ECO 165 Exam 1a
According to economists, economic self-interest:
Is a reality that underlies economic behavior.
Is more characteristic of men than of women.
Has the same meaning as selfishness.
Is usually self-defeating.
You should decide to go to a movie:
If the marginal cost of the movie exceeds its marginal benefit.
If the marginal benefit of the movie exceeds its marginal cost.
If your income will allow you to buy a ticket.
Because movies are enjoyable.
The assertion that "There is no free lunch" means that:
There are always tradeoffs between economic goals.
All production involves the use of scarce resources and thus the sacrifice of alternative goods.
Marginal analysis is not used in economic reasoning.
Choices need not be made if behavior is rational.
If someone produced too much of a good, this would suggest that:
Rational choice cannot be applied to many economic decisions.
The good was produced to the point where its marginal cost exceeded its marginal benefit.
Certain goods and services such as education and health care are inherently desirable and should be produced regardless of costs and benefits.
The good was produced to the point where its marginal benefit exceeded its marginal cost.
In deciding whether to study for an economics quiz or go to a movie, one is confronted by the idea(s) of:
Scarcity and opportunity costs.
Money and real capital.
Complementary economic goals.
Full production.
Kara was out jogging and despite being tired, decided to run one more mile. Based on her actions, economists would conclude that Kara:
Must be an avid runner.
Decided that the marginal benefit of running one more mile would outweigh the cost of the additional mile.
Decided that the marginal cost of running one more mile would outweigh the benefit of the additional mile.
Was not very tired, so the marginal cost of the extra mile was very low.
The process by which economists test hypotheses against facts to develop theories, principles, and models is called:
The economic perspective.
The scientific method.
Policy economics.
Microeconomics.
In constructing models, economists:
Make simplifying assumptions.
Include all available information.
Must use mathematical equations.
Attempt to duplicate the real world.
The Latin term "ceteris paribus" means:
That if event A precedes event B, A has caused B.
That economics deals with facts, not values.
Other things equal.
Prosperity inevitably follows recession.
The term "other things equal" means that:
The associated statement is normative.
Many variables affect the variable under consideration.
A number of relevant variables are assumed to be constant.
When variable X increases so does related variable Y.
Microeconomics:
Is the basis for the "after this, therefore because of this" fallacy.
Is not concerned with details, but only with the overall big picture of the economy.
Is concerned with individual economic units and specific markets.
Describes the aggregate flows of output and income.
Which of the following is a positive statement?
The humidity is too high today.
It is too hot to jog today.
The temperature is 92 degrees today.
Summer evenings are nice when it cools off.
Ben says that "An increase in the tax on beer will raise its price." Holly argues that "Taxes should be increased on beer because college students drink too much." We can conclude that:
Ben's statement is normative, but Holly's is positive.
Holly's statement is normative, but Ben's is positive.
Both statements are normative.
Both statements are positive.
"Macroeconomics is the part of economics concerned with individual units such as a person, a household, a firm, or an industry." This statement is:
Positive, but incorrect.
Positive and correct.
Normative, but incorrect.
Normative and correct.
Which of the following is a capital resource?
A computer programmer
A corporate bond issued by a computer manufacturer
Silicon (sand) used to make computer chips
A piece of software used by a firm
The four factors of production are:
Land, labor, capital, and money
Land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurial ability
Labor, capital, technology, and entrepreneurial ability
Labor, capital, entrepreneurial ability, and money
Which of the following is a land resource?
A farmer
An oil drilling rig
A machine for detecting earthquakes
Natural gas
Which of the following do economists consider to be capital?
A pair of stockings
A construction crane
A savings account
A share of IBM stock
Which of the following is not considered by economists to be an economic resource?
Money
Factory workers
Computers at a retail store
A forest
The production possibilities curve illustrates the basic principle that:
The production of more of any one good will in time require smaller and smaller sacrifices of other goods.
An economy will automatically obtain full employment of its resources.
If all the resources of an economy are in use, more of one good can be produced only if less of another good is produced.
An economy's capacity to produce increases in proportion to its population size.
Which of the following will not produce an outward shift of the production possibilities curve?
An upgrading of the quality of a nation's human resources
The reduction of unemployment
An increase in the quantity of a society's labor force
The improvement of a society's technological knowledge
If the production possibilities curve is a straight line:
The two products will sell at the same market prices.
Economic resources are perfectly substitutable between the production of the two products.
The two products are equally important to consumers.
Equal quantities of the two products will be produced at each possible point on the curve.
A nation's production possibilities curve is bowed out from the origin because:
Resources are not generally equally efficient in producing every good.
The originator of the idea drew it this way and modern economists follow this convention.
Resources are scarce.
Wants are virtually unlimited.
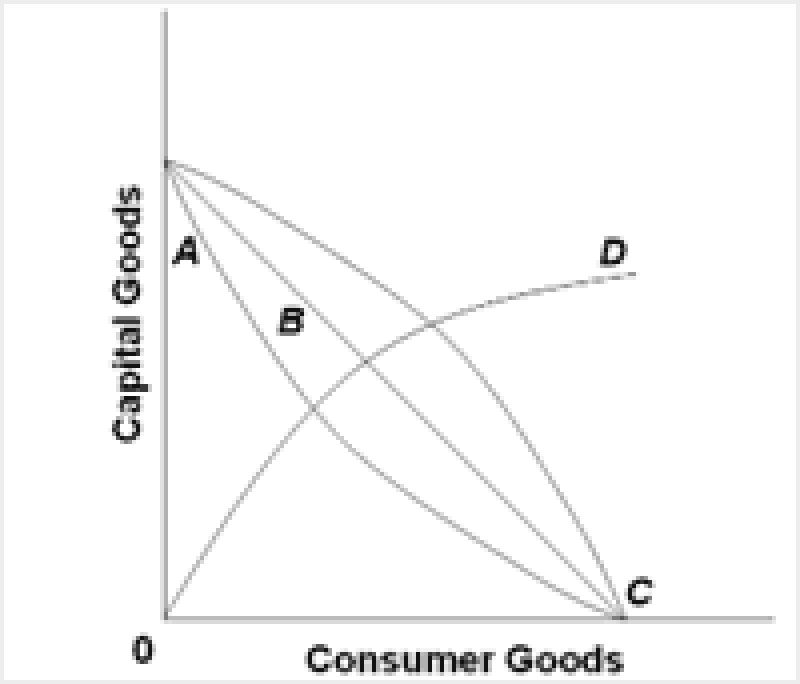
Refer to the above diagram. As it relates to production possibilities analysis, the law of increasing opportunity cost is reflected in curve:
A
B
C
D
The fact that the slope of the production possibilities curve becomes steeper as we move down along the curve indicates that:
The principle of increasing opportunity costs is relevant.
Society's resources are limited.
The opportunity cost of producing each product is constant.
Resources are perfectly shiftable between alternative uses.
The law of increasing opportunity costs is reflected in a production possibilities curve that is: an ups
An upsloping straight line.
A downsloping straight line.
Bowed out from the origin.
Bowed in toward the origin.
The optimal allocation of resources is found:
Where MB = MC.
At every point along a production possibilities curve.
Where the marginal benefit is at its greatest.
Where the marginal cost is at its lowest.
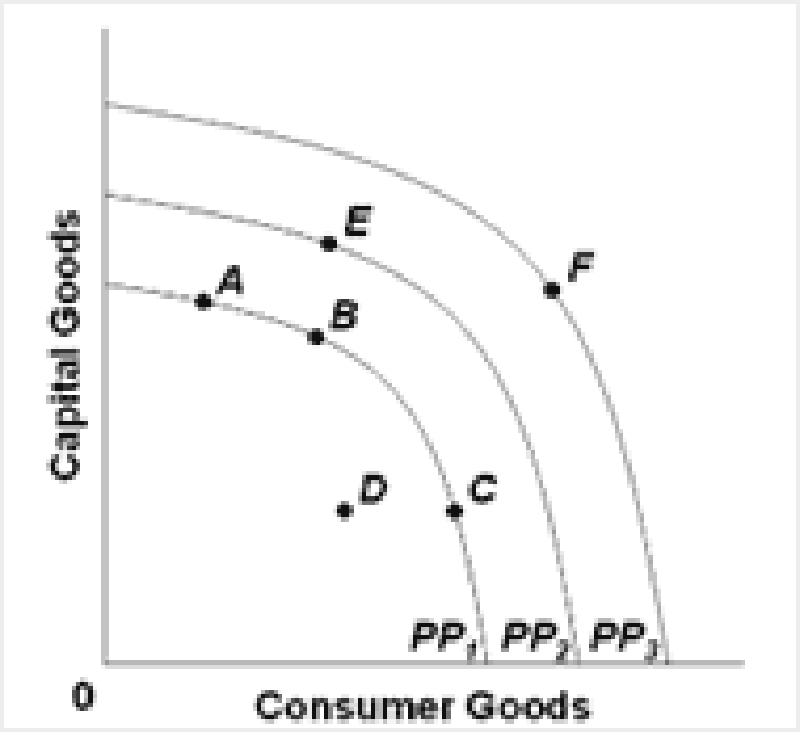
Refer to the above diagram. An improvement in technology will:
Shift the production possibilities curve from PP1 to PP2.
Shift the production possibilities curve from PP2 to PP1.
Move the economy from A to C along PP1.
Move the economy from A, B, or C on PP1 to D.
(Consider This) A direct cost of going to college is:
Tuition, while an indirect cost (opportunity cost) is books and other supplies.
Forgone income while in college, while an indirect cost (opportunity cost) is tuition.
Tuition, while an indirect cost (opportunity cost) is forgone income while in college.
Books and supplies, while an indirect cost (opportunity cost) is food and housing.
(Last Word) The fallacy of composition states that:
Because economic systems are composed of so many diverse economic units, economic laws are necessarily inexact.
The anticipation of a particular event can affect the composition of that event when it occurs.
What is true for the individual must necessarily be true for the group.
Because event A precedes event B, A is necessarily the cause of B.
(Last Word) The safest way for an individual to leave a burning theater is to run for the nearest exit; it is therefore also the best means of escape for a large audience. This assertion illustrates the:
"after this, therefore because of this" fallacy.
Correlation fallacy.
Fallacy of composition.
Fallacy of limited decisions.
Because economic generalizations are simplifications from reality, they are impractical and useless.
True
False
Marginal analysis means that decision-makers compare the extra benefits with the extra costs of a specific choice.
True
False
Which of the following is a distinguishing feature of a command system?
Private ownership of all capital.
Central planning.
Heavy reliance on markets.
Wide-spread dispersion of economic power.
Examples of command economies are:
The United States and Japan.
Sweden and Norway.
Mexico and Brazil.
Cuba and North Korea.
Which of the following is a distinguishing feature of a market system?
Public ownership of all capital.
Central planning.
Wide-spread private ownership of capital.
A circular flow of goods, resources, and money.
An economic system:
Requires a grouping of private markets linked to one another.
Is a particular set of institutional arrangements and a coordinating mechanism used to respond to the economizing problem.
Requires some sort of centralized authority (such as government) to coordinate economic activity.
Is a plan or scheme that allows a firm to make money at some other firm's expense.
Economic systems differ according to which two main characteristics?
Who owns the factors of production, and the methods used to coordinate economic activity.
The technology used in production, and the quantity and quality of natural resources.
How goods are produced, and who gets them.
The political system in place, and the degree of scarcity facing the economy.
Which of the following is a fundamental characteristic of the market system?
Property rights.
Central planning by government.
Unselfish behavior.
Government-set wages and prices.
Property rights are important because they:
Ensure an equal distribution of income.
Encourage cooperation by improving the chances of mutually agreeable transactions.
Guarantee that any exchange will make all parties better off than prior to the exchange.
Allow the government to control how resources are allocated.
Specialization in production is important primarily because it:
Results in greater total output.
Allows society to avoid the coincidence-of-wants problem.
Allows society to trade by barter.
Allows society to have fewer capital goods.
Specialization-the division of labor-enhances productivity and efficiency by:
Allowing workers to take advantage of existing differences in their abilities and skills.
Avoiding the time loss involved in shifting from one production task to another.
Allowing workers to develop skills by working on one, or a limited number, of tasks.
All of the means identified in the other answers.
The presence of market failures implies that:
Money is not an effective tool for exchange in a market system.
There is an active role for government, even in a market system.
Individuals and firms should strive to be self-sufficient rather than specialize.
Command systems are superior to market systems in the allocation of resources.
In a competitive market economy firms select the least-cost production technique because:
Such choices will result in full employment of available resources.
To do so will maximize the firms' profits.
This will prevent new firms from entering the industry.
"dollar voting" by consumers mandates such a choice.
The market system's answer to the fundamental question "Who will get the goods and services?" is essentially:
"Those willing and able to pay for them."
"Those who physically produced them."
"Those who most need them."
"Those who get utility from them."
"Consumer sovereignty" refers to the:
Fact that resource prices are higher than product prices in capitalistic economies.
Idea that the pursuit of self-interest is in the public interest.
Idea that the decisions of producers must ultimately conform to consumer demands.
Fact that a Federal agency exists to protect consumers from harmful and defective products
The invisible hand refers to the:
Fact that the U.S. Tax system redistributes income from rich to poor.
Notion that, under competition, decisions motivated by self-interest promote the social interest.
Tendency of monopolistic sellers to raise prices above competitive levels.
Fact that government controls the functioning of the market system.
In what type of business do the owners bear no personal financial responsibility for the company's debts and obligations?
Partnerships.
Corporations.
Sole proprietorships.
In all of the businesses listed in the other answers.
In the resource market:
Businesses borrow financial capital from households.
Businesses sell services to households
Businesses sell services to households. Households sell resources to businesses.
Firms sell raw materials to households.
Central planning often suffers from a coordination problem and an incentive problem.
True
False
{"name":"ECO 165 Exam 1a", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"According to economists, economic self-interest:, You should decide to go to a movie:, The assertion that \"There is no free lunch\" means that:","img":"https://cdn.poll-maker.com/12-538702/13252704738993239803.png?sz=1200"}
More Quizzes
What is Your Patronus
7497
LDShadowlady Quiz
421212
Which oc are you
13612
What's Your Child-proofing Score?
1890
Miley Cyrus Real Name - Can You Guess It?
201016588
T-Mobile Assessment Answers - Sales Associate Practice
201019695
Marketing Test - Free Online Knowledge Check
201017063
Harry Potter for Kids - Which Character Are You?
201017511
30 Rock Trivia - How Well Do You Know the Show?
201018287
What's My Future Husband's Name? Take the Free
201016588
Wizard - Discover Your Magical Side (Free)
201016588
Affirmative Action Policies: Which Statement Is True?
201017922