Microeconomics Mock Quiz Questions

Microeconomics Mastery Quiz
Test your knowledge and understanding of microeconomic principles with our engaging quiz designed for students, teachers, and anyone interested in economics. With 58 comprehensive questions, this quiz covers various topics essential for mastering microeconomic concepts.
Key Features:
- Variety of questions ranging from basic to advanced levels
- Immediate feedback on your performance
- Enhance your understanding of utility, profit, production, and market structures
When apples go on sale, people buy apples instead of bananas. This is an example of
The income effect.
The complement effect.
the substitution effect.
The elasticity effect.
You only buy two goods, pizza and burritos. Both goods are normal goods. When the price of pizza goes up, you buy fewer burritos. Based on this information, what must be true about the income and substitution effect for burritos?
The income effect is bigger than the substitution effect.
The substitution effect and income effect are the same size.
The substitution effect is bigger than the income effect.
The substitution effect and income effect have the effect of increasing the number of burritos you buy.
For which good would you expect a price increase of 10% to have the greatest income effect?
College tuition
A television set
A big mac
A gallon of gasoline
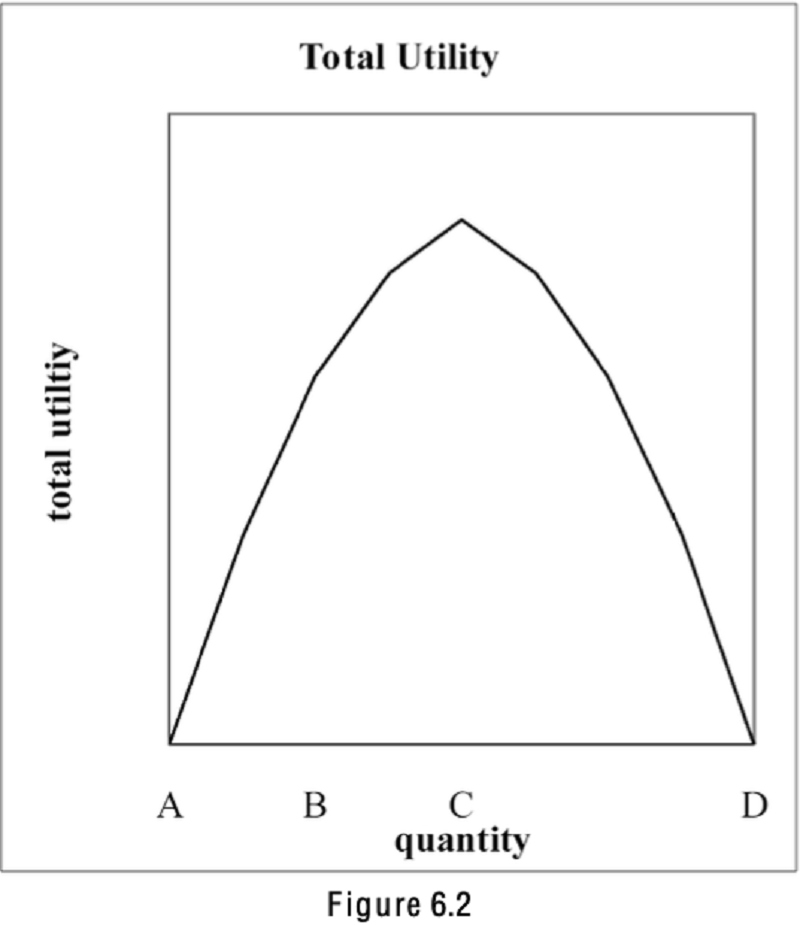
Refer to Figure 6.2. At what quantity is the satiation point?
A
B
C
D
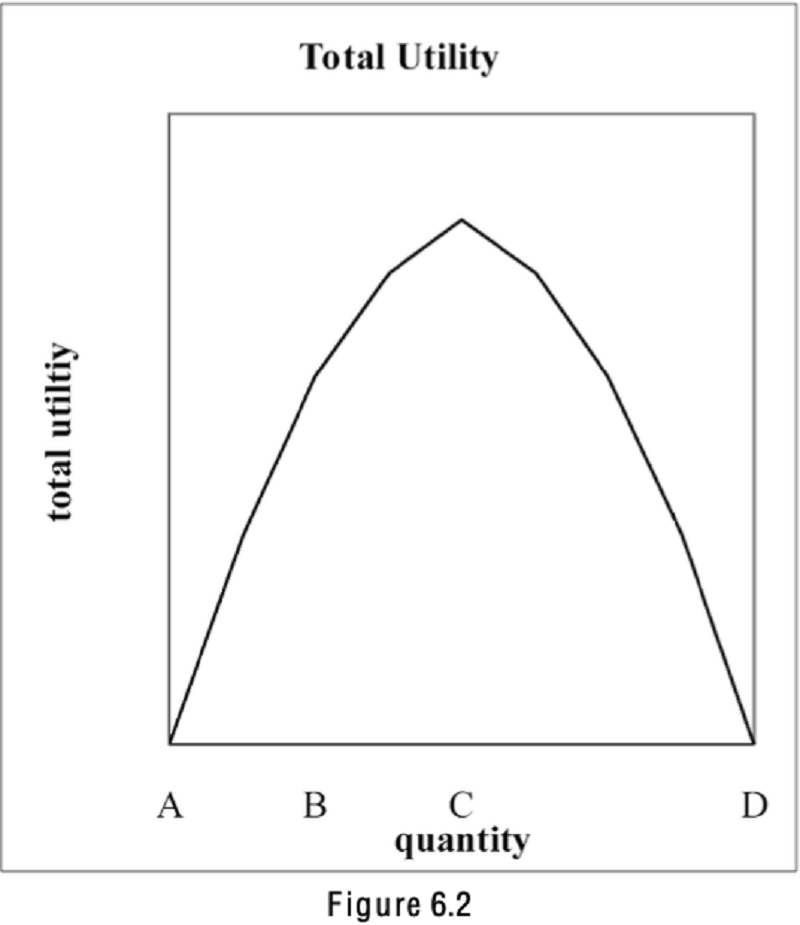
Refer to Figure 6.2. If the price of the product were zero, what quantity should you choose to buy?
A
B
C
D
Which of the following statements is consistent with the principle of diminishing marginal utility?
David thought he would hate Economics, but the more he studies Economics, the more he likes studying it.
The more Mark eats, the hungrier he seems to get.
Sue said that she could rock climb forever and never get tired of it.
Carrie likes to rent videos but after watching the third video of the night she is ready to play cards instead.
States that the first unit of a good is the most satisfying, after which additional units provide progressively less and less additional utility.
The law of supply
The principle of increasing opportunity cost
The law of demand
The principle of diminishing marginal utility
When Kevin has a second cookie, his total utility rises from 15 to 25 utils. Kevin's marginal utility of the second cookie is
10 Utils
5 Utils
40 Utils
Not measurable with the information given.
Consumers want to maximize
Marginal utility.
Quantity consumed.
Total utility.
All of the above

Refer to Table 6.3. If the price of concerts is $20, what is the marginal utility per dollar for the 2nd concert?
3
6.5 (16.5)
1200
1.5
Which of the following is not a legal form a firm can operate in?
Partnership
Corporation
Dual proprietorship
Sole proprietorship
________ make up a majority of the firms in the United States and ________ receive the majority of revenues earned by U.S. firms.
Corporations; corporations
Sole proprietorships; corporations
Corporations; sole proprietorships
Sole proprietorships; sole proprietorships
Stocks can be issued by
Partnerships
Corporations
Sole proprietorships
All of the above
Ivan sells a share of IBM stock on the New York Stock Exchange for $100. Which of the following statements is accurate?
IBM gets the difference between the price Ivan paid for the stock and the price Ivan sold it for.
IBM gets paid the price of the stock ($100) when the stock is sold.
IBM gets 15% of the price of the stock, in this case $15.
IBM does not get any money when Ivan sells his stock.
All other things held equal, a corporation's market value increases when the firm's
Sales increase.
Stock price increases.
Price of the product it sells increases.
Profits increase.
Profit is calculated as
Total cost - total revenue
Marginal cost - marginal revenue
Total revenue - total cost
Marginal revenue - marginal cost
Economic analysis of firms usually assumes the goal of firms is to
Maximize profits.
Minimize costs.
Maximize revenues.
Maximize market share.
Which of the following statements about profit is incorrect?
Normal profit = total revenue - implicit opportunity costs
Accounting profit = total revenue - explicit costs
Economic profit = Accounting profit - implicit opportunity costs
Economic profit = Accounting profit - normal profit
Kathy is considering quitting her job as a professor, where she earns $50,000 per year, to open a little business renting jet skis on a beautiful beach in the Caribbean. She calculates that she could make about $80,000 in revenue a year from her business. The cost of jet skis and all her other equipment would be $35,000 per year. How much are Kathy's economic profits? How much are Kathy's accounting profits?
Economic profits = -$5,000; accounting profits = $45,000
Economic profits = $80,000; accounting profits = $30,000
Economic profits = $45,000; accounting profits = -$5,000
Economic profits = $30,000; accounting profits = $80,000
A firm is willing to stay in business if it has
Zero normal profit.
Zero accounting profit.
Zero economic profit.
None of the above
The breakeven point is when the firm has
Zero accounting profit.
Zero economic profit.
Zero total revenue.
Zero normal profit.
When economists refer to the "short run" they are referring to
The time frame where managers must consider at least one input in production as fixed in quantity.
The time frame where managers must consider all inputs in production as fixed in quantity.
One year.
One month.
Which of the following statements is true about the law of diminishing returns?
The marginal product of using more of a variable input declines
The total product curve can still be increasing.
There is at least one fixed input in production, meaning the amount of that input can not change.
All of the above
Short-run decision making about production focuses
Only on the fixed inputs.
Only on the variable inputs.
On neither the fixed or variable inputs.
On both the fixed and variable inputs.
Marginal product is found by taking
Change in total product/total labor.
Change in total product/change in total labor.
Total product/total labor.
Total product/change in total labor.
When Brady has three workers in his bakery they can make 40 pastries an hour. When he has four 26) workers they can make 50 pastries an hour. Average product with four workers is
12.5
10
200
160
When Brady has three workers in his bakery they can make 40 pastries an hour. When he as four 27) workers they can make 50 pastries an hour. The marginal product of the 4th worker is
12.5
10
200
160

Refer to Table 7.3. What is the marginal product of the 3rd worker?
20
60
80
140
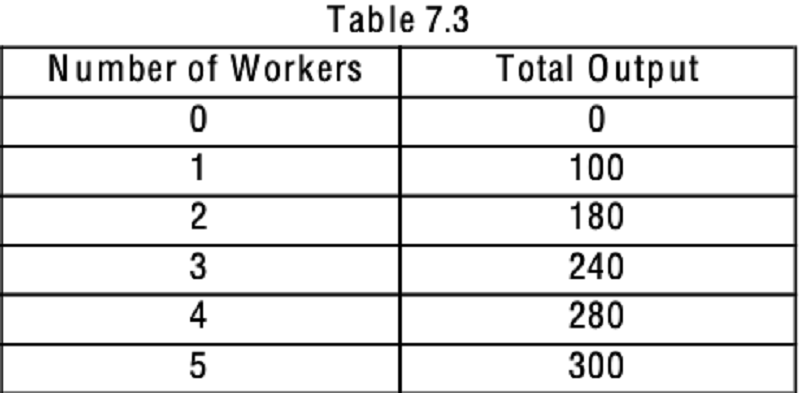
Refer to Table 7.3. What is the average product of the 5th worker?
20
60
80
140
The point of diminishing returns occurs at the point where
The slope of the total product curve is negative.
The slope of the total product curve is positive.
The slope of the total product curve begins decreasing.
The slope of the total product curve is zero.
Total variable costs ________ in the short run as the quantity of output increases.
Increase
Decrease
Decrease at first and then increase
Remain constant
Total cost ________ in the short run as the quantity of output increases.
Decreases
Decreases at first and then increases
Remains constant
Increases
Your mother yells at you for skipping your Economics class last week. She says, "I paid good money for you to take that class, now I expect you to attend." You respond to your mother, "I have learned a lot in economics, and one of the things is that the money you spent on tuition is a ________ so I ________ consider it in making my decision."
Sunk cost; should not
Opportunity cost; should not
Sunk cost; should
Opportunity cost; should
If a firm has labor as its only variable input, the total cost curve is shaped identically to the
Total product curve.
Labor requirements curve.
Fixed cost curve.
Marginal product curve.
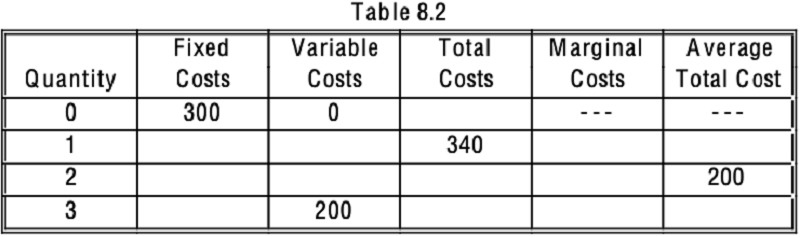
Refer to Table 8.2. What is the marginal cost of producing the 1st unit?
140
100
40
340
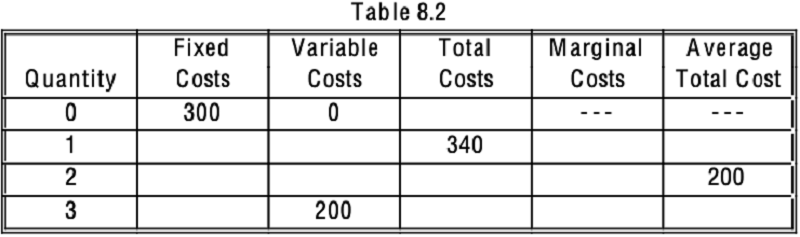
Refer to Table 8.2. What is the variable cost of producing the 2nd unit?
100
300
150
50
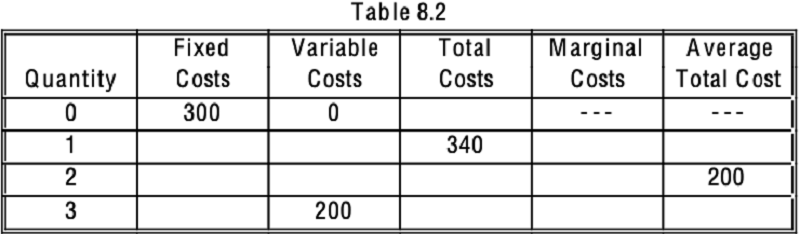
Refer to Table 8.2. What is the total cost of producing the 3rd unit?
300
500
200
450
McDonald's has fixed costs of $200. When McDonald's makes 500 hamburgers, their variable costs are $150. When McDonald's makes 600 hamburgers, their variable costs are $250. The average total cost when they are making 600 hamburgers is ________. The marginal cost for the range between 500 and 600 hamburgers is ________.
ATC = $0.75; MC = $1.00
ATC = $1.30; MC = $2.00
ATC = $0.75; MC = $2.00
ATC = $1.30; MC = $1.00
The rule of profit maximization says that firms should produce at the point where
Price equals average cost.
Price equals total cost.
Marginal revenue equals marginal cost
Total revenue equals total cost
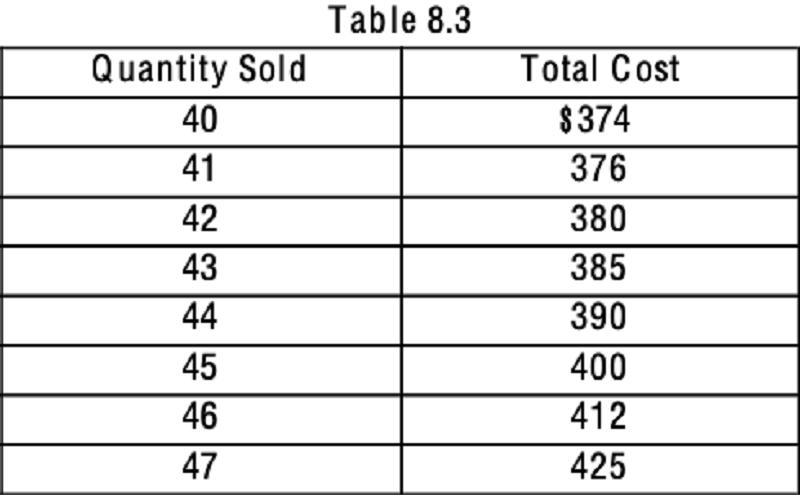
Refer to Table 8.3. If the market price is $10, what quantity of output would the price-taking firm produce?
43 units
42 units
45 units
46 units
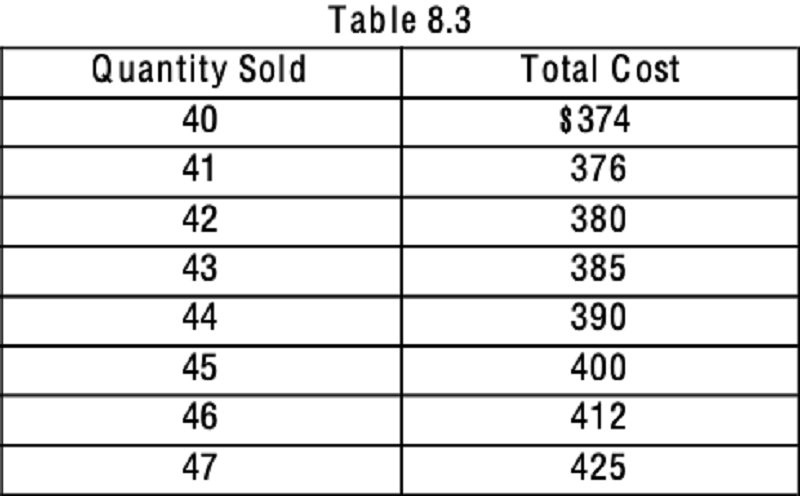
Refer to Table 8.3. If the market price is $10, what is the maximum profit a price-taking firm can earn?
$40
$50
$20
$378
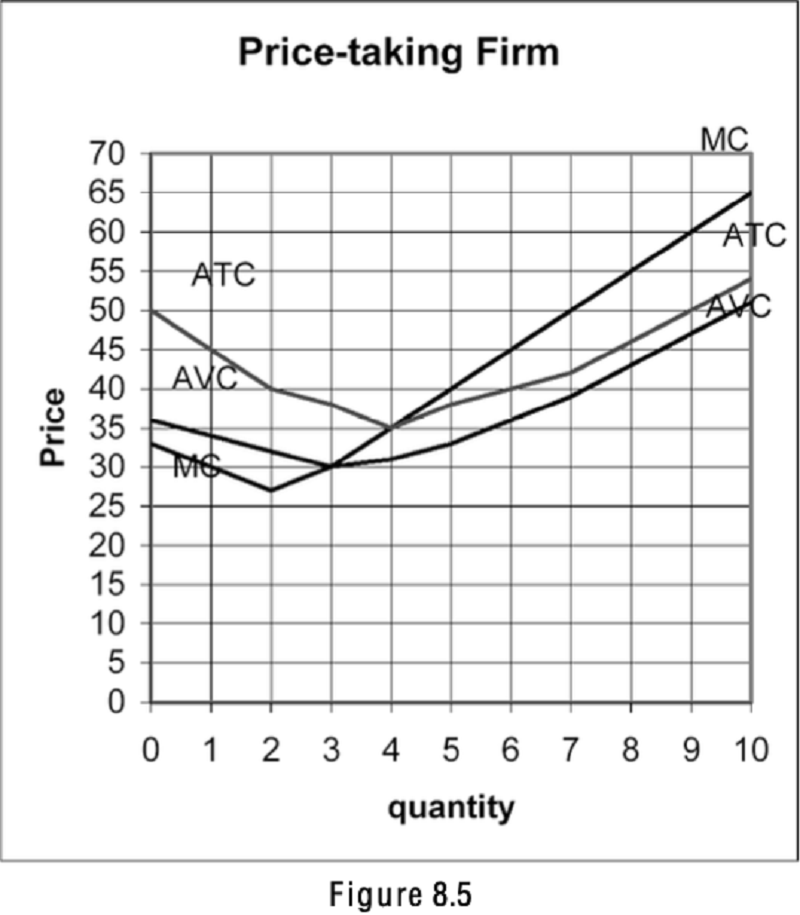
Refer to Figure 8.5. If the market price is $60, what will be the quantity that the firm will sell?
4
3
7
9
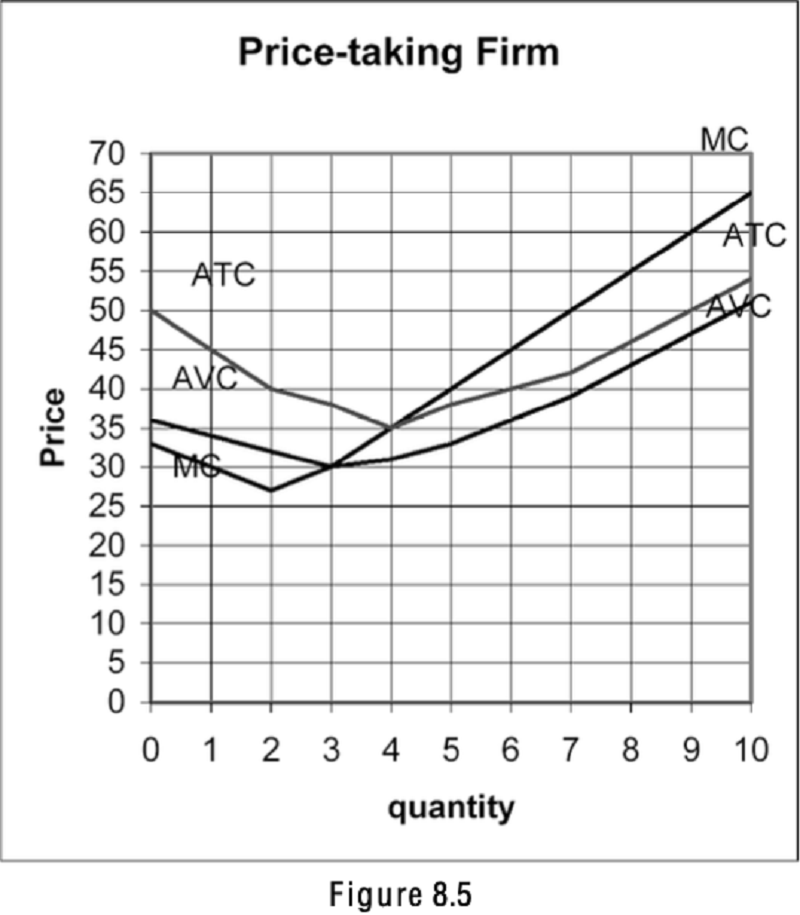
Refer to Figure 8.5. If the price is $60, how much are the firm's profits?
$108
$0
$40
$90
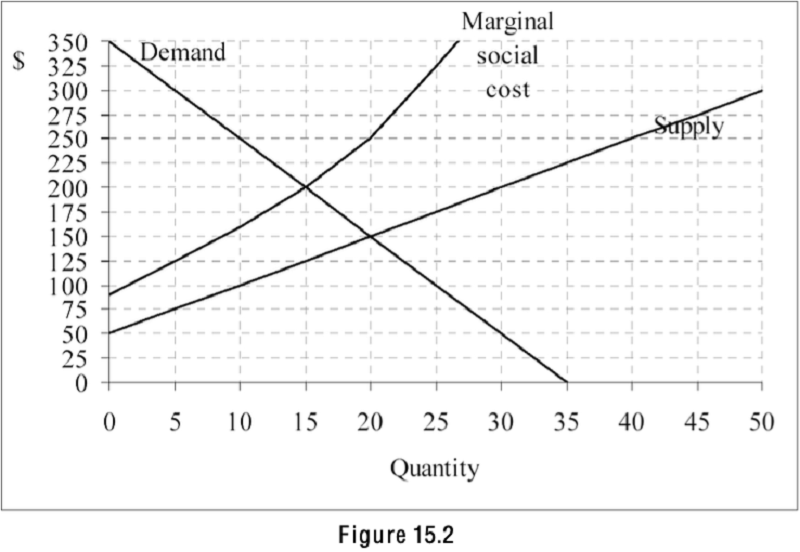
Refer to Figure 15.2. The graph shows the demand, supply, and marginal social cost for a product. If there were no government intervention, what quantity of the product would be supplied by the market?
15
20
35
50
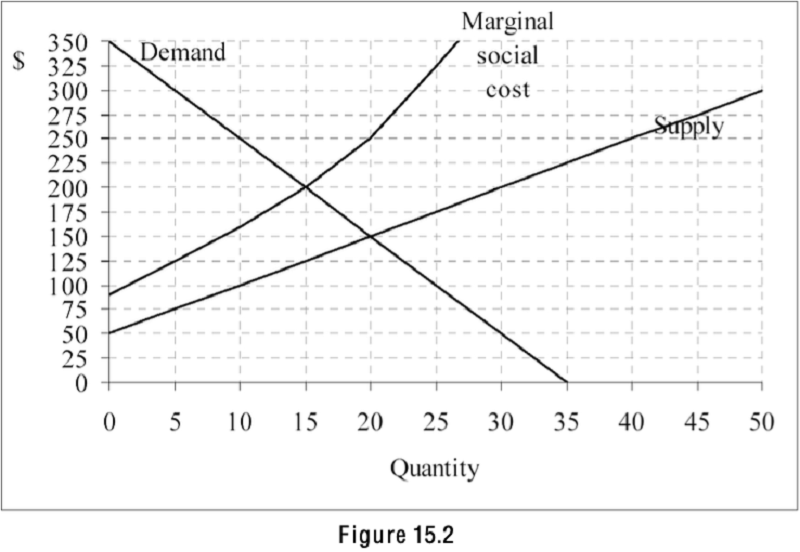
Refer to Figure 15.2. The graph shows the demand, supply, and marginal social cost for a product. 45) What is the efficient quantity of the product?
15
20
35
50
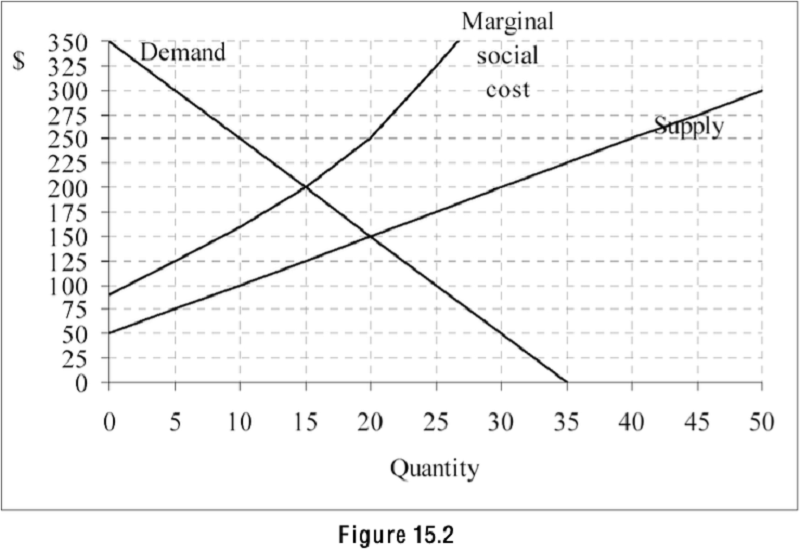
Refer to Figure 15.2. The graph shows the demand, supply, and marginal social cost for a product. Which of the following statements is true?
The product has a positive externality.
The product does not have an externality.
The product is a common property resource.
The product has a negative externality.
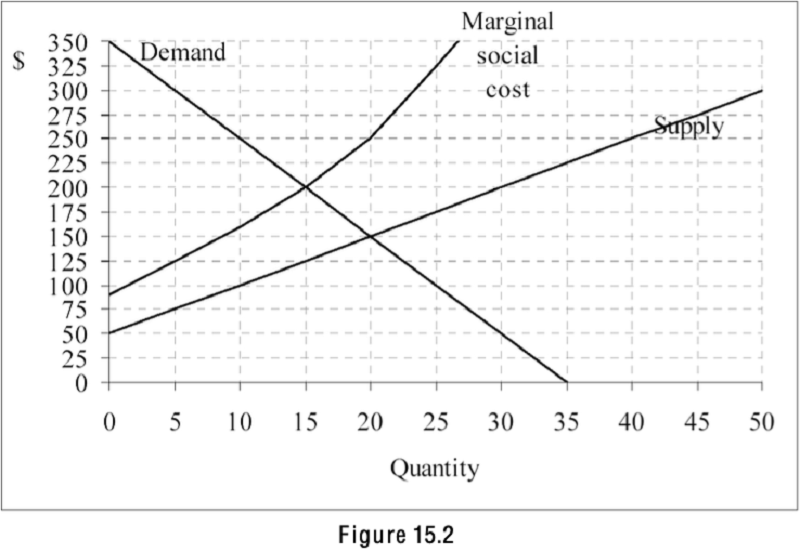
Refer to Figure 15.2. The graph shows the demand, supply, and marginal social cost for a product. For a quantity of 25, what is the marginal external cost of the 25th unit?
150
325
175
100
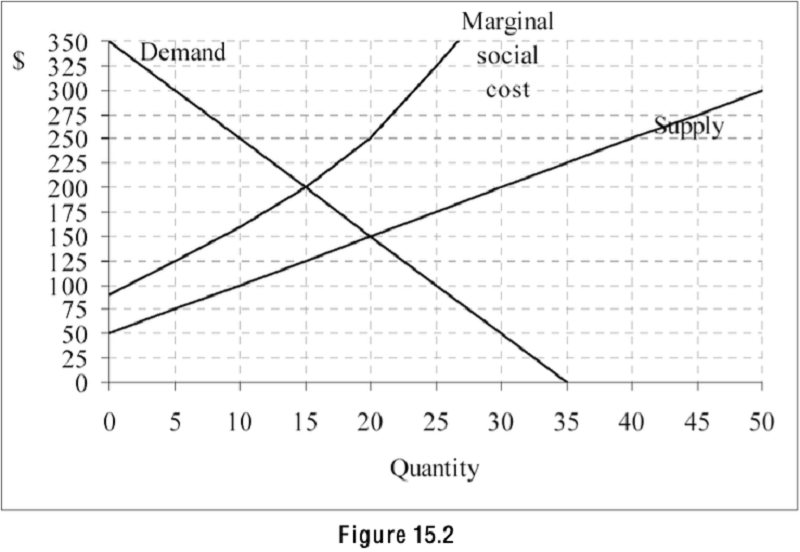
Refer to Figure 15.2. The graph shows the demand, supply, and marginal social cost for a product. Which of the following statements is true?
Marginal external costs are rising with output.
Marginal external costs do not change as output changes.
Marginal external costs are falling with output.
There are no marginal external costs.
The social costs of a transaction that has a negative externality are the
Private costs - external costs.
Private costs + external costs.
External costs only.
Private costs only.
A price-taking firm is selling 100 units of a good for the market price. If the marginal cost of the 100th unit is higher than the marginal revenue of that unit,
The firm could increase profit by selling more units at the current price.
The firm could increase profit by selling fewer units at the current price.
The firm could increase profit by lowering the price.
The firm could increase profit by increasing the price.
Which of the following is an example of a negative externality?
Not studying as much for your econ test as you should have so you get a lower grade than you want
Getting your car washed
Allowing your cell phone to ring in class
Getting a flu immunization shot
Jason loves to listen to his music loudly. He would be willing to pay $10 an hour to have his music as loud as it is but since he is listening in his own house he doesn't have to pay anything. Mark is Jason's neighbor and he hates loud music. He would be willing to pay $2 an hour to have Jason turn down his music. The music Jason listens to is free on the radio so there are no other benefits or costs involved with Jason listening to music. The private cost of the music is ________ and the social cost of the music is ________.
$10 private cost; $0 social cost
$0 private cost; $2 social cost
$10 private cost; $12 social cost
$0 private cost; $10 social cost
Jason loves to listen to his music loudly. He would be willing to pay $10 an hour to have his music as loud as it is but since his is listening in his own house he doesn't have to pay anything. Mark is Jason's neighbor and he hates loud music. He would be willing to pay $2 an hour to have Jason turn down his music. The music Jason listens to is free on the radio so there are no other benefits or costs involved with Jason listening to music. The private benefit of the music is ________.
$0
$12
$2
$10
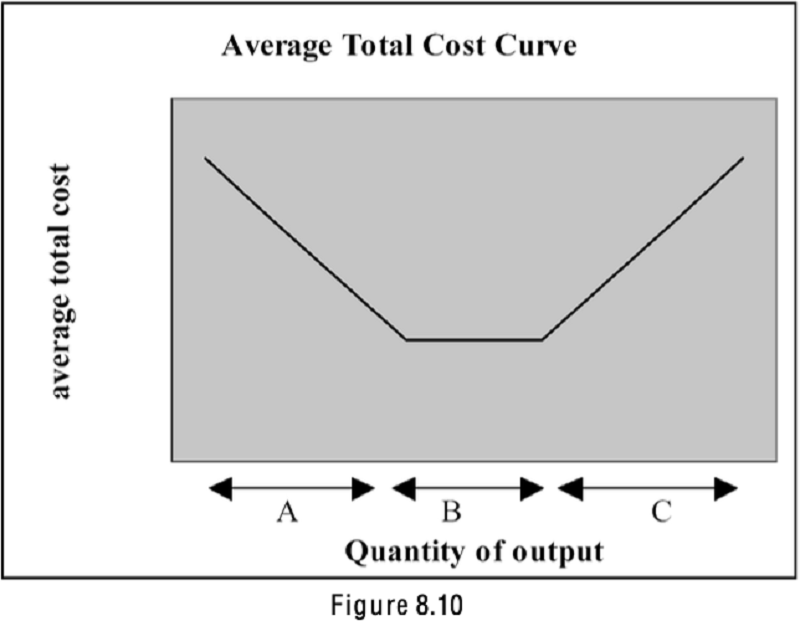
Refer to Figure 8.10. For which range would a doubling of inputs more than double the output the firm produces?
A
B
C
All of the above
Which of the following is a possible government solution to common property resources?
Charge fees for the use of the common resources
Selling the property rights to the common resources to a single user
Use permits or other regulations to limit production
All of the above
When the government uses technology mandates to address the problem of pollution it
requires firms pay a tax for the pollution they create.
Instructs producers as to the exact technology to install to reduce pollution.
Charges a user fee for those who use products that pollute.
Is appealing to the social conscience of people and exhorting them to do the right thing.
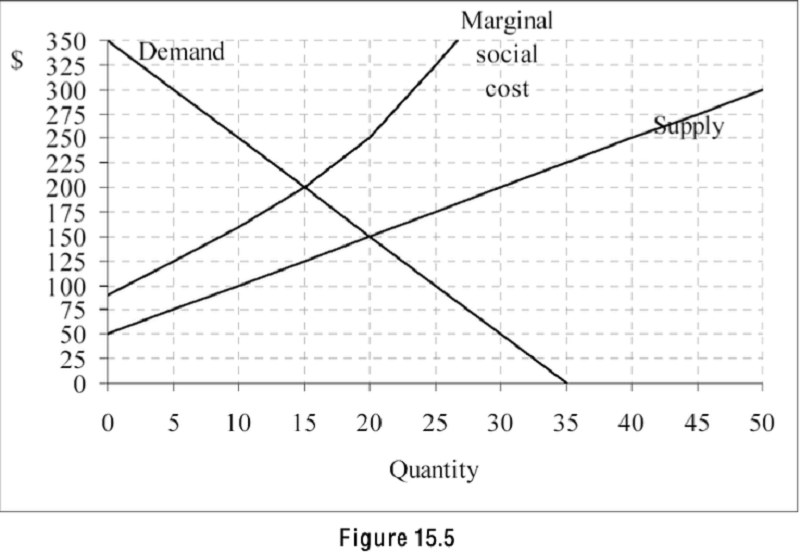
Refer to Figure 15.5. The graph shows the demand, supply, and marginal social cost of a product. If the government wants to use a tax on the product to get the efficient quantity of the good, the tax should be set equal to
125
75
150
45
Which of the following is a difficulty with using taxes to solve the problem of pollution?
Taxes do not give firms an incentive to find cheaper ways to reduce pollution.
It is difficult to set the appropriate tax level because external damages of pollution may vary by time and place.
It is not possible to put a price on the environment so only an infinitely high tax would result in the efficient outcome.
It imposes all costs of pollution cutbacks on the "moral" firms that are willing to pay the tax.
{"name":"Microeconomics Mock Quiz Questions", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Test your knowledge and understanding of microeconomic principles with our engaging quiz designed for students, teachers, and anyone interested in economics. With 58 comprehensive questions, this quiz covers various topics essential for mastering microeconomic concepts.Key Features:Variety of questions ranging from basic to advanced levelsImmediate feedback on your performanceEnhance your understanding of utility, profit, production, and market structures","img":"https:/images/course3.png"}
More Quizzes
Economics
5263
Econ
291414
Functions in php
630
Which stray kids member should you fight
8491
What Should I Do Today? - Find a Fun Activity
201016632
What Do I Like - Free Personality Type Results
201016632
Wentworth Characters - Can You Name Them All?
201018053
Kindness - What's Your Kindness IQ?
201020558
Molecular Geometry - Free VSEPR Shapes Practice
201016632
Find My Doppelganger Free - Celebrity Look-Alike
201017909
CHP Practice Test: First Aid for School Bus Drivers - Free
201018199
FBI: Can You Pass These Test Questions?
201016632