USS DES Test 9A (Start from page 1654)
1) An African-American boy is in the newborn nursery with a bulge on his abdomen that was identified immediately after birth and is most pronounced during crying. The patient was born to an 18-year-old woman who did not receive prenatal care or take prenatal vitamins. Vitals are normal. Examination shows a soft swelling at the umbilical ring. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis and best course of action for this patient?
Gastroschisis, refer for surgical management
Omphalocele, refer for operative management
Umbilical hernia, observe for spontaneous resolution
Umbilical hernia, refer for operative management
Umbilical granuloma, apply silver nitrate
2) A 14-year-old girl is brought to the physician’s office because of irregular menstrual periods. She had her menarche at age 13, and since then her periods have been irregular with the cycles varying from 3 to 6 weeks. She has no other symptoms. Physical examination is unremarkable. She has age appropriate secondary sexual characteristics. A urine pregnancy test is negative. Serum prolactin and thyroid stimulating hormone levels are normal. Administration of micronized oral progesterone results in withdrawal bleeding in 3 days. Which of the following most likely explains her irregular periods? .
Marked estrogen deficiency
Insufficient gonadotropin secretion
Excess LH secretion
Marked androgen excess
Uterine adhesions
3) Parents bring their 17-year-old son to the emergency department due to his strange behavior at times during the past few weeks. The boy is normally polite and soft-spoken, but he has recently become irritable, impatient, and rude. His parents initially dismissed his behavior as a “phase” with the expectatioin that he would grow out of it. However, they became very concerned on discovering that he had stolen money from their wallets and was sleeping erratically. When questioned by his father about his strange behavior, the boy responsed, “I’m on a secret mission. The king of Norway has sent me here to spy on the US government.” His temperature is 36.6 C, BP is 144/94 mmHg, pulse is 118/min, and respirations are 18/min. On physical examination, the patient appears to be irritated. He is sweating profusely and his pupils are dilated. He is observed in the emergency department for several hours, his condition improves, and he is discharged to the care of his parents. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Amphetamine intoxication
Anticholinergic poisoning
Brief psychotic disorder
Heroin withdrawal
Manic episode
4) A 10-year-old boy presents to the emergency room with chief complaints of fever and increasing fatigue. He was well until 2 weeks ago when he had an upper respiratory illness (URI). He has a decreased appetite and has lost 2 lbs over the last 2 weeks. He has some shortness of breath when he climbs the stairs. His past medical history is unremarkable. On examination his vital signs are normal, and his height and weight are at the 80th percentile. His conjunctiva are pale, and he has bilateral, mobile (about 1-2cm) and non-tender nodes in the cervical, axillary, and inguinal regions. Hepatosplenomegaly is present, and skin shows no lesions. Labs are Hemoglobin 7.3g/dl, platelet count 20,000/mm3, WBC count 42,100/mm3, with 24% lymphoblasts, 70% lymphocytes, and 6% atypical lymphocytes. Chest X-rays show clear lung fields but a wide mediastinum. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Hodgkin's disease
Acute myeloid leukemia
Aplastic anemia
Immune thrombocytopenic purpura
5) A 7-year-old boy is referred by his school for psychiatric evaluation. The teachers have noticed that, in the past year, he has been unable to sustain attention in class, and has been fidgeting and talking to his peers during class. He seems unable to wait for others to finish speaking and keeps interrupting and blurting out answers before questions are completed. At home, his parents state that he is forgetful and losses things easily. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
Bipolar disorder
Conduct disorder
Posttraumatic stress disorder
Rett syndrome
6) An 8-year-old boy falls on his right hand with the arm extended, and he breaks his elbow by hyperextension. X-ray films show a supracondylar fracture of the humerus. Which of the following complications is of greatest concern with this type of injury?
Instability that requires open reduction and internal fixation
Insufficient remodeling
Growth plate damage
Malunion
Vascular and nerve injuries
7) An 18-year-old girl has hepatosplenomegaly, an intention tremor, dysarthria, dystonia, and deterioration in her school performance. She also developed abnormal urine with excess glucose, protein, and uric acid. She has a several-year history of elevated liver enzymes of unknown etiology. Which of the following best explains her condition?
Indian childhood cirrhosis
α1-Antitrypsin deficiency
Menkes syndrome
Dubin-Johnson syndrome
Wilson disease
8) The 7-year-old boy now in your office was last seen 2 weeks ago with a mild viral upper respiratory tract infection. Today, however, he presents with fever, ataxia, weakness, headache, and emesis. In the office he has a 3 minutes left-sided tonic-clonic seizure. You send him to the hospital and order a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain, the results of which show disseminated multifocal white matter lesions that enhance with contrast. This boy’s likely diagnosis is which of the following?
Multiple sclerosis
Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis
Malignant astrocytoma
Bacterial meningitis
Neurocysticercosis
9) A 15-year-old girl presents to a pediatric cardiology clinic with a complaint of chest pain. She states the pain has come and gone over the past year, but has increased in frequency over the past few weeks. She describes it as a sharp pain over her left chest. Physical examination reveals a healthy-appearing 15-year-old girl. Her temperature is 37.2 C (99 F), pulse is 90/min, and respiratory rate is 20/min. Lung examination is normal. Cardiac examination reveals a late systolic murmur preceded by a click at the apex. No heave or rub is present. An electrocardiogram and chest x-ray film are unremarkable. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Atrial septal defect
Mitral regurgitation
Mitral stenosis
Mitral valve prolapse
Tricuspid regurgitation
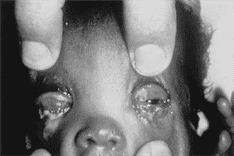 P1657 Q10
|
10) The newborn pictured below was born at home and has puffy, tense eye- lids; red conjunctivae; a copious amount of purulent ocular discharge; and chemosis 2 days after birth. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis? |
Dacryocystitis
Chemical conjunctivitis
Pneumococcal ophthalmia
Gonococcal ophthalmia
Chlamydial conjunctivitis
11) A 1-year-old Caucasian boy is brought to your office with necrotic periodontal infection. The past medical history is significant for recurrent cutaneous and sinus infections revealing S. aureus and P. aeruginosa isolates. The separation of the umbilical cord was delayed (4 weeks). CBC shows leukocytosis and increased neutrophils. The number of peripheral lymphocytes is normal. Gamma-globulin level is increased on plasma protein electrophoresis. The Nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT) test is normal. Which of the following is the most likely defect present in this patient?
Adenosine deaminase deficiency
Complement deficiency
Opsonization defect
Destruction ofT lymphocytes
Impaired leukocyte adhesion
12) A 2-year-old girl is brought to the emergency department due to severe, sudden-onset abdominal pain. She has nausea and vomiting, and her stools contain blood and mucus. Her parents say that she was in her usual state of health when she developed this problem. Her pulse rate is 116/min, blood pressure is 90/60mm Hg, temperature is 37.7C (100F), and respirations are 28/min. She looks lethargic and ill. She is crying and drawing her knees towards her chest. Her abdomen is tender to palpation, and there is a palpable, sausage-like abdominal mass. The bowel sounds are increased, and rectal examination reveals bloody mucus. What is the most likely cause of her symptoms?
Pyloric stenosis
Lymphoma
Henoch-schonlein purpura
Meckel's diverticulum
Intussusception
13) A 9-year-old boy presents with a 3-month history of multiple episodes of sudden awakening at night. His mother states that when he wakes up suddenly, he screams, "Go! Get away! Go!" and does not respond to the parents. His eyes are wide open, and he sweats heavily and looks scared. The parents have had to struggle to awaken him. After the episodes, he has no memory of what happened. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Confusional arousals
Night terrors
Nightmares
Obstructive sleep apnea
Panic disorder
14) A 16-year-old girl presents with lower abdominal pain and fever. On physical examination, a tender adnexal mass is felt. Further questioning in private reveals the following: she has a new sexual partner; her periods are irregular; she has a vaginal discharge. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Appendiceal abscess
Tubo-ovarian abscess
Ovarian cyst
Renal cyst
Ectopic pregnancy
15) A 6-year-old girl with acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) is admitted to the hospital with a generalized vesicular rash and high fever. She has no previous history of chickenpox and has never received immunization for varicella. Her 4-year-old sister recently recovered from chickenpox that started about 10 days ago. On admission, her temperature is 38.4 C (101.1 F), blood pressure is 94/58 mm Hg, pulse is 80/min, and respirations are 20/min. Which of the following is the most serious complication of varicella that might occur in this patient?
Arthritis
Cellulitis
Endocarditis
Hepatitis
Pneumonia
16) An 18-year-old male college student is seen in the student health clinic for urinary frequency, dysuria, and urethral discharge. Which of the following is likely to explain his condition? . Herpes simplex . Escherichia coli urinary tract infection . Chlamydial urethritis . Syphilis . HIV infection
Herpes simplex
Escherichia coli urinary tract infection
Chlamydial urethritis
Syphilis
HIV infection
17) A 1-year-old girl is brought to the emergency department by her mother because the child's "eyes and feet are dancing." On physical examination, the girl is well developed and in no acute distress. Her temperature 37.0 C (98.6 F), blood pressure is 100/55 mm Hg, pulse is 100/min, and respirations are 20/min. The patient has opsoclonus, myoclonus, and ptosis of the right eye. On history, the mother notes the child was born "looking like a blueberry muffin" and has had a persistent cough since the age of 2 months. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis? Astrocytoma Glioblastoma multiforme
Astrocytoma
Glioblastoma multiforme
Hyperthyroidism
Neuroblastoma
Wilms tumor
18) A 15-day-old male infant is brought to the emergency department by his mother due to vomiting and bloodstained stools since yesterday. The vomitus is green. Recently, the neonate has been feeding poorly. His birth history is not significant: he was absolutely normal and passed meconium within the first 12 hours of life. He has been breastfed since birth. His pulse rate is 122/min and blood pressure is 80/50mm Hg. He is irritable, his mucous membranes are dry, and his abdomen is distended. Based on these findings, what is the most likely diagnosis?
Pyloric stenosis
Duodenal atresia
Midgut volvulus
Hirschsprung disease
Meconium ileus
19) A married couple brings their 2-week-old infant to the office for the evaluation of lethargy, poor feeding and hypotonia. The infant was "fine" until yesterday, when he started to present with these symptoms. The mother's medical history is unremarkable, and her pregnancy was uneventful. On examination, hypotonia, poor reflexes and bulging fontanel are noted. There are no focal neurological signs. He is hypotensive and tachycardiac. His temperature is 39.4 C (103F). Initial investigation reveals a WBC count of 16,000/mm3 with 18% bands. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Congenital toxoplasmosis
Group B streptococcal meningitis
Escherichia coli meningitis
Herpes simplex encephalitis
Listeria meningitis
20) A 5-week-old infant is brought to the clinic for a 4-week history of noisy breathing that has not improved. She has otherwise been healthy except for a current upper respiratory infection for the past 4 days, which according to the parents, has worsened the noisy breathing. On examination, she has inspiratory stridor. The noisy breathing improves when the infant is asleep. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Bronchoalveolar carcinoma
Foreign object obstruction
Laryngomalacia
Bacterial pneumonia
Tuberculosis
21) A 1-day-old infant who was born by a difficult forceps delivery is alert and active. She does not move her left arm spontaneously or during a Moro reflex. Rather, she prefers to maintain it internally rotated by her side with the forearm extended and pronated. The rest of her physical examination is normal. This clinical scenario most likely indicates which of the following?
Fracture of the left clavicle
Fracture of the left humerus
Left-sided Erb-Duchenne paralysis
Left-sided Klumpke paralysis
Spinal injury with left hemiparesis
22) A 2-year-old girl is brought to the physician because of protracted irritability, crying, and loss of appetite. She recently had a sore throat. Her temperature is 38.5 C (101.3 F). Physical examination is unremarkable, except for abnormalities of the tympanic membrane detected on otoscopic examination. Which of the following signs or symptoms correlates best with a diagnosis of acute otitis media?
Color change of tympanic membrane
Fever
Opacification of tympanic membrane
Otalgia
Reduced tympanic membrane mobility
23) A 5-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department with high-grade fevers, irritability, dyspnea and difficulty swallowing that started just hours ago. His mother reports that he had been well before going to bed, but then awoke in the middle of the night with respiratory distress. His vaccination history is uncertain. On physical examination, his temperature is 39. 1 °C (102 .4°F), pulse is 130/min, and respirations are 46/min. He appears anxious and restless, and he is drooling. While observing his respirations, you note that inspiring causes him particular distress. There is no stridor. Sitting upright with his neck hyperextended seems to give the child some relief. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Peritonsillar abscess
Angioedema
Vascular ring
Croup
Epiglottitis
24) A 3-year-old boy is brought to the clinic due to an abdominal mass that his mother noted while she was bathing him. She seems distressed about the matter, and seeks your "expert opinion." The patient does not have any significant past medical history. On examination, he is calm and quiet. A firm abdominal mass is palpated in the left quadrant, which does not cross the midline. The mass is tender on deep palpation, but is not pulsatile Urinalysis reveals a trace amount of blood. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Pheochromocytoma
Wilms tumor
Neuroblastoma
Lymphoma
Sarcoma
25) A pediatrician is called to the delivery room because a full-term infant has developed cyanosis and respiratory distress immediately after birth. A brief examination of the infant reveals cyanosis on room air not completely relieved by oxygen administered by mask, subcostal and intercostal retractions, absent air entry on the left with audible bowel sounds in the left chest, and poor air entry on the right chest. The heart is best heard in the right hemithorax; the abdomen is flat without organomegaly. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis? Congenital diaphragmatic hernia Hyaline membrane disease
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia
Hyaline membrane disease
Meconium aspiration
Pneumonia
Tracheoesophageal fistula
26) A 5-year-old child develops an earache, but her mother is too busy to take her to the pediatrician. Two weeks later, the child still has not improved and now has a painful, swollen, red area behind the pinna. At this point, the child is taken to the emergency department, where the physician additionally notes the presence of fever and a creamy discharge in the ear canal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis? 26) A 5-year-old child develops an earache, but her mother is too busy to take her to the pediatrician. Two weeks later, the child still has not improved and now has a painful, swollen, red area behind the pinna. At this point, the child is taken to the emergency department, where the physician additionally notes the presence of fever and a creamy discharge in the ear canal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Acute mastoiditis
Barotitis media
Chronic otitis media
Meniere disease
Secretory otitis media
27) A 3-day-old newborn is ready to be discharged from the neonatal nursery, when his mother reports that a rash has appeared on his abdomen and chest. He otherwise appears healthy. He has no fever and no risk factors for infection. Examination reveals a nontoxic neonate with erythematous papules and vesicles surrounded by patches of erythema. Microscopic evaluation of the pustules reveals numerous eosinophils. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Neonatal varicella
Erythema toxicum
Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome
Milia
Sebaceous hyperplasia
28) An athletic 12-year-old boy complains of left knee pain when he runs and plays sports. The pain resolves when he rests. He has otherwise been well. His physical examination is normal, except for swelling and increased prominence over the left tibial tubercle. A radiograph of the left knee is normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease
Osgood-Schlatter disease
patellar subluxation
popliteal cyst
slipped capital femoral epiphysis
|
P1663 Q29
 |
29) The adolescent shown presents with a 14-day history of multiple oval lesions over her back. The rash began with a single lesion over the lower abdomen (Image A); the other lesions developed over the next days (image B). These lesions are slightly pruritic. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis? |
Contact dermatitis
Pityriasis rosea
Seborrheic dermatitis
Lichen planus
Psoriasis
30) A 14-month-old male infant presents to the emergency room with a chief complaint of high grade fever with no response to antipyretic therapy. This illness started suddenly with the abrupt onset of fever early yesterday morning. He then developed a severe cough and increased work of breathing. The mother reports that he is frequently ill. He was hospitalized 2 months ago for pneumococcal pneumonia. On examination: PR: 145/min; RR: 55/min; BP 100/60mm Hg; oxygen saturation 91%; weight 7 kg (154 lbs). He is listless, tired, and small for age. Both ear canals contain purulent drainage. An immunologic work-up is done and found to have markedly elevated IgM, undetectable IgG and IgA with diminished total B-lymphocytes and neutrophils. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Bruton's agammaglobulinemia (XLA)
Common variable immunodeficiency
Transient hypogammaglobulinemia of infancy (THI)
Hyper-IgM syndrome (HIM)
Selective IgA deficiency
31) A 4-year-old girl is brought to the office due to easy bruising and a rash for the past 3 days. She had an upper respiratory infection approximately two weeks ago. She has never had palpable bruises, hemarthroses, or deep muscle bleeding in the past. She has 2 older brothers, neither of which has had bleeding symptoms before. Her family history is negative for any bleeding disorders. Her vital signs are normal. Physical examination reveals a diffuse petechial rash on her neck, trunk, extremities and groin. There is no hepatosplenomegaly. Nonpalpable ecchymoses of varying ages are present on the shins and arms. The laboratory findings are as follows: Hemoglobin 12 .8 g/dl, Hematocrit 38.5%, WBC 6,000/mm3, Platelets 5,000/mm3, PT 12.0 sec, PTT 30 sec. Peripheral smear shows normal morphology of the red and white blood cell lines. The platelets are reduced in number, and majority of them are increased in size. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Immune thrombocytopenic purpura
Hemolytic uremic syndrome
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura
Hemophilia Von
Willebrand's disease
32) On the second day after birth, a mother reports that her newborn infant does not move his left hand and his left eyelid droops. On examination, you confirm the findings of the mother and elicit myosis in the left eye. Pregnancy was uneventful, and delivery uncomplicated. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Erb-Duchenne palsy
Klumpke paralysis
Phrenic nerve paralysis
Facial nerve paralysis
Clavicular fracture
33) During a physical examination for participation in a sport, a 16-year- old girl is noted to have a late apical systolic murmur, which is preceded by a click. The rest of the cardiac examination is normal. She states that her mother also has some type of heart “murmur” but knows nothing else about it. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
ASD
Aortic stenosis
Tricuspid regurgitation
Mitral valve prolapse
VSD
34) A 4-year-old boy is brought to the office for a routine exam. He has a small face, upslanting palpebral fissures, a speckled iris, and a simian crease. Auscultation reveals a loud P2. His mother informs you that he has trisomy. What is the most likely congenital heart disorder in this patient?
Tetralogy of F allot
Atrial septal defect
Endocardial cushion defect
Coarctation
Patent ductus arteriosus
35) An 8-year-old boy is brought to the pediatrician with a rash on his abdomen. The mother first noticed the rash about 3 weeks ago. The boy has no fever or other symptoms. On examination, there is a well-circumscribed, circular, erythematous, scaly annular patch on his abdomen. The border of the skin lesion is raised and well defined. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Erythema multiforme
Erythema nodosum
Impetigo
Nummular eczema
Tinea corporis
36) A 16-year-old arrives to your office soon after beginning basketball season. He states that he has had progressive pain in his knees. A physical examination reveals, in addition to tenderness, a swollen and prominent tibial tubercle. Radiographs of the area are unremarkable. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Osgood-Schlatter disease
Popliteal cyst
Slipped capital femoral epiphysis
Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease
Gonococcal arthritis
37) A 3-year-old girl is brought to the physician's office for a routine physical examination. Her facial appearance, short stature, short webbed neck and widely spaced nipples are suggestive of a chromosomal abnormality, which is subsequently confirmed by karyotyping. What is the cardiovascular anomaly that is most likely to be present in this child?
Atrial septal defect
Tetralogy of F allot
Coarctation of aorta
Patent ductus arteriosust
Ventricular septal defec
38) A neonate develops severe cyanosis that begins within minutes of birth. Blood drawn one hour after birth shows metabolic acidosis with respiratory acidosis. A chest x-ray film shows a narrow base to the great vessels and the heart resembles an egg on its side. ECG is normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Aortic valve stenosis
Complete atrioventricular canal defect
Tetralogy of Fallot
Transposition of the great arteries
Underdeveloped (hypoplastic) left ventricle syndrome
39) A 13-year-old boy is seen for right knee pain that has persisted for the past 2 months despite the use of over-the-counter analgesics. His mother states that he has been limping since he started to have the pain. The pain is of insidious onset, but its intensity sometimes suddenly increases. On physical examination, the boy is obese; his weight is higher than the 90th percentile. Flexion of the right hip causes marked outward rotation and reproduces the pain. Internal rotation of the right hip is limited, and the right leg is slightly shortened compared with the left leg. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis
Legg-Calve-Perthes disease
Septic arthritis
Slipped capital femoral epiphysis
Toxic synovitis
40) A 2-week-old male infant is brought to the office by his mother due to fever and vomiting for the past two days. He appeared normal until two days ago. He is being breastfed. He was born at 32 weeks gestation and weighed 2.7kg (6 Ib) at birth. On examination, he is ill-looking, lethargic, and febrile. His abdomen is distended, bowel sounds are absent, and stool is guaiac-positive. An abdominal x-ray demonstrates pneumatosis intestinalis. What is the most likely diagnosis of this patient?
Intestinal obstruction
Malrotation
Meconium ileus
Necrotizing enterocolitis
Intestinal perforation
P1667 Q41

41) A 2-year-old boy is brought into the emergency room with a complaint of fever for 6 days and the development of a limp. On examination, he is found to have an erythematous macular exanthem over his body as shown in (image A), ocular conjunctivitis, dry and cracked lips, a red throat, and cervical lymphadenopa- thy. There is a grade 2/6 vibratory systolic ejection murmur at the lower left sternal border. A white blood cell (WBC) count and differential show predominant neutrophils with increased platelets on smear. Later, he develops the findings as seen in (image B). Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Scarlet fever
Rheumatic fever
Kawasaki disease
Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis
Infectious mononucleosis
42) The parents of a 5-year-old boy come to the physician concerned about their child's recurrent leg pains. The boy has been complaining for several weeks about pain in both legs, usually occurring soon after going to bed. He derives relief from rubbing his legs and knees. He does not limp and is able to participate in sports activities. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
"Growing" pains
Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis
Osgood-Schlatter disease (osteonecrosis of the tibial tuberosity)
Osteoid osteoma
Osteosarcoma
43) A young black male with sickle cell trait is preparing for his travel to West Africa from North America. While obtaining his visa, he is advised by the health inspector to obtain some immunizations, although his chances of getting a certain tropical disorder are low. What disease has the sickle cell trait been shown to convey protection against?
Tuberculosis
Malaria
Lymphoma
Histoplasmosis
Leprosy
44) A 5-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department by his mother. One week ago, he developed a low grade fever followed by persistent bouts of coughing that last 20-30 minutes each. The coughing spells are severe, unresponsive to antitussive medications, and appear to worsen with eating and drinking cold liquids. On physical examination, there is subconjunctival hemorrhage and extensive subcutaneous emphysema over the anterior chest. What is the most likely organism responsible for this child's illness?
Actinomyces
Haemophilus influenza
Bordetella pertussis
Pseudomonas
Rickettsia rickettsia
45) A one-week-old infant is admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit due to vomiting, abdominal distension, and poor feeding. His vomitus is bile-stained. There is frank blood in his stools. He has been formula- fed since birth. Physical examination shows diminished bowel sounds. Abdominal x-rays reveal dilated loops of bowel with intramural air Laboratory studies show elevated WBCs. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Food poisoning
Necrotizing enterocolitis
Hirschsprung's disease
Pyloric stenosis
Duodenal atresia
46) A child has a 2-week history of spiking fevers, which have been as high as 40°C (104°F). She has spindle-shaped swelling of finger joints and complains of upper sternal pain. When she has fever, the parents note a faint salmon-colored rash that resolves with the resolution of the fever. She has had no conjunctivitis or mucositis, but her heart sounds are muffled and she has increased pulsus paradoxus. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Rheumatic fever
Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis
Toxic synovitis
Septic arthritis
Osteoarthritis
47) In the newborn nursery it is noted that a child has uneven gluteal folds. Physical examination of the child's hips reveals that one of them can be easily dislocated posteriorly with a jerk and a "click," and returned to normal position with a "snapping" sound. The family is concerned because a previous child had the same problem. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Developmental dysplasia of the hip
Legg-Perthes disease (avascular necrosis of the femoral head)
Septic hip
Slipped capital femoral epiphysis
Traumatic delivery
48) A cyanotic newborn is suspected of having congenital heart disease. He has an increased left ventricular impulse and a holosystolic murmur along the left sternal border. The ECG shows left-axis deviation and left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH). Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Transposition of the great arteries
Truncus arteriosus
Tricuspid atresia
Tetralogy of Fallot
Persistent fetal circulation
49) A 3-day-old infant with a single second heart sound has had progressively deepening cyanosis since birth but no respiratory distress. Chest radiography demonstrates no cardiomegaly and normal pulmonary vasculature. An ECG shows an axis of 120°and right ventricular prominence. Which of the following congenital cardiac malformations is most likely responsible for the cyanosis?
Tetralogy of Fallot
Transposition of the great vessels
Tricuspid atresia
Pulmonary atresia with intact ventricular septum
Total anomalous pulmonary venous return below the diaphragm
50) A 2-year-old child is brought to the office due to vomiting. He is recovering from an upper respiratory infection, which was treated by his mother with over-the-counter aspirin. On examination he is irritable, lethargic, agitated and uncooperative. His height, weight and head circumference are at the 50th percentile. The pupils are equal and have a sluggish reaction to light. The sclera is non-icteric. The neck is supple and without adenopathy. The abdomen is flat, with normal bowel sounds. The lab findings are as follows: Serum bilirubin Normal, Serum ASAT and ALAT Increased, Serum ammonia Increased, Prothrombin time Prolonged. A CT scan of the brain shows cerebral edema. CSF analysis is normal, except for increased pressure. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Aseptic meningitis
Reye syndrome
Carnitine deficiency
Sepsis
Viral encephalitis
51) A 1-month-old baby boy has bloody diarrhea. No infectious agent is identified, but the baby is found to be profoundly thrombocytopenic. The baby is also noted to have a skin rash, and a dermatologist diagnoses eczema. By three months of age, the baby begins to develop recurrent respiratory infections. If this child survives until adolescence, he is at particularly high risk of developing which of the following?
Congestive heart failure
Crohn disease
Lymphoma
Rheumatoid arthritis
Wilms tumor
52) An ill-appearing 2-week-old baby girl is brought to the emergency room. She is pale and dyspneic with a respiratory rate of 80 breaths per minute. Heart rate is 195 beats per minute, heart sounds are distant, a gallop is heard, and she has cardiomegaly on x-ray. An echocardiogram demonstrates poor ventricular function, dilated ventricles, and dilation of the left atrium. An ECG shows ventricular depolarization complexes that have low voltage. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis based on this clinical picture?
Myocarditis
Endocardial fibroelastosis
Pericarditis
Aberrant left coronary artery arising from pulmonary artery
Glycogen storage disease of the heart
53) A newborn infant has mild cyanosis, diaphoresis, poor peripheral pulses, hepatomegaly, and cardiomegaly. Respiratory rate is 60 breaths per minute, and heart rate is 250 beats per minute. The child most likely has congestive heart failure caused by which of the following?
Large ASD and valvular pulmonic stenosis
VSD and transposition of the great vessels
Total anomalous pulmonary venous return
Hypoplastic left heart syndrome
Paroxysmal atrial tachycardia
54) A healthy 7 -year-old Caucasian boy is brought to the office by his mother because of fever and pain in the ear. He has had these symptoms for the past three days. He has no other medical problems. Family history is not significant. He takes no medication. His temperature is 38.3 C (101 F). Otoscopic examination reveals an ear discharge, and the tympanic membrane is immobile with insufflation. He has a boil just behind the pinna of the involved ear. His WBC count is 12,000/mm3. He is diagnosed with otitis media. Which of the following is most specific for the diagnosis of otitis media?
Presence of ear discharge
Presence of a septic focus (boil)
Immobile tympanic membrane
Elevated WBC count
Presence of light reflex
55) A 3 year old male has sudden onset of dry cough with a small amount of bright red blood produced when he coughs. He has had no fevers, runny nose, or vomiting. In the Emergency Department a chest x-ray shows hyperexpansion of the right lung and clear lung fields. Which of the following is the most likely etiology of this child's symptoms?
Bacterial pneumonia
Cystic fibrosis
Foreign body aspiration
Pulmonary arteriovenous malformation
Tuberculosis
56) A female neonate is undergoing an examination after birth. She was born to a 33-year-old primigravid mother at term via a normal spontaneous vaginal delivery. The pregnancy was uncomplicated, except for a positive maternal group B Streptococcus culture at 36 weeks' gestation, for which the mother received penicillin during labor. The infant's APGAR scores are 8 at 1 minute and 9 at 5 minutes. The mother notices that the infant has prominent labia and a dull pink vaginal epithelium. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the appearance of the infant's genitalia?
Exposure to maternal estrogen
Exposure to penicillin
Infection with Chlamydia
Infection with group B Streptococcus
Sexual abuse
57) A 2-year-old boy presents to the emergency department with fever, irritability, and a skin rash 5 days after the onset of an upper respiratory infection. On examination, his temperature is 39.8 C (103.6 F), and his pulse is 94/min. There is an erythematous skin rash that involves his face, chest, back, and upper extremities. His skin is very tender to touch. Rubbing the skin causes separation of the epidermal layer. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Kawasaki disease
Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome
Streptococcal scarlet fever
Toxic epidermal necrolysis
Toxic shock syndrome
58) A 9-year-old girl is brought by her sister to her pediatrician with the complaint of severe, intermittent headaches for the past several months, one of which resulted in her going to the ER. The physical examination today, including a careful neurologic examination, is normal. The headache is diffuse, throbbing, lasts several hours, and is not associated with vomiting or other symptoms. The child cannot feel the headaches coming on; they appear on all days of the week; and usually the headaches are gone when she awakens from a nap. The child reports that she is doing well in school, plays clarinet in the school band, and has “lots of friends.” The sister is not sure, but she thinks their father, who lives in another state, may have headaches. The most likely explanation for this girl’s headache is which of the following?
Migraine
Tensionheadache
Sinusitis
Brain tumor
Fungal meningitis
59) Examination of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of an 8-year-old, mildly febrile child with nuchal rigidity and intermittent stupor shows the following: WBCs 85/μL (all lymphocytes), negative Gram stain, protein 150 mg/dL, and glucose 15 mg/dL. A computed tomographic (CT) scan with contrast shows enhancement of the basal cisterns by the contrast material. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Tuberous sclerosis
Tuberculous meningitis
Stroke
Acute bacterial meningitis
Pseudotumor cerebri
60) A full term neonate is being evaluated following an uncomplicated pregnancy and delivery on day 1 of life. He weighs 3.6kg (8ib), is 20in (50.8cm) tall, and has a head circumference of 13.5in (34cm). His physical examination is unremarkable. Initial laboratory data is shown below. Complete blood count: Hemoglobin 20g/L, Hematocrit 73%, Platelets 200,000/mm3, Leukocyte count 5,500/mm3, Neutrophils 56%, Eosinophils 1%, Lymphocytes 33%, Monocytes 10%. Which of the following findings is most likely to be detected in this neonate?
Respiratory distress
Necrotizing enterocolitis
Disseminated intravascular coagulation
Hyperglycemia
Renal failure
61) An 8-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department with a head injury. He hit his head on the ground when he fell off his bicycle. He was not wearing a helmet at the time. There was no loss of consciousness. He vomited 2 times after the accident and now complains of a right-sided headache and inability to hear with his right ear. There is no photophobia or diplopia. On physical examination, his blood pressure is 110/72 mm Hg, pulse is 104/min, and respirations are 22/min. He is alert and oriented and responds appropriately to questions. There is a round hematoma on the right side of his head. Bloody drainage is noted from his right ear. Which of the following injury is most consistent with these findings?
Concussion
Epidural hematoma
Subdural hematoma
Temporal bone fracture
Tympanic membrane perforation
62) A 16-year-old girl comes to the physician's office because she has not begun menstruating yet. Both her mother and an older sister started menstruation at age 12. She takes no medication and denies strenuous exercise or excessive dieting. Her height is at the 50fh percentile for age; her weight is at the 60fh percentile. Both her breast and pubic hair development are at Tanner stage 4. Pelvic ultrasonography reveals a normal uterus and ovaries. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Imperforate hymen
Physiologic pubertal delay
Prolactinoma
Testicular feminization syndrome
Turner syndrome
63) A 12-year-old boy presents with a 2-month history of recurrent headache and deteriorating school performance. Neurologic examination is unremarkable except for bitemporal deficits in his visual field. X-ray and MRI of the head are performed. X-ray films show calcifications in the suprasellar region, while MRI images reveal a multicystic tumor displacing the optic chiasm. The patient undergoes neurosurgical operation for excision of the tumor. During the procedure, the surgeon notices that the cystic cavities contain a "machinery oil"-like fluid. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Craniopharyngioma
Cysticercosis
Ganglioglioma
Pilocytic astrocytoma
Pituitary adenoma
64) A 5-year-old female child is brought to the emergency department due to fever, chills and abdominal pain. She has been complaining of burning micturition and abdominal pain for the last 2 days. Her temperature is 102 F (38.9C), respirations are 20/min, pulse is 130/min, and blood pressure is 90/60 mmHg. Physical examination reveals costovertebral angle tenderness. Urine analysis shows pyuria, significant bacteriuria, WBC casts, positive nitrite, and esterase. What is the most likely cause of this condition in children?
Hydronephrosis
Wilm's tumor
Vesicoureteral reflux
Ureteral duplication
Renal stones
65) A 10-year-old girl is brought to the office for a follow-up visit. She has been previously diagnosed with vesicoureteral reflux, and has had multiple episodes of acute urinary tract infections in the past. Intravenous pyelography (performed on her last visit) reveals bilateral focal parenchymal scarring and blunted calyces. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Hydronephrosis
Ureteropelvic obstruction
Chronic pyelonephritis
Nephrosclerosis
Kidneys Stones
66) A patient presents to the emergency center with a 6-hour history of fever to 38.9C (102F). Her mother reports that the patient appeared to be feeling poorly, that she had been eating less than normal, and that she vomited once. About 2 hours prior to arrival at the ER, the mother states that she noted a few purple spots scattered about the body on the patient, especially on the buttocks and legs. On the 30-minute ride to the ER, the purple areas spread rapidly and became coalesced in areas, and the patient is now obtunded. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Henoch-Schönlein purpura
Toxicshock syndrome caused by S aureus
Measles
Rocky Mountain spotted fever
Meningococcemia
67) A term neonate appears healthy at birth and receives routine perinatal care. Ten days after delivery, the infant develops severe eyelid edema with copious drainage of mucopurulent material and pseudomembrane formation. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Adenovirus conjunctivitis
Chemical conjunctivitis
Chlamydial ophthalmia
Gonorrhea ophthalmia
Herpetic kerato conjunctivitis
68) A 4-year-old boy presents with severe pains in both of his legs. On physical examination, his temperature is 37.7 C (99.8 F), blood pressure is 108/68 mm Hg, pulse is 96/min, and respirations are 17/min. He is noted to have marked pallor on his lips and palpebral conjunctiva. Numerous purpura and petechiae are noted on his skin. His spleen is palpable 3 cm below his left costal margin. Laboratory evaluation reveals a white blood cell count of 1600/mm3; hemoglobin, 6.1 g/dL; and platelets, 36,000/mm3. Which of the following diagnoses is most consistent with these findings?
Acute lymphocytic leukemia
Aplastic anemia
Henoch-Schönlein purpura
Immune thrombocytopenic purpura
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura
69) A 13-year-old healthy boy presents to the physician for a routine health maintenance visit. A urinalysis reveals 1+ proteinuria. There is no hematuria or bacteruria. His physical examination is unremarkable, revealing no edema and a normal blood pressure. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis? Acute glomerulonephritis . IgA nephropathy
Acute glomerulonephritis
IgA nephropathy
Minimal change disease
Orthostatic proteinuria
Urinary tract infection
70) A previously healthy 18-month-old has been in a separate room from his family. The family notices the sudden onset of coughing, which resolves in a few minutes. Subsequently, the patient appears to be normal except for increased amounts of drooling and refusal to take foods orally. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for this toddler’s condition?
Severe gastroesophageal reflux
Foreign body in the airway
Croup
Epiglottitis
Foreign body in the esophagus
71) A 2-month-old infant is brought to the clinic for the evaluation of poor feeding. He was born at 32 weeks of gestation with a birth weight of 1200 g. The pertinent physical findings are pallor, tachypnea, tachycardia, and flow murmurs. The laboratory studies are as follows: Hb 7 g/dl, WBC 7,000/mm3, Platelets 230,000/mm3, Reticulocytes Low. The peripheral smear shows normocytic normochromic RBC. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Alpha thalassemia
Beta thalassemia
Hemolytic disease of newborn
Sickle cell anemia
Anemia of prematurity
72) A 5-year-old girl presents with a 3-day history of fever, dyspnea, and intermittent joint pain. She has a history of sore throat about 1 month ago. On physical examination, her temperature is 39.6 C (103.2 F), blood pressure is 94/60 mm Hg, pulse is 114/min, and respirations are 22/min. Her knees and elbow joints are swollen and tender to palpation. There is a grade III/VI diastolic murmur best heard at the apex. Multiple fine, pink macules are noted on her trunk. These macules are blanching in the middle. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis
Lyme disease
Rheumatic fever
Scarlet fever
Septic arthritis
73) An 8-year-old boy presents to the physician for a routine health maintenance visit. His mother states that he has had difficulty reading and concentrating in his second-grade class. On examination, seven café-au-lait spots on his body, as well as two small, soft masses above his orbit, are seen. He also has axillary freckling. His mother also has café-au-lait spots on her arms. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Congenital hypothyroidism
Marfan syndrome
Neurofibromatosis
Osteogenesis imperfecta
Tuberous sclerosis
74) A one-year-old girl is brought to the emergency department (ED) by her mother due to a one-day history of fever and drowsiness. The child has been irritable since yesterday. On examination, she is hypothermic, lethargic and has nuchal rigidity. She flexes her hips when her neck is flexed. She appears septic, and large petechial and purpuric lesions are developing on her body. In the ED, she suddenly becomes hypotensive. Despite aggressive fluid and antibiotic resuscitation, the child dies. What will most likely be revealed as the cause of death during the autopsy of this child?
Myocarditis and heart failure
Acute respiratory distress syndrome
Bone marrow failure
Adrenal gland failure
Acute renal failure
75) A 1 and half -year-old girl is sent to a children's hospital for evaluation following a nosebleed which was so severe as to require nasal packing and transfusion of platelet concentrates. When a blood sample had been drawn in the emergency room for serum chemistry studies, the local hospital laboratory had noted that the clot that formed was unusual in that it failed to retract. Peripheral blood smear obtained by finger puncture showed an appropriate number of normal-sized platelets, all of which were individual, without clumping. At the children's hospital, it was noted that the child's parents were cousins. Special platelet studies showed that the child's platelet's failed to aggregate with any physiologic aggregating agent, including a high concentration of exogenous ADP. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Bernard-Soulier syndrome
Chediak-Higashi syndrome
May-Hegglin anomaly
Thrombasthenia
Von Willebrand disease
76) A boy has returned home from visiting his grandmother in a rural area. He spent most of his time swimming, playing in the yard, helping in the gardens, and chasing his Chihuahua; his grandma says “he was generally dirty!” He was noted 2 weeks ago to have “infected mosquito bites” on his neck and chin for which the local doctor had him just scrub with soap; a few remain and are shown in the photograph below. His mother brings him into the office with the complaint of dark urine, swelling around his eyes, and shortness of breath. You also find him to have hypertension and hepatomegaly. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his problem?
IgA nephropathy
Post streptococcal glomerulonephritis
Idiopathic hypercalciuria
Pyelonephritis
Sexually transmitted disease
77) A 4-year-old boy and his family have recently visited a local amusement park. Several of the family members developed “gastroenteritis” with fever and diarrhea, but the 4-year-old’s stool was slightly different, as it contained blood. His mother reports that in the past 24 hours he developed pallor and lethargy; she relates that his face looks swollen and that he has been urinating very little. Laboratory evaluation reveals a hematocrit of 28% and a platelet count of 72,000/μL. He has blood and protein in the urine. Which of the following diagnoses is most likely to explain these symptoms?
Henoch-Schönlein purpura
Intussusception
IgA nephropathy
Meckel diverticulum
Hemolytic-uremic syndrome
78) A 4-day old pre term male neonate is being managed in the neonatal intensive care unit. He was born in the 34th week of gestation via lower segment caesarian section. On the first day of life, he developed tachypnea, grunting and nasal flaring. Chest x-rays showed a ground glass appearance of both lungs. He underwent endotracheal intubation and therapy with intravenous fluids, positive pressure ventilation, and intravenous antibiotics. He consequently showed remarkable improvement; however, he is currently beginning to have increased gastric residues. What is the most likely cause for this child's increased gastric residues?
Tracheo-esophageal fistula
Necrotizing enterocolitis
Duodenal atresia
Meconium aspiration syndrome
Pyloric stenosis
79) A 14-month-old infant suddenly develops a fever of 40.2C (104.4F). Physical examination shows an alert, active infant who drinks milk eagerly. No physical abnormalities are noted. The WBC count is 22,000/μL with 78% polymorphonuclear leukocytes, 18% of which are band forms. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis? Pneumococcal bacteremia . Roseola
Pneumococcal bacteremia
Roseola
Streptococcosis
Typhoid fever
Diphtheria
80) The parents of a 7-day-old infant bring her to your office for a swollen eye. Her temperature has been normal, but for the last 2 days she has had progressive erythema and swelling over the medial aspect of the right lower lid near the punctum. Her sclera and conjunctiva are clear. Gentle pressure extrudes a whitish material from the punctum. Which of the following ophthalmic conditions is the correct diagnosis?
Chalazion
Dacryocystitis
Preseptal cellulitis
Hyphema
Congenital Sjögren syndrome
81) A 14-year-old girl awakens with a mild sore throat, low-grade fever, and a diffuse maculopapular rash. During the next 24 hours, she develops tender swelling of her wrists and redness of her eyes. In addition, her physician notes mild tenderness and marked swelling of her posterior cervical and occipital lymph nodes. Four days after the onset of her illness, the rash has vanished. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Rubella
Rubeola
Roseola
Erythema infectiosum
Erythema multiforme
82) A 5-day-old male term neonate has been passing maroon-colored stools for the past three days, along with frequent episodes of vomiting. He is being breastfed by his mother, who is an asthmatic. His vital signs are within normal limits. The physical examination is unremarkable. Stool examination is positive for RBCs and eosinophils. What is the most likely cause of this patient's findings?
Necrotizing enterocolitis
Viral gastroenteritis
Meckel's diverticulum
Milk protein intolerance
Hirschsprung's disease
83) A term neonate develops apnea, tachypnea, and seizures in the first 2 hours of life. The infant is large for gestational age and appears obese. Physical examination is otherwise unremarkable. Serum studies demonstrate a blood glucose level of 30 mg/dL. The mother most likely has which of the following conditions?
Diabetes mellitus
Emphysema
Hepatic cirrhosis
Hyperthyroidism
Rheumatoid arthritis
84) A 4-year-old child was brought in for evaluation of sleep problems. He cried and screamed within an hour of falling asleep. He seemed disoriented and confused; he did not seem aware of his parents’ presence. They were unable to arouse him to comfort him. This resolved spontaneously, and he had no recollection of the event the next morning. You informed the parents that he was most likely experiencing which of the following?
nightmares
night terrors
somnambulism
somniloquy
narcolepsy
85) A male infant was found to be jaundiced 12 hours after birth. At 36 hours of age, his serum bilirubin was 18 mg/dL, hemoglobin concentration was 12.5 g/dL, and reticulocyte count 9%. Many nucleated RBCs and some spherocytes were seen in the peripheral blood smear. The differential diagnosis should include which of the following? Pyruvate kinase deficiency . Hereditary spherocytosis
Pyruvate kinase deficiency
Hereditary spherocytosis
Sickle-cell anemia
Rh incompatibility
Polycythemia
86) On a routine well-child examination, a 1-year-old boy is noted to be pale. He is in the 75th percentile for weight and the 25th percentile for length. Results of physical examination are otherwise normal. His hematocrit is 24%. The answer to which of the following questions is most likely to be helpful in making a diagnosis?
What is the child’s usual daily diet!
Has anyone in the family received a blood transfusion!
Is the child on any medications!
What is the pattern and appearance of his bowel movements!
Did the child receive phototherapy for neonatal jaundice!
87) A 4-year-old boy is seen in the office for a general check-up. The child appears well nourished and has normal developmental milestones. His temperature is 36.6 C (98 F), pulse rate is 80/min, and blood pressure is 110/70 mmHg. On abdominal palpation, there is a lobular right-sided flank mass, and the kidneys are palpable bilaterally. What is the most likely cause of the flank mass in this child?
Tumor originating from the metanephros
Malignancy of neural crest cells
Polycystic kidney disease, infantile type
Renal cell carcinoma, embryonal variant
Acquired renal cystic disease
88) A 5-month-old boy is brought to the office for a mass in his left groin area. The infant is on the examination table, quietly sucking on his pacifier. On examination, there is a fluid-filled sac that does not reach the inguinal ring and transilluminates well. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Hematoma
Hydrocele
Inguinal hernia
Testicular torsion
Testicular tumor
89) A 6-month-old infant is taken to the emergency department because he had a seizure. Physical examination demonstrates premature closure of cranial sutures and markedly bowed legs. Laboratory studies demonstrate low serum phosphate levels, with normal vitamin D and parathyroid hormone levels. Urinalysis shows high phosphate levels, but no increased excretion of glucose, amino acids, or protein. The child's maternal grandfather had crippling bone disease, and his mother has mild bowing of the legs. Which of the following is most likely diagnosis?
Fanconi syndrome
Hypophosphatemic rickets
Osteogenesis imperfecta
Osteomalacia
Paget disease of bone
 |
90) The mother of a 3-day-old infant brings her child to your office for an early follow-up visit. The mom notes that the child has been eating well, has had no temperature instability, and stools and urinates well. She notes that over the previous 3 days the child has had a progressive rash on the face as pictured here. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis? |
P1682 Q90
Herpes
Neonatal acne
Milia
Seborrheic dermatitis
Eczema
|
P1682 Q91
 |
91) An 8-hour-old infant develops increased respiratory distress, hypothermia, and hypotension. A complete blood count (CBC) demonstrates a white blood cell (WBC) count of 2500/μL with 80% bands. The chest radiograph is shown below. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis? |
Congenital syphilis
Diaphragmatic hernia
Group B streptococcal pneumonia
Transient tachypnea of the newborn
Chlamydial pneumonia
92) A 3-year-old child is taken to a pediatrician because he develops burning pain, erythema, and swelling minutes after being exposed to the sun. Physical examination demonstrates erythema with swelling of the hands and arms. The skin is thickened on the backs of the hands but does not show blistering or scarring. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Acute intermittent porphyria
Erythropoietic protoporphyria
Hepatoeryfhropoietic porphyria
Porphyria cutanea tarda
Variegate porphyria
93) An infant born at 35 weeks’ gestation to a mother with no prenatal care is noted to be jittery and irritable, and is having difficulty feeding. You note coarse tremors on examination. The nurses report a high-pitched cry and note several episodes of diarrhea and emesis. You suspect which of the following?
Fetal alcohol syndrome
Prenatal exposure to marijuana
Heroin withdrawal syndrome
Cocaine exposure in utero
Tobacco use by the mother
94) A previously healthy full-term infant has several episodes of duskiness and apnea during the second day of life. Diagnostic considerations should include which of the following?
Hemolytic anemia
Congenital heart disease
Idiopathic apnea
Harlequin syndrome
Hyperglycemia
95) A very concerned mother brings a 2-year-old child to your office because of two episodes of a brief, shrill cry followed by a prolonged expiration and apnea. You have been following this child in your practice since birth and know the child to be a product of a normal pregnancy and delivery, to be growing and developing normally, and to have no chronic medical problems. The first episode occurred immediately after the mother refused to give the child some juice; the child became cyanotic, unconscious, and had generalized clonic jerks. A few moments later the child awakened and had no residual effects. The most recent episode (identical in nature) occurred at the grocery store when the child’s father refused to purchase a toy for her. Your physical examination reveals a delightful child without unexpected physical examination findings. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Seizure disorder
Drug ingestion
Hyperactivity with attention deficit
Pervasive development disorder
Breath-holding spell
96) You are called to examine a 2-day old male infant due to difficulty in feeding. He becomes cyanotic and short of breath when he feeds, but turns pink when he cries. His prenatal, birth and family histories are unremarkable. His vital signs are normal. Chest auscultation is normal. His peripheral pulses are full and symmetric. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Cyanotic heart disease
Acyanotic heart disease with left-to-right shunt
Choanal atresia
Transient tachypnea of the newborn
Laryngomalacia
97) A neonate has an obviously abnormal foot. The foot is in a markedly plantar flexed position, with the sole facing the adjacent leg in a position of marked adduction. No other anomalies are noted on physical examination. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Epispadias
Hypospadias
Talipes calcaneovalgus
Talipes equinovarus
Torticollis
98) A mentally retarded 10-year-old boy presents with arthritis, nephrolithiasis, and progressive renal failure. Since his first years of life, he manifested peculiar neurologic abnormalities consisting of self-mutilative biting of the lips and fingers, choreoathetosis, and spasticity. Two male relatives on his mother's side presented with a similar condition and died in their teens. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Chronic lead intoxication
Fragile-X syndrome
Gout
Huntington disease
Lesch-Nyhan syndrome
99) A previously healthy 7-year-old girl comes to the office with complaints of episodic abdominal pain over the past several months. The pain is periumbilical and sharp but does not wake her from sleep or interfere with play. She has no fever, joint complaints, or constipation or diarrhea. Growth and development have been normal. The physical examination is within normal limits. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Acute appendicitis
Acute cholecystitis
Crohn disease
Functional abdominal pain
Irritable bowel syndrome
100) A 4-month-old male infant is brought to the office by his parents due to progressive lethargy, poor feeding, fatigue and increasing pallor for the past four weeks. His antenatal and birth histories are unremarkable. His diet consists mainly of breast milk. His immunizations are up-to-date. His mother's blood type is 0 +. Physical examination reveals a webbed neck, cleft lip, shielded chest, triphalangeal thumbs, and pale mucous membranes and conjunctivae. Cardiac auscultation reveals mild tachycardia and a systolic ejection murmur over the left upper sternal border. The initial investigations reveal the following: Hb 8 g/dl, Ht 26%, WBCs 7,000/mm3, Platelets 300,000 /mm3, Reticulocytes 04%, MCV 104 fl, Blood type A -, Bilirubin direct 0.1 mg/dl, Bilirubin total 1.0 mg/dl. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Diamond-Biackfan anemia
Wiskott-Aidrich syndrome
Transient erythroblastopenia of childhood
Fanconi's anemia
Idiopathic aplastic anemia
{"name":"USS DES Test 9A (Start from page 1654)", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QG29LOG","txt":"1) An African-American boy is in the newborn nursery with a bulge on his abdomen that was identified immediately after birth and is most pronounced during crying. The patient was born to an 18-year-old woman who did not receive prenatal care or take prenatal vitamins. Vitals are normal. Examination shows a soft swelling at the umbilical ring. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis and best course of action for this patient?, 2) A 14-year-old girl is brought to the physician’s office because of irregular menstrual periods. She had her menarche at age 13, and since then her periods have been irregular with the cycles varying from 3 to 6 weeks. She has no other symptoms. Physical examination is unremarkable. She has age appropriate secondary sexual characteristics. A urine pregnancy test is negative. Serum prolactin and thyroid stimulating hormone levels are normal. Administration of micronized oral progesterone results in withdrawal bleeding in 3 days. Which of the following most likely explains her irregular periods? ., 3) Parents bring their 17-year-old son to the emergency department due to his strange behavior at times during the past few weeks. The boy is normally polite and soft-spoken, but he has recently become irritable, impatient, and rude. His parents initially dismissed his behavior as a “phase” with the expectatioin that he would grow out of it. However, they became very concerned on discovering that he had stolen money from their wallets and was sleeping erratically. When questioned by his father about his strange behavior, the boy responsed, “I’m on a secret mission. The king of Norway has sent me here to spy on the US government.” His temperature is 36.6 C, BP is 144\/94 mmHg, pulse is 118\/min, and respirations are 18\/min. On physical examination, the patient appears to be irritated. He is sweating profusely and his pupils are dilated. He is observed in the emergency department for several hours, his condition improves, and he is discharged to the care of his parents. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?","img":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/3012/images/ogquiz.png"}