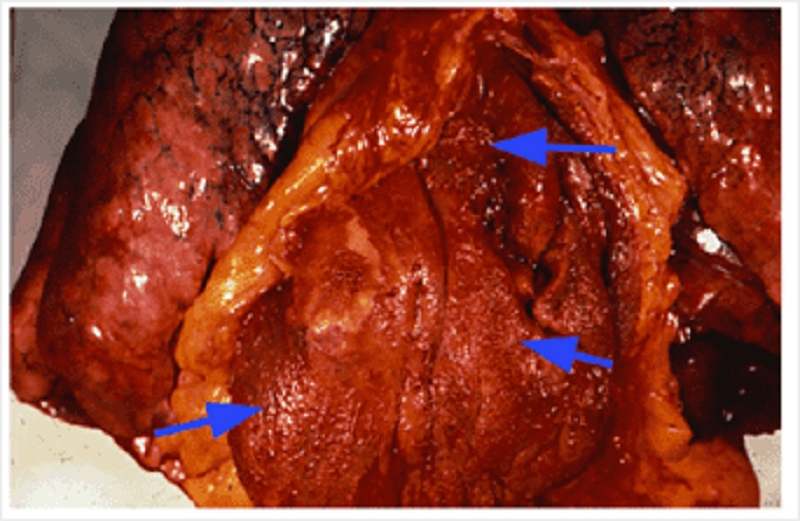
A 24 year old man in South Africa presented with a 6 week history of flitting joint pains, fever and tachycardia. Over the next few weeks he developed congestive cardiac failure and despite treatment, he died. What is indicated by the arrows in the autopsy specimen of his heart?
Pericarditis
Endocarditis
Myocarditis
Pancarditis
Metaplastic response
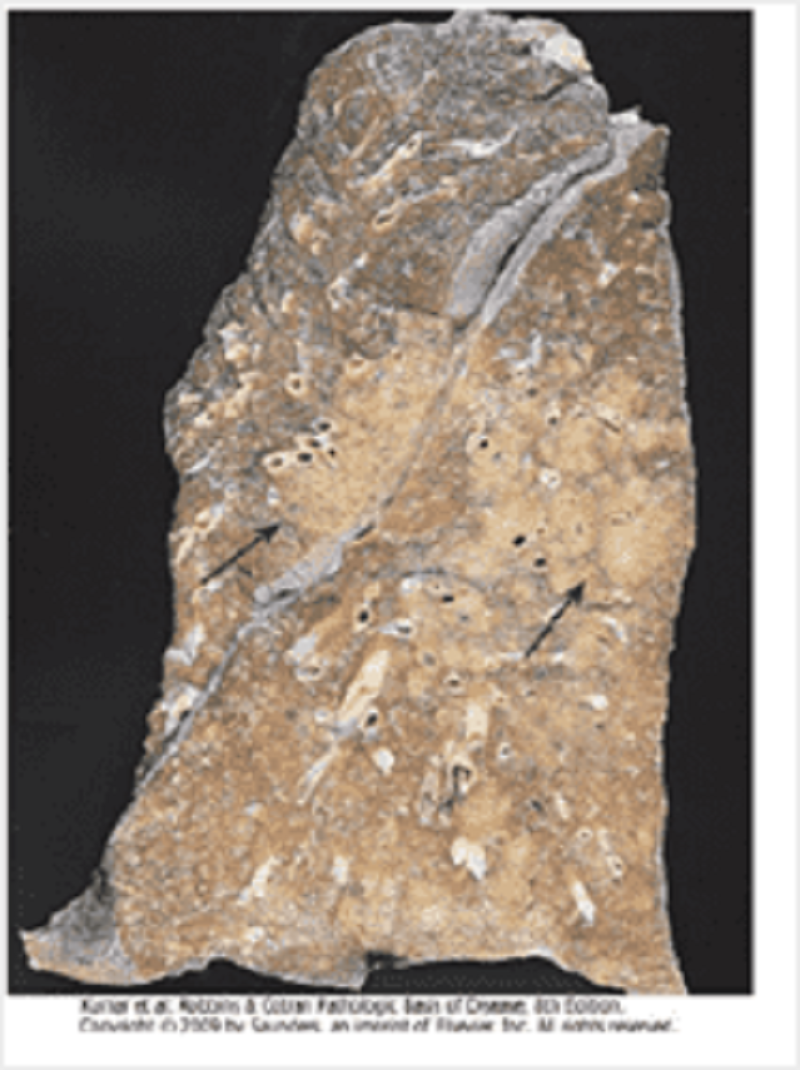

In this pathology specimen of the lung, the arrows mark:
Granulomas
Consolidation (bronchopneumonia)
Consolidation (lobar pneumonia)
Fibrosis
Cavitation
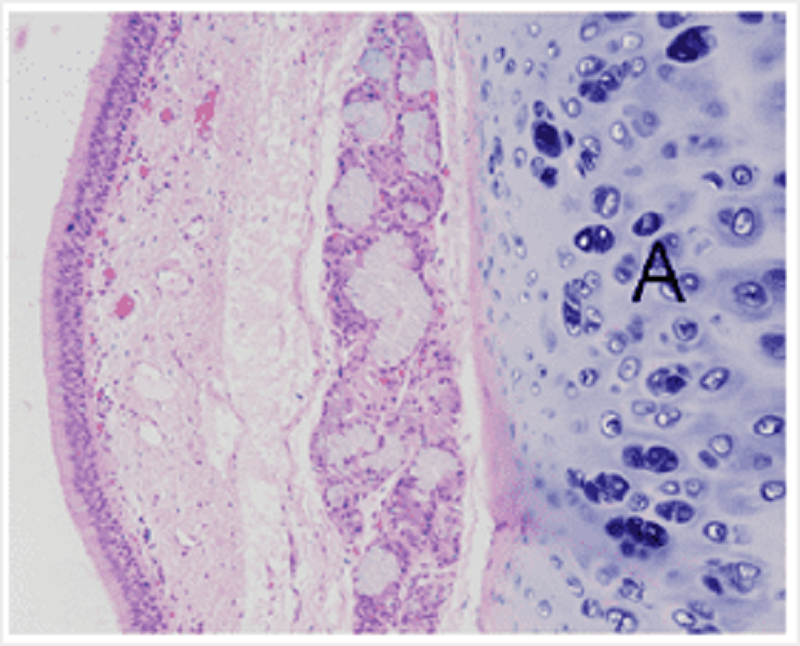
This image shows a part of the respiratory tract. Identify the tissue labelled A.
Hyaline cartilage
Fibrocartilage
Compact bone
Cancellous bone
Smooth muscle
Adipose tissue
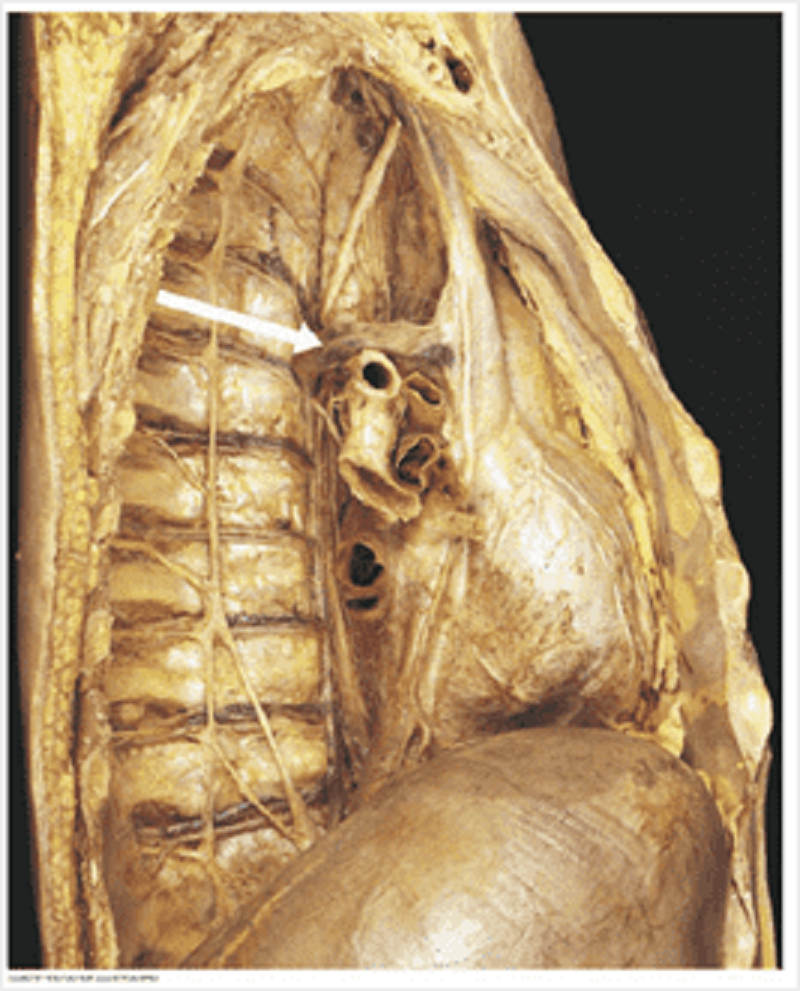
Name the structure labelled.
Azygos vein
Superior vena cava
Inferior vena cava
Hemiazygos vein
Right posterior thoracic vein
Left posterior thoracic vein
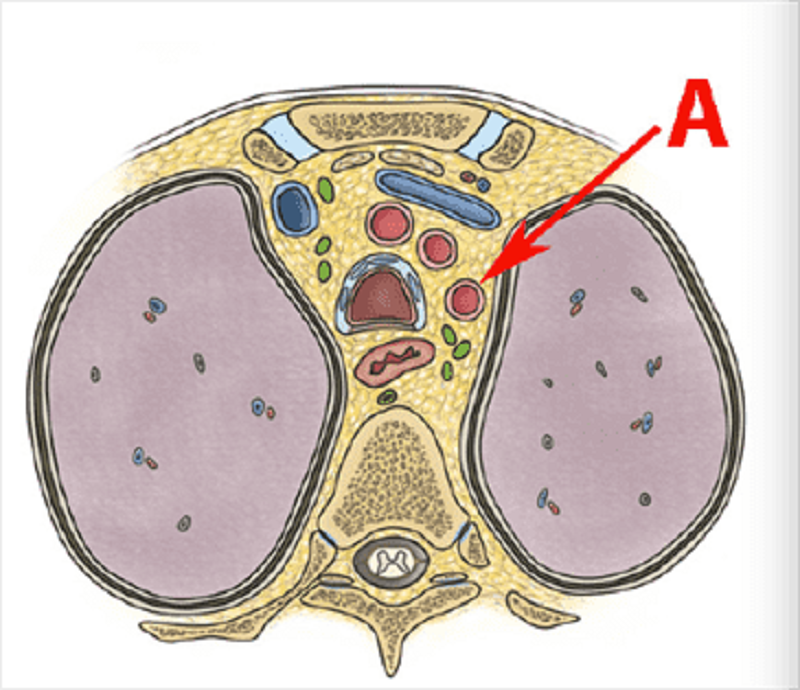
This is a cross section at T3. Identify vessel A.
Left subclavian artery
Right subclavian artery
Brachiocephalic trunk
Left common carotid artery
Right common carotid artery
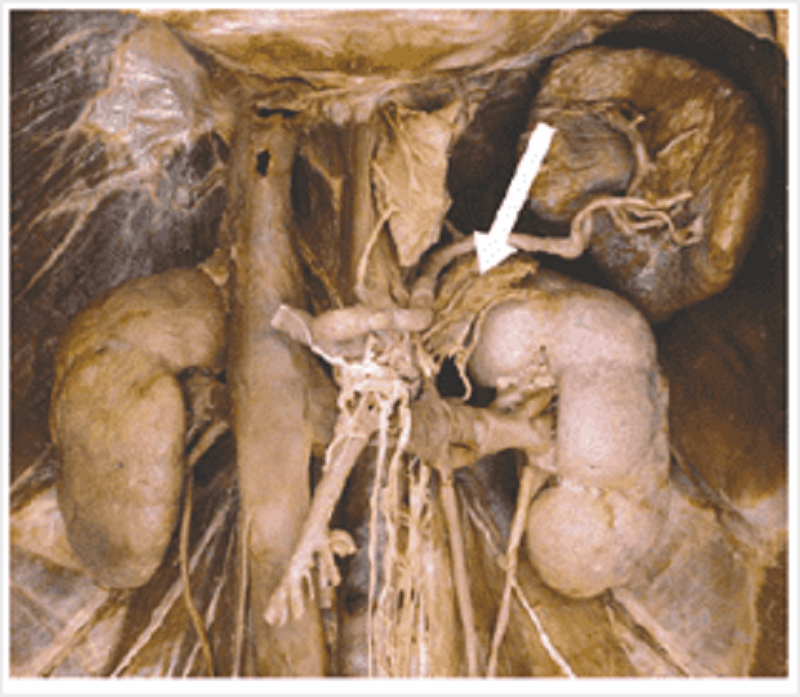
Adrenals: on the left, venous blood from this structure drains into:
Left renal vein
Inferior vena cava
Left inferior phrenic vein
Left splenic vein
Left gonadal vein
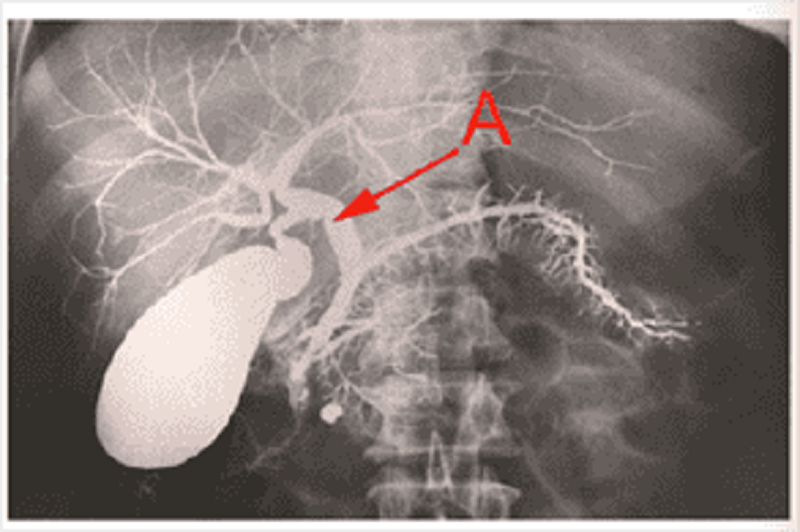
Name structure A.
Common bile duct
Hepatic duct
Pancreatic duct
Cystic duct
Common hepatic duct
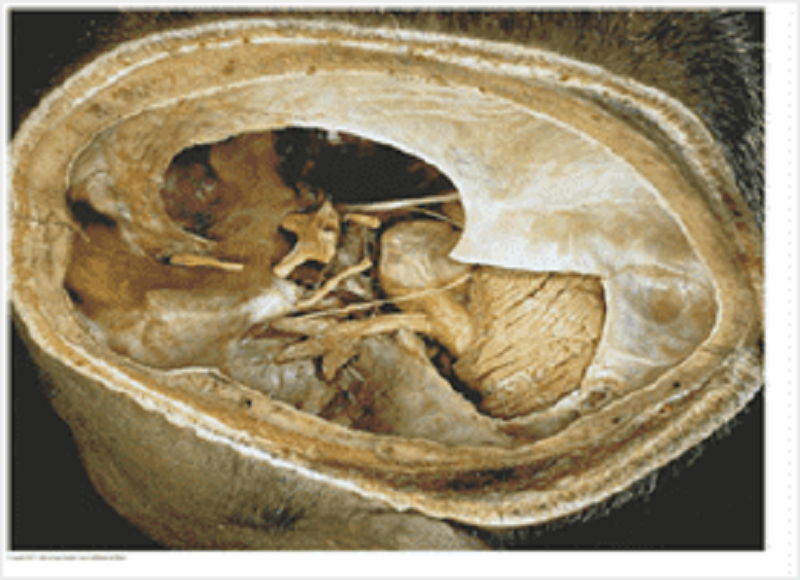
What structures are all found in the cavernous sinus?
Opthalmic, maxillary, mandibular
Trochlear, opthalmic, abducens
Oculomotor, mandibular, internal carotid artery
Optic, trochlear, abducens
Optic, oculomotor, internal carotid artery
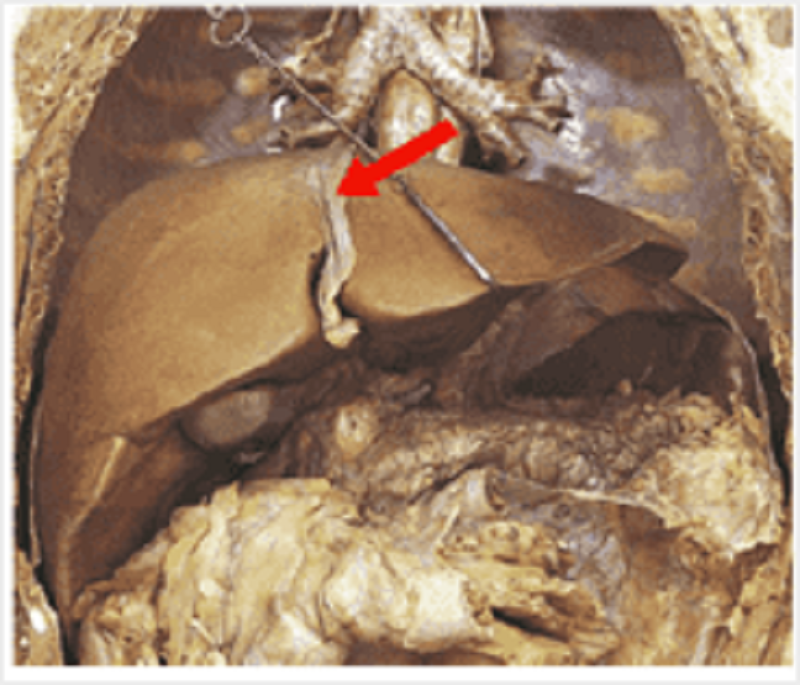
Name the structure labelled.
Falciform ligament
Round ligament
Greater omentum
Ligamentum terez
Left triangular ligament
Left coronary ligament
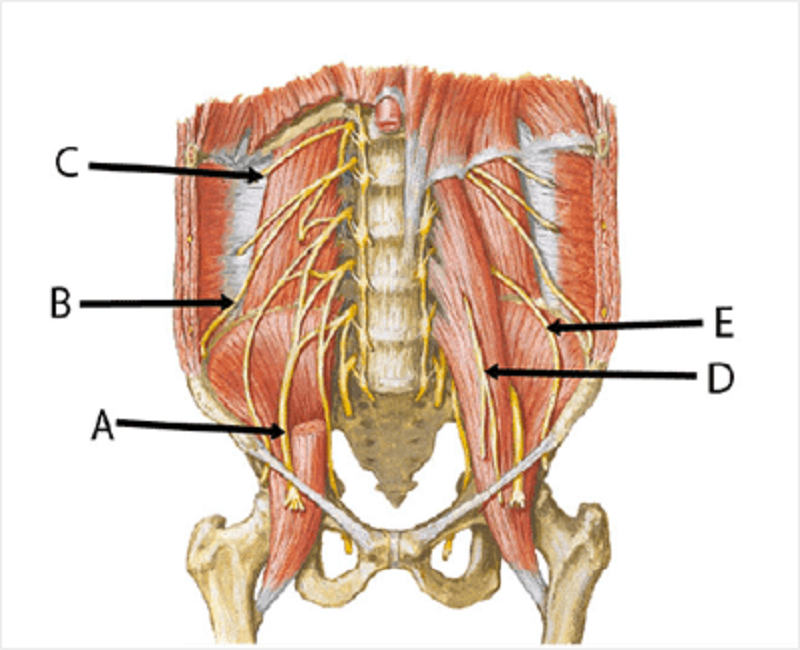
Lumbar plexus. Match the letters to appropriate nerves. A
Femoral
Ilioinguinal
Subcostal
Genitofemoral
Lateral femoral cutaneous
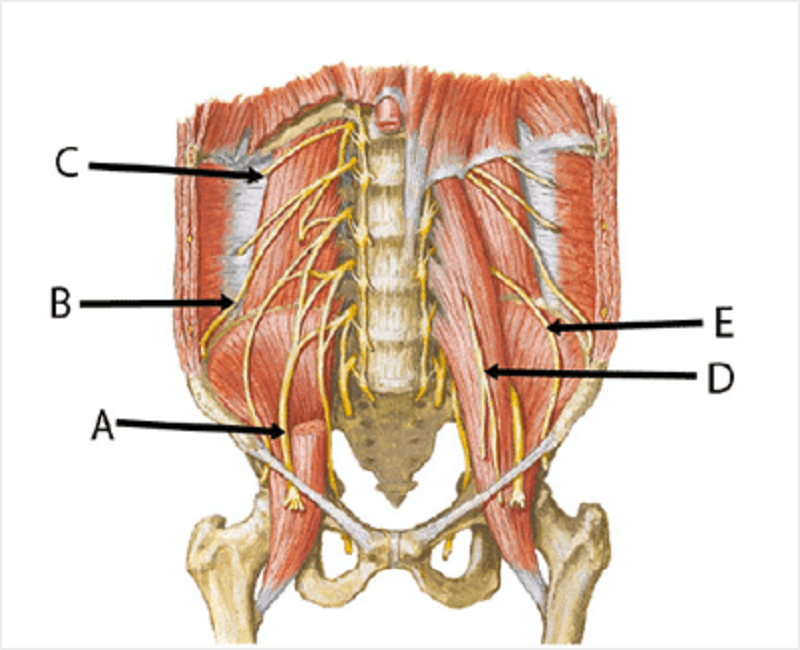
B
Femoral
Ilioinguinal
Subcostal
Genitofemoral
Lateral femoral cutaneous
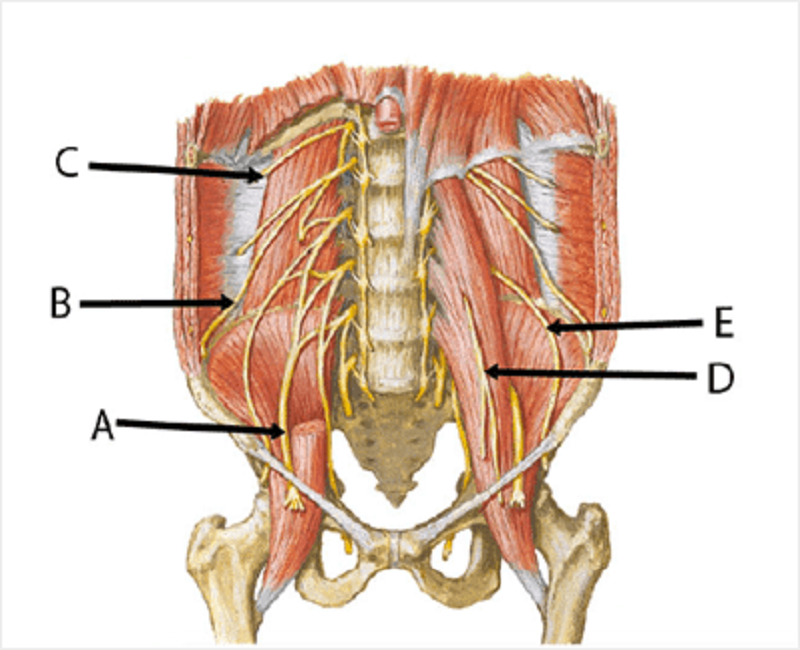
C
Femoral
Ilioinguinal
Subcostal
Genitofemoral
Lateral femoral cutaneous
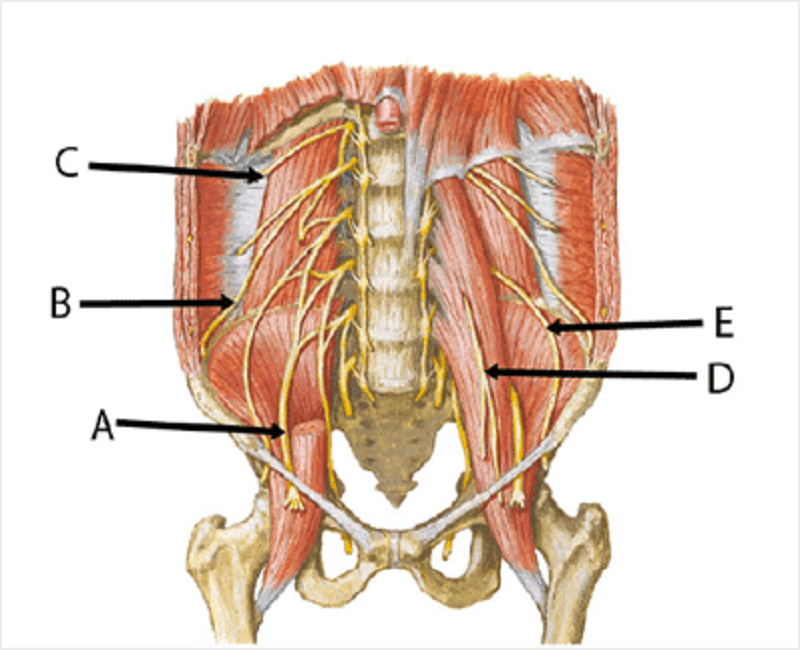
D
Femoral
Ilioinguinal
Subcostal
Genitofemoral
Lateral femoral cutaneous
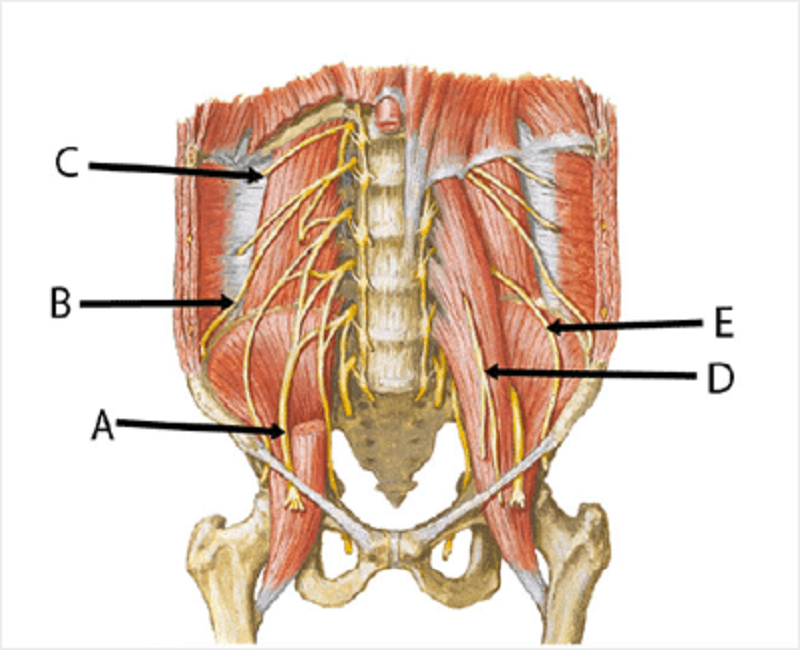
E
Femoral
Ilioinguinal
Subcostal
Genitofemoral
Lateral femoral cutaneous
Name the structure labelled
Segmental artery
Renal artery
Interlobar artery
Arcuate artery
Interlobular (cortical radiate) artery
Thyroid muscles: name the muscle labelled.
Omohyoid
Sternothyroid
Sternohyoid
Digastric
Cricothyroid
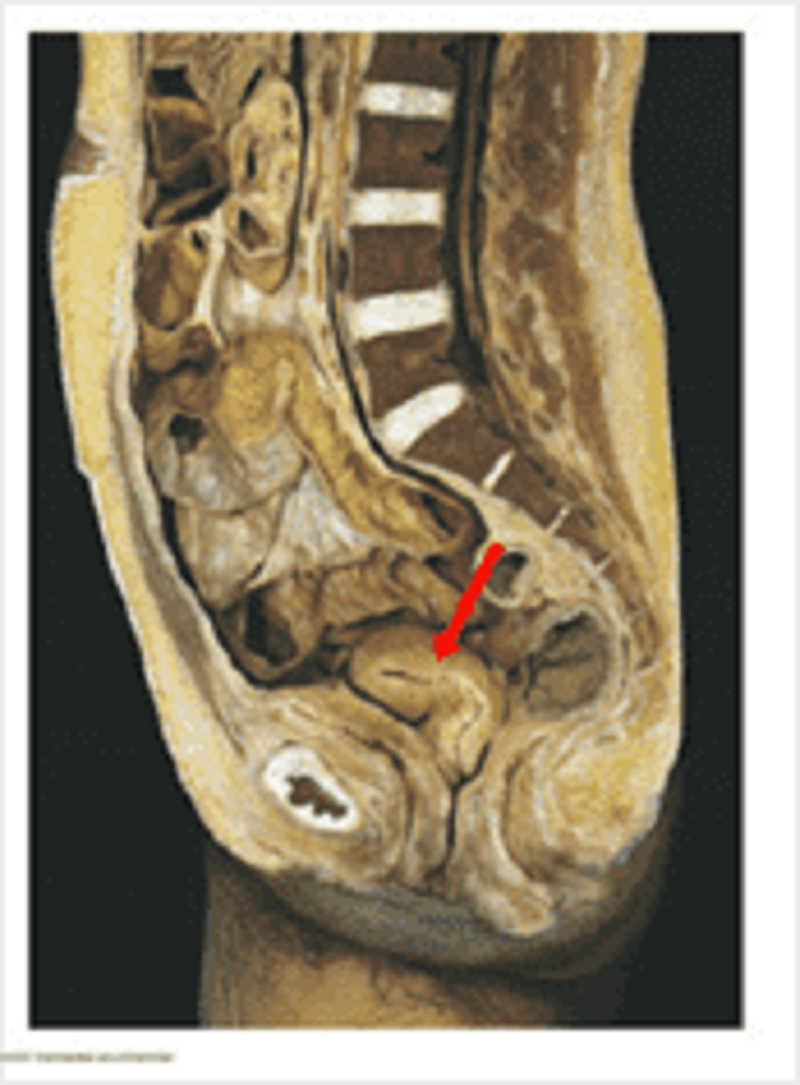
Uterus: blood supply the the structure labelled is a direct branch of which blood vessel?
Internal iliac artery
External iliac artery
Common iliac artery
Abdominal aorta
Gonadal artery
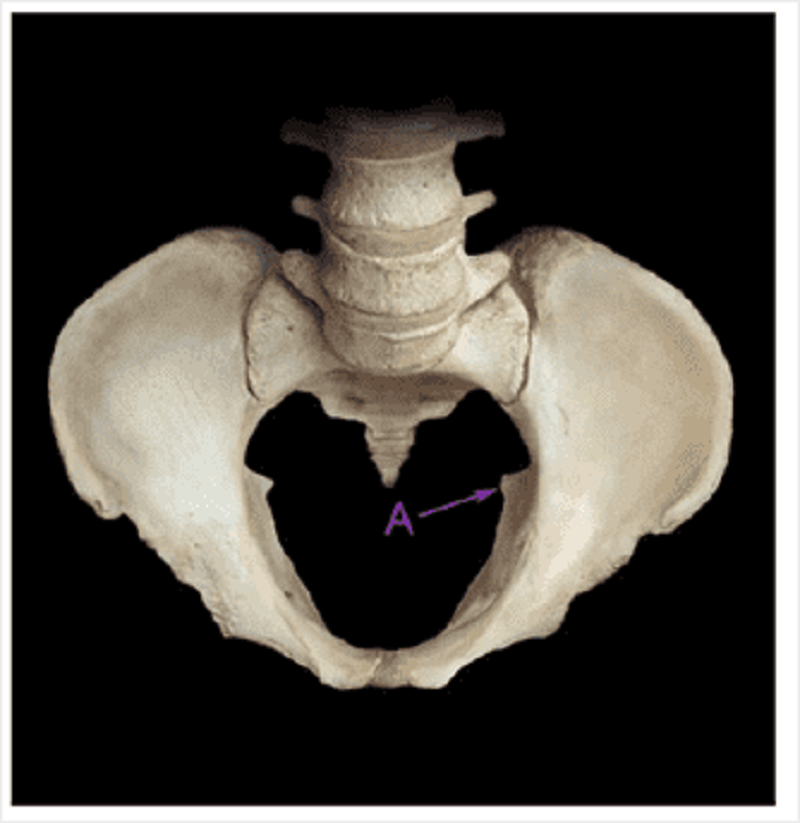
Identify A on the bony pelvis.
Ischial spine
Posterior inferior iliac spine
Ischial tuberosity
Posterior superior iliac spine
Iliac crest
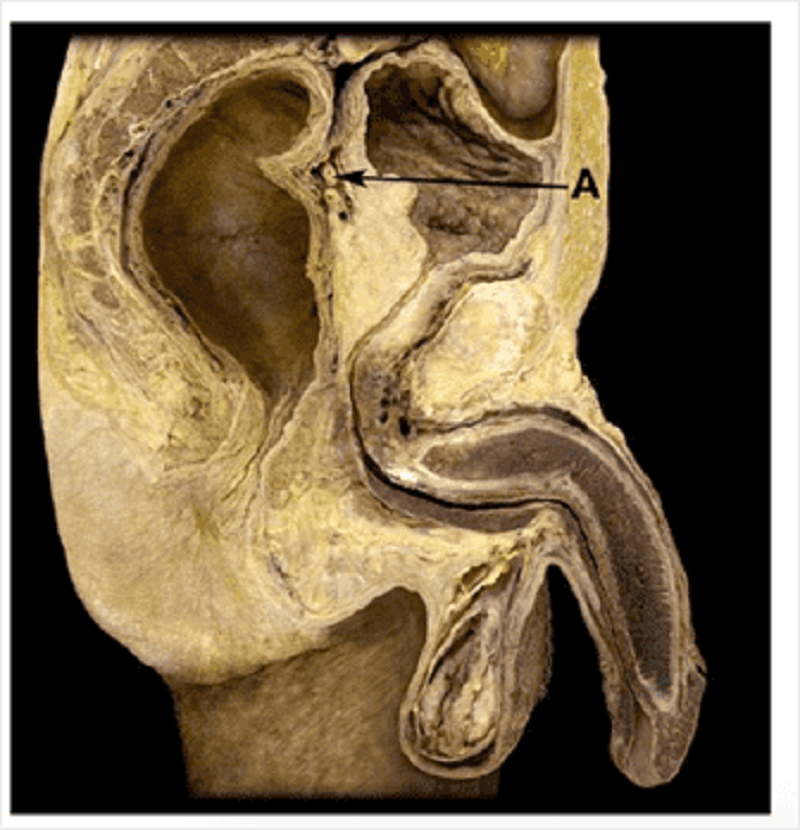
Male sagittal section: on the sagittal section, identify A.
Seminal vesicle
Rectovesical pouch
Prostate gland
Ureter
Ejaculatory duct
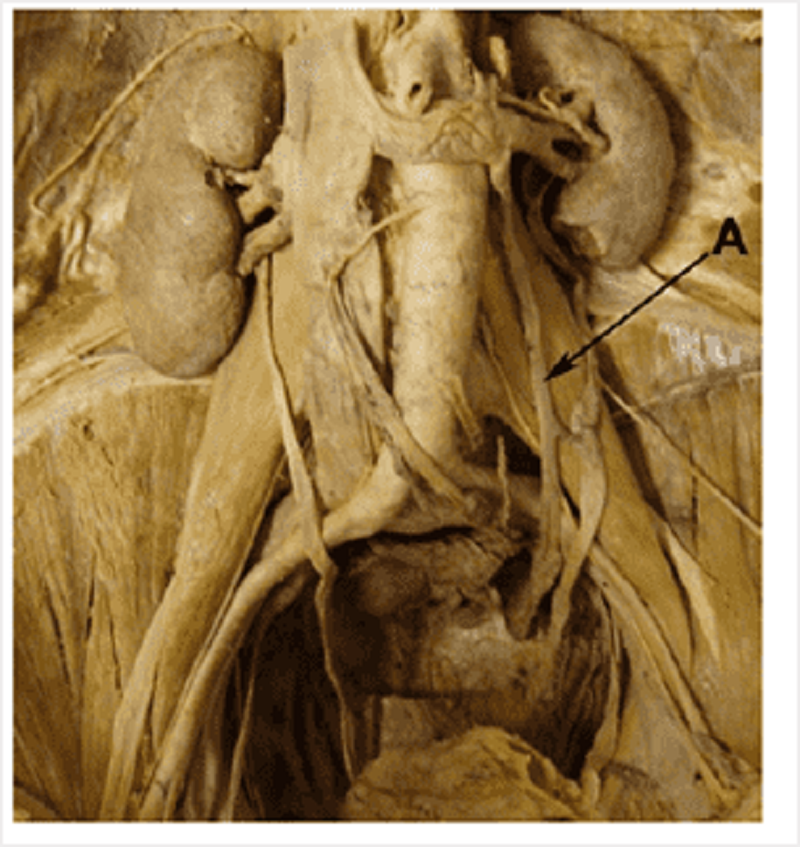
Posterior abdominal wall: identify A
Left ovarian vein
Ureter
Left ovarian artery
Inferior mesenteric artery
Inferior mesenteric vein
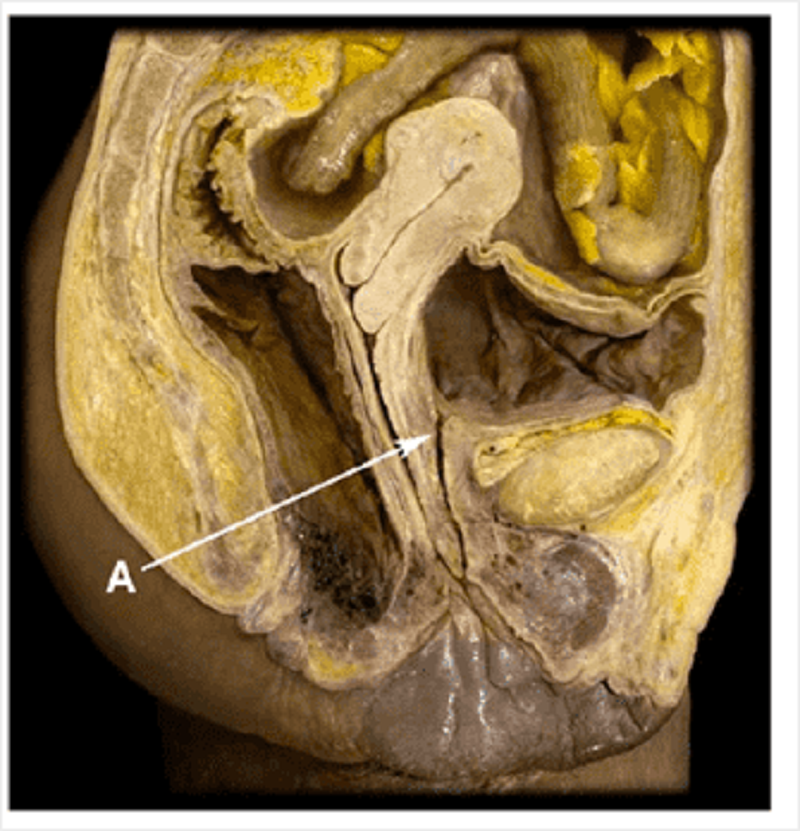
Sagittal female pelvis: identify A
Internal urethral sphincter
External urethral sphincter
Detruser muscle
Levator ani
Ureteric orifice
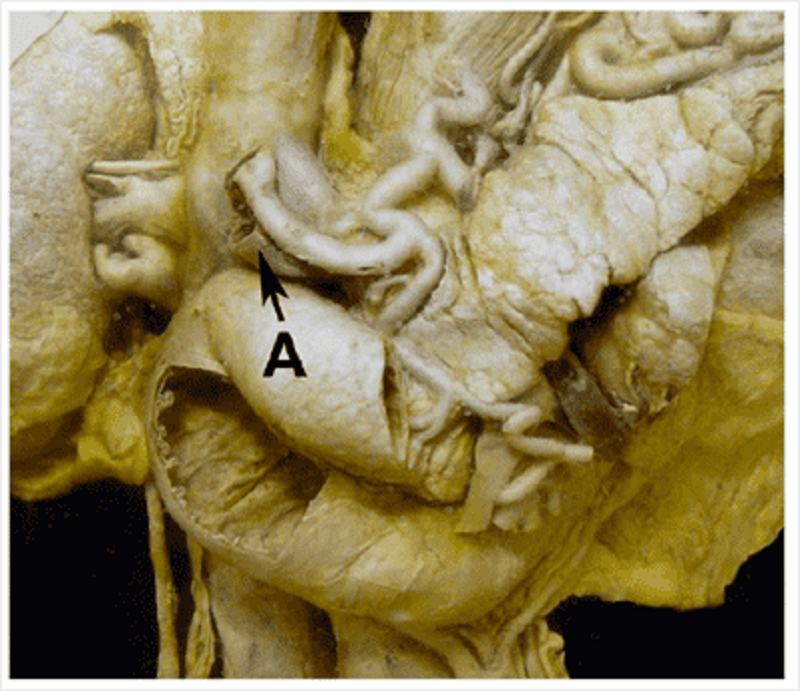
This prosection demonstrates retroperitoneal organs and the branches of the coeliac trunk. Identify A.
Bile duct
Pancreatic duct
Hepatic duct
Hepatic artery proper
Common hepatic artery
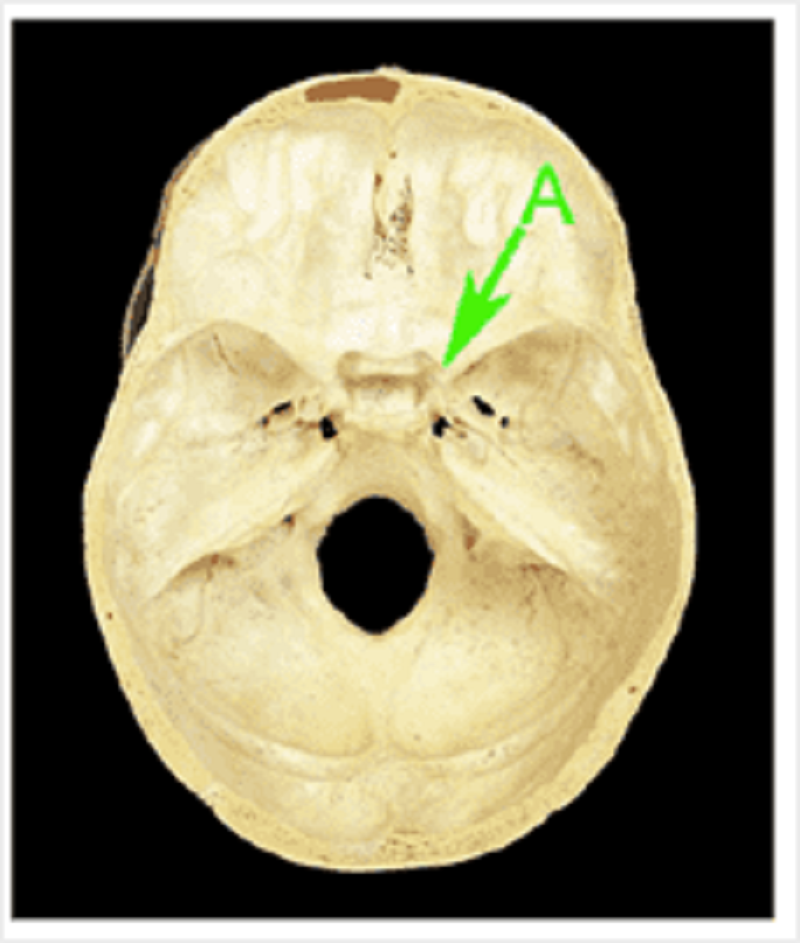
Identify A
Anterior clinoid process
Lesser wing of sphenoid
Sella turcica
Dorsum sellae
Posterior clinoid process
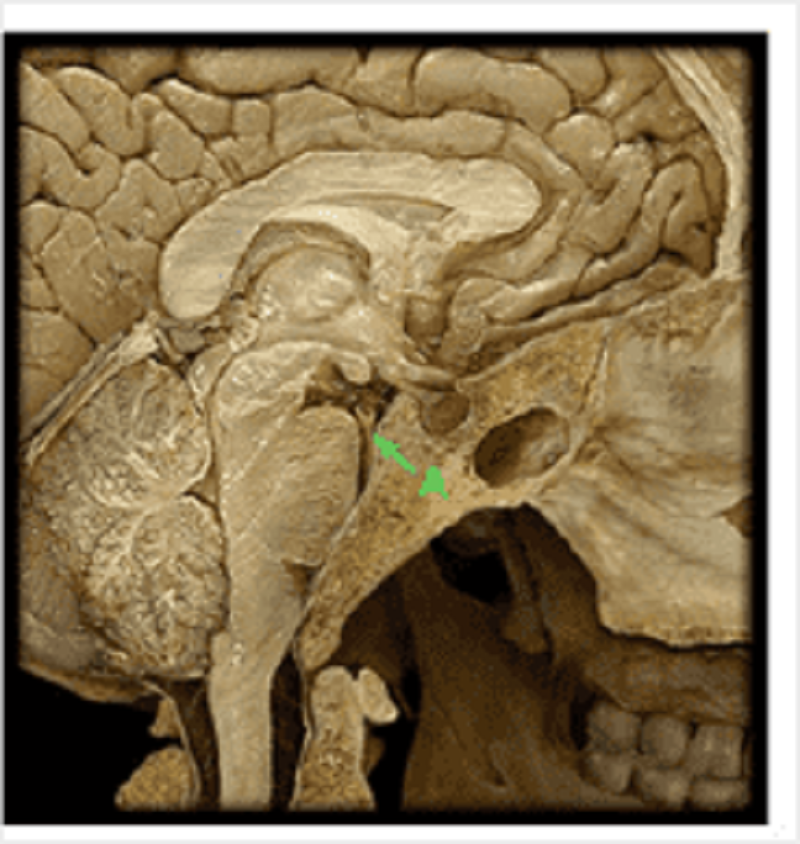
Identify vessel A
Basilar artery
Internal carotid artery
Vertebral artery
Middle cerebral artery
Posterior communicating artery
Identify A
Hepatic artery proper
Common hepatic artery
Gastroduodenal artery
Splenic artery
Right gastric artery
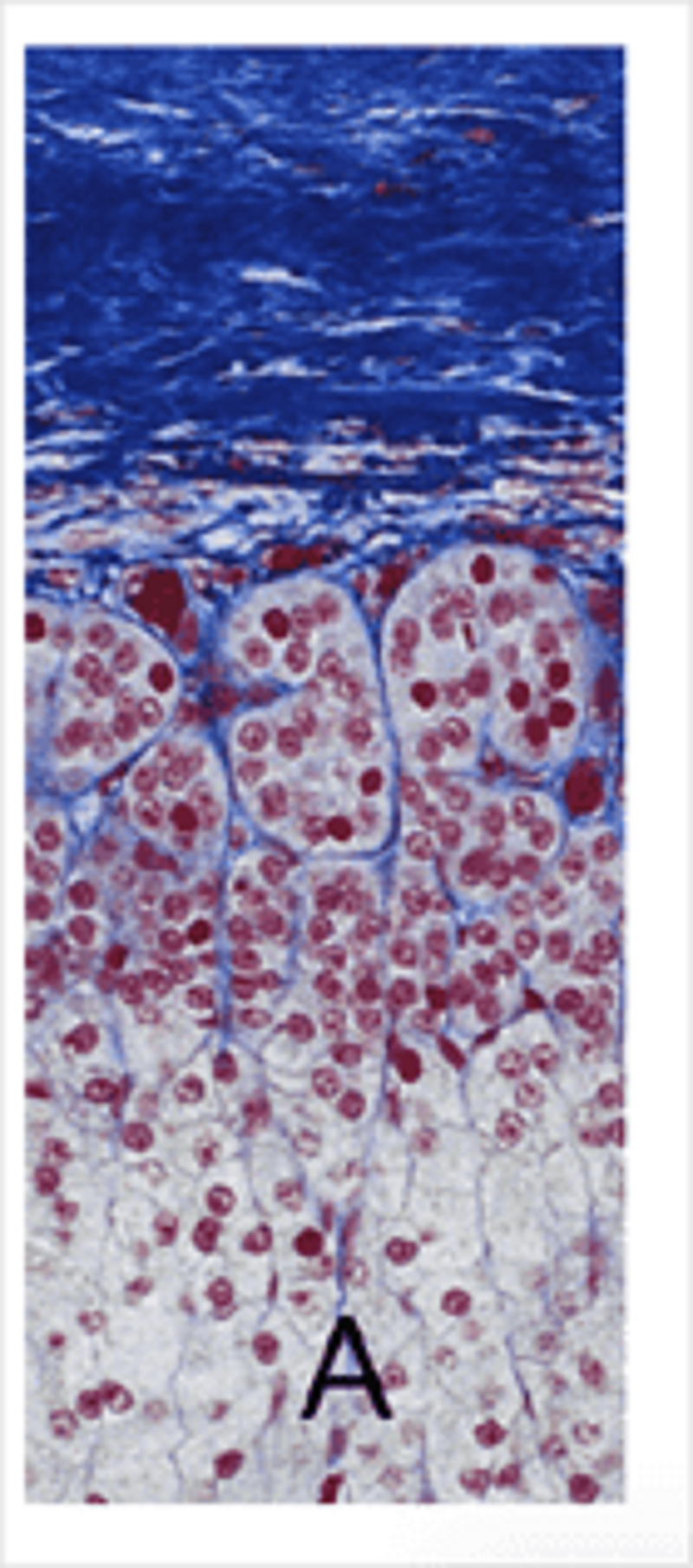
Adrenal gland. Collagen in this image is stained blue. A marks cells that synthesise:
Adrenocorticotrophic hormone
Aldosterone
Androgenic steroids
Cathecholamines
Cortisol
Angiotensin
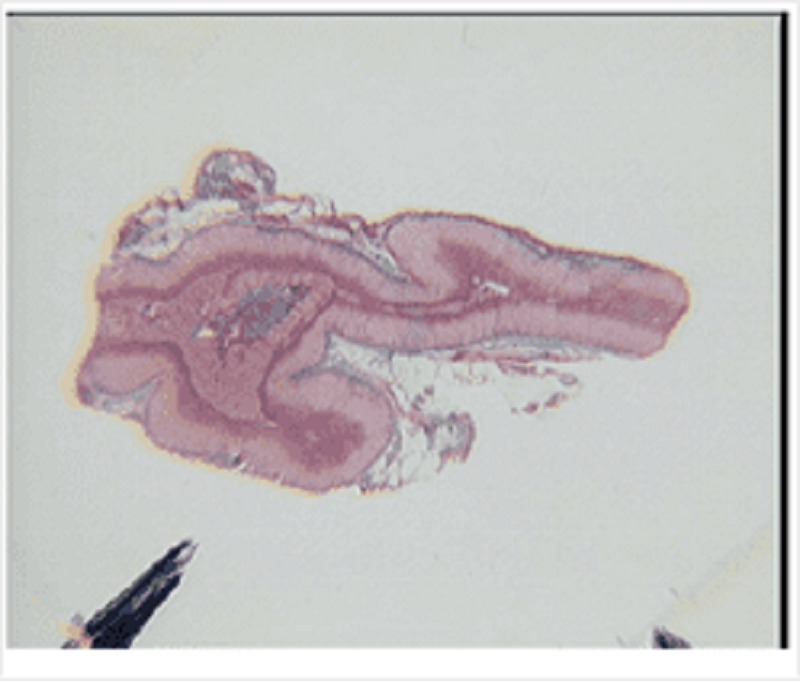
Endocrine organ stained with MSB stain. Collagen is green. What is this organ?
Adrenal gland
Thyroid gland
Parathyroid gland
Anterior pituitary gland
Posterior pituitary gland
Pancreas
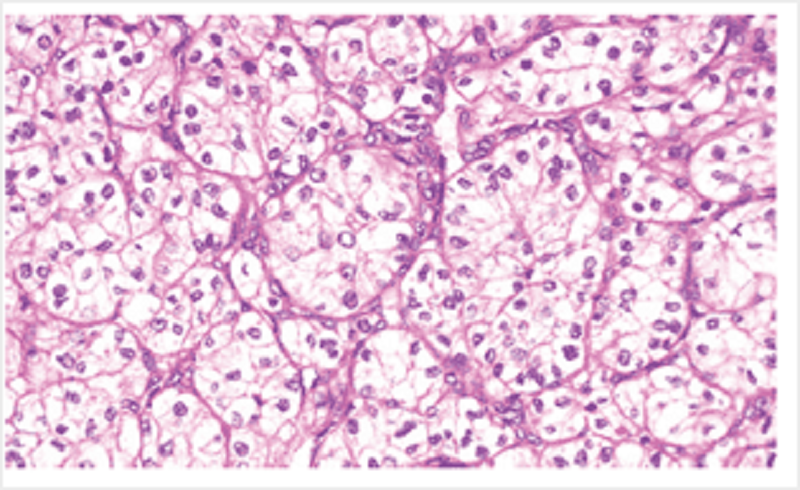
In this photomicrograph from a tumour in the kidney, the cells are derived from:
Endothelial cells
Tubule cells
Mesangial cells
Stromal cells
Mesothelial cells
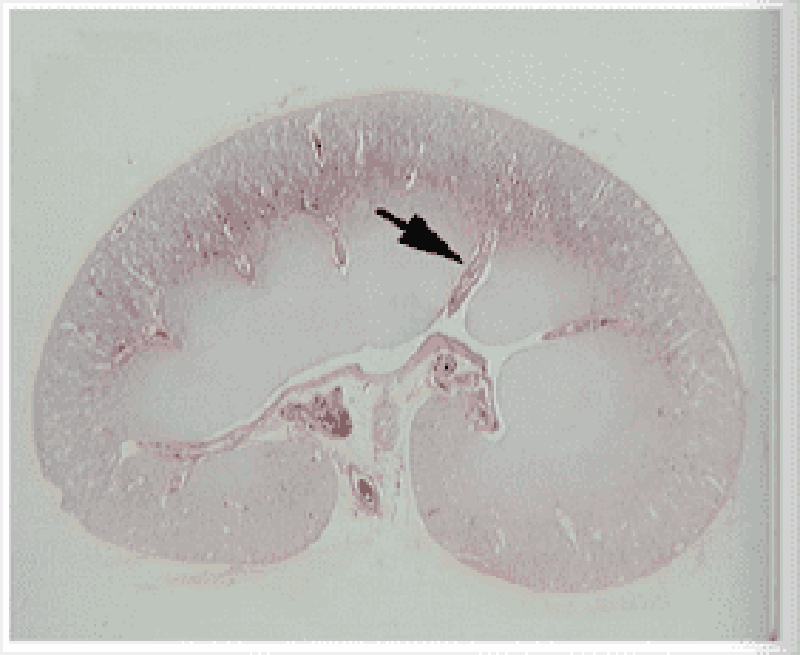
Kidney: this is a/an:
Arcuate vessel
Interlobar vessel
Interlobular vessel
Medullary ray
Cortical ray
Afferent arteriole
Efferent arteriole
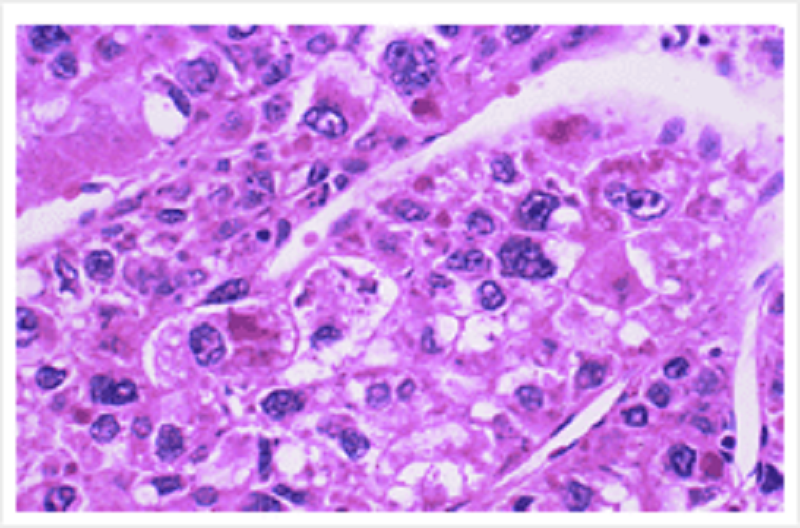
Histopathology specimen of a liver tumour. The cells shown here are:
Arranged in glands
Without vasculature
Pleomorphic
Normochromic
Arranged in lobules
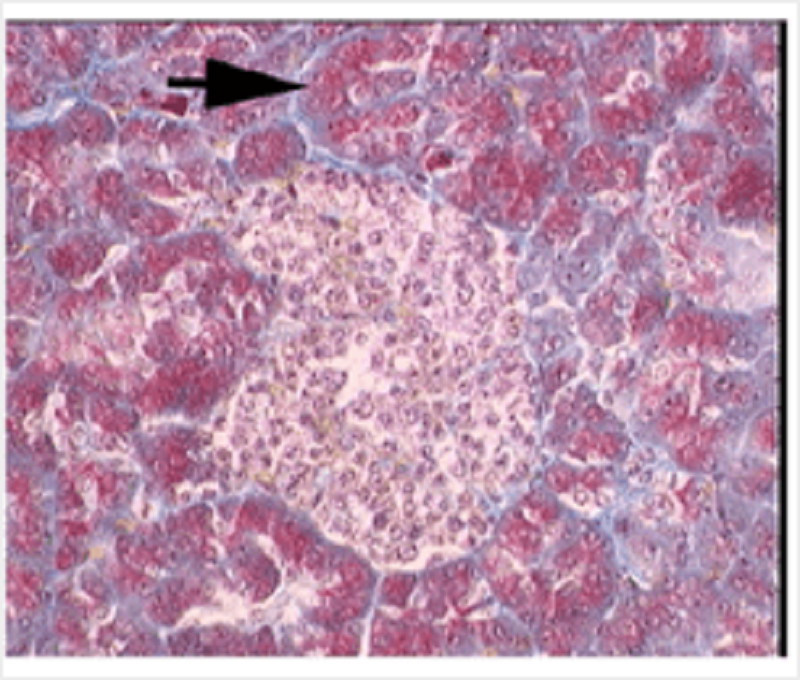
Endocrine organ. The arrow indicates:
Acinar cells
Alpha cells
Beta cells
Chief cells
Duct cells
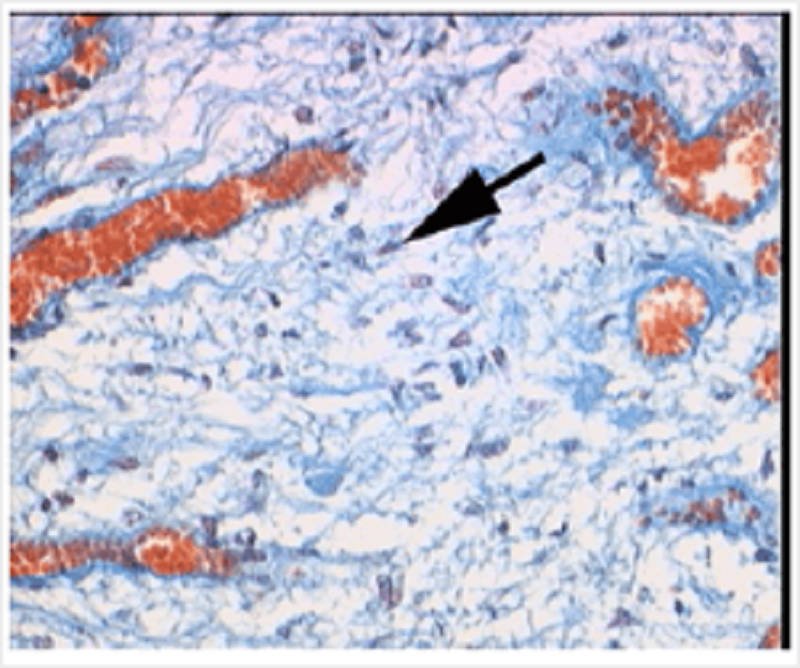
Pituitary gland. The arrow indicates a(n):
Endothelial cell
Glandular epithelial cell
Pituicyte
Smooth muscle cell
Somatotroph
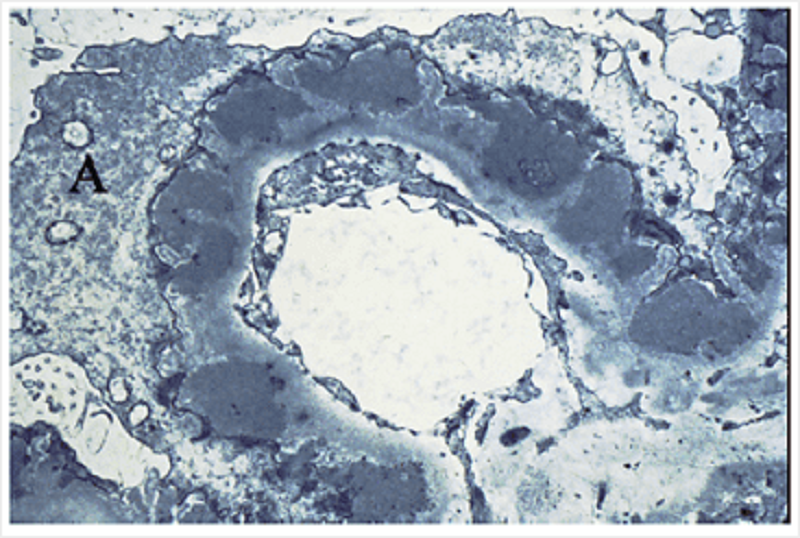
In this kidney section showing membranous glomerulonephrophathy, identify A.
A process of a visceral Bowman's capsule epithelial (podocyte) cell
A process of a mesangial cell
A process of a mesothelial cell
A process of a parietal Bowman's capsule epithelial cell
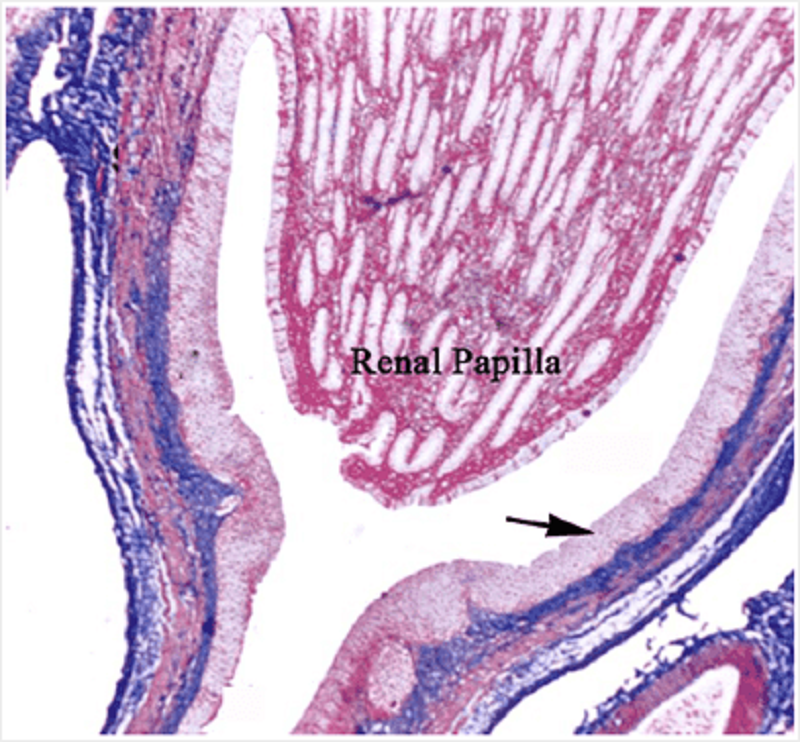
In this section of a renal papilla, identify the cells marked with an arrow
Transitional epithelium
Stratified squamous epithelium
Parietal layer of Bowman's capsule
Visceral layer of Bowman's capsule
Renal clear cell carcinoma
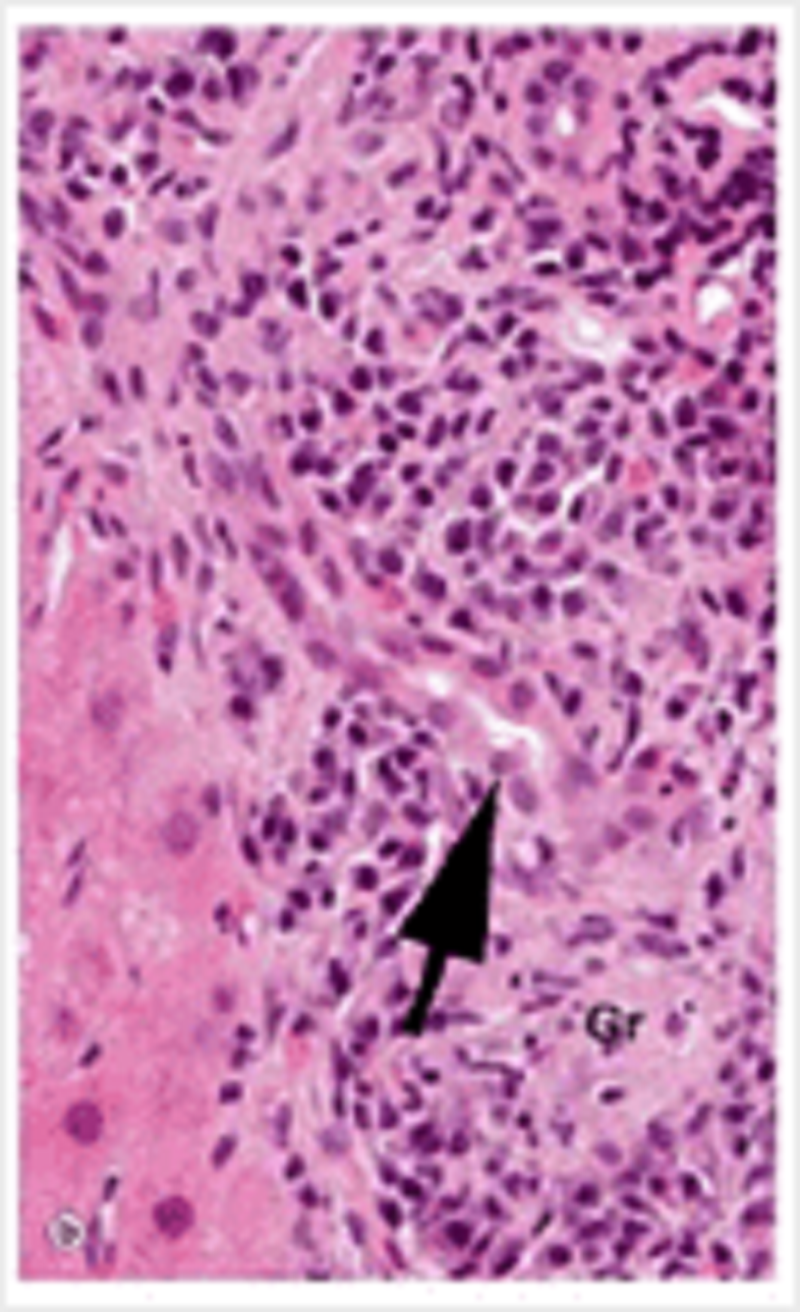
In this liver biopsy, inflammation is centred on the structure indicated by the arrow. What is this structure?
Bile duct
Central vein
Dysplastic gland
Canaliculus
Sinusoid
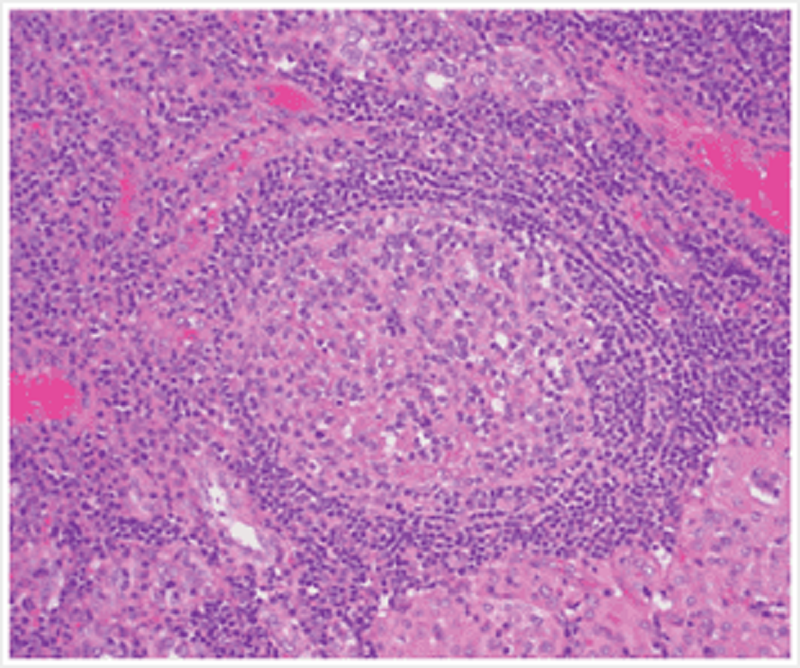
This histopathology specimen is from the thyroid gland. In the centre of the field there is a/an:
Lymphoid follicle
Parathyroid nodule
Thyroid follicle
Oxyphil cell adenocarcinoma
Follicular cell carcinoma
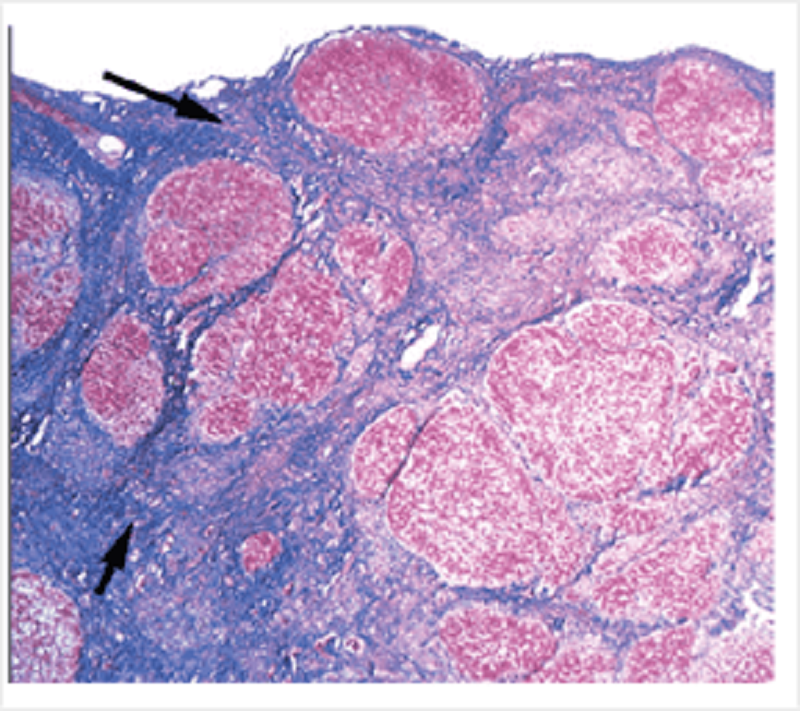
The histopathology specimen shown at low magnification is from the liver. The blue tissue indicated by the arrows is:
Dense irregular fibrocollagenous tissue
Reticular tissue
Granulation tissue
Fibrocartilage
Dense regular fibrocollagenous tissue
Hyaline cartilage
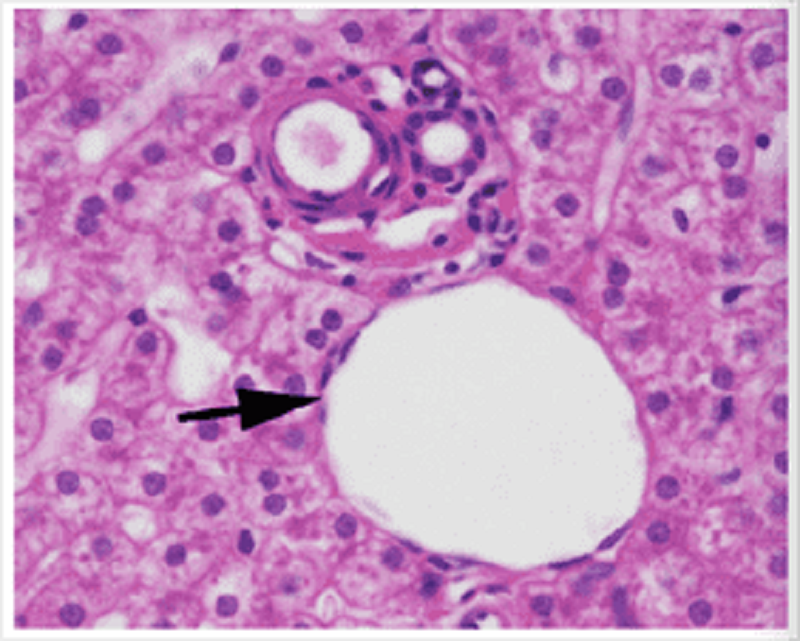
The liver. The arrow indicates a:
Portal vein
Hepatic artery
Central vein
Bile duct
Sinusoid
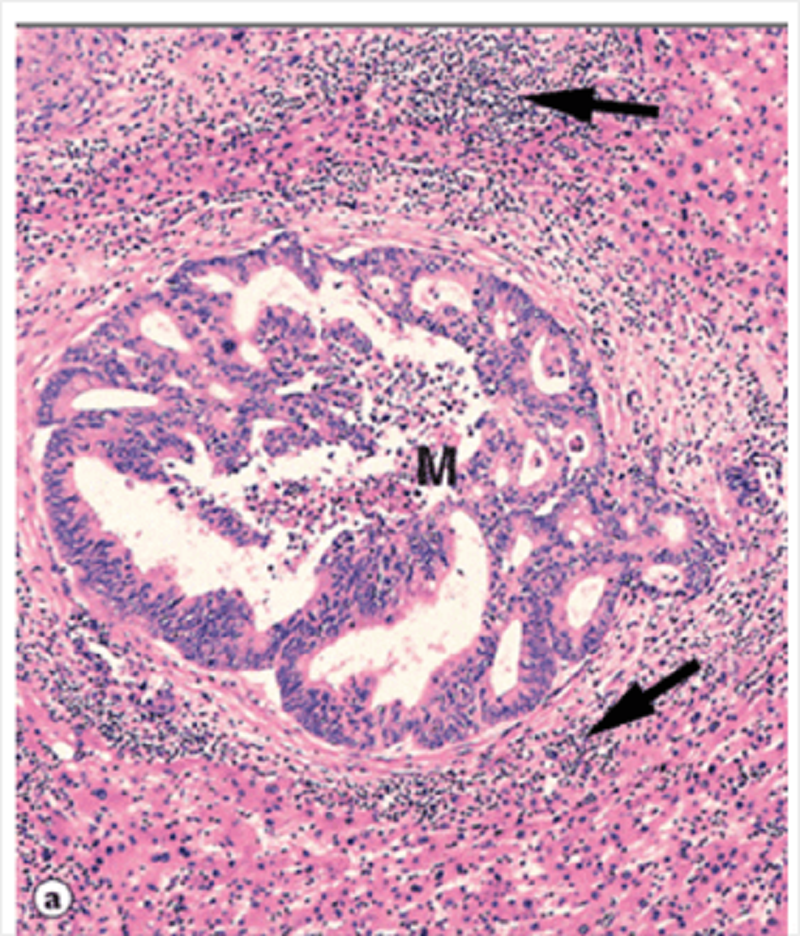
The photomicrograph shows a metastatic tumour in the liver. The majority of the cells indicated by the arrows are:
Lymphocytes
Fibroblasts
Hepatocytes
Colonic epithelial cells
Eosinophils
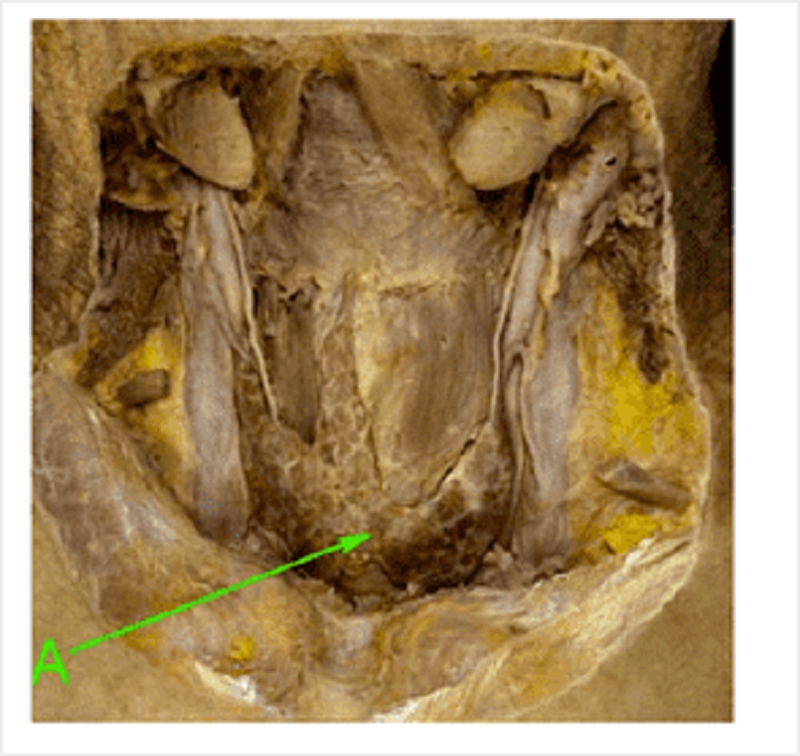
Identify A
Isthmus of thyroid
Pyramidal lobe of thyroid
Medial lobe of thyroid
Lateral lobe of thyroid
Parathyroid
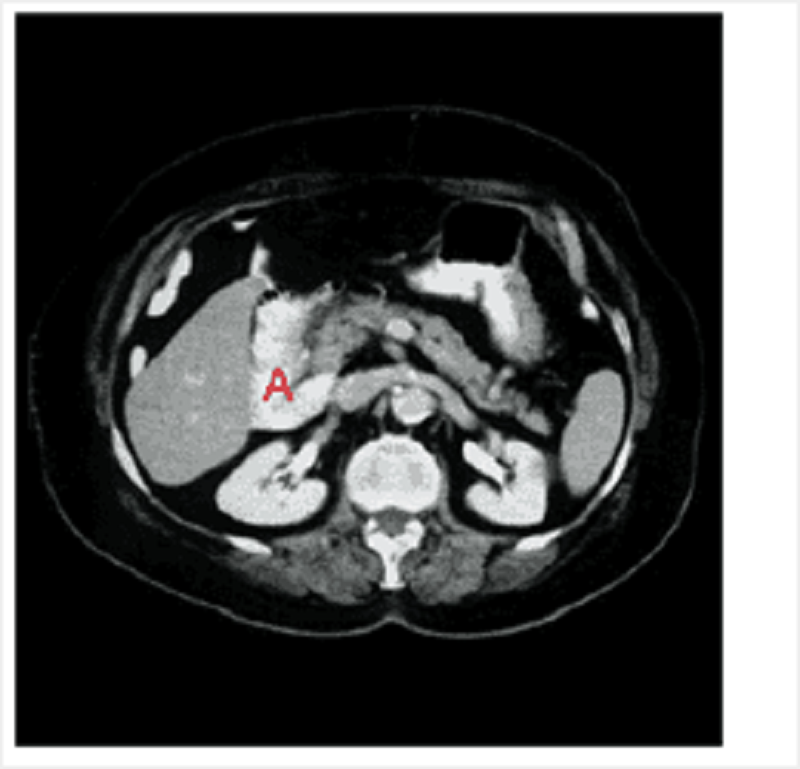
Identify A on this axial CT at the level of the first lumbar vertebrae.
Duodenum
Head of pancreas
Gall bladder
Liver
Spleen
{"name":"Practice spotter 11\/12", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Prosection of deep surface of anterior thoracic wall. Identify A., A (PA chest film), B","img":"https://cdn.poll-maker.com/14-606232/screen-shot-2017-02-11-at-09-39-56.png?sz=1200"}
More Quizzes
Da lukas quiz
1368
WHOLE NUMBER
1050
Negotiating in South Korea
10532
If You're A Woman We Can Guess Whether You Were Born Before or After 1993 With Just 6 Questions
6334
Federalist or Anti-Federalist? Alignment
201018474
Should I Get a Tattoo? Free Readiness
201021372
Running Trivia - Marathon, Track & Records
201024346
Am I Constipated - Free Symptom Checker
201022027
Which Celebrity Body Type Matches You? Free
201018559
Should I Get Married or Stay Single? Free
201019990
Raymond's Run - Reading Comprehension (Free)
201019886
Big Bang Theory - Free TBBT Trivia Challenge
201020651