Business Economics
1. The Cash Flow from financing activities includes among others:
A. Cash payed to employees
B. Cash inflow from a new loan
C. Purchase property, plant and equipment
D. Cash inflows from sale of goods and services
2. Market Concentration The top 4 largest firms produce 95 % of the goods in the market. Their shares on the market are the following: Firm 1: 40% Firm 2: 25% Firm 3: 20% Firm 4: 10% Evaluate the market concentration using the Herfindahl–Hirschman Index. The result provides information that the market is:
A. unconcentrated
B. Moderately concentrated
C. Highly concentrated
D. Highly competitive
3. Internal financial sources include:
A. Sale of share
B. Bank overdraft
C. Accrued liabilities/retained earnings
D. Trade credit
4. Assets in the Balance Sheet include:
A. Accrued liabilities
B. Accounts receivable
C. Accounts payable
D. Retained earnings
5. Prime cost is also reported as:
A. Opportunity cost
B. Fixed cost
C. Direct cost
D. Indirect cost
6. A combination of two or more companies to form a new company on a relatively equal basis is called:
A. Conglomerate
B. Cartel
C. Merger
D. Acquisition
7. The Profit and Loss Account (Income Statement) reports all of the following except:
A. Expenses incurred
B. Revenues earned
C. Assets owned by a business
D. Net income (profit) or loss
8. Target sales How many products must be produced and sold in a given period to achieve the target profit of € 7,000? Following cost data is given: selling price: € 99/unit variable cost: € 85/unit fixed cost: € 16,380/period
A. 1670
B. 670
C. 1170
D. 2170
9. Which of the following economic category can be calculated by including implicit costs?
A. Accounting Profit
B. Operating Profit
C. Gross Profit
D. Economic Profit
10. The difference between budgeted sales revenue and the break-even point is called:
A. Target profit
B. Margin of safety
C. Gross margin
D. Contribution margin
11. Debt financing includes:
A. Retained earnings
B. Trade credit/accrued liabilities
C. Sale of share
D. depreciation
12. The length of time it takes to recover the initial investment is called:
A. Net Present Value
B. Average Rate of Return
C. Payback Period
D. Return on Investment
13. What items do not affect working capital?
A. Inventory
B. Payables
C. Receivables
D. Financial Investments
14. A sunk cost can be considered as:
A. Opportunity cost
B. Variable cost
C. Direct cost
D. Irrelevant cost
15. Which of the following operations does not represent cash flow?
A. Increase in accounts receivable
B. Increase in stocks by the purchase of raw materials
C. Borrowing money from a bank
D. Paying dividends to shareholders
16. The cost that includes both a variable and a fixed component is called:
A. semi-fixed cost
B. semi-variable cost
C. Indirect cost
D. Prime cost
17. Which factor of the PEST analysis can be identified as an economic factor?
A. Population movements (migration)
B. Research and development
C. Trade restrictions and tariffs
D. Inflation rate
18. Investment Decision An investment requires an initial cost of € 5,000 and has the following expected net cash inflows for the four year period. Expected cash inflows: year 1: € 1,500 year 2: € 1,800 year 3: € 1,700 year 4: € 1,500 What is the average rate of return?
A. 7.5%
B. 23.0%
C. 13.0%
D. 3.25%
19. The legal entity (general) partnership is characterized by:
A. Sharing risk among owners
B. Limited liability
C. Raising funds by selling shares
D. Specialized professional management separated from owners
20. Efficiency:
A. Is a measure of achieving maximum output with minimum resources
B. Is the degree to which objectives are achieved
C. Is a measure of profitability
D. Is a measure of liquidity
21. The Straight Line method is used for:
A. Assets depreciation
B. Determining the return on assets
C. Determining the payment period
D. Loan repayments
22. Costs that are not affected by a managerial decision in a particular business situation are called:
A. Irrelevant costs
B. Indirect costs
C. Implicit costs
D. Marginal costs
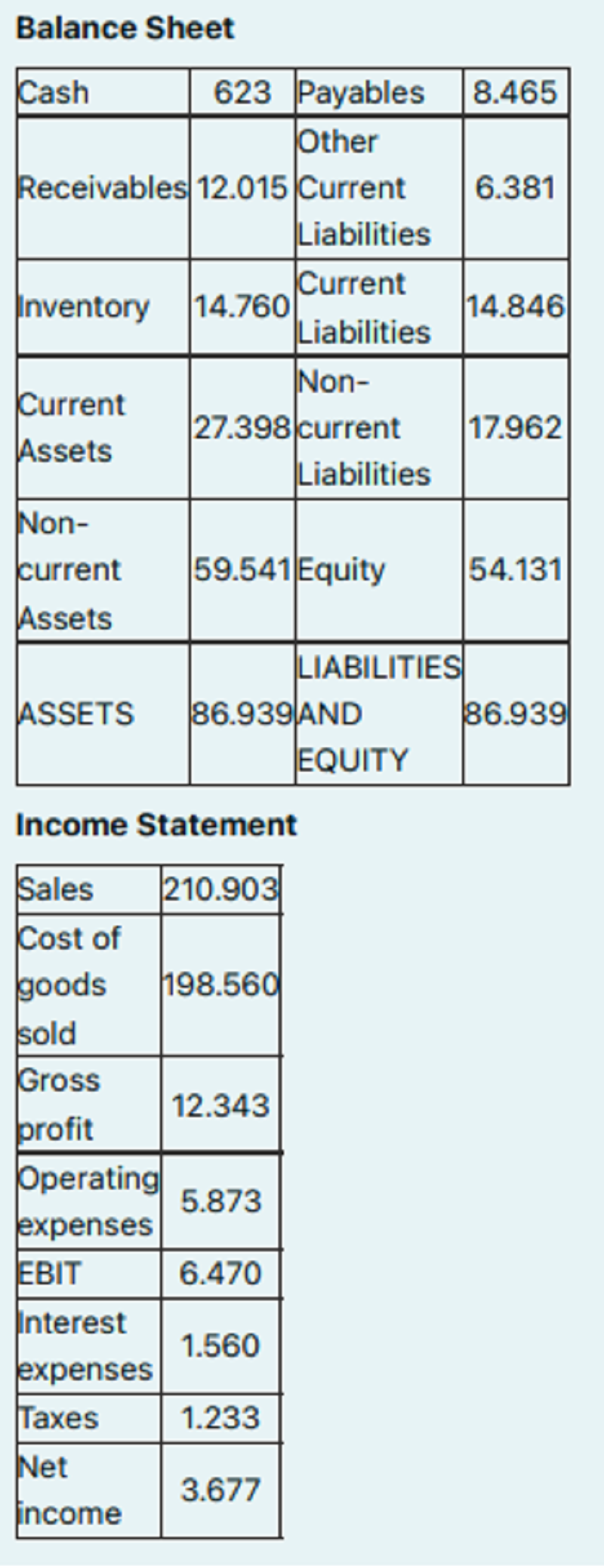
23. Financial Analysis, Which figure represents the Debt to Equity Ratio?
A. 1.65
B. 1.6061
C. 0.6965
D. 0.6061
24. Liquidity ratios used in the financial analysis include:
A. Debt to Assets Ratio
B. Return on Assets
C. Cash Ratio
D. Equity Multiplier
25. Investment Decision An investment requires an initial cost of € 8,000 and has the following expected net cash inflows for the four year period. Expected cash inflows: year 1: € 2,000 year 2: € 2,100 year 3: € 2,200 year 4: € 2,100 What is the average rate of return?
A. 1.25%
B. 2.05%
C. 1.05%
D. 26.25%
26. Equity financing includes:
A. Bank borrowings
B. Trade credit
C. lease
D. Sale of share
27. Which of the following operations does not represent cash flow?
A. Increase in accounts payable
B. Paying a tax
C. Paying dividends to shareholders
D. Purchasing shares of another company
28. Which of the following methods is not used for assets depreciation?
A. Residual Value Method
B. Straight Line Method
C. Declining Balance Method
D. Sum of Years` Digits Method
29. Market Concentration The top 4 largest firms produce 70 % of the goods in the market. Their shares on the market are the following: Firm 1: 20% Firm 2: 18% Firm 3: 17% Firm 4: 15% Evaluate the market concentration using the Herfindahl–Hirschman Index. The result provides information that the market is:
A. Highly concentrated
B. Highly competitive
C. unconcentrated
D. Moderately concentrated
30. The method providing information about the average annual percentage return that the investment will generate over its life is called:
A. Payback Period
B. Net Present Value
C. Average Rate of Return
D. Return on Assets
31. The Profit and Loss Account (Income Statement) gives information about firm´s:
A. liabilities
B. Opportunity costs
C. Current assets
D. Earnings before interest and taxes/sales (revenues)
32. The legal entity limited partnership is characterized by:
A. Specialized professional management separated from owners
B. Limited liability of general partners
C. Two groups of partners (general and limited partners)
D. Double taxation
33. An accounting profit does not include:
A. Indirect costs
B. Opportunity costs
C. Irrelevant costs
D. Variable costs
34. Stability ratios used in the financial analysis include:
A. Equity Multiplier
B. Current Ratio
C. Quick Ratio
D. Return on Equity
35. Break-even Point How many products must be produced and sold in a given period to achieve the breakeven point? Following cost data is given: selling price: € 90/unit variable cost: € 70/unit fixed cost: € 82,500/period
A. 4125
B. 4500
C. 3750
D. 4250
36. Implicit costs are also referred to as:
A. Prime costs
B. Relevant costs
C. Opportunity costs
D. out-of-pocket costs
37. Which of the cost items can be characterized as overhead cost?
A. Fabric used to manufacture clothing
B. Salary of factory supervisor
C. Depreciation of a single-purpose machine
D. Wood used to manufacture a desk
38. Which of the cost items can be characterized as a fixed cost?
A. Energy for production machine
B. Energy consumed for heating and lightning
C. Direct labour wages
D. Purchase of raw materials
39. Equity in the Balance Sheet includes:
A. Accounts receivable
B. Accounts payable
C. Retained earnings
D. cash
40. The margin of safety:
A. Is the difference between fixed costs and variable costs
B. Is the difference between budgeted sales and the break-even sales
C. Is the difference between budgeted sales and real sales
D. Is the difference between budgeted sales and budgeted costs
41. A common business project of two or more independent companies in a limited and specific way is called:
A. Joint-Venture
B. Merger
C. Conglomerate
D. Cartel
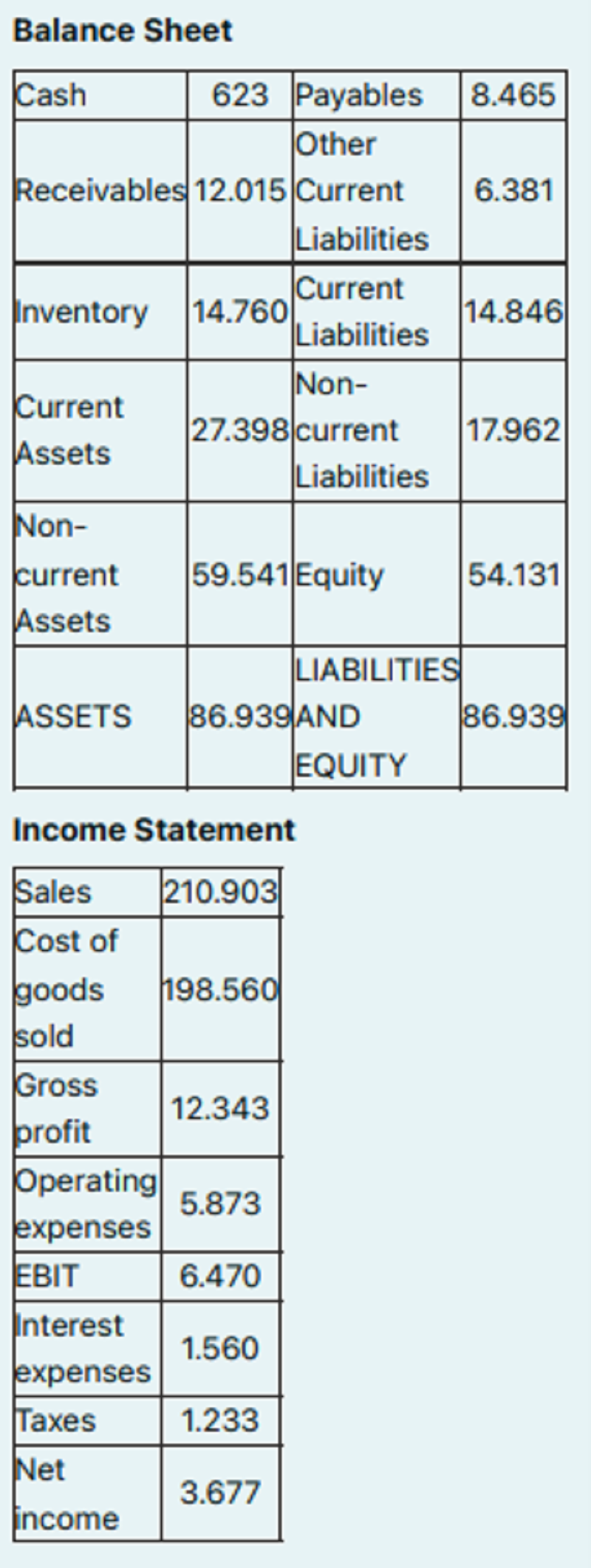
42. Financial Analysis, Which figure represents the Equity Multiplier Ratio? (Total Assets/Total Equity) 1.606 Which figure represents the Cash Ratio? (Cash/Current Liabilities)
A. 0.8513
B. 0.0736
C. 0.042
D. 1.8455
43. Equity financing includes:
A. Trade credit
B. Retained earnings
C. Accrued liabilities
D. Bank overdraft
44. Investment Decision An investment requires an initial cost of € 12,000 and has the following expected net cash inflows for the four year period. Expected cash inflows: year 1: € 3,200 year 2: € 3,500 year 3: € 3,600 year 4: € 3,500 What is the average rate of return?
A. 3.75%
B. 28.75%
C. 2.15%
D. 11.5%
45. Marginal cost is:
A. A cost that cannot be accurately identified with a particular cost object
B. A cost that is not affected by changes in the level of production
C. An additional cost corresponding to an additional unit of output
D. A cost that is not affected by managerial decisions
46. Profitability ratios used in the financial analysis include:
a. Equity Multiplier
B. Cash Ratio
C. Return on Assets
D. Debt to Assets Ratio
47. Working Capital is calculated as:
A. Current assets minus equity
B. Current assets minus current liabilities
C. Total assets minus current assets
D. Current assets plus current liabilities
48. The legal entity corporation is characterized by:
A. Simple formalities required for setting up a corporation
B. Lack of financial sources which are limited to bank borrowings
C. Unlimited liability of shareholders
D. Specialized professional management separated from owners
49. External financial sources include:
A. depreciation
B. Trade credit
C. Accrued liabilities
D. Retained earnings
50. The cost that changes abruptly at intervals of activity is called:
A. semi-variable cost
B. semi-fixed cost
C. Indirect cost
D. Prime cost
51. The Declining Balance method is used for:
A. Assets depreciation
B. Determining the cost of capital
C. Determining the payment period
D. Loan repayments
52. Economies of Scope means:
A. Benefits arising from carrying on related activities
B. Reduction in the average cost of production when output is increased
C. Benefits arising from diversification
D. Reduction in the total material costs when output is increased
53. The Cash Flow from operating activities includes among others:
A. Purchase financial investments
B. Cash paid to suppliers
C. Payment of dividends to shareholders
D. Cash inflow from a new loan
54. A parent organisation that owns and controls other companies is called:
A. Joint-Venture
B. Cartel
C. Merger
D. Holding
55. The break-even point:
A. Is the level of sales at which revenues equal total costs
B. Is the level of sales at which profit is maximized
C. Is the level of sales at which revenues equal variable costs
D. Is the level of sales at which revenues equal fixed costs
56. Equity in the Balance Sheet includes:
A. inventory
B. Accounts payable
C. Capital stock
D. Capital assets
57. The Profit and Loss Account (Income Statement) reports all of the following except:
A. Revenues earned
B. Expenses incurred
C. Assets owned by a business
D. Net income (profit) or loss
58. Market Concentration The top 4 largest firms produce 90 % of the goods in the market. Their shares on the market are the following: Firm 1: 65% Firm 2: 10% Firm 3: 8% Firm 4: 7% Evaluate the market concentration using the Herfindahl–Hirschman Index. The result provides information that the market is:
A. Highly competitive
B. unconcentrated
C. Moderately concentrated
D. Highly concentrated
59. Overheads (overhead costs) are also reported as:
A. Opportunity costs
B. Indirect costs
C. Direct costs
D. Fixed costs
60. Which of the following operations does not represent cash flow?
A. Increase in stocks by the purchase of raw materials
B. Borrowing money from a bank
C. Paying dividends to shareholders
D. Increase in accounts receivable
61. Which factor of the PEST analysis can be identified as a political factor?
A. Inflation rate
B. Trade restrictions and tariffs
C. Research and development
D. Population movements (migration)
62. Which of the following methods of evaluating capital investments considers the time value of money?
A. Payback Period
B. Return on Investment
C. Average Rate of Return
D. Net Present Value
63. Economic Profit
A. Affects the amount of taxes paid if a profit is achieved
B. Takes into account both implicit and explicit costs
C. Is identical with accounting profit
D. Is recorded in the Profit and Loss Account (Income Statement)
64. Target sales, How many products must be produced and sold in a given period to achieve the target profit of € 9,000? Following cost data is given: selling price: € 125/unit variable cost: € 115/unit fixed cost: € 16,400/period
A. 740
B. 2540
C. 1640
D. 2740
65. Stability ratios used in the financial analysis include:
A. Quick Ratio
B. Return on Equity
C. Inventory Turnover
D. Debt to Assets Ratio
66. Which of the following methods is not used for assets depreciation?
A. Residual Value Method
B. Straight Line Method
C. Declining Balance Method
D. Sum of Years` Digits Method
67. The break-even point:
A. Is the level of sales at which profit is maximized
B. Is the level of sales at which revenues equal fixed costs
C. Is the level of sales at which revenues equal total costs
D. Is the level of sales at which revenues equal variable costs
68. Investment Decision , An investment requires an initial cost of € 10,000 and has the following expected net cash inflows for the four year period. Expected cash inflows: year 1: € 2,800 year 2: € 3,000 year 3: € 3,000 year 4: € 2,900 What is the average rate of return?
A. 11.7%
B. 4.25%
C. 29.25%
D. 21.7%
69. The Cash Flow from operating activities includes among others:
A. Purchase property, plant and equipment
B. Cash inflow from a new loan
C. Payment of dividends to shareholders
D. Cash inflows from sale of goods and services
70. Which of the following operations represents cash flow?
A. Decrease in accounts payable
B. Issuing shares
C. Depreciation of an acquired machine
D. Increase in accounts receivable
71. The legal entity sole trader/sole proprietor is characterized by:
A. Unlimited liability
B. Strong regulation
C. Double taxation
D. Separation of management from ownership
72. Which of the cost items can be characterized as a fixed cost?
A. Energy for production machine
B. Energy consumed for heating and lightning
C. Purchase of raw materials
D. Direct labour wages
73. Effectiveness:
A. Is a measure of liquidity
B. Is a measure of profitability
C. Is a measure of achieving maximum output with minimum resources
D. Is the degree to which objectives are achieved
74. An agreement between independent, otherwise competing companies to regulate the price and sales conditions of the products or services they offer, is called:
A. Cartel
B. Conglomerate
C. Merger
D. Joint-Venture
75. Working Capital is calculated as:
A. Total assets minus long-term assets
B. Total assets minus total liabilities
C. Current assets minus current liabilities
D. Total assets minus current assets
76. Marginal cost is:
A. A cost that is not affected by managerial decisions
B. An additional cost corresponding to an additional unit of output
C. A cost that cannot be accurately identified with a particular cost object
D. A cost that is not affected by changes in the level of production
77. External financial sources include:
A. Accrued liabilities
B. Sale of share
C. Retained earnings
D. depreciation
78. The method providing information about the average annual percentage return that the investment will generate over its life is called:
A. Average Rate of Return
B. Return on Assets
C. Net Present Value
D. Payback Period
79. Explicit costs are also referred to as:
A. Opportunity costs
B. out-of-pocket costs
C. Relevant costs
D. Prime costs
80. The Profit and Loss Account (Income Statement) reports all of the following except:
A. Operating profit
B. Net income (profit) or loss
C. Earnings before interest and taxes
D. Economic profit
81. Which factor of the PEST analysis can be identified as a social factor?
A. Research and development
B. Inflation rate
C. Trade restrictions and tariffs
D. Population movements (migration)
82. Market Concentration The top 4 largest firms produce 80 % of the goods in the market. Their shares on the market are the following: Firm 1: 30% Firm 2: 26% Firm 3: 14% Firm 4: 10% Evaluate the market concentration using the Herfindahl–Hirschman Index. The result provides information that the market is:
A. Moderately concentrated
B. Highly competitive
C. Highly concentrated
D. unconcentrated
83. Which of the cost items can be characterized as overhead cost?
A. Electricity cost of a single-purpose machine
B. Wood used to manufacture a desk
C. Depreciation of a single-purpose machine
D. Depreciation of a multi-purpose machine
84. The contribution margin:
D. Is the difference between revenues and variable costs
{"name":"Business Economics", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"1. The Cash Flow from financing activities includes among others:, 2. Market Concentration The top 4 largest firms produce 95 % of the goods in the market. Their shares on the market are the following: Firm 1: 40% Firm 2: 25% Firm 3: 20% Firm 4: 10% Evaluate the market concentration using the Herfindahl–Hirschman Index. The result provides information that the market is:, 3. Internal financial sources include:","img":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/3012/CDN/97-4777073/picture1.png?sz=1200-00000000001000025978"}
More Quizzes
Would Le Criball Date U?
11613
Class 3 Quiz (z-scores, probability)
210
Do you have any recommendations in new papers today?
100
Philippians 1-4 (Malayalam)
10516
Musculoskeletal System - Free Anatomy Practice
201022605
Special Forces - Which Unit Are You? Free
201022179
When to Put Your Cat Down - Free Self-Check
201021642
Bikini Bottom Genetics - Traits & Inheritance
201018568
Which Lorax Character Are You? Free Personality
201021386
Monogatari Character - Which One Are You? (Free)
201020436
What Will My Baby Look Like - Free Predictor
201020436
Am I Emotionally Immature? Free & Self-Assessment
201018482