Chir Management P1 201 to q 249
201) A previously healthy 45-year-old man presents with a 9-month history of a slow-growing, painless right neck mass. He is a nonsmoker and has no significant past medical history. On examination, there is a nontender, discrete, 3-cm mass over the angle of the right mandible. Facial muscle function and sensation are normal. An oropharyngeal examination is normal. Which of the following is the best next step in the management of this patient?
. antibiotics
. Excisional biopsy
. Observation with re-evaluation in 2–4 weeks
. Superficial parotidectomy
. Chest x-ray
202) A 63-year-old man underwent a 3-vessel coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) 5 hours ago. Initially, his mediastinal chest tube output was 300 mL blood/h, but an hour ago, there was no further evidence of bleeding from the tube. His mean arterial pressure has fallen, and several fluid boluses were administered. His central venous pressure (CVP) is elevated to 20 mm Hg, and he has required the addition of inotropes. Which of the following is the best management strategy?
. Addition of vasopressors along with the inotropes
. Transfusion of packed red blood cells
. Return to the operating room for exploration of the mediastinum
. Placement of an intraaortic balloon pump
. Infusion of streptokinase into the mediastinal chest tube
203) An 89-year-old man has lost 30 lb over the past 2 years. He reports that food frequently sticks when he swallows. He also complains of a chronic cough. Barium swallow is shown here. What is the best treatment option for this patient?
Placement of an esophageal stent
. Diverticuloplasty
. Excision of the diverticulum
. Excision of the diverticulum and administration of a promotility agent
. Excision of the diverticulum and cricopharyngeal myotomy
204) A 23-year-old man presents to the emergency department with a soft-tissue injury to the left lower extremity. The injury was sustained 8 hours earlier in a motorcycle accident on a gravel road. On examination, the patient has a 7-cm deep laceration to the calf, with visible road debris. He had full tetanus immunization as a child and a tetanus booster immunization at age 15. Appropriate management of this injury would include which of the following?
Irrigation and debridement of the wound
. Irrigation and debridement of the wound; tetanus toxoid and tetanus immune globulin
. Irrigation and debridement of the wound; tetanus toxoid
. Irrigation and debridement of the wound; IV antibiotics
. Tetanus toxoid and IV antibiotics
205) A 6-year-old boy presents to the emergency department with a painful, markedly swollen elbow. While ice-skating, he fell with his arm outstretched. Radiographs of the elbow demonstrate a displaced, supracondylar fracture of the humerus. On examination, there is pain on passive flexion at the wrist and a decreased radial pulse, with diminished capillary refill in the hand. Which of the following is the most appropriate management of this injury?
Admission to hospital for close observation, with immobilization of the elbow at 90 of flexion
Closed reduction with percutaneous pinning under general anesthesia
Open reduction and pinning under general anesthesia
Open reduction with pinning, and exploration of the brachial artery
Open reduction with pinning, exploration of the brachial artery, and decompression fasciotomy of the forearm fascial compartments
206) A 25-year-old man is stabbed in the right chest. He comes in fully awake and alert, and, in a normal tone of voice, he states that he feels short of breath. His vital signs are normal and stable. On physical examination, he has no breath sounds at the right base, and only faint breath sounds at the apex. He is dull to percussion over the right base. A chest x-ray film confirms that he has a hemothorax on that side. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Oxygen by mask, analgesics, and no specific intervention
. Intubation and use of a respirator
. Insertion of a chest tube in the right second intercostal space
. Insertion of a chest tube at the right base
. Exploratory thoracotomy
207) A 35-year-old woman with a history of previous right thyroidectomy for a benign thyroid nodule now undergoes completion thyroidectomy for a suspicious thyroid mass. Several hours postoperatively, she develops progressive swelling under the incision, stridor, and difficulty breathing. Orotracheal intubation is successful. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step?
Fiberoptic laryngoscopy to rule out bilateral vocal cord paralysis
. Administration of intravenous calcium
. Administration of broad-spectrum antibiotics and debridement of the wound
. Wound exploration
. Administration of high-dose steroids and antihistamines
208) In a 6-month-old previously healthy male infant, an abnormality is revealed during a routine diaper change, as illustrated in Figure 6-19. The parents have noted this finding on and off on several occasions over the last month. On each occasion, the child has been feeding well, and is content and playful. Which of the following is the most appropriate management at this time? pic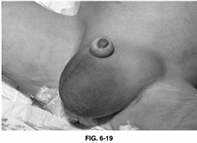

Antibiotics
. Reassurance to the parents that the abnormality will resolve without intervention
. Referral to the emergency department for immediate surgical consultation
. Referral for elective surgical repair
. Scrotal support
209) A 60-year-old man seeks medical attention because of recurrent urinary tract infections. The patient also reports a history of increasing difficulty in urination (decreased flow, straining, and hesitancy) over the last several months. A prostate-specific antigen (PSA) level is mildly elevated and a prostate biopsy proves benign. Which of the following is the most appropriate initial management of this patient with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)?
. α-Adrenergic blocker
. 5-alpha reductase inhibitor
. α-Adrenergic blocker and 5-alpha reductase inhibitor
. Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP)
. Open prostatectomy
210) An 83-year-old woman presents to a mammographic facility for a screening mammogram. The technician notices a mass in the lateral right breast. The patient denies any breast pain, nipple discharge, skin changes, or breast trauma. A right breast CC view is shown in Figure 6-7. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management? pic

. Incisional biopsy
. Needle biopsy
. lumpectomy, axillary dissection, and irradiation
. Total mastectomy
. Modified radical mastectomy
211) A 25-year-old unhelmeted man involved in a motorcycle collision has multiple cerebral contusions on head computed tomographic (CT) scan. He is agitated but hemodynamically stable, with a heart rate of 80 beats per minute and a mean arterial pressure (MAP) of 90 mm Hg. An intracranial pressure monitor is placed, and the initial ICP reading is 30 mm Hg. Which of the following is the most appropriate in the management of his traumatic brain injury (TBI) over the next few days?
. Hyperventilation to maintain a cerebral PCO2 of 25 to 30 mm Hg
. Administration of neosynephrine to increase his MAP and, consequently, his cerebral perfusion pressure (CPP)
. Administration of mannitol (1 g/kg) to reduce his ICP
. Placement of the patient in Trendelenburg position to increase cerebral perfusion
. Avoidance of all sedating drugs in the first 24 to 48 hours in order to accurately assess his neurologic status
212) A 50-year-old woman complains of headaches and lateralizing weakness. A CT scan of the brain reveals an irregular mass in the right cerebral hemisphere. A biopsy documents that this is a glioblastoma. Which of the following is the best treatment strategy for potential cure?
Chemotherapy with temozolomide alone
. Combination chemotherapy with carmustin, cisplatin, and temozolomide
. External beam radiation alone
. Surgical resection alone
. Combined surgical resection, external beam radiation, and chemotherapy with temozolomide
213) An 85-year-old man presents to the emergency room with an acute onset of midepigastric pain, nausea, vomiting, and hiccups starting 2 days ago. He is unable to keep any food down. Past history is pertinent for a long-standing hiatal hernia, hypertension, and diet-controlled diabetes. Examination reveals vital signs of pulse rate 82/min, BP 100/52 mmHg, respiratory rate 16/min, and temperature 97.2°F. The patient is in no acute distress, but has epigastric tenderness without guarding. Laboratory analysis revealed a hematocrit of 46 and a normal white blood cell (WBC) count. A chest x-ray is shown in Figure 6-5a. A fluoroscopically guided NG tube was placed using contrast, and his stomach was decompressed. After adequate fluid and electrolyte resuscitation, an upper gastrointestinal (UGI) contrast study was obtained and is shown in 6-5b. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?pic

Laparotomy or laparoscopy and operative repair
. continued NG tube decompression and initiation of total parenteral nutrition (TPN)
. Thoracotomy or thoracoscopy and operative repair
. Endotracheal intubation and initiation of ventilatory support
. Upper endoscopy
214) A 49-year-old woman presents to her physician with dysphagia, regurgitation of undigested food eaten hours earlier, and coughing over the last 6 months. She was hospitalized 1 month ago for aspiration pneumonia and successfully treated with antibiotics. Examination reveals a thin-appearing woman with normal vital signs and unremarkable chest, heart, and abdominal examination. A UGI contrast study is performed and reveals a pharyngoesophageal (Zenker’s) diverticulum. Which of the following is the most important aspect of treatment?
. Resection of the diverticulum
. Cricopharyngeal muscle myotomy
. H2 blockers
. Elevation of the head of the bed
. diverticulopexy
215) A 40-year-old alcoholic is brought to the emergency department with frostbite to both lower extremities. His core body temperature is 36°C. Which of the following is the most appropriate initial treatment for the patient’s thermal injury?
Sympathectomy without any delay
. Debridement of devitalized tissues
. Slow rewarming at room temperature
. Slow rewarming with dry heat
. Rapid rewarming in warm water
216) A 35-year-old woman presents with a serum calcium level of 15.2 mg/dL and an elevated parathyroid hormone level. Following correction of the patient’s hypercalcemia with hydration and furosemide, which of the following is the best therapeutic approach?
Administration of steroids
. Radiation treatment to the neck
. Neck exploration and resection of all 4 parathyroid glands
. Neck exploration and resection of a parathyroid adenoma
. Avoidance of sunlight, vitamin D, and calcium-containing dairy products
217) A 65-year-old man presents to the emergency department with sudden onset of pain and weakness of the left lower extremity of 2-hour duration. Past history reveals chronic atrial fibrillation following a myocardial infarction 12 months ago. On examination, he is found to have a cool, pale left lower extremity with decreased strength and absent popliteal and pedal pulses. The opposite leg has a normal appearance with palpable pulses. Following successful treatment for an embolus to the left femoral artery with no evidence of a reperfusion injury (anticoagulation with heparin and thromboembolecctomy), which of the following long-term treatments would most likely decrease the chance of recurrent embolus?
. anticoagulation
. Exercise program
. Coronary artery bypass grafting
. Aortofemoral bypass grafting
. Placement of a vena cava filter
218) A 63-year-old man has a chylothorax that after 2 weeks of conservative therapy appears to be persistent. The chest tube output is approximately 600 mL/day. Appropriate management at this time includes which of the following procedures?
Neck exploration and ligation of the thoracic duct
. Subdiaphragmatic ligation of the thoracic duct
. Thoracotomy and repair of the thoracic duct
. Thoracotomy and ligation of the thoracic duct
. Thoracotomy and abrasion of the pleural space
219) A 32-year-old woman has a CXR screening, and a 1.5-cm mass is noted in the right lower lobe. She is a nonsmoker. Bronchoscopy shows a mass in the right lower lobe orifice, covered with mucosa. Biopsy indicates this is compatible with a carcinoid tumor. Imaging suggests ipsilateral mediastinal lymph node involvement but no extrathoracic disease. Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment plan?
. Right lower lobectomy and mediastinal lymph node dissection
. Right lower lobectomy and mediastinal lymph node dissection followed by adjuvant chemotherapy
. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy followed by right lower lobectomy and mediastinal lymph node dissection
. Neoadjuvant chemoradiation followed by right lower lobectomy and mediastinal lymph node dissection
. Chemoradiation
220) A 55-year-old woman presents with a 6-month history of weight loss, abdominal cramps, and intermittent nonbloody diarrhea. On examination, her abdomen is mildly distended and there is a palpable mass in the right lower quadrant. Stool cultures yield normal fecal flora. CT scan with oral contrast demonstrates an inflammatory mass in the right lower quadrant, with thickening of the terminal ileum and ileocecal valve.Initial management should include which of the following?
Antibiotics and IV fluids
. lactose-free diet
. antispasmodics
. Nutritional supplementation and systemic steroids
. laparotomy
221) A 33-year-old woman is found to have a palpable thyroid nodule during a routine medical checkup. A sonogram confirms the presence of a solid, 1.5-cm nodule in the right lobe of the thyroid gland. Fine needle aspirate cytology (FNA) is reported as "follicular tumor, otherwise unspecified." At surgery, a frozen section is read as follicular carcinoma. With the neck open, the surgeon can feel for enlarged jugular and peritracheal lymph nodes, and finds none. Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment?
Enucleation of the tumor
. Right thyroid lobectomy
. Total thyroidectomy
. Total thyroidectomy plus postoperative radioactive iodine
. Total thyroidectomy, radical neck dissection, and postoperative radioactive iodine
222) A 63-year-old woman with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) presents with a several-week history of fever, night sweats, weight loss, and cough. Her CXR is noted to have a density in the left upper lobe with a relatively thin-walled cavity. Bronchoscopy and computed tomographic (CT) scan are suggestive of a lung abscess rather than a malignant process. Which of the following is the most appropriate initial management of this patient?
Percutaneous drainage of the lung abscess
. Systemic antibiotics directed against the causative agent
. Tube thoracostomy
. Left upper lobectomy
. Surgical drainage of the abscess
223) A 4-year-old previously healthy girl presents to the emergency department with a 24-hour history of rectal bleeding and dizziness. She has no other gastrointestinal symptoms. On examination, she appears pale. Her heart rate is 140 beats/min, and she has a 20 mmHg postural drop in systolic blood pressure. The child’s abdomen is nondistended and nontender, and fresh blood and clots are in the rectal vault on rectal examination. Definitive management of this child should include which of the following?
Immediate exploratory laparotomy
. IV fluid resuscitation, transfusion with blood products as indicated, followed by a laparotomy with Meckel’s diverticulectomy and ileal resection
. IV fluid resuscitation, followed by a colonoscopic polypectomy
. hemorrhoidectomy
. Stool softeners and topical steroids
224) A 29-year-old nonhelmeted motorcycle driver is involved in a single vehicular crash, resulting in a significant closed-head injury. He is intubated in the field and transported to a level 1 trauma center. On arrival, he is oxygenating well with assisted ventilation and has a normal blood pressure and moderate tachycardia. His Glasgow Coma Score is 7, and his pupils are equal and sluggishly reactive. After stabilization in the emergency department, the patient undergoes a CT scan of the head that demonstrates a small amount of subarachnoid blood and a right frontal lobe contusion with edema with no midline shift. CT scan of the abdomen is normal. The patient is transferred to the ICU. The optimal initial management of this patient’s intracranial pressure (ICP) would be which of the following?
. craniotomy
. Fluid restriction, hyperventilation, and osmotic diuresis
. Fluid restriction, hyperventilation, and ventriculostomy
. Hyperventilation and IV steroids
. normovolemia, normocarbia, sedation, and ventriculostomy
225) A 49-year-old obese man has become irritable, his face has changed to a round configuration, he has developed purplish lines on his flanks, and he is hypertensive. A 24-hour urine collection demonstrates elevated cortisol levels. This is confirmed with bedtime cortisol measurements of 700ng/mL. Which of the following findings is most consistent with the diagnosis of Cushing disease?
. Decreased ACTH levels
. Glucocorticoid use for the treatment of inflammatory disorders
. A 3-cm adrenal mass on computed tomography (CT) scan
. Suppression with high-dose dexamethasone suppression testing
. A 1-cm bronchogenic mass on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
226) A 70-year-old man presents with back pain and increasing difficulty with initiating a urinary stream. On rectal examination, he is found to have a hard, irregularly enlarged prostate. He has an elevated prostate-specific antigen (PSA), and osteoblastic lesions in the vertebral column and bones of the pelvis. A needle biopsy of the prostate shows well-differentiated adenocarcinoma. Which of the following is the treatment of choice?
. Radical prostatectomy
. Transurethral prostatectomy
. Cytotoxic chemotherapy
. Hormonal manipulation
. radiotherapy
227) A 69-year-old man with mild hypertension and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) presents with transient ischemic attacks and the angiogram shown here. Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment recommendation? pic

. Medical therapy with aspirin 325 mg/day and medical risk factor management
. Medical therapy with warfarin
. Angioplasty of the carotid lesion followed by carotid endarterectomy if the angioplasty is unsuccessful
. Carotid endarterectomy
. Medical risk factor management and carotid endarterectomy if neurologic symptoms develop
228) A 5-week-old infant presents with a 1-week history of progressive nonbilious emesis, associated with a 24-hour history of decreased urine output. The infant continues to be active and eager to feed. On examination, the infant has a sunken fontanelle and decreased skin turgor. The abdomen is scaphoid, and with a test feed, there is a visible peristaltic wave in the epigastrium. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management of this infant?
. Immediate surgical exploration
. Send the child home with an oral electrolyte rehydration solution
. Change the infant’s formula and feeding regimen
. IV fluid resuscitation, followed by surgical intervention
. Initiate therapy with a prokinetic agent
229) A 49-year-old woman has a firm, 2-cm mass in the right breast that has been present for 3 months. Mammogram has been read as "cannot rule out cancer," but it cannot diagnose cancer either. A fine-needle aspiration of the mass (FNA) and cytology do not identify any malignant cells. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management? Chir Management P1
. Reassurance and reappointment in a year
. Repeat mammogram and FNA in 1 month
. Core or incisional biopsies
. Lumpectomy and axillary dissection
. Modified radical mastectomy
230) A 60-year-old man sees a urologist for what he describes as bloody urine. A urine sample is positive for cytologic evidence of malignancy. Cystoscopy confirms the presence of superficial transitional cell carcinoma. Which of the following is the recommended treatment for stage A (superficial and submucosal) transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder?
. Topical (intravesicular) chemotherapy
. Radical cystectomy
. Radiation therapy
. Local excision and topical (intravesicular) chemotherapy
. Systemic chemotherapy
231) A 36-year-old man presents to the emergency room with renal colic. His vital signs are normal and a urinalysis shows microscopic hematuria. A radiograph reveals a 1.5-cm stone. Which of the following is the most appropriate management of this patient?
. Hydration and analgesics
. α-Adrenergic blocker
. Extracorporeal lithotripsy
. Percutaneous nephrostomy tube
. Open surgery to remove the stone
232) An 8-month-old boy is seen by a pediatrician for the first time. The physician notes that there are no testes in the scrotum. Which of the following is the optimal management of bilateral undescended testicles in an infant?
. Immediate surgical placement into the scrotum
. Chorionic gonadotropin therapy for 1 month; operative placement into the scrotum before age 2 if descent has not occurred
. Observation until age 2; operative placement into the scrotum if descent has not occurred
. Observation until age 5; if no descent by then, plastic surgical scrotal prostheses before the child enters school
. No therapy; reassurance of the parent that full masculinization and normal spermatogenesis are likely even if the testicle does not fully descend
233) A 55-year-old man presents to the emergency department with left lower quadrant abdominal pain. The pain has been present for 1 week, but has increased in intensity over the last 2 days associated with nausea, constipation, and dysuria. Past history is unremarkable. Examination reveals a temperature of 101°F, pulse rate of 95/min, BP of 130/70 mmHg, and normal heart and lung examinations. Abdominal examination reveals fullness and marked tenderness in the left lower quadrant, with voluntary guarding and decreased bowel sounds. Laboratory tests reveal a WBC count of 18,000 with a left shift and 20–50 WBCs in the urinalysis. A CT scan of the abdomen reveals a thickened sigmoid colon with pericolonic inflammation. He is admitted to the hospital for treatment. We find this patient has diverticulitis. Which of the following is the most appropriate management of this patient?
. NPO, IV fluids, and IV antibiotics for gram-negative and anaerobic coverage
. NPO, IV fluid hydration, followed by immediate sigmoid colon resection
. NPO, IV fluids, and anticoagulation
. NPO, IV fluids, evaluation of stool for Clostridium difficile toxin, and either metronidazole or vancomycin antibiotic therapy
. NPO, IV fluids, initiation of bowel preparation for elective sigmoid colon resection during the current hospitalization
234) A 39-year-old woman completed her last course of postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer 6 months ago. She now comes to the clinic complaining of constant back pain for about 3 weeks. She is tender to palpation over two well-circumscribed areas in the thoracic and lumbar spine. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
. CT scan of the trunk
. Needle biopsy of the tender spots
. Radionuclide bone scan
. Sonogram of the affected areas
. X-ray films of the affected areas
235) A 42-year-old woman returns to the clinic following an uneventful biopsy for a well-defined, mobile mass. The pathology report describes the mass as a fibro adenoma, but LCIS is identified in the breast parenchyma adjacent to the fibro adenoma and extending to the margin of resection. She has no current illnesses, is on no medications, and her family history is negative for breast cancer. Breast imaging studies show fatty breasts with no abnormal findings except for the fibro adenoma. Which of the following is the most appropriate management option?
. re-excision of the biopsy cavity to gain negative margins of resection
. Ipsilateral mastectomy
. Contralateral breast biopsy
. Observation including examinations and mammography
. Bilateral total mastectomies
236) A 59-year-old man is found to have a 6-cm thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm which extends to above the renal arteries for which he desires repair, but he is concerned about the risk of paralysis postoperatively. Which of the following maneuvers should be employed to decrease the risk of paraplegia after repair?
. Infusion of a bolus of steroids immediately postoperatively with a continuous infusion for 24 hours
. Maintenance of intraoperative normothermia
. Clamping of the aorta proximal to the left subclavian artery
. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) drainage
. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation
237) A man who weighs 65 kg sustains second and third degree burns over both of his lower extremities when his pants catch on fire. When examined shortly thereafter, it is ascertained that virtually all of the skin from both groins to the tip of the toes, front and back, has been burned. According to the modified Parkland formula, which of the following is the approximate total amount of IV fluid that he can be expected to require during the first 24 hours post-burn?
. 3,460 mL
. 4,960 mL
. 6,760 mL
. 8,160 mL
. 11,360 mL
238) A 65-year-old man presents to the emergency department with sudden onset of pain and weakness of the left lower extremity of 2-hour duration. Past history reveals chronic atrial fibrillation following a myocardial infarction 12 months ago. On examination, he is found to have a cool, pale left lower extremity with decreased strength and absent popliteal and pedal pulses. The opposite leg has a normal appearance with palpable pulses. Which of the following is the most appropriate first step in management of this patient?
. echocardiography
. Anticoagulation with heparin
. Anticoagulation with warfarin
. arteriography
. Alkalinization of the urine with IV sodium bicarbonate
239) A 29-year-old woman with a history of difficulty becoming pregnant presents to her primary care physician and is diagnosed with Grave disease on iodine uptake scan; her thyrotropin (TSH) level is markedly suppressed and her free thyroxine (T4) level is elevated. She desires to conceive as soon as possible and elects to undergo thyroidectomy. After she is rendered euthyroid with medications preoperatively, which of the following management strategies should also be employed to reduce the risk of developing thyroid storm in the operating room?
. Drops of Lugol iodine solution daily beginning 10 days preoperatively.
. Preoperative treatment with phenoxybenzamine for 3 weeks.
. Preoperative treatment with propranolol for 1 week.
. Twenty-four hours of corticosteroids preoperatively.
. No other preoperative medication is required.
240) A 72-year-old woman with severe COPD who requires home oxygen is unable to ambulate inside her home without experiencing severe left hip pain. She was hospitalized 1 year ago for a viral pneumonia and was ventilator-dependent at that time for 6 weeks. On examination, her blood pressure is 165/80 mm Hg. She has weakly palpable bilateral femoral pulses. An angiogram demonstrates severe aortoiliac disease involving bilateral iliac vessels. Which of the following is the most appropriate vascular procedure for this patient?
. Femorofemoral bypass
. Axillofemoral bypass
. Femoropopliteal bypass
. Aortobifemoral bypass
. Common femoral and profunda femoral endarterectomise
241) A 52-year-old woman has terminal cervical cancer with extensive pelvic invasion, and requires strong opiate analgesia to control severe pain. Intermittent nausea and vomiting have precluded the use of oral agents. She was on fentanyl patches but she developed allergic skin reactions to the adhesive and now requests to be switched to parenteral medication. Because of prior chemotherapy treatments she has no available venous access, but she is willing to have her family administer intramuscular injections. Assuming equianalgesic dosages, which of the following would be the most appropriate pharmacotherapy?
. Codeine
. Hydromorphone (Dilaudid)
. Meperidine (Demerol)
. Methadone
. Morphine sulfate
242) A 71-year-old woman with a 40-year smoking history is noted to have a peripheral nodule in her left upper lobe on chest x-ray. Workup is consistent with small cell lung cancer with ipsilateral mediastinal lymph node involvement but no extrathoracic disease. What is the best treatment option for this patient?
. Thoracotomy with left upper lobectomy and mediastinal lymph node dissection
. Thoracotomy with left upper lobectomy and mediastinal lymph node dissection followed by adjuvant chemotherapy
. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy followed by thoracotomy with left upper lobectomy and mediastinal lymphnode dissection
. Neoadjuvant chemoradiation followed by thoracotomy with left upper lobectomy and mediastinal lymph-node dissection
. Chemoradiation
243) A 42-year-old homeless man presents with a 3-week history of shortness of breath, fevers, and pleuritic chest pain. Chest x-ray (CXR) reveals a large left pleural effusion. Thoracentesis reveals thick, purulent-appearing fluid, which is found to have glucose less than 40 mg/dL and a pH of 6.5. A chest tube is placed, but the pleural effusion persists. Which of the following is the most appropriate management of this patient?
. Placement of a second chest tube at the bedside and antibiotic therapy
. Infusion of antibiotics via the chest tube
. Intravenous antibiotics for 6 weeks
. Thoracotomy with instillation of antibiotics into the pleural space
. Thoracotomy with decortication and antibiotic therapy
244) During a campaign appearance, a political candidate is shot point blank in the right chest with a .22 caliber revolver. The entrance wound is well above the nipple line, just under the third rib, at the level of the anterior axillary line. His motorcade brings him to the emergency department, but he makes it a point to walk in, holding his right chest with a bloody hand and waving for the news media. A chest x-ray shows a hemothorax on the right, and the bullet is seen to be embedded in the right paraspinous muscles. A chest tube is placed in the right pleural cavity, and 650 mL blood is recovered. Over the ensuing 4 hours, he continues to drain between 250 and 350 mL blood per hour. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
. Continued observation and appropriate blood replacement
. A second chest tube in a better position to drain the blood
. Thoracotomy and ligation of bleeding vessels
. Thoracotomy, ligation of bleeding vessels, and removal of the bullet
. Thoracotomy and pneumonectomy
245) A 65-year-old woman presents to the physician’s office for a second opinion on the management options for recently diagnosed breast cancer. She presents with a 2.5-cm mass in the upper outer quadrant of the left breast associated with a palpable axillary node suspicious for metastatic disease. The remainder of her examination is normal. Mammography demonstrates the cancer and shows no other suspicious lesions in either breast. Chest x-ray, bone scan, and blood test panel, including liver function tests, are normal. Family history is positive for breast cancer diagnosed in her sister at age 65. Past history is unremarkable. The first physician recommended modified radical mastectomy. Which of the following is the most appropriate management option for locoregional control yielding results equally effective as mastectomy?
. Radical mastectomy
. lumpectomy, irradiation, and axillary node dissection
. Lumpectomy and axillary node dissection
. Irradiation of the breast and axilla
. quadrantectomy, irradiation, and axillary node dissection
246) During a hunting trip, a young man is bitten by a coyote. The animal is captured and brought to the authorities alive. Which of the following is the most important criterion to determine the patient's need for rabies prophylaxis?
. The patient's history of previous immunizations
. The patient's clinical course over the next few weeks
. Observing the animal's behavior over the next few days
. Killing the animal and examining the brain
. The events that took place have already established the need to proceed with rabies immunization
247) A 64-year-old man with a history of a triple coronary artery bypasses 2 years ago presents with peripheral arterial occlusive disease. His only medication is a thiazide diuretic. Which of the following medications would be most appropriate in the medical management of his atherosclerosis?
. Aspirin
. Warfarin
. Low-dose heparin
. High-dose heparin
. Low-molecular-weight heparin
248) A 45-year-old man presents to the physician’s office for evaluation of a skin lesion on his abdomen. He states that the lesion has been present for 1 year, but has recently enlarged over the last 2 months. The mass is nontender, and he is otherwise asymptomatic. Past history is unremarkable. Examination reveals a 3-cm, pigmented, irregular skin lesion located in the left lower quadrant of the abdomen, as shown in Figure 6-12. Heart, lung, and abdominal examination are normal. There are no palpable cervical, axillary, or inguinal lymph nodes. Chest x-ray and liver fun

. Wide excision with 2 cm margin
. Wide excision with 2 cm margin and SLN mapping
. Shave biopsy
. Excisional biopsy with 1–2 mm margins
. Mohs’ surgical excision
249) A 62-year-old man has had gastroesophageal reflux disease diagnosed by pH monitoring, and present for several years. He has been less than totally compliant with medical management, which he follows when the pain is bad, but discontinues when he feels better. Endoscopy and biopsies show severe peptic esophagitis, with Barrett's esophagus and early dysplastic changes, but no overt carcinoma. Additional tests show good esophageal motility, with low pressure in the lower esophageal sphincter and normal gastric emptying. Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment at this time?
. Heller myotomy of the lower esophageal sphincter
. Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication
. Transhiatal total esophagectomy
. Transthoracic resection of the lower esophagus
. Vagotomy, pyloroplasty, and fundic gastric wrap
{"name":"Chir Management P1 201 to q 249", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"How a u?.","img":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/3012/images/ogquiz.png"}
More Quizzes
Ő�昭彤陳星宇拍拖一周年紀念小測驗
1050
VVHV
30150
Questionnaire
1058
Zkušební kvíz gangu medvídka pú
940
Am I Emotionally Ready to Retire? Free Online
201019074
Electrosurgery Generator Knowledge Test - Free
201019959
Spanish-Speaking Countries & Capitals - Free Practice
201017584
What Minion Am I? Free to Find Your Despicable Me Match
201020845
What Harry Potter House Is My Dog? - Free Sorting Hat
201019552
Which Beauty and the Beast Character Are You?
201019167
Fandom: Test Your Knowledge for Free
201019357
Should We Move In Together? - Marriage vs Cohabitation
201019261