IPPC part 1
Which of the following clinical features makes bacterial tonsillitis LESS likely?
A.Temperature >39oC
B.Cough
C.Age 5-10 years
D.Tender lymphadenopathy
E.Purulent tonsillar exudate
What is the most frequent cause of bacterial meningitis in neonates?
A.Streptococcus pneumoniae
B.Escherichia coli
C.Staphylococcus aureus
D.Streptococcus agalactiae
E.Streptococcus pyogenes
Which of the following results has the highest specificity for UTI?
A.Urinalysis positive for leukocyte esterase
B.Urinalysis positive for blood
C.White Blood Cell count >15
D.Urinalysis positive for Nitrites
E.Urine microscopy showing > 100 WCC
Which of the following is the gram stain appearance of Neisseria meningitidis?
A.Gram positive rods?
B.Gram negative rods?
C.Gram positive cocci in chains?
D.Gram negative cocci?
E.Gram positive cocci in clusters?
Which of the following statements are true?
A. Abdominal pain with defecation is common in Crohn disease
B. Lactose intolerance is a common cause of diarrhoea in children
C. Opiates are contraindicated in children with inflammatory bowel disease
D. Stool microscopy is helpful in the diagnosis of fat malabsorption
A 15 year old female presents with 6 months of bloody diarrhoea, abdominal pain and 5 kg weight loss. On examination she is pale, pre-pubertal, height has fallen from the 50th to 3rd percentile. She is malnourished and has painful raised discoid lesions over her shins. She has finger clubbing, no findings on abdominal examination and a discharging perianal fistula on examination of anus. Which of the following statements are True?
A) Stool cultures would be useful
B) Ulcerative colitis is an important differential diagnosis
C) Skin lesions likely to be an allergic reaction
D) FBC, biochemistry and inflammatory markers (ESR, CRP) would help in the diagnosis
E) Upper endoscopy and Colonoscopy would be next step in diagnosis
F) MRE ( Magnetic Resonance Enterography ) not indicated at this stage
G) Steroids would be first line therapy
Which of the following statements are True?
A) Likely diagnosis is sclerosing cholangitis
B) Liver biopsy is next line of investigation
C) Azathioprine should be commenced
D) Patient is likely to require liver transplant before adult life
Which of the following questions is/are true? (you have 1 attempt)
A) The definition of conjugated hyperbilirubinaemia is a direct bilirubin fraction of greater than 30% or >30mmol/l
B) A baby is said to have prolonged jaundice if the jaundice persists more than 1 week
C) The best test to check for synthetic liver function in a child with abnormal liver function tests is the internal normalized ratio (INR)
D) Conjugated hyperbilirubinaemia in a neonate is always pathological
E) Urinary tract infections can cause unconjugated or conjugated jaundice in a neonate
What is the most important question when faced with a jaundiced infant at 3 weeks of age ? (you have 1 attempt)
A) Type of feeding – breast or formula ?
B) Is the baby gaining weight appropriately ?
C) Is the jaundice conjugated or unconjugated ?
D) Family history of neonatal jaundice ?
A 6 month old boy presents to your office with a history of high grade fever of two days’ duration, irritability and refusal to feed. On examination he is alert but withdrawn, becomes very irritable on handling, has stable vital signs, and has a bulging fontanelle. Neurological examination is otherwise normal, there is no neck stiffness and Kernig sign is negative. Which ONE of the following statements is true? (you have 1 attempt)
A) Meningitis is unlikely in the absence of neck stiffness and a negative Kernig sign
B) Absence of papilloedema in an infant or child excludes significantly raised intracranial pressure
C) A bulging fontanelle is a contraindication for doing a lumbar puncture in a case of suspected meningitis
D) If you suspect meningitis in a child who is clinically stable and has no neurological signs, the child may be observed and managed conservatively for a period of 2 to 4 hours if you are uncertain about the clinical diagnosis
E) A CT scan of the head is ideal to rule out raised intracranial pressure prior to doing a lumbar puncture in a child with suspected meningitis
F) A lumbar puncture (LP) is the investigation of choice in a child with suspected meningitis who does not have clinical features to suggest severely raised intracranial pressure
Which ONE of the following statements is true regarding bacterial meningitis? (you have 1 attempt)
A) Organisms most commonly causing meningitis in neonates are Streptococcus pneumoniae and Neisseria meningitidis.
B) Ampicillin and cefotaxime are the antibiotic combination of choice for empiric treatment of meningitis in the first six months of life
C) Meningococcus type C is the commonest cause of meningococcal infection in Australia
D) The Australian immunisation schedule includes routine immunisation of all children against type B meningococcal infection at 1 year of age
E) Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccine has a 60% efficacy rate in terms of protection against bacterial meningitis caused by Haemophilus influenzae type b
Which of the following statements are true?
A) A majority of children with recurrent abdominal pain have no underlying organic pathology
B) Recurrent abdominal pain syndrome is unlikely in pre-schoolers, especially before three years of age.
C) Two percent of children of school going age have recurrent abdominal pain syndrome
D) Recurrent Abdominal Pain Syndrome is characterised by changes in bowel habits
E) Dysphagia is suggestive of underlying organic pathology
F) Eosinophilic oesophagitis may responds to proton pump inhibitors
G) A negative tissue transglutaminase test rules out the possibility of coeliac disease
H) Inflammatory bowel disease is unlikely in the absence of an gross abnormalities of initial blood screen
I) A family history of irritable bowel syndrome is often present in cases of recurrent abdominal pain syndrome
J) An inspection of the anal region (for fissures) is an important part of physical assessment in children with recurrent abdominal pain.
What is the etiology of GORD?
A) Transient relaxations of lower esophageal sphincter
B) Presence of hiatal hernia
C) Abnormalities of esophago-gastric junction
D) All of the above
How do you generally diagnose gastroesophageal reflux disease (GORD)?
A) Through a history of typical reflux symptoms
B) Through esophageal and gastric ultrasonography
C) Through barium contrast radiography
D) Through specific testing (upper GI endoscopy and/or esophageal pHmonitoring)
E) It depends on the age of the child
In an infant younger than 1 year of age with uncomplicated recurrent regurgitation and vomiting you prescribe PPIs:
A) If symptoms are frequent and troublesome
B) If symptoms are unresponsive to acid buffering agents
C) Only if ultrasonographic evidence of reflux is available
D) Only if barium contrast radiography is suggestive of reflux
E) Never
Which of the following statements are true? (you have 1 attempt)
A) A morbilliform rash may be seen following MMR vaccination
B) Post auricular and occipital lymphadenopathy are classically a feature of measles infection
C) In utero rubella infection at any time up to 16 weeks gestation can cause sensorineural deafness.
D) The rash in roseola infantum is associated with resolution of fever
E) In utero infection with parvovirus B19 can cause non-immune hydrops fetalis
Which of the following statements are true? (you have 1 attempt)
A) The rash in viral urticaria is classically pruriticclose
B) Koebner’s phenomenon is a bacterial toxin mediated reaction
C) Adenoviral infections may cause an exudative tonsillitis in toddler
D) The rash in scarlet fever is typically urticarial
E) Herpes simplex virus infection is characterised by individual papules which never coalesce
Which statement is correct? (you have 1 attempt)
A) Following TB exposure/infection young children are the least vulnerable and rarely develop active TB disease
B) Adolescent children do not develop sputum sm+ TB and or not infectious
C) In children, the vast majority of those who develop active TB disease do so within 12 months of TB infection
Which statement is correct? (you have 1 attempt)
A) Diagnosing TB in children is too difficult and a waste of time
B) Doing an incision biopsy is the best way to confirm a diagnosis of TB cervical adenitis
C) Most children with TB will present to the TB clinic (TB program)
D) Children can be diagnosed with good accuracy using a simple logical approach
Which statement is correct? (you have 1 attempt)
A) BCG is a poor vaccine and not important in TB endemic countries
B) TB preventive therapy is a luxury and can only be given to children in rich countries
C) Children are more difficult to treat than adults
D) Children do not get drug resistant TB
E) Children usually show excellent response to TB treatment
Which of the following statements is/are true in regards to viral gastroenteritis? (You only have 1 attempt)
A) When giving a fluid bolus, half normal saline (N/2) with 2.5% dextrose is an appropriate fluid to use.
B) Nasogastric rehydration with an oral rehydration solution is as safe as (or safer than) and as effective as intravenous fluid in the treatment of gastroenteritis with moderate dehydration.
C) Anti-motility agents are useful in decreasing diarrhoea in viral gastroenteritis
D) Continued breast feeding is recommended throughout the illness.
F) Lactose free formula is recommended in children with acute gastroenteritis in the recovery phase.
When examining a newborn: which of the following is true (You have 1 attempt)
A) Answer All variation from average require further investigation
B) Abnormalities documented prior to discharge from hospital can be followed appropriately
C) Birth growth parameters do not need documentation if the child has a good birth weight
D) There is no bearing of the gestational age on a child’s weight
E) The child should be examined in isolation of his/her parent to allow a calm environmentclose
Which of the following statements is true regarding newborn examination? (you have 1 attempt)
A) Mongolian spots are raised unlike bruises
B) A pustular rash in a newborn may be of benign etiology
C) Cephalohematoma crosses skull sutures
D) Hemangiomas are always present at birth
E) Erythema toxicum requires early antibiotics
Which of the following statements is true? (you have 1 attempt)
A) A pink stain in the nappy in the first 2 days of life should prompt immediate investigation with urine sent for culture
B) A newborn’s heart rate is normally between 120-160 beats per minute
C) Umblical granulomas have surrounding erythema
D) A hazy cornea, buphthalmos and excessive lacrimation are signs of infantile cataract
E) Leukocoria is a transient condition in the newborn examination
Regarding Developmental Dysplasia of the hip (DDH), which of the following is true (You have 1 attempt)
The family history is always positive
Breech presentation is a known risk factor for DDH
Is confirmed by a hip Xray in the first weeks of life
Is quite obvious on observation of a baby
Will require treatment with a Pavlik harness in the majority of cases
What is/are risk factors for adverse neuro-developmental outcomes? (you have 1 attempt)
A) Birth weight 1000gm
B) Gestational age 28 weeks
C) Need for a major surgical intervention
D) All of the above
What is not correct when immunising an infant born at premature gestation? (you have 1 attempt)
A) Preterm infants generally respond satisfactorily to vaccines
B) Immunisation has been associated with an increased risk of apnoea in preterm infants vaccinated in hospital, particularly those still requiring complex medical care and/or with an existing history of apnoea
C) infants should be vaccinated according to the recommended schedule at the usual chronological age, without correction for prematurityclose
D) Low-birth-weight preterm newborn infants respond as well to hepatitis B-containing vaccines as full-term infants
A four week old term infant has presented to you with history of jaundice and clay coloured stools. What is the likely diagnosis?
A) Physiological jaundice
B) G-6-PD deficiency
C) Late-onset breast milk jaundice
D) Biliary atresia
A three week old term male infant of Asian ethnic background has presented with lethargy, poor feeding, deep jaundice and exposure to naphthalene balls. What is the likely diagnosis?
A) Physiological jaundice
B) G-6-PD deficiency
C) Late-onset breast milk jaundice
D) Biliary atresia
Which of the following statements are true with regard to poverty: (You only have 1 attempt)
A) Families have insufficient income to maintain basic subsistence
B) It does not have an impact on early childhood developmentclose
C) Families have sufficient income to allow family members to maintain social roles, participate in relationships and be full members of society
D) Poverty in childhood is associated with a greater risk of low birth weight, child mortality, being unimmunised, poor school attendance and performance, emotional disorders, child abuse and neglect, injuries and respiratory disorders.
Which of the following statements is true regarding inequality and inequity? (You only have 1 attempt)
A) Inequality just means something is different
B) Inequity is an unjust and unpreventable difference in health outcomes
C) Inequity has a moral dimension
D) Social gradients are rare
Which of the following statements is true about early childhood? (You only have 1 attempt)
A) How a brain develops depends on the genes you are born with
B) Brain development is linearclose
C) The experiences you have before age three have a limited impact on later development
D) A toddler’s brain is much more active than the brain of a university student
Which of the following statements are true? (you have 1 attempt)
A) Measles vaccination may be administered before 12 months of age
B) The immune system responds to polysaccharide vaccines from birth
C) Conjugate vaccines are immunogenic under 2 years old and require several doses
D) The MMRV vaccine is given at 24 months as part of the Australian immunisation schedule
E) Adolescents are susceptible to pertussis
Which of the following statements are true? (you have 1 attempt)
A) The highest notification rates for pertussis is in infants under one year old
B) Varicella vaccine has 100% efficacy
C) Varicella vaccination is not required in adolescents and young adults
D) House hold contacts of immuno-suppressed persons should NOT receive varicella vaccine
E) Influenza vaccine is recommended in children under five years of age
F) The HPV vaccine is currently being administered to females aged 10-13 years
Parents bring their 3 month old with concern “My child stops breathing”. What is next best step or investigation? (You have 1 attempt)
A) Admit to hospital
B) Refer to sleep specialist
C) Organise chest X-ray
D) Blood test to rule out anaemia
E) Detailed history and examination and systematic approach to investigation
Which of the following statements is/are true in relation to Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS)? (More than one answer is correct)
A) The peak age of incidence for SIDS is 2-5 months
B) Immunisation increases the risk of SIDS
C) There is a summer peak for SIDS
D) Parental smoking has not been associated with an increased risk for SIDS
E) A baby at increased risk for SIDS often appears perfectly normal on examination
F) A parental history of obstructive sleep apnea is a strong indication for sleep study in a baby
G) All babies should ideally have a home apnea monitor.
What measures can prevent SIDS or reduce its risk? (you have 1 attempt)
A) Sleeping with your child and observing
B) Apnea monitor/ baby monitor
C) Breast feeding
D) Bottle feeding with low reflux formula
E) Sleeping the baby in prone position
In which of the below situation the infant should be referred to Sleep specialist/Tertiary children’s service? (More than one answer is correct) (you have 1 attempt)
A. A child presenting with settling issues
B. 3 month old child with snoring
C. Infant after MMR vaccination
D. 6 weeks old infant with stridor and failure to thrive
E. Infant with sibling died of SIDS
Frequent and longer breastfeeding after two weeks of age mean: (you have 1 attempt)
A) An emptier breast therefore increased amounts of FIL.
B) An emptier breast therefore decreased amounts of FIL
C) Increased maternal prolactin levels therefore more milk production
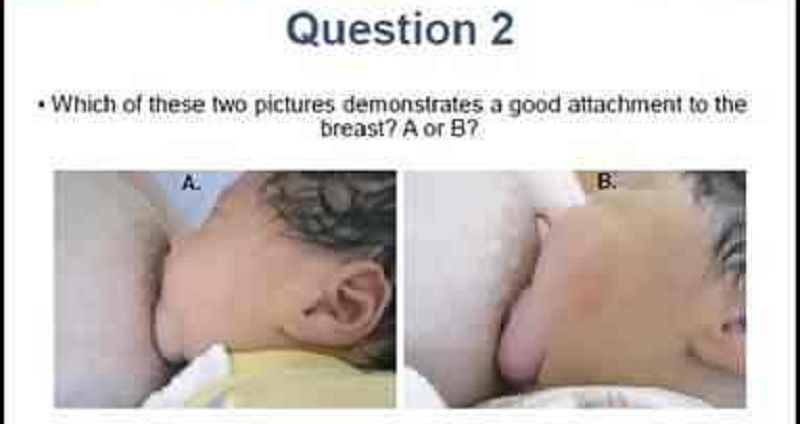
Which of the two pictures in the previous slide demonstrates a good attachment to the breast? A or B? (you have 1 attempt)
A) A
B) B
What signs can indicate that a breast feeding mother has candida infection of the breast? (you have 1 attempt)
A) The mother reports a stabbing shooting pain that ascends from the nipple into the breast
B) Mothers nipple and areola present with redness, and dry flaky skin?
C) The mother complains of burning, itchy or stinging feeling of the breast?
D) The breastfeeding infant presents with thrush to the mouth or bottom.
E) All of the above
How often can a newborn infant be expected to breast feed? (you have 1 attempt)
A) 4-6 times a day
B) 7-9 times a day
C) As often as 8-12 times a day
Which of the following strategies would you advise to a mother to help increase her milk supply? (you have 1 attempt)
A) Increase frequency of breastfeeding to 2-3hrly
B) Express following breast feeding for a few minutes on each side
C) Encourage mother to increase her fluid intake
D) All of the above measures
Should breast feeding be discontinued in infant’s with breast milk jaundice? (you have 1 attempt)
A) Yes
B) No
Solids are introduced at around 6 months because: (you have 1 attempt)
A) there is a need to meet increasing needs for micronutrients, energy and protein.
B) this is the age at which most babies are able to sit up, and have good head and neck control.
C) at 6 months the gastrointestinal tract is mature enough to manage food antigens and foodborne pathogens.
D) All of the above
Select the correct statement: (you have 1 attempt)
A) Babies should remain on smooth puree until they’re 12 months of age
B) Babies cannot chew foods at 7 or 8 months because they may not have teeth
C) It’s best to offer only fruit and vegetables for the first few months
D) Offering a wide variety of foods, increasing in textural complexity is the best way to progress with infant feeding
Foods that are potentially allergenic should be introduced: (you have 1 attempt)
A) Within the first 12 months of life
B) Never
C) After the child’s 2nd birthday
D) Before 3 months of age
Which statement is true? (you have 1 attempt)
A) Children should never have snacks – just three meals a day
B) It’s ok for children to drink as much milk as they want – there’s no such thing as too much milk
C) If a child eats less on one day, they may make up for it the next day – children are good at regulating their appetite and food intake
D) Role modelling from parents at meal times is not important
If a child refuses to eat parents should: (you have 1 attempt)
A) Hold their arms down and force-feed with a spoon
B) Yell at the child – anger is an effective tool at the table
C) Remain calm and positive, allow the child a reasonable period of time with the food and then remove it
D) Make a different meal for the child
Which of the following are true? (You only have 1 attempt)
A. “Purple” crying can begin at 8 weeks of age
B. Empathy is of little valueclose
C. These babies are at increased risk
D. There are no long term sequelae
Which of the following is false: (You only have 1 attempt)
A. GORD is common in this age group
B. GORD is best managed by proton pump inhibitors in this age group
C. There is much to learn about the relationship between the gut biome and brain functioningclose
D. A role for prebiotics is intriguing but not established
Distressed babies that cry their way to to the doctor have distressed parents. In managing such a distressed family which of the following are true? (You only have 1 attempt)
A. The timeline of the crying and the evening amplification must be established by the history
B. When not crying the history must establish that the baby is Alert, Active and Appropriately socially interactive, Breathing without chest recession, good Colour and Drinking enough to produce 5 wet nappies in 24 hours (the ABCDs)
C. Maternal exhaustion can look like PND
Which of the following are true?
A) Heart disease in the newborn usually presents with either heart failure or cyanosis.
B) The action of prostaglandin is to assist in closing a patent ductus arteriosus.close
C) Hypercalcaemia commonly occurs in Velocardiofacial Syndrome (VCFS).
D) Oxygen should not be administered when the patient’s wellbeing is dependant on high pulmonary resistance.
Which of the following symptoms and signs of heart failure in the newborn is/are true?
A) Tachypnoea
B) Tachycardia
C) Dyspnoea/increased work of breathing
D. Poor feeding
E. Hepatomegaly
F. Late signs include poor perfusion and circulatory collapse.
G. All of the above
Which of the following are true? (you have 1 attempt)
A) Transposition of the great vessels requires mixing of oxygenated with deoxygenated blood for survival.
B) If a baby is cyanosed in the 1st week of life, it requires urgent, usually inpatient referral.
C) Anatomically, a coarctation of the aorta usually occurs distal to the Subclavian artery.
D) Tetralogy of Fallot usually presents as heart failure in the newborn.
Which of the following are true? (you have 1 attempt)
A) The majority of neonates with SVT will go on to have episodes of SVT through childhood.
B) Long QT Syndrome is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner.
C) Long QT Syndrome can cause SVT.
D) Adenosine is administered to neonates with Long QT Syndrome.
E) None of the above
Which of the following statements are true? (You only have 1 attempt)
A) A normal physical examination at birth rules out the likelihood of congenital heart disease.
B) The recurrence risk of congenital heart disease in siblings of an affected child is increased two folds.
C) Babies with a congenital heart disease may not be symptomatic until several weeks of age
D) Innocent murmurs typically have varying intensity upon review at different times
Which of the following statements are true? (You only have 1 attempt)
A) A child with facial dysmorphism and a systolic murmur should be investigated for the possibility of heart disease
B) A normal foetal cardiac scan rules out the possibility of congenital heart diseaseclose
C) The 2008 guidelines for infective endocarditis prophylaxis for procedures, have ruled out the need for prophylaxis for several cardiac lesions that previously mandated prophylaxis
D) Children with acyanotic heart disease are predisposed to paradoxical emboli and brain abscess formation
Which of the following statements is/are true?
A) All children with snoring should have adenoidectomy
B) Topical nasal steroid spray can be useful for treatment of children with snoring due to allergic rhinitis
C) Children with quinsy have trismus
D) Children with Down syndrome are at risk of obstructive sleep apnoea
E) Children who have had 6 or more attacks of tonsillitis in a year or 4-5 attacks per year for 2 years or 3 attacks per year for 3 years warrant tonsillectomies
Which of the following statements is/are true? (you have 1 attempt)
A) Early detection of hearing impairment is crucial because of its impact on speech outcomes.
B) A child should ideally be fitted with hearing aids at 12 months of age.
C) Normal conversation occurs at 50 – 75 dB
D) Auditory brainstem response testing is an objective assessment of hearing suitable for neonates
Which of the following are true? (You have 1 attempt)
A) Permanent hearing loss in children can be caused by congenital infections, ossicle anomalies and Connexin 26 mutations.
B) Genetic hearing loss is always present at birthclose
C) MRI is the preferred imaging modality for sensorineural hearing loss
D) A family history of hearing loss is always present if the cause is genetic
Which of the following are true? (You have 1 Attempt)
A) Unilateral hearing loss is not clinically significantclose
B) A child with unilateral hearing loss can pass VROA hearing test
C) Children with unilateral hearing loss do not need ongoing hearing tests
D) Children with unilateral hearing loss should be offered Connexin 26 gene testing
Which of the following is/are true? (You have 1 attempt)
A) Conductive hearing loss in children is always permanent
B) Children with permanent conductive hearing loss benefit from amplification and early intervention
C) CT scan should be done in infancy for permanent conductive hearing loss.
D) Permanent mixed hearing loss always means that there is a problem with both the middle and inner ear.
Which of the following is/are true? (You have 1 attempt)
A) Children who pass newborn hearing screening never need another hearing test
B) Congenital cytomegalovirus infection causes hearing loss in both symptomatic and asymptomatic babies
C) Valganciclovir is indicated in babies with congenital CMV infection and isolated sensorineural hearing loss
D) Psychosocial factors are important mediators of the outcome of children with hearing loss
Which of the following statements are true?
A) Pneumonia kills almost 1 million children <5 years of age, worldwide, each year
B) Death rates from childhood pneumonia are rising worldwide
C) The pneumococcal vaccine is the only vaccine which can help reduce rates of pneumoniaclose
D) Pneumococcal vaccine was introduced for all Australian children in 2000
E) Aboriginal/Torres strait Islander people are at higher risk of severe pneumonia than non-Aboriginal people
Which of the following statements are true?
A) Pneumonia can present as fever and tachypnoea, without cough
B) A child with pneumonia will always have crackles on auscultation
C) A child with suspected pneumonia should always have a CXR
D) CRP should always be checked in pneumonia
E) A child with pneumonia and oxygen saturations 90% in room air has mild disease
Which of the following statements are true?
A) Oral amoxicillin is first line treatment for a child with mild pneumonia
B) Suspected atypical pneumonia should be treated with roxithromycin/azithromycin
C) Group B strep causes low grade infection in neonates
D) Viruses generally cause lobar pneumonia
E) Clindamycin should be added in severe pnuemonia
Which of the following statements are true?
A) SIADH should be managed with fluid restriction and monitoring electrolytes
B) Pleural effusion always requires drainageclose
C) Necrotising pneumonia is associated with a very poor outcome
D) Loss of a clear right heart border on CXR suggests right middle lobe involvement
Which of the following statements are true? (you have 1 attempt)
A) The dose of salbutamol for acute asthma is 6 puffs (via spacer) or 2.5 milligrams (via nebuliser) in children below 6 years of age.
B) In children below 6 years of age, systemic steroid therapy should be reserved for moderate to severe asthma episodes, particularly those requiring hospitalisation.
C) The current recommended dose of oral prednisolone in moderate to severe asthma flare-up is 1-2 milligram per kilogram (maximum 50 milligrams) initial dose and 1 milligram per kilogram per day given for three to five days
D) Carbon dioxide retention detected on a venous or arterial blood gas is suggestive of a moderate acute asthma episode.
E) Pulse oximetry during acute asthma episodes is a good guide for discharge from hospital.
F) A chest X- ray is indicated during every episode of acute asthma in a child.
A two year old child presents to hospital and is treated for a mild episode of acute asthma. Prior to presentation, the parents had been treating him at home with salbutamol via spacer without much response over the last 12 hours. The child responded quickly and well to standard management in hospital. What factors may have contributed to lack of response to treatment at home? (you have 1 attempt)
A) Parents did not initiate oral steroids at home
B) Parents used a spacer device as opposed to a nebuliser which is more effective in young children
C) Parents were giving 2 puffs of salbutamol fourth hourly
D) You checked the technique of spacer use and the parents had been administering one puff followed by one breath and then the next puff
A 4 year old known asthmatic child presents to you for evaluation. She gives a history of having had acute asthma episodes 2 or 3 times in the last one year, on a background of occasional symptoms that occur once a month or less. The acute episodes are however severe and on one occasion warranted admission to the intensive care unit. Which of the following are true in regards to her asthma management? (You only have 1 attempt)
A) As per the Global Asthma Initiative Classification of asthma this child may be classified as having frequent intermittent asthma.
B) As she has infrequent symptoms she does not require preventive therapy.
C) You will refer this child to a specialist in view of the severity of her acute asthma episodes.
D) It is important to try and identify possible triggers for this child’s asthma.
Which of the following statements are true? (You only have 1 attempt)
A) Long term use of inhaled corticosteroids can cause severe retardation of growth velocity in children.
B) Long acting beta agonists may be used in isolation in the management of moderately severe asthma.
C) Monteleukast Sodium, a leukotriene receptor antagonist is useful in the management of exercise induced asthma.
D) Peak expiratory flow rate measurement is helpful in the diagnosis of asthma.
Which of the following statements are true? (you have 1 attempt)
A) The current recommendation is that every child with asthma should have an asthma action plan
B) Asthma action plans can guide parents on how to manage asthma in acute asthma episodes and in between attacks
C) Asthma action plans should also be given to schools, childcare and sporting organisations
D) In paediatric asthma management the doses of inhaled steroids should be doubled in acute asthma episodes
E) Every asthma action plan requires oral steroids to be included as a part of acute asthma management
Which of the following statements are true? (you have 1 attempt)
A) There is evidence that the use of paediatric asthma action plans improve adherence to acute and interval therapies
B) There is evidence that the use of paediatric asthma action plans reduce GP and ED visits
C) There is evidence that the use of paediatric asthma action plans does not improve self-efficacy
D) Review of asthma action plan is optional
A two year old boy presents to you late at night. He woke up in the middle of the night with cough and breathing difficulty. He has an inspiratory stridor, tracheal tug and subcostal retractions. He is alert but withdrawn and irritable on handling. He has a respiratory rate of 40, heart rate of 160, temperature 37.6 degC. His mother states that he was well that day other than a slight runny nose and cough that has been present for the past 2 days. What is your provisional diagnosis in this case? (you have 1 attempt)
A) Pneumonia
B) Laryngotracheobronchitis (croup)
C) Imagine foreign body aspiration
D) Epiglottitis
QuestionA 4 week male infant presents to you for check up. The parents are concerned that he has noisy breathing when he is awake, that generally subsides once he is asleep. On examination he has an inspiratory stridor but otherwise appears well, with no respiratory distress. What will your management be? (you have 1 attempt)
A) Reassure parents and monitor progress.
B) X -ray of the upper airways and chest.
C) Arrange for specialist review and bronchoscopy
Which of the following infants would be considered to be at a high risk of severe airway compromise if they developed bronchiolitis? (you have 1 attempt)
A) Infants under 10 weeks of age
B) Preterm or low birth weight infants
C) Infants with chronic lung disease
D) Infants with congenital acyanotic heart disease
E) All of the above
Which of the following should be considered in the differential diagnosis of bronchiolitis in a 12 month old infant? (you have 1 attempt)
A) Asthma with intercurrent viral illness
B) Pneumonia
C) Foreign body
D) Cardiac failure
E) All of the above
Which of the following statements are true? (you have 1 attempt)
A) Cystic fibrosis (CF) may present initially as recurrent viral lower respiratory tract infections
B) Finger clubbing is a late manifestation of Cystic fibrosis
C) Children with cystic fibrosis should not be given antibiotics for “mild” cough
D) Children with cystic fibrosis are predisposed to infections by Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Haemophilus influenzae
Which is/are true? (you have 1 attempt)
A) Newborn infant has insufficient strength to hold body straight when held in supine position
B) At age 0-1 month, Grasping response cannot be elicited
C) At age 0-1 month Head righting response can be elicited
D) Moro reflex present in newborn infant
E) At age 3 months, infant can noticeably respond to auditory and visual stimuli
F) At age 3 months and beyond, ATNR can be elicited
Which of the following is/are true? (you have 1 attempt)
A) A normal newborn hearing test rules out a hearing abnormality
B) If there is any parental concern about hearing the child should be referred for a formal hearing test
C) All children with speech and language delay should have a formal hearing test
D) By 2 years most children will have a vocabulary of at least 50 words
E) A child without 2 word phrases at 2 years is developmentally appropriate for their age
Is the following statement true or false? Autism Spectrum Disorder is a neurodevelopmental disorder typically characterized by impairments in three domains including communication skills, social interaction and restricted and repetitive patterns of behaviour.
True
False
The prevalence of Autism has increased since the 1970’s. What is the current accepted prevalence globally?
A) 1/60
B) 1/160
C) 1/600
Which of these is not a feature of oppositional defiant disorder? (you have 1 attempt)
A) Argumentative behaviour
B) Destruction of property
C) Angry outbursts
D) Refusal to comply with instructions
When assessing for behavioural problems, which of the following statement is incorrect? (you have 1 attempt)
A) Consider the function of the behaviour and sequence of events around the behaviour
B) Understand the factors that contribute and maintain the problem behaviour
C) Ask questions about the child’s behaviour but there is no need to consider family/parental issues
D) Determine what stressors, traumas or attachment difficulties are present for the child or within the family system
Which of the following statements is true? (you have 1 attempt)
A) Attention deficit disorder can result in behavioural difficulties however depression and anxiety do not.
B) The first-line treatment for childhood behavioural disorders is behavioural management training for the parent in conjunction with antipsychotics for the child.
C) Only positive attention is a reinforcer for children’s behaviour, therefore giving a child negative attention (e.g. Telling them repeatedly to stop what they are doing) will reduce their difficult behaviour.
D) Parent behavioural management strategies are most effective if they are built on a foundation of relationship/attachment.
E) It is not important to discuss children’s feelings or other emotional difficulties and relationship problems in other family members.
You have a parent sitting in your room telling you about how naughty their child is and that they always hit and scream and don’t follow instructions and they’ve tried everything and nothing has worked. What do you do? Select all that apply. (you have 1 attempt)
A) Don’t ask any further questions because you won’t be able to do anything about it
B) Ask further questions to clarify differential diagnosescheck
C) Refer for further assessment and testing and review progress at future appointments
D) Provide some basic behavioural management strategies for parents to trial (e.g., determining family rules, consistency between parents, following through with limits)
My 3-year-old daughter doesn’t seem to follow instructions well. I’m wondering if she has a hearing problem. She talks a lot though – she always repeats what I say and she loves saying lines from her favourite TV shows. She says them all with a lisp, which sounds so cute!’ Which two features of the above might be consistent with a language disorder? (You have 1 attempt)
A) Receptive language is better than expressive language.
B) Frequent use of echolalia.
C) Stereotyped, rote-learned language.
D) Speech sound errors.
�My 3-year-old daughter leaves out lots of sounds in her words. We struggle to understand what she is saying most of the time. She throws tantrums when we don’t know what she is trying to say.’ Would you refer this child to a speech therapist (Choose two answers)? (you have 1 attempt)
A) No. Most children will grow out of their speech errors naturally.close
B) No. Her speech errors are developmentally appropriate.close
C) Yes. Leaving sounds out of words is generally more concerning than substituting sounds in words.
D) Yes. A 3-year-old’s speech should be 100% intelligible.
E) Yes. Research indicates that children with speech sound disorders are at risk for literacy difficulties.
�My 5-year-old son started school this year and the teacher has asked me if I’ve seen a doctor about his hoarse voice. I suppose I never really noticed it – everyone in our family is really loud and I’ve got a naturally husky voice myself. He likes to shout a lot so I’m wondering if he’s done some damage to his voice. Should I get it checked out or is it just the way his voice is?’ What do we know to be true about voice and its disorders in children? (choose one answer) (You have 1 attempt)
A) Children should have clear voices if their larynx is structurally and functionally normal.
B) Vocal papilloma is the most common cause of voice disorders in children.
C) Some children can naturally have husky or hoarse voices.
D) Shouting can damage the voice so encourage the child to whisper to protect their voice.
�My 4-year-old daughter is stuttering. It started about a year ago and I was hoping it would just go away. Her brother had a stutter too at her age but he’s alright now. Though her uncle never grew out of his... I know I’m an anxious person myself and I feel like she might be a bit like me. Should I be worried or is it just a phase for her?’ You instinctively feel that this child needs to see a speech pathologist. What aspects of the situation cause you concern? (choose two answers) (You have 1 attempt)
A) Stuttering that persists greater than 6 months after 3 years of age is less likely to show spontaneous recovery.
B) Stuttering is more common in families with a history of anxiety disorders.
C) A family history of persistent stuttering is a risk factor for persistent stuttering.
D) Girls are more likely to stutter than boys.
Which of the following statements are true?
A) As most Aboriginal people live in remote areas, Aboriginal Health is the responsibility of remote GP’s
B) Aboriginal child mortality rates have decreased significantly since 1998
C) All Aboriginal people are unhealthy
D) The United Nations have adopted a single definition for the term ‘Indigenous’
Which of the following statements are true?
A) Colonisation happened a long time ago and is no longer affecting Aboriginal people
B) Factors affecting Aboriginal health status include social and economic status, health behaviours and lack of access to medical care
C) “The Gap” refers to inequalities between countries
D) Education and income have limited effect on health behaviours
Which of the following statements are true?
A) Colonisation happened a long time ago and is no longer affecting Aboriginal people
B) Factors affecting Aboriginal health status include social and economic status, health behaviours and lack of access to medical care
C) “The Gap” refers to inequalities between countriescheck
D) Education and income have limited effect on health behaviours
Which of the following statements are true?
A) Always tell families it would be better if the school gave medications
B) Some parents find a single IM iron injection less distressing for their children than daily iron dosing
C) Chronic moist cough can be a sign of bronchiectasis
D) You don’t need to test for Type 2 Diabetes in children
Which of the following statements are true? (You only have 1 attempt)
A) Life expectancy in individuals with disability is a function of their underlying diagnosis.
B) Health care for individuals with disability is highly specialised and can only be provided by specialist in disability.close
C) Routine health screening is essential for individuals with a disability.
D) The degree of disability a person experience is dependant on their underlying diagnosis.
E) Improved wheelchair access to medical centres improved health outcomes for individuals with physical disabilities.
Which of the following statements are true? (You only have 1 attempt)
A) A 7 year old boy with no language, who requires full support with all activities of daily living and attends a supported school can be described as having a global developmental delay.
B) You can reassure the mother of a 2 year old that her son who has single words only (less than 20) will catch up, boys always talk later than girls.
C) A 14 month old boy with no words, who doesn’t point, wave or respond to his name should be reviewed by a paediatrician.
D) An cognitive score of 65 on a standardised psychometric assessment means this patient has an intellectual disability in the mild range on DSM 5.
E) Mental retardation is not longer an acceptable term.
Which of the following statements are true? (You only have 1 attempt)
A) Children with Developmental Disabilities have the same health needs as all children.
B) Growth measurements should be part of routine care of all children with developmental disabilities.
C) Sleep issues are a behavioural consequence of a child’s Developmental Disability.
D) Fragile X is frequently diagnosed in a developmental service.
E) All children with language delay should have a hearing test.
Is there risk involved if one does not consider a child’s development in the context of their immediate family and social environment? Please choose the TRUE answers (you have 1 attempt)
A) There is little risk as the child’s biological makeup largely determines their developmental abilities
B) There is greater risk in trying to address family and social environment in considering a child’s development as parents will get offended and not return to see you again
C) The risk of not addressing family or social issues is that one can potentially miss opportunities to use environmental influences eg parenting or preschool placements to positively enhance a child’s developmental trajectory
Why is it important to understand brain development in terms of their “critical periods”? (you have 1 attempt)
A) It helps us to know the timelines for the development of critical skills to know if there is a delay to be concerned about
B) It helps us to know with certainty if the child has an underlying genetic condition that has led to the delay
C) It helps us with knowing the degree of urgency in which we need to act to have the child assessed and treated appropriately
{"name":"IPPC part 1", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Which of the following clinical features makes bacterial tonsillitis LESS likely?, What is the most frequent cause of bacterial meningitis in neonates?, Which of the following results has the highest specificity for UTI?","img":"https://cdn.poll-maker.com/47-1585006/shfdjkas.jpg?sz=1200-00000010141000005300"}
More Quizzes
Arrange a Party and I'll Tell you What Left 4 Dead Infected you Are!
7419
Quiz Catequese
11610
Fundemental Political Principle
520
3rd grade election 16-17
6337
Which Nintendo Character Are You? Free Personality
201017067
Harp Performance Skills - Free Online Practice
15815317
Intake and Output Practice Questions - Free Nursing
201017320
Java OOP - Test Your Object‑Oriented Skills
201015942
Am I With the Right Person? - Free Relationship Check
201017192
Kanto Pokémon: Which Gen 1 Pokémon Are You?
201018297
Trig Identities - Free Practice Online
201017652
Which F1 Driver Are You? Take the Ultimate F1!
201016648