Molecular Genetics 3 - Lecture Quiz's
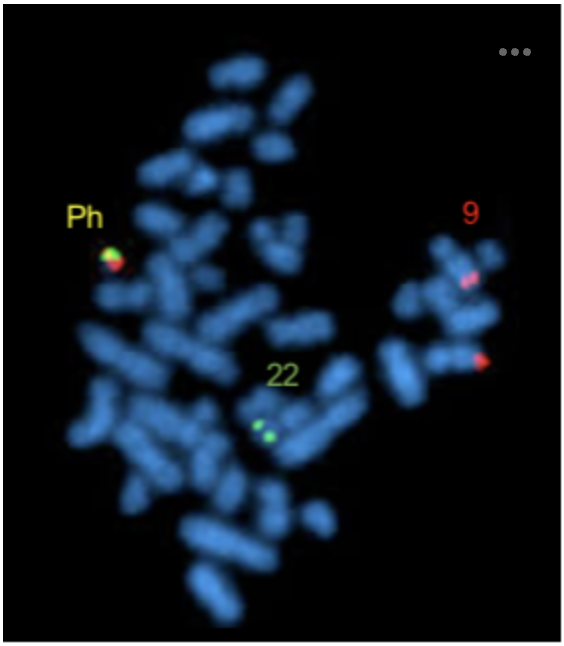
The image below shows fluorescence in situ hybridisation (FISH) to detect the Philadelphia chromosom (Ph), which causes chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) and results from a reciprocal translocation between 9q and 22q. In this FISH experiment a red fluorescently labelled DNA probe that can hybridize to 9q and a green labelled DNA probe than can hybdridise to 22q were used. Fluorescence signal from the two DNA probes that are close together can fuse to form one dot. Using the image below as a reference alongside your understanding of chromosome nomenclature and FISH, select ALL the correct statements from the list below. Note: partial credit will be awarded for each correct answer, while points will be detracted from incorrect choices.
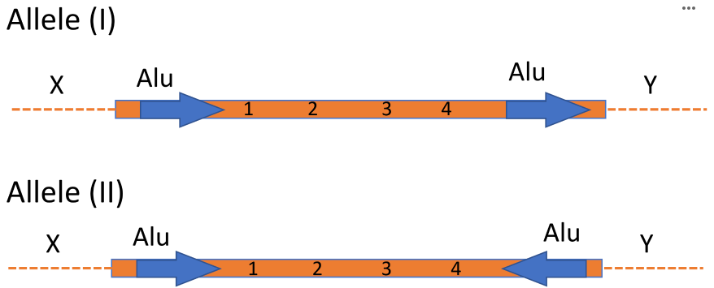
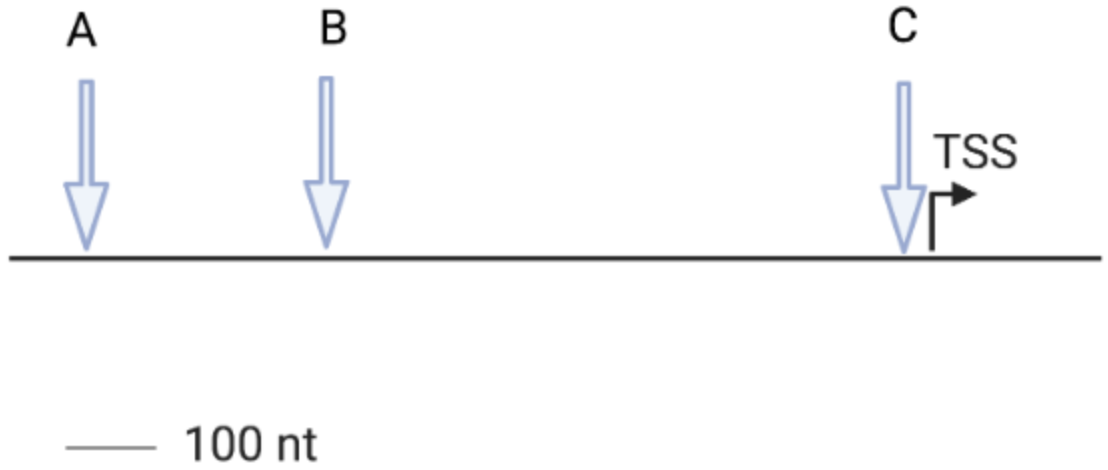
After recombination between the Alu sequences within allele I the sequence 1-2-3-4 will be [1].
After recombination between the Alu sequences within allele II, the sequence 1-2-3-4 will be [2].
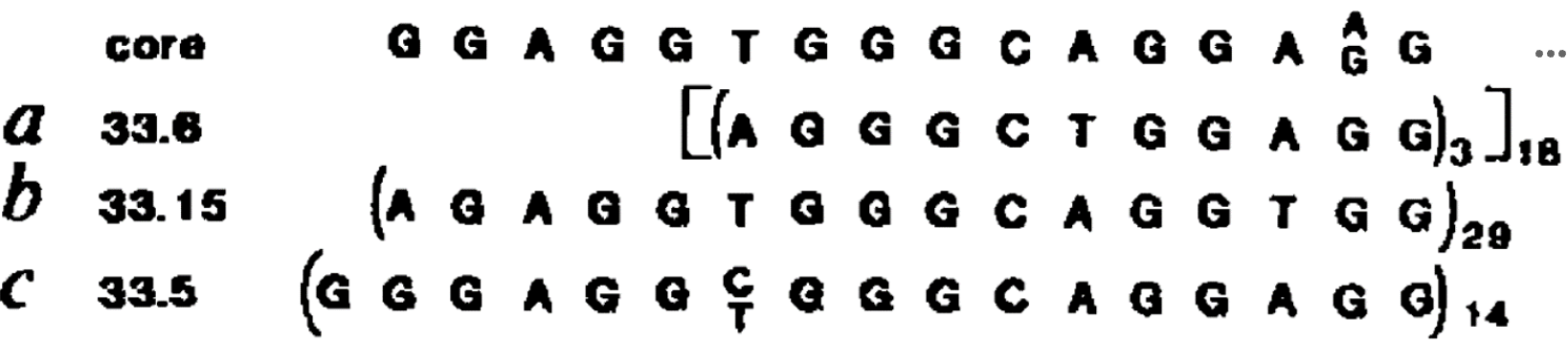
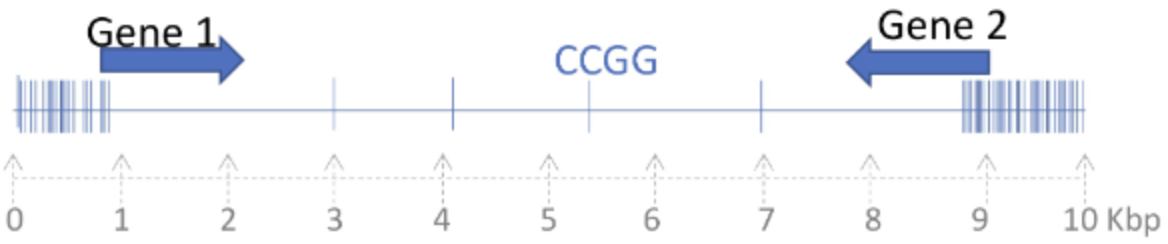
MspI digestion is expected to generate [1] detected by the cosmid probe.
HpaII is expected to generate [2] detected by the cosmid probe.

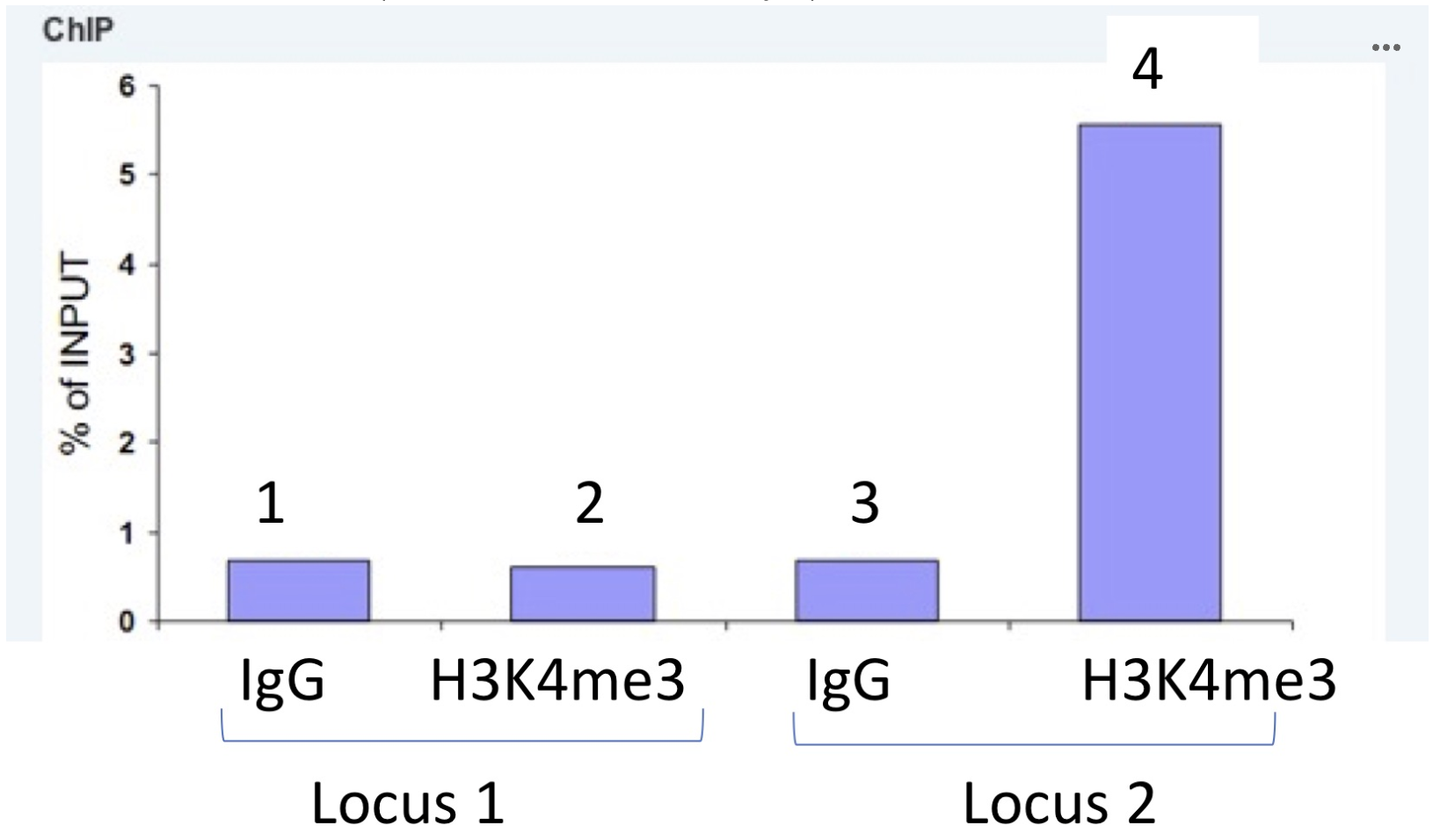
Bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) are secreted during development to induce chondrocytes differentiation and promote the expression of cartilage-specific genes. One of these genes is Fgfr3. In order to study the dynamics of nucleosome remodelling on the Fgfr3 promoter upon BMP-2 stimulation, DNase I sensitivity analysis was performed. Cells are stimulated or not with BMP-2, nuclei are isolated and digested with increasing amounts of DNAse I. Genomic DNA is extracted, digested with HindIII, run on an agarose gel and Southern blotting is performed with a probe recognising Exon 2 of Fgfr3 to visualise the Fgfr3 promoter region.
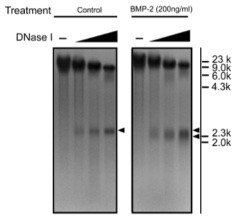
What does the additional band appearing upon BMP-2 stimulation represents?
In Drosophila melanogaster the Polycomb complex PRC2 is responsible for tri-methylation of histone H3K27. How PRC2 is recruited to specific sites in the genome is under investigation. In this work, the authors analysed the role of the Zn-finger transcription factors Pho and Spps.
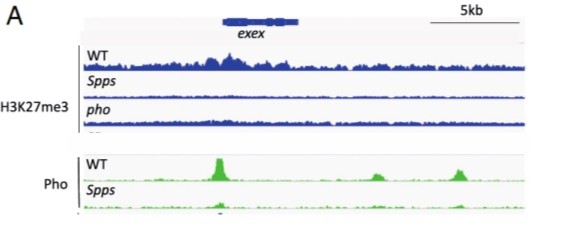
Results are shown above of analysis of DNA sequencing of chromatin immunoprecipitations (CHIP-seq) done for H3K27me3 and Pho for the region encompassing the exex locus in wild type (WT), Spps and Pho mutant larvae. Which conclusion(s) (A to D below) based on these CHIP-seq results is/are correct?

These are three examples 1, 2 and 3 above of polonies (clusters) in a flow cell of an Illumina DNA sequencer slide. What could be the explanation for the significantly different densities of polonies in the three examples?
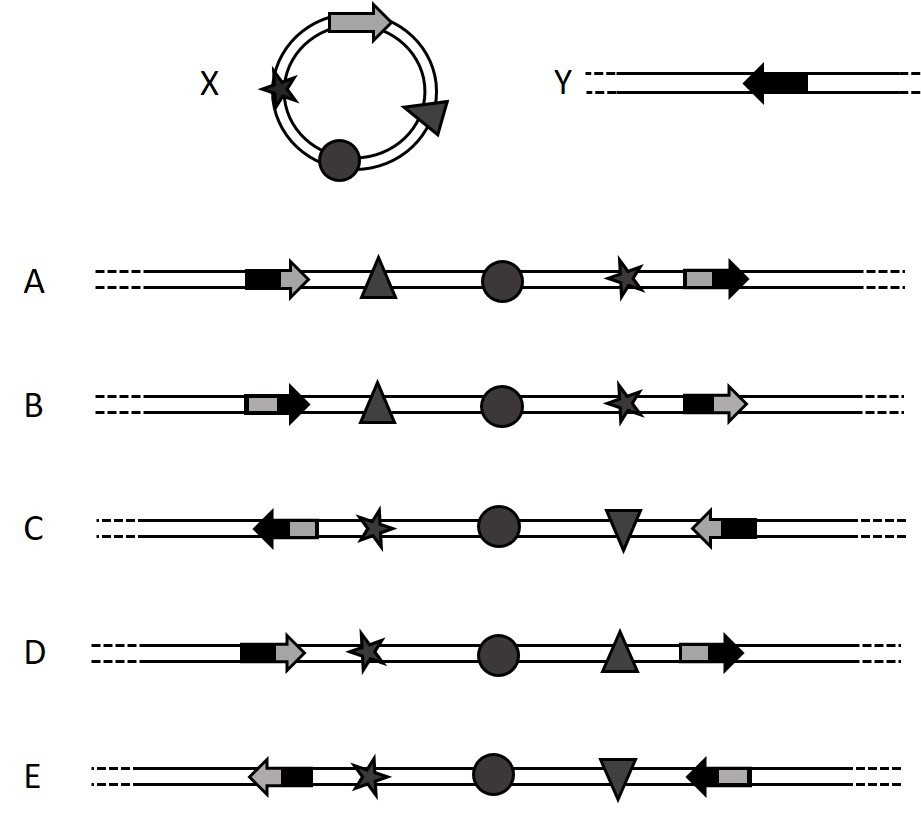
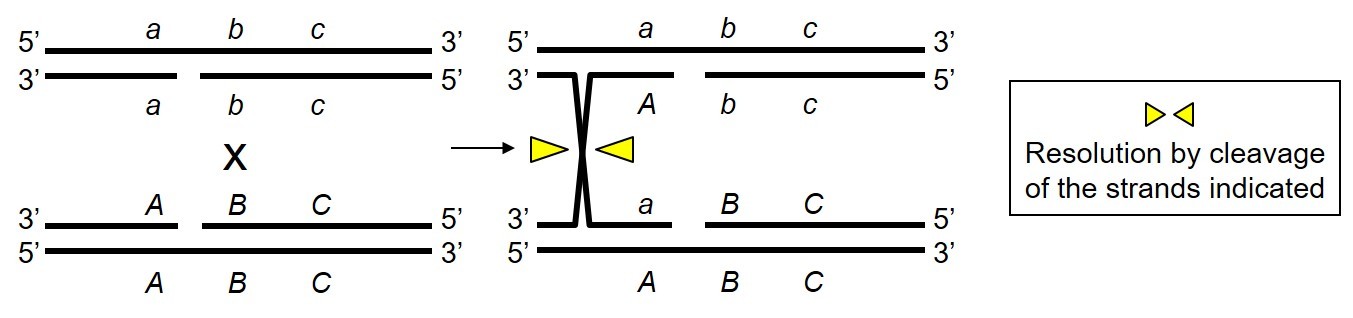
The DNA molecule X has been formed by resolution of two Holliday junctions by RuvABC. Where did RuvABC cleave the DNA intermediate as indicated by the triangles (select all possible answers)?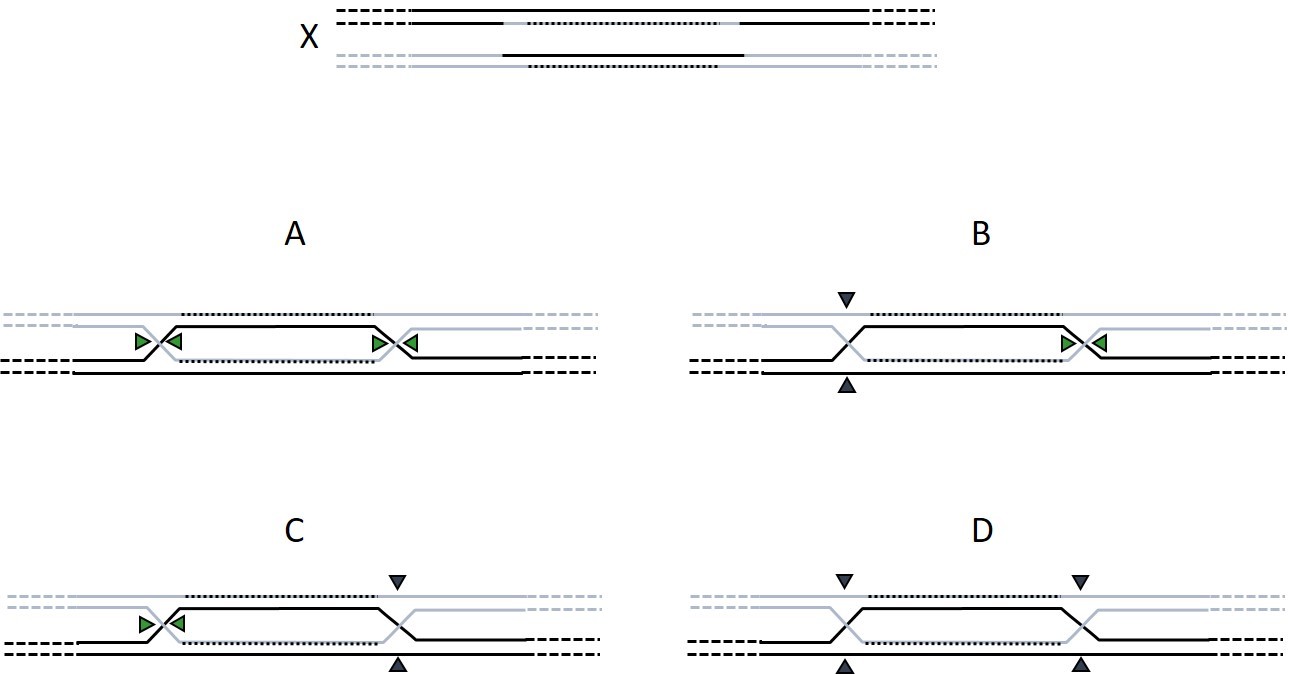
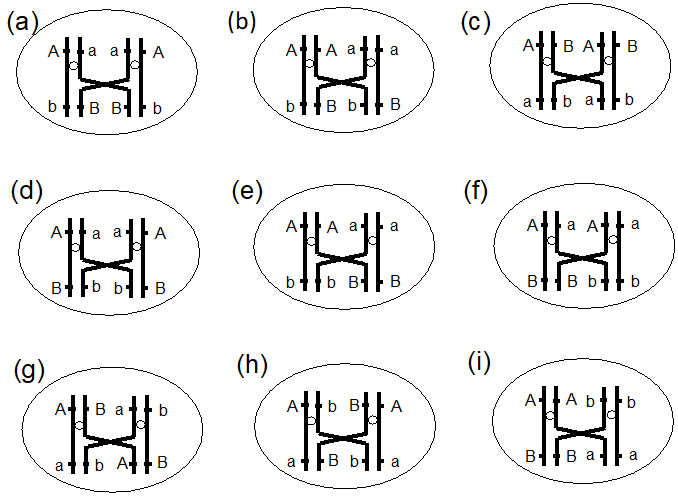
What molecule(s) may be created by site specific recombination between molecules X and Y. The arrows represent recombination sites and the star, circle and triangle are genetic markers (select all possible answers)?
Scientists isolated bacteriophages A that lyse E. coli strain K-1 but not K-9. They carried out a PCR of 6 kb and mapped the amplified fragment using restriction enzymes NotI, BamHI and HindIII. They observed the restriction pattern shown below on an electrophoresis gel.
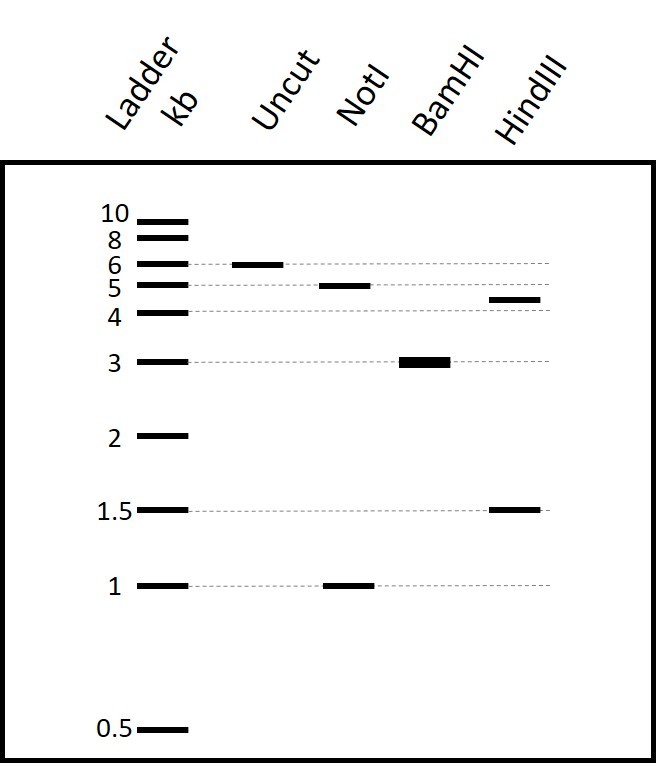
Part 1: Type how many cutting sites for each enzyme are in the PCR fragment, based on the restriction pattern shown in the gel in Figure 1. Type your answer as a number: 1, 2, 3...
NotI
BamHI
HindIII
Scientists carried out a heat-shock on bacteriophage A and noticed that some of the heat-shocked bacteriophages acquired the ability to also lyse E. coli strain K-9. They called this population bacteriophages H and carried out on bacteriophages H the same PCR and restriction mapping as on bacteriophages A. They observed the restriction pattern below on an electrophoresis gel.
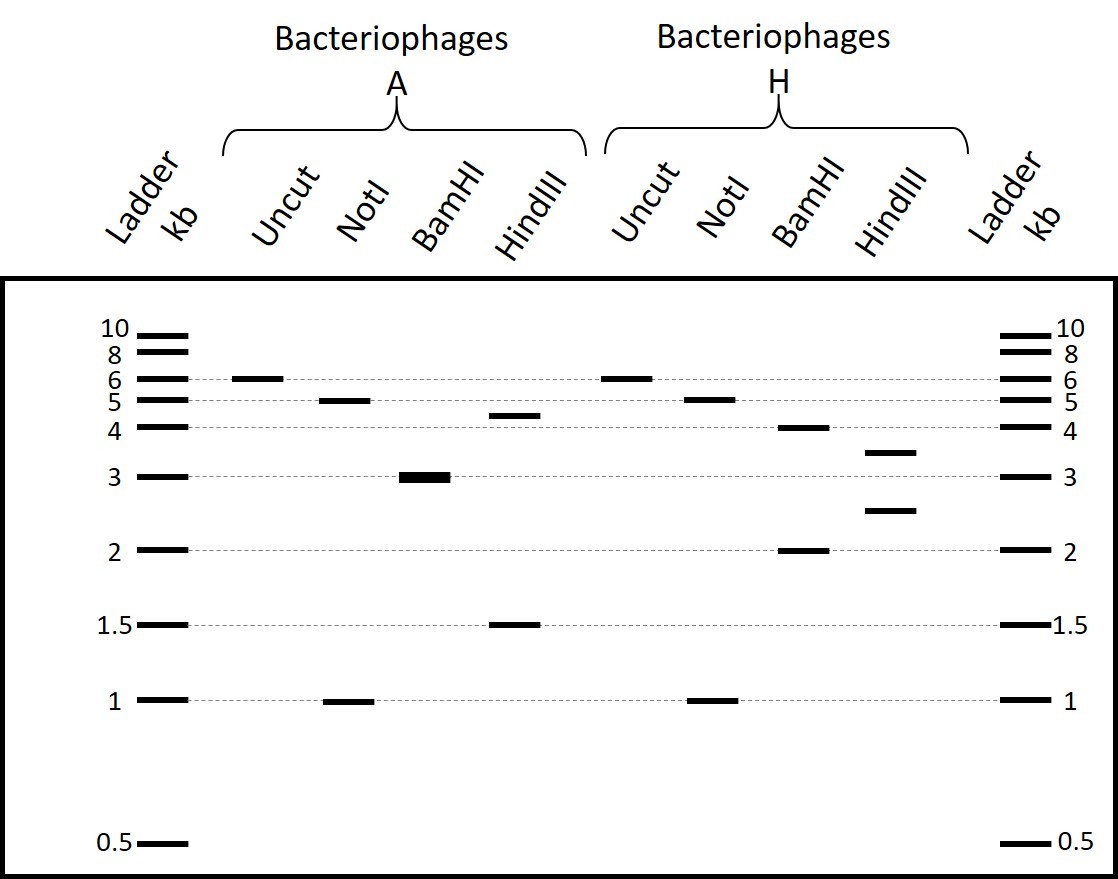
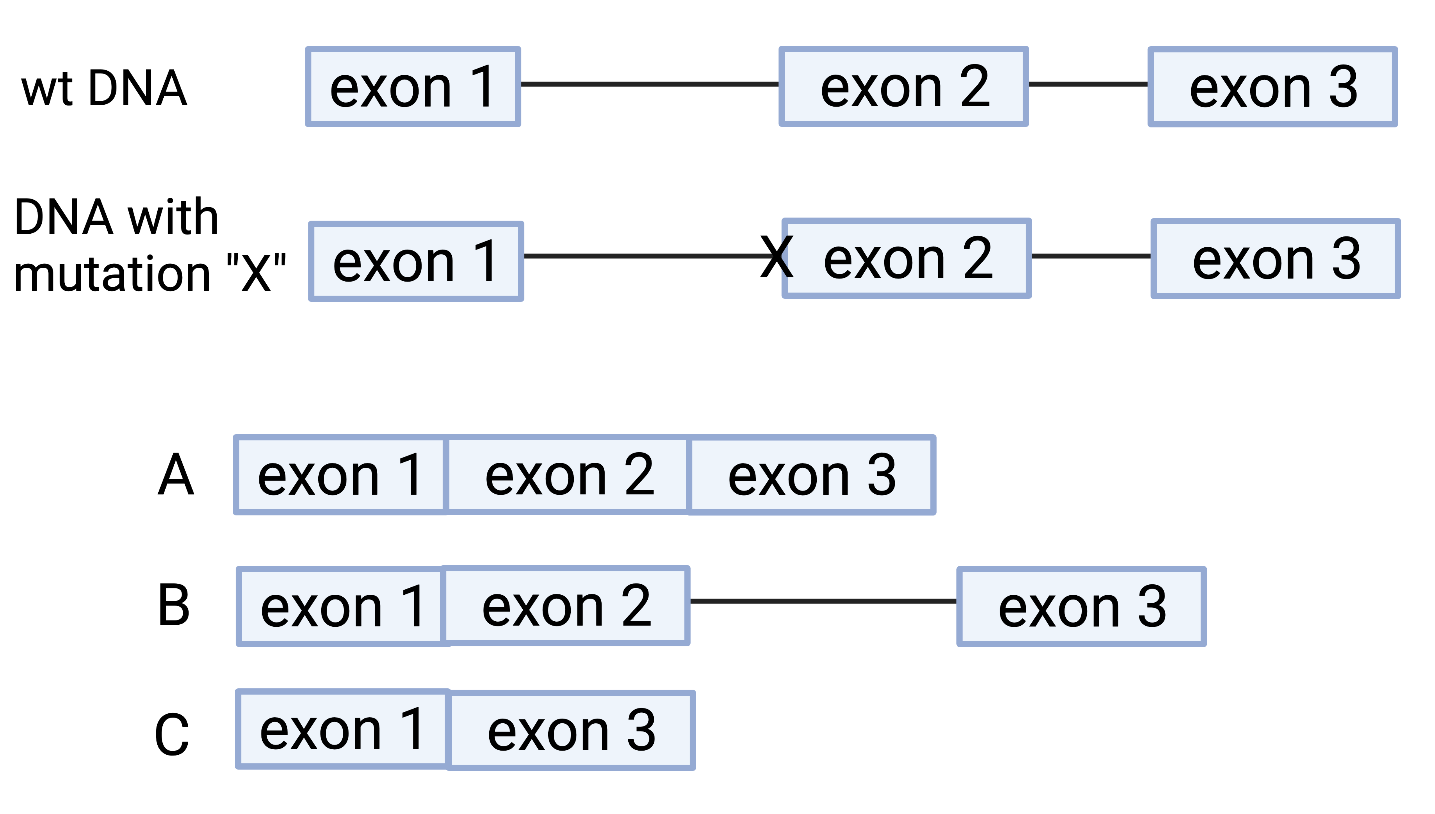
What type of DNA sequence(s) should be present in this region to explain the result of this recombination event (select all possible answers)?
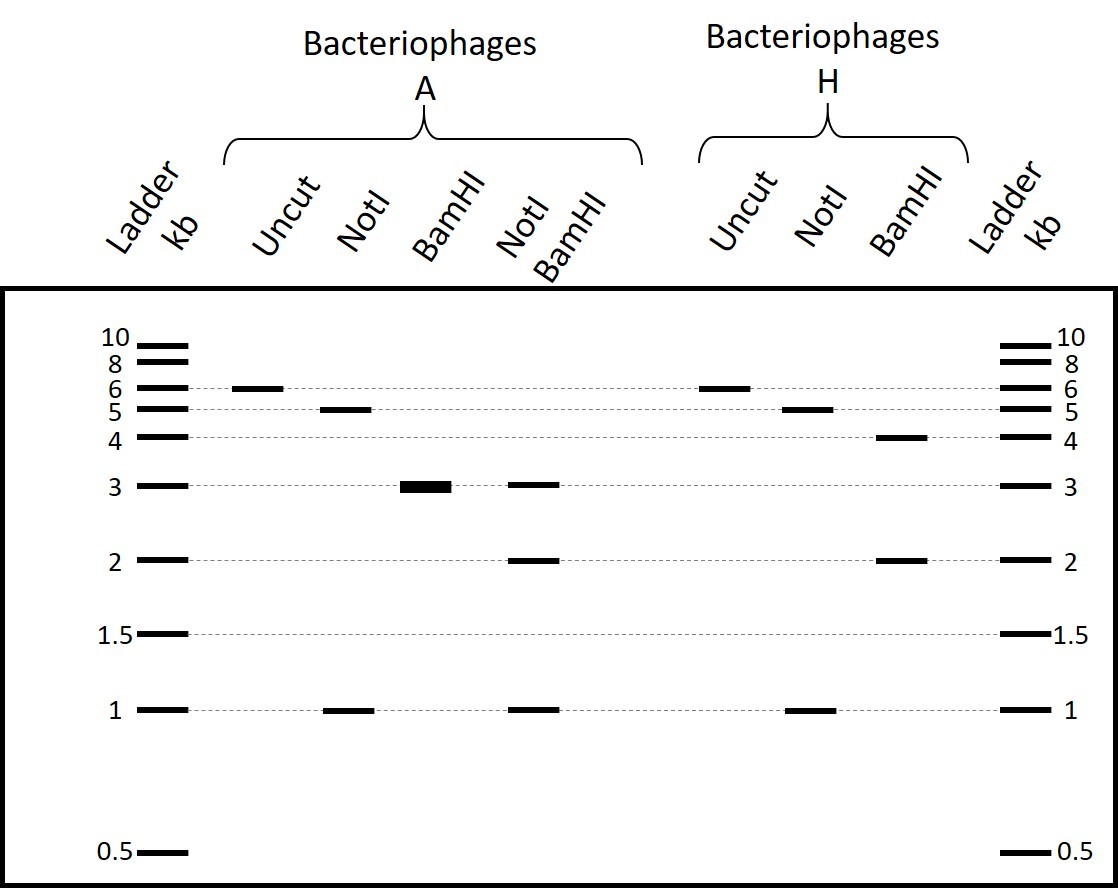
If a double digestion with NotI and BamHI of the PCR fragment from bacteriophages A results in the restriction pattern shown on the electrophoresis gel below, what would be the expected band sizes of the same digestion of the PCR fragment from bacteriophages H (select all possible answers)?
Select all TRUE statements about the molecular process described in the figure below
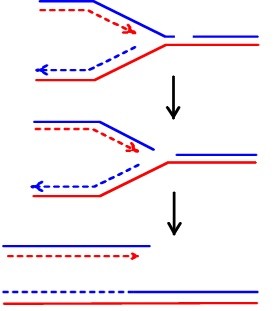
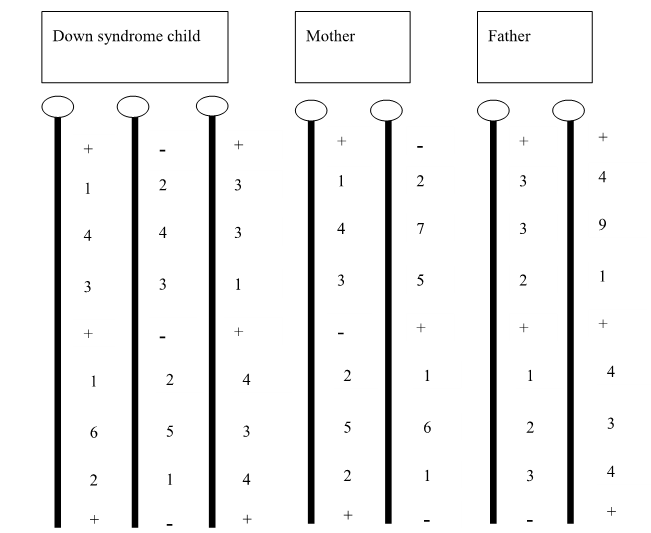
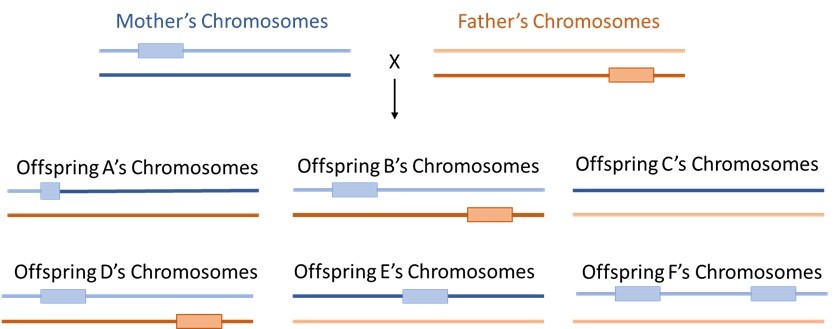
Looking again at the family from Question 15.3, in which you had sequenced the genomes of two Drosophila parents and six of their virgin offspring, identified a new transposable element (TE) occurring once in each parental genome, and assigned offspring chromosomes to their parent of origin:
Recall that the maternal copies of the chromosome arm are shown in blue (one light blue, one dark blue) and the paternal copies of the chromosome arm are shown in orange (one light orange, one dark orange).
Based on this figure and the information provided, which of the following types of TE is this most likely to be?
A three-factor cross (between factors d, e and f, placed in alphabetical order on the chromosome) was carried out. The progeny was as shown below (please note that we know that the markers do not affect the frequency of recombination and there is reciprocality in the population). What are the type and level of interference in this cross?
|
Genotype |
DeF |
def |
DEf |
DEF |
Def |
dEf |
deF |
dEF |
|
Number in the progeny |
46 |
200 |
250 |
190 |
4 |
44 |
260 |
6 |
Two dsDNA molecules differ in three markers (A, B and C). An event creates a single strand break in both molecules between markers A and B. A cross-over recombination event happens in front of marker A. The cross-over recombination event is resolved by cleavage. What can you say about this process (select all possible answers)?
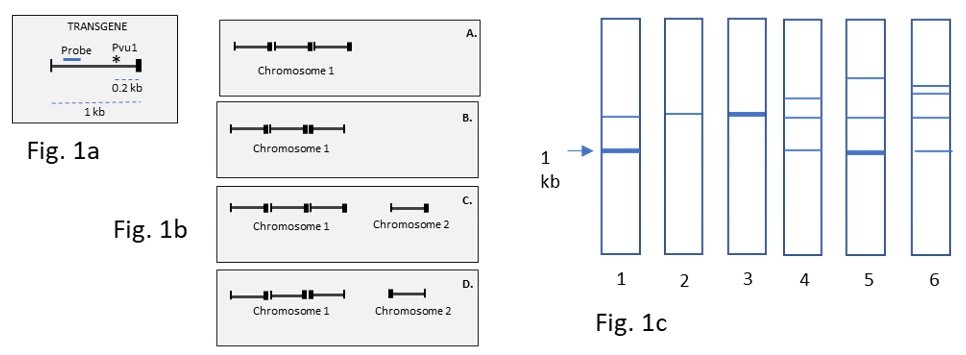
A transgenic mouse line has been generated by pronuclear injection and researchers decided to investigate integration sites of the transgene using Southern blotting. They digested mouse genomic DNA with Pvu1 (unique restriction site in the transgene, which cuts mouse genome with low frequency = 0.036/ 10 kb) and DraI, which does not cut the transgene but cuts mouse genome with high frequency 1/ 1 kb. The transgene is shown in Fig. 1a. Consider four transgene integration patterns (A, B, C, D) in Fig. 1b and match them with 4 variants from Southern blots represented in Fig. 1c.
Seven DNA constructs were used to target a genetic locus. Each construct contained left and right homology arms (LHA and RHA, respectively) and selection markers, each driven by a ubiquitous promoter: Puror (Puromycin resistance cassette, similar to Neor) and HSV-tk in different positions. Some constructs also contained a GFP reporter.
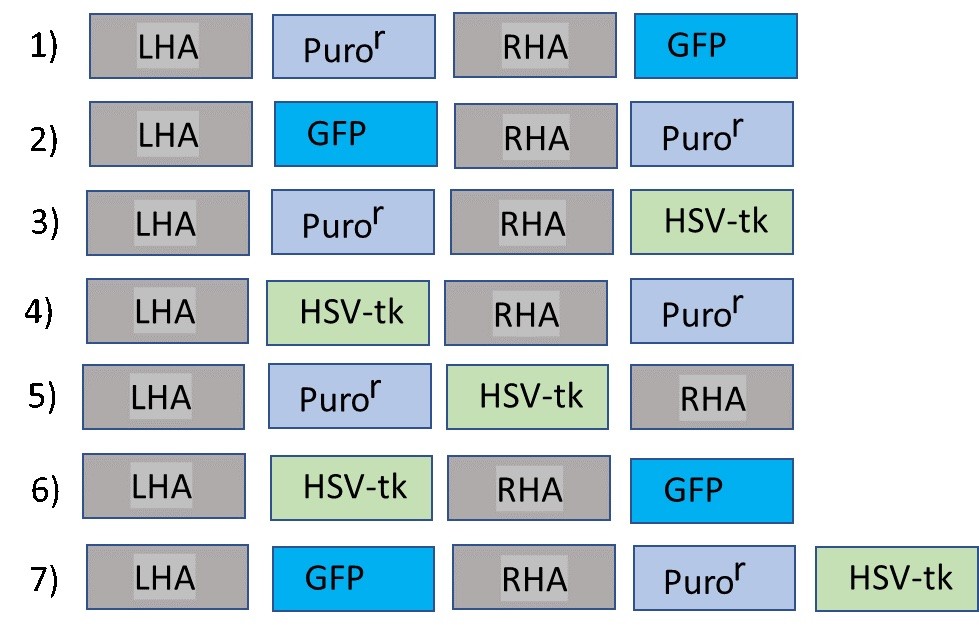
After electroporation with individual constructs in separate experiments, the cells were cultured in selection media containing first puromycin and subsequently ganciclovir. At the end of each culture, researchers obtained one of the following results (only cells with intact transgenes were considered):
- No live cells
- Correctly targeted clones only
- Correctly targeted clones and clones with random transgene integration
- Cells with random integration only
For each of the 7 constructs, indicate which result (a,b,c, or d) would be obtained after targeting?
Mouse ES cells are planned to be used for the generation of mutant mice using CRISPR/Cas9 system. An essential sequence chosen for mutation of gene of interest is shown in Fig. 1. Eight variants of potential protospacer sequence within gRNA have been considered corresponding to coloured horizontal fragments, boundaries of which are delineated by thin vertical lines. Which of these potential protospacers can be considered for inclusion in gRNA to cut genomic DNA?

A gene targeting experiment was performed to introduce an insert (red) into a genetic locus (blue) using targeting construct with left and right homology arms (LHA and RHA) as shown in Fig. 2. There are two unique restriction sites (EcoRI; HindIII) in the locus near the site of insert, which are also present in LHA and RHA, respectively. Which of the following restriction digests will identify correctly targeted clones by Southern blot using the probe indicated in Fig. 2? Choose variants in Table below.
HINT: you should be able to discriminate correctly targeted clones from wild type clones and from clones with random transgene integration.
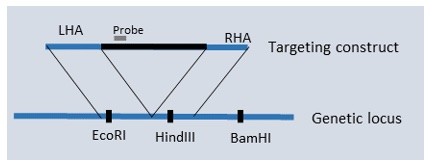
|
HindIII; EcoRI; BamHI |
|
EcoRI; BamHI |
|
HindIII; BamHI |
|
HindIII; EcoRI |