BIOL 230 Lab Exam 2 Review ("HOLY COW" Edition)

BIOL 230 Lab Exam 2 Review Quiz
Prepare yourself for the BIOL 230 Lab Exam with our comprehensive review quiz designed specifically for biology students. This engaging quiz will test your knowledge of bacterial structures, motility, and essential staining techniques.
Key Features:
- 50 carefully crafted questions.
- In-depth coverage of major concepts.
- Instant feedback on your responses.
The _________ anchors the flagellum to the cell wall and cytoplasmic membrane and acts as a rotary molecular motor.
Filament
Hook
Basal Body
Golgi Body
Taxis is a motile response to an environmental stimulus and functions to keep bacteria in an optimum environment.
True
False
Direct observation of motility using special-purpose microscopes allow for the observation of live bacteria. The two 2 types are what?
Phase contrast microscopy
Dark-field microscopy
Electron microscopy
Prism microscopy
In order to see Flagella, special dyes are used that build up as layers of precipitate along the length of the flagella . This is known as Flagella staining.
True
False
Motility test medium may be used to detect motility. The agar concentration (0.3%) is sufficient to form a soft gel without hindering motility.
True
False
When motile organisms are stabbed into the medium, growth only occurs along the line of inoculation.
True
False
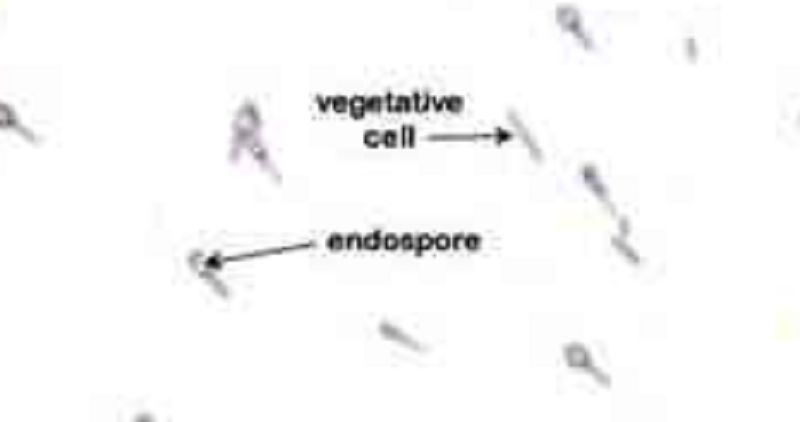
Note the endospore within the rod(Clostridium tetani) gives the bacterium a "tennis racquet" shape (arrows)
Note the endospore within the rod(Clostridium tetani) gives the bacterium a "tennis racquet" shape (arrows)
A dye or stain used to differentiate one component or cellular structure from another is what?
Differential stain
Occlusive stain
Phase stain
Gram staining is called a differential stain since it differentiates between gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria.
True
False
Describe a gram-negative cell wall.
Stain Purple
10-20% of the cell wall is peptidoglycan
Outer membrane
Has lipid A
60-90% of the cell wall is peptidoglycan
State the 4 reagents used to perform a gram stain
Guaiacol
Crystal violet
Peroxide
Iodine
Acetone
Safranin
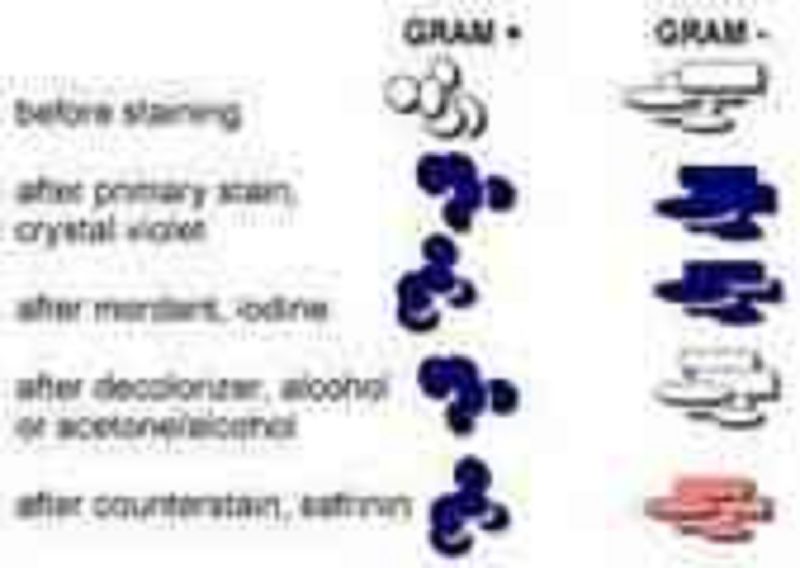
The color of a gram-positive and a gram-negative bacterium at each step in the process.
The color of a gram-positive and a gram-negative bacterium at each step in the process.
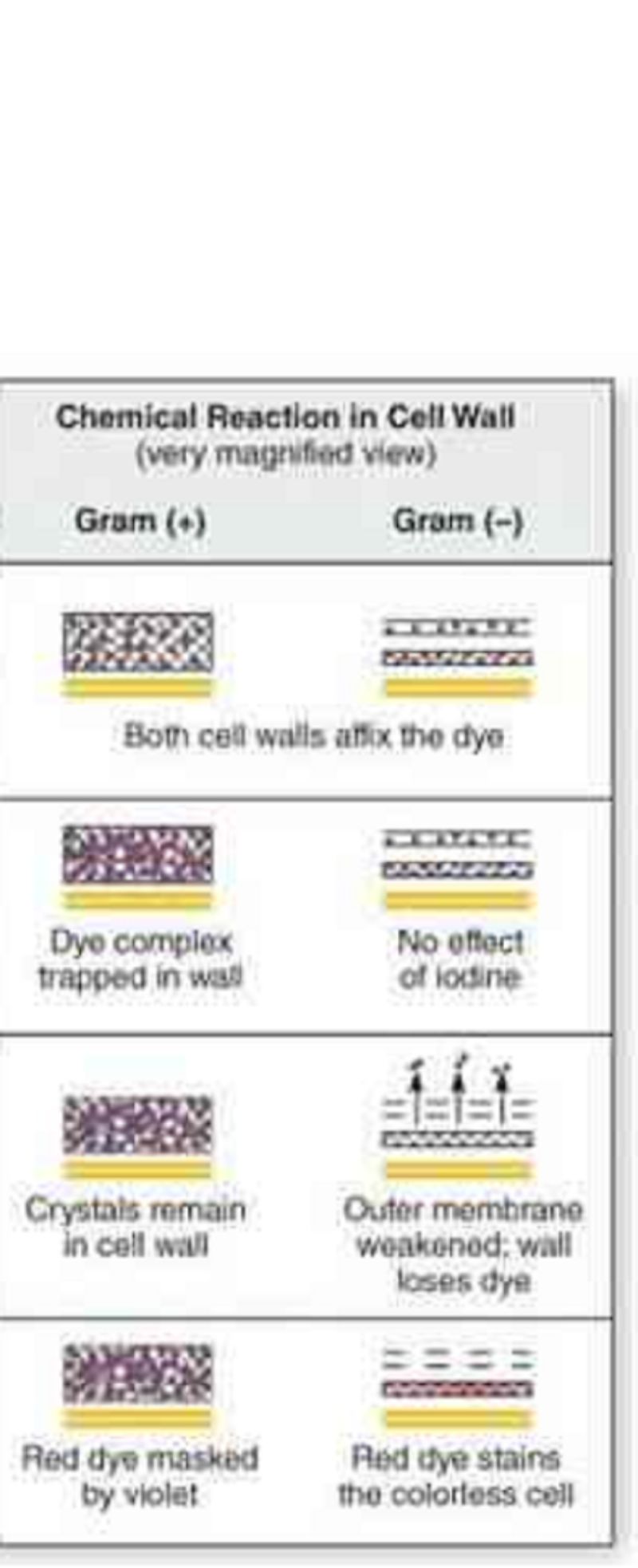
The theory as to why gram-positive bacteria retain the crystal violet-iodine complex while gram-negative bacteria become decolorized.
The theory as to why gram-positive bacteria retain the crystal violet-iodine complex while gram-negative bacteria become decolorized.
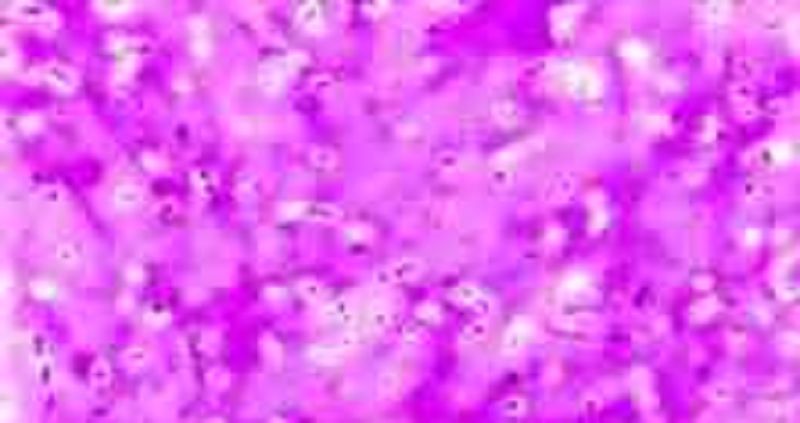
Capsules help many pathogenic and normal flora bacteria to initially resist phagocytosis by the host's phagocytic cells. In soil and water, capsules help prevent bacteria from being engulfed by protozoans. Capsules also help many bacteria to adhere to surfaces and thus resist flushing. It also enables many bacteria to form biofilms. Enterobacter aerogenes; Note the colorless capsules surrounding purple bacilli.
Capsules help many pathogenic and normal flora bacteria to initially resist phagocytosis by the host's phagocytic cells. In soil and water, capsules help prevent bacteria from being engulfed by protozoans. Capsules also help many bacteria to adhere to surfaces and thus resist flushing. It also enables many bacteria to form biofilms. Enterobacter aerogenes; Note the colorless capsules surrounding purple bacilli.
_____________ are secreted by bacteria into the surrounding environment in order to break down larger nutrient molecules so they may enter the bacterium.
Endoenzyme
Exoenzyme
_______________ are located within the bacterium and function to further break down nutrients that come into the cell to yield energy for driving various cellular functions or to form building blocks for the synthesis of cellular components .
Exoenzymes
Endoenzymes
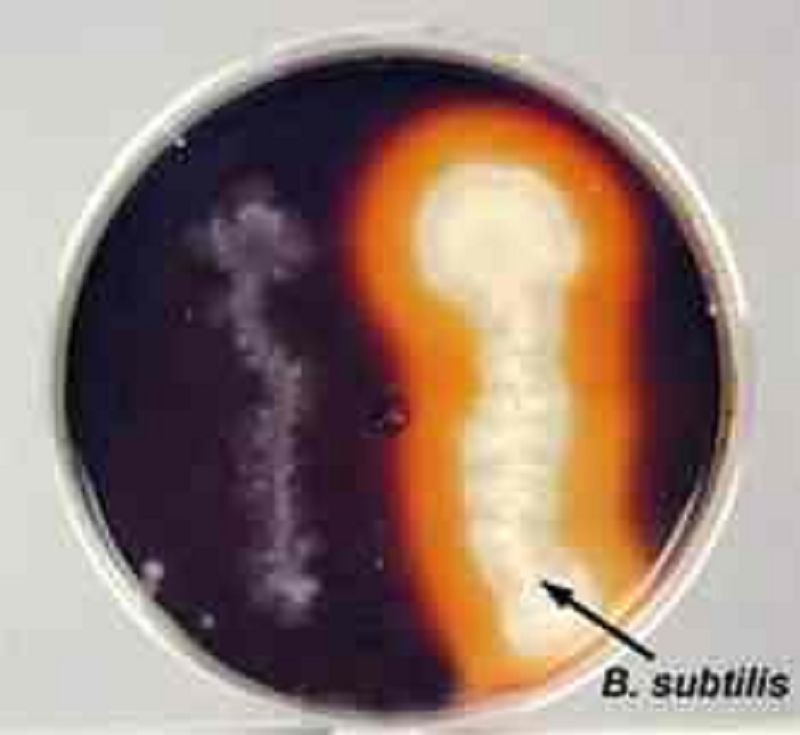
Starch Hydrolysis by Bacillus subtilis on Starch Agar. The clear zone around the growth of Bacillus subtilis no longer contains starch to react with the iodine. The starch was hydrolized by a diastase produced by the bacterium.
Starch Hydrolysis by Bacillus subtilis on Starch Agar. The clear zone around the growth of Bacillus subtilis no longer contains starch to react with the iodine. The starch was hydrolized by a diastase produced by the bacterium.
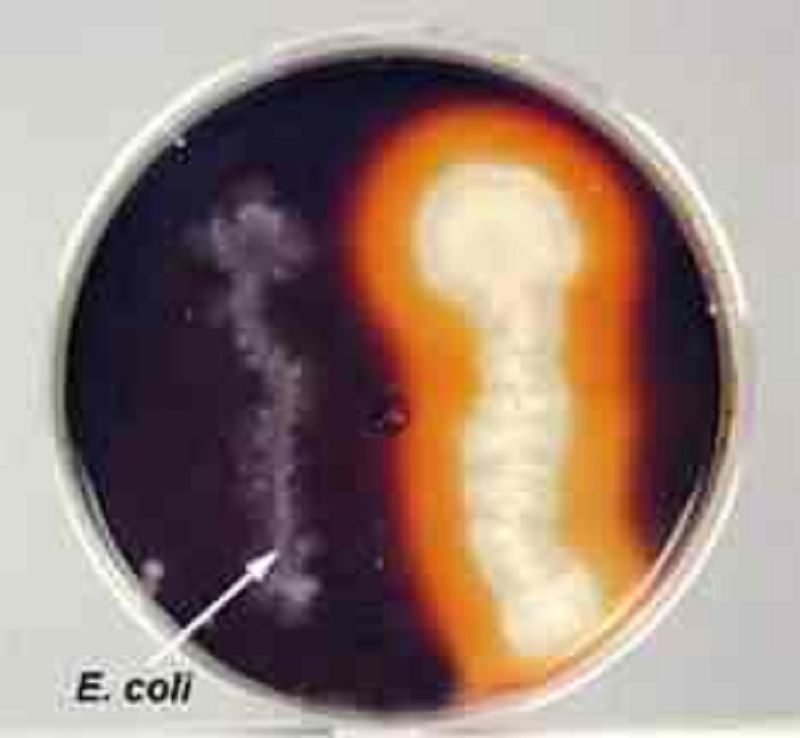
No Starch Hydrolysis by Escherichia coli on Starch Agar. The starch was not hydrolized by the Escherichia coli on the left. The starch reacts with the iodine producing the dark color.
No Starch Hydrolysis by Escherichia coli on Starch Agar. The starch was not hydrolized by the Escherichia coli on the left. The starch reacts with the iodine producing the dark color.
The hydrolysis of protein is termed protease and the enzyme involved is called a proteolysis. In lab 8 bacteria hydrolyze the protein casein.
True
False
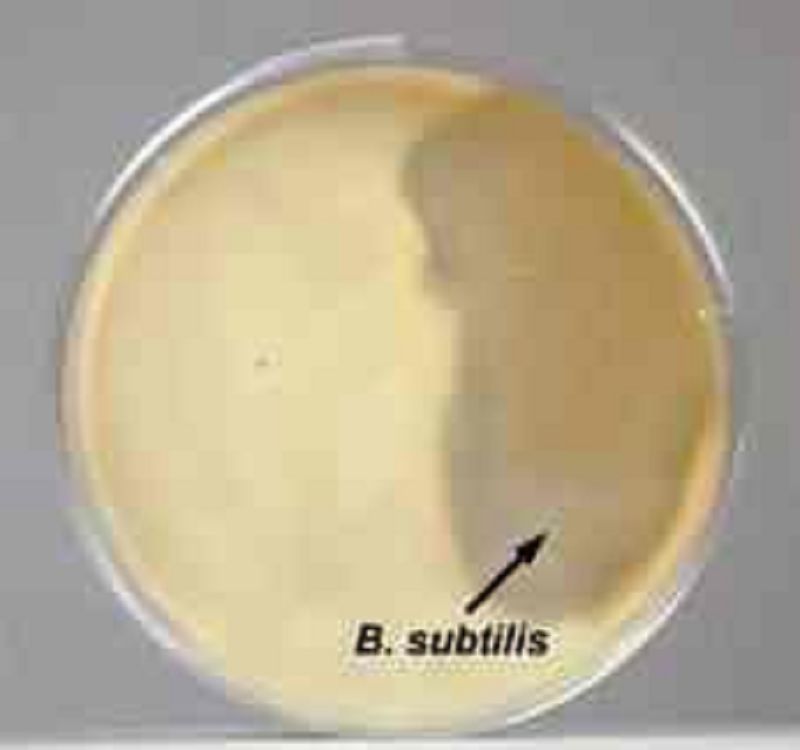
The clear zone around the growth of the Bacillus subtilis on the right no longer contains casein. The casein was hydrolized by a protease produced by the bacterium.
The clear zone around the growth of the Bacillus subtilis on the right no longer contains casein. The casein was hydrolized by a protease produced by the bacterium.
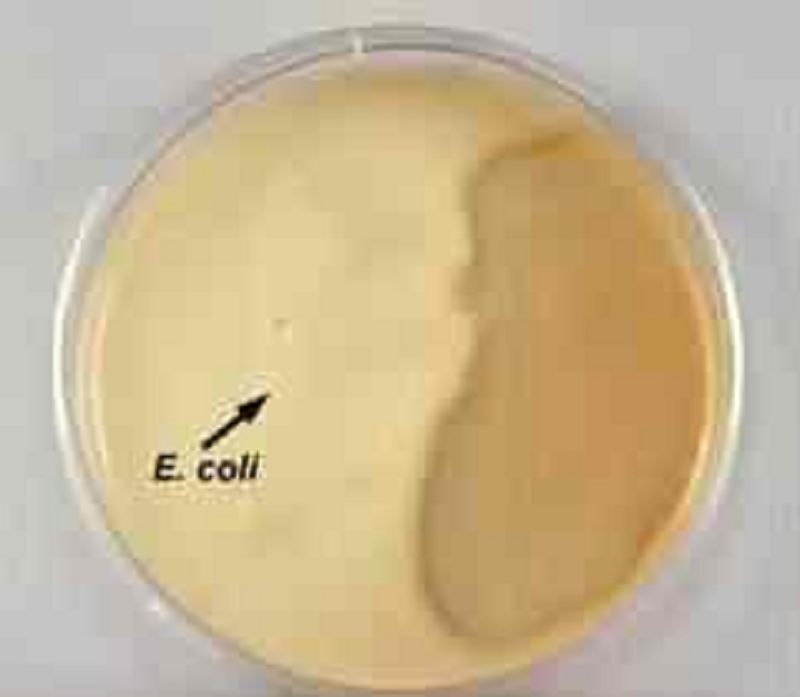
The casein was not hydrolized by the Escherichia coli on the left. The agar remains white and opaque.
The casein was not hydrolized by the Escherichia coli on the left. The agar remains white and opaque.

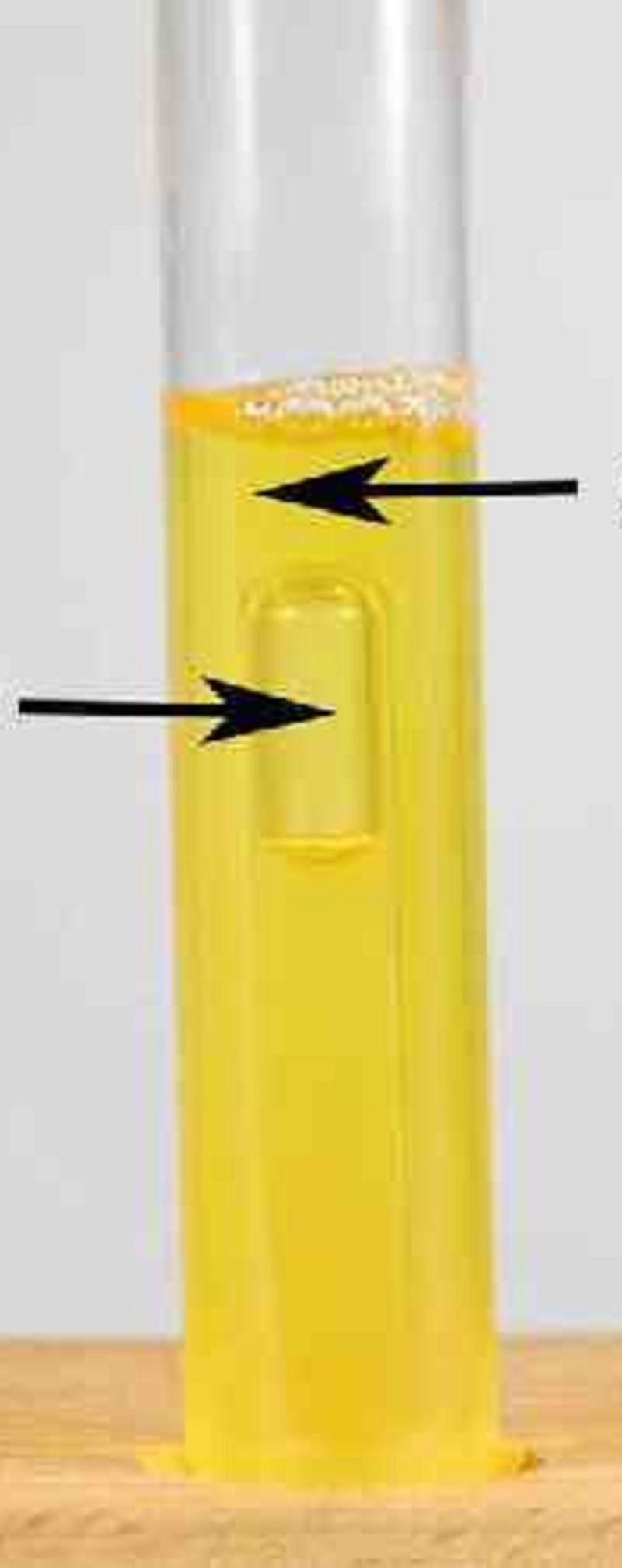
Using the pH Indicator Phenol Red to Detect Acid. What does this tube indicate about the presence of fermenting microorganisms?
They can ferment
They can't ferment
Select all that apply about this tube in relation to the fermentation of carbohydrates.
Acid end products
Gas production
Alkaline end products
Some bacteria use the enzyme tryptophanase to convert the amino acid tryptophan into molecules of indole, pyruvic acid and ammonia.
True
False
To test for indole and hydrogen sulfide production, SAM (sulfide, amonnium, motility) medium is used
True
False
Some bacteria produce hydrogen sulfide as a result of their metabolism they use sulfur as a final electron acceptor in anaerobic cellular respiration.
True
False
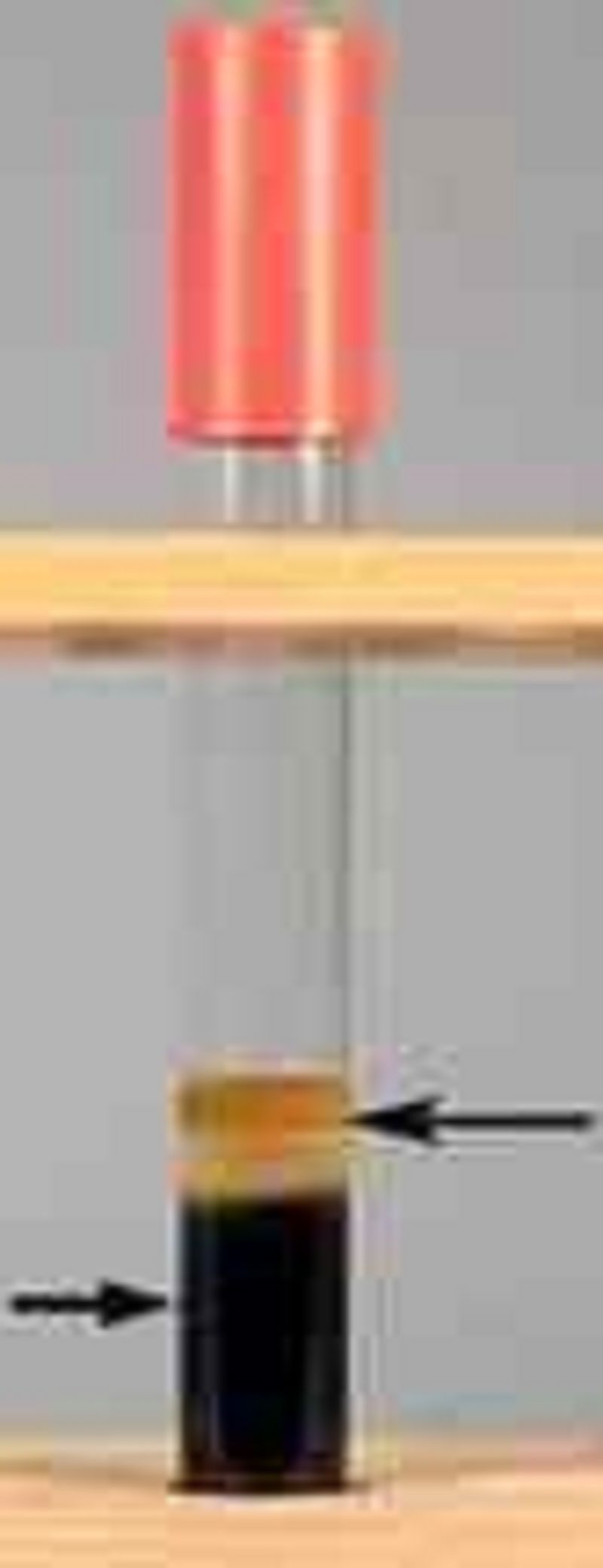

Interpret the hydrogen sulfide and indole results in this SIM medium tube.
(+) Indole
(-) Indole
(+) Hydrogen sulfide
(-) Hydrogen sulfide
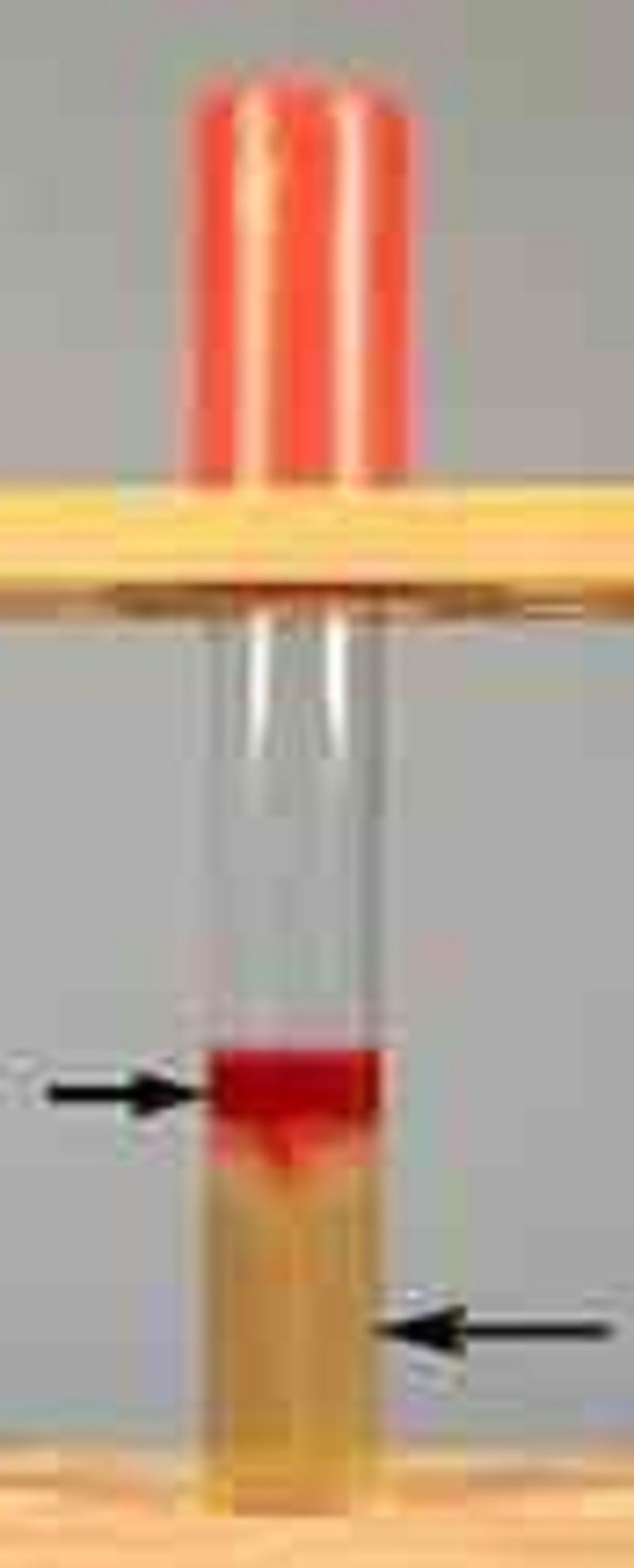

Interpret the hydrogen sulfide and indole results in this SIM medium tube. Hint Kovac's reagent is added.
(+) Indole
(-) Indole
(+) Hydrogen sulfide
(-) Hydrogen sulfide
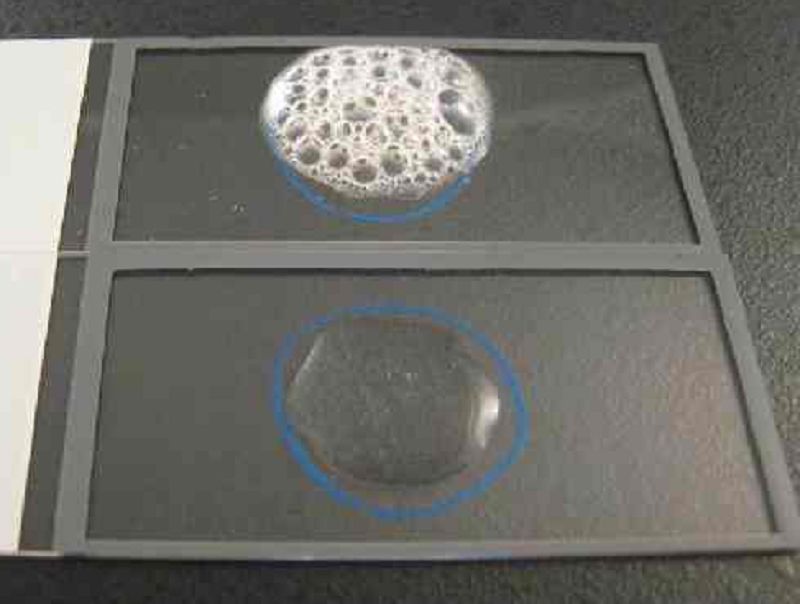
Catalase is the name of an enzyme found in most bacteria which initiates the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) into water (H2O) and free oxygen (O2). Therefore what does this sample of Staphylococcus aureus(TOP SLIDE) indicate?
(+) Catalase
(-) Catalase
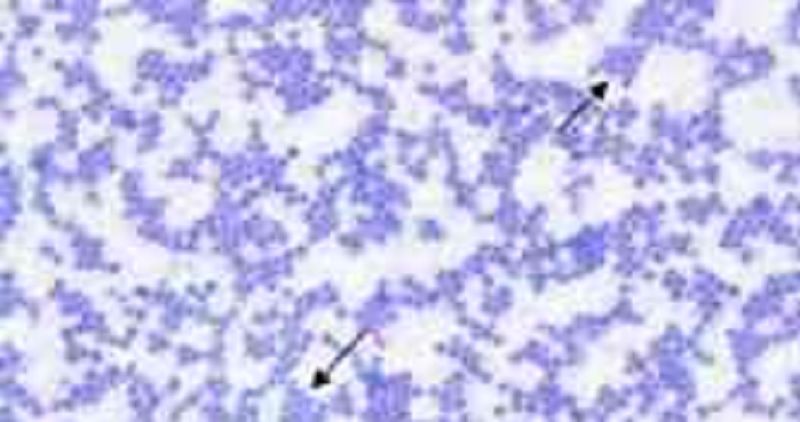
With a basic dye, the positively charged color ion combines with the negatively charged bacterial cytoplasm. Therefore The organism becomes _____________.
Directly stained
Indirectly stained
Negative staining
{"name":"BIOL 230 Lab Exam 2 Review (\"HOLY COW\" Edition)", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Prepare yourself for the BIOL 230 Lab Exam with our comprehensive review quiz designed specifically for biology students. This engaging quiz will test your knowledge of bacterial structures, motility, and essential staining techniques.Key Features:50 carefully crafted questions.In-depth coverage of major concepts.Instant feedback on your responses.","img":"https:/images/course5.png"}
More Quizzes
Microbiology
1368
Mid micro
47240
Cancer Quiz
5227
Sei un ciclope o un marsupio?
14723
Real Estate Agent Career - Should You Become One?
201019114
Bridge Questions and Answers - Free Trivia
201016902
What Is My Christian Name? Free Baptismal Name
201017536
My Type of Man - Find Your Ideal Match
201016666
Philosophy - Introductory Knowledge (Free)
201016168
Am I Sleep Deprived? - Free Self-Assessment
201016608
What Is My Best Quality? Free Personality Online
201017670
DBMS Concepts True/False - Test Your Knowledge
201018703







