Bio 60 Exam 2

Genetics and Cell Biology Quiz
Test your knowledge on genetics and cell biology with our comprehensive quiz! This quiz covers a range of topics, including inheritance patterns, chromosomal abnormalities, and cellular processes.
Prepare for an engaging challenge with:
- 50 thought-provoking questions
- Diverse question formats
- Timely feedback on your answers
1. A man and woman are both of normal pigmentation, but both have one parent who is albino (without melanin pigmentation). Albinism is an autosomal (not sex-linked) recessive trait. What is the probability that their first child will be an albino?
0
1/8
1/2
1/4
1
2. A cell that has 2n + 1 chromosomes is
trisomic
monosomic
Triploid
polyploid
euploid
3. A pedigree analysis for a given disorder's occurrence in a family shows that, although both parents of an affected child are normal, each of the parents has had affected relatives with the same condition. The disorder is then which of the following?
Recessive
Dominant
Incompletely Dominant
Maternally inherited
A new mutation
4. An individual heterozygous for cystic fibrosis _______.
Is a carrier of cystic fibrosis
Cannot reproduce
Has cystic fibrosis
Cannot have children with cystic fibrosis
None of the above
5. A couple has a child with Down syndrome when the mother is 39 years old at the time of delivery. Which is the most probable cause?
The woman inherited this tendency from her parents
One member of the couple carried a translocation.
One member of the couple underwent nondisjunction in somatic cell production
One member of the couple underwent nondisjunction in gamete production
Both parents underwent nondisjunction in gamete production
6. Which of the following represents the Klinefelter syndrome in man?
XXY
XYY
XXX
XY
XX
7. Duchene muscular dystrophy is a human disorder that causes gradual deterioration of the muscles. Only boys are affected, and they are always born to phenotypically normal parents. Due to the severity of the disease, the boys die in their teens. Is this disorder likely to be caused by a dominant or recessive allele? Is its inheritance sex-linked or autosomal?
Dominant, sex-linked
recessive, autosomal
Recessive, sex-linked
incomplete dominant, sex-linked
Y-linked
8. Which of the following is true of a species that has a chromosome number of 2n = 32?
The species is diploid with 64 chromosomes per cell
Each cell has 16 homologous pairs
During the S phase of the cell cycle there will be 64 separate chromosomes
A gamete from this species has 8 chromosomes
The species has 32 sets of chromosomes per cell
9. How is plant cell cytokinesis different from animal cell cytokinesis?
The cleavage furrow in animal cells is composed of protein contractile filaments; the contractile filaments found in plant cells are structures composed of carbohydrates.
Plant cells have cell plate; animal cells form a cleavage furrow.
The structural carbohydrates of the plant cells separate the two cells, whereas in animal cells, a cell membrane separates the two daughter cells.
Animal cells have centrosomes that are involved in this process, but plant cells have microtubule-organizing centers that are not detectable during most of the cell cycle.
Plant cells form a cleavage furrow; animal cells form cell plate.
10. Sickle-cell anemia represents the most common genetic disorder among African Americans that is manifested as
Homozygous dominant
Homozygous recessive
Heterozygous condition
interaction between two genes
Hemizygous condition
11. Nerve cells lose their ability to undergo mitosis. Instead, they are permanently stuck in _____.
G0
G2
S of interphase
Metaphase
Prophase
12. A man has six fingers on each hand and six toes on each foot. His wife and their daughter have the normal number of digits. Extra digits is a dominant trait. What fraction of this couple's children would be expected to have extra digits?
1/2
1/4
¾
None
All
13. Prior to mitosis, each chromosome of a eukaryotic cell consists of a pair of identical structures called
Chromatin.
Sister chromosomes.
DNA transcripts.
Sister chromatids
Kinetochores
14. Which one of the following is false?
The genetic makeup of an organism constitutes its genotype.
An organism with two different alleles for a single trait is said to be heterozygous.
Alleles are alternate forms of a gene.
An allele that is fully expressed is referred to as recessive.
Chromosomes determine sex in many species.
15. Interphase is the part of the cell cycle when
A cell ceases to function
A germ cell forms its spindle apparatus
A cell grows and duplicates DNA
Mitosis proceeds
Chromosomes separate into chromatids
16. What it the total number of chromosomes you would expect to find in the karyotype of a female with Turner syndrome?
23
47
45
22
46
17. The frequency of crossing over between any two linked genes will be which of the following?
Higher if they are recessive
Proportional to the distance between them
Dependent on how many alleles there are in a population
Determined by their relative dominance
The same as if they were not linked
18. A particular cell has half as much DNA as some other cells in a mitotically active tissue. The cell in question in most likely in
G1
G2
Prophase
Metaphase
Anaphase
19. You have in your possession a microscope slide with meiotic cells on it and a light microscope. What would you look for if you wanted to identify metaphase I cells on the slide?
A visible nuclear envelope.
Tetrads lined up at the center of the cell.
Separated sister chromatids at each pole of the cell.
A cleavage furrows.
Cytokinesis.
20. If a female of this species has one chromosome 12 with a blue allele of a gene and another chromosome 12 with an orange allele, she will produce which of the following egg types?
Only blue gene eggs.
Only orange gene eggs.
3/4 blue and 1/4 orange gene eggs.
1/2 blue and 1/2 orange gene eggs.
An undetermined frequency of blue and orange gene eggs.
21. In eukaryotic cells, chromosomes are composed of _____.
DNA and RNA
DNA only
DNA and proteins
DNA and phospholipids
DNA and carbohydrates
22. The observable traits of an organism are its__________
Phenotype
Pedigree
Genotype
Population
Punnett square
23. One possible result of chromosomal breakage is for a fragment to join a nonhomologous chromosome. What is this alteration called?
Deletion
Translocation
Inversion
Duplication
Disjunction
24. Cycle of life for humans requires
Meiosis
Gametes
Fertilization
Mitosis
All of the above
25. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency (G6PD) is inherited as a recessive allele of an X-linked gene in humans. A woman whose father suffered from G6PD marries a normal man. (a) What proportion of their sons is expected to be G6PD? (b) If the husband was not normal but was G6PD deficient, would you change your answer in part (a)?
(a) 100%; (b) no
(a) 1/2; (b) yes
(a) 2/3; (b) no
(a) 1/2; (b) no
(a) zero; (b) no
26. Family pedigree shows
Inheritance of a given trait in a family.
Blood relationship of family members.
Possible future generations.
Affected individuals in a family
All of the above.
27. What is the genotype of an individual who is heterozygous for dimples?
DD
Dd
Dd
Dimples
None of the above
28. Asexual reproduction takes place by which of the following processes?
Meiosis
Fertilization
Chromosome exchange between organisms of the same species
Mitosis
All
29. Sister chromatids are separated from each other
The statement is true for mitosis only.
The statement is true for meiosis I only.
The statement is true for meiosis II only.
The statement is true for mitosis and meiosis II.
The statement is true for mitosis and meiosis I.
30. The mitotic spindle is a microtubular structure that is involved in _____.
Splitting of the cell (cytokinesis) following mitosis
Triggering the compaction and condensation of chromosomes
Dissolving the nuclear membrane
Separation of sister chromatids
Disintegration of nuclear envelope
31. Metaphase occurs prior to the splitting of centromeres. It is characterized by _____.
Aligning of chromosomes on the equator
Splitting of the centromeres
Cytokinesis
Separation of sister chromatids
Crossing-over
32. Which of the following events occurs during telophase?
Chromosomes align on the midline of the cell
The cleavage furrow forms
Tetrads form
Centromeres divide
Mitotic spindle forms
33. In birds, sex is determined by a ZW chromosome scheme that is much like the typical XY scheme seen in humans and many other organisms, except that the system is reversed: Males are ZZ (similar to XX in humans) and females are ZW (similar to XY in humans). A lethal recessive allele that causes death of the embryo occurs on the Z chromosome in pigeons. What would be the sex ratio in the offspring of a cross between a male heterozygous for the lethal allele and a normal female?
1:1 male to female
4:1 male to female
3:1 male to female
1:2 male to female
2:1 male to female
34. Siblings of the same biological parents can look very much alike, but they are not identical, because of
Crossing-over between homologous chromosomes
Independent assortment of different homologous pairs
Random fertilization
All of the above
A and b
35. When the coding sequence ONEREDEYEFLYEATONEREDBUG, changes to ONEREDEEYEFLYEATONEREDBUG, this mutation represents
Base-pair substitution.
Insertion.
Base-pair substitution with missense.
Insertion with frameshift.
Inversion with frameshift.
36. A homozygous tomato plant with red fruit and yellow flowers was crossed with a homozygous tomato plant with golden fruit and white flowers. The F1 all had red fruit and yellow flowers. The following phenotypes were obtained in the F2: Red fruit and yellow flowers—41 Red fruit and white flowers—7 Golden fruit and yellow flowers—8 Golden fruit and white flowers—44 How many map units separate these genes?
15
85
48
52
51
37. Scientists isolate cells in various phases of the cell cycle. They isolate a group of cells that have 1 1/2 times more DNA than G1 phase cells. What is the most likely part of the cell cycle from which these cells were isolated?
Between the G1 and S phases in the cell cycle
In the G2 phase of the cell cycle
In the M phase of the cell cycle
In the S phase of the cell cycle
In cytokinesis
38. In a diploid cell with 5 chromosome pairs (2n = 10), how many sister chromatids will be found in a nucleus at prophase of mitosis?
5
10
20
40
80
39. How do cells at the completion of meiosis compare with cells that are in prophase of meiosis I?
The cells have half the number of chromosomes and half the amount of DNA.
The cells have the same number of chromosomes and half the amount of DNA.
The cells have half the number of chromosomes and one-fourth the amount of DNA.
The cells have half the amount of cytoplasm and twice the amount of DNA.
The cells have half the amount of cytoplasm and the same amount of DNA.
40. The bulldog ant has a diploid number of two chromosomes. Therefore, following meiosis, each daughter cell will have a single chromosome. In addition to mutations, how might genetic diversity be generated in this species?
Crossing over only
Independent assortment only
Crossing over and random fertilization
Nothing else
Random fertilization only
41. A sexually reproducing animal has two unlinked genes, one for head shape (H) and one for tail length (T). Its genotype is HhTt. Which of the following genotypes is possible in a gamete from this organism?
Hh
HhTt
T
HT
Htt
42. Mendel crossed yellow-seeded and green-seeded pea plants and then allowed the offspring to self-pollinate to produce an F2 generation. The results were as follows: 6,022 yellow and 2,001 green (8,023 total). Which of the following statements correctly describes the relationship of the allele for green seeds to the allele for yellow seeds?
The green allele is dominant to the yellow allele.
The two alleles exhibit incomplete dominance.
The green allele is recessive to the yellow allele.
The two alleles are codominant.
The two alleles are recessive
43. Which of the following inheritance patterns describes the ability of a single allele to have multiple phenotypic effects?
Incomplete dominance
Multiple alleles
Pleiotropy
Epistasis
Codominance
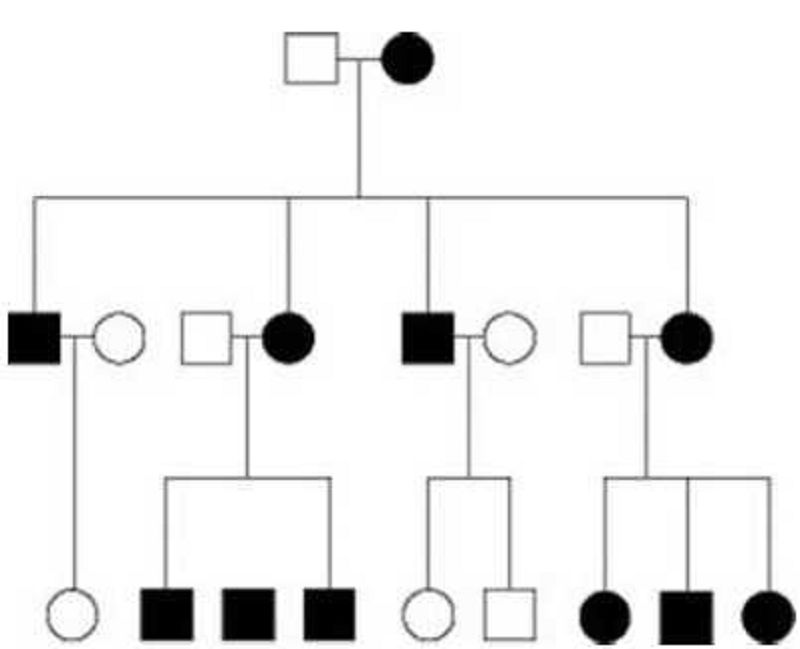
44. Use the following figure to answer the question. The pedigree in the figure shows the transmission of a trait in a particular family. Based on this pattern of transmission, the trait is most likely ________.
Mitochondrial
Sex-linked dominant
Sex-linked recessive
Autosomal dominant
Autosomal recessive
45. The most commonly occurring mutation in people with cystic fibrosis is a deletion of a single codon. What is the result of this type of mutation?
A base-pair substitution
A frameshift mutation
A polypeptide missing an amino acid
A nonsense mutation
Translocation
46. A single base substitution mutation is likely to have a less deleterious effect when the base change exhibits which of the following results?
A stop codon
A codon that specifies the same amino acid as the original codon
An amino acid substitution that alters the tertiary structure of the protein
An amino acid substitution at the active site of an enzyme
An exon that is occasionally removed
47. When Thomas Hunt Morgan crossed his red-eyed F1 generation flies to each other, the F2 generation included both red- and white-eyed flies. Remarkably, all the white-eyed flies were male. What was the explanation for this result?
The gene involved is located on the Y chromosome.
The gene involved is located on the X chromosome.
The gene involved is located on an autosome, but only in males.
Other male-specific factors influence eye color in flies.
The gene involved is located on the X chromosome but it is silent in female flies.
48. Gene S controls the sharpness of spines in a type of cactus. Cacti with the dominant allele, S, have sharp spines, whereas homozygous recessive ss cacti have dull spines. At the same time, a second gene, N, determines whether or not cacti have spines. Homozygous recessive nn cacti have no spines at all. The relationship between genes S and N is an example of which of the following inheritance patterns?
Incomplete dominance
Epistasis
Pleiotropy
Codominance
Environmental effect
49. Sex determination in mammals is due to the SRY gene found on the Y chromosome. Which of the following situations could allow a person with an XX karyotype to develop a male phenotype?
The loss of the SRY gene from an autosome
Translocation of SRY to an X chromosome
The presence of an extra autosomal chromosome
The presence of one normal and one shortened (deleted) X
The presence of one normal and one longer (duplicated) X
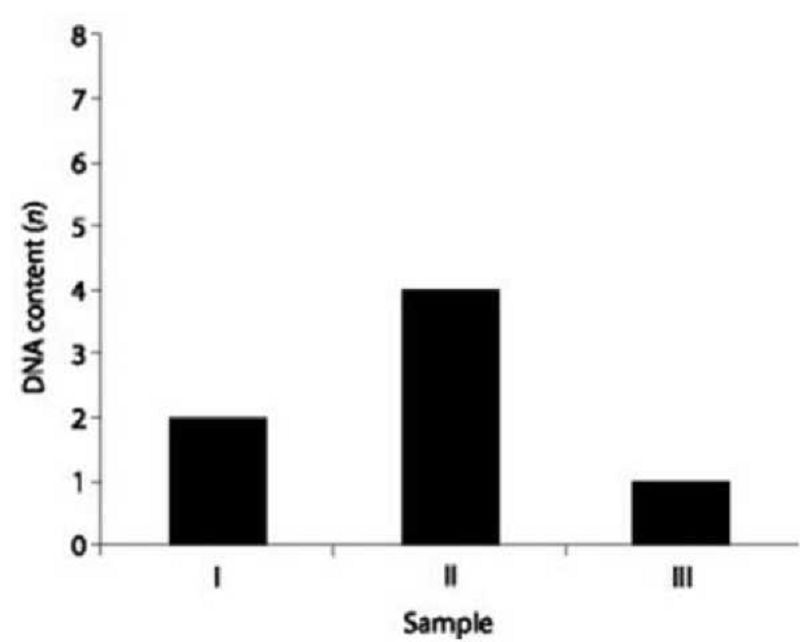
50. DNA was isolated from three different cell types of the same organism, the relative DNA content foreach type was determined, and the results were plotted on the graph shown in the figure below. Refer to the graph to answer the following questions. Which sample of DNA might be from a cell that stopped the process of cell division in G0 phase of the cell cycle prior to meiosis?
I
II
III
either I or II
none
{"name":"Bio 60 Exam 2", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Test your knowledge on genetics and cell biology with our comprehensive quiz! This quiz covers a range of topics, including inheritance patterns, chromosomal abnormalities, and cellular processes.Prepare for an engaging challenge with:50 thought-provoking questionsDiverse question formatsTimely feedback on your answers","img":"https:/images/course3.png"}
More Quizzes
DNA (because it's cool)
1367
SMART INSTITUTE NMDCAT BIOLOGY-1 TS
3015130
All about Marriott Marquis
8462
The Plants vs Zombies Garden Warfare 1/2 Quiz!
1580
First Aid Exam Questions & Answers - Free Practice
201018112
Once Upon a Time Season 1 - Test Your Knowledge
201018335
Am I Boy Crazy? - Hot Crazy Test (Free)
201016977
Racing Trivia - 201+ NASCAR & F1 Questions
201015342
Patriotic Trivia - Test Your U.S. History Knowledge
201021068
Big City Greens - Which Character Are You?
201016856
BOP Eligibility: Is a Six-Story Office Building Eligible?
201017038
Do I Have a Demon Attached to Me? Free Possession
201019052