3DD/Partial Denture/Dr.Sok Ly/
1. A clasp most common use is
σ� Ring clasp
σ� Back action clasp
σ� Aker clasp
σ� Embrasure
2. Infrabulge clasps originate
σ� above the 12mm undercut areas
σ� above the occlusal surface of most premolars
σ� above the height of contour
σ� below the height of contour
3. Reciprocation between bracing and retentive components requires
I bars be used
σ� Aker clasp be used
σ� Bracing components contacts after retentive components
σ� Correct timing of contact during seating and removed of RPD
4. The basic movement of mandible
σ� hinge movement
σ� translatory movement
σ� lateral movement
σ� hinge ,lateral and translatory movement
5. Maxillary major connectors most common use is
σ� full palatal strap
σ� palatal strap
σ� anterior posterior palatal strap
σ� anterior palatal strap
6. Anterior posterior palatal strap especially use is
Maximum rigidity
σ� minimum bulk
σ� use in most cases
σ� torus palatal
7. Which of the following maxillary major connectors possesses the least strength and rigidity?
Anterior posterior palatal strap
σ� palatal plate
σ� horse –shoe
Modified palatal strap
8. Which of the following clasps commonly utilize lingual undercut?
σ� Extended arm clasp
σ� Ring clasp
σ� Back action clasp
σ� Embrasure clasp
9. The external finish line is
σ� the external of framework metal and supporting tissues
σ� the external of framework metal and denture base plastic
σ� the external of framework metal and the natural teeth
σ� the external of the natural teeth and the denture base plastic
10. Functions of a Major connector
σ� component of RPD connect to acrylic resin
σ� kind of metal chrome cobalt
σ� functions as one unit
σ� unification, stress distribution, cross arch stabilization
11. Requirements of a Major connector
σ� rigidity, non interference with tissues, minimize food impaction and unobtrusive
Partial denture acts as one unit
σ� distributes functional loads to both teeth and mucosa
Connects various parts
12. The superior border of mandibular lingual bar major connector should be
σ� as far from gingival margin as possible
σ� at least 3mm from the tooth/ junction
At least 3mm above the tooth/ junction
at least 3mm from the tooth/ tissue junction
13. The internal finish line is
The butt joint between the metal and resin acrylic on the tissue side of the edentulous area
σ� the butt joint between the metal and resin acrylic on the outer surface of the RPD
σ� a type of posterior palatal seal
A special type of above
14. A combination clasp assembly generally has
A bracing arm , a retentive arm and rests
A retentive arm ,rests and indirect retainer
σ� rests, a retentive arm and proximal plate
Rests , a bracing arm and proximal plate
15. The external finish line on a maxillary class 1 RPD originates from the lingual of the guide plane of the terminal abutment and ends
σ� at the hamular notch
σ� in the glenoid fossa
Opposite the buccal pouch
Opposite stenon’s duct
16. The Gridwork of Minor Connector on a maxillary class 1 RPD
σ� covers the hamular notch
σ� covers the tuberosity
σ� does not cover the tuberosity
σ� covers the crest and tuberosity
17. The removable partial denture design should be finalized prior to
σ� any emergency treatment
Any fixed prosthodontics treatment and preparation of rest seats
σ� remove third molar
Remove crown bridge
18. In general lingual plating should be supported
σ� by the inclined surfaces of the mandibular incisors
σ� with minor connector
With bracing arms
σ� with rests
19. Occlusal rest preparation should be
Teardrop shaped, at least 1/2 the bucco lingual width of the occlusal surface, at least 15mm deep
Pear shaped, at least 1/2 the bucco lingual width of the occlusal surface, at least 15mm deep
Flat shaped, at least1/3 the bucco lingual width of the occlusal surface, at least 1mm deep
σ� spoon shaped, at least1/3 the bucco lingual width of the occlusal surface, at least 1m deep
20. A lingual plate major connector may be selected be cause
The mandibular incisors are tilted lingually, mandibular tori present, high lingual frenum
The mandibular incisors are tilted facially, high floor of the mouth
The mandibular incisors are tilted facially, mandibular tori present ,high lingual fremum
The mandibular incisors are tilted lingually ,high floor of the mouth, high lingual frenum
21. Guide plates for anterior teeth
Should be kept to the cingula for esthetics
σ� should be kept to the labial for esthetics
σ� should be kept to the proximal faces for esthetics
σ� should be kept to the lingual and be thinned on labial for esthetics
22. An anterior posterior palatal strap major connector is less rigid than a horseshoe major connector because it (the AP strap) has less width
The first statement is true but the reason is false
The first statement is false and the reason is also false
σ� The first statement is true and the reason is true
σ� The first statement is false but the reason is true
23. In a circumferential clasp assembly, the arms may extend into an undercut
σ� The bracing arm
σ� The reciprocating arm and retentive arm
σ� The bracing arm and retentive arm
The retentive arm
24. Which of the following steps is done LAST ?
σ� Rest preparation
σ� Framework try in
Centric relation records
σ� Altered cast impression
25. Direct retainer (clasps)
σ� help stabilize the RPD by controlling occlusal movement
σ� help stabilize the RPD by controlling gingival movement
May also function as indirect retainers
Prevent excessive biting forces on the abutment
26. What are the indications for a linguo plate as a major connector for a mandibular RPD?
σ� Present high floor of the mouth and facially anterior teeth
Present high lingual frenum and buccally anterior teeth
σ� Present lingual tori and big tongue
σ� High floor of the mouth, high lingual frenum, lingual tori
27. Incisal rests should generally not used on maxillary incisors Why?
For mandibular class 4 kennedy only
σ� for maxillary class 4 kennedy only
For maxillary and mandibular class 1 and 2 kennedy
Poor esthetics and interferences with opposing occlusion
28. Component of a clasp assembly are:
σ� One rest, a retentive arm , a bracing or reciprocating element, one minor connector
σ� One or two rests, a retentive arm, a bracing or reciprocating element, one minor connectors, one major connector
One minor connector, one major connector, one rest, two rests, one retentive arm, one bracing arm
σ� Two minor connectors, one major connector , one rest, one retentive arm, one bracing or reciprocating element
29. The basic philosophy of dental treatment for a partially edentulous patient
Preserve what remains and restore what is missing
σ� Replace the missing teeth
Improve the path of insertion
σ� Reshape rotated teeth
30. Full palatal plate
σ� Minimum tissue support
σ� Connector of choice in short distal extension cases
σ� Six or more anterior teeth remain
σ� Six or less anterior teeth remain
σ� Maximum tissue support , connector long distal extension cases, six or less anterior teeth remain
31. Physiologic Rest is a position of vertical dimension which can be recorded with
σ� Centric relation
σ� Centric occlusion or MIP
Edge to edge incisor contact
Posselt’s envelope
32. A jaw which is moving in a ”left or right” motion would be called what type of movement:
Lateral pure hinge
Ateral protrusion
σ� lateral
σ� horizontally protrusive
33. The condyle on the working side is called the working condyle, which is also known as the:
Orbiting condyle
σ� balancing condyle
Rotating condyle
σ� translatory condyle
34. Considering the design of an RPD for the mandibular arch…
σ� Survey crowns should be done to correct the mesial tilt of the molar
σ� Retentive clasps are required next to each edentulous space
σ� The lingual plate would be the major connector of space
A dual path of insertion should be considered
35. Which one of the following Kennedy classes of RPD, never has an axis of rotation?
σ� class I of Kennedy
σ� class II of Kennedy
Class III of Kennedy
Class IV of Kennedy
36. A class I modification 0 of RPD normally are have many clasps?
σ� 1 clasp
σ� 2 clasps
σ� 3 clasps
σ� 4 clasps
37. Cleaning a removable partial denture in sodium hypochlorite may result in
Increased caries activity
Increased periodontal problems
Whitening acrylic resin and artificial teeth
σ� corrosion of the metal the framework
38. During biting a maxillary class I RPD with rotate around a line determined by the rigid metal above the survey line and closed to the extension areas This line is called
Dual path line
σ� Frankfurt line
σ� Camper’s line
σ� Axis of rotation
39. Mandibular gridwork design of minor connectors
Maximum bulk of the acrylic resin
prevents thin, edges fracturing
Extend fully to the hamular notch
Extend 2/3 of the way from abutment tooth to retromolar pad
40. The correct answer the basic movements of the mandible:
Hinge, chewing and yawing
Translatory movements relative to centric relation
Lateral, dimension, excursion
Hinge , lateral and translatory movement
41. A mandibular movement which is<< either opening or closing motions of the mandible around a horizontal axis that is common to both condyles >> would be best classified as a…………movement
σ� translatory excursion
centric relation
σ� lateral
hinge
42. Protrusive or Retrusive movements can also be called………………movement
translatory or vertical
Translatory or shifting
Translatory or sliding
Sliding crossbite excursions
43. Use long guide plane on class IV Kennedy for
Retention denture base
Stabilization denture base
Path of insertion
Esthetic denture
44. Retentive tip of a clasp should usually be designed to be placed in
The occlusal 1/3
σ� The gingival 1/3
σ� The occlusal 2/3
The gingival 2/3
45. Height of contour determine is a
σ� Path of insertion
Placed of the clasp
Proximal plate
Infrabulge and suprabulge
46. When the survey line is height on the Mesial or Distal but low on the center, which one design clasp46. When the survey line is height on the Mesial or Distal but low on the center, which one design clasp
σ� I clasp
σ� Y clasp
σ� T clasp
σ� U clasp
47. More acceptable esthetically and less caries formation for bar clasp is
σ� Y clasp
σ� I clasp
σ� T clasp
σ� U clasp
48. Reciprocal clasp arm of RPD should be
σ� Horizontal force
Vertical force
σ� Direct contact
σ� Lied above high of contour
49. Best selection of preventing abutments tooth of class I Kennedy from the negative effects of the additional load applied to them is by:
σ� Splinting abutment with adjacent teeth
Placing distal rests on the distal abutment
Keeping a light occlusion on the distal extensions
Regular relining of distal extensions
50. When designing palatal connectors, relief should be given for
σ� Ridge area
σ� Elevated mid suture line
σ� Rugae area
σ� Palatal torus
51. For the preparation of rest seat:
Marginal ridge should be reduced by 25 mm
σ� Marginal ridge should be reduced by 1 mm
σ� The outline to have greater length than width
The outline to have greater width than length
52. Which of the following chronic conditions may cause tooth abrasion?
σ� Pipe smoking
Occlusion trauma
σ� Hard brush using and strong brushing
σ� Strong mastication
53. What is the most common use material for casting framework of RPD ?
σ� Platinum
σ� Titanium
Nickel chrome
σ� Chrome cobalt
54. Tripod of dental surveyor is the method used:
For giving clasp assemblies at 3 points
Determine the undercut areas on the tooth
Surveyor to have reproducible position of the cast on the surveyor
Surveyor for recording the relation of the cast to the surveyor
55. What are the typical positions of the maxillary and mandibular teeth, and the tongue during empty mouth swallowing?
σ� Centric occlusion, the tongue touches the palate
σ� Occlusion, the tongue touches the lingual aspects of the anterior teeth
Retruded contact, the tongue touches the palate
σ� Retruded contact, the tongue touches the lingual aspects of the anterior teeth
56. In which of following mandibular position would you find the greats increase in VDO from centric occlusion ?
σ� Centric relation
σ� Maximum protrusion
Anterior edge to edge position
Postural position
57. Mesh type of grid work minor connectors is
Potentially superior retention
σ� Interferes with setting of teeth
σ� Struts are too thick
Potentially more rigid
58. Lattice type of grid work minor connectors is
σ� Flatter
Potentially more rigid
Less retention for acrylic resin
Potentially superior retention
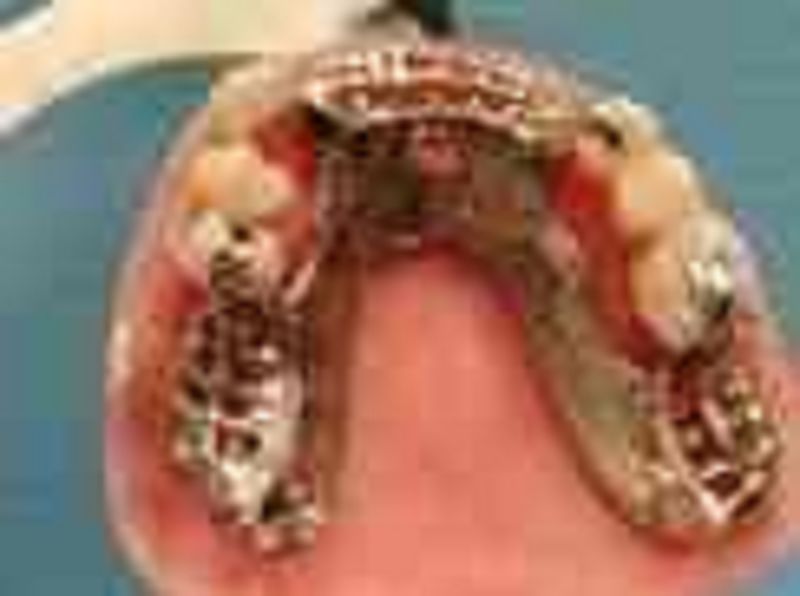
59. The kennedy classification of this RPD is
σ� class IV mod II
σ� class II mod I
σ� class I mod II
σ� Class I mod I
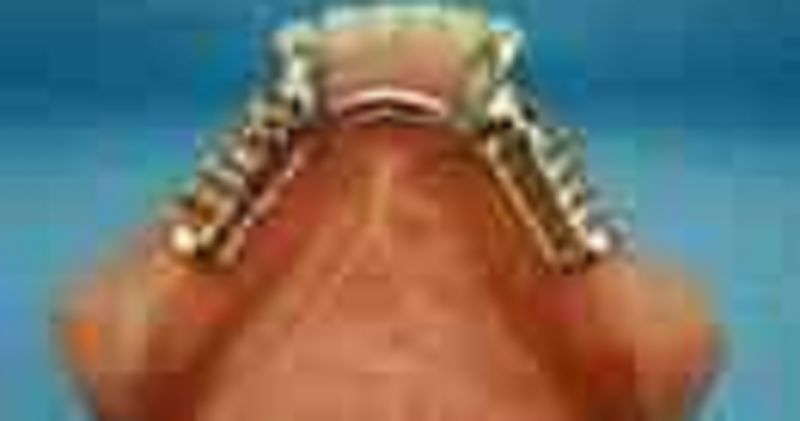
60. The kennedy classification of this RPD is
σ� Kennedy class II
σ� Kennedy class I
σ� Kennedy class I mod I
σ� kennedy class II mod I
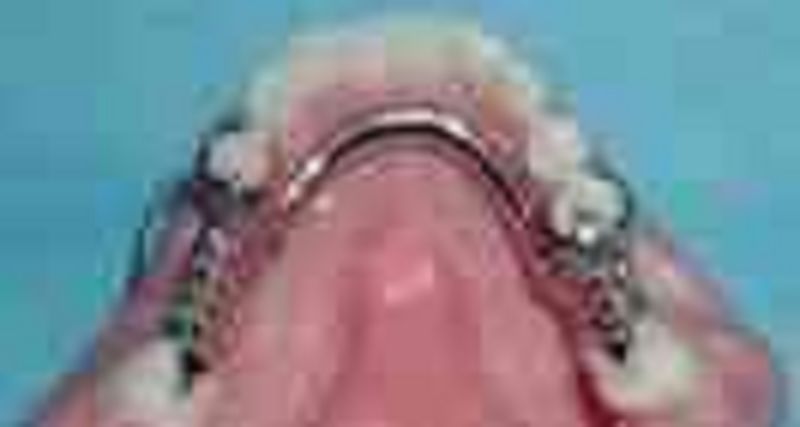

61. The Kennedy classification of this RPD is
σ� Kennedy class III
σ� Kennedy class III mod I
σ� Kennedy class IV mod I
σ� Kennedy class II mod I
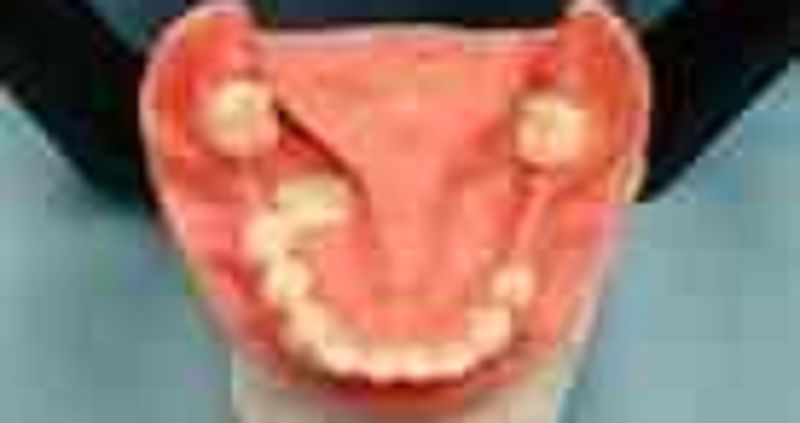
62. The Kennedy Classification for this cast is
σ� Class III mod I
σ� class III mod II
σ� class III
σ� class III mod III
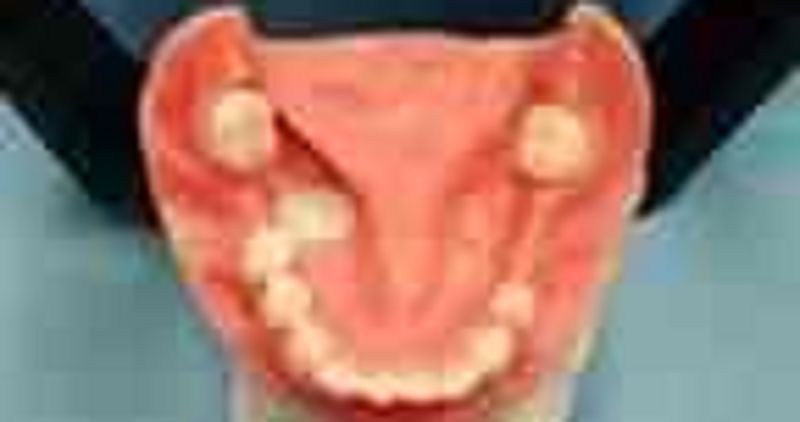
63. Considering the design of an RPD for the mandibular arch
σ� Survey crowns should be done to correct the mesial tilt of the molars
σ� Retentive clasps are required next to each edentulous space
σ� The lingual plate would be the major connector of space
σ� A dual path of insertion should be considered
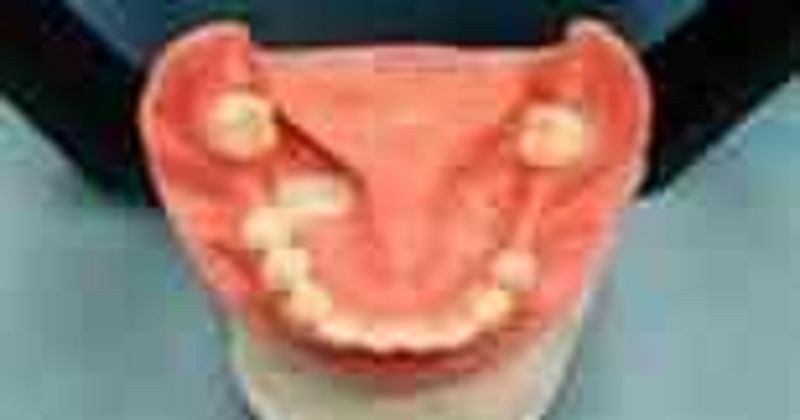
64. What is a RPD component is not needed in this type of case?
σ� Major connector
σ� Guide planes
σ� Direct retainers
σ� Indirect retainers

65. If this RPD was fabricated exactly as drawn on the design cast, which component(s) would be inadequate?
σ� Minor connectors
σ� lingual bar
σ� Direct and Indirect retainers
σ� All are correct
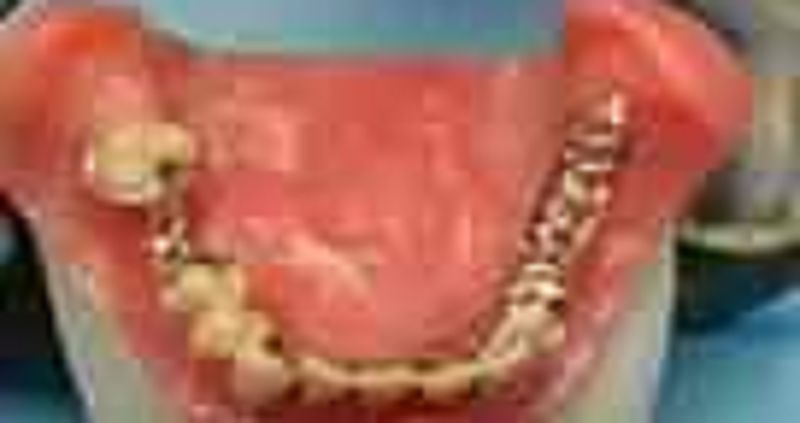
66. The denture base acrylic resin minor connector on the patient’s left side should correctly be located
σ� 2/3 to ½ the length of the residual ridge
σ� On the retromolar pad
σ� 1/3 the length of the residual ridge
σ� Have a mesh acrylic retention area
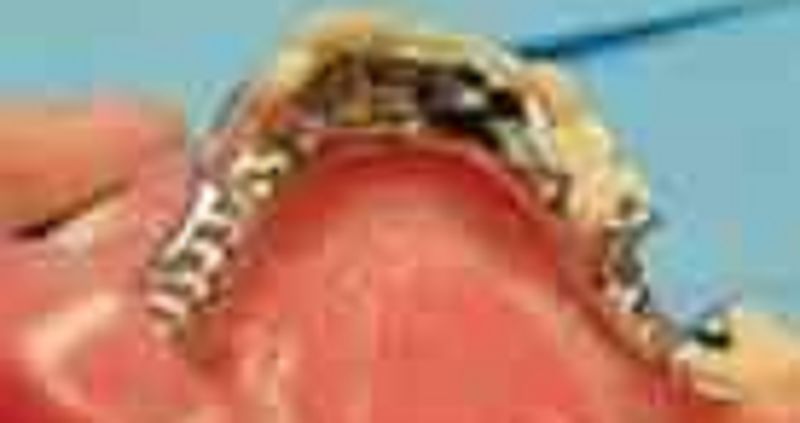
67. The external finish lines on this framework are
σ� Indistinct
σ� Would allow for acrylic and metal
σ� too deep or over contoured
σ� Correct
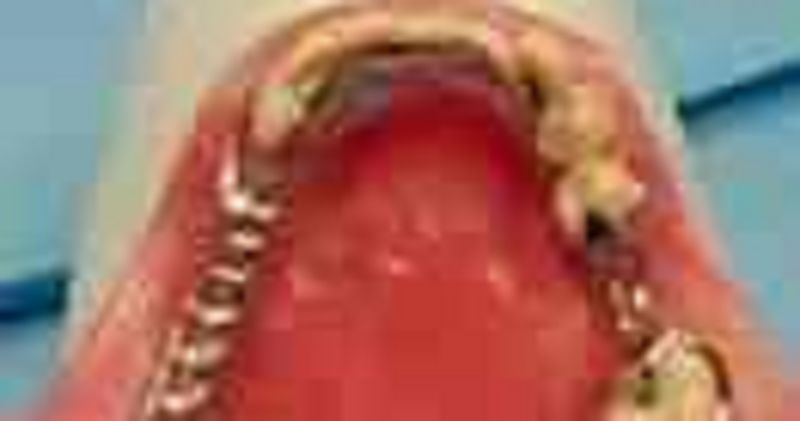
68. The superior border of this major connector
σ� Is not acceptably adapted to the teeth
σ� Is correctly adapted to the teeth
σ� is too low
σ� is too small
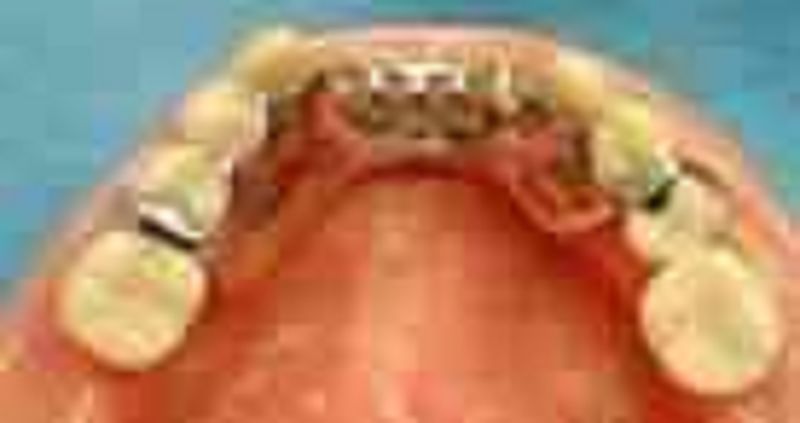
69. Which of the following is missing from the clasp on #45?
σ� Minor connector
σ� Rest
σ� Reciprocating arm
Retentive clasp arm
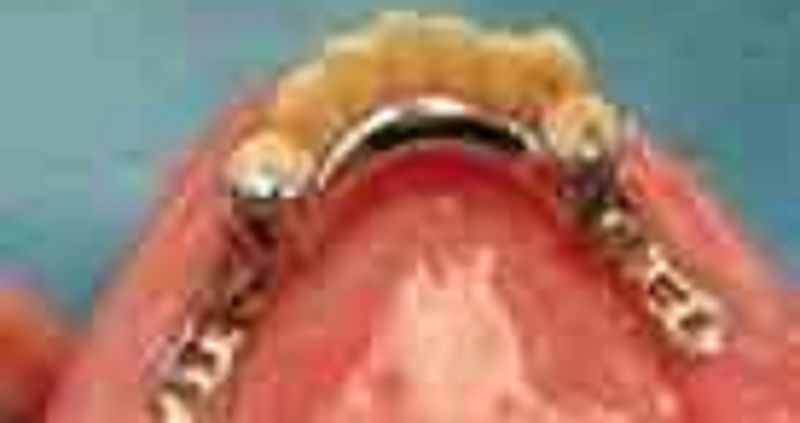
70. The major connector in this mandibular class I removable partial denture
σ� Is to long occlusal gingivally
σ� Is too close to the free gingival margin
σ� Is missing an indirect retainer
σ� All are correct
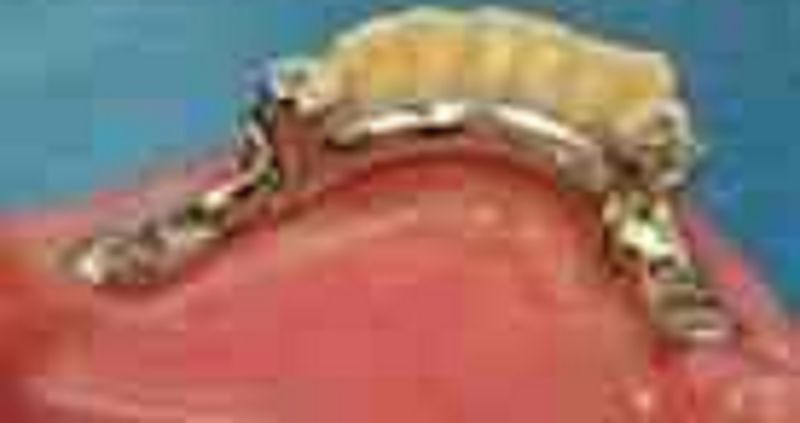
71. The major connector in this mandibular class I removable partial denture
σ� Is a lingual bar and its superior border is too close to the free gingival margins
σ� Is a lingual bar and its superior border is placed correctly
σ� Is a lingual bar and the placement of the superior border of the lingual bar is of no importance to the soft tissues
σ� Is a lingual bar too short and too close the free gingival margins
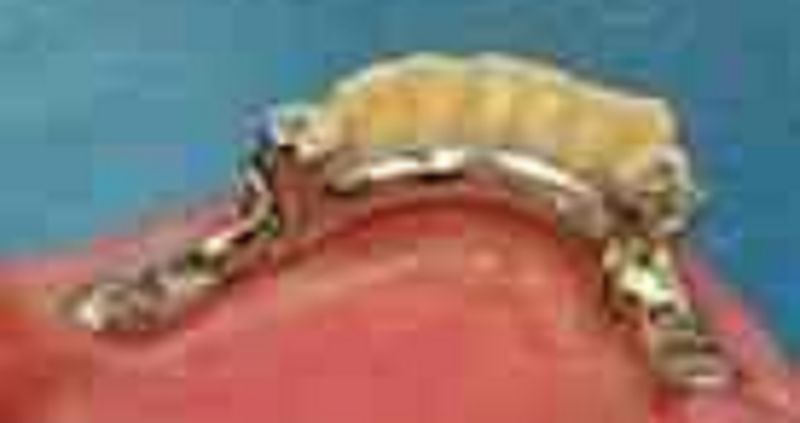
72. In this Class I mandibular removable partial denture, rests preparations on the cingulum of(#33+)
σ� Would provide indirect retention for the removable partial denture if covered by the major connector
σ� Would provide indirect retention for the removable partial denture
σ� Are not indicated in this case
σ� Are correct if rests preparations are good
73. A lingual plate major connector may be selected be cause
σ� the mandibular incisors are tilted lingually
There are mandibular tori present
σ� there is a high lingual frenum
σ� All are correct
74. Occlusal rest preparation should be
σ� spoon shaped
At least 1/3 the bucco lingual width of the occlusal surface
σ� at least one millimetre deep
σ� all are correct
75. Incisal rests
σ� a generally more positive vertical stops than cingulum rests
σ� may interfere with the opposing occlusion
σ� should not be used on maxillary incisors
σ� ll are correct
76. The function of the guide plate is to
σ� Help establish a definitive path of insertion/dislodgement
σ� Stabilize the RPD by controlling its horizontal position
σ� Provide contact with the adjacent tooth
σ� All are correct
77. In which of the following mandibular positions are the teeth in contact?
σ� Centric Relation and Centric Occlusion
σ� Edge to Edge Incisor Contact
σ� Maximum Mandibular Protrusion
σ� Negative, Horizontal and Vertical Overlaps at incisors
σ� All are correct
78. A clasp assembly should
σ� have a retentive arm with adequate length and taper for flexibility
σ� have a retentive arm that terminates in an undercut
σ� have elements that considered together provide 180 degree encirclement
σ� All are correct
79. Reason (s) for selecting lingual plate major connectors is/are?
σ� the presence of lingual tori
σ� Anticipated loss of one or more of the remaining teeth
σ� A high lingual frenum
σ� All are correct
80. Function of the teeth is /are
σ� Mastication
σ� Phonation
Esthetic
All are correct
81. Indication of Removable Partial Denture
Large edentulous space, deep undercut of abutment, not posterior of abutment
σ� Periodontitis of abutment, esthetic for posterior tooth, not posterior of abutment
σ� Large edentulous space, not posterior of abutment, periodontitis of abutment
σ� Deep undercut of abutment, periodontitis of abutment, not posterior of abutment
82. An ideal design framework of RPD should be:
σ� Determine the path of insertion
As guiding planes
σ� Locate retention areas
Locate the height of contour
σ� All are correct
83. An ideal design a major connector should possess the following qualities:
σ� Unification
σ� Stress distribution
σ� Cross Arch stabilization
σ� Rigidity
σ� All are correct
84. The diagnosis of master cast of RPD be for design framework should be:
Determine path of insertion
Determine high of contour
Determine parallelism of abutments
Determine guiding planes
σ� All are correct
85. The goal of extension of RPD framework should be:
σ� Stability framework
Function, Occlusion
Tissues adaptation
σ� All are correct
86. The function of the guide plate is to:
σ� Help establish a definitive path of insertion/ dislodgement
σ� Stabilize the RPD by controlling its horizontal position
Provide contact with the adjacent tooth
σ� All are correct
87. What would be the best denture base connectors when there is limited inter occlusal space (<3mm)
Open lattice type
Mesh type
σ� All metal base
All plastic base
88. All of the following clasps are infrabulge clasps except ?
σ� Ibar
σ� Modified T bar
σ� Roach clasp
σ� Akers clasp
89. Which of the following clasps commonly utilize lingual undercut ?
Ring clasp , I bar clasp
Extended arm clasp, Akers clasps
Half and half clasp, Back action clasp
Half and half clasp, Ring clasp
90. A cingulum rest should be placed
σ� between the occlusal and middle thirds of the incisors teeth
Above the middle third of the incisor teeth
σ� on the disto incisal edges of the incisor teeth
σ� at the junction of the gingival and middle thirds of the incisor teeth
91. An area undercut may preclude the selection of
σ� A suprabulge clasp
σ� An infrabulge clasp
σ� A Half and half clasp
σ� A combination clasp
92. A removable partial denture may be:
σ� All tooth supported
σ� Tooth and tissue supported
σ� All tooth supported and tissue supported
σ� All tissue supported
93. Following condition(s) is/are also called as distal extension partial denture:
σ� Kennedy’s class IV
σ� Applegate class VI
Kennedy’s class I
Applegate class V
94. Floor of the rest seat should be:
σ� Convex
σ� Concave
σ� Flat
Spoon shaped
95. Following structure of RPD gives both occlusal support and horizontal stabilization:
Occlusal rest
Interproximal occlusal rest
σ� Internal occlusal rest
σ� Indirect retainer
96. Removable partial denture movements away from tissue may occur due to following except:
Pull of food
σ� Moving border tissues
σ� Gravity
σ� Mastication
97. Parts that offer support for removable partial denture are following:
σ� Rest and reciprocal arm
Rest and retentive arm
σ� Rest and denture base
σ� Rest and minor connector
98. Denture bases of removable partial denture offer:
σ� Primary retention
σ� Mechanical retention
Primary and mechanical retention
Secondary retention
99. In distal extension denture base, when there is no modification area exists on opposite side of the arch a………clasp is suitable at that side:
σ� Ring clasp
Back action clasp
σ� Reverse circumferential clasp
Embrasure clasp
100. Multiple clasps are joined at :
σ� Tip of retentive terminals
Tip of reciprocal terminals
σ� Back of occlusal rests
101. Following parts of a removable partial denture may act as indirect retainer, except:
σ� Rests
σ� Proximal plates
σ� Minor connector supporting rests
Retentive tip
102. When designing palatal major connectors ,relief should for:
σ� Palatal torus
σ� Ridge area
σ� Elevated mid suture line
σ� Rugae areas
103. Kennedy classification is determined by:
σ� The most anterior tooth missing
σ� The first tooth to be lost
σ� The largest tooth in the space
σ� The most posterior tooth missing
104. Labial bar is indicated when:
σ� There is a diastema
σ� There is labial inclination of teeth
σ� There is linqual inclination of teeth
σ� There are periodontally weak teeth
105. The superior border of linqual bar should be:
σ� Deep in the linqual sulcus
σ� At least 4 mm below the gingival margin
σ� At the cingulum of anterior teeth
σ� At least 7 mm below the gingival margin
106. Tripoding is the method used:
σ� for giving clasp assemblies at 3 points
σ� for recording the relation of the cast to the surveyor
σ� to determine the areas on the tooth where the gingivally approaching clasp, occlusal rest of the reciprocal arm are going to be placed
σ� to have reproducible position of the cast on the surveyor
107. What are the functions of an indirect retainer:
σ� to prevent horizontal dislodgement of the distal extension bases of removable partial denture.
σ� to connect the parts of the prosthesis located on one side of the arch with those on the opposite side.
σ� to prevent vertical dislodgement of the distal extension base of removable partial denture.
σ� to link the major connector and other parts of the prosthesis together
108. In the mesial rest, guide plane and i-bar design, reciprocation is achieved by:
σ� flexible plating
σ� minor connectors
σ� major connectors
σ� retentive clasp arm
109. All of the following are advantages of the gingivally approaching clasps as compared to occlusally approaching clasps, except:
σ� less tooth contact
σ� less distortion of coronal contours
σ� less bothersome to vestibular tissues
σ� esthetically superior in most cases
110. Stability is mainly against:
σ� horizontal forces
σ� functional forces
σ� horizontal forces and functional forces
σ� forces against removal of prosthesis
111. An undercut in relation to tooth lies:
σ� below the survey line
σ� above the survey line also
σ� below the survey line and above the survey line also
σ� on occlusal surface
112. Guiding plane are:
σ� usually single
σ� usually multiple
σ� usually parallel
σ� usually multiple and usually parallel
113. Indirect retainer:
σ� assists direct retainer
σ� resists lever action
σ� prevents displacement of RPD
σ� maintains all of the above
114. Rest:
σ� is placed on rest seat always
σ� need not have rest seat
σ� mainly offers stability
σ� is placed on rest seat always and mainly offers stability
115. In removable partial denture, health of gingival tissue is ensured by:
σ� keeping minimum of 6 mm distance for major connector
σ� keeping minimum of 4 mm distance for major connector
σ� keeping minimum of 6 mm distance for major connector and keeping minimum of 4 mm distance for major connector
σ� minor connectors joining major connector at <90>
116. Method to determine height of floor of the mouth is:
σ� use of periodontal probe
σ� use of straight probe
σ� use of individualized impression tray
σ� use of periodontal probe and use of individualized impression tray
117. Sublingual bar is placed:
σ� inferior to lingual bar
σ� inferior and posterior to lingual bar
σ� inferior and anterior to lingual bar
σ� inferior to lingual bar and inferior and anterior to lingual bar
118. A removable partial denture may be :
σ� all tooth support supported
σ� tooth and tissue supported
σ� all tooth support supported and tooth and tissue supported
σ� all tissue supported
119. Guiding plane are:
σ� usually single
σ� usually multiple
σ� usually parallel
σ� usually single and usually multiple
120. Contraindication for sublingual bar are following except:
σ� lingual tori
σ� high lingual frenum
σ� large tongue
σ� high elevation of floor of mouth
121. A continuous bar is otherwise known as:
σ� kennedy bar
σ� cingulum bar
σ� kennedy bar and cingulum bar
σ� linguoplate
122. Continuous bar lies:
σ� on lingual side of anterior teeth
σ� on cingulum of anterior teeth
σ� on or above cingula of anterior teeth
σ� on incisal third of the lingual side of the anterior teeth
123. A minor connector located at embrasure should be:
σ� Thinnest toward lingual surface
σ� Tapering away from contact area
σ� Thickest toward buccal surface
Thickest toward lingual surface
124. When a minor connector contacts tooth surface on either side of embrasure, it should:
σ� Abruptly end at the tooth
σ� Be sharply angled
σ� Not have space between it and the tooth
σ� All of the above are true
125. Bulkiest position of a proximal minor connector is towards its:
σ� Buccal side
σ� Centre
σ� Lingual side
σ� Inferior
126. Angle at junction between major connector and denture base minor connector should be:
σ� > 90 degrees
σ� > 110 degrees
σ� 90 degrees
σ� < = 90 degrees
127. Minor connector for mandibular distal extension will extend unto:
σ� One-third the length of edentulous ridge
σ� Two-third the length of edentulous ridge
σ� Entire length of edentulous ridge
σ� Half the length of edentulous ridge
128. Minor connector for maxillary distal extension denture base extend unto:
σ� One-third the length of edentulous ridge
σ� Two-third the length of edentulous ridge
σ� Entire the length of edentulous ridge
σ� Half the length of the edentulous ridge
129. Tissue stops are useful in:
σ� Stabilizing framework during processing
σ� Stops the tissue impingement by tray
σ� Stabilizing framework during processing and Stops the tissue impingement by tray
σ� Engaging buccal slope of the residual ridge
130. Finishing line junction with major connector should have angle:
σ� =90 degrees
σ� < =90 degrees
σ� > =90 degrees
σ� > 90 degree
131. Small window in relief wax distal to terminal abutment in distal extension denture base removable partial denture acts as:
σ� Tissue stop
σ� Finishing line
σ� Finishing index tissue stop
σ� Nail head retention
132. Setting of a RPD may occur due to one of the following reasons, except:
σ� Improper rest design
σ� Flow of amalgam underneath restorations
σ� Giving canine rest seat
σ� Intrusion of abutment
133. Deepest part of a rest seat is towards:
σ� Disto- buccal line angle
σ� Disto-lingual line angle
σ� Central fossa
σ� Marginal ridge
134. Marginal ridge for a rest seat should be reduced by at least:
σ� 1mm
σ� 2mm
σ� 1.5mm
σ� 3mm
135. An angle > 90 degrees between rest and its minor connector may result in:
σ� Slippage of prosthesis
σ� More support for prosthesis
σ� Orthodontic correction of the abutment
σ� All are corrects
136. When rest seals are prepared at inter proximal area on two adjacent teeth:
σ� It should extend for lingually
σ� They avoid wedging by the framework
σ� They do not shunt food
σ� It should extend for lingually and They avoid wedging by the framework
137. Interproximal occlusal rest seats:
σ� Violate contact points
σ� Extend far lingually
σ� Do not avoid wedging effect by framework
σ� All are corrects
138. Internal occlusal rests are indicated in:
σ� Tooth tissue supported class I designs
σ� Tooth tissue supported class II designs
σ� Tooth supported class III designs
σ� All distal extension denture base designs
139. Difference between internal occlusal rest and internal attachment is that:
σ� Internal attachment also provides support
σ� Internal attachment rest also provides retention
σ� Internal attachment rest also provides stabilization
σ� Internal attachment also provides retention
140. When internal occlusal rests are used, we can use:
σ� Buccal reciprocal arm
σ� Proximal retentive arm
σ� Lingual reciprocal arm
σ� Lingual retentive arm
141. Advantage of internal occlusal rest are following except:
σ� Provide retention
σ� Eliminates visible clasp arm
σ� Rest seat is located in a more favorable position
σ� Provides support and stabilization
142. RPD movements away from tissues may occur due to following except:
σ� Pull of food
σ� Moving border tissues
σ� Gravity
σ� Mastication
143. Vertical tissue ward movement of denture is controlled by following except:
σ� Total amount of occlusal load applied
σ� Retentive tip of the clasp
σ� Accurately fitting denture base
σ� Tissue of residual ridge
144. Usually rest seats are located at:
σ� The junction of enamel and dentin
σ� Enamel
σ� Dentin
σ� At cement enamel junction
145. Floor of the cingulum rest seats is placed towards:
σ� Mesial axial wall
σ� Distal axial wall
σ� Cervical end
σ� Incisal end
146. Approach for a cingulum rest is:
σ� Perpendicular to lingual slope
σ� Horizontal to lingual slope
σ� Parallel to lingual slope
σ� Cervical to lingual slope
147. Most apical portion of a cingulum rest is:
σ� Mesial corner
σ� Distal corner
σ� Distal corner
σ� Floor of the preparation
148. Incisal rests:
σ� Mostly used as axillary rests
σ� Mostly used as indirect retainer
σ� Mostly used as axillary rests and Mostly used as indirect retainer
σ� Mostly preferred for maxillary anterior
150. Full incisal rests are indicated in following except:
σ� To provide anterior guidance
σ� To abrade anatomy of teeth
σ� To provide retention
σ� To provide stabilization
149. Disadvantages of incisal rest are following except:
σ� Less esthetic
σ� Unfavorable leverage on teeth
σ� Causes intrusion of anterior teeth
σ� Causes orthodontic movement of teeth
150. Full incisal rests are indicated in following except:
σ� To provide anterior guidance
σ� To abrade anatomy of teeth
σ� To provide retention
σ� To provide stabilization
{"name":"3DD\/Partial Denture\/Dr.Sok Ly\/", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"1. A clasp most common use is, 2. Infrabulge clasps originate, 3. Reciprocation between bracing and retentive components requires","img":"https://cdn.poll-maker.com/20-806795/-.jpg?sz=1200-00000000001000007495"}
More Quizzes
How Well Do U Know Me?
1680
Why your business is not successful yet? Take this quiz to find out what you need to focus on today to create a successful business.
Each yes = 1 point. Count your points, it will help you know your results.
1260
Which kind of psychopath lays in you?
10511
Quiz de catecolaminas
5219
Who Looks Like Me - Find Your Doppelgänger
201019225
BLACKPINK's Jisoo: What Is Her Favorite Color?
201030766
5th Grade Literature - Free Trivia Questions for Kids
201027031
What's My Hair Type? Free with Instant Results
201019038
Am I Buddhist - How Buddhist Are You?
201022359
Am I Being Sexually Harassed? - Workplace Scenarios
201018503
Solar Eclipse - When Is the Next One After 2024?
201030157
Pop Music Trivia - Test Your Knowledge for Free
201017851