QCU/DES/USMLE/ ENT+OPT

Advanced Medical Quiz on ENT Disorders
Welcome to our comprehensive medical quiz focused on ENT disorders, tailored for healthcare professionals and students alike. Challenge your knowledge and enhance your understanding of key concepts related to ear, nose, and throat conditions through engaging multiple-choice questions.
- 68 carefully crafted questions
- Covers a range of topics from diagnosis to treatment
- Ideal for USMLE and other medical examination preparations
A 28-year-old Caucasian male presents to the emergency department complaining of neck pain for the past two days. He states that a chicken bone scratched the back of his throat a week ago. Two weeks ago, he was in Arizona visiting his friends. He is otherwise healthy and has never been hospitalized. His temperature is 39°C (102.2F), blood pressure is 125/85 mmHg, and heart rate is 120/min. On examination, he refuses to fully open his mouth. Neck movements, especially neck extension, are restricted secondary to pain. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Meningitis
B. Herpangina
C. Epiglottitis
D. Diphtheria
E. Retropharyngeal abscess
A 55-year-old female presents to the office with a one-week history of left-sided ear pain and itchiness. The pain is especially bothersome at night, and is exacerbated by chewing. She denies any hearing loss. Her past medical history is significant for hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia, and gout. Current medications include lisinopril, allopurinol, and metformin. She has missed her last two appointments with her primary care physician. Her temperature is 38.3°C (101.0F), blood pressure is 140/90 mmHg, and pulse is 98/min. On examination, there is granulation tissue in the left ear canal with a scant amount of discharge. Which of the following is the best initial treatment for this patient?
A. Topical neomycin
B. Topical low-strength corticosteroids
C. Ciprofloxacin
D. Ampicillin/sulbactam
E. Surgical debridement
A 7-year-old boy with a 6-day history of nasal discharge presents with a swollen and painful left eye. His blood pressure is 100/70 mm Hg, pulse is 92/min, respirations are 18/min, and temperature is 39.4°C (103F). Examination of the left eye reveals swollen and erythematous eyelids, mild protrusion of the eyeball, and pain with eye movements. The affected eye is tender and his visual acuity is decreased. Funduscopic examination is normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Anterior uveitis
B. Cavernous sinus thrombosis
C. Conjunctivitis
D. Optic neuritis
E. Orbital cellulitis
A 45-year-old Asian male complains of a progressively worsening sore throat and difficulty swallowing for the past 24 hours. You notice that his voice is muffled and he is drooling. He also has a harsh shrill associated with respiration. His temperature is 39.3°C (103F), blood pressure is 120/80 mmHg, pulse is 106/min, and respiratory rate is 22/min. On examination, a few cervical lymph nodes are palpable and there is tenderness to palpation over his larynx. Which of the following are the two most common organisms that cause this condition?
A. Haemophilus influenzae and Streptococcus pyogenes
B. Mycobacterium tuberculosis and herpes simplex virus
C. Haemophilus influenzae and Candida species
D. Streptococcus pyogenes and Klebsiella pneumoniae
E. Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa
A 60-year-old man comes to your office complaining of difficulty hearing for the past few weeks. He has type 2 diabetes mellitus, which is well-controlled by diet alone. His past medical history is also significant for essential hypertension, congestive heart failure secondary to diastolic dysfunction, and chronic renal failure. Medications include aspirin, diuretics, an ACE inhibitor, and a beta-blocker. His pulse is 82/min, blood pressure is 140/90 mmHg, and respirations are 14/min. Examination reveals hearing loss in both ears Which of the following medication is a potential cause of this patient's hearing problems?
A Lisinopril
B Aspirin
C. Metoprolol
D. Furosemide
E. Hydrochlorothiazide
A 32-year-old male complains of difficulty hearing in his left ear for the past month. He denies any headaches, fever, chills, weight loss, or ear discharge. He is HIV positive, and is currently being treated with highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART). He also takes trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole daily. His most recent CD4 count was 425/ mm3. Examination of the affected ear shows a dull, hypomobile tympanic membrane. What is the most likely cause of hearing loss in this patient?
A. Neoplasia
B. Non-infectious effusion
C. Otosclerosis
D. Opportunistic infection
E. Demyelinization
A 65-year-old female complains of difficulty eating over the last two days. She states that food drops out of her mouth. She has also been having some discharge in her left ear recently. She denies any sore throat, nasal discharge, chest pain, cough, or difficulty breathing. Her past medical history is significant for type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia. She has been poorly complaint with follow-up appointments. Her temperature is 38.8°C (101.7 F), pulse is 96/min, blood pressure is 140/90 mmHg, and respirations are 18/min. Examination of the left ear canal shows granulations. There is facial asymmetry, and the angle of the mouth on the left is deviated downward. Which of the following is the most likely causative organism for this patient's condition?
A. Rhizopus species
B. Pseudomonas aeruginosa
C. Staphylococcus aureus
D. Aspergillus niger
E. Herpes zoster
A 7 -year-old boy is brought to your office with a sore throat, decreased appetite, and nausea. His past medical history is insignificant. All of his vaccinations are up-to-date. He has no known allergies. His temperature is 39.0°C (102.5F), blood pressure is 110/70 mmHg, pulse is 104/min, and respirations are 16/min. On examination, the pharynx and tonsils are red, swollen, and have white exudates on their surface. There is also bilateral tender cervical lymphadenopathy. The rapid diagnostic test for streptococcal antigen is positive. What is the most appropriate next step in management?
A. Throat culture
B. Monospot test
C. Antistreptolysin 0 antibodies
D. Oral penicillin V
E. Oral azithromycin
A 37-year-old woman presents to your office with severe vertigo, postural instability, and vomiting. She also complains of "a buzzing sound" in her right ear. She has had two similar episodes over the previous year that lasted several hours and resolved spontaneously. She has no other medical problems. Her mother died of breast cancer at 55 years of age and her father is currently suffering from colon cancer. Her heart rate is 90/min and blood pressure is 130/80 mmHg. Her BMI is 25.3 kg/m2. Examination reveals horizontal nystagmus. Which of the following could have prevented this patient's symptoms?
A. Caloric restriction
B. Low salt diet
C. Gluten-free diet
D. High complex carbohydrate diet
E. Calcium supplementation
A 36-year-old woman presents to your office with complaints of worsening throat pain for the past six days. She also has pain in her ears and neck as well as difficulty swallowing. On examination, she has excessive salivation and difficulty opening her mouth. Her temperature is 39°C (102.2F), blood pressure is 130/80 mmHg, pulse is 100/min, and respiratory rate is 18/min. Which of the following neck space infections carries the highest risk of mediastinal involvement?
A. Submandibular space
B. Sublingual space
C. Parapharyngeal space
D. Retropharyngeal space
E. Retro-obital
A 23-year-old male comes to your office with a 10-day history of severe headaches. He states that they are sharp in character and are mostly right-sided involving the frontal area. The headaches interfere with his sleep, and he also complains of double vision, nausea, and malaise. His blood pressure is 120/80 mm Hg, pulse is 103/min, respirations are 14/min, and temperature is 38.0°C (100.5F). Examination reveals bilateral periorbital edema. There is subtle right-sided lateral gaze palsy. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Orbital cellulitis
B. Acute angle-closure glaucoma
C. Common migraine
D. Cavernous sinus thrombosis
E. Cluster headaches
A 24-year-old Caucasian female complains of recurrent painful ulcers in her mouth and occasional abdominal pain. She has also unintentionally lost 5 pounds over the last six months. She is not sexually active, and denies use of tobacco, alcohol, or drugs. Past medical history is noncontributory and she takes no regular medications. Her mother suffers from asthma and her father has prostate cancer. She is afebrile with a blood pressure of 118/69 mmHg and pulse of 71/min. Physical examination reveals mild abdominal tenderness primarily in the lower abdomen without guarding or rebound. Several shallow ulcers are seen on the buccal mucosa. A biopsy of one of the ulcers demonstrates granulomatous inflammation. Her hematocrit is 42%. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's complaints?
A. Celiac disease
B. Folic acid deficiency
C. Crohn's disease
D. Oral candidiasis
E. Squamous cell carcinoma
A 70-year-old man comes to your office with complaints of difficulty hearing. His wife says that he has been raising the television volume much louder recently. The patient claims that he can hear well when he talks to his family members at home, but he has significant difficulty hearing in restaurants or during other family gatherings, which is why he prefers to stay at home most of the time. He worked in a shipbuilding yard for 30 years, and retired five years ago. He has no history of significant noise exposure. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Otosclerosis
B. Presbycusis
C. Middle ear effusion
D. Meniere's disease
E. Acoustic neuroma
A 12-year-old girl comes to the office complaining of a small amount of left-sided ear discharge that has persisted for the last three weeks. She has completed two courses of antibiotics that were prescribed during her previous visits. She also complains of hearing loss on the left side. On examination, she is afebrile. Otoscopy reveals an intact left tympanic membrane with peripheral granulation and some skin debris. The patient should be evaluated for which of the following?
A. Meniere's disease
B. Craniopharyngioma
C. Otosclerosis
D. Cholesteatoma
E. Middle ear osteoma
A 33-year-old Caucasian female has suffered from recurrent episodes of dizziness over the last six months. She describes the episodes as a sensation of severe spinning that last one to two hours and are accompanied by intense nausea. She also feels unsteady during the episode, and has to lie down with her eyes closed for relief. There is no particular factor that precipitates the episodes. She denies any headaches, but complains of fullness in her right ear. She has no ear pain or ear discharge. She has used some over-the-counter ear drops with minimal relief of the fullness sensation. She prefers holding her cell phone on the left side. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
A. Middle ear disease
B. Inner ear disease
C. Cranial nerve VIII lesion
D. Cerebellar disease
E. Lesion in the medulla
A 62-year-old male comes to your office for a routine follow-up appointment. He has smoked one pack of cigarettes per day for the past 30 years and adamantly refuses to quit. He also drinks six to ten beers each weekend. His past medical history is significant for type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypertension. His last hemoglobinA1c was 8.3%. He is overweight with a current BMI of 27.5 kg/m2. While examining him, you notice a whitish patch over the anterior floor of his mouth. The lesion appears to have a granular texture and is not removed by scraping with a tongue depressor. Which of the following is most likely cause of his oral lesion?
A Candidiasis
B. Leukoplakia
C. Herpes simplex virus infection
D. Melanoma
E. Squamous cell carcinoma
6-year-old boy is brought to the office by his mother due to a decreased appetite and irritability for the past three days. He also had an episode of diarrhea yesterday. Lately, he has been sitting close to the television with the volume turned up very loudly. His temperature is 38.1°C (100.5.F), blood pressure is 110/60 mmHg, and heart rate is 110/min. On examination, there is left-sided yellowish ear discharge. His nasal mucosa appears boggy and postnasal drip is present. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A Bullous myringitis
B. Acute otitis media
C. Otitis extern a
D. Cholesteatoma
E. Sinusitis
A 28-year-old African American female complains of recurrent nasal discharge and increasing nasal congestion. She has a constant sensation of dripping in the back of her throat, and states that food has tasted bland to her recently. She is known to have sickle cell trait. She came to the emergency department for severe wheezing after taking naproxen for menstrual cramping one year ago. She has no history of head trauma. She does not smoke cigarettes, but she admits to smoking marijuana occasionally. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Angiofibroma
B. Inverted papilloma
C. Nasal polyp
D. Perforated nasal septum
E. Pyogenic granuloma
A 26-year-old man comes to your office with a one-week history of right-sided ear pain. The pain often wakes him up at night, and increases in severity when he chews food. He cannot recall any recent episodes of pharyngitis. He denies having any ear discharge, sinus tenderness, or skin rash. He exercises by swimming frequently at a local club. He is sexually active and uses condoms "quite regularly." He lives with his brother, who often comments on his habit of grinding his teeth at night. On examination, his ears are normal with a mild amount of wax. Pain is not elicited by pulling on the pinna. There are no hearing deficits appreciated. Mobility of the tympanic membrane is normal, and the Weber and Rinne test results are within normal limits. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Ramsay Hunt syndrome
B. Glossopharyngeal neuralgia
C. Otitis media
D. Temporomandibular joint dysfunction
E. Otitis externa
A 30-year-old school teacher presents with a three-day history of fever, chills, and sore throat. He also complains of difficulty swallowing that started yesterday. He denies any cough, chest pain, or difficulty breathing. He is married and denies any new sexual encounters. His temperature is 39°C (102.2F), blood pressure is 118/76 mmHg, pulse is 102/min, and respirations are 19/min. On examination, his voice is muffled. Enlarged, tender cervical lymph nodes are palpated on the left, and his uvula is deviated to the right. What is the most appropriate treatment for this patient?
A. Throat swabs and oral antibiotics
B. Monospot test and oral antibiotics
C. Emergency laryngoscopy
D. Cricothyroidotomy
E. Needle peritonsillar aspiration
A 1-year-old boy is brought to the clinic by his 28-year-old Caucasian mother for the evaluation of his eyes. For the past several months, he has been bumping into objects. His perinatal history is unremarkable. Physical examination of the eyes reveals a bilateral white reflex. The retina cannot be visualized properly. Fundal reflection is absent, and the pupil is white. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Congenital glaucoma
B. Congenital cataract
C. Retinoblastoma
D. Pterygium
E. glocoma
A 53-year-old man comes to the office because of difficulty reading fine print over the last year. He now has to hold books, menus, and magazines at an arm’s length in order to read them. He has never had visual problems before. Which of the following is most likely abnormal in this patient?
A. Corneal shape
B. Lens elasticity
C. Lens opacity
D. Macula
E. Peripheral retina
A 65-year-old white man is complaining of a sudden loss of vision in his left eye which resolved after 15 minutes. "It seemed like a curtain was falling down in my eye!" said the patient. He recalls having a similar episode 3 months ago. His past medical history is significant for hypertension, for which he takes lisinopril (20mg) and hydrochlorothiazide (25mg) daily. His pulse is 82/min, blood pressure is 140/90 mm Hg, respirations are 14/min, and temperature is normal. Fundoscopy reveals zones of whitened, edematous retina following the distribution of the retinal arterioles. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Central retinal artery occlusion
B. Amaurosis fugax
C. Central retinal vein occlusion
D. Vitreous hemorrhage
E. Hypertensive retinopathy
A 22-year-old Caucasian female presents to the office with several months history of decreased visual acuity and decreased brightness sensation in the right eye. Slight exophthalmos of the right eye is present on physical examination, and ophthalmoscopy shows pallor of the right optic disk. Several cafe-au-lait spots and intensive axillary freckling are present. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's visual problems?
A Pigment retinitis
B. Retinal hamartoma
C. Optic glioma
D. Pituitary adenoma
E. Optic neuritis
A 65-year-old African American man comes to the emergency department due to a sudden loss of vision in his right eye. He has had diabetes, and has been treated with metformin and glyburide for the past 10 years. Visual acuity is reduced to light perception in his right eye, and normal in his left. His vital signs are normal. Ophthalmoscopy reveals loss of fundus details, floating debris and a dark red glow. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A.Retinal detachment
B. Diabetic retinopathy
C. Vitreous haemorrhage
D. Central retinal vein occlusion
E. Age related macular degeneration
A 62-year-old female is brought in by EMS due to a severe right-sided headache, nausea and eye pain. She was fixing a light bulb, when she suddenly felt pain in her right eye. She decided to rest, but the eye pain only got worse. In the next few minutes, she developed loss of vision, photophobia and redness in the same eye. She took medications to relieve the accompanying headache, but the eye pain persisted. She denies any trauma. Her past medical history is significant for diabetes and hypertension. She appears to be in intense pain with bouts of nausea. Her right eye is red, with conjunctival flushing and visual acuity of 20/200. Her right pupil is mid-dilated and non-reactive to light. The same eye feels hard on palpation. The one treatment that should be avoided in this patient is:
A Mannitol
B. Acetazolamide
C. Pilocarpine
D. Timolol
E. Atropine
A 60-year-old woman complains of decreasing vision and a dull ache over her left eye for the past 12 hours. She had a successful surgical cataract extraction in her left eye five days ago. Her blood pressure is 140/90 mmHg, pulse is 92/min, respirations are 14/min, and temperature is 38.1C (101.7F). Examination of the left eye reveals a swollen eyelid, edematous conjunctiva, and exudates in the anterior chamber. Testing with Snellen's chart demonstrates decreased visual acuity in her left eye. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Conjunctivitis
B. Corneal ulceration
C. Uveitis
D. Postoperative endophthalmitis
E. Cavernous sinus thrombosis
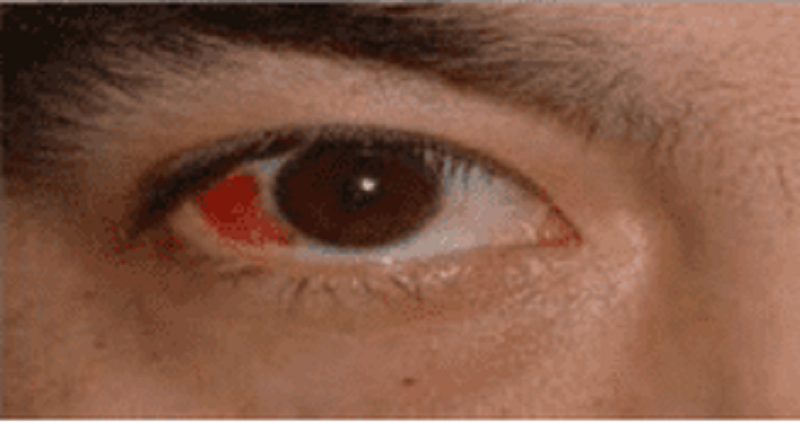
A 34-year-old male presents to the emergency department with a red eye. He says, "I just woke up this morning and saw that my right eye was red." He denies any itching, pain or discharge. He has no known drug or environmental allergies. He takes no medication. His vital signs are stable. The photo of his eye is shown below.What is the best next step in his management?
A. Check intraocular pressure
B. Refer to ophthalmologist
C. Check coagulation parameters
D. Observation
E. Antibiotics
A 65-year-old male comes to the emergency department because of a sudden, painless loss of vision in his right eye that occured a half an hour ago. Five hours ago, he experienced a similar but transient loss of vision in the same eye, which lasted for five minutes. He has hypertension, diabetes, hypercholesterolemia, and peripheral vascular disease. He had an anterior wall myocardial infarction six years ago. His medications include glyburide, captopril, atenolol, simvastatin and aspirin. His temperature is 36.7C (98.0F), respirations are 16/min, pulse is 88/min, and blood pressure is 146/88 mmHg. Examination of the right eye reveals visual acuity of 20/60 and subtle retinal whitening. A right carotid bruit is heard. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient?
A. Acetazolamide IV
B. Ocular massage and high flow oxygen
C. Administer systemic steroids
D. Instillation of topical beta blocker
E. Administer thrombolytics
A 26-year-old male complains of itching and excessive watering of both eyes since this morning. He denies blurring of vision. He uses albuterol inhaler regularly for his bronchial asthma. His vital signs are normal. On examination, both eyes are noted to have conjunctival edema, hyperemia, swollen eyelids, and profuse watery discharge. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Atopic keratoconjunctivitis
B. Allergic conjunctivitis
C. Toxic conjunctivitis
D. Blepharitis
E. Dacryocystitis.
A 4-year-old boy is brought by his mother to a Medical Camp for the Uninsured for the evaluation of his inflamed right eye. He has had a nasal discharge for the past 10 days. His brother has similar symptoms. His vital signs are stable. There are follicles and inflammatory changes in the conjunctiva of his right eye. The cornea shows neovascularization. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Herpes simplex keratitis
B. Orbital cellulitis
C. Trachoma
D. Gonococcal conjunctivitis
E. Viral conjunctivitis
A 60-year-old woman comes to the emergency department due to a sudden onset of severe pain in her left eye with blurred vision, nausea, and vomiting. The symptoms began a few minutes ago, while she was watching a movie in a nearby theatre. Her blood pressure is 140/90 mm Hg, pulse is 82/min, respirations are 14/min, and temperature is 98.4 F. Examination reveals decreased visual acuity. Her left eye appears red, with a hazy cornea, shallow anterior chamber, and dilated, fixed pupil. Her left eye is stony hard to touch. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Primary open angle glaucoma
B. Conjunctivitis
C. Acute angle closure glaucoma
D. Anterior uveitis
E. Corneal abrasion
A 32-year-old male construction worker presents with complaints of pain, watering, and redness in his left eye for the past 2 days. He reports having similar symptoms in the same eye a few months ago. Examination of his left eye reveals vesicles and dendritic ulcers in the cornea. His vital signs are stable. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Bacterial retinitis
B. Herpes simplex keratitis
C. Herpes zoster ophthalmicus
D. Corneal abrasion
E. Fungal keratitis
A 30-year-old male comes to the emergency department screaming, "Something blew into my right eye while I was drilling I' He complains of a foreign body sensation in the right eye, photophobia, and excessive lacrimation. Gross examination of the right eye with a penlight after the application of a topical anesthetic is insignificant. What is the best next step in the management of this patient?
A. Tonometry
B. Fluorescein examination
C. Topical antibiotic
D. Ultrasonography
E. MRI of the orbits
A 35-year-old HIV-positive male is complaining of deterioration of his vision over the past week. He initially experienced eye pain and mild conjunctivitis, followed by rapid progressive visual loss. Examination of his eyes reveals marked keratitis. Funduscopy shows widespread, pale, peripheral retinal lesions and central necrosis of the retina. Which of the following is the most likely causative organism of this patient's condition?
A. Pseudomonas
B. Cytomegalovirus
C. Herpes simplex
D. Candida albicans
E. Epstein Barr virus
A 38-year-old man with AIDS (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome) is complaining of diminished vision in both eyes. His CD4 count last month was 50 ells/uL. He has been on highly active antiretroviral therapy for the past several months. He is afebrile, and his vital signs are stable. Ophthalmoscopic examination reveals yellow-white patches of retinal opacification and retinal hemorrhages. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Ocular toxoplasmosis.
B. Herpes simplex keratitis.
C. Herpes-zoster ophthalmicus.
D. CMV Retinitis.
E. HIV retinopathy.
A 65-year-old man presents with complaints of decreased vision in both eyes. His visual impairment has been progressively worsening over the past five months. He was diagnosed with diabetes ten years ago. His current medications are metformin and glyburide. His blood pressure is 140/90 mm Hg, pulse is 82/min, respirations are 14/min, and temperature is 98.4F (36.88C). Examination shows decreased visual acuity in both eyes. Ophthalmoscopy reveals microaneurysms, dot and blot hemorrhages, hard exudates, and macular edema. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Central retinal vein occlusion
B. Diabetic retinopathy
C. Macular degeneration
D. Retinal detachment
E. Open angle glaucoma
A 69-year-old white male presents to your office complaining of progressive bilateral loss of vision over the past several months. He only has problems with his central vision. His peripheral field and navigational vision are not affected. He denies smoking and alcohol intake. He does not have any history of diabetes or hypertension Two years ago, he had cataracts removed from both eyes. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Open angle glaucoma
B. Macular degeneration
C. Recurrent cataracts
D. Central retinal artery occlusion
E. Retinal detachment
A 57-year-old female with a history of type 2 diabetes mellitus complains of fatigue, urinary frequency, increasingly blurred vision and worsening leg cramps over the past week. She reports that the symptoms all began following an upper respiratory infection 7 or 8 days ago. She does not take any medications, but adheres to a diet low in saturated fat and simple carbohydrates to manage her diabetes. On physical examination, her blood pressure is 160/90 mmHg and her heart rate is 90/min. Her mucous membranes are dry. Her urine is positive for glucose but negative for ketones. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's vision impairment?
A. Cataracts
B. Diabetic retinopathy
C. Arterial hypertension
D. Hyperosmolarity
E. Eye infection
An 80-year-old white male comes to the emergency department due to a sudden loss of vision in his left eye that occurred this morning upon waking up. He has had hypertension for the past several years. Current medications include ramipril and atenolol. His blood pressure is 140/90 mm Hg, pulse is 86/min, respirations are 14/min, and temperature is 36.8°C (98.4.F). Examination of the left eye reveals no abnormalities. Funduscopic examination shows swelling of the optic disk, retinal hemorrhages, dilated and tortuous veins, and cotton wool spots. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Acute angle-closure glaucoma
B. Central retinal vein occlusion
C. Optic neuritis
D. Amaurosis fugax
E. Acute anterior uveitis
A 32-year-old woman comes to the office distraught because "the colors look washed out I" She has had this vision impairment since yesterday. She also complains of pain on eye movements. Her vital signs are stable, and she is afebrile. Examination reveals decreased visual acuity, sluggish afferent pupillary response to light, and changes in color perception. Fundoscopy reveals a swollen disc. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Orbital cellulitis
B. Optic neuritis
C. Acute anterior uveitis
D. Open angle glaucoma
E. Episcleritis
A 34-year-old obese Caucasian female complains of periodic visual obscurations. She has episodes during which she "goes blind" for several seconds when standing up or stooping forward abruptly. She also describes frequent morning headaches over the last two months for which she has had to take ibuprofen or aspirin almost every morning. She takes no other medications. Past medical history is insignificant aside from one uncomplicated vaginal delivery. She denies use of alcohol, tobacco, or illicit drugs. She is afebrile with a blood pressure of 138/88 mmHg and pulse of 93/min. Visual field testing shows enlarged blind spots. There are no other significant findings on neurologic examination. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
A. Optic neuritis
B. Glaucoma
C. Cataract
D. Papilledema
E. Amaurosis fugax
A 33-year-old man presents with a 1-day history of localized, small swelling along the margin of the upper eyelid. He feels pain, which does not seem to come from the conjunctival surface. He has a 10- pack year smoking history. He occasionally drinks alcohol. He is sexually active, and does not use condoms regularly. He is worried about the swelling. What is the best next step in the management of this patient?
A. Use warm compresses
B. Incision and drainage
C. Incision and curettage
D. Take biopsy of the lesion
E. Oral Penicillin
An 85-year-old man presents with a rash over his forehead, tip of nose and left eye. He also complains of pain and decreased vision. He has had fever, malaise, and a burning sensation around his left eye for the past 5 days. His blood pressure is 140/90 mm Hg, pulse is 92/min, respirations are 14/min, and temperature is 38.1C (101F). Physical examination reveals a vesicular rash on the periorbital region and lid margins. The left eye is red, with chemosis of the conjunctiva. Dendriform ulcers are seen on the cornea. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Herpes simplex keratitis
B. Dacryocystitis
C. Bacterial keratitis
D. Trigeminal neuralgia
E. Herpes zoster ophthalmicus
A 75-year-old African American man comes to your office for his annual check-up. He is a known diabetic and hypertensive. His medications include lisinopril and atenolol. His vital signs are normal. Examination of his fundus reveals cupping of the optic disc. Visual field examination reveals constricted peripheral vision. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A Diabetic retinopathy
B. Closed angle glaucoma
C. Macular degeneration
D. Primary open angle glaucoma
E. Cataract
A 30-year-old man is concerned about "floating spots" and blurred vision in his right eye. He had a serious injury of his left eye several weeks ago, which eventually led to vision loss in that eye. Inspection reveals a moderate perilimbal flush. What is the most probable cause of this patient's condition?
A. Reagin-mediated disease
B. Circulating immune complexes
C. Non-caseating granulomas
D. Uncovering of 'hidden' antigens
E. Non-immune injury
A 65-year-old female is complaining of seeing a sudden burst of flashing lights and blurred vision in her left eye. These symptoms started this morning. She now sees small spots in her field of vision. She felt "like a curtain came down" over her eye. She had a successful cataract extraction in her left eye 4 months ago. Her vital signs are stable. Examination shows a sluggish left pupil. Ophthalmoscopy reveals retinal tears and a grayish-appearing retina. What is the most probable diagnosis?
A. Choroidal rupture
B. Retinal detachment
C. Central retinal artery occlusion
D. Proliferative diabetic retinopathy
E. Exudative macular degeneration
A 67 -year-old Caucasian male complains of progressive visual loss in his right eye over the past several months. He has a history of hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Current medications include a daily baby aspirin, hydrochlorothiazide, lisinopril, and metformin. There is no family history of visual problems. He has a 35 pack year smoking history and admits to occasional alcohol use. He is afebrile with a blood pressure of 137/82 mmHg and pulse of 73/min. Cardiac and pulmonary examinations are unremarkable. A neurologic examination demonstrates no focal motor or sensory abnormalities. The patient is asked to cover his left eye and to look at a small spot on a grid made of parallel vertical and horizontal lines. He describes the vertical lines as being bent and wavy. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's complaints?
A. Lens opacity
B. Enlarged blind spot
C. Increased intraocular pressure
D. Macular degeneration
E. Peripheral retinal degeneration
A 35-year-old white female is complaining of blurry vision and pain with eye movements. She is on no medications and denies any trauma. Last year, she developed bladder incontinence and an episode of leg weakness, which both improved without therapy. Physical examination reveals reduced vision and swollen optic discs. The one diagnosis that may explain her symptoms is·
A. Parkinson disease
B. Myasthenia gravis
C. Multiple sclerosis
D. Subdural hematoma
E. Transient ischemic attacks
A 3-day-old female infant is noticed to have copious, purulent discharge from both eyes. Lid edema and chemosis are also noted. She was born by normal vaginal delivery. Her mother is a 20-year-old primigravida who had no prenatal care. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A Chlamydia trachomatis
B. Staphylococcus aureus conjunctivitis
C. Chemical conjunctivitis
D. Nasolacrimal duct obstruction
E. Gonococcal conjunctivitis
A 65-year-old woman presents with complaints of pain and swelling over the inner aspect of her right eye for the past two days. Examination of the eye reveals tenderness, edema, and redness over the medial canthus. Slight pressure over the area causes expression of purulent material. Visual acuity is normal. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Episcleritis
B. Dacryocystitis
C. Hordeolum
D. Chalazion
E. Orbital cellulitis
A 65-year-old man complains of gradual onset blurred vision for the past two months. He also has difficulty driving at night and reading fine print. He has diabetes and hypertension. His medications include ramipril and metoprolol. His vital signs are stable. His best corrected vision is OD (right eye) 20/80, OS (left eye) 20/100, with full fields. Ophthalmoscopic examination with good pupillary dilatation reveals a loss of transparency of lens in both eyes. The red fundal reflex is normal, but retinal details are difficult to visualize. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Open angle glaucoma.
B. Retinal detachment.
C. Macular degeneration.
D. Cataract
E. Central retinal vein occlusion.
A 24-year-old woman presents to the emergency department (ED) complaining of right eye pain and blurry vision since waking up this morning. She states that the pain began after taking out contact lenses that were in her eyes for over 1 week. Her blood pressure (BP) is 120/75 mm Hg, heart rate (HR) is 75 beats per minute, temperature is 99.1°F, and respiratory rate (RR) is 16 breaths per minute. Her right and left eye visual acuity is 20/60 and 20/20, respectively. Her conjunctivae are injected. The slitlamp examination reveals a large area of fluorescein uptake over the visual axis. Which of the following is the most appropriate therapy?
A. Call the ophthalmology consult for an emergent corneal transplant.
B. Prescribe a systemic analgesic for pain control and advise the patient to not wear her contact lenses for the next week.
C. Prescribe ciprofloxacin eye drops, oral analgesia, update tetanus prophylaxis, and arrange for ophthalmology follow-up
D. Prescribe oral amoxicillin, a topical anesthetic, such as tetracaine, and have patient follow-up with an ophthalmologist.
E. Prescribe ciprofloxacin eye drops and have patient strictly wear an eye patch until her pain resolves.
A 60-year-old woman presents to the ED complaining of pain in her right eye and burning sensation over half of her forehead and scalp. On physical examination, you notice a patch of grouped vesicles on an erythematous base located in a dermatomal distribution on her scalp and forehead. There are also a few vesicles located at the tip of the patient’s nose. Her visual acuity is 20/20 bilaterally, heart is without murmurs, lungs are clear, abdomen is soft, and there are no gross findings on neurologic examination. Which of the following is the most concerning complication of this patient’s clinical presentation?
A. Central nervous system (CNS) involvement leading to meningitis
B. Ophthalmic involvement leading to anterior uveitis or corneal scarring
C. Cardiac involvement leading to endocarditis
D. Permanent scarring of her face
E. Nasopalatine involvement leading to epistaxis
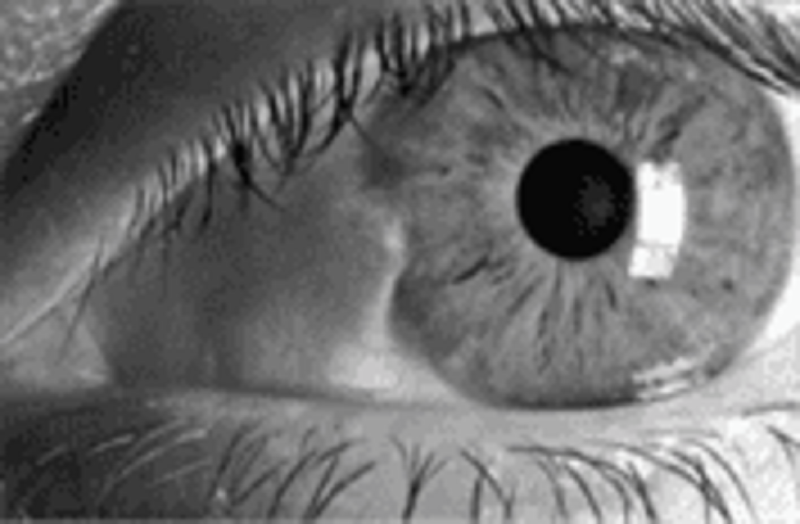
A 31-year-old nurse in your hospital has noticed a lesion in her left eye. She denies change in vision, pain, fevers, or discharge. A picture of her eye is shown below. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Hordeolum
B. Chalazion
C. Dacryocystitis
D. Pinguecula
E. Pterygium
A 72-year-old man presents with right eye pain for 1 day. The patient has a history of diabetes, hypertension, and “some type of eye problem.” He does not recall the name of his eye problem or the name of his ophthalmic medication. However, he does remember that the eye drop has a yellow cap. Which class of ophthalmic medication is the patient taking?
A. Antibiotic
B. β-Blocker
C. Mydriatic/cycloplegic agent
D. Miotic
E. Anesthetic
A 35-year-old woman presents with a right-sided red eye for 3 days. She denies pain and notes that she has watery discharge from the eye. She has been coughing and congested for the past 5 days. On examination, the patient has a temperature of 98.4°F, HR of 72 beats per minute, BP of 110/70 mm Hg, and RR of 14 breaths per minute. Her visual acuity is 20/20. On inspection, the conjunctiva is erythematous with minimal chemosis and clear discharge. The slit-lamp, fluorescein, and funduscopic examinations are otherwise unremarkable. The patient has a nontender, preauricular lymph node and enlarged tonsils, without exudates. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Gonococcal conjunctivitis
B. Bacterial conjunctivitis
C. Viral conjunctivitis
D. Allergic conjunctivitis
E. Pseudomonal conjunctivitis
A 24-year-old woman presents to the ED at 4 AM with severe left eye pain that woke her up from sleep. She wears soft contact lenses and does not routinely take them out to sleep. She is in severe pain and wearing sunglasses in the examination room. You give her a drop of proparacaine to treat her pain prior to your examination. On examination, her vision is at baseline and she has no afferent pupillary defect. There is some perilimbic conjunctival erythema. On fluorescein examination, a linear area on the left side of the cornea is highlighted when cobalt blue light is applied. No underlying white infiltrate is visualized. No white cells or flare are visualized in the anterior chamber. What is the most appropriate treatment for this condition?
A. Immediate ophthalmology consult
B. Tobramycin ophthalmic ointment
C. Erythromycin ophthalmic ointment
D. Eye patch
E. Proparacaine ophthalmic drops
A 45-year-old woman presents with right eye pain and redness for 1 day. She has photophobia and watery discharge from the eye. She does not wear glasses or contact lenses and has no prior eye problems. On examination, the patient’s visual acuity is 20/20 in the left eye and 20/70 in the right eye. She has conjunctival injection around the cornea and clear watery discharge. On slit-lamp examination, the lids, lashes, and anterior chamber are normal. When fluorescein is applied, a branching, white-colored epithelial defect is seen. The remainder of the head examination is normal and the patient has no cutaneous lesions. Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment for this patient?
A. Admission for intravenous (IV) antibiotics
B. Admission for IV antiviral agents
C. Topical steroids
D. Topical antiviral medication
E. Immediate ophthalmology consultation
A 28-year-old mechanic with no past medical history presents to the ED after a small amount of battery acid was splashed in his right eye. He is complaining of extreme pain and tearing from his eye. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
A. Call ophthalmology now.
B. Check visual acuity.
C. Check the pH of the tears.
D. Irrigate with normal saline.
E. Apply erythromycin ointment.
A 45-year-old man lacerated his right forehead after an altercation in a local bar. Instead of seeking medical attention, the patient applied super glue to his wound. He successfully stopped the bleeding, but some of the glue got into his right eye and now he comes to the ED with difficulty opening his right eye. What is the most appropriate treatment of this patient?
A. Call ophthalmology immediately.
B. Wash eye with acetone.
C. Wash eye with normal saline.
D. Use forceps to remove all the glue from the eye.
E. Apply erythromycin ointment.
The local sorority house recently installed a sun-tanning station. Two days later three sorority girls present to the ED with bilateral eye pain, tearing, and photophobia. After ophthalmic anesthesia instillation, a complete eye examination is performed. Visual acuity is normal. Extraocular eye movements are intact and pupils are equal, round, and reactive to light. IOP is normal. Slit-lamp examination is normal, but fluorescein examination under cobalt blue light illuminates small dots throughout the cornea. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Ultraviolet keratitis
B. Anterior uveitis
C. Herpes simplex keratitis
D. Allergic conjunctivitis
E. Corneal ulcer
A 12-year-old girl presents to the ED for left eye pain and swelling for 2 days. The patient has had cough, congestion, and rhinorrhea for the last week that is improving. On examination, her temperature is 100.8°F, HR 115 beats per minute, RR 12 breaths per minute, and BP 110/70 mm Hg. On eye examination, there is purple-red swelling of both upper and lower eyelids with injection of the conjunctiva. Pupils are equal and reactive to light. There is restricted lateral gaze. Visual acuity is 20/70 in the left eye and 20/25 in the right eye. The rest of the physical examination is normal. What is the most appropriate next step in management?
A. Administer diphenhydramine.
B. Administer amoxicillin/clavulanate.
C. Administer vancomycin IV.
D. Perform computed tomographic (CT) scan of orbits and sinuses.
E. Administer artificial tears.
A 60-year-old man with a history of hypertension and migraine headaches presents to the ED with a headache. He describes left-sided headache and eye pain that is associated with nausea and vomiting. The patient has a long history of migraines, but says his migraines do not usually include eye pain. On examination, his temperature is 97.6°F, HR 84 beats per minute, RR 12 breaths per minute, and BP 134/80 mm Hg. His neurologic examination is normal. His left eye is mid-dilated and nonreactive. His cornea is cloudy. His corrected visual acuity is 20/50 in the left eye and 20/20 in the right eye. What is the most appropriate next step in management?
A. Administer hydromorphone.
B. Perform head CT scan.
C. Check IOP.
D. Check erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR).
E. Discharge patient.
A 22-year-old man presents to the ED for left eye pain. He was in an altercation yesterday and was punched in the left eye. On examination, his left eye is ecchymotic and the eyelids are swollen shut. He has tenderness over the infraorbital rim but no step-offs. You use an eyelid speculum to examine his eye. His pupils are equal and reactive to light. His visual acuity is normal. On testing extraocular movements, you find he is unable to look upward with his left eye. He also complains of diplopia when looking upward. Funduscopic examination is normal. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Orbital blowout fracture
B. Ruptured globe
C. Retinal detachment
D. Cranial nerve III palsy
E. Traumatic retrobulbar hematoma
You are examining the pupils of a patient. On inspection, the pupils are 3 mm and equal bilaterally. You shine a flashlight into the right pupil and both pupils constrict to 1 mm. You then shine the flashlight into the left pupil and both pupils slightly dilate. What is this condition called?
A. Anisocoria
B. Argyll Robertson pupil
C. Afferent pupillary defect
D. Horner syndrome
E. Normal pupil reaction
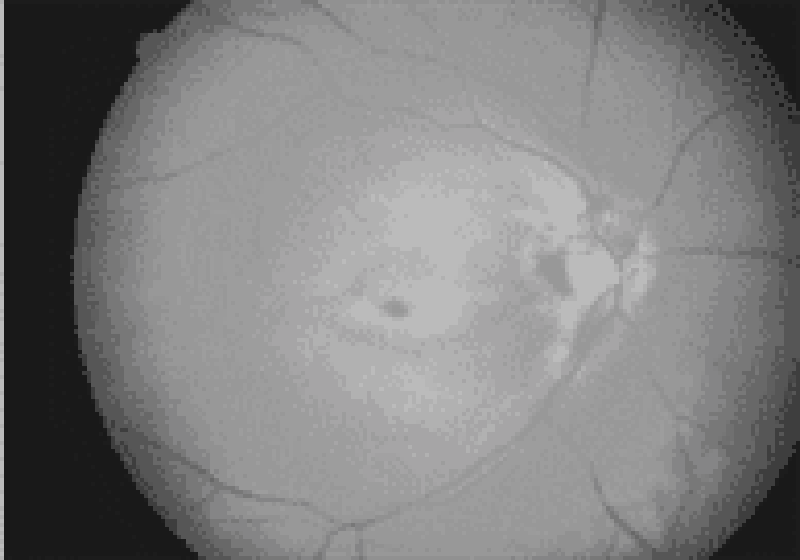
A 65-year-old man with a history of diabetes, hypertension, coronary artery disease, and atrial fibrillation presents with loss of vision in his left eye since he awoke 6 hours ago. The patient denies fever, eye pain, or eye discharge. On physical examination of the left eye, vision is limited to counting fingers. His pupil is 3 mm and reactive. Extraocular movements are intact. Slit-lamp examination is also normal. The dilated funduscopic examination is shown below. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Retinal detachment
B. Central retinal artery occlusion
C. Central retinal vein occlusion
D. Vitreous hemorrhage
E. Acute angle-closure glaucoma
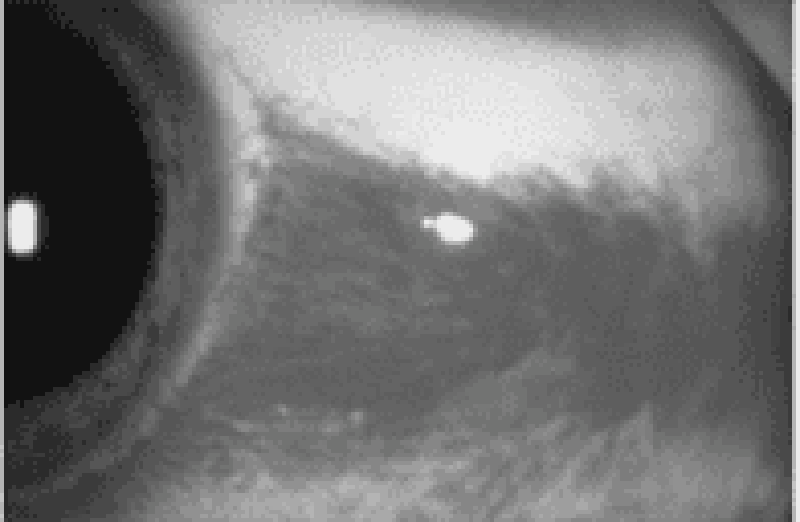
A 21-year-old man presents to the ED with a red eye. The patient complains of rhinorrhea and a nonproductive cough but has no eye pain or discharge. He also has no associated ecchymosis, bony tenderness of the orbit, or pain on extraocular eye movement. His vision is normal, extraocular movements are intact, and intraocular pressure (IOP) is 12. A picture of his eye is shown below. What is the most appropriate management of this condition?
A. Call ophthalmology immediately.
B. Administer 1% atropine.
C. Elevate patient’s head.
D. Administer ophthalmic timolol.
E. Reassurance only.
{"name":"QCU\/DES\/USMLE\/ ENT+OPT", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Welcome to our comprehensive medical quiz focused on ENT disorders, tailored for healthcare professionals and students alike. Challenge your knowledge and enhance your understanding of key concepts related to ear, nose, and throat conditions through engaging multiple-choice questions.68 carefully crafted questionsCovers a range of topics from diagnosis to treatmentIdeal for USMLE and other medical examination preparations","img":"https:/images/course3.png"}
More Quizzes
AST review #2
520
Physical Assessment Pretest
10535
24120
BVLgari Allegra
13617
Wine Knowledge Level 1 (Free)
201018081
K-Pop Girl Group Name Generator - Free
201019313
Ultimate Bollywood - Test Your Hindi Cinema Knowledge
201025926
Hunger Games Book - Test Your Panem Knowledge
201018847
Do I Still Love My Boyfriend - Free Self-Check
201020345
Isaac Asimov: I, Robot Trivia - Free
201019410
Simple Interest: Free Practice Questions Online
201018847
Positivity - Are You a Positive Person? Free
201020684