Systemic-final-q

Medical Knowledge Challenge
Test your medical knowledge with our comprehensive quiz designed for healthcare professionals and students alike. From dermatology to hematology, this quiz spans a wide range of topics that challenge your expertise and enhance your understanding.
Features of the quiz include:
- 30 multiple-choice questions
- Detailed explanations for each answer
- Instant feedback on your performance
The skin lesion which is not associated with disorders of pigmentation is;
Freckles
Melasma
Leucoderma
Psoriasis
Vitiligo
A 60-year-old woman with small cell carcinoma of the lung notes rounding of her face, upper truncal obesity, and muscle weakness. Physical examination reveals thin, wrinkled skin, abdominal striae, and multiple purpuric skin lesions. The patient’s blood pressure is 175/95 mm Hg. Laboratory studies will likely show elevated serum levels of which of the following hormones?
1- Aldosterone
2- Corticotropin
3- Epinephrine
4- Prolactin
5- Thyrotropin
A 40 year old male presented with right testicular enlargement. Orchidectomy was performed and histological diagnosis of Seminoma was given. An identical tumour aries in the ovary is called as
Embryonal carcinoma
Dysgerminoma
Granulosa cell tumour
Choriocarcinoma
A 10 year old boy complains of intermittent abdominal pain. Endoscopy fails to demonstrate peptic ulcer or chronic gastritis. The clinician suspects that the patient may have a heterotopic rest of gastric mucosa that is producing enough acid to cause ulceration of adjacent mucosa. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Ectopic pancreatic tissue
B. Meckel’s diverticulum
C. False diverticulum
D. Appendicitis
E. Cancer of the cecum
A 70 yr old man who is hypertensive presents to ER with complaint of severe occipital headache that he describes as worst headache I ever had, on examination he has nuchal rigidity, and CT scan brain is advised. What do you think the patient is suffering from?
A) ruptured berry aneurysm
B) space occupying lesion
C) meningitis
D) encephalitis
An 8-year-old African American boy presents to the emergency department complaining of severe pain in both legs. The pain began after the boy attended a pool party and spent much of the day swimming. He reports that he has suffered from severe bouts of back and chest pain in the past owing to a preexisting medical condition. Routine laboratory studies demonstrate a severe anemia. You place the child on oxygen, begin aggressive intravenous fluid hydration, and call the blood bank to prepare for a blood transfusion. What is most likely the diagnosis?
Sickle cell anemia
Iron deficiency anemia
Megaloblastic anemia
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency
A 15-year-old girl presents to the emergency department with a petechial rash, bleeding of the oral mucosa, fatigue, and a history of recurrent sinus infections over the past 2 months. She does remember having had a bad flu- like virus about 3 months ago that caused her to miss 4 days of school. There is no hepatosplenomegaly on examination. Laboratory tests reveal anemia, neutropenia, and thrombocytopenia. There are no abnormal cell types seen on peripheral blood smear. You decide to admit the patient to the hospital and you schedule a bone marrow biopsy. What does the bone marrow biopsy show?
Hypocellular and demonstrating fatty change with no hematopoietic cells
Sticking expansion hematopoietically active bone marrow
Hypercellular bone marrow
Normocellular bone marrow
A 28-year-old man presents to his GP with a 4cm mobile anterior neck mass. A fine needle aspirate is performed which reveals cells with ‘orphan Annie eye’ nuclei and psammoma bodies. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Thyroglossal duct cyst
Follicular carcinoma
Medullary carcinoma
Papillary carcinoma
An 8-year-old boy presents to the emergency department with a swollen right knee. He denies a history of trauma to the knee. Physical examination reveals a warm, swollen, erythematous joint with a significant effusion. Upon taking a family history, you learn that two of the boy's maternal uncles suffer from a bleeding disorder. Laboratory tests reveal a prolonged PTT, a normal PT, and a normal bleeding time. To provide the proper treatment, you immediately order a clotting factor assay. What if the diagnosis?
Von Willebrand disease
Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura 3
Vilamin K deficiency
Hemophilias
A 30-year-old man presents to the emergency room with a cold, pale left foot with absent pedal pulse. He complains of loss of feeling in his left foot after several months of painful bouts in the involved area. He has smoked two packs of cigarettes a day for the past 10 years. You order an arterial biopsy of the affected region, which demonstrates intimal proliferation and thrombi with inflammatory infiltrates. You explain to the patient that the condition is associated with his smoking and that the most effective treatment is smoking cessation
Thromboangiitis Obliterans (Buerger Disease)
Kawasaki disease
Kaport sarcoma
Von-hippel lindau disease
Alzheimer disease is the most common cause of dementia in the elderly. Autopsy of the patient died of this disease shows characteristic histological features in the brain which of the following is not a feature of this disease.
1. Neuritic plaques
2. Neurofibrillary tangles
3. Cerebral amyloid angiopathy
4. Granulovacuolar degeneration
5. Lewy body
A 20-year old female complained of multiple bullae and vesicles on the face, axilla, and trunk. The lesions were noted to rupture easily that leaves shallow erosions. This disorder is caused by autoantibodies that result in dissolution of intercellular attachments within the epidermis and mucosal epithelium. The autoantibodies are directed against?
A. Desmoglein
B. Hemidesmosomes
C. Reticulin
D. Laminin
E. Keratin
In a 30 year old female breast lump of 2cm is excised having irregular borders. Histopathology report shows sclerosing adenosis. Which lesion is not a part of benign proliferative breast disease?
1. Complex sclerosing lesion
2. Duct ectasia
3. Epithelial hyperplasia
4. Fibrocystic change
5. Papilloma
A 26-year-old pregnant woman presents to your office for a checkup. She states that her pregnancy has been proceeding smoothly, although she has been feeling more tired than she expected. Her physical examination is largely unremarkable except for marked pallor. You order serum studies and find that she has decreased hematocrit, decreased ferritin, and increased total iron-binding capacity. Her peripheral blood smear shows red blood cells that are both microcytic and hypochromic. You reassure her that these findings are most likely associated with her pregnancy status and recommend iron supplements
Iron Deficiency Anemia
Sideroblastic anemia
Sickle cell anemia
Megaloblastic anemia
A 57 year old woman with anemia is found to have a decreased Vitamin B12 level. Antibodies to intrinsic factor are identified. Levels of all other vitamins are within normal limits. Which of the following is most likely to be associated with this condition?
A. Duodenal ulcer
B. Ulcerative colitis
C. Dietary Vit. B12 deficiency
D. Atrophic gastritis
E. Angiodysplasia
A 30-year-old man with Marfan syndrome presents to the emergency room with severe, sudden, tearing chest pain radiating to the abdomen and back. The pain has progressively shifted downward over the last several hours. On physical examination, he is found to have asymmetric pulses and a pericardial friction rub. ECG studies are normal and angiography shows an ascending aortic abnormality. You schedule the patient for immediate surgical repair. Which of the following statements is false?
Presents with sudden, severe, tearing left chest pain, often radiating through the back
Associated with hypertension, trauma, Marfan syndrome, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome,
Tear in aortic intima allowing formation of intramural hematoma;
Is a vascular disorder affecting children and typically follows a viral or streptococcal infection
A 62 year gentleman presents to the clinic with a 5 cm painless neck mass as well as diarrhoea for the past 3 months . A biopsy is taken and he is subsequently diagnosed with medullary carcinoma. Which of the following features is consistent with medullary carcinoma?
Grossly soft and tender mass
Diagnosis of MEN-1 syndrome
High levels of calcitonin
A 34-year-old female was brought to the physician. The patient has sinusitis, cough, skin nodules, significant purpura also noted on the extremities as well as carpal tunnel syndrome. The patient's CBC shows eosinophilia. Pulmonary function tests show an obstructive pattern improved with beta-agonist and diagnosis of asthma was made. Which of the following is correct about her condition?
1- Patient is positive to anti ds DNA antibodies
2- Patient has inflammation of the aortic arch
3- Patient has elevated IgE levels
4- Her condition is inherited as autosomal dominant pattern
5- She has vasculitis associated with hepatitis C infection.
A 50 yr old lady presents with weakness and dizziness, on examination diffuse hyperpigmentation can be seen on buccal mucosa & skin creases.lab reports show eosinophilia, lymphocytosis & neutropenia. What is your diagnosis?
A) Addisons disease
B) Graves disease
C) Adrenogenital syndrome
D) Cushing disease
Nephritic syndrome is characterised by all except:
Oliguria
Hypertension
Heavy hematuria
Haematuria
A 30-year-old woman arrives at the emergency room complaining of fatigue and dark-colored urine. While obtaining the history of her present illness, you learn that she has been recovering from a recent bout of pneumonia, for which she had been treated appropriately by her primary care physician with a course of antibiotics. Physical examination reveals an enlarged spleen and slight scleral icterus. You obtain a blood sample and decide to order a direct Coomb test. What is do you suspect?
Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemias
Iron deficiency anemia
Megaloblastic anemia
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency
An old lady 58 years of age c/o gradual on set of bone pain, anorexia, constipation, polyuria, polydipsia and muscular weakness. Her serum Ca and Alk phosphatase were raised and PO4 was low. She was probably suffering from:
1. Hypercalcemia
2. Hypophosphatemia
3. Bone tumor
4. Hyperparathyroidism
5. Hypoparathyroidism
A 70-year-old white woman presents to the clinic complaining of severe unilateral headaches and transient blurry vision. Upon physical examination, you find that there is pain upon palpation of her temples. When laboratory tests reveal an elevated ESR, you initiate treatment with prednisone to prevent possible blindness. You also ask for an ophthalmological consult and you order a temporal artery biopsy, which you suspect will reveal granulomatous inflammation and the presence of giant cells. The most likely diagnosis of this patient is:
Takayasu Arteritis
Temporal Arteritis
Chug strauss syndrome
Wegener granulomatosis
A 45-year-old obese white man presents to the clinic for an annual checkup. He has no complaints other than occasional headaches. During the history, you find that he is a smoker and has a family history of heart disease. His physical examination is significant for mild obesity and a blood pressure of 160/100. You suggest lifestyle changes including weight loss, a low-salt diet, and smoking cessation, and you also prescribe hydrochlorothiazide to treat his condition. Which of the following statement false?
Complications include CAD, MI, CVA, CHF, peripheral vascular disease, aortic dissection, retinopathy, and renal failure
Microscopic changes will show Hyaline thickening of vessels;
Primary (idiopathic) (90%): Risk factors include old age, race, diabetes, smoking, obesity, and positive family history
Most common cause of injury is immunologic mechanism (perhaps hypersensitivity reaction)
A 60 year old man presents to his physician because of progressive dysphagia, first to solids and then to liquids. Endoscopy reveals a large fungating mass 2cm above the Gastroesophageal junction. Biopsy of the mass shows that the glands have extended into muscular layer and contain large hyperchromatic nuclei. A diagnosis of esophageal adenocarcinoma is made. Which of the following conditions can result in the development of this lesion?
A. Esophageal rings
B. Esophageal webs
C. Reflux esophagitis
D. Scleroderma
E. Sliding hiatal hernia
The following Changes occur in minimal change glomerulonephritis:
Proliferation of epithelial and mesangial cells
Proliferation of mesangial cells
All of the above
None of the above
Proliferation of capsular epithelium
A 10-year-old girl presents to the clinic with fever, malaise, migratory polyarthritis, and a blanching erythematous ring-shaped rash over her proximal extremities. On further questioning, you find out that she suffered from a severe sore throat 2 to 3 weeks ago. Serum studies demonstrate an ESR of 100 and a positive anti–streptolysin O titer. You worry that she may suffer from valvu-lar heart disease during her adult years as a result of her current condition. What if the diagnosis?
Acute Rheumatic Fever
Goat
Osteoarthritis
Pseudogout
A 25 year old lady suffers from secondary amennorhea (loss of mensus) and galactorhea, she is diagnosed the most common pituitary tumor, the lady is suffering from
A) Acromegaly
B) Prolactinoma
C) Growth hormone adenoma
D) Bronchogenic carcinoma
A 6-year-old boy presents to your office complaining of fatigue, fever, and a history of recurrent epistaxis (nose bleeds) and urinary tract infections. He has an enlarged liver and spleen and a petechial rash over his entire body. Concerned, you send him for some blood tests, which demonstrate pancytopenia with the presence of multiple blast forms. You fear that a bone marrow biopsy may demonstrate cells that would stain positive for TDT and CALLA. Which of the following statements if false?
It also accounts for 80% of all adult leukemias.
Bone marrow finding Hypercellular; composed mostly of lymphoblasts;
Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TDT) is a marker of immature T and B lymphocytes and is present in 95% of cases.
Is the most common childhood cancer.
Risk factors include prior exposure to radiation and chemotherapy
A 50-year-old man experiences episodes of severe substernal chest pain every time he performs a task that requires moderate exercise. The episodes have become more frequent and severe over the past year, but they can be relieved by sublingual nitroglycerin. On physical examination, he is afebrile, his pulse is 78/min and regular, and there are no murmurs or gallops. Laboratory studies show creatinine, 1.1 mg/dL; glucose, 130 mg/dL; and total serum cholesterol, 223 mg/dL. Which of the following cardiac lesions is most likely to be present?"
1- Rheumatic mitral stenosis
2- Serous pericarditis
3- Restrictive cardiomyopathy
4- Coronary atherosclerosis
Which of the following anemia profiles is typical of thalassemia?
1- ↓ MCV, ↓ plasma iron, ↓ ferritin, ↓ total iron binding capacity (TIBC)
2- ↓ MCV, ↓ ferritin, ↑ plasma iron, normal TIBC
3- ↑ MCV, normal ferritin, normal plasma iron, normal TIBC
4- ↓ MCV, normal ferritin, normal plasma iron, normal TIBC
Reed-Sternberg (RS )CD15 +and CD30+ seen in which of the following blood cell neoplasia?
1- Chronic myelogenous leukemia(CML )
2- Chronic lymphoblastic leukemia (CLL)
3- Hodgkin lymphoma (HL)
4- Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL)
Which of the following is the BEST explanation of polycythemia?
1- An illegal way that professional athletes get a competitive edge
2- A blood disorder in which there are too many red blood cells
3- A blood disorder in which the red blood cells are lacking in enzymes
4- Ableeding disorder in which a person is missing important clotting factors.
A previously healthy 67-year-old man presents to the emergency room with numbness of his left leg. Temperature and blood pressure are normal. Physical examination shows pallor and a cool left leg with absence of distal pulse. An ECG reveals no abnormalities. An arteriogram demonstrates a markedly dilated abdominal aorta and occlusion of the left popliteal artery. The blockage is removed surgically, and the patient recovers. Which of the following is the most likely source of the arterial thromboembolus in this patient?
1- Deep venous thrombosis
2- Left ventricular mural thrombus
3- Nonbacterial endocarditis
4- Paradoxical emboli
5- Thrombus from an atheromatous aorta
80 year old patient, previously healthy woman feels a lump in her right breast. The physician palpates a 2.5-cm firm mass in the upper outer quadrant. Nontender right axillary lymphadenopathy is present. A lumpectomy with axillary lymph node dissection is performed. Microscopic examination shows that the mass is an infiltrating ductal carcinoma. Three of 10 axillary nodes contain metastases. Flow cytometry on the carcinoma cells shows a small aneuploid peak and high S-phase. Immunohistochemical tests show that the tumor cells are positive for estrogen and progesterone receptor (ER/PR), negative for HER2/neu expression, and positive for cathepsin D expression. What is the most important prognostic factor for this patient?"
1- Lack of HER2/neu expression in the carcinoma
2- Histologic subtype of carcinoma
3- Expression of stromal proteases in the carcinoma
4- Presence of lymph node metastases
5- Age at diagnosis
6- DNA content in the carcinoma
7- Estrogen receptor positivity
- A 45-year-old man has had a fever and a productive cough for the past 3 days. On physical examination there is dullness to percussion over the right upper lung. His temperature is 37.9°C. A chest radiograph reveals right upper lobe consolidation. Laboratory findings include serum total protein of 6.0 g/dL, albumin 2.7 g/dL, AST 185 U/L, ALT 98 U/L, total bilirubin 1.0 mg/dL, alkaline phosphatase 31 U/L, and prothrombin time 20 sec. An abdominal CT scan shows hepatomegaly with decreased hepatic attenuation. Which of the following conditions is the most likely underlying cause of death?
1- Alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency
2- Wilson disease
3- Acute hepatitis C
4- Diabetes mellitus
A 55-year-old, obese man (BMI = 34 kg/m2) comes to the physician for a routine physical examination. His past medical history is significant for type 2 diabetes mellitus that is controlled by medication and diet. The patient neither drinks nor smokes. Physical examination shows mild hepatomegaly. Laboratory studies reveal normal serum levels of albumin and bilirubin and mildly elevated serum levels of AST and ALT (80 and 100 U/L, respectively). The serum level of alkaline phosphatase is normal (70 U/L), and total serum cholesterol is elevated to 290 mg/dL. The CBC is normal. Abdominal ultrasound reveals diffuse fatty infiltration of the liver. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
1 © Glycogen storage disease
2 © Autoimmune hepatitis
3nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
4 © Diabetic ketoacidosis
5 © Cirrhosis of the liver
An infant suffering from recurrent pyogenic;, joLec,tions has defective expression of CD 40 As a result, his antibody isotype switching jsJ o:iRaired. Which of the following antibody levels are most likely to be high in this patient?
1-Igm
2-igGA
3-ige
4IgG
All of the following are features of rheumatic fever except
1©_ erythema nodosum
2© elevated antistreptolysin
3 © Carditis
4 © subcutaneous nodules
5 © _aschoff bodies in the heart
A 35-year-old woman consults a gynecologist because she has postcoital vaginal bleeding. The Papanicolaou (Pap) smear is abnormal. Colposcopy and cervical biopsy lead to a diagnosis of carcinoma of the cer vix. Which of the following is most characteristic of this disorder?
1 -History of exogenous estrogen therapy
2-assosiation with human papillomavirus
3- Most common gynecologic malignancy
4 -Spontaneous regression following menopause
5 Secretion of AFP
A 35-year-old prostitute is seen in a community health care clinic. About 4 months earlier, she had a painless labial sore and swelling of a right inguinal lymph node, both of which had subsided uneventfully over a period of several weeks. About 3 weeks later she developed fever and a generalized maculopapular skin rash that involved the palms of the hands and the soles of the feet. She has developed a flattened, wart-like labial lesion that is most likely a
1- chancroid
2- condyloma lata
3 -papillary hidradenoma
4 - condyloma acuminatum
A 43-year-old multigravida presents with nausea, vomiting, fever, and right upper quadrant pain. On examination, she displays arrested inspiration on palpation of the right upper quadrant (Murphy sign). Her laboratory results reveal neutrophilia with a “left shift.” Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
1- Cholangiocarcinoma
2-Acute cholecystitis
3-Carcinoma of the ampulla of Vater
4 - Sclerosing cholangitis
Breast cancer is suggested by physical findings which include all of the following except
1-nipple inversion
2 - alterations of breast contour
3.-skin dimpling
4 -pain on palpation
5 - edema of the skin
An 18-year-old presents to clinic with fever and tender lesions on her finger and toe pads. On physical examination, anew murmur is detected, as well as retinal hemorrhages and splinter hemorrhages on nail beds . What is the most likely diagnosis?
1-endocarditits
2-Pericarditis
3-Myocarditis
4- Dilated cardiomyopathy
Autopsy findings in a 42-year-old Caucasian female are shown on the image below . She suffered from exertional dyspnea and experienced sudden death.The most likely diagnosis is:
1-Dilated cardiomyopathy
2 -Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
3 - Myxoma
4-Restrictive cardiomyopathy
Crescentic glomerulonephritis with pauci-immune glomerulonephritis is associated with:
1 - Membranous glomerulonephritis
2 - Goodpasture’s syndrome
3 - Post infectious glomerulonephritis
4 - Wegener's glomerulonephritis
A 68-year-old pcnt onset of vaginal bleeding, and a diagnosis of type | endometrial carcinoma is made on endome trial biopsy. Which of the following is a risk factor for this condition?
1-Obesity
2 -Endometriosis
3- Salpingitis
4-Multiparity
5 -Early sexual activity
The most common primary tumor of the heart:
1-Sarcoma
2- Lipoma
3 - Rhabdomyoma
4-Myxoma
A previously healthy 6-year-old boy presents to the emergency department complaining of abdominal pain. His mother reports that he has had nausea, and vomiting for the past two days. She also notes that he has been urinating more often than usual and seems to be breathing heavily Urine analysis is positive for ketones. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
1. Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH)
2 -diabetes mellitus type 2
3 -diabetes insipitus
4 -diabetes mellitus type 1
A 12-year-old boy presents with smoky brown-colored urine, oliguria, azotemia, and hypertension. After further tests, the patient is diagnosed with a nephritic syndrome. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
1 -Diabetic nephropathy
2 -Renal amyloidosis
3 -Membranous glomerulonephritis
4 - Poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis _
5 -Minimal change disease
Squamous cell lung carcinoma
1 -has excellent prognosis
2 -is most commonly associated with Smokers
3 -is commonest in females
4 -is commonest peripherally
Hereditary nephritis is seen in:
1. -Alport syndrome.
2-Analgesic nephropathy
3 - Balkan nephropathy
4 -Eosinophilic nephritis
A 54-year-old male is found to have a hemorrhagic pleural effusion. He has worked at a shipyard for the past 25 years and has smoked for the past 30 years. A CT scan of his chest shows diffuse nodular thickening of the pleura. Pleural biopsy shows columnar cells joined by desmosomes, with abundant tonofilaments and studded with very long microvilli. This patient most likely suffers from:
1. Adenocarcinoma 2-
2. Squamous cell carcinoma
3. ©) Small cell carcinoma
4. Mesothelioma
A female patient Nargis comes to your OPD with complaints of fever, malaise, increased frequency, urgency and painful micturition. Further investigations reveal that she is suffering from acute urinary tract infection. Which of the following is not a risk factor for the increased predisposition of females for development of UTI?
1 -Hormonal changes affecting adherence of bacteria to the mucosa
2-Absence of antibacterial properties in vaginal fluid
3- Shorter urethra in females
4- Urethral trauma during sexual intercourse
Which one of the following is ANCA associated vasculitis?
1-Goodpasture disease
2-. Takayasu arteritis
3 -Kawasaki disease
4-Chrug-Strauss Syndrome
A 60-year-old woman presents with increasing morning stiffness and pain in her fingers and hands. She has severe tenderness over her metacarpophalangeal (MCP) and proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joints and has had difficulty using her hands due to the pain. She has severe swan neck deformities and boutonniere deformities of her hands. The woman also notes that she has had difficulty breathing and has pain when she takes deep breaths. Which of the following is a risk factor for this disease?
1 ©. Anticentromere antibodies
2 © Anti-Sm antibodies
3 © Anti-dsDNA antibodies
4 © HLA-DR4 positive
5 ©) HLA-B27 positive
This pneumoconioses is seen as radiographically as an eggshell calcification of hilar lymph nodes described as stained glass in appearance?
1 -Coal worker's pneumoconioses
2-Berylloisis
3-Asbestosis
4- Silicosis
3-year-old boy, an inner city resident, has multiple bony abnormalities, including bowlegs and knockknees, thickening of the skull with frontal bossing, knobby deformi ties of the costochondral junctions and, at the ends of the long bones, distortion of the rib cage with flaring over the diaphragm, and pigeonbreast deformity. A decrease in which of the following is characteristic of this condition?
1-Bony osteoblastic activity
2-Release of parathyroid hormone
3- Calcificationot of osteoid
4 -Serum alkaline phosphatase activity
Which of the following is the most common cause of chronic pancreatitis?
1- Gallstones
2- Hypercholesterolemia
3-Hereditary predisposition
4-Alcoholism
5 – Smoking
Alport Syndrome
1 - is associated with defective assembly of collagen IV in GBM
2- causes diffuse thickening of glomerular basement membrane (GBM)
3 -is an immune complex mediated glomerulonephritis
4 - presents as rapidly progressive renal failure
A 25-year-old Asian woman presents to the clinic with complaints of intermittent chest pain that is not associated with exercise or stress. Often the chest pain will occur when she is sitting or resting. What is the most likely diagnosis?
1 © Amyocardial infarction
2 © Stable angina
3 © _ Prinzmetal angina
4©_ Endocarditis
What is the microscopic finding in diabetic glomerulonephropathy?
1© All of the above
2 © GBM thickening
3 © Eosinophilic nodular glomerulosclerosis
4 © Renal atherosclerosis
5 © Mesangial expansion
In what organs are tumors characteristically found in individuals with MEN type 1?
1©_ Kidneys, adrenal, and liver
2©_ Adrenal, thyroid, and parathyroid
3 © _ Pituitary, parathyroid, and pancreas
4 © Parathyroid, pineal, and pancreas
A 28-year-old man is evaluated for recurrent peptic ulcer disease, apparently refractory to pharmacologic intervention. Serum gastrin is markedly elevated. These findings are most characteristic of which of the following?
1©_ Cushing syndrome
2 © Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
3© Acromegaly
4 © Whipple triad
Reed-Sternberg (RS )CD15 +and CD30+ seen in which of the following blood cell neoplasia?
1© _ Chronic lymphoblastic leukemia (CLL)
2 © Hodgkin lymphoma (HL)
3 © Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL)
4 © _ Chronic myelogenous leukemia(CML )
Subepithelial deposits with ‘M' spike is seen in:
1-membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis
2 - Minimal change disease
3 -Membranous glomerulonephritis
4- RPGN
True about ulcerative colitis, all except
1-Pancolitis
2- Rectum involved
3 -Noncaseating granuloma
4-Pseudopolyps
Gross examination of the heart from an autopsy of a 38-year-old man who was a long-term alcoholic and died from congestive heart failure reveals the heart to be markedly enlarged, banana shaped, and flabby, with dilation of all four chambers. The walls of the ventricles are thin and there are multiple small mural thrombi present. No abnormalities of the cardiac valves are seen. The coronary arteries are within normal limits. What is the best classification for this abnormal heart?
1 -Dilated cardiomyopathy
2 -Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
3 -Restrictive cardiomyopathy
4- Hyperplastic cardiomyopathy
A patient presents with recurrent attacks of hypoglycemia that seem to follow fasting or strenuous exercise with relief of symptoms following glucose ingestion. The patient most likely has
1 -hemochromatosis
2 -carcinoma of the tailof the pancreas
3 -beta-cell adenoma of pancreatic islets
4 -diabetes insipidus
In adult respiratory distress syndrome:
1-The pattern of the functional abnormality is obstructive
3- Pathogenesis localized alveolar capillary damage
4 -It responds readily to oxygen therapy
2-Neutrophils can injure pulmonary endothelial cells through release of toxic oxygen metabolites
Ascites
1 - Is associated with hepatic sinusoidal hypertension
2 -Is a rare complication of cirrhotic liver disease
3 -Is diagnosed clinically by the presence of generalized edema
4 -Is commonly associated with hyperproteinemia
5 -Occurs as an early complication of cardiac failure
What is the most frequent type of hyperfunctioning pituitary adenoma?
1 - Gonadotroph adenoma
2 -Somatotroph adenoma
3-Corticotroph adenoma
4 -Lactotroph adenoma
A middle aged man Nitesh complains of increasing difficulty in swallowing over the past 3 years. He reports a feeling of pressure in his chest occurring 2-3 seconds after swallowing a solid bolus. He also experiences regurgitation of undigested food eaten hours previously. Manometry shows the absence of esophageal peristalsis with swallowing and a lower esophageal sphincter that fails to relax. What is the most likely diagnosis?
1 -Oropharyngeal dysphagia
2 - Diffuse esophageal spasm
3 -Achalasia
4 -Incompetent lower esophageal sphincter
Hemolytic anemia:
1 - serum haptoglobin is elevated in intravascular hemolysis
2 -serum bilirubin is largely conjugative in severe hemolysis
3 -malaria infection can cause hemolytic anemia
4 -complement fixation does not occur during transfusion reaction
5 © senescent RBC distribution occurs in the vascular system
A 65-year-old woman with a history of multinodular goiter complains of increasing nervousness, insomnia, and heart palpitations. She has lost 9 kg over the past 6 months. Physical examination reveals a diffusely enlarged thyroid. There is no evidence of exophthalmos. Laboratory studies show elevated serum levels of T3 and T4. Serologic tests for antithyroid antibodies are negative. Which of the following is an important complication of this patient's endocrinopathy?
1 -Autoimmune hepatitis
2- Myxedema
3 -Follicular carcinoma of the thyroid
4 -Medullary carcinoma of the thyroid
5 -Cardiac arrhythmia
An 8-month-old infant boy presents with an enlarging abdominal mass. Laboratory evaluation finds normal urinary levels of vanillylmandelic acid (VMA). The mass is removed surgically and microscopic sections reveal undifferentiated mesenchymal cells, immature tubules, and abortive glomerular formation. This tumor is most closely associated with abnormalities involving which one of the listed genes?
1-METgene
2 -pl6iNk4a gene
3 - WT-17-13 gene
4-WT-1gene
1 O Atrophy of the epidermis with dermal fibrosis _
2 O Atypia of the epidermis with dysplasia
3 O Loss of pigment in the basal layers of the epidermis
4 O Hyperplasia of the epidermis with hyperkeratosis
A 47-year-old man presents with increasing peripheral edema and dark, tea-colored urine. \aboratory examination finds decreased serum albumin, while examination of a 24-h urine specimen reveals marked prétéinuria. Microscopic examination of this pati reveals numerous red cells along with rare red cell casts. Electron microscopic examination of a renal biopsy from this patient reveals dense, ribbon-like deposits in the lamina densa of the glomerular basement membrane. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
1- gA nephropathy
2 -Lipoid nephrosis
3 - Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis
4 -Acute glomerulonephritis
A 67-year-old man is found on rectal examination to have a single, hard, irregular nodule within his prostate. A biopsy of this lesion reveals the presence of small glands lined by a single layer of cells with enlarged, prominent nucleoli. From what portion of the prostate did this lesion most likely originate?
1 -Peripheral zone
2-Anterior zone
3 -Transition zone
4- Periurethral glands
Which of the following histologic changes is most likely to be seen when examining a mucosal biopsy of the urinary bladder from an individual with acute cystitis due to infection with Escherichia coli?
A. An infiltrate of lymphocytes and plasma cells
B. An infiltrate of neutrophils
C. Inflammation with eosinophils
D. Noncaseating granulomas
E. Sheets of macrophages with granular cytoplasm
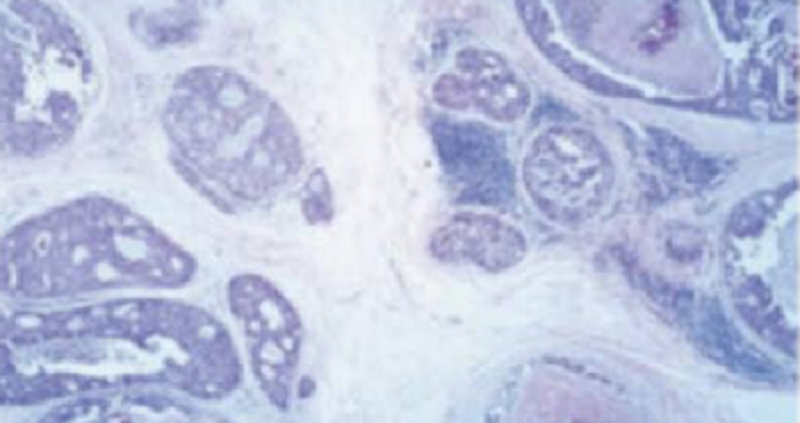
A 45-year-old woman discovers a solitary, freely movable mass in her right breast on self-examination, which is confirmed on physical examination. Mammography demonstrates focal calcification, with a linear configuration in the region of the breast mass. A breast biopsy (shown in the image N29) reveals large, pleomorphic epithelial cells confined to dilated ducts, with central zones of necrosis. What is the appropriate pathologic diagnosis?
1 -Phyllodes tumor
2 -Tubular carcinoma type
3-Ductal carcinoma in situ, comedocarcinoma type
4-Colloid carcinoma
An uncircumcised 49-year-old man presents with the sudden onset of severe pain in the distal portion of his penis. The emergency room physician examines the patient and finds that the foreskin is retracted but cannot be rolled back over the glans penis. The ER physician calls the urologist, who performs an emergency resection of this patient's foreskin. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
1 -omphalocele
2 -Epispadias
3-Balanoposthitis
4 -Paraphimosis
A 49-year-old woman presents with increasing problems swallowing food (progressive dysphagia). X-ray studies with contrast reveal that she has a markedly dilated esophagus above the level of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES). No lesions are seen within the lumen of the esophagus. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this disorder?
A. Decreased LES resting pressure
B. Absence of myenteric plexus in the body of esophagus
C. Absence of myenteric plexus at the LES
D. Absence of submucosal plexus in the body of esophagus
E. Absence of submucosal plexus at the LES
A female newborn is being worked up clinically for several congenital abnormalities. During this workup, it is discovered that normal development of the vagina and uterus in this female infant has not occurred. Failure of the uterus to develop (agenesis) is directly related to the failure of which one of the following embryonic structures to develop?
1-Urogenital ridge
2 - Epoophoron
3 -Mesonephric duct
4 -Paramesonephric duct
A 58-year-old man has been a smoker for 40 years. He has worsening orthopnea over the past year. On examination, he has a body mass index of 35. He is afebrile. His blood pressure is 165/110 mm Hg. Auscultation of his chest reveals rales in lower lung fields bilaterally. A chest x-ray shows bilateral lower lobe infiltrates and a prominent left heart border. Laboratory studies show his Hgb A1C is 10%. Which of the following pulmonary problems is he most likely to have?
1- Emphysema
2-Pneumonia
3-Fibrosis
4-edema
A 44-year-old man presents with painless enlargement of one testicle. Physical examination reveals a single testicular mass that does not transilluminate. The mass is resected, examined histologically, and radiation therapy is subsequently given based on the pathologist's diagnosis. Which of the following best describes the expected microscopic appearance of this tumor?
1 -Numerous lymphocytes in the fibrous stroma between groups of tumor cells having distinct cell membranes and clear cytoplasm
2 -A mixture of malignant cytotrophoblasts and syncytiotrophoblasts
3 -Abnormal tissue derived from all three germ levels with scattered immature neural elements
4 -Large tumor cells with abundant eosinophilic, granular cytoplasm, and rare intracytoplasmic rhomboid crystals
A 55-year-old man with a 50 pack year history of smoking cigarettes has recently experienced an episode of hemoptysis along with his usual cough. On physical examination he has no abnormal findings. A sputum for cytology on microscopic examination shows atypical cells with hyperchromatic nuclei and orange-pink cytoplasm. Labortory studies show a serum calcium of 11.3 mg/dL, with phosphorus 2.1 mg/dL. Which of the following chest radiographic findings is this man most likely to have?
1-Peripheral nodule
2 -Carinal coffipression
3 -Left pleural thickening
4 -large hilar mass
A 45-year-old obese woman (BMI = 32 kg/m2) with a history of diabetes and poorly controlled hypertension complains of increased menstrual blood flow of 3 months in duration. An endometrial biopsy is shown in the image N28. Which of the following most likely accounts for the pathogenesis of endometrial hyperplasia in this patient?
1-History of chronic endometritis
2-Prenatal exposure todiethylstilbestrol
3 -History of oral contraceptive use
Excess estrogen stimulation
A 28-year-old man presents with multiple, raised lesions on the shaft of his penis. Physical examination shows condyloma acuminata. Biopsy of the lesion is shown in the image = N23. This benign lesion is caused by infection with which of the following pathogens?
1-Chlamydia trachomatis
2-Human papillomavirus
3- Haemophilus ducreyi
68-year-old man complains f vague abdominal pain, intermittent fever, and a 20-Ib (9-kg) weight loss \pver the past 6 months. For the past 12 years, he has suffered from chronic hepatitis B. On physical examination, the patient shows diffuse “hepatomegaly, and mild jaundice. A CT scan of the abdomen reveals a diffusely nodular liver, with a dominant mass measuring 3 cm in diameter. A needle biopsy is shown in the image N37. Which of the following serum markers is useful for monitoring the progression of disease in this patient?
1 - Carcinoembryonic antigen
2 - Alpha-fetoprotein
3 - Alkaline phosphatase
4 - Anti hBc antibody
5 - Human chorionic gonadotropin
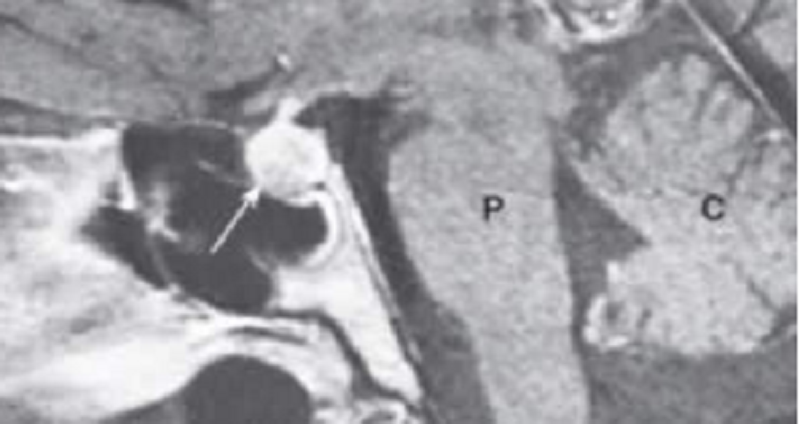
A 35-year-old woman with a history of schizophrenia complains of headaches, visual disturbances, and irregular menses for 9 months. On physical examination the breasts are fi rm and tender. MRI shows enlargement of the anterior pituitary (arrow). Which of the following is the most likely cause of pituitary enlargement in this patient?
1) Corticotrope adenoma
2) Gonadotrope adenoma
3) Lactotrope adenoma
4) Null cell adenoma
5) Somatotrope adenoma
A 36-year-old woman is evaluated for an abnormal Pap smear. A cervical biopsy shows atypical squamous cells throughout the entire thickness of the epithelium, with no evidence of epithelial maturation (shown in the image N27). The basal membrane appears intact. What is the appropriate diagnosis?
(A) Clear cell adenocarcinoma
(B) Invasive squamous cell carcinoma
(D) Severe dysplasia (CIN-3)
(E) Squamous metaplasia of the transformation zone
(C) Mild dysplasia (cervical intraepithelial neoplasia [CIN]-1)
An asymptomatic 24-year-old woman is found to have microscopic hematuria with a routine urinalysis. Her blood pressure and kidney function are within normal limits, but it is discovered that several members of her family also have asymptomatic microscopic hematuria. Which of the following abnormalities is most likely to be present in this woman?
A. A hereditary defect in the renal transport of neutral amino acids
B. A lack of the globular domain of type IV collagen
C. A mutation involving the cytoplasmic btk gene
D. Diffuse thinning of the glomerular basement membrane
E. The presence of C3 nephritic factor in the serum
A 55-year-old man presents with prolonged epigastric pain and severe vomiting. Laboratory evaluation finds that his blood pH is increased to 7.46, while his serum bicarbonate is increased to 30 mM. Blood gases also reveal the arterial carbon dioxide to be increased. Physical examination finds the man to be afebrile with dry mucous membranes and decreased skin turgor. His heart rate is increased, but his respiratory rate is decreased in frequency. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Metabolic alkalosis with respiratory compensation
B. Mixed metabolic acidosis and metabolic alkalosis
C. Respiratory acidosis with renal compensation
D. Respiratory alkalosis with no compensation
E. Respiratory alkalosis with renal compensation
A 26-year-old woman presents with increasing fatigue and malaise. She states that recently she develops a red facial rash whenever she goes outside on a sunny day. Physical examination finds that she is afebrile, but her blood pressure is slightly increased and slight peripheral edema is found. Laboratory evaluation finds slightly elevated BUN and creatinine, while dipstick examination of her urine reveals slight proteinuria with microscopic hematuria. Very rare granular and red cell casts are seen. Laboratory examination is also positive for serum antinuclear antibodies, one of which is anti- double-stranded DNA. A renal biopsy reveals changes of diffuse proliferative glomerulonephritis, and the diagnosis of class IV lupus nephritis is made. Which of the following histologic changes is most characteristic of class IV lupus nephritis?
A. Mesangial deposits form a “holly leaf” pattern
B. Positive immunofluorescence staining forms a “string of popcorn” pattern
C. Splitting of the basement membrane forms a “tram-track” pattern
D. Thickening of the basement membrane forms a “spike and dome” appearance
E. Thickening of the glomerular capillaries forms a “wire-loop” appearance
A 24-year-old man is being evaluated for infertility, and during physical examination the urethral orifice is noted to be on the ventral surface of the penis. Which of the following is the basic defect that caused this abnormality?
1-Exstrophy of the bladder
2 - Abnormal fusion of the paramesonephric ducts
3 -normal development of the prepuce
4-Abnormal development of the prepuce
27-year-old man presents with a testicular mass, which is resected and diagnosed as being a yolk sac tumor. Which of the following substances is most likely to be increased in this patient's serum as a result of being secreted from the cells of this tumor?
1- alfa fetoprotein
2 - B-human chorionic gonadotropin (B-hCG)
3 - Acid phosphatase
4 -Prostate-specific antigen (PSA)
A 49-year-old man who is a long-term smoker presents with frequency and hematuria. Histologic examination of sections taken from an exophytic lesion of the urinary bladder reveals groups of atypical cells with frequent mitoses forming finger-like projections that have thin, fibrovascular cores. These groups of atypical cells do not extend into the lamina propria and muscularis. No glands or keratin production are found. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
1-Adenocarcinoma, noninvasive
2 -Transitional cell carcinoma in situ
3 -Inverted papilloma, noninvasive
4 -Papillary transitional cell carcinoma, noninvasive
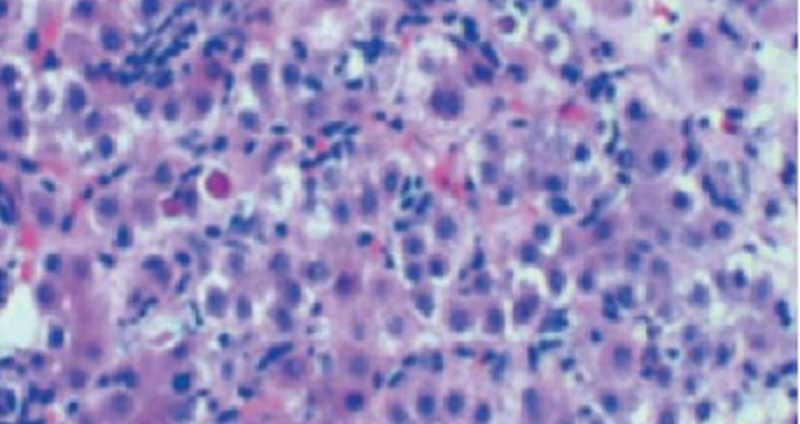
A previously healthy 38-year-old man presents, complaining of 1 month of yellow discoloration of his eyes, abdominal pain, and low-grade fever. Physical examination demonstrates a distended abdomen, right upper quadrant tenderness, and a palpable liver edge 2 cm below the right costal margin. Total serum bilirubin is 7.4 mg/dL. Serum levels of AST and ALT are elevated (229 U/L and 495 U/L, respectively). The prothrombin time is prolonged (18 seconds). A liver biopsy is shown. The pathologic findings are indicative of which of the following liver diseases?
1-Hemochromatosis
2 - Alcoholic cirrhosis
3 - Acute viral hepatitis
4- Cardiac cirrhosis
A 21-year-old woman presents because her urine has turned a brown color. She states that about 2 months ago her urine turned brown 2 days after a cold and stayed brown for about 3 days. At the current time a urinalysis reveals 2+ blood with red cells and red cell casts. Further laboratory tests include a complete blood count (CBO), serum electrolytes, BUN, creatinine, glucose, antinuclear antibodies (ANAs), and serum complement levels (C3 and C4). All of these tests are within normal limits. Immunofluorescence examination of a renal biopsy from this patient reveals the presence of large, irregular deposits of IgA/C3 in the mesangium. A linear staining pattern is not found. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Berger’s disease
B. Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis
C. Goodpasture’s syndrome
D. Lipoid nephrosis
E. Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis
A 28-year-old man presents with moderate proteinuria and hypertension. Histologic sections of a kidney biopsy reveal the combination of normalappearing glomeruli and occasional glomeruli that have deposits of hyaline material. No increased cellularity or necrosis is noted in the abnormal glomeruli. Additionally, there is cystic dilation of the renal tubules, some of which are filled with proteinaceous material. Electron microscopy reveals focal fusion of podocytes, and immunofluorescence examination finds granular IgM/C3 deposits. Further workup finds a mutation involving the NPHS2 gene, the product of which is found within the slit diaphragm of the glomerulus. What is the normal protein product of this gene?
A. Cubilin
B. Megalin
C. Nephrin
D. Podocin
E. Polycystin
A newborn infant is noted to have coughing and cyanosis during feeding. This infant is also noted to have marked gastric dilation due to “swallowed” air. Workup reveals that this infant has the most common type of esophageal atresia. Which one of the following statements correctly describes this type of congenital abnormality?
A. Atresia of the esophagus with fistula between both segments and the trachea
B. Atresia of the esophagus with fistula between the trachea and the blind upper segment
C. Atresia of the esophagus with fistula between the trachea and the distal esophageal segment
D. Atresia of the esophagus without tracheoesophageal fistula
E. Fistula between a normal esophagus and the trachea
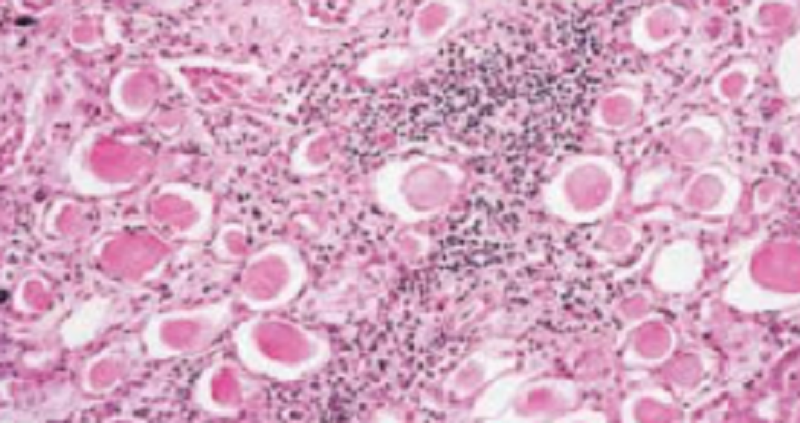
A 50-year-old woman complains of severe headaches and dizziness. The patient has a history of repeated urinary tract infections. The blood pressure is 180/110 mm Hg. = Laboratory studies show elevated levels of BUN (38 mg/dL) and creatinine (2.8 mg/dL). A CT scan of the lower abdomen reveals small, irregularly shaped kidneys with deep coarse scars. A Ppcutancous renal biopsy is shown in the image N22. Which of the following is the appropriate diagnosis?
_Nephrosclerosis
2 O Acute pyelonephritis
3 © Acute tubular necrosis
4 ©) Chronic pyelonephritis
A 63-year-old woman complains of rectal bleeding of 1 week in duration. Laboratory studies show hypochromic, microcytic anemia (hemoglobin = 7.6 g/dL and MCV = 70 pim3). Colonoscopy reveals a large polypoid mass, which is removed (surgical specimen shown in the image N32). The arrow points to a malignant tumor. The patient asks about the relative rigk of cancer arising in various types of gastrointestinal polyps. Which of the following types of colonic polyps is most likely to undergo malignant transformation?
Tubular adenoma
2 © Lymphoid polyp
3 © _ Villous adenoma
4 © _Peutz-Jeghers polyp
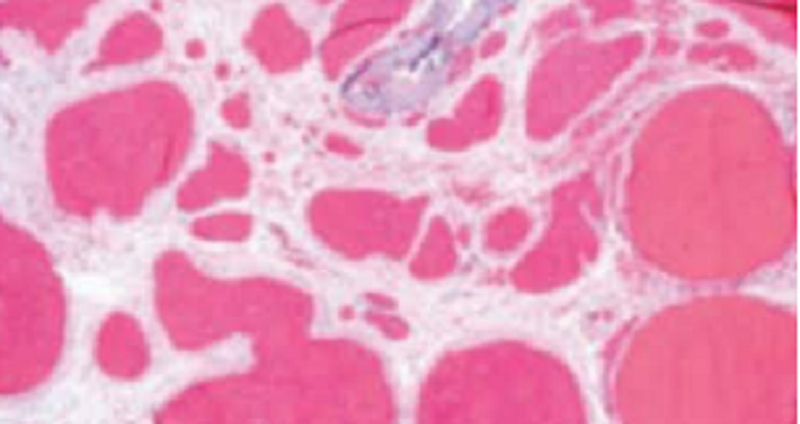
A 58-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department 4 hours after vomiting blood and experiencing bloody stools. The patient was diagnosed with alcoholic cirrhosis 2 years ago. The patient subsequently goes into shock and expires. The histologic appearance of the esophagus at autopsy is shown in the image N30. Which of the following is the most “t underlying cause of hematemesis and hematochezia in this patient?
Ischemia of the gastric mucosa
Mallory-Weiss syndrome
Portal hypertension
47-year-old man presents with the sudden onset of fever, chills, and dysuria. Rectal examination finds the prostate gland to be edematous and very sensitive; examination is quite painful. Microscopic examination of prostatic secretions reveals the presence of numerous neutrophils. Which of the following organisms is the most likely cause of this illness?
1 © _ Proteus mirabillis
2 © _ Staphylococcus aureus
3 © _ Escherichia coli
4 © _ Bacillus Calmette-Guerin
An 8-month-old male infant presents with progressive renal and hepatic failure. Despite intensive medical therapy, the infant dies. At the time of autopsy, the external surfaces of his kidneys are found to be smooth, but cut section reveals numerous cysts that are lined up in a row. Which of the following is the mode of inheritance of this renal abnormality?
1-autosomal dominant
2 -Minked recessive
3 -linked dominant
4 -Autosomal recessive
Histologic examination of an excision specimen from a lesion on the dorsal surface of the penis reveals a papillary lesion with clear vacuolization of epithelial cells on the surface and extension of the hyperplastic epithelium into the underlying tissue along a broad front. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Squamous cell carcinoma
2 - Condyloma acuminatum
3 -Verrucous carcinoma
A 19-year-old man presents with dysuria and a mucoid or watery urethral discharge. No prostatic pain is present. Microscopic examination of the discharge reveals numerous neutrophils, but no organisms are seen. Which of the following organisms is the most likely cause of this patient's signs and symptoms? A 19-year-old man presents with dysuria and a mucoid or watery urethral discharge. No prostatic pain is present. Microscopic examination of the discharge reveals numerous neutrophils, but no organisms are seen. Which of the following organisms is the most likely cause of this patient's signs and symptoms?
A. Chlamydia trachomatis
B. Escherchia coli
C. Mycoplasma genitalium
D. Mycoplasma hominis
E. Trichomonas vaginalis
A 35-year-old woman recovering from hepatitis B develops hematuria, proteinuria, and red cell casts in the urine. Which one of the following statements best describes the expected renal changes in this patient?
A. Plasma cell interstitial nephritis
B. IgG linear fluorescence along the glomerular basement membrane
C. Granular deposits of antibodies in the glomerular basement membrane
D. Diffuse thickening of the glomerular basement membrane by subepithelial immune deposits
E. Nodular hyaline glomerulosclerosis
A 43-year-old man with a history of microscopic polyarteritis acutely develops renal failure with oliguria and hematuria. Laboratory examination reveals the presence of serum pANCA (antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies). A renal biopsy is diagnostic of type III rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis. Which of the following histologic changes is most likely to have been present in this biopsy specimen?
1-Eosinophilic masses were seen attached to the capsule of Bowman's space
2 - The basement membrane was seen to be split by mesangial cells
3 -Large numbers of neutrophils were seen in the interstitium and tubules
4 - Numerous crescents were present in the glomeruli L
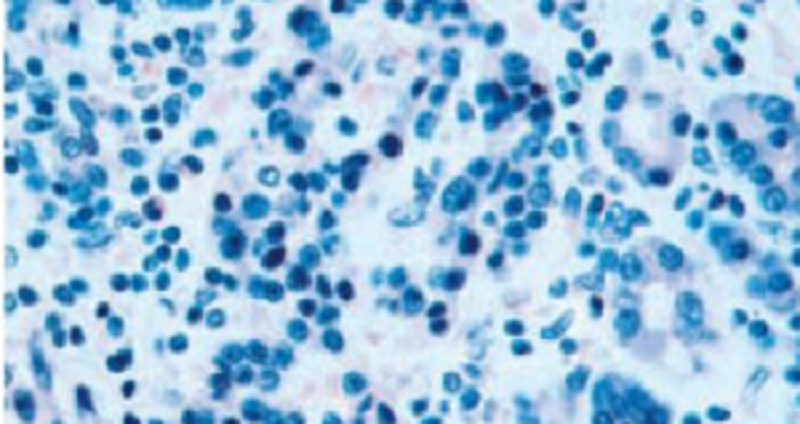
A 43-year-old woman complains of low-grade fever and has a 3-day history of pain in her neck. Physical examination reveals a slightly enlarged thyroid. A CBC is normal. A biopsy of the thyroid reveals granulomatous inflammation and the presence of giant cells (shown in the image N41). What is the appropriate diagnosis?
Lymphadenoid thyroiditis
2 - Subacute (deQuervain) thyroiditis
3 © __ Nontoxic multinodular goiter
4 ©) __ Hashimoto thyroiditis
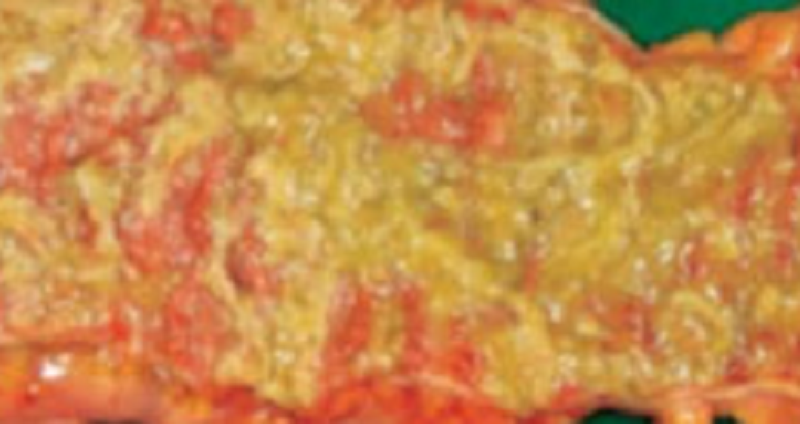
A 53-year-old woman complains of acute diarrhea and severe abdominal pain. She was recently treated with broad-spectrum antibiotics for community-acquired pneumonia. A CBC shows a WBC count of 24,000/pL. The patient subsequently develops septic shock and dies. A portion of her colon is shown at autopsy in the image N34. These findings are typical of ich of the following gastrointestinal diseases?
1 -Diverticulitis
2 - Ulcerative colitis
3- Crohndisease
4 -Ischemic colitis
5 -Pseidamembranaous colitis
A 38-year-old man presents with a 10-month history of a painless testicular mass. Physical examination reveals a small nodule of the left testis. The mass cannot be transilluminated and appears to be solid on ultrasound examination. A testicular biopsy is shown in the image N25. The multinucleated giant cells in this neoplasm are derived from which of the following cell types?
Smooth muscle cells
Chondrocytes
Leydig cells
Tropholytic cells
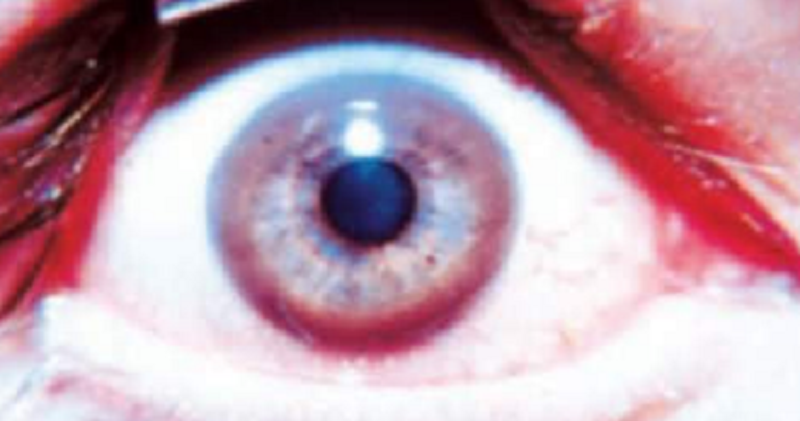
15-year-old boy complains of a 2-month history of fatigue, abdominal pain, and yellow eyes and skin. Physical examination shows tremor of his hands, lack of coordination, and mild jaunfijce. The results of an ophthalmic examination are shown in the image N36. This patient most likely has an inborn error of metabolism associated with tissue overload of which of We following elements?
1-Mercury
2-Lead
3-Magnesium
Copper
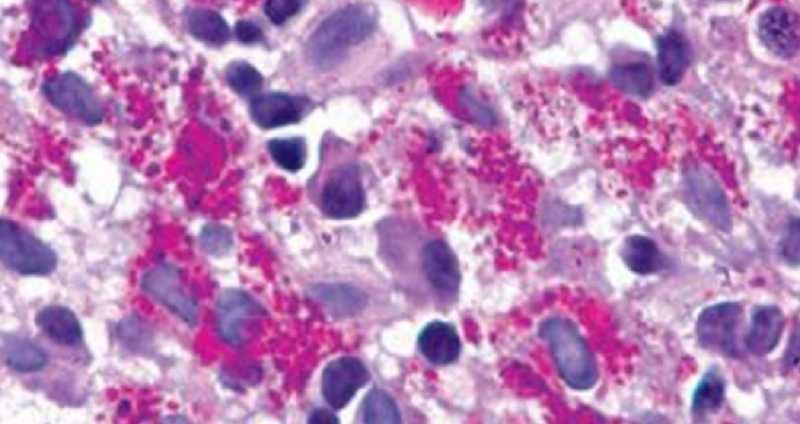
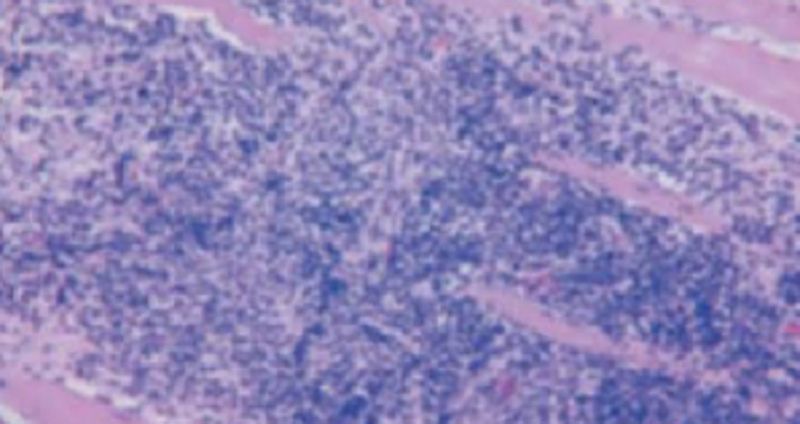
A 36-year-old man presents with fever and painful joints for 2 weeks. Physical examination shows skin pigmentation, glossitis, angular cheilitis, and generalized lymphadenopathy. The patient has lost 9 kg (20 lb) over the past 6 months. He reports that his stools are pale and foul smelling. Blood cultures are negative. The patient is started on antibiotic therapy and exhibits remarkable clinical improvement. Biopsy of the small intestine shows marked distortion of the intestinal villi, and a periodic acid-Schiff stain reveals large, foamy macrophages filled with glycoprotein-rich granules (shown in the image). Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A) Angiodysplasia of ileum
(B) Crohn disease
(C) Ménétrier disease
(D) Peutz-Jeghers syndrome
(E) Whipple disease
A 69-year-old male presents with urinary frequency, nocturia, dribbling, and difficulty instarting and stopping urination. Rectal examination reveals the prostate to be enlarged,firm, and rubbery. A needle biopsy reveals increased numbers of glandular elements andstromal tissue. The glands are found to have a double layer of epithelial cells. Prominentnuclei or back-to-back glands are not seen. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A.Acute prostatitis
B.Chronic bacterial prostatitis
C.Granulomatous prostatitis
D.Benign prostatic hyperplasiaE.Prostatic adenocarcinoma
Ich ae following is the most likely cause of the clinical combination of generalized edema, hypoalbuminemia, and hypercholesterolemia in an adult whose urinalysis demonstrated marked proteinuria, with fatty casts and oval fat bodies?
__Nephrotic syndrome
2 © Renal tubular defect
3 ©) _Nephritic syndrome
4 ©) Acute renal failure
27-yeal Nd man presents with painless scrotal enlargement. He reports a sensation of “heaviness” in his scrotum. He denies any history of fever, chills, nausea, or vomiting. Physical examination finds an approximate 1-cm mass in the superior portion of the scrotum, anteriorly located to the testis. Because the mass transilluminates, the diagnosis of hydrocele is considered. Which of the following is the best method to confirm that this mass is in fact a benign cyst and not a solid tumor
1 ©) _ Doppler flow study
2 O Testicular scintigraphy
3 O Imaging ultrasound,
4 © _ Surgical biopsy
A 2-year [3 boy is being evaluated for the development of progressive peripheral edema. Physical examination finds that he is afebrile, and his blood pressure is within normal limits. Laboratory examination finds decreased serum albumin, increased serum cholesterol, and normal BUN and creatinine levels. Examination of his urine finds massive proteinuria and lipiduria, but no red blood cells are seen. The loss of albumin in the urine is much greater than the loss of globulins. A histologic section from a renal biopsy examined with a routine H&E stain is unremarkable, but electron microscopic examination finds flattening and fusion of the foot processes of the podocytes. The basement membrane is not fragmented and electron dense deposits are not found. What is the best diagnosis?
1- Diffuse proliferative glomerulonephritis (OPGN)
2 -Minimal change disease (MOD) eg
3 © __ Membranous glomerulopathy (MGN)
4 © __ Heymann glomerulonephritis (HGN)
Physical Lymination of a 3-day-old male infant reveals urine leaking from the area of the umbilicus. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
1- Urachal fistula
2- Meckel's diverticulum
3- Omphalocele
4 - Meckel's cyst
A 35-yeal Nd woman presents with the sudden onset of severe, colicky pain on the right side of her abdomen. She does not relate the pain to food, but says that she cannot find a pain-free position. Physical examination finds marked tenderness over the right costovertebral angle, but rebound tenderness is not present. A pelvic examination is unremarkable. Microscopic examination of her urine reveals the presence of numerous red blood cells. The urine is negative for esterase and nitrite, and no bacteria are seen. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her signs and symptoms?
Calcium oxalate kidney stones
2 © Cholesterol gallstones
3 (©) _ Magnesium ammonium phosphate kidney stones
4 © Acute uric acid nephropathy
A 40-year-old woman complains of chronic eee and anoyulatory cycles for the last 8 months. Her vital signs are normal. Physic and a firm, diffusely enlarged thyroid gland. T3 and T4 are abnormally low. A thyroid biopsy is shown in the image N40.
1-Acute necrotizing thyroiditis
2- Multinodular goiter
3 - Autoimmune thyroiditis
4- Subacute (DeQuervain) thyroiditis
An anxiof Ss 9-year-ald woman presents with perioral numbness and carpopedal spasm. Laboratory examination reveals decreased PCO2 and decreased bicarbonate. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Metabolic acidosis due to ketoacidosis
B. Metabolic acidosis due to renal tubular acidosis
C. Metabolic alkalosis due to thiazide diuretic
D. Respiratory acidosis due to hypoventilation
E. Respiratory alkalosis due to hyperventilation
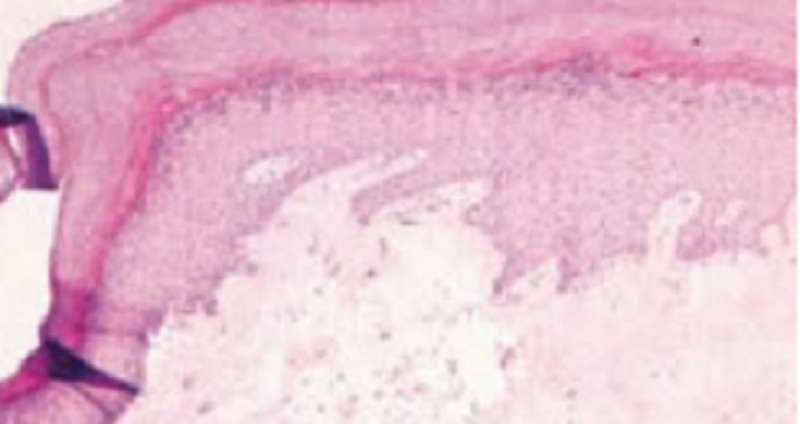
A 52-year-old woman with hypothyroidism presents with a 2-year history of vulvar itching and painful intercourse. Physical examination reveals vulval white plaques, atrophic skin, and a parchment-like appearance. Biopsy of the lesion (shown in the image N26) demonstrates hyperkeratosis, loss of rete ridges, and a homogeneous, acellular zone in the upper dermis. This patient's vulvar dermatitis is most commonly associated with which of the following underlying conditions?
© __ Autoimmune disease
2 © Hyperlipidemia
3 ©) _ Diabetes mellitus
A 35-year-old woman during her first pregnancy develops oligohydramnios. At 34 weeks of gestation she delivers a stillborn infant with abnormal facial features consisting of wide-set eyes, low-set floppy ears, and a broad-flat nose. Which of the following abnormalities is most likely to be present in this still-born infant?
1 - Congenital biliary atresia
2 -Urinary bladder exstrophy
3 - Bilateral renal agenesis
4 - Absence of the thymus
A 28-year-old man with a history of malaise and hemoptysis presents with the acute onset of renal failure. Laboratory examination reveals increased serum creatinine and BUN, but no antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA) nor antinuclear (ANA) antibodies are present. Urinalysis reveals the microscopic presence of red blood cells and red blood cell casts, while a renal biopsy reveals crescents within Bowman’s space of many glomeruli. Immunofluorescence reveals linear deposits of IgG and C3 along the glomerular basement membrane. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
1 ©) _Henoch-Schénlein purpura
2 © ___ Wegener's granulomatosis
3 © __ Goodpasture's syndrome
4 ©) _ Diabetic glomerulopathy
Which of the following describes multiple small mucinous cysts of the endocervix that result from blockage of the endocervical glands by overlying squamous metaplastic epithelium?
1-chocolate cysts
2 ©) _ Follicular cysts
3 O Bartholin’s cysts
4 © Nabothian cysts
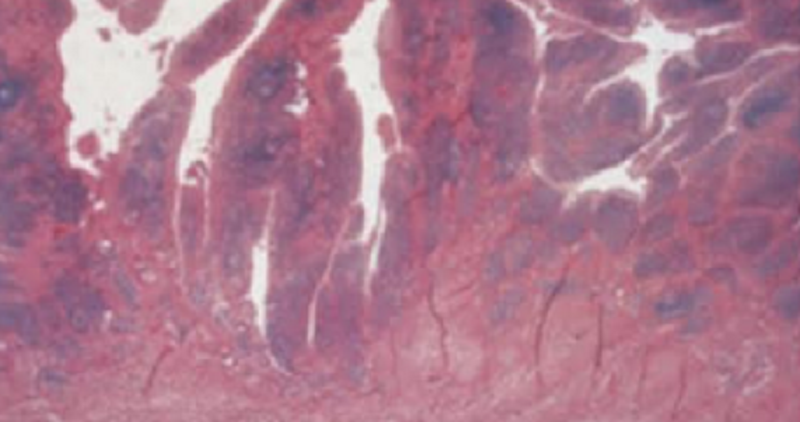
A 58-year-old man has developed a non-productive cough worsening over the past 2 months. Last week he noted the appearance of blood-streaked sputum. On physical examination there are some expiratory wheezes auscultated over the left lung. A chest radiograph reveals a 5 cm mass near the left lung hilum. A sputum cytology reveals the presence] “{ small clusters of very hyperchromatic, pleomorphic cells with scant cytoplasm. Which of the following is the most likely predisposing factor to the development of his pulmonary disease?
1-Smoking
2 - Sillicosis
3 - Asbestosis
A 6-year |S boy presents with bilateral swelling around his eyes. His parents state that the child’s eyes have become “puffy” over the past several weeks, and his urine has become smoky-colored. Physical examination reveals mild bilateral periorbital edema, but peripheral edema is not found. The boy is afebrile and his blood pressure is slightly elevated. A urinary dipstick reveals mild proteinuria, while microscopic examination of the boy's urine reveals hematuria with red blood cell casts. Laboratory tests reveal increased ASO titers and decreased serum C3 levels, but C2 and C4 levels are normal. A microscopic section from the kidney reveals increased numbers of cells within the glomeruli. An electron microscopic section of the kidney reveals large electron-dense deposits in the glomeruli that are located between the basement membrane and the podocytes. The foot processes of the podocytes are otherwise unremarkable. Which one of the listed infections did this child most like recently have that precipitated this renal disease?
1-A fungal infection of the urethra or urinary bladder
2 - A viral infection of the upper or lower respiratory tract
3 - A streptococcal infection of the pharynx or skin
4- An E. Coli infection of the small or large intestines
Histologic sections of a kidney reveal patchy necrosis of epithelial cells of both the proximal and distal tubules with flattening of the epithelial cells, rupture of the basement membrane (tubulorrhexis), and marked interstitial edema. Acute inflammatory cells are not seen. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
1- Diffuse cortical necrosis
2 © Acute tubular necrosis a
3 O Acute pyelonephritis
4© Chronic glomerulonephritis
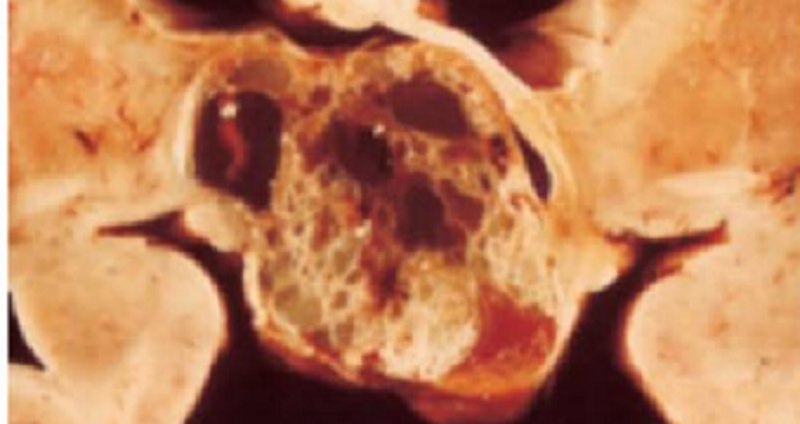
A 14-year-old boy presents with 3 months of lethargy, headaches, and muscle weakness his parents note that he drinks water excessively. His vital signs are normal. A 24-hour urine collection shows polyuria. The fasting blood sugar is normal. An X-ray film of the brain reveals suprasellar calcification. An autopsy specimen of a similar case is shown in the image N38. Which of the following neoplasms is the most likely cause of polyuria in this patient
Retinoblastoma
Pituitary adenoma
Pheochromocytoma
Craniopharyngioma
{"name":"Systemic-final-q", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Test your medical knowledge with our comprehensive quiz designed for healthcare professionals and students alike. From dermatology to hematology, this quiz spans a wide range of topics that challenge your expertise and enhance your understanding. Features of the quiz include: 30 multiple-choice questions Detailed explanations for each answer Instant feedback on your performance","img":"https:/images/course8.png"}
More Quizzes
DES 2016-2017 : 2040-2299 (Fabien) 1
101500
Oral Medicine
221110590
PE Pre-test
740
Elegi tu cotorrita
8431
Which Blackpink Member Are You? Free Personality
201016976
Free Online Bible - Test Your Knowledge
201017755
Am I Ready for Sex? - Hookup vs Dating
201018885
Which H2O Character Are You? Free Just Add Water
201017099
Growth Mindset - Which Mindset Are You?
201017484
General Shop Safety Practice Test with Answers - Free
201015970
Tarot Reader Certification - Free Final Exam Practice
201021177
Which Cyberpunk: Edgerunners Character Are You? Free
201017686