AP Physics 1 Misconceptual Questions

AP Physics 1 Misconceptual Quiz
Challenge your understanding of AP Physics 1 with our engaging quiz featuring 42 thought-provoking questions. Each question is designed to test your grasp of core concepts and common misconceptions in physics.
Prepare to think critically about topics such as motion, forces, circular motion, energy, and momentum. Test your knowledge and see how well you can navigate these conceptual problems!
A bullet fired from a rifle begins to fall
As soon as it leaves the barrel
After air friction reduces its speed
Not at all if air resistance is ignored
A baseball player hits a ball that soars high into the air. After the ball has left the bat, and while it is traveling upward, what is the direction of acceleration?
0%
0
0%
0
0%
0
One ball is dropped vertically from a window. At the same instant, a second ball is thrown horizontally from the same window. Which ball has the greater speed at ground level?
The dropped ball
The thrown ball
Neither
It depends on how hard the ball was thrown
You are riding in an enclosed train moving at 90 km/h. If you throw a baseball straight up, where will it land?
In front of you
Behind you
In your hand
Can't determine
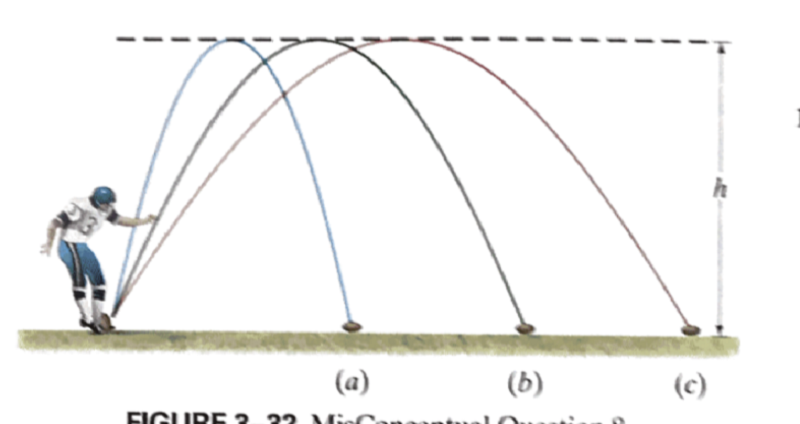
Which of the three kicks is in the air for the longest?
A
B
C
All at the same time
A baseball is hit high and far. Which of the following statements is true? At the highest point,
The magnitude of the acceleration is zero
The magnitude of the velocity is zero
The magnitude of the velocity is the slowest
More than one is true
None are true
A hunter aims at a monkey. At that instant, he pulls the trigger. What happens?
The bullet will miss the monkey
The bullet will hit the monkey
It depends on how far the hunter is
Which statements are not valid for a projectile? Take up as positive.
The projectile has the same x velocity at any point
The acceleration is positive and decreasing when the projectile is moving upwards, zero at the top, and increasingly negative as it descends
The acceleration is constantly negative
The y component of the velocity is zero at the highest point
The velocity at the highest point is zero
While driving fast around a sharp right turn, you find yourself pressing against the car door. What is happening?
Centrifugal force is pushing you into the door
The door is exerting a rightward force on you
Both
Neither
Which of the following point towards the center of the circle in uniform circular motion?
Acceleration
Velocity, acceleration, net force
Velocity, acceleration
Velocity, net force
Acceleration, net force
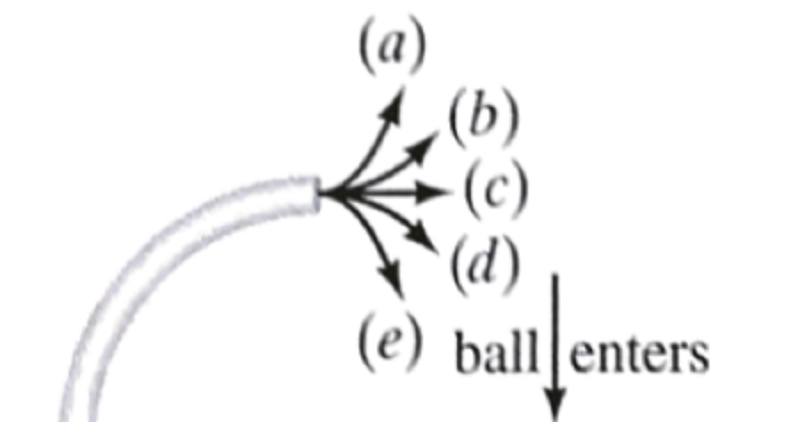
A ping pong ball is shot into a circular tube. When it exits, which path will it follow?
A
B
C
D
E
A car drives at steady speed around a perfectly circular track.
Acceleration is zero
Net force is zero
Both the acceleration and net force point outward
Both the acceleration and net force point inward
If there is no friction, the acceleration is outward
A child whirls a ball in a vertical circle. Assuming the speed of the ball is constant, when would the tension in the cord connected to the ball be greatest
At the top
At the bottom
A little after the bottom when it is climbing
A little before the bottom when it is descending
Nowhere
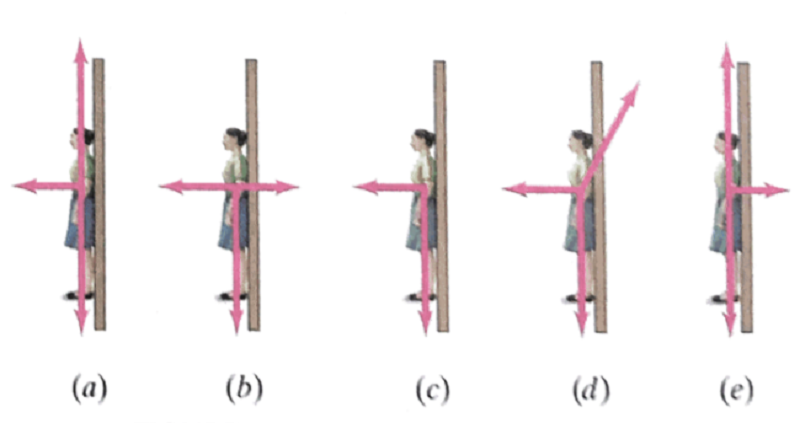
In a rotating vertical cylinder a rider finds herself pressed with her back to the rotating wall. Which is the correct free body?
A
B
C
D
E
The moon doesn't crash into earth because
Net force is zero
It is beyond the main pull of earth's gravity
It is being pulled by the sun and the earth
It is freely falling but has a high tangential velocity
Which pulls harder, the earth on the moon, or the moon on the earth? Which accelerates more?
Earth on moon. earth
Earth on moon. moon
Moon on earth. earth
Moon on earth. moon
Both the same. earth
Both the same. moon
In the ISS which orbits earth, astronauts experience weightlessness because
The station is far from the center of earth
The station is kept in orbit by a centrifugal force that counteracts the gravity
The astronauts and the station are in free fall towards the center of earth
There is no gravity in space
The station's high speed nullifies the effects of gravity
Two satellites orbit the earth in circular orbits of the same radius. One is twice as massive. Which statement is true
The heavier satellite moves twice as fast as the lighter one
The two satellites have the same speed
The lighter satellite moves twice as fast as the heavier one
The ratio of their speeds depends on the orbital radius
A space shuttle in orbit around the earth carries its payload with its mechanical arm. Suddenly, the arm malfunctions and releases the payload. What will happen to the payload?
Fall straight down and hit earth
Follow a curved path and eventually hit earth
Remain in the same orbit with the shuttle
Drift out into deep space
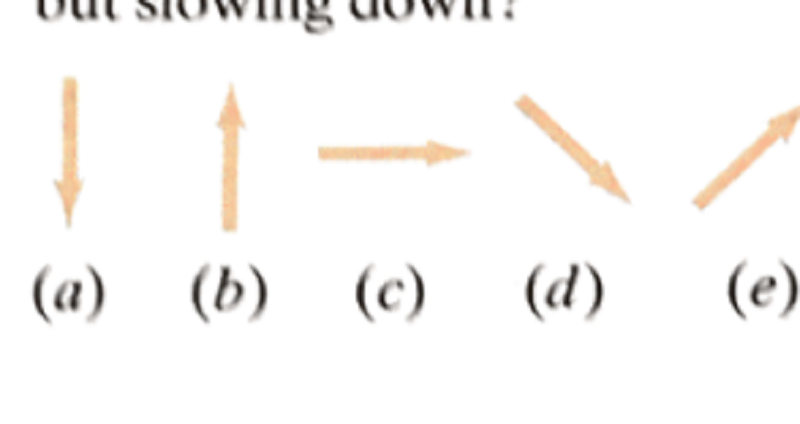
A penny is placed on a turntable which is spinning clockwise. If the power to turn the turntable is turned off, which arrow best represents the direction of the acceleration of the penny at point P while it is still spinning but slowing down?
A
B
C
D
E
Bonnie sits on the outer rim of a merry-go-round, and Jill sits midway between the center and the rim. The merry-go-round makes one complete revolution every two seconds. Jill's linear velocity is:
The same as bonnie
Twice bonnie
Half of bonnie
One quarter of bonnie
Four times bonnie
An object at rest begins to rotate with a constant angular acceleration. If this object rotates through an angle X in time t, through what angle did it rotate in the time 0.5t?
.5X
.25X
X
2X
4X
A car speedometer that is supposed to read the linear speed uses a device that actually measures the angular speed. If larger diameter tires are mounted on the car instead, how will that affect the speedometer reading?
Still reads accurately
Will read low
Will read high
Two spheres have the same radius and equal mass. One sphere is solid, and the other is hollow and made of a denser material. Which one has the bigger moment of inertia about an axis through its center?
The solid one
The hollow one
Both the same
A small solid sphere and a small thin hoop are rolling along a horizontal surface with the same translational speed when they encounter a 20 degree rising slope. If these two objects role up the slope without slipping, which will rise farther?
The sphere
The hoop
Both the same
Need more info
A small mass m on a string is rotating without friction in a circle. The string is shortened by pulling it through the axis of rotation without any external torque. What happens to the angular velocity?
It increases
It decreases
It remains the same
A small mass m on a string is rotating without friction in a circle. The string is shortened by pulling it through the axis of rotation without any external torque. What happens to the tangential velocity?
It increases
It decreases
It remains the same
If there were a great migration of people toward the earth's equator, the length of the day would
Increase because of conservation of angular momentum
Decrease because of conservation of angular momentum
Decrease because of conservation of energy
Increase because of conservation of energy
Remain unaffected
Which of the objects below is accelerating?
Object moving at constant speed along a straight line
Object moving at constant speed in a circle
Object slowing down while moving in a straight line
Both b and c describe accelerating objects
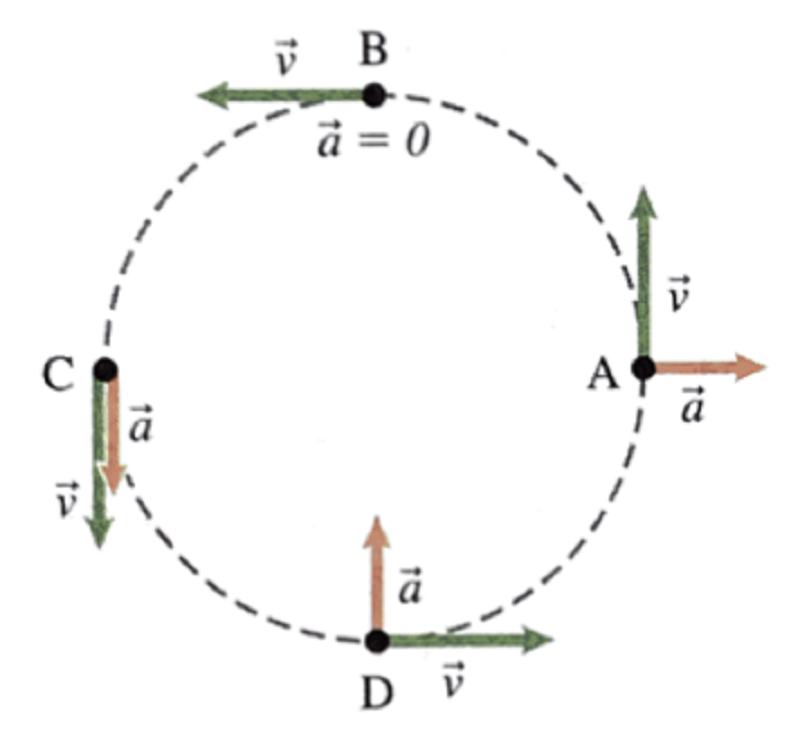
The circle represents the path followed by an object moving at constant speed. At four different positions on the circle, the object's motion is described using velocity and acceleration arrows. Choose the location where the descriptions are correct.
A
B
C
D
One of your classmates drew a force diagram for a pendulum bob at the bottom of its swing. He put a horizontal force arrow in the direction of the velocity. Evaluate his diagram by choosing from the statements below:
He is incorrect since the force should point partly forward and tilt partly down
He is incorrect since there are no forces in the direction of the object's velocity
He is correct since any moving object has a force in the direction of its velocity
He is correct but also needs to add an outward (down) force
Why is it difficult for a high-speed car to negotiate an un-banked turn
A huge force is pushing the car outward
The magnitude of the friction force might not be enough to provide the necessary radial acceleration
The sliding friction force is too large
The faster the car moves, the harder it is for the driver to turn the steering wheel
How does a person standing on the ground explain why you, sitting on the left side of a slippery back car seat, slide to the right when the car makes a high-speed left turn?
You tend to move in a straight line and thus slide with respect to the seat that is moving to the left under you
There is a net outward force being exerted on you
The force of motion propels you forward
The car seat pushes you forward
A pilot performs a vertical loop-the-loop at constant speed. The pilot's head is always pointing toward the center of the circle. Where is the blackout more likely to occur?
At the top of the loop
At the bottom of the loop
At both the top and bottom
None are correct
Why is the following an inaccurate statement about blackout? "as the g forces climb up toward 7 g's..."
There is no such thing as a g force
7 gs are not a big force
G forces are constant and do not climb
G forces are not responsible for blackout but can cause dizziness
Why do you feel that you are being thrown upward out of your seat when going over an upward arced hump on a roller coaster
There is an additional force lifting up on you
At the top you continue going straight and the seat moves out from under you
You press on the seat less than when the coaster is at rest. Thus the seat presses less on you
Both b and c are right
Both a, b, and c are right
Compare the magnitude of the normal force of a car seat on you with the magnitude of the force that Earth exerts on you when the car moves across the bottom of a dip in the road
The normal force is more than earth's gravitational force
The normal force is less than earth's gravitational force
The two forces are equal
It depends on whether it's moving to the right or to the left
If you put a penny on the center of a rotating turntable, it does not slip. Which answer below explains this observation
The penny moves faster at the edge and hence needs a greater force to keep it moving
The edge is more slippery since the grooves are farther apart
The radial acceleration is greater at the edge, and the friction force is not enough to keep the penny in place
The outward force responsible for slipping is greater at the edge than at the middle
Where on earth's surface would you expect to experience the greatest radial acceleration as a result of earth's rotation
On the poles
On the equator
On the highest mountain
The acceleration is the same everywhere
What observational data might newton have used to decide that the gravitational force is inversely proportional to the distance squared between the centers of objects
The data on the acceleration of falling apples
The data describing the moon's orbit and the motion of falling apples
The data on comets
The data on moonrise and moonset times
What observations combined with his second and third laws helped Newton decide that the gravitational force of one object is directly proportional to the product of the masses of the interacting objects
The data on the acceleration of falling apples
The data on moon phases
The data on comets
The data on moonrise and moonset times
What would happen to the force exerted by the sun on earth if the sun shrank and became half its present size while retaining the same mass
The force would be half the present force
The force would be one fourth of the present force
The force would double
The force would stay the same
{"name":"AP Physics 1 Misconceptual Questions", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Challenge your understanding of AP Physics 1 with our engaging quiz featuring 42 thought-provoking questions. Each question is designed to test your grasp of core concepts and common misconceptions in physics.Prepare to think critically about topics such as motion, forces, circular motion, energy, and momentum. Test your knowledge and see how well you can navigate these conceptual problems!","img":"https:/images/course8.png"}
More Quizzes
Momentum - Anna Meier
630
Science Quiz
5235
Streefs Speed Round Quiz
10514
Kojoj državi pripada koji novogodišnji običaj?
1050
Flag Football - Free Rules & Strategy Challenge
201021286
Free Cooking - Test Your Kitchen Knowledge
201017550
What Movie Should I Watch - Find the Best Family Film
201016677
Which Haircolor Uses an Alkalizing Agent to Lighten & Deposit? Free
201018641
CompTIA A+ Core 2 (220-1002) Practice Test - Free
201018109
Notre Dame Football Trivia - Test Your Knowledge
201016620
Australian Slang Vocabulary - Play Free Online
201015918
East Asia Capitals Map - Identify Each Capital
201022629