USLME_RHUMATOLOGY_EXAM_DES

USLME Rheumatology Exam Quiz
Test your knowledge on rheumatology with our comprehensive quiz tailored for USLME preparation. This quiz covers various topics related to rheumatology, ensuring that you are well-prepared for your exams.
Key Features:
- Multiple choice questions
- Diverse clinical scenarios
- Instant feedback on your answers
- Ideal for medical students and professionals
1. A 40-year-old female presents to your office complaining of the pain in her right hip. She denies trauma and says that the pain began two weeks ago and gradually increased. Her past medical history is significant for systemic lupus erythematosus diagnosed seven years ago. Her current medications include prednisone, hydroxychloroquine, and lansoprazole. There is no local tenderness on physical examination and the range of motion of the right hip is normal. Hip radiograph is normal. What is the next best step in the management of this patient?
A. Joint aspiration
B. Low-dose NSAIDs
C. Increase the dose of prednisone
D. MRI of the hip
E. Observation
2. A 44-year-old white male presents with a long history of joint pains in several joints. He has seen a physician before but no diagnosis was made. He has been taking ibuprofen with partial relief. He has now developed fever, diarrhea and weight loss. He denies any genitourinary or eye symptoms. He does not use tobacco, alcohol or drugs. He is a farmer. On examination, he has generalized lymphadenopathy and non-deforming arthritis. Small intestinal biopsy reveals periodic Acid-Schiff (PAS)-positive macrophages. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Reactive arthritis
B. Sarcoidosis
C. Lnflammatory bowel disease
D. Whipple's disease
E. Celiac disease
3. A 35-year-old female presents to your office complaining of knee pain. She has a long history of rheumatoid arthritis affecting her hand and knee joints. The stiffness and pain has persisted over the last several months and has responded poorly to NSAIDs. Over the last two days the pain in her right knee has been interfering with her sleep. She had an episode of chills this morning. Her blood pressure is 120/70 mmHg, pulse is 90/min, temperature is 38.7C (102F) and respiratory rate is 18/min. Physical examination reveals swelling in the joints of her hand and wrist. The right knee is red and swollen; active and passive range of motion at the right knee is limited due to pain. This patient's current condition can be best treated with which of the following?
A Colchicine
B. Corticosteroids
C. Anti-cytokine agents
D. Antibiotics
E. Antimetabolites
4. A 32-year old woman comes to the physician because of pain and paresthesias in her thumb, first two fingers and the radial-half of the ring finger. Her pain is worse at night and interferes with sleep. She feels tired and unable to work effectively in her office lately. She takes an over-the-counter stool softener for constipation but otherwise has no known medical problems. Her vital signs are within normal limits. When you ask the patient to maintain acute wrist flexion for 30seconds she experiences severe pain and paresthesias. Her skin is dry. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her hand symptoms?
A. Amyloid fibril deposition
B. Tenosynovial inflammation
C. Accumulation of matrix substances
D. Synovial tendon hyperplasia
E. Accumulation of fluid in carpal tunnel
5. A 61-year-old man presents to your office with a two-week history of low back pain. He describes the pain as constant, dull, and aching. It is non-radiating. The pain is not affected by movement and cannot be fully relieved by lying down. He denies fever and urinary frequency or hesitancy. He has started taking sleeping pills because the pain disturbs him during the night. On physical examination, the paraspinal muscles are non-tender. Percussion over the lumbar vertebrae does not elicit tenderness. Knee reflexes are symmetric and he has 5/5 strength in the extremities bilaterally. A straight leg raise test is negative. Which of the following is the best test for this patient?
. Electromyography
B. HLA genotyping
C. Urethral cultures
D. Prostate-specific antigen (PSA)
E. Abdominal ultrasonography
6. A 51-year-old man complains of difficulty walking and mild right-sided foot pain for the past several weeks. His medical history is significant for type 1 diabetes mellitus, hypertension and hypercholesterolemia. Physical examination reveals a significantly deformed right foot and a mildly deformed left foot. X-rays suggest effusions in several of the tarsometatarsal joints, large osteophytes, and several extraarticular bone fragments. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's complaints?
A. Hyperuricemia
B. Poor vascular supply
C. Nerve damage
D. Rheumatoid arthritis
E. Bone demineralization
7. A 33-year-old tennis player comes to you with a complaint of pain in his right shoulder. He says that the pain is absent at rest but present when he lifts his arm over his head. The pain is compromising his play. On examination, active motion at right shoulder is limited due to pain. Pain is most severe on passive internal rotation and flexion at the right shoulder. No atrophy of the shoulder muscle is seen. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
A. Tear of long head of bicep tendon
B. Tennis elbow
C. Subacromial bursitis
D. Anterior dislocation of shoulder
E. Axillary nerve palsy
8. A 68-year-old Caucasian male complains of right-sided leg pain over the last year. The pain is poorly controlled with over-the-counter pain medications. He also complains of frequent headaches. His past medical history is significant for hypertension and recent hearing loss. An X-ray of the skull shows areas of bone resorption and sclerosis. Which of the following are the most likely findings on laboratory work-up? Serum calcium, serum phosphate, alkaline phosphatase, Urinary hydroxyproline)
A. Normal Normal Normal High
B. Normal Normal High High
C. High Low High Normal
D. High Normal Normal Normal
E. Low High Normal Normal
9. A 25-year-old female presents to the physician's office complaining of fatigue, joint pains, and frequent mouth ulcers over the past three months. She has no medical problems and does not take any medications. She does not use tobacco, alcohol or drugs. Her temperature is 37.5°C (99.5.F), blood pressure is 150/100 mmHg and pulse is 78/min. Examination shows erythema over the cheeks and nose. Labs reveal a serum creatinine of 2.8 mg/dl and her urinalysis shows 2+ protein and 20 RBC/HPF. Anti-double stranded antibodies (anti-dsDNA) are positive. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management of this patient?
A. Kidney biopsy
B. Methotrexate
C. Methylprednisolone
D. Cyclophosphamide
E. Cyclophosphamide and methylprednisolone
10. A 68-year-old African-American woman presents to the ER in acute distress. She complains of a sudden onset of complete visual loss in her right eye. Her vision had been blurry for the past few days and acutely worsened one hour ago. She also describes right-sided headaches of two months duration for which she has taken ibuprofen without relief. She has no nausea or vomiting. She has diabetes, hypertension, and degenerative joint disease. Her temperature is 37.2°C (98.9.F) and blood pressure is 146/86 mmHg. Examination reveals complete loss of vision in the right eye. Her pupils are 4 mm bilaterally. Fundoscopy shows a swollen pale disc with blurred margins. A bruit is heard in the right subclavicular area. Motor and sensory examination is within normal limits. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
A. Temporal artery biopsy
B. Low dose prednisone
C. Methotrexate therapy
D. MRI of the brain with contrast
E. High dose prednisone
11. A 75-year-old white male comes to the physician's office for his routine health maintenance examination. He has no symptoms. He has a past medical history significant for hypertension and hyperlipidemia. He takes aspirin, hydrochlorothiazide and simvastatin. He does not smoke and consumes 1-2 beers on weekends. He walks 2 miles every morning and eats a balanced diet. His vital signs are within normal limits. His chest is clear to auscultation, and his abdomen is soft and nontender. Rectal examination shows a diffusely enlarged, firm prostate without nodules. Stool for occult blood is negative. The distal interphalangeal joints are enlarged, and his gait is normal. His labs are as follows: Total bilirubin 1.0 mg/dl Alkaline phosphatase 420 U/L Aspartate aminotransferase (SGOT) 20 U/L Alanine aminotransferase (SGPT) 25 U/L Serum creatinine 0.8 mg/dl Calcium 8.8 mg/dl Serum PSA 2.1 ng/ml Which of the following is the most likely cause of the elevated alkaline phosphatase in this patient?
A. Metastatic bone disease
B. Plasma cell neoplasia
C. Simvastatin
D. Paget's disease of bone
E. Alcohol use
12. A 43-year-old man was brought to the ED after he was unable to get out of his bed today due to leg weakness. He has been having constant back pain over the past several days. His past medical history is significant for poorly controlled diabetes mellitus and hypertension. His temperature is 38.3°C (101.F), pulse is 100/min, respirations are 18/min, and blood pressure is 150/100 mmHg. On examination, he smells of urine. His back is tender to palpation over L2-L5. Neurologic exam reveals 3/5 strength in the lower extremities with decreased sensation to temperature and light touch. He has an extensor plantar response bilaterally. Which of the following is the best next step in evaluating this patient?
A. Electromyography
B. CT scan of the spine
C. Lumbar puncture
D. MRI of the spine
E. HbA1c level
13. A 21-year-old Caucasian female presents with a one-week history of low-grade fever and joint pain. She describes symmetric swelling of the small hand joints. Her rheumatoid factor tests positive, and antinuclear antibodies are weakly positive at a 1:40 dilution. She is treated with NSAIDs. Four weeks later, the patient reports not taking the prescribed drugs since she feels no pain. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A Septic arthritis
B. Rheumatoid arthritis
C. Crystalline arthritis
D. Systemic lupus erythematosus
E. Viral arthritis
14. A 52-year-old female presents with a rash over her face for the past few weeks. She also complains of recent-onset difficulty with rising from a seated position and climbing stairs. On examination, you notice a dusky malar rash and a violaceous periorbital edema. Her vital signs are within normal limits. Examination shows symmetric proximal muscle weakness in legs. This patient's condition is most often associated with which of the following?
A. Aortic aneurysms
B. Renal failure
C. Alveolar hemorrhage
D. Malignancy
E. Carpal tunnel syndrome
15. A 64-year-old male comes to the physician's office because of increasing pain in his right groin for the past several months. The pain increases with activity and is relieved with rest. He also has difficulty moving after a period of rest. He denies any trauma or falls. He has no fever, weight loss or loss of appetite. He has had lumbar disk herniation in the past but denies any current back pain. He has no other active medical problems. His vital signs are within normal limits. He weighs 95 kg (210 lb) and is 168 cm (66 in) tall. Examination shows pain on passive internal rotation of right hip joint. Direct pressure over the groin did not increase the pain. His reflexes are 2+, and there are no sensory deficits. Muscle bulk, tone and power are within normal limits. Pulses are 2+ in both legs. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his hip pain?
A. Cutaneous nerve compression
B. Inflammation of the trochanteric bursa
C. Degenerative joint disease
D. Disruption of bone vasculature
E. Referred pain from the lumbosacral are
16. A 24-year-old Caucasian female complains of weakness, skin rash, low-grade fever and joint pain. She describes pain and swelling of the hand joints and pain in her knees. Her mother suffers from rheumatoid arthritis. Her blood pressure is 145/90 mmHg, and her heart rate is 90/min. Her hematocrit is 40% and ESR is 43 mm/hr. Urinalysis is 2+ for protein. Which of the following is the best statement about this patient's joint symptoms?
A. Excessive bony growth is characteristic
B. Permanent deformity is uncommon
C. Subluxation and tendon damage cause permanent deformity
D. Cartilage degradation and muscle atrophy cause deformity
E. Bone resorption of the distal phalanges may result
17. A 36-year-old female who is currently having regular menstrual periods comes to the emergency room because of malaise and a high-grade fever with chills. She also complains of pain in multiple joints. She always uses highly absorbent tampons during her menses. She uses intravenous heroin and cocaine and works as a prostitute. Her temperature is 39.3C (103.4F), pulse is 102/min, blood pressure is 120/80mmHg and respirations are 14/min. Examination shows multiple pustules on the extensor surfaces of her forearms. Joint examination does not show redness, swelling or tenderness. Three sets of blood cultures are negative Based on these findings, which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
A. Infective endocarditis
B. Disseminated gonococcal infection
C. Toxic shock syndrome
D. Acute HIV infection
E. Secondary syphilis
18. A 54-year-old retired schoolteacher comes to the physician's office because of worsening low back pain. The pain started three weeks ago. It is continuous and is worse at night. He has had little relief with over-the-counter nonsteroidal analgesics. He has no other symptoms. He had a surgical resection of a lung tumor one year ago for non-small cell carcinoma of the lung. Preoperative positron emission tomography (PET) scanning did not reveal any evidence of metastasis. His vital signs are within normal limits. Examination shows local spinal tenderness at the L4-L5 level. What is the most likely cause of his back pain?
A. Lumbar strain
B. Central spinal canal stenosis
C. Disc herniation
D. Vertebral compression fracture
E. Metastatic disease
19. A 45-year-old woman presents to your office complaining of one week of fatigue and weakness in her shoulders and hips. She reports difficulty performing household tasks, climbing the stairs, or rising from a chair. She denies any facial weakness or blurry vision. She has a history of gastroesophageal reflux disease and takes over the counter ranitidine. Her family history is positive for breast cancer in her mother. Her vital signs are within normal limits and examination shows normal sensation and deep tendon reflexes. Strength is 4 out of 5 in the proximal muscles groups of the arms and legs, and there is no limitation in the range of motion. Other physical examination is within normal limits. The ESR is 80 mm/hour and her serum creatine kinase is elevated. The TSH is within normal limits. Which of the following is the best initial treatment for this patient?
A. Indomethacin
B. Corticosteroids
C. Colchicine
D. Riluzole
E. Amitriptyline
20. A 60-year-old man presents to the emergency department after being awoken from sleep by severe pain in his right great toe. He reports that his toe is suddenly swollen and very tender to touch. On review of systems, the patient also describes occasional headaches and pruritus that can be "unbearable" after a hot bath. He does not smoke or drink alcohol. On physical examination, his lungs are normal. The liver span is 10 cm and the spleen is palpable 2 cm below the costal margin. Aspiration of the affected toe joint reveals negatively birefringent crystals. Which of the following is most likely responsible for this patient's symptoms?
A. Chronic kidney disease
B. Myeloproliferative disorder
C. Hemochromatosis
D. Inherited enzyme deficiency
E. Hyperparathyroidism
21. A 67-year-old man presents to your office with two days of back pain. He was moving boxes in the garage when the pain started. The pain is not relieved by lying down and increases in intensity upon straining and coughing. He could not sleep during the night due to pain and took several tablets of acetaminophen without relief. He has never had such pain before. Physical examination reveals symmetric knee reflexes. Plantar reflexes are flexor bilaterally. Straight leg raise is negative. Local tenderness is evident upon percussion of the fourth lumbar vertebra. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
A. Ligamentous sprain
B. Intervertebral disk degeneration
C. Apophyseal joint arthritis
D. Nerve root demyelinization
E. Vertebral body demineralization
21. A 67-year-old man presents to your office with two days of back pain. He was moving boxes in the garage when the pain started. The pain is not relieved by lying down and increases in intensity upon straining and coughing. He could not sleep during the night due to pain and took several tablets of acetaminophen without relief. He has never had such pain before. Physical examination reveals symmetric knee reflexes. Plantar reflexes are flexor bilaterally. Straight leg raise is negative. Local tenderness is evident upon percussion of the fourth lumbar vertebra. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
A. Ligamentous sprain
B. Intervertebral disk degeneration
C. Apophyseal joint arthritis
D. Nerve root demyelinization
E. Vertebral body demineralization
22. A 54-year-old man presents to the emergency room with acute pain, swelling and redness of his right knee. He had one episode of gouty arthritis a year ago that resolved quickly with indomethacin. He also has type 2 diabetes, hypertension and chronic renal disease. He does not use any illicit drugs. His temperature is 38.3°C (100.9F), blood pressure is 110/65 mmHg, and pulse is 110/min. Examination reveals a tender, erythematous effusion of the right knee with decreased range of motion. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
A. Serum uric acid level
B. Indomethacin
C. X-ray of the knee
D. MRI of the knee
E. Synovial fluid analysis
23. A 38-year-old male with steroid-dependent sarcoidosis presents to the physician's office because of progressive right hip pain. He localizes the pain to right groin and states that the pain is present on weight bearing and at rest. His temperature is 37.2C (98.9 F) and blood pressure is 156/86 mm Hg. Examination shows decreased range of motion due to pain. He also has a round face and fullness in supraclavicular area. Purple striae are present on skin. Muscle power is slightly decreased in the proximal thigh muscles in both legs. Reflexes are 2+, and there are no sensory deficits. Plain films of the right hip show no significant abnormalities ESR is 10 mm/hr. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his hip pain?
A. Inflammatory arthritis
B. Cartilage degeneration
C. Disruption of bone vasculature
D. Inflammation of the trochanteric bursa
E. Aortoiliac occlusion
24. A 29-year-old woman presents to your office complaining of easy fatigability over the last several months. She tires easily after walking short distances. She also has difficulties combing her hair due to an inability to hold her hands over her head for a long time. She reports a weight loss of two or three pounds over the last two months. She denies fever or loss of appetite. She does not smoke or consume alcohol. On family history, her father died of a stroke when he was 54 years old and her mother has diabetes mellitus. On examination, she is afebrile with a pulse of 105/min. Cardiac exam reveals regular rhythm with no murmur. Her gait is normal but, when asked to sit down slowly, she drops into the chair. A fine finger tremor is evident when she extends her arms. Her muscles are non- tender to palpation. She appears to have decreased muscle mass in her shoulders. Deep tendon reflexes are normal. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
A. Upper motor neuron disease
B. Polyneuropathy
C. Lnflammatory muscle disease
D. Thyroid disease
E. Cerebellar dysfunction
25. A 62-year-old male treated for hypertension and hyperlipidemia complains of nagging right knee pain that is worse in the evening. The pain has been present for several months and it seems to limit his physical activities. His blood pressure is 160/100 mmHg and his heart rate is 70/min. His BMI is 32 kg/m2, and palpation of the knee reveals a cool joint with bony tenderness. His blood cholesterol level is 200 mg/dl and his serum uric acid level is 9.0 mg/dl. Which of the following additional findings is likely on further examination of the right knee?
A. Soft tissue swelling
B. Painful tibial tuberosity
C. Palpable popliteal mass
D.Bony crepitus
E. Subcutaneous nodules
26. A 34-year-old man complains of back tightness and persistent low back pain. The pain has a dull and aching quality. It is worse during the night and in the morning but improves gradually during the day. He has no significant past medical history. He does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. He is married and lives with his wife. His pulse is 80/min, respirations are 14/min, and blood pressure is 120/76 mmHg. Which of the following most likely accounts for this patient's symptoms?
A. Ligamentous sprain
B. Lumbar disk degeneration
C. Apophyseal joint arthritis
D. Nerve root demyelinization
E. Abnormal bone mineralization
27. A 23-year-old man complains of progressive low back pain for the past several months. He has morning stiffness that lasts for one hour. He has no history of trauma to his back and denies any recent illness. He had an episode of pain, blurring, and photophobia of his right eye two years ago that required ophthalmology evaluation. His vital signs are within normal limits. Examination shows tenderness in both sacroiliac joints and reduced range of motion of the lower back. If measured, which of the following is most likely to be present in this patient?
A. Rheumatoid factor
B. Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (CCP) antibodie
C. Anti dsDNA antibodies
D. HLA B 27 positivity
E. Glutamic acid decarboxylase antibodies
28. A 65-year-old man comes to the emergency room complaining of 2 days of severe pain and swelling of his right knee. He denies any recent respiratory illness, diarrhea or urinary symptoms. He has a history of severe degenerative joint disease and underwent total knee replacement four years ago. He drinks one can of beer every night and does not use tobacco or illicit drugs. His temperature is 40°C (104F), blood pressure is 120/60 mmHg, and pulse is 110/min. Examination shows warmth, swelling, and tenderness over the knee. His range of motion is restricted. Synovial fluid white blood cell count is 98,000/microl. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his current condition?
A. Streptococcus species
B. Staphylococcus aureus
C. Neisseria gonorrhoea
D. Chlamydia trachomatis
E. Borrelia burgdorferi
29. A 34-year-old woman with a skin rash, joint pains, and oral ulcers is diagnosed with systemic lupus erythematosus. She has no renal or central nervous system involvement, and her past medical history and review of systems are otherwise negative. Therapy with hydroxychloroquine is started. Which of the following screening tests is most important in this patient?
A. Complete blood count
B. Liver function panel
C. Urinalysis
D. Audiometry
E. Eye examination
30. A 68-year-old man with hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and diabetes is hospitalized for an acute myocardial infarction. It is complicated by pulmonary edema and he undergoes angiography of the left anterior descending artery. On post-operative day 3, he complains of abdominal pain and discoloration of his toes. His vital signs are stable. Examination shows bluish discoloration of his right great toe and of all the toes on his left foot. The skin over the toes is cold and clammy. Bilateral pedal pulses are present and full. His abdomen is soft and mildly tender at the center. Chest auscultation is clear. Laboratory studies show a rise in creatinine to 2.3 g/dl from his baseline of 1.2 g/dl. An EKG shows sinus rhythm and Q waves in anterior leads. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his toe discoloration?
A. Ketoacidosis
B. Vasospasm
C. Right to left shunt
D. Autoimmune vasculitis
E. Cholesterol embolism
31. A 50-year-old man presents to your office complaining of pain and swelling of the right knee. He bumped his right knee into a pole 2 days ago while working. He had one episode of similar pain two years ago that resolved with over-the-counter analgesics. He denies any illicit drug use. He has no other medical problems and does not take any medications. His temperature is 37.2°C (98.9F), and blood pressure is 126/76 mmHg. Examination reveals swelling, warmth and decreased range of motion of the right knee. All other joints are within normal limits. Synovial fluid analysis shows positive birefringent crystals and negative Gram stain. These crystals are most likely composed of?
A Hydroxyapatite
B. Monosodium urate
C. Calcium pyrophosphate
D. Calcium oxalate
E. Ammonium phosphate
32. A 32-year-old man presents to the clinic with one week of escalating lower back pain. He describes the pain as dull and aching. It increases with motion and it is not completely relieved by rest. He has no significant past medical history. He smokes one pack of cigarettes per day and consumes alcohol occasionally. He admits to being "under a lot of stress" and has recently used injectable drugs. His family history is significant for prostate cancer in his father. His temperature is 36.7C (98.F), pulse is 90/min, respirations are 16/min, and blood pressure is 120/80 mmHg. Gentle percussion over the lumbar vertebrae elicits pain. A full neurologic exam including straight leg raise is normal. Laboratory results are shown below: Complete blood count: Leukocyte count 6,500/mm3 Hematocrit 46% Platelets 400,000/mm3 Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Ankylosing spondylitis
B. Lumbar disk herniation
C. Lumbar spinal stenosis
D. Vertebral osteomyelitis
E. Vertebral compression fracture
33. A 35-year-old African-American woman comes to the physician's office complaining of blurred vision, cough and shortness of breath. For the past few days she has had mild fevers, malaise and easy fatigability. She has never had these symptoms before and is anxious to uncover a diagnosis. She was recently incarcerated for two months. She practices unprotected sex with her new boyfriend. Her temperature is 37.2°C (98.9F) and her blood pressure is 116/80 mmHg. On exam, her right eye is red and slit lamp examination shows leukocytes in the anterior chamber. Lungs have patchy rales. Chest x-ray shows bilateral reticulonodular infiltrates and hilar adenopathy. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
A. Acute HIV infection
B. Disseminated tuberculosis
C. Sarcoidosis
D. Histoplasmosis
E. Ankylosing spondylitis
34. A 55-year-old man presents to his physician with 6 months of mild intermittent pain in both knees. The pain is aggravated by walking and weight bearing, and is partially relieved by rest. He also complains of morning stiffness that lasts for 10 minutes. He does not smoke but drinks alcohol occasionally. His BMI is 25 Kg/m2, temperature is 37C (98.6.F), pulse is 75/min, and blood pressure is 130/80 mmHg. Examination reveals crepitus over both knee joints. Which of the following is the most appropriate initial treatment for this patient?
A. Antibiotics
B. Ketorolac
C. Acetaminophen
D. Colchicine
E. Oxycodone
35. A 65-year-old man presents with right shoulder pain and weakness after falling on his outstretched hand. The pain is worse when he tries to position his arm above the shoulder level or when he pulls or pushes. He also complains of pain when he lies on the affected shoulder. He has a 40-pack-year history of cigarette smoking. His father died of multiple myeloma. His vital signs are within normal limits. Examination shows limitation of mid arc abduction and external rotation that does not improve after lidocaine injection. There is no swelling, redness or warmth of the joint. Radial pulse is normal. Muscle tone and bulk is within normal limits. Which of the following would be most helpful in confirming the patient's diagnosis?
A. X-ray shoulder
B. Chest-X ray
C. Bone marrow biopsy
D. MRI of the shoulder
E. MRI of the cervical spine
36. A 38-year-old woman complains of chronic aching pain and stiffness around the neck, shoulders, low back and hips. She fatigues easily and has been having problems with sleep. Even minor exertion worsens her pain. She has no muscle weakness, fever, malaise, weight loss or rash. She has a history of irritable bowel syndrome. Her vital signs are within normal limits. Examination shows multiple tender spots over specific points on her body. Power is 5/5 in all extremities and deep tendon reflexes are 2+. No sensory abnormalities are noted. Labs show: ESR 9 mm/hr Hematocrit 43% WBC count 7,000/microL Platelet count 200,000/microL TSH 3 microU/L CPK 100 IU/L Which of the following is the most appropriate pharmacotherapy for this patient?
A. Naproxen
B. Amitriptyline
C. Prednisone
D. Colchicine
E. Oxycodone
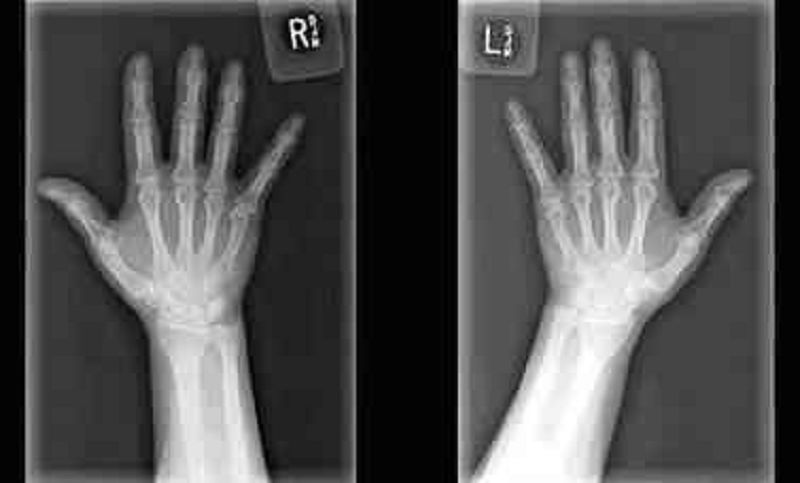
37. A 60-year-old Caucasian woman comes to the physician because of joint pains in both hands. Her other medical problems include obesity and gastroesophageal reflux disease. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or drugs. Family history is not significant. Her medications include omeprazole and acetaminophen. Her vital signs are within limits. X-ray of the joints is shown below.Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Rheumatoid arthritis
B. Systemic lupus erythematosus
C. Osteoarthritis
D. Reactive arthritis
E. Gouty arthritis
38. A 35-year-old man presents to your office with severe back pain. The pain started three days ago when the patient was carrying a heavy pack. The pain radiates to the posterior surface of the right thigh. The straightleg raise test is positive. There is no bladder or bowel incontinence. Pain and temperature perception is preserved in the affected extremity, as well as in the perineal area. Anal reflex is normal. Which of the following is the best next step in the management of this patient?
A MRI of the spine
B. CT scan of the spine
C. Early mobilization and NSAIDs
D. Plain roentgenogram
E. Surgical decompression
39. A 67-year-old male hospitalized after elective hernia repair complains of severe right knee pain. Physical examination reveals redness and swelling of the right knee with limited motion due to pain. His temperature is 38.9 (102F), blood pressure is 160/110 mm Hg, pulse is 80/min, and respirations are 16/min. Synovial fluid analysis reveals the following findings: WBC count 30,000mm3 Neutrophils 90% Crystals rhomboid-shaped, positively birefringent Gram stain negative Which of the following is most likely associated with this patient's current condition?
A. Tophi
B. Transient bacteremia
C. Chondrocalcinosis
D. Rheumatoid factor
E. Heberden nodes
40. A 43-year-old Caucasian female presents to your office complaining of joint pain and swelling in her hand. On history, she endorses easy fatigability and loss of energy that has been worsening insidiously. It is especially difficult for her to do daily activities in the morning due to prolonged stiffness. She also describes frequent knee pain accompanied by a low-grade fever. She takes ibuprofen and naproxen to relieve her symptoms. Her hematocrit is 33%. The patient is at the greatest risk of which of the following?
A. Osteitis fibrosis cystica
B. Osteitis deformans
C. Avascular bone necrosis
D. Osteomalacia
E. Osteoporosis
41. A 31-year-old Caucasian male complains of joint pains. He describes right knee pain, right heel pain and lowback pain. He was recently treated for urethral discharge at an outside clinic. He has no history of trauma or illicit drug use. He is afebrile, and his vital signs are stable. His right knee is swollen, tender and warm to touch; tenderness is also present over the Achilles tendon. Oral examination shows mouth ulcers. Synovial fluid analysis from the right knee shows a white blood cell count of 10,000/mm3 with many polymorphonuclear leukocytes but a negative Gram stain. Which of the following is the most appropriate initial pharmacotherapy for this patient?
A. Antihistamines
B. NSAIDs
C. Antibiotics
D. Colchicine
E. Allopurinol
42. A 32-year-old Caucasian male complains of inability to grip his cup of coffee and hold a pen in the morning. He says that he is 'fully functional' in the afternoon. His ESR is 45 mml hr. Which of the following is most likely to be affected by this patient's disease?
A. Sacral spine
B. Sacroiliac joints
C. Lumbar spine
D. Thoracic spine
E. Cervical spine
43. A 21-year-old woman presents with 4 months of slowly progressive low back pain. Her back pain is associated with early morning stiffness that improves as the day progresses. She has no fever or gastrointestinal complains. She denies any recent illness. On examination, there is limited range of motion of her back. Other examination is unremarkable. Plain X-ray films show bilateral sacroiliitis. Which of the following conditions is this patient at greatest risk of developing?
A. Aortic coarctation
B. Thoracic aortic aneurysm
C. Renal failure
D. Oral ulcers
E. Anterior uveitis
44. A 30-year-old female comes to your office with a complaint of pain over the lateral side of her wrist for the last four days. She is two months postpartum and notes that her pain is most severe when she lifts her infant from a crib. On examination, there is tenderness over the radial side of wrist and first dorsal compartment. Passive stretching of the thumb tendons over the radial styloid while the thumb is held in flexion aggravates the pain. She denies any recent trauma over the tender area. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
A. Osteoarthritis of first metacarpophalangeal joint
B. Trigger thumb
C. De Quervain tenosynovitis
D. Scaphoid fracture
E. Flexor carpi radialis tenosynovitis
45. A 44-year-old female complains of generalized weakness, low-grade fever and joint pain. Her daily activities are limited due to joint stiffness, especially in the morning. Her hand joints are swollen symmetrically. The inferior pole of the spleen is palpable on physical examination. Her hematocrit is 34%. Liver and renal function tests are normal. Two months after the initial visit, the patient develops painful oral ulcers. Her laboratory values are: Hematocrit 33% AST 120 U/L ALT 90 U/L Alkaline phosphatase 90 U/L Bilirubin 1.1 mg/dl Creatinine 0.8 mg/dl BUN 16 mg/dl Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's current complaints?
A Viral hepatitis
B. Felty syndrome
C. Lymphoid cell proliferation
D. Antimetabolite agent
E. Corticosteroid treatment
46. A 70-year-old male presents with malaise, pain and stiffness of his neck, shoulders and hips for the last 3 months. His stiffness is worse in the morning and lasts about 30-40 minutes. He also complains of a recent weight loss of 71bs and mild fevers. He has no headache, scalp tenderness, visual symptoms or jaw claudication. Examination shows no swelling or tenderness of the involved joints with normal range of motion on active and passive movement. The arteries of the scalp, neck and extremities are normally palpable without any tenderness. Labs show a hematocrit of 31% and an ESR of 65 mm/hr. Blood cultures are negative. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management of this patient?
A. Temporal artery biopsy
B. Treatment with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents
C. Treatment with low-dose prednisone
D. Treatment with high-dose prednisone
E. Measure antinuclear antibodies and rheumatoid factor levels
47. A 49-year-old African American female complains of progressive exertional dyspnea. She also complains of swelling and pain in her finger joints over the last 6 months. She has been treated for severe heartburn with pantoprazole and for hypertension with lisinopril and hydrochlorothiazide. Her blood pressure is 145/100 mmHg and her heart rate is 80/min. Physical examination reveals prominent jugular venous distention. Her lungs are clear to auscultation, and no murmurs are present on cardiac auscultation. Her skin is thickened and discolored over the fingertips and interphalangeal joints. There is mild pitting ankle edema. Which of the following is most likely to be positive in this patient?
A. Anti-topoisomerase-1 antibodies
B. Rheumatoid factor
C. Antimitochondrial antibodies
D. Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies
E. Anti-smooth muscle antibodies
48. A 52-year-old woman presents with gradual-onset weakness in her leg muscles. She has noted difficulty climbing stairs and raising from a chair that has been worsening for the past few years. She initially related her symptoms to simply being "out of shape." She has no problem with chewing food. She has no pain in her muscles and has no skin rash. She takes metoprolol and hydrochlorothiazide for hypertension. She does not use tobacco, alcohol or drugs. Her vital signs are within normal limits. Examination reveals mild weakness of the thigh muscles in both legs. Deep tendon reflexes and sensory examination shows no abnormalities. Babinski sign is negative. Which of the following is most likely abnormal in this patient?
A MRI of the spine
B. Electroencephalogram
C. Temporal artery biops
D. Lumbar puncture
E. Muscle biopsy
49. A 62-year-old Caucasian female complains of difficulty swallowing solid food. She needs to take sips of water during every meal to help with swallowing. Her past medical history is significant for hypertension controlled with metoprolol. She uses some over-the-counter eye drops for eye dryness. Her blood pressure is 140/90 mmHg and heart rate is 60/min. Physical examination reveals prominent dental caries. There are bilateral firm submandibular swellings present on neck palpation. Which of the following is the best test to confirm this patient's diagnosis?
A. Antibodies to Ro/SSA
B. Antimitochondrial antibodies
C. Barium swallow test
D. CT scan of the neck
E. Esophageal endoscopy with biopsy
50. A 43-year-old construction worker presents to your office 2 weeks after an episode of acute back pain. The pain started after lifting a heavy box, was localized to the lower back with little radiation to the buttocks, and quickly responded to conservative treatment. His past medical history is insignificant. He smokes 2 packs a day and consumes alcohol occasionally. He is concerned about the possibility of recurrence of the pain. Which of the following would be most helpful in preventing another episode of back pain in this patient?
A. Limiting the physical activity as much as possible
B. Sleep on the stomach
C. Regular exercise with repetitive twisting and bending
D. Bend at the waist, not at the knees
E. Keep the back straight while lifting an object
51. A 35-year-old woman presents with complaints of aching pain and stiffness over her entire body for the past 3 months. She also reports, easy fatigability, poor sleep and frequent headaches. She has been using over the counter pain medications with no relief. While examining her, she complains of extreme pain to gentle palpation over her neck, shoulders and back. Her vital signs are stable. What is your diagnosis?
A. Chronic fatigue syndrome.
B. Polymyalgia rheumatica.
C. Rheumatoid arthritis.
D. Polymyositis.
E. Fibromyalgia
52. A 60-year-old male presents to the emergency room with a two-week history of low back pain and low-grade fever. His past medical history is insignificant. He tried several over-the-counter pain medications with little success. His temperature is 38.3 C (101 F), blood pressure is 120/76 mmHg, pulse is 90/min, and respirations are 16/min. Physical examination reveals percussion tenderness over the lumbar vertebrae and local paravertebral muscular spasm. Neurological examination shows 2+ deep tendon reflexes and 5/5 muscle power. The straight-leg raising test is negative at 90 degrees. Laboratory values are: Hemoglobin 12.2 g/dL Leukocyte count 10,700/cmm Segmented Neutrophils 63% Bands 4% Eosinophils 3% Basophils 0% Lymphocytes 23% Monocytes 6% Platelets 400,000/cmm ESR 75 mm/hr What is the next step in the management of this patient?
A Plain radiograph
B.Bone scan
C. MRI of the spine
D. Serum rheumatoid factor
E. Physiotherapy
53. A 25-year-old immigrant from Eastern Europe is being evaluated for right shoulder pain and swelling. He also complains of heel pain while walking. Palpation over the heels, iliac crests and tibial tuberosities elicits tenderness. Which of the following additional findings is most likely in this patient?
A. Positive rheumatoid factor
B. Proteinuria
C. Limited spine mobility
D. Subcutaneous nodules
E. Hand joint deformities
54. A 52-year-old man presents with 24 hours of pain and swelling of his right knee. He also reports having constipation, excessive urination, and fatigue for the past several months. He denies fevers, chills, and trauma to the knee. He does not use tobacco, alcohol or drugs. His temperature is 37.2°C (98.9.F), and blood pressure is 130/76 mmHg. Examination shows tenderness, erythema, and swelling of the right knee. His lab values are: Serum sodium 138 mEq/L Serum potassium 4.0 mEq/L Serum creatinine 1.1 mg/dl Serum calcium 11.9 mg/dl Serum phosphorous 1.9 mg/dl Blood glucose 98 mg/dl Which of the following would synovial fluid analysis from the knee most likely reveal?
A. Needle shaped crystals with negative birefringenc
B. Coffin lid shaped crystals
C. Rhumboid shaped crystals with positive birefringence
D. Numerous polymorphs filled with gram positive cocci
E. Numerous lymphocytes and budding yeast
55. A 24-year-old Caucasian male undergoes pulmonary function testing. The following values are obtained: FEV 80% of predicted FEV1/FVC 85% FRC 110% of predicted He has no current complaints except for occasional low back pain treated with naproxen. He smokes one pack per day and drinks a six-pack of beer each weekend. His ESR is 47 mm/hr. Which of the following best explains the pulmonary function test findings in this patient?
A. Emphysema
B. Small airway obstruction
C. Pulmonary fibrosis
D. Chest wall motion restriction
E. Pulmonary vascular disease
56. A 53-year-old Caucasian man comes to the emergency department at 2 am because of severe pain in his right great toe for the past 2 hours. He complains that the pain began suddenly as a dull, aching pain, and has worsened over time to a severe throbbing pain, not relieved by acetaminophen. His other medical problems include hypertension, diabetes mellitus-type 2, hypercholesterolemia, and peptic ulcer disease. He has smoked 2 packs of cigarettes daily for 30 years. He drinks 5-6 ounces of alcohol daily. He eats a lot of junk food and exercises infrequently. Both his father and mother have diabetes and hypertension. His older brother died of a myocardial infarction 2 years ago. His medications include glyburide, lisinopril, atenolol, simvastatin and famotidine. His temperature is 37.8 C (100 F), blood pressure is 160/90 mm Hg, pulse is 88/min and respirations are 16/min. On examination, the right great toe appears markedly swollen, red, and is warm to touch. Aspiration of the joint fluid reveals negatively birefringent needle shaped crystals. Apart from prescribing oral indomethacin, what other intervention would be most important to prevent the development of further attacks?
A. Smoking cessation
B. Alcohol cessation
C. Stopping lisinopril
D. Stopping simvastatin
E. Stopping glyburide
57. A 54-year-old woman comes to the physician's office complaining of chronic, bilateral knee and hip pain. The pain increases with activity and is relieved by rest. She denies fever, chills or weight loss. The review of systems is unremarkable. She currently weighs 80 kg (180lb) and is 146 cm (59 in) tall. Her knee joints are tender but there is no warmth, erythema or effusion. X-rays show narrow joint space, subchondral bone cysts, and bony spurs in both knees. Which of the following interventions would provide the greatest long-term benefit to this patient?
A. Muscle strengthening exercise
B. Non-steroidal antiinflammatory agents
C. Weight loss
D. Chondroitin sulfate
E. Acetaminophen with codeine
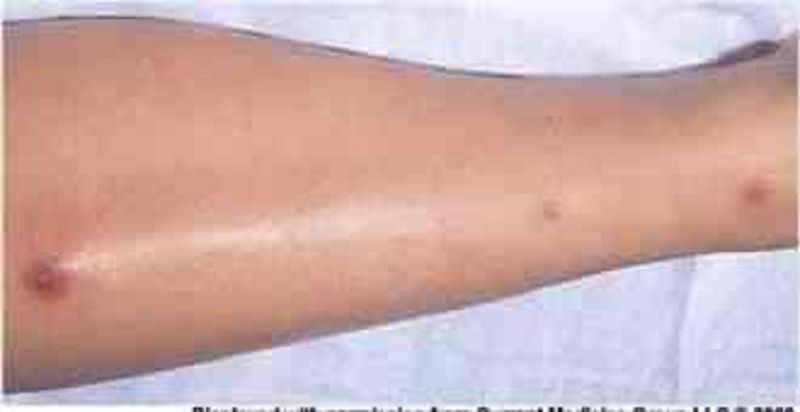
58. A 24-year-old woman comes to the physician complaining of a skin rash and pain in her wrists, ankles and elbows over the past 4 days. She has also had a fever and sweats, but denies headache, nausea or vomiting. She has no significant past medical history and does not take any medications. She recently took a vacation with her new boyfriend. She denies any previous sexually transmitted diseases but acknowledges having unprotected sex with her new boyfriend. She does not use tobacco, alcohol or illicit drugs. Her temperature is 38.5°C (101.3F) and her pulse is 98/min. Her oropharynx is clear and there is no thrush or lymphadenopathy. Her abdomen is benign and the pelvic examination is within normal limits. She has pain along the tendon sheaths with active and passive hand movement. A photo of her skin rash is shown below. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her symptoms?
A. Lyme disease
B. Syphilis
C. Gonococcemia
D. Meningococcemia
E. Acute HIV infection
58. A 24-year-old woman comes to the physician complaining of a skin rash and pain in her wrists, ankles and elbows over the past 4 days. She has also had a fever and sweats, but denies headache, nausea or vomiting. She has no significant past medical history and does not take any medications. She recently took a vacation with her new boyfriend. She denies any previous sexually transmitted diseases but acknowledges having unprotected sex with her new boyfriend. She does not use tobacco, alcohol or illicit drugs. Her temperature is 38.5°C (101.3F) and her pulse is 98/min. Her oropharynx is clear and there is no thrush or lymphadenopathy. Her abdomen is benign and the pelvic examination is within normal limits. She has pain along the tendon sheaths with active and passive hand movement. A photo of her skin rash is shown below. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her symptoms?
A. Lyme disease
B. Syphilis
C. Gonococcemie
D. Meningococcemia
E. Acute HIV infection
59. A 9-year-old Caucasian male complains of fever, sore throat and difficulty swallowing. Small tender lymph nodes are palpated in the cervical region. The symptoms subside quickly on penicillin therapy. Ten days later, the patient presents again with fever, skin rash and fleeting joint pain in the lower extremities. Physical examination reveals scattered urticaria and palpable lymph nodes in the cervical, axillary and inguinal regions. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's current complaints?
A. Rheumatic fever
B. Drug-induced reaction
C. Lymphoproliferative disorder
D. Henoch-Schonlein purpura
E. Infective endocarditis
60. A 58-year-old woman has had bilateral hip and knee pain for the past several months. The pain is worse with activity and better with rest. Recently she has noticed swelling of the right knee. She reports morning stiffness of about 10-15minutes duration. She denies fever or weight loss. Her past medical history is significant for hypertension, type 2 diabetes, gastroesophageal reflux disease, and obstructive sleep apnea. She takes hydrochlorothiazide, lisinopril, omeprazole, insulin and aspirin. She does not use tobacco, alcohol or drugs. Her temperature is 37.2°C (98.9.F), and blood pressure is 146/86 mmHg. Examination shows a mild effusion, tenderness, and decreased range of motion of the right knee. Synovial fluid analysis reveals the following: Cell count 1100/ml Gram stain negative Crystals absent Plain films of her knee joint would most likely reveal?
A. Punched out erosions with a rim of cortical bone
B. Periarticular osteopenia and joint margin erosions
C. Narrowing of joint space and osteophyte formation
D. Normal joint space with soft tissue swelling
E. Calcifications of cartilaginous structures
61. A 45-year-old man complains of sudden pain and swelling in his left first metatarsophalangeal joint. He is undergoing high dose induction chemotherapy for acute leukemia. Joint fluid aspiration reveals negative birefringent crystals and elevated white cell count. Which of the following prophylactic measures would most likely have prevented this condition?
A. Urine acidification
B. N-acetylcysteine
C. Allopurinol
D. Mesna
E. Adequate hydration
62. A 23-year-old white woman presents complaining of 6 months of progressive low back pain. She complains of morning stiffness that lasts one hour, and says her symptoms improve with physical activity. She denies rash, eye pain, urinary problems, and diarrhea. Her past medical history is significant only for an appendectomy at the age of 16 years. She has been taking birth control pills for the past two years. She is afebrile with normal weight and height. Examination reveals reduced forward flexion of the lumbar spine and tenderness over the sacroiliac joints. The remainder of the physical examination is normal. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient?
A HlA-827 testing
B. ANA and rheumatoid factor levels
C. Bone scan
D. MRI of the spine
E. X-ray of the sacro-iliac joints
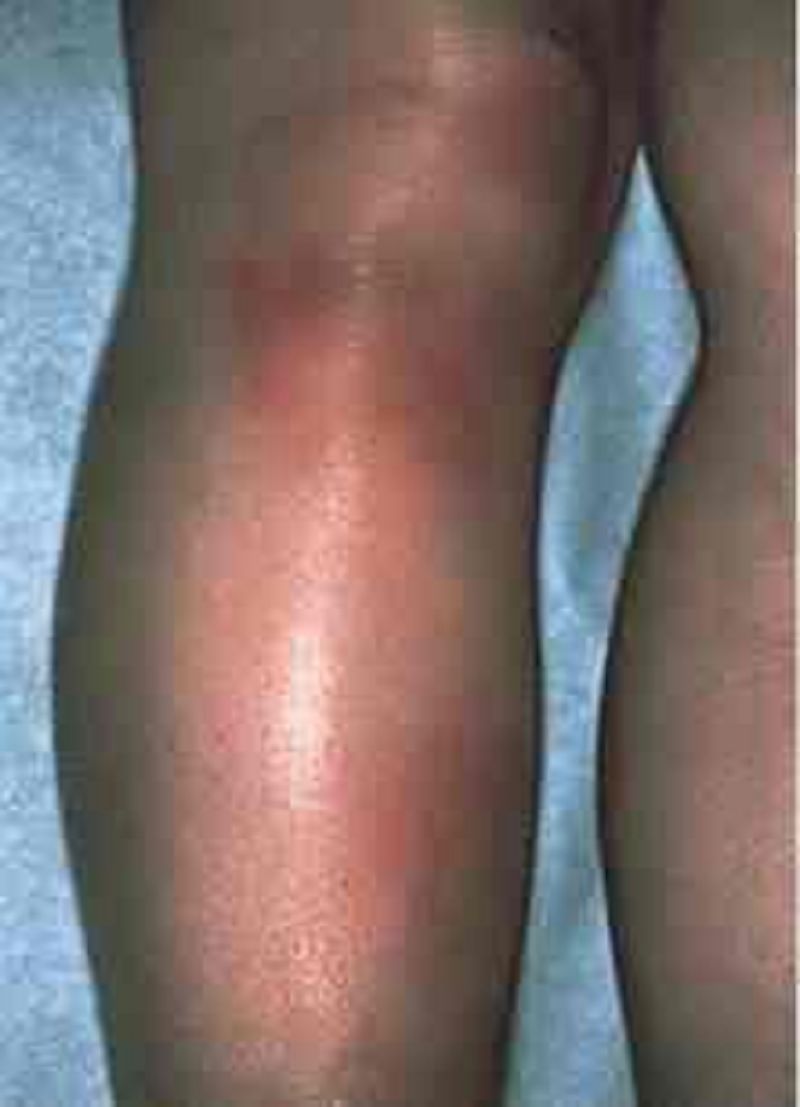
63. A 33-year-old African-American woman presents with one week of painful skin lesions on her legs. She has no cough, shortness of breath or bowel symptoms, and denies any recent illness or travel. She has no other significant past medical history and does not take any medication. She smokes one pack of cigarettes and drinks one glass of wine daily. She denies a history of sexually transmitted diseases and has been married to a monogamous partner for the past eight years. Her mother was diagnosed with ovarian cancer at age 65. Her temperature is 37.2°C (98.9.F), and blood pressure is 126/76 mmHg. On examination, she has multiple tender pink to reddish nodules noted below the knee on the extensor surface, as shown below. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in her management
A. CT scan of the abdomen
B. HIV testing
C. Chest x-ray
D. Rectal swab for culture
E. Colonoscopy
64. A 60-year-old male presents to your office complaining of right-sided neck pain and numbness over the posterior surface of the forearm. He had several such episodes over the last two years that responded to NSAIDs and physical therapy. Physical examination reveals limited neck rotation and lateral bending. There is decreased pinprick sensation on the posterior aspect of the right forearm, but no muscle weakness is present. Triceps reflex is normal. Which of the following is the most likely finding on the neck radiography of this patient?
A. Reversed lordotic curve
B. Bony spurs
C. Vertebral body osteoporosis
D. Osteolytic lesions
E. Compression fracture
64. A 60-year-old male presents to your office complaining of right-sided neck pain and numbness over the posterior surface of the forearm. He had several such episodes over the last two years that responded to NSAIDs and physical therapy. Physical examination reveals limited neck rotation and lateral bending. There is decreased pinprick sensation on the posterior aspect of the right forearm, but no muscle weakness is present. Triceps reflex is normal. Which of the following is the most likely finding on the neck radiography of this patient?
A. Reversed lordotic curve
B. Bony spurs
C. Vertebral body osteoporosis
D. Osteolytic lesions
E. Compression fracture
65. A 66-year-old man comes to the physician's office complaining of progressive lower back pain. Over- the-counter ibuprofen has provided him with moderate relief. The back pain is associated with bilateral leg pain that is precipitated by walking. The pain improves upon lying down or sitting. He has no pain at night, and no problems with bowel and bladder function. He underwent coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) 6 years ago for a 3-vessel coronary artery disease. His medications include aspirin, enalapril, atenolol, and lovastatin. Physical examination shows normal strength, reflexes and sensation in his legs. A straight leg raise test fails to reproduce pain. His femoral, popliteal and pedal pulses are full bilaterally and he has no bruits. Plain films of the lumbosacral spine show degenerative changes of the vertebrae. Ankle brachial index measurement is within normal limits. Which of the following is most likely responsible for his current condition?
A. Atherosclerosis
B. Spinal canal narrowing
C. Bulging disc
D. Vertebral metastasis
E. Spinal cord compression
66. A 43-year-old Caucasian female has a long history of polyarthritis. She also complains of fatigue, low-grade fever, weakness and recent weight loss. Her current medications are methotrexate, naproxen and ranitidine. Physical examination reveals deformed hand joints and a soft, tender mass palpated in the right popliteal fossa. The latter finding is best explained by:
A. Subcutaneous abscess
B. Inflamed synovium
C. Lymphedema
D. Venous thrombosis
E. Bony growth
67. A 30-year-old Caucasian female patient is seen at the rheumatology clinic. She has a 4-year history of rheumatoid arthritis. Over the past year, she has noticed an improvement in her symptoms. Examination of her joints reveals less swelling and erythema than on the previous visit Laboratory studies show: CBC: Hb 10.8g/dL Ht 32% MCV 104 fl Platelet count 226,000/cmm Leukocyte count 7,500/cmm Neutrophils 65% Eosinophils 1% Lymphocytes 28% Monocytes 6% Serum: Serum Na 140 mEq/L Serum K 3.9 mEq/L Chloride 100 mEq/L Bicarbonate 18 mEq/L BUN 16 mg/dL Serum Creatinine 1.1 mg/dL Calcium 9.8 mg/dL Blood Glucose 98 mg/dL Which of the following medications is this patient most likely taking?
A Hydroxychloroquine
B. Prednisone
D. Azathioprine
E. Methotrexate
68. A 35-year-old female presents with a complaint of oral ulcers that are extremely painful. She had a similar presentation three months ago and the ulcers healed without any scarring. Her medical history includes a recent visit to the ophthalmologist with complaints of blurred vision and she is now being treated for anterior uveitis. She has also had recurrent painful ulcers in her genital area for which she has regular follow-up with her gynecologist. On examination, you notice many hyper-pigmented areas over her extremities and few painful, nodular lesions. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Sarcoidosis
B. Reiter's Syndrome
C. Herpes simplex infection
D. Behcet's syndrome
E. Systemic lupus erythematosus
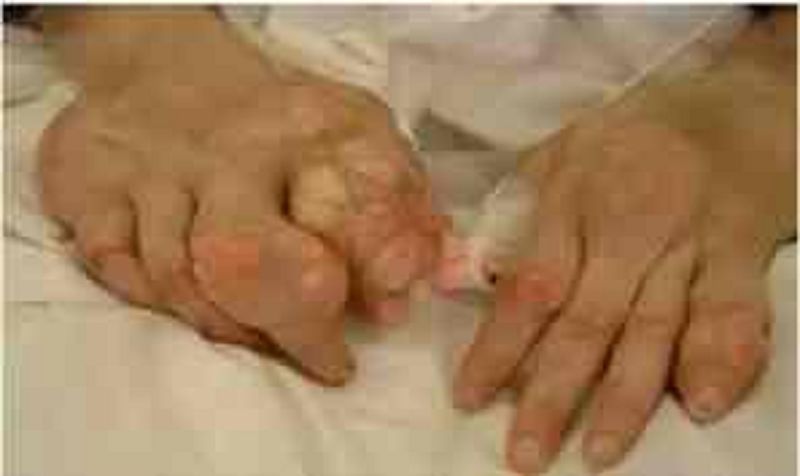
69. A 71-year-old female is brought to your clinic by her daughter with a complaint of severe pain in her fingers. Her daughter says, "Mom has horrible problems with her joints and she has never tried to get help". The patient adds that her fingers have been swollen and painful for a few weeks. She claims that she had a similar condition in her foot last year. She was given a pain pill, but it was ineffective. She takes a water pill for her blood pressure. What is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
A. Rheumatoid nodules
B. Gouty arthritis
C. Severe osteoarthritis
D. Bone tumor
E. Severe psoriatic arthritis
70. A 62-year-old Caucasian female complains of frequent headaches, fatigue and recent weight loss. Her shoulder muscles feel stiff in the morning. Her ESR is 85 mm/hr. Which of the following will be the most likely complication of this patient's condition?
A. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia
B. Hypothyroidism
C. Aortic aneurysm
D. Ulcerative colitis
E. Membranous glomerulonephritis
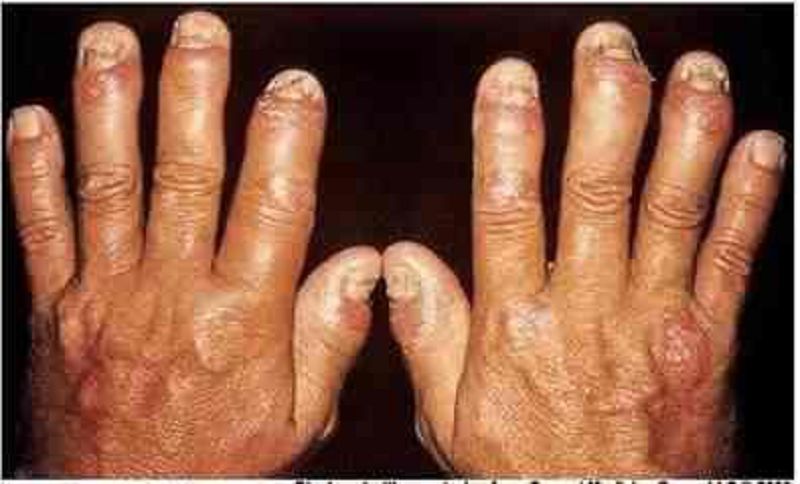
71. A 52-year-old male presents with a long history of joint pain. He describes pain and stiffness of the small joints of his hand that is worse in the morning and can last several hours. He also complains of occasional digit swelling. A picture of the patient's hands is shown on the slide below. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosi
A. Enteropathic arthritis
B. Rheumatoid arthritis
C. Psoriatic arthritis
D. Crystalline arthritis
E. Sarcoidosis
72. A 46-year-old woman suffering from systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) develops hematuria and proteinuria. She was diagnosed with SLE four years ago and has been treated with hydroxychloroquine. A renal biopsy is performed and shows diffuse proliferative glomerulonephritis. She is started on cyclophosphamide and prednisone and hydroxychloroquine is stopped. She continues these two medications for several weeks because of the low therapeutic response. This new therapeutic regimen puts her at an increased risk for which of the following conditions?
A. Cochlear dysfunction
B. Optic neuritis
C. Bladder carcinoma
D. Peripheral neuropathy
E. Digital vasospasm
73. A 30-year-old white male presented to your office with low back pain and stiffness. His pain is worse in the morning and is improved with activity. He has also been having bloody diarrhea for the past few days. On examination, he has painful erythematous nodules over his shins. Pain and stiffness is present in his lower back. Plain radiographs show sacroiliac joint inflammation. Stool cultures are negative. Laboratory studies show anemia and thrombocytosis. P-ANCA is positive in high titers. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his symptoms?
A. Reactive arthritis from diarrhea
B. Lnflammatory bowel disease
C. Infection with T ropheryma whippelii
D. Gluten-sensitive enteropathy
. Infection with Giardia Iamblia
74. A 42-year-old male presents to your office complaining of back pain that started two days ago after carrying heavy packages. He denies any weakness or sensory changes in his legs. His past medical history is insignificant. He is not taking any medications and denies drug abuse. His temperature is 36.7 C (98 F), blood pressure is 120/76 mmHg, pulse is 80/min, and respirations are 16/min. Physical examination reveals paravertebral tenderness. Lower extremity power is 5/5 and the deep tendon reflexes are 2+. Babinski's sign is negative. Straight-leg raising test is negative at 90 degrees. What is the most probable diagnosis in this patient?
A. Multiple myeloma
B. Ankylosing spondylitis
C. Compression fracture of the vertebrae
D. Lumbosacral strain
E. Herniated disk
75. A 30-year-old obese woman comes to the emergency department complaining of four days of progressive pain, swelling and redness of her right leg. She has no obvious trauma or insect bites. She does not use tobacco, alcohol or illicit drugs. Her temperature is 38.7C (103.OF), pulse is 106/min, and blood pressure is 130/80 mmHg. Her right calf is swollen, erythematous, and extremely tender and warm to the touch over a 6 x 3 cm region. There is a tender, palpable mass in her right groin. There is no overlying crepitus and no bullae are seen. The toe webs are fissured and macerated. Laboratory studies show: Complete blood count Hemoglobin 14.0 g/L Platelets 222,000/mm3 Leukocyte count 14,500/mm3 Neutrophils 86% Lymphocytes 14% Which of the following is the most likely cause of her current leg condition?
A. Celluliti
B. Arterial thrombosis
C. Deep venous thrombosis
D. Necrotizing fascitis
E. Ruptured Baker's cyst
76. A 40-year-old school teacher comes to the physician's office complaining of joint pain. Her symptoms began 10 days ago and consist of pain in the metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joints, proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joints, wrists, knees and ankles, bilaterally. She describes joint stiffness lasting 10 to 15 minutes after a prolonged rest. She denies fever, malaise, weight loss and skin rash. Her past medical history is insignificant. She does not take any medications. On examination, there is no evidence of swelling, redness or tenderness of the involved joints. The remainder of the physical examination is unremarkable. Which of the following is most likely elevated in this patient?
A. Rheumatoid factor
B. Anti-B 19 IgM antibody
C. Anti-dsDNA
D. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
E. Antinuclear antibodies
77. A 27-year-old African-American woman presents with several complaints. She has had pain and swelling of her hands and wrists for the past few days. She also complains of easy fatigability and frequent mouth ulcers. She has no significant past medical history and does not take any medications. Her temperature is 37.1°C (98.9.F), blood pressure is 140/90mmHg, and pulse is 76/min. Examination reveals swollen, tender metacarpophalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joints. There are superficial ulcers on her buccal mucosa. X-ray of hands and wrists shows no bony erosions. Laboratory studies show: Hemoglobin 11.0 g/L Platelets 90,000/mm3 Leukocyte count 4,500/mm3 Urinalysis shows 2+ protein and red blood cell casts. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her joint pains?
A. Systemic lupus erythematosus
B. Dermatomyositis
C. Sarcoidosis
D. Neuropathic joint disease
E. Systemic iron overload
78. A 63-year-old painter presents with pain in his right shoulder for the past few weeks. He experiences pain when he tries to reach for objects and he is unable to lift his arm above his head. He denies trauma to the shoulder, fevers, chills and weight loss. Vital signs are within normal limits. On exam, the physician raises the patient's arm while asking him to relax the shoulder. At 60 degrees, the patient begins to shrug his shoulder and complain of pain. In spite of the pain, his range of motion is normal. A lidocaine injection into the shoulder leads to a significant decrease in pain upon lifting the arm. Which of the following is most likely responsible for his current condition?
A. Rotator cuff tear
B. Adhesive capsulitis
C. Rotator cuff impingement
D. Crystal arthritis
E. Bacterial infection
79. A 22-year-old Caucasian female comes to your office complaining of difficulty swallowing. She says that solid food sticks in the middle of her chest, and that's why she prefers liquids. She has lost 10 pounds over the last 3 months. She also complains of recent severe heartburn that does not respond well to over-the-counter antacids. On review of systems, she denies cough, shortness of breath and palpitations. She has noticed occasional swelling and pain in her small finger joints. Her fingers turn blue upon cold exposure, and she always wears gloves to keep them warm. She does not smoke or drink alcohol. She denies illegal drug use. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A. CREST syndrome
B. Esophageal neoplasm
C. Achalasia
D. Diffuse esophageal spasm
E. Rheumatoid arthritis
80. A 28-year-old woman presents to her physician's office because of pain in her left knee joint. She reports having mild discomfort and pain in right wrist 4 days ago and left ankle pain two days ago. She denies any recent respiratory illness, diarrhea, or urinary symptoms. She has no vaginal discharge. She has no previous medical problems and does not take any medications. She drinks half a pint of vodka daily but denies intravenous drug abuse. She is single and sexually active. Her last menstrual period was one week ago. Her temperature is 38.5°C (101.3F), blood pressure is 120/80 mmHg, pulse is 98/min, and respirations are 15/min. Examination of the knee reveals warmth, tenderness, decreased range of motion, and an effusion. No skin lesions are present and her pelvic examination is unremarkable. Synovial fluid analysis shows a white blood cell count of 75,000/microl. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her symptoms?
A. Non-gonococcal septic arthritis
B. Gonococcal septic arthritis
C. Acute rheumatic fever
D. Acute HIV infection
E. Crystal induced arthritis
81. A 45-year-old tennis player comes to your office with a complaint of pain over the lateral side of the right elbow. He has been a professional tennis player for 15 years but has never had this kind of pain before. Range of motion at both elbows is normal. There is point tenderness over the lateral side of the distal end of right humerus. Pain is exacerbated by extension of wrist against resistance. The rest of the physical examination is normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
A. Lateral epicondylitis
B. Rotator cuff injury
C. Radial tunnel syndrome
D. Posterior interosseous nerve entrapment
E. Rupture of long head of biceps tendon
82. A 65-year-old man complains of periodic back pain radiating to his thigh and buttock. The pain is related to walking or climbing the stairs but is promptly relieved by leaning forward. He also has noticed tingling and numbness in both lower extremities. He has a history of hypertension and takes hydrochlorothiazide. He does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. His pulse is 76/min, respirations are 14/min, and blood pressure is 140/80 mmHg. Lumbar extension reproduces the pain and tingling, while lumbar flexion relieves the symptoms. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
A. Iliac artery atherosclerosis
B. Abdominal aortic aneurysm
C. Degenerative central canal stenosis
D. Lumbar disk herniation
E. Spina bifida occulta
83. A 51-year-old Caucasian female complains of low-back pain radiating to the buttocks. She also complains of persistent muscle pain that gets worse with exercise. Physical examination reveals normal muscle strength. Her joints are not swollen, but palpation over the outer upper quadrants of the buttocks and the medial aspect of the knees elicits tenderness. Her ESR is 12mm/hr. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Seronegative spondyloarthropathy
B. Polymyalgia rheumatica
C. Polymyositis
D. Rheumatoid arthritis
E. Fibromyalgia
84. A 35-year-old white female presents with pain and stiffness of her wrist and hand joints for the last several months. Her morning stiffness lasts for more than an hour. She also complains of redness and joint swelling. Her past medical history is significant only for a similar episode one year ago. That episode resolved with over the counter ibuprofen. Examination of her joints shows redness, warmth, swelling and tenderness of proximal interphalangeal joints, metacarpophalangeal joints and wrists. X- ray shows periarticular osteopenia and erosions of the proximal interphalangeal and metacarpophalangeal joints. She started taking indomethacin with good relief. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient?
A. Glucocorticoids
B. Methotrexate
C. Celecoxib
D. Azathioprine
E. Etanercept
85. A 27-year-old male presents to the physician's office because of pain on the medial side of the tibia just below the knee. The pain does not radiate and is continuous. He relates the onset of his pain to falling on the ground while playing football two weeks ago. He denies fever, malaise and weight loss. His past medical history is not significant. On examination, a well-defined area of tenderness is present on the upper tibia below the medial knee joint. There is no redness, warmth or swelling. His gait is normal. A valgus stress test has no effect on his pain. X-ray of the knee and tibia shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his current symptoms?
A. Anserine bursitis
B. Prepatellar bursitis
C. Medial collateral ligament strain
D. Medial compartment osteoarthritis
E. Patellofemoral syndrome
86. A 16-year-old boy presents with a seven-month history of intermittent right knee pain and swelling. He states that his discomfort first began after a baseball injury. This injury was associated with pain, swelling, and restriction of movement in his right knee. He has had three subsequent episodes of pain and swelling in his right knee, not precipitated by trauma. The last episode occurred three days ago. He denies history of fevers or chills. There is no history of recent travel, other than a camping trip with his friends to Long Island, New York a few months ago. On physical examination, he has a marked effusion of his right knee and is unable to fully flex or extend his leg. X-ray reveals no bony abnormalities. What is the most probable diagnosis?
A Rheumatoid arthritis
B. Septic arthritis
C. Lyme arthritis
D. Reactive arthritis
D. Reactive arthritis E. Osteomyelitic
87. A 75-year-old female comes to the emergency room with acute onset of severe back pain. The pain started while lifting a turkey from the freezer. She had no obvious trauma preceding the pain. She denies weakness or sensory loss in the legs. Her past medical history is significant for temporal arteritis diagnosed several months ago and has been taking prednisone. She does not smoke or consume alcohol. Her temperature is 36.7 C (98 F), blood pressure is 140/70 mmHg, pulse is 80/min, and respirations are 16/min. Physical examination reveals local tenderness of the lumbar spine area. Bilateral ankle reflex is absent. Knee reflex is 2+ in both legs. Babinski's sign is absent bilaterally. Muscle power is 5/5 in both legs. Bilateral straight-leg raising to 90 degrees does not increase the pain What is the most probable diagnosis in this patient?
A Multiple myeloma
B. Ankylosing spondylitis
C. Compression fracture of the vertebrae
D. Lumbosacral strain
E. Herniated disk
88. A 40-year-old woman complains of 7 weeks of pain and swelling in both wrists and knees. She has several months of fatigue. After a period of rest, resistance to movement is more striking. On examination, the metacarpophalangeal joints and wrists are warm and tender. There are no other joint abnormalities. There is no alopecia, photosensitivity, kidney disease, or rash. Which of the following is correct?
A. The clinical picture suggests early rheumatoid arthritis, and a rheumatoid factor should be obtained
B. The prodrome of lethargy suggests chronic fatigue syndrome.
C. Lack of systemic symptoms suggests osteoarthritis.
D. X-rays of the hand are likely to show joint space narrowing and erosion.
E. An aggressive search for occult malignancy is indicated.
89. A 70-year-old man complains of fever and pain in his left knee. Several days previously, he suffered an abrasion of his knee while working in his garage. The knee is red, warm, and swollen. An arthocentesis is performed, which shows 200,000 leukocytes/μL and a glucose of 20 mg/dL. No crystals are noted. Which of the following is the most important next step? 89. A 70-year-old man complains of fever and pain in his left knee. Several days previously, he suffered an abrasion of his knee while working in his garage. The knee is red, warm, and swollen. An arthocentesis is performed, which shows 200,000 leukocytes/μL and a glucose of 20 mg/dL. No crystals are noted. Which of the following is the most important next step?
A. Gram stain and culture of joint fluid
B. Urethral culture
C. Uric acid level
D. Antinuclear antibody
E. Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody
90. A 60-year-old woman complains of dry mouth and a gritty sensation in her eyes. She states it is sometimes difficult to speak for more than a few minutes. There is no history of diabetes mellitus or neurologic disease. The patient is on no medications. On examination, the buccal mucosa appears dry and the salivary glands are enlarged bilaterally. Which of the following is the best next step in evaluation?
A. Lip biopsy
B. Schirmer test and measurement of autoantibodies
C. IgG antibody to mumps virus
D. A therapeutic trial of prednisone for 1 month
E. Administration of a benzodiazepine
91. A 40-year-old man complains of exquisite pain and tenderness in the left ankle. There is no history of trauma. The patient is taking hydrochlorothiazide for hypertension. On examination, the ankle is very swollen and tender. There are no other physical examination abnormalities. Which of the following is the best next step in management?
A. Begin colchicine and broad-spectrum antibiotics
B. Perform arthrocentesis
C. Begin allopurinol if uric acid level is elevated
D. Obtain ankle x-ray to rule out fracture.
E. Apply a splint or removable cast.
92. A 48-year-old woman complains of joint pain and morning stiffness for 4 months. Examination reveals swelling of the wrists and MCPs as well as tenderness and joint effusion in both knees. The rheumatoid factor is positive, antibodies to cyclic citrullinated protein are present, and subcutaneous nodules are noted on the extensor surfaces of the forearm. Which of the following statements is correct?
A. Prednisone 60 mg per day should be started.
B. The patient has RA and should be evaluated for disease-modifying antirheumatic therapy
C. A nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug should be added to aspirin.
D. The patient’s prognosis is highly favorable.
E. The patient should receive a 3-month trial of full-dose nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agent before determining whether and/or what additional therapy is indicated
93. A 45-year-old woman with long-standing, well-controlled rheumatoid arthritis develops severe pain and swelling in the left elbow over 2 days. She is not sexually active. Arthrocentesis reveals cloudy fluid. Synovial fluid analysis reveals >100,000 cells/mL; 98% of these are PMNs. What is the most likely organism to cause this scenario?
A. Streptococcus pneumoniae
B. Neisseria gonorrhoeae
C. Escherichia coli
D. Staphylococcus aureus
E. Pseudomnonas aeruginosa
94. A 66-year-old man complains of a 1-year history of low-back and buttock pain that worsens with walking and is relieved by sitting or bending forward. He has hypertension and takes hydrochlorothiazide but has otherwise been healthy. There is no history of back trauma, fever, or weight loss. On examination, the patient has a slightly stooped posture, pain on lumbar extension, and has a slightly wide base gait. Pedal pulses are normal and there are no femoral bruits. Examination of peripheral joints and skin is normal. What is the most likely cause for this patient’s back and buttock pain?
A. Lumbar spinal stenosis
B. Herniated nucleus pulposus
C. Atherosclerotic peripheral vascular disease
D. Facet joint arthritis
E. Prostate cancer
95. A 60-year-old man complains of pain in both knees coming on gradually over the past 2 years. The pain is relieved by rest and worsened by movement. The patient is 5ft 9 in. Tall and weighs 210 lb. There is bony enlargement of the knees with mild warmth and small effusions. Crepitation is noted on motion of the knee joint bilaterally. There are no other findings except for bony enlargement at the distal interphalangeal joint. Which of the following is the best way to prevent disease progression?
A. Weight reduction
B. Calcium supplementation
C. Total knee replacement
D. Long-term nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) administration
E. Oral prednisone
96. A 22-year-old man develops the insidious onset of low-back pain improved with exercise and worsened by rest. There is no history of diarrhea, conjunctivitis, urethritis, rash, or nail changes. On examination, the patient has loss of mobility with respect to lumbar flexion and extension. He has a kyphotic posture. A plain film of the spine shows sclerosis of the sacroiliac joints. Calcification is noted in the anterior spinal ligament. Which of the following best characterizes this patient’s disease process?
A. He is most likely to have acute lumbosacral back strain and requires bed rest.
B. The patient has a spondyloarthropathy, most likely ankylosing spondylitis
C. The patient is likely to die from pulmonary fibrosis and extrathoracic restrictive lung disease
D. A rheumatoid factor is likely to be positive.
E. A colonoscopy is likely to show Crohn disease.
97. A 20-year-old woman has developed low-grade fever, a malar rash, and arthralgias of the hands over several months. High titers of anti-DNA antibodies are noted, and complement levels are low. The patient’s white blood cell count is 3000/µL, and platelet count is 90,000/µL. The patient is on no medications and has no signs of active infection. Which of the following statements is correct?
A. If glomerulonephritis, severe thrombocytopenia, or hemolytic anemia develops, high-dose glucocorticoid therapy would be indicated
B. Central nervous system symptoms will occur within 10 years.
C. The patient can be expected to develop Raynaud phenomenon when exposed to col
D. Joint deformities will likely occur
E. The disease process described is an absolute contraindication to pregnancy
98. A 45-year-old woman has pain in her fingers on exposure to cold, arthralgias, and difficulty swallowing solid food. What is the best diagnostic test?
A. Rheumatoid factor
B. Antinucleolar antibody
C. ECG
D. BUN and creatinine
E. Reproduction of symptoms and findings by immersion of hands in cold water
99. A 20-year-old man complains of arthritis and eye irritation. He has a history of burning on urination. On examination, there is a joint effusion of the right knee and a rash of the glans penis. Which of the following is correct?
A. Neisseria gonorrhoeae is likely to be cultured from the glans penis.
B. The patient is likely to be rheumatoid factor—positive.
C. An infectious process of the GI tract may precipitate this disease
D. An ANA is very likely to be positive.
E. CPK will be elevated.
100. Last week a 20-year-old college student developed acute wrist pain and swelling. This resolved in four days. Yesterday, he developed pain and swelling in his left knee. Two months ago he went on a backpacking trip in Rhode Island. A week or so later he developed an enlarging circular red spot that persisted for 2 weeks and then resolved. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Acute rheumatoid arthritis
B. Parvovirus infection
C. Psoriatic arthritis
D. Lyme disease
E. Inflammatory bowel disease
101. A 75-year-old man complains of headache. On one occasion he transiently lost vision in his right eye. He also complains of aching in the shoulders and neck. There are no focal neurologic findings. Carotid pulses are normal without bruits. Laboratory data show a mild anemia. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) is 85. Which of the following is the best approach to management?
A. Begin glucocorticoid therapy and arrange for temporal artery biopsy
B. Schedule temporal artery biopsy and begin corticosteroids based on biopsy results and clinical course.
C. Schedule carotid angiography
D. Follow ESR and consider further studies if it remains elevated.
E. Start aspirin and defer any invasive studies unless further symptoms develop.
102. A 55-year-old man with psoriasis has been troubled by long-standing destructive arthritis involving the hands, wrists, shoulders, knees, and ankles. Hand films demonstrate pencil-in-cup deformities. He has been treated with naproxen 500 mg bid, sulfasalazine 1 g bid, prednisone 5 mg qd, and methotrexate 17.5 mg once a week without substantive improvement. Which of the following treatments is most likely to provide long-term benefit?
A. Cyclophosphamide
B. Addition of folic acid supplementation
C. Oral cyclosporine
D. Tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibitor
E. Higher-dose steroids in the range of 20 mg of prednisone per day
103. A 65-year-old man develops the onset of severe knee pain over 24 hours. The knee is red, swollen, and tender. He has a history of diabetes mellitus and cardiomyopathy. An x-ray of the knee shows linear calcification. Definitive diagnosis is best made by which of the following?
A. Serum uric acid
B. Serum calcium
C. Arthrocentesis and identification of positively birefringent rhomboid crystals
D. Rheumatoid factor
E. ANA
104. A 35-year-old woman complains of aching all over. She says she sleeps poorly and all her muscles and joints hurt. Her symptoms have progressed over several years. She reports she is desperate because pain and weakness often cause her to drop things. Physical examination shows multiple points of tenderness over the neck, shoulders, elbows, and wrists. There is no joint swelling or deformity. A complete blood count and erythrocyte sedimentation rate are normal. Rheumatoid factor is negative. Which of the following is the best therapeutic option in this patient?
A. Graded aerobic exercise
B. Prednisone
B. Prednisone
C. Weekly methotrexate
D. Hydroxychloroquine
E. A nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug
105. A 38-year-old man has pain and stiffness of his right knee. This began 2-weeks ago after he fell while skiing. On two occasions he had the sense that his knee was locked in a semiflexed position for a few seconds. He has noted a popping sensation when he bends his knee. On examination there is tenderness over the medial joint line of the knee. Marked flexion and extension of the knee are painful. The Lachman test (anterior displacement of the lower leg with the knee at 20°of flexion) and the anterior drawer test are negative. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Medial meniscus tear
b. Osteoarthritis
C. Anterior cruciate ligament tear
D. Chondromalacia patella
E. Lumbosacral radiculopathy
106. Over the last six weeks a 45-year-old nurse has developed progressive difficulty getting out of chairs and climbing stairs. She can no longer get in and out of the bathtub. She has no muscle pain and takes no regular medications. She does not use alcohol and does not smoke cigarettes. On examination she has a purplish rash that involves both eyelids (see figure). There is weakness of the proximal leg muscles. What is the best next diagnostic test?
A. Vitamin B12 level
B. Chest x-ray
C. HLAB27
D. MRI scan of the lumbar spine
E. CPK
107. A 63-year-old painter complains of severe right shoulder pain. The pain is located posteriorly over the scapula. These symptoms began after he fell from a ladder 2 weeks ago. The pain is especially bad at night and makes it difficult for him to sleep. In addition, he has had some pain in the right upper arm. Treatment with acetaminophen and ibuprofen has been unsuccessful in controlling his pain. On examination the patient appears uncomfortable. The right shoulder has full range of motion. Movement of the shoulder is not painful. There is no tenderness to palpation of the scapula. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Subdeltoid bursitis
B. Rotator cuff tendonitis
C. Adhesive capsulitis
D. Osteoarthritis
E. Cervical radiculopathy
108. A 50-year-old woman with rheumatoid arthritis has been treated with meloxicam (Mobic). You add hydroxychloroquine. Six weeks later her arthritis is mildly improved. The same joints are still involved but she now reports only 1-hour morning stiffness. She has, however, developed epigastric burning and melena for the past 3 days. Stool is strongly positive for occult blood. Which of the following is the most likely cause for the melena in this case?
A. Emotional stress over her illness resulting in acid peptic disease
B. Hydroxychloroquine-induced acid peptic disease
C. Gastric lymphoma associated with autoimmune disease
D. NSAID gastropathy
E. Meckel diverticulum
109. A 55-year-old woman with long-standing rheumatoid arthritis is on prednisone 5 mg daily and etanercept (Enbrel) 50 mg subcutaneously once a week. Her arthritis is well-controlled. However, she complains of a 2-day history of headaches, chills, and spiking fevers to 39.4C (103F). You suspect which of the following?
A. An allergic febrile reaction to etanercept
B. Fever related to her underlying autoimmune disease
C. A serious infection
D. A viral syndrome
E. An occult malignancy
110. A 32-year-old Japanese woman has a long history of recurrent aphthous oral ulcers. In the last 2 months she has had recurrent genital ulcers. She now presents with a red painful eye that was diagnosed as anterior uveitis. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Herpes simplex
B. HIV infection
C. Behçet disease
D. Diabetes mellitus
E. Systemic lupus erythematosus
111. A 53-year-old man presents with arthritis and bloody nasal discharge. Urinalysis reveals 4+proteinuria, RBCs, and RBC casts. ANCA is positive in a cytoplasmic pattern. Antiproteinase 3 (PR3) antibodies are present, but antimyeloperoxidase (MPO) antibodies are absent. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Behçet syndrome
B. Sarcoidosis
C. Wegener granulomatosis
D. Henoch-Schönlein purpurqa
E. Classic polyarteritis nodosa
112. A 50-year-old white woman presents with aching and stiffness in the trunk, hip, and shoulders. There is widespread muscle pain after mild exertion. Symptoms are worse in the morning and improve during the day. They are also worsened by stress. The patient is always tired and exhausted. She has trouble sleeping at night. On examination, joints are normal. ESR is normal, and Lyme antibody and HIV test are negative. A diagnosis is best made by which of the following?
A. Trial of glucocorticoid
B. Muscle biopsy
C. Demonstration of 11 tender points
D. Psychiatric evaluation
E. Trial of an NSAID
113. A 35-year-old right-handed construction worker presents with complaints of nocturnal numbness and pain involving the right hand. Symptoms wake him and are then relieved by shaking his hand. There is some atrophy of the thenar eminence. Tinel sign is positive. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Carpal tunnel syndrome
B. De Quervain tenosynovitis
C. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
D. Rheumatoid arthritis of the wrist joint
E. Guillain-Barré syndrome
{"name":"USLME_RHUMATOLOGY_EXAM_DES", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Test your knowledge on rheumatology with our comprehensive quiz tailored for USLME preparation. This quiz covers various topics related to rheumatology, ensuring that you are well-prepared for your exams.Key Features:Multiple choice questionsDiverse clinical scenariosInstant feedback on your answersIdeal for medical students and professionals","img":"https:/images/course3.png"}
More Quizzes
Emergency USMLE 3 (216-300)
24120
USMLE_Diagnosis VI
1005089
UTME Mathematics (Practice test 15) (www.tklesson.com)
50250
Digital Sales October
4227
10th Grade Geometry - Free Practice Questions
201017504
Which Lilo & Stitch Character Are You? Free
201022260
Big Bang Practice - Evidence and the Universe's Origin
201021088
The Kinks Member - Which Bandmate Are You?
201021985
Guess the Baby Name - Play Free Online
201019960
Hard DNA & Genetics Trivia for College Students - Free
201018888
Cartoon Characters - How Many Can You Name?
201026207
Maryland GNA Exam Practice Test - Free Online Prep
201023141