DES C_Diagnosis (13) Prepared : CHILLY
A previously healthy 8-year-old boy has a 3-week history of low-grade fever of unknown source, fatigue, weight loss, myalgia, and headaches. On repeated examinations during this time, he is found to have developed a heart murmur, petechiae, and mild splenomegaly. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Rheumatic fever
Kawasaki disease
Scarlet fever
Endocarditis
Tuberculosis
A previously healthy 8-year-old boy is brought to the office by his mother because he has multiple staring episodes. During these episodes, he is unresponsive to verbal or tactile stimuli, and produces lip-smacking movements. Each episode lasts for a few minutes, after which he remains confused for some time. He has no family history of any seizure disorder. His neurological examination is unremarkable. EEG performed before and after hyperventilation is normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Complex partial seizure
Atypical absence seizure
Typical absence seizure
Juvenile myoclonic epilepsy
Lennox-Gastaut syndrome
A previously healthy full-term infant has several episodes of duskiness and apnea during the second day of life. Diagnostic considerations should include which of the following?
Hemolytic anemia
Congenital heart disease
Idiopathic apnea
Harlequin syndrome
Hyperglycemia
A previously healthy, active, 18-month-old African American child presents with unilateral nasal obstruction and foul-smelling discharge. The child’s examination is otherwise unremarkable. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Foreign body
Nasal polyps
Frontal sinusitis
Deviated septum
Choanal atresia
A previously healthy, intoxicated, 19-year-old man is driving a car without using a seat belt. He crashes the car into the back of a parked truck. In the process he slams his abdomen into the steering wheel and ruptures his spleen. Which of the following is the most important problem associated with this type of injury?
Bacteremia
Electrolyte abnormalities
External blood loss
Internal blood loss
Peritonitis
A psychiatric resident is called to consult on the case of a 75-year-old woman who had undergone a hip replacement 2 days before. On examination, the resident notes that the patient states the date as 1956, and she thinks she is at her son’s house. These impairments best illustrate which aspect of the mental status examination?
Concentration
Memory
Thought process
Orientation
Level of consciousness
A psychiatrist is seeing a patient in his outpatient practice. The patient treats the psychiatrist as if he were unreliable and punitive, though he had not been either. The patient’s father was an alcoholic who often did not show up to pick her up from school and frequently hit her. The psychiatrist begins to feel as if he must overprotect the patient and treat her gingerly. Which of the following psychological mechanisms best describes the psychiatrist’s behavior?
Reaction formation
Projection
Countertransference
Identification with the aggressor
Illusion
A school teacher calls you to report that his 7-year-old student had about 10 episodes of eye blinking and gabbling today, which lasted approximately 30 seconds each. The child sat in his chair and did not have any postictal confusion. The teacher noticed several similar episodes during the last month, as well as a decline in the child's school performance. What type of seizure does this child have?
Generalized tonic-clonic seizures
Atonic seizures
Simple partial seizures
Absence seizures
Complex partial seizures
A seven-year-old girl is brought to the physician's office because of a sudden onset of growth spurt, pubic hair development, and breast enlargement. Her family history is not significant. She has no other medical problems. On examination, there is no hirsutism or acne. Her weight is 70th percentile and her height is 98th percentile. Examination showed a pelvic mass. Pelvic ultrasonogram showed a right ovarian mass. Initial evaluation showed elevated estrogen levels. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Dysgerminoma
Granulosa cell tumor
Sertoli-Leydig cell tumor
Mature teratoma
Serous cystadenoma
A single mother brings her 10-year-old son to see the pediatrician. The mother says that she is "absolutely fed up" with her son's behavior and is unable to control him. The boy frequently gets into fights with his siblings, neighbors, and classmates at school. When asked to help with household chores, he refuses. He is very short-tempered and argues frequently with his parents and teachers. A few days ago, he got into an argument with the elderly woman who lives next door, and in a fit of anger he "grabbed a marker and wrote an obscenity on her front door." What is the most likely diagnosis?
Conduct disorder
Tourette's disorder
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
Oppositional defiant disorder
Antisocial personality disorder
A specific pattern of abnormalities has been identified among infants born to mothers who consume moderate-to-large amounts of alcohol during their pregnancies. Which of the following abnormalities is characteristic of these infants?
Cataracts
Gonadal dysgenesis
Developmental dysplasia of the hip
Neural tube defects
Mental retardation
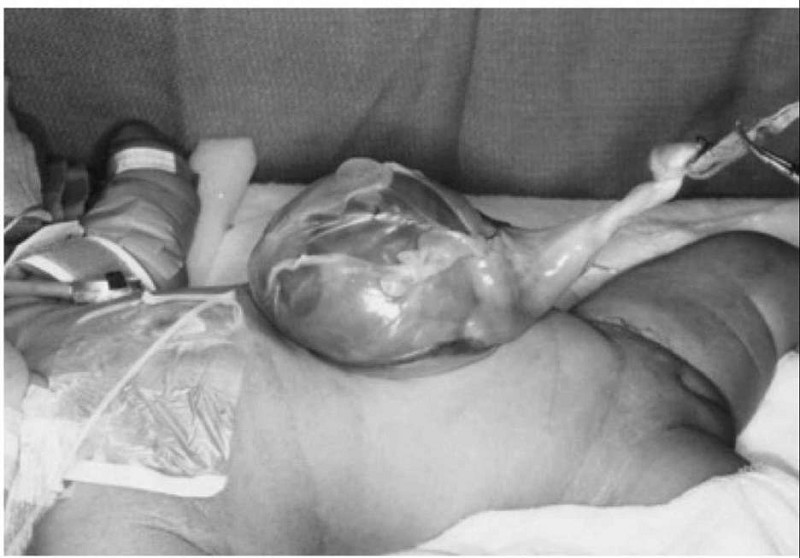
A term infant is born at a small community hospital by caesarean section for failure to progress. The infant is noted to have the following abnormality at birth. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Umbilical hernia
Omphalitis
Omphalocele
Gastroschisis
Traumatic evisceration
A term male infant is found to be cyanotic shortly after birth and requires endotracheal intubation. On physical examination, his blood pressure is 68/34 mm Hg (equal in all four extremities), pulse is 180/min, and respirations are 32/min. His precordium is dynamic, has a grade III systolic murmur, and a single S2. Chest radiography shows a normal heart size and increased pulmonary vascular markings. An arterial blood gas on an FiO2 of 100% shows pH 7.34; PaCO2: 47 mm Hg; PaO2: 46 mm Hg. Which of the following diagnoses is most consistent with these findings?
Atrial septal defect
Tetralogy of Fallot
Hypoplastic left heart syndrome
Patent ductus arteriosus
Total anomalous pulmonary venous return
A term neonate appears healthy at birth and receives routine perinatal care. Ten days after delivery, the infant develops severe eyelid edema with copious drainage of mucopurulent material and pseudomembrane formation. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Adenovirus conjunctivitis
Chlamydial ophthalmia
Chemical conjunctivitis
Gonorrhea ophthalmia
Herpetic kerato conjunctivitis
A term neonate develops apnea, tachypnea, and seizures in the first 2 hours of life. The infant is large for gestational age and appears obese. Physical examination is otherwise unremarkable. Serum studies demonstrate a blood glucose level of 30 mg/dL. The mother most likely has which of the following conditions?
Diabetes mellitus
Emphysema
Hepatic cirrhosis
Hyperthyroidism
Rheumatoid arthritis
A term neonate is small for date and has a small head. Further physical examination of the infant demonstrates small eyes with short palpebral fissures, a flattened nose, and abnormal palmar creases. With which of the following maternal conditions is this presentation most likely associated?
Alcohol abuse
Cirrhosis
Cocaine abuse
Diabetes mellitus
Hypothyroidism
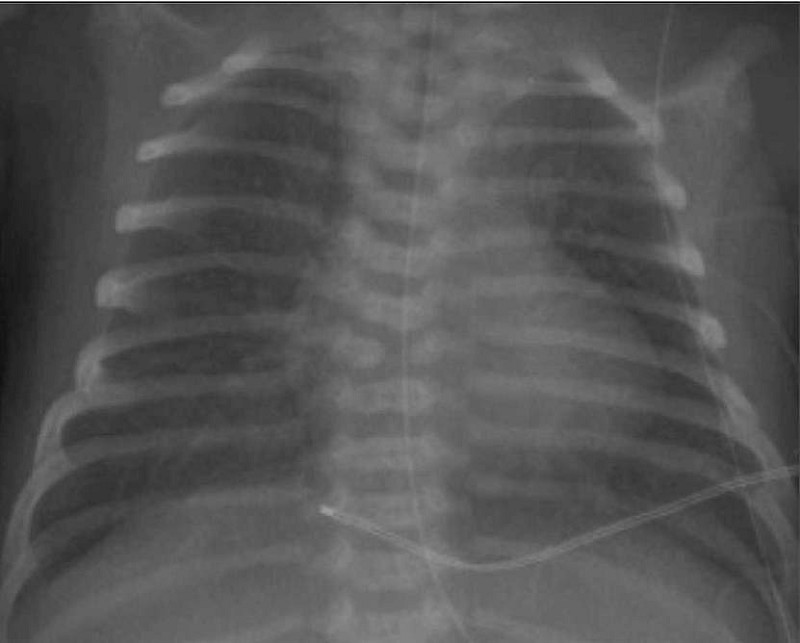
A term, 4200-g (9-lb, 4-oz) female infant is delivered via cesarean section because of cephalopelvic disproportion. The amniotic fluid was clear, and the infant cried almost immediately after birth. Within the first 15 minutes of life, however, the infant’s respiratory rate increased to 80 breaths per minute, and she began to have intermittent grunting respirations. The infant was transferred to the level 2 nursery and was noted to have an oxygen saturation of 94%. The chest radiograph is shown. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Diaphragmatic hernia
Idiopathic respiratory distress syndrome
Meconium aspiration
Pneumonia
Transient tachypnea of the newborn
A trauma patient with a closed-head injury is being monitored in the neurosurgical intensive care unit (ICU). His ICP measurement is seen to rise precipitously. An acute increase in ICP is characterized by which of the following clinical findings?
Respiratory irregularities
Compression of the fifth cranial nerve
Decreased blood pressure
Tachycardia
Papilledema
A very concerned mother brings a 2-year-old child to your office because of two episodes of a brief, shrill cry followed by a prolonged expiration and apnea. You have been following this child in your practice since birth and know the child to be a product of a normal pregnancy and delivery, to be growing and developing normally, and to have no chronic medical problems. The first episode occurred immediately after the mother refused to give the child some juice; the child became cyanotic, unconscious, and had generalized clonic jerks. A few moments later the child awakened and had no residual effects. The most recent episode (identical in nature) occurred at the grocery store when the child’s father refused to purchase a toy for her. Your physical examination reveals a delightful child without unexpected physical examination findings. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Seizure disorder
Pervasive development disorder
Breath-holding spell
Drug ingestion
Hyperactivity with attention deficit
A vomiting infant is brought to the emergency room. The blood work results reveal a normal blood count, but a hyponatremic, hypochloremic, metabolic alkalosis. Which of the following would be consistent with these findings?
Diabetes mellitus
Cystic fibrosis
Ethanol poisoning
Iron ingestion
Isoniazid ingestion
A week-old infant presents blood in his stools. He was born at home, with the father assisting in the delivery; no physician or midwife was present. He has been breast-fed and has been nursing well. On examination, you also note some blood in his nose. He is not jaundiced; a rectal examination and guaic test of the stool confirms that blood is present. His examination is otherwise normal. He is on no medications. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Child abuse
Vitamin K deficiency
Breast milk allergy
Sepsis
Liver disease
A woman comes to an emergency department because she is in labor. She has had no prenatal care. Her baby is delivered and appears to be of about 32 weeks' gestation. The newborn is very pale and shows severe, generalized edema. Cord-blood hematocrit is 22%, and cord-blood bilirubin is 7 mg/dl. Ultrasound examination demonstrates pleural effusions, ascites, cardiomegaly, and hepatomegaly. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
ABO incompatibility
Beta thalassemia
Congenital spherocytosis
Sickle cell anemia
Rh incompatibility
A young black male with sickle cell trait is preparing for his travel to West Africa from North America. While obtaining his visa, he is advised by the health inspector to obtain some immunizations, although his chances of getting a certain tropical disorder are low. What disease has the sickle cell trait been shown to convey protection against?
Tuberculosis
Malaria
Lymphoma
Histoplasmosis
Leprosy
A young Caucasian mother brings her 5-year-old daughter to the pediatrician two months after the girl first began attending kindergarten. She says that earlier this week, her daughter's teacher called to say that the girl persistently refuses to answer questions or to speak to others in class. The teacher added that the girl also does not smile at, play with, or otherwise engage her fellow students. The mother finds this very surprising because her daughter is very verbal and talkative at home, plays happily with her siblings, and is an affectionate child. Further questioning reveals that the girl is "a little shy" at social gatherings. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Separation anxiety disorder
Social phobia
Selective mutism
Autism
Stranger anxiety
A young infant is noted to have developed constipation over the past week, and then facial diplegia and difficulty sucking and swallowing. The child has been colicky, and the maternal grandmother has been treating the child with a mixture of weak tea, rice water, and honey. Which of the following disorders is the most likely culprit in this child?
Infantile spinal muscular atrophy
Congenital myotonic dystrophy
Myastheniagravis
Duchenne muscular dystrophy
Botulism
A young mother complains of pain along the radial side of the wrist and the first dorsal compartment. She relates that the pain is often caused by the position of wrist flexion and simultaneous thumb extension that she assumes to carry the head of her baby. On physical examination, the pain is reproduced by asking her to hold her thumb inside her closed fist, and then forcing the wrist into ulnar deviation. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis? .
Palmar fascial contracture (Dupuytren's contracture)
Tenosynovitis of the abductor or extensor tendons of the thumb (De Quervain's tenosynovitis)
Hairline unrecognized fracture of the carpal navicular (scaphoid) bone
Acute and chronic bursitis
Carpal tunnel syndrome
A40-year-old man with a history of alcohol abuse presents after an episode of binge drinking. He is complaining of epigastric pain, radiating to the back, associated with nausea and vomiting. On examination, he has marked tenderness in the epigastrium, with guarding, decreased bowel sounds, and moderate abdominal distention. Laboratory findings include leukocytosis and increased serum amylase and lipase. Abdominal roentgenograms demonstrate several dilated bowel loops in the upper abdomen. Select the most likely diagnosis?
Gastroenteritis
Acute appendicitis
Sigmoid diverticulitis
Acute pancreatitis
Acute cholecystitis
About 12 days after a mild upper respiratory infection, a 12-year-old boy complains of weakness in his lower extremities. Over several days, the weakness progresses to include his trunk. On physical examination, he has the weakness described and no lower extremity deep tendon reflexes, muscle atrophy, or pain. Spinal fluid studies are notable for elevated protein only. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
Bell palsy
Guillain-Barré syndrome
Muscular dystrophy
Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease
Werdnig-Hoffmann disease
Acute renal failure occurs following aortic angiography in a 72-year-old man. His weight has been rising, his lungs show rales at both bases, and he is dyspneic. His fractional excretion of sodium is greater than 1. He has eosinophilia on his peripheral smear, an elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and proteinuria with microscopic hematuria. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his renal failure?
Hypovolemia
Acute tubular necrosis
Cardiogenic shock
Aortic dissection
Renal artery cholesterol embolism
After a grand mal seizure, a 32-year-old epileptic woman notices pain in her right shoulder, and she cannot move it. She goes to a minor emergency clinic, where she has a limited physical examination and anteroposterior (AP) x-ray films of her shoulder. The films are read as negative, and she is diagnosed as having a sprain and given pain medication. The next day, she still has the same pain and is unable to move her arm. She comes to the emergency department holding her arm close to her body, with her hand resting on her anterior chest wall. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Anterior dislocation of the shoulder
Posterior dislocation of the shoulder
Acromioclavicular separation
Articular cartilage crushing
Torn teres major and minor muscles
After an appropriate diagnostic evaluation, a 59-year-old woman with postmenopausal bleeding had a total abdominal hysterectomy and bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy (TAH-BSO). The pathologic diagnosis is adenocarcinoma of the endometrium. An endometrial adenocarcinoma that is confined to the uterus and extends more than 50% through the myometrium is at which stage?
IC
IIA
IIB
IIIA
IVA
After an uncomplicated pregnancy and cesarean section for breech presentation, twins are born at 32 weeks’ gestation to a 24-year-old primigravida mother. Twin A weighs 1610 g (3.5 lb) and has Apgar scores of 8 and 9 at 1 and 5 minutes, respectively. Twin B weighs 1600 g (3.5 lb) and has Apgar scores of 7 and 8 at 1 and 5 minutes, respectively. Within minutes of birth, twin B becomes mildly cyanotic and tachypneic with subcostal retractions, expiratory grunting, and nasal flaring. Twin B’s blood pressure is 58/39 mm Hg, heart rate is 130/min, respiratory rate is 100/min, and temperature is 37.0°C (98.6°F). Twin B is intubated and given 70% fraction of inspired oxygen. Compared to twin A, what is twin B at greater risk of developing?
Apnea of prematurity
No difference because they are both premature
Hyperbilirubinemia
Retinopathy of prematurity
Gastroesophageal reflux disease
After being delivered following a benign gestation, a newborn infant is noted to have a platelet count of 35,000/µL, decreased fibrinogen, and elevated fibrin spilt products. On examination you note a large cutaneous hemangioma on the abdomen that is purple and firm. Which of the following anomalies might also be expected in this infant?
Kaposiform hemangioendothelioma
Nevus simplex
Nevus flammeus
PHACE(S) syndrome
Infantile fibrosarcoma
Among the conditions that cause edema of the eyelids is orbital cellulitis. This is a serious infection that must be recognized early and treated aggressively if complications are to be avoided. Which of the following features is useful in differentiating orbital cellulitis from periorbital (preseptal) cellulitis?
Proptosis
Elevated WBC count
Fever
Lid swelling
Conjunctival inflammation
An 11-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department for evaluation of an injury from jumping off a 10 ft wall, 2 days ago. He had some pain in his feet immediately following the jump, but was able to walk. The past 2 days, he has had increasing pain in his right foot with walking. He has no pain at rest. He has some "crunching" in the right foot. Physical examination shows the foot appears normal with the exception of suffusion on the plantar surface. Passive motion of the second toe and passive dorsiflexion of the foot produces pain in the middle of the foot. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Stress fracture of second metatarsal
Metatarsophalangeal joint dislocation
Fracture of second metatarsal
Tenosynoviitis of toe flexors
Hematoma in middle plantar space
An 11-year-old boy is brought to the office by his mother because "he is sick." He has had headaches for the past several weeks, and has vomited 4 times in the past 5 days. He drinks large amounts of water and goes to the bathroom all the time. He is no longer interested in playing football and going out with his friends. His temperature is 37.0C (98.6F), blood pressure is 118/78 mm Hg, pulse rate is 84/min, and respirations are 16/min. On examination, there is loss of peripheral visual fields. His laboratory findings are as follows: W BC 7,800/mm3, Hemoglobin 12.6 g/dl, Hematocrit 35%, Platelets 199,000/mm3, Sodium 145 mEq/L, Potassium 3.6 mEq/L, Bicarbonate 24 mEq/L, Blood urea nitrogen 18 mg/dl, Serum creatinine 1.0 mg/dl, Blood glucose 88 mg/dl. X-rays of the head reveal a calcified lesion above the sella. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Pituitary adenoma
Meningioma
Empty sella syndrome
Craniopharyngioma
Ependymoma
An 18-month-old boy presents with a history of fever to 39.0°C for 5 days. He has also been irritable and has not been drinking well. Associated symptoms include red eyes, a rash, and some trouble walking. On physical examination, he has a temperature of 39.5°C. He has bilateral bulbar conjunctivitis, a strawberry tongue, an inflamed oral pharynx, edema of the hands and feet, a morbilliform rash, and cervical lymphadenopathy. He is very irritable. His CBC shows a WBC of 15,000/mm3 with 60% neutrophils, 35% lymphocytes, and 5% monocytes. His hemoglobin is 12.0 g/dL and platelet count is 500,000/ mm3. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Erythema infectiosum (fifth disease)
Kawasaki disease
Rubella
Rubeola (measles)
Rheumatic fever
An 18-month-old Caucasian boy is brought to the emergency department due to a 3-day history of fever and facial rash. His past medical history is significant for atopic dermatitis, which was diagnosed 1 week ago and treated with topical steroids. Examination reveals numerous umbilicated vesicles over erythematous skin of both cheeks. Submandibular adenopathy is present. What is the most probable diagnosis?
Varicella
Contact dermatitis
Impetigo contagiosa
Atopic dermatitis exacerbation
Eczema herpeticum
An 18-month-old girl is brought to the physician’s office for evaluation of left neck mass. Examination reveals a 2-cm soft, nontender, fluctuant mass in the left lateral neck. This is located at the anterior border of the sternomastoid, midway between the mastoid and clavicle. Which one is the most likely diagnosis?
Thyroid carcinoma
Thyroglossal duct cyst
Acute suppurative lymphadenitis
Lipoma
Branchial cleft cyst
N 18-year-old boy comes to clinic to discuss an embarrassing problem. For the last 6 weeks he has noticed a painless mass in his right testis. This is not bothering him at all, but it is becoming larger. He is afraid that his girlfriend may notice it and find out about his other partners. He has multiple partners, and does not use condoms. He has no fever and no other medical complaints. His cousin has SLE but otherwise family history is unremarkable. On ultrasound you suspect testicular cancer and order a few tests. Results are as follows: Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) Increased, Beta subunit of the human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) Normal, Placental Alkaline phosphate (PLAP) Normal, Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) Slightly Increased, Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) Increased. What could be the most likely diagnosis?
Seminoma
Embryonal carcinoma
Choriocarcinoma
Teratoma
Sertoli cell tumor
An 18-year-old college freshman is brought to the emergency department by his friends. They say that he is normally happy and good-natured, but became unusually withdrawn and aloof a few hours after a football game. He complains of a dry mouth. Physical examination reveals injected conjunctivae and tachycardia. Which of the following is most consistent with this patient's presentation?
Opioid overdose
Adrenal crisis
Alcohol intoxication
Cocaine withdrawal
Cannabis abuse
An 18-year-old female college student presents to student health services with a complaint of a burning sensation while urinating and abdominal pain. She denies urinary urgency or increased frequency. She has no significant past medical history. She is currently sexually active with a new partner. She does not use barrier contraception. She denies any previous history of sexually transmitted diseases. On examination she is afebrile, heart rate is 70/min, and blood pressure is 120/60 mm Hg. Examination reveals no peritoneal signs but there is tenderness to palpation over the suprapubic region. On pelvic examination the cervix appears edematous and friable with a small amount of discharge from the os. A urine sample reveals numerous WBCs but no organisms on Gram stain. A cervical swab is sent for Gram stain and culture. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for these findings?
Infection with Escherichia coli
Infection with Proteus mirabilis
Infection with Chlamydia trachomatis
Infection with Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Interstitial cystitis
An 18-year-old football player is seen in the emergency ward with severe knee pain incurred after being hit by a tackler while running. Which of the following findings on physical examination is most sensitive for an anterior cruciate ligament injury?
Excessive valgus laxity of the knee
Excessive varus laxity of the knee
Locked knee
Positive Lachman test
Positive posterior drawer test
An 18-year-old G0 comes to see you complaining of a 3-day history of urinary frequency, urgency, and dysuria. She panicked this morning when she noticed the presence of bright red blood in her urine. She also reports some midline lower abdominal discomfort. She had intercourse for the first time 5 days ago and reports that she used condoms. On physical examination, there are no lacerations of the external genitalia, there is no discharge from the cervix or in the vagina, and the cervix appears normal. Bimanual examination is normal except for mild suprapubic tenderness. There is no flank tenderness, and the patient’s temperature is normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Chlamydia cervicitis
Pyelonephritis
Acute cystitis
Acute appendicitis
Monilial vaginitis
An 18-year-old gang member is stabbed in the back, just to the right of the midline. Physical examination shows paralysis and loss of proprioception distal to the injury on the right side, and loss of pain perception distal to the injury on the left side. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Central cord syndrome
Hemisection of the spinal cord
Anterior cord syndrome
Posterior cord syndrome
Complete transection of the spinal cord
An 18-year-old girl comes to the emergency department for sudden-onset redness and swelling of her skin over exposed areas. She had just spent 1 hour at the beach when she began to experience a burning sensation, followed by redness and swelling of those areas. Her face has a few inflammatory nodules as well as open and closed comedones, and she was recently prescribed "some medication for the past month or so" for her facial lesions. Her pulse is 82/min, blood pressure is 120/80 mmHg, respirations are 14/min and temperature is 37.2°C (99°F). On examination, you notice erythema, edema and vesicles on her face, neck, dorsal hands and upper chest. She has no mucosal lesions. Which of the following best explains her condition?
Erythromycin-induced phototoxicity
Doxycycline-induced phototoxicity
Allergic contact dermatitis
Benzoyl peroxide induced phototoxicity
Stevens-Johnson syndrome
An 18-year-old girl comes to the emergency department with a rash and arthralgias. She is sexually active and has had the same sexual partner for the past 4-months. Recent medical history is significant for an episode of dysuria and increased urinary frequency, both of which started 5-days ago. Her primary care physician prescribed TMP+SMX (Bactrim) for this. She developed her present symptoms 3-days after starting the medication. Her aunt has Lupus. Her temperature is 38.5°C (101.3°F), pulse is 86/min, and respirations are 16/min. Physical examination shows a disseminated maculopapular rash; there is no costovertebral tenderness or flank pain; serum creatinine is 2 mg/dL. Urinalysis shows 2-5 RBC/hpf, numerous white blood cell casts made mostly of eosinophils, and mild proteinuria. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Post-infectious acute glomerulonephritis
Drug induced interstitial nephritis
Disseminated gonococcemia
Lupus nephritis
Pyelonephritis
An 18-year-old girl has hepatosplenomegaly, an intention tremor, dysarthria, dystonia, and deterioration in her school performance. She also developed abnormal urine with excess glucose, protein, and uric acid. She has a several-year history of elevated liver enzymes of unknown etiology. Which of the following best explains her condition?
Indian childhood cirrhosis
α1-Antitrypsin deficiency
Menkes syndrome
Dubin-Johnson syndrome
Wilson disease
An 18-year-old male college student is seen in the student health clinic for urinary frequency, dysuria, and urethral discharge. Which of the following is likely to explain his condition?
Herpes simplex
Chlamydial urethritis
Escherichia coli urinary tract infection
Syphilis
HIV infection
An 18-year-old male comes to the physician's office because of dull aching and fullness of the scrotum. Examination shows soft left-sided scrotal swelling; transillumination testing is negative. The scrotal swelling increases when the patient performs the Valsalva maneuver. The physical examination is otherwise unremarkable. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his condition?
Hypoalbuminemia
Testicular neoplasia
Dilatation of pampiniform plexus
Fluid in the tunica vaginalis
Cystic dilations of the efferent ductules
An 18-year-old male comes to the physician's office because of dull aching and fullness of the scrotum. Examination shows soft testicular swelling; transillumination testing is negative. The scrotal swelling increases when the patient performs the Valsalva maneuver. The physical examination is otherwise unremarkable. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his condition?
Hypoalbuminemia
Testicular neoplasia
Cystic dilations of the efferent ductules
Dilatation of pampiniform plexus
Fluid in the tunica vaginalis
An 18-year-old male undergoes elective hernia repair. During the operation, he suffers considerable blood loss, and receives a blood transfusion. He then experiences an anaphylactic transfusion reaction. He is resuscitated and further hospital course is uncomplicated. His past medical history is significant for recurrent sinopulmonary infections and intermittent episodes of diarrhea since childhood. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his symptoms?
IgA deficiency
X linked agammaglobulinemia
DiGeorge Syndrome
Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome
Cystic fibrosis
An 18-year-old man is admitted to the ER following a motorcycle accident. He is alert and fully oriented, but witnesses to the accident report an interval of unresponsiveness following the injury. Skull films disclose a fracture of the left temporal bone. Following x-ray, the patient suddenly loses consciousness and dilation of the left pupil is noted. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A ruptured berry aneurysm
An intra-abdominal hemorrhage
An acute subdural hematoma
An epidural hematoma
A ruptured arteriovenous malformation
An 18-year-old man is brought to the emergency room by the police after he is found walking along the edge of a high building. In the emergency room, he mumbles to himself and appears to be responding to internal stimuli. When asked open-ended questions, he suddenly stops his answer in the middle of a sentence, as if he has forgotten what to say. Which of the following symptoms best describes this last behavior?
Incongruent affect
Blocking
Perseveration
Tangentiality
Thought insertion
An 18-year-old man is seen by a psychiatrist in the emergency room. During the history, the patient is asked to describe his mood. He answers the following, “My mood is flextitating, I am up and down.” The patient is exhibiting which of the following thought disorders?
Clang association
Thought blocking
No thought disorder is apparent
Tangentiality
Neologism
An 18-year-old man was traveling at a high speed when his car slammed into a wall. He is brought into the emergency department by ambulance. His blood pressure is 60/40 mmHg, pulse is 115/min and weak, respirations are 18/min, and central venous pressure is 2 cmH2O. He is responsive only to painful stimuli. Breath sounds are equal bilaterally, and cardiac auscultation reveals only tachycardia. The abdomen is soft, nondistended, and nontender with active bowel sounds. A chest x-ray film shows a widened mediastinum. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Cardiac contusion
Cardiac tamponade
Flail chest
Ruptured thoracic aorta
Tension pneumothorax
An 18-year-old nullipara has suddenly stopped menstruating. She recently lost 8.6 kg when she started long-distance running. The laboratory test most consistent with her cause of secondary amenorrhea is which of the following?
A serum FSH level of 3 mIU/mL (normal 5–18)
A serum testosterone level of 156 ng/dL (normal 40–110)
A serum estradiol level of 128 pg/mL (normal 40–300)
A serum LH level of 48 mIU/mL (normal 6–35)
A serum prolactin level of 86 ng/mL (normal < 20)
An 18-year-old patient presents to you for evaluation because she has not yet started her period. On physical examination, she is 5ft 7 in tall. She has minimal breast development and no axillary or pubic hair. On pelvic examination, she has a normally developed vagina. A cervix is visible. The uterus is palpable, as are normal ovaries. Which of the following is the best next step in the evaluation of this patient?
Order an MRI of the brain to evaluate the pituitary gland
Prescribe a progesterone challenge to see if she will have a withdrawal bleed
Draw her blood for a karyotype
Test her sense of smell
Draw her blood for TSH, FSH, and LH levels
An 18-year-old white female is brought to the emergency department due to severe vomiting, fever and rashes. She was fine until today, when she developed a fever, flu-like symptoms and dizziness. She has a history of asthma and allergic rhinitis. She denies taking drugs or alcohol, or being exposed to other sick individuals. She had her period yesterday, but did not place a tampon until today, 6 hours prior to becoming ill. Her last menstrual period was 6 weeks ago. She appears alert but listless. Her temperature is 38.8°C, pulse is 120/min, respirations are 23/min, and blood pressures are 100/66 mmHg, supine and 66/30 mmHg, standing. On examination, there are erythematous flat and raised rashes on her trunk and extremities. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Toxic shock syndrome
Meningococcemia
Scarlet fever
Stevens-Johnson syndrome
Toxic epidermal necrolysis
An 18-year-old woman arrives in your clinic with primary amenorrhea, sexual infantilism, and clitoromegaly. She has a history of ambiguous external genitalia noted at birth. Reviewing her records, you see that laparotomy performed at 17 months of age revealed normal internal female genitalia and ovarian biopsy performed at that time revealed normal-appearing primordial follicles. Laboratory studies today reveal a normal female karyotype and high serum testosterone and androstenedione concentrations. Estradiol and estrone are undetectable in the serum. Serum FSH and LH concentrations are high. Pelvic imaging shows multiple ovarian cysts. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia
McCune-Albright syndrome
Aromatase deficiency
Kallmann's syndrome
Galactosemia
An 18-year-old woman at 9 weeks' gestation is brought to the emergency department because of an open fracture of the tibia and fibula. She is hemodynamically stabilized and referred to the orthopedic department. She is scheduled for internal fixation of the tibia for the following day. However, before the surgery she develops severe dyspnea and confusion. Her temperature is 37.70C (99.90F), blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg, pulse is 110/min, and respirations are 22/min. Examination shows numerous non-palpable petechiae in the upper part of the body. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Air embolism
Thromboembolism
Amniotic fluid embolism
Fat embolism
Acute respiratory distress syndrome
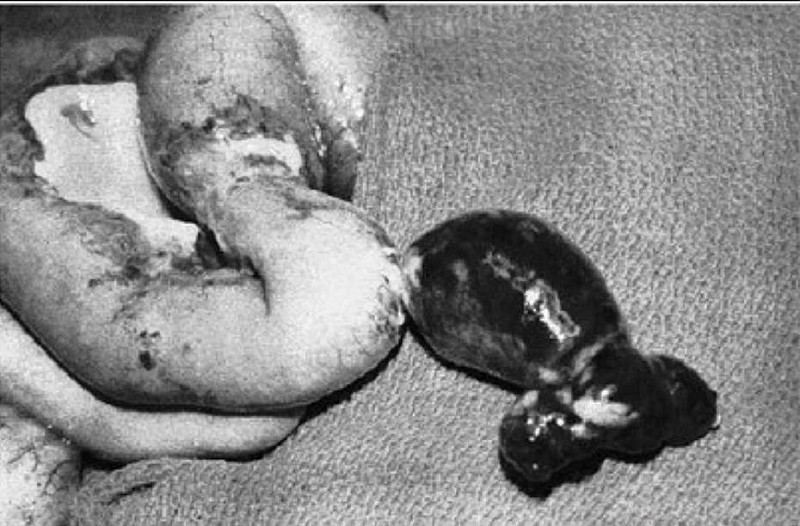
N 18-year-old woman presents with abdominal pain, fever, and leukocytosis. With the presumptive diagnosis of appendicitis, a right lower quadrant (McBurney) incision is made and a lesion 60 cm proximal to the ileocecal valve is identified (see photo). Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Intestinal duplication
Ileoileal intussusception
�Christmas tree” type of ileal atresia
Mesenteric cyst
Meckel diverticulum
An 18-year-old woman presents with amenorrhea and is found to have normal secondary sex characteristics and normal-appearing external genitalia. Her first menstrual period was at age 13, and her cycle has been unremarkable until now. She states that her last menstrual period was 8 weeks prior to this visit. A urine test for hCG is positive. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Ectopic pregnancy
Stein-Leventhal syndrome
Intrauterine pregnancy
Turner syndrome
Weight loss syndrome
An 18-year-old woman presents with headache, anorexia, chilly sensations, and discomfort on both sides of her jaw. She has also noticed discomfort in both lower abdominal quadrants. Physical examination reveals bilateral enlarged parotid glands that are doughy, elastic, and slightly tender; with a reddened orifice of Stensen’s duct. Her abdomen is soft with bilateral lower quadrant abdominal tenderness; a temperature of 38.5°C; and a pulse rate of 92/min. Laboratory data show hemoglobin 13 g/dL; hematocrit 40%; white blood cells (WBC) 9000/mL, with 35% segmented neutrophils, 7% monocytes, and 58% lymphocytes. Which of the following is the most likely cause for her abdominal pain and tenderness?
Mesenteric lymphadenitis
Oophoritis
Gonorrhea
Peritoneal metastases
Intestinal hyperperistalsis
An 18-year-old woman visits her physician because of 3 weeks of malaise, 2 weeks of fever, and a sore throat. Physical examination shows pharyngeal infection with enlarged tonsils and a patchy, white exudate; enlarged, palpable anterior and posterior cervical, axillary, and inguinal lymph nodes; tenderness in the right upper quadrant; and minimal splenomegaly. Laboratory data show hemoglobin 14 g/dL; hematocrit 42%; platelets 380,000/mL; WBC 8500/mL, with 35% segmented neutrophils, 1% eosinophils, and 64% lymphocytes, of which 36% were atypical. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Infectious hepatitis
Hodgkin’s disease
Lymphocytic leukemia
Infectious mononucleosis
Cat-scratch fever
An 18-year-old woman, gravida 1, now para 1, just delivered a 3,500 g (7 lb 12 oz) healthy male neonate without complications. At the beginning of this pregnancy, at 8 weeks’ gestation, she was noted to have a 5-cm right adnexal cystic mass that appeared as a simple, thin-walled, round, fluid-filled cyst structure. The mass spontaneously involuted and was no longer seen on sonogram at 16 weeks’ gestation. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Follicular cyst
Corpus luteum cyst
Theca-lutein cyst
Luteoma of pregnancy
Endometrioma
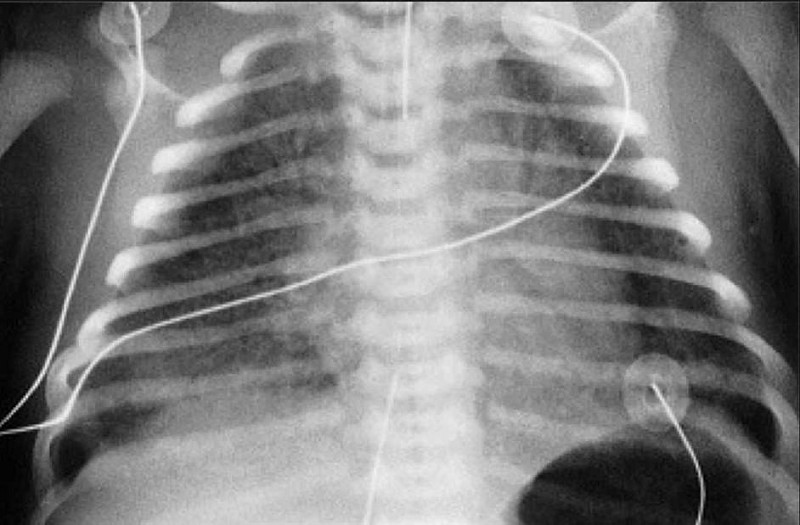
An 8-hour-old infant develops increased respiratory distress, hypothermia, and hypotension. A complete blood count (CBC) demonstrates a white blood cell (WBC) count of 2500/μL with 80% bands. The chest radiograph is shown below. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Congenital syphilis
Transient tachypnea of the newborn
Chlamydial pneumonia
Diaphragmatic hernia
Group B streptococcal pneumonia
An 8-month-old pale child is referred by a nurse practitioner due to "pale mucous membranes, irritability, and listlessness." The stool examination is negative for occult blood, ova and parasites. Laboratory studies reveal: Hemoglobin 6.0 g/L, MCHC 25%, MCH 16.5 pg, MCV 68 fl, Reticulocytes 0.6%, Platelets 230,000/mm3, Leukocyte count 5,500/mm3, Neutrophils 56%, Eosinophils 1%, Lymphocytes 33%, Monocytes 10%, Serum Iron 40 mg/dL, TIBC 460 mg/dL (normal 300-350 mg/dL), Percent saturation of transferrin 8.7%, Total serum bilirubin 0.9 mg/dL. The peripheral blood smear shows marked anisocytosis, microcytosis, hypochromia, and poikilocytosis. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Iron deficiency anemia
Dimorphic anemia
Sideroblastic anemia
Megaloblastic anemia
Anemia of chronic disease
An 8-year-old boy falls on his right hand with the arm extended, and he breaks his elbow by hyperextension. X-ray films show a supracondylar fracture of the humerus. Which of the following complications is of greatest concern with this type of injury?
Instability that requires open reduction and internal fixation
Growth plate damage
Insufficient remodeling
Malunion
Vascular and nerve injuries
An 8-year-old boy is brought to his physician by his mother, who is worried by the child's frequent episodes of daydreaming, which have apparently resulted in a decline in school performance. The child's psychomotor development appears normal. EEG recording reveals bilateral and symmetric 3 Hz spike-and-wave discharges, which begin and end abruptly on a normal background. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Absence seizures (petit mal)
Pseudoseizures
Complex partial seizures
Tonic-clonk seizures (grand mal)
Simple partial seizures
An 8-year-old boy is brought to the clinic by his mother, who states that he has been complaining of pain in both knees. The mother also states that he had a rash on his leg 3 weeks ago. She said it was there for almost 2 weeks and then went away. She describes the rash as reddish and circular, with a small clear area in the center. She said the rash was not itchy or painful. The child has also complained of headaches and muscle aches over the past several weeks. On questioning, the mother states that they were vacationing in Wisconsin about 1 month ago and the boy was hiking in the woods when he was bitten by a tick. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Babesiosis
Colorado tick fever
Lyme disease
Rocky Mountain spotted fever
Tularemia
An 8-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department with a head injury. He hit his head on the ground when he fell off his bicycle. He was not wearing a helmet at the time. There was no loss of consciousness. He vomited 2 times after the accident and now complains of a right-sided headache and inability to hear with his right ear. There is no photophobia or diplopia. On physical examination, his blood pressure is 110/72 mm Hg, pulse is 104/min, and respirations are 22/min. He is alert and oriented and responds appropriately to questions. There is a round hematoma on the right side of his head. Bloody drainage is noted from his right ear. Which of the following injury is most consistent with these findings?
Concussion
Subdural hematoma
Temporal bone fracture
Tympanic membrane perforation
Epidural hematoma
An 8-year-old boy is brought to the office due to headaches and impaired walking. These symptoms started seven days ago, and progressed gradually. He just recently recovered from otitis media that was superimposed on an acute respiratory infection. His past medical history is significant for three episodes of otitis media and one episode of pneumonia. His temperature is 36.7C (98F), blood pressure is 100/60 mm Hg, pulse is 110/min, and respirations are 20/min. Physical examination reveals mild right-sided hemiparesis and a slightly dilated left pupil. The funduscopic examination is normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Brain abscess
Bacterial meningitis
Toxoplasmosis
Venous thrombosis
Arterial thrombosis
An 8-year-old boy is brought to the office due to itchy rashes with blisters over his face, trunk and legs for the past 2 days. His vital signs are normal, except for a temperature of 37.7°C (100°F). On examination, you notice macules, pustules, vesicles, and honey-colored crusts around his mouth, nose, legs, buttocks and trunk area. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Contact dermatitis
Herpes simplex infection
Impetigo
Erythema multiforme
Varicella zoster infection
An 8-year-old boy is brought to the pediatrician with a rash on his abdomen. The mother first noticed the rash about 3 weeks ago. The boy has no fever or other symptoms. On examination, there is a well-circumscribed, circular, erythematous, scaly annular patch on his abdomen. The border of the skin lesion is raised and well defined. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Erythema multiforme
Erythema nodosum
Impetigo
Nummular eczema
Tinea corporis
An 8-year-old boy presents to the physician for a routine health maintenance visit. His mother states that he has had difficulty reading and concentrating in his second-grade class. On examination, seven café-au-lait spots on his body, as well as two small, soft masses above his orbit, are seen. He also has axillary freckling. His mother also has café-au-lait spots on her arms. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Congenital hypothyroidism
Marfan syndrome
Neurofibromatosis
Osteogenesis imperfecta
Tuberous sclerosis
An 8-year-old boy presents with a 2-day history of rash. The rash started on the head and spread downward to his trunk and extremities. He also complains of a fever, cough, and a runny nose for the past 5 days. On physical examination, his temperature is 38.2 C (100.7 F), blood pressure is 88/56 mm Hg, pulse is 76/min, and respirations are 16/min. There is a small, irregular red spot with a central gray color on his buccal mucosa. The rash on his body is erythematous and maculopapular in quality. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Erythema infectiosum
Roseola infantum
Hand-foot-mouth disease
Measles
Rubella
An 8-year-old Caucasian boy is brought to the office for the evaluation of high-grade fever, flank pain and burning micturition for the last two days. He has had two previous episodes of acute pyelonephritis. Physical examination reveals costovertebral angle tenderness. Urinalysis shows pyuria, significant bacteriuria, WBC casts, positive nitrite and esterase. The voiding cystourethrogram (VCUG) reveals vesicoureteral reflux. What is the most likely complication of this condition, if left untreated?
Hydronephrosis
Renal stones
Renal scarring
Renal abscess
Renal cell carcinoma
An 8-year-old Cub Scout who returned from an outing 9 days ago is brought to the clinic with the rapid onset of fever, headache, muscle pain, and rash. The maculopapular rash began on the flexor surfaces of the wrist and has become petechial as it spread inward to his trunk. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Lyme disease
Tularemia
Measles
Toxic shock syndrome
Rocky Mountain spotted fever
An 80-year-old female is brought to your office, by her son, because of severe fatigue. She lives alone and is suffering from severe degenerative joint disease, which puts her in a house arrest-type state. Her son usually helps with getting grocery. Her only other medical problem is hypertension. She takes hydrochlorothiazide and acetaminophen. Her vitals are stable. On examination, she has pallor, and evidence of severe degenerative joint disease. Which of the following is the most likely cause of pallor in this patient?
Vitamin D deficiency
Vitamin C deficiency
Iron deficiency
Folate deficiency
Chronic hemolysis
An 80-year-old man with history of symptomatic cholelithiasis presents with signs and symptoms of a small-bowel obstruction. Which of the following findings would provide the most help in ascertaining the diagnosis?
A pH of 7.5, PCO2 of 50 kPa, and paradoxically acid urine
A palpable mass in the pelvis
Pneumobilia
Coffee-grounds aspirate from the stomach
A leukocyte count of 40,000/mL
An 80-year-old white male comes to the emergency department due to a sudden loss of vision in his left eye that occurred this morning upon waking up. He has had hypertension for the past several years. Current medications include ramipril and atenolol. His blood pressure is 140/90 mm Hg, pulse is 86/min, respirations are 14/min, and temperature is 36.8°C (98.4°F). Examination of the left eye reveals no abnormalities. Funduscopic examination shows swelling of the optic disk, retinal hemorrhages, dilated and tortuous veins, and cotton wool spots. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Acute angle-closure glaucoma
Optic neuritis
Central retinal vein occlusion
Amaurosis fugax
Acute anterior uveitis
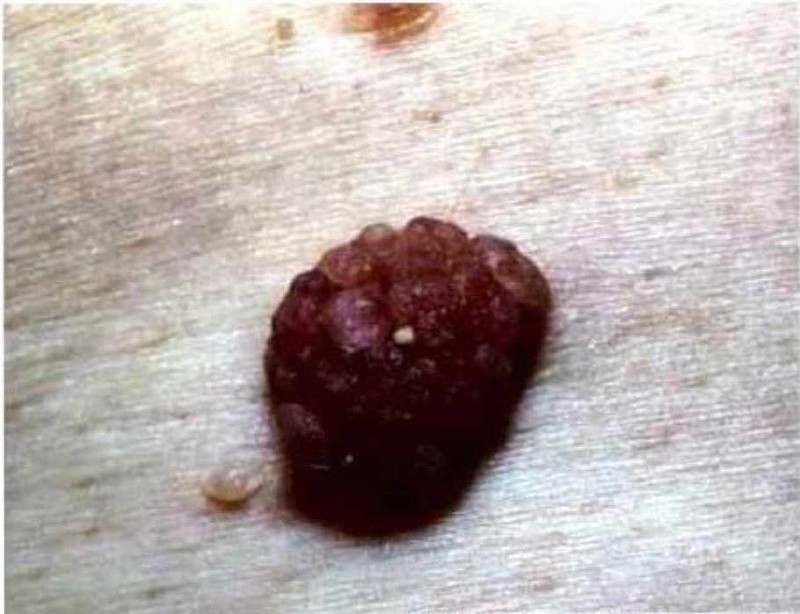
An 80-year-old woman comes to the office and appears very upset. She requests removal of a lesion on her neck because "it is greasy and unsightly." She is tired of people constantly staring at her neck. The lesion has been present "for quite a while," and has been gradually darkening. Aside from occasional itching, there are no other symptoms. A picture of the lesion is shown below. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Basal cell carcinoma
Acrochordon
Melanoma
Seborrheic keratosis
Actinic keratosis
An 81-year-old diabetic woman with a history of atrial fibrillation is transferred to your emergency department (ED) from the local nursing home. The note from the facility states that the patient is complaining of abdominal pain, having already vomited once. Her vital signs in the ED are temperature 100.1°F, blood pressure (BP) 105/75 mm Hg, heart rate (HR) 95 beats per minute, and respiratory rate (RR) 18 breaths per minute. You examine the patient and focus on her abdomen. Considering that the patient has not stopped moaning in pain since arriving to the ED, you are surprised to find that her abdomen is soft on palpation. You decide to order an abdominal radiographic series. Which of the findings on plain abdominal film is strongly suggestive of mesenteric infarction?
Sentinel loop of bowel
No gas in the rectum
Presence of an ileus
Pneumatosis intestinalis
Air fluid levels
An 81-year-old man with Alzheimer disease who lives in a nursing home undergoes surgery for a fractured femoral neck. On the 5th postoperative day, it is noted that his abdomen is grossly distended and tense, but not tender. He has occasional bowel sounds. The rectal vault is empty on digital examination, and there is no evidence of occult blood. X-ray films show a few distended loops of small bowel and a much distended colon. The cecum measures 9 cm in diameter, and the gas pattern of distention extends throughout the entire large bowel, including the sigmoid and rectum. No stool is seen in the films. Other than the abdominal distention, and the ravages of his mental disease, he does not appear to be ill. Vital signs are normal for his age. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Fecal impaction
Ogilvie syndrome
Mechanical intestinal obstruction
Paralytic ileus
Volvulus of the sigmoid colon
An 83-year-old man is brought to the office by his wife because he has had frequent falls for the past 3 months. The wife says that, "He's not his usual self these days. He needs help with everything, even everyday things." The patient has mask-like facies. He speaks very softly with a poorly modulated voice, and he has a fine tremor in both hands. The resting tremor in his hands disappears with voluntary movements. The other pertinent findings include a shuffling gait with short steps, stooped posture, tendency to fall and rigidity of both upper limbs. What skin condition is associated with this patient's neurologic diagnosis?
Tinea versicolor
Seborrheic dermatitis
Pityriasis rosea
Dermatophytosis
Lichen simplex chronicus
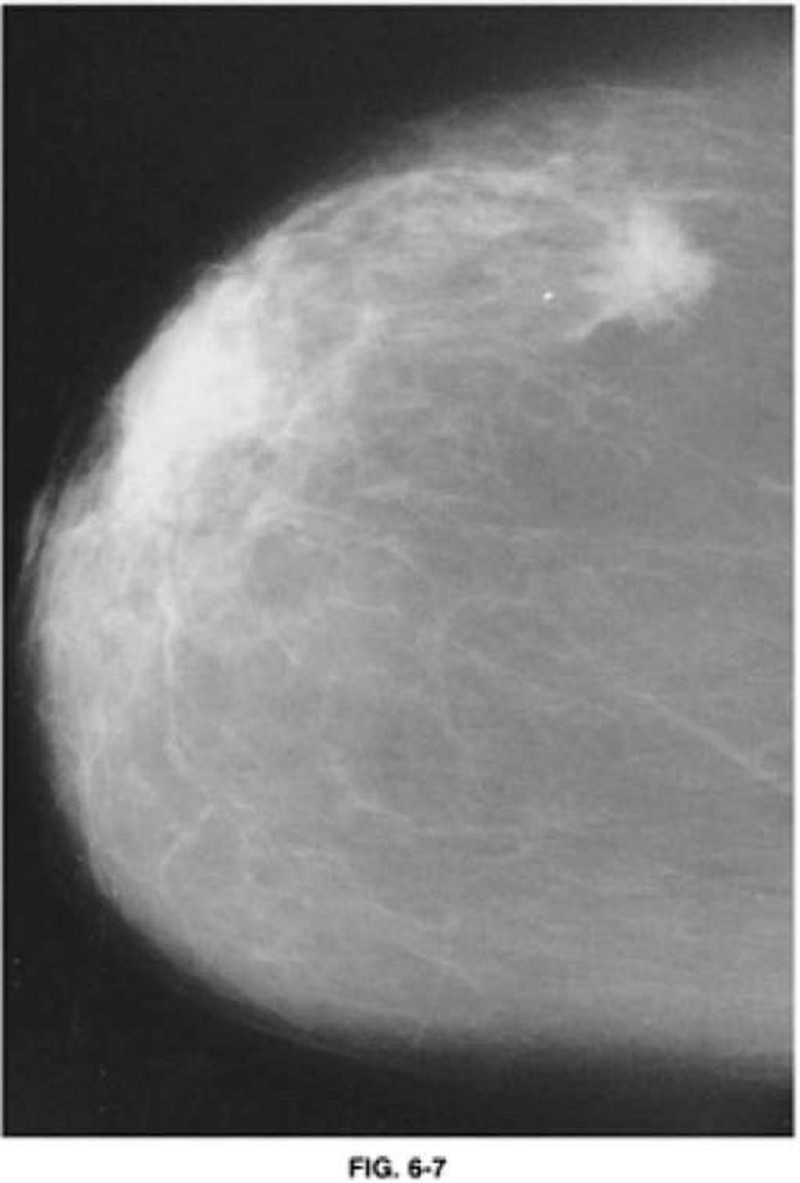
An 83-year-old woman presents to a mammographic facility for a screening mammogram. The technician notices a mass in the lateral right breast. The patient denies any breast pain, nipple discharge, skin changes, or breast trauma. A right breast CC view is shown in Figure 6-7. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Papilloma
Invasive carcinoma
Cystosarcoma phyllodes
DCIS
Fat necrosis
An 83-year-old woman presents with a 1-year history of progressively severe crampy abdominal pain after eating. She has started avoiding food because of the pain. The pain is often associated with bloating, nausea, and occasional diarrhea. She has had a 15 kg (33 lb) weight loss over the past year. Her other medical problems include hypertension, diabetes mellitus-type 2, hypercholesterolemia, peripheral vascular disease, coronary artery disease and myocardial infarction. Social history is not significant. Abdomen is soft, nontender and non-distended. Abdominal x-ray and CT scan are unremarkable. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Chronic pancreatitis
Crohn' s disease
Irritable bowel syndrome
Celiac disease
Atherosclerosis of the mesenteric arteries
An 85-year-old male is placed on mechanical ventilation after a complicated elective hernia repair. After five days of endotracheal intubation with mechanical ventilation, the ratio of the rate of carbon dioxide produced to the rate of oxygen uptake is 1.05. What is the best explanation for these findings?
Sepsis
High inspired oxygen fraction
High-protein tube feeding
Carbohydrate excess in the diet
Pulmonary atelectasis
An 84-year-old man is brought to the emergency department because of 1 hour of severe back pain. He also had syncope that lasted < 1 minute. Before arriving at the hospital, he had an episode of gross hematuria, which he has never had before. He also complains of some shortness of breath. He denies chest pain, cough, nausea, vomiting, headache, and neck pain. His blood pressure is 72/55 mm Hg and pulse is 112/min and regular. His pulse oximetry shows 92% on room air. His ECG shows sinus tachycardia with prominent horizontal ST segment depression in the anterior chest leads. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Acute mesenteric ischemia
Massive pulmonary embolism
Abdominal aortic aneurysm rupture
Acute myocardial infarction
Nephrolithiasis with renal colic
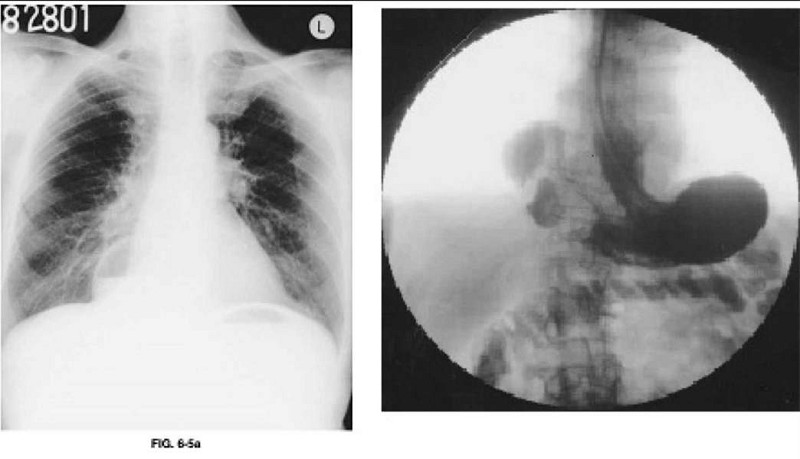
An 85-year-old man presents to the emergency room with an acute onset of midepigastric pain, nausea, vomiting, and hiccups starting 2 days ago. He is unable to keep any food down. Past history is pertinent for a long-standing hiatal hernia, hypertension, and diet-controlled diabetes. Examination reveals vital signs of pulse rate 82/min, BP 100/52 mmHg, respiratory rate 16/min, and temperature 97.2°F. The patient is in no acute distress, but has epigastric tenderness without guarding. Laboratory analysis revealed a hematocrit of 46 and a normal white blood cell (WBC) count. A chest x-ray is shown in Figure 6-5a. A fluoroscopically guided NG tube was placed using contrast, and his stomach was decompressed. After adequate fluid and electrolyte resuscitation, an upper gastrointestinal (UGI) contrast study was obtained and is shown in 6-5b. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Sliding hiatal hernia
Paraesophageal hernia
Eventration of the diaphragm (central diaphragm)
Hernia of Morgagni (parasternal congenital diaphragmatic hernia)
Hernia of Bochdalek (posterorlateral congenital diaphragmatic hernia)
An 85-year-old man presents with a rash over his forehead, tip of nose and left eye. He also complains of pain and decreased vision. He has had fever, malaise, and a burning sensation around his left eye for the past 5 days. His blood pressure is 140/90 mm Hg, pulse is 92/min, respirations are 14/min, and temperature is 38.1°C (101°F). Physical examination reveals a vesicular rash on the periorbital region and lid margins. The left eye is red, with chemosis of the conjunctiva. Dendriform ulcers are seen on the cornea. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Herpes simplex keratitis
Bacterial keratitis
Dacryocystitis
Trigeminal neuralgia
Herpes zoster ophthalmicus
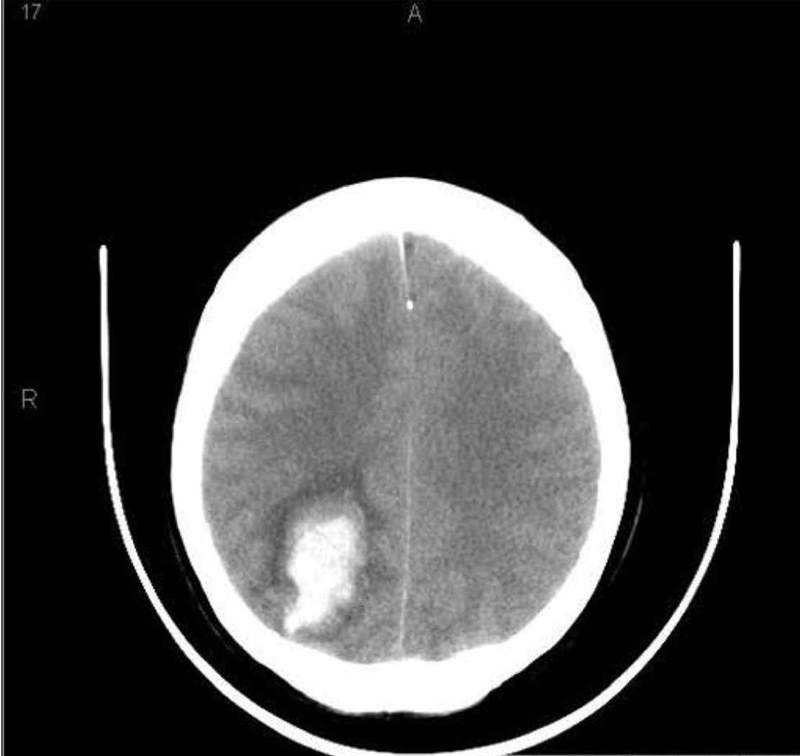
An 86-year -old known hypertensive woman is brought to the emergency department due to weakness of her left side, confusion, drowsiness and slurred speech for the last 2 hours. Her past medical history is significant for an inferior wall myocardial infarction 12 years ago, chronic atrial fibrillation, and severe backache secondary to osteoarthritis. She is currently on aspirin, warfarin, losartan, indomethacin, atenolol, and simvastatin. She doesn't go to anticoagulation clinic regularly. Her blood pressure is 180/110 mm Hg, temperature is 38°C (100°F), respirations are 16/min, and pulse is 70/min, irregularly irregular. The pertinent physical findings are: carotid bruit on both sides, 2/5-muscle strength in the left arm and leg, and slurred speech. Her deep tendon reflexes are exaggerated on the left side, and the Babinski sign is positive. EKG reveals atrial fibrillation. Her CT scan (performed in the ED) is shown below. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Cerebral haemorrhage
Cerebral infarction
Lacunar infarction
Subarachnoid haemorrhage
Cerebellar hemorrhage
An 88-year-old male complains of severe right calf pain several hours after undergoing a right femoral artery embolectomy. He also complains of a burning sensation in his posterior right leg. He has a long history of atrial fibrillation and hypertension. His past medical history also includes stroke, bleeding duodenal ulcer, diabetes mellitus and diabetic nephropathy. On physical examination, his blood pressure is 160/70 mm Hg and his heart rate is 100 per minute and irregular. His right calf is swollen, tense and exquisitely tender; the pain is worsened by passive extension of the right knee. Dorsalis pedis and posterior tibial pulses are palpable in the bilateral lower extremities. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
Recurrent embolism
Venous thrombosis
Soft tissue swelling
Bone infarction
Anaerobic infection
An African-American boy is in the newborn nursery with a bulge on his abdomen that was identified immediately after birth and is most pronounced during crying. The patient was born to an 18-year-old woman who did not receive prenatal care or take prenatal vitamins. Vitals are normal. Examination shows a soft swelling at the umbilical ring. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis and best course of action for this patient?
Omphalocele, refer for operative management
Umbilical granuloma, apply silver nitrate
Umbilical hernia, observe for spontaneous resolution
Umbilical hernia, refer for operative management
Gastroschisis, refer for surgical management
An alcoholic man has been suffering excruciating pain from chronic pancreatitis recalcitrant to analgesics and splanchnic block. A surgeon recommends total pancreatectomy. A patient who has a total pancreatectomy might be expected to develop which of the following complications?
Diabetes mellitus and steatorrhea
Hypoglycemia
Diabetes mellitus and constipation
Hypoglycemia and steatorrhea
Hypoglycemia and constipation
An anxious mother brings her 4-year-old son to clinic for a new patient visit. She says that her son was progressing well developmentally and meeting all milestones until three months ago. Since then, she and her husband have noticed a marked restriction in the boy's activities. He keeps to himself, refuses to play with his siblings, speaks only when spoken to, and appears indifferent to the presence of others. Attempts to engage the child in conversation are unsuccessful. He seems disinterested and refuses to make eye contact. While in the examination room, he starts banging his head against the wall. Given this clinical presentation, which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Autism
Childhood disintegrative disorder
Rett disorder
Asperger syndrome
Oppositional defiant disorder
An anxious mother brings in her 12-year-old daughter to your clinic for "severe hair loss". On examination, you find several alopecic patches on her head. While taking a detailed history, you find out that the young girl has been pulling out her hair when stressed. Although she has been indulging in this behavior periodically since childhood, she finds a recent increase in the same. She reveals to you that she is "really nervous" about her upcoming exams, and has disturbed sleep. She also adds that she feels so stressed that she has been avoiding going out with her friends and keeps to her books all the time. She denies any alterations in weight, but does admit to a decreased appetite. What do you think is the underlying diagnosis in this case?
Alopecia areata
Trichotillomania
Lupus erythematosus
Generalized anxiety disorder
Major depressive disorder
An athletic 12-year-old boy complains of left knee pain when he runs and plays sports. The pain resolves when he rests. He has otherwise been well. His physical examination is normal, except for swelling and increased prominence over the left tibial tubercle. A radiograph of the left knee is normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease
Osgood-Schlatter disease
Patellar subluxation
Popliteal cyst
Slipped capital femoral epiphysis
An elderly bedridden patient in the hospital develops cough, fever, and shortness of breath. On examination, the JVP is 4 cm, heart sounds are normal, and there are crackles on inspiration in the right lower lobe. A CXR reveals a new right lower lobe infiltrate and his WBC is 15,000/mL. He was admitted to the hospital 7 days ago for the treatment of congestive heart failure. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Hospital-acquired pneumonia
Community-acquired pneumonia
Atelectasis
Pulmonary embolism
Asymmetric congestive heart failure
An elderly diabetic woman with chronic steroid-dependent bronchospasm has an ileocolectomy for a perforated cecum. She is taken to the ICU intubated and is maintained on broad-spectrum antibiotics, renal dose dopamine, and a rapid steroid taper. On postoperative day 2, she develops a fever of 39.2°C (102.5°F), hypotension, lethargy, and laboratory values remarkable for hypoglycemia and hyperkalemia. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for her deterioration?
Sepsis
Hypovolemia
Adrenal insufficiency
Acute tubular necrosis
Diabetic ketoacidosis
An elderly man is involved in a rear end automobile collision in which he hyperextends his neck. He develops paralysis and burning pain of both upper extremities, while maintaining good motor fun
Anterior cord syndrome
Reflex sympathetic dystrophy
Spinal cord hemisection
Central cord syndrome
Posterior cord syndrome
An ill-appearing 2-week-old baby girl is brought to the emergency room. She is pale and dyspneic with a respiratory rate of 80 breaths per minute. Heart rate is 195 beats per minute, heart sounds are distant, a gallop is heard, and she has cardiomegaly on x-ray. An echocardiogram demonstrates poor ventricular fun
Endocardial fibroelastosis
Pericarditis
Myocarditis
Glycogen storage disease of the heart
Aberrant left coronary artery arising from pulmonary artery
An infant born at 35 weeks’ gestation to a mother with no prenatal care is noted to be jittery and irritable, and is having difficulty feeding. You note coarse tremors on examination. The nurses report a high-pitched cry and note several episodes of diarrhea and emesis. You suspect which of the following?
Fetal alcohol syndrome
Heroin withdrawal syndrome
Prenatal exposure to marijuana
Cocaine exposure in utero
Tobacco use by the mother
An infant is born prematurely and is small for gestational age. At birth, the infant is obviously ill with jaundice, fever, hepatosplenomegaly, myocarditis, and rashes. Neurologic involvement is prominent, with hydrocephalus, intracranial calcifications, and seizures. The mother has a cat and continued to clean the cat's litter box during the pregnancy. Which of the following is the most likely causative agent?
Cytomegalovirus
Herpes simplex
Rubella virus
Toxoplasma
Treponema pallidum
An infant is delivered at full term by a spontaneous vaginal delivery to a 29-year-old primigravida. At delivery, the infant is noted to have subcostal retractions and cyanosis despite good respiratory effort. The abdomen is scaphoid. On bag and mask ventilation, auscultation of the lungs reveals decreased breath sounds on the left, with heart sounds louder on the right. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Dextrocardia with situs inversus
Pneumonia
Diaphragmatic hernia
Pulmonary hypoplasia
Spontaneous pneumothorax
An irritable 6-year-old child has a somewhat unsteady but nonspecific gait. Physical examination reveals a very mild left facial weakness, brisk stretch reflexes in all four extremities, bilateral extensor plantar responses (Babinski reflex), and mild hypertonicity of the left upper and lower extremities; there is no muscular weakness. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Pontineglioma
Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis
Progressive multi focal leukoencephalopathy
Cerebellar astrocytoma
Tumor of the right cerebral hemisphere
An obese 46-year-old G6P1051 with type 1 diabetes since age 12 presents to your office complaining of urinary incontinence. She has been menopausal since age 44. Her diabetes has been poorly controlled for years because of her noncompliance with insulin therapy. She often cannot tell when her bladder is full, and she will urinate on herself without warning. Which of the following factors in this patient’s history has contributed the most to the development of her urinary incontinence?
Menopause
Obesity
Obstetric history
Age
Diabetic status
An obese 50-year-old woman undergoes a laparoscopic cholecystectomy. In the recovery room, she is found to be hypotensive and tachycardic. Her arterial blood gases reveal a pH of 7.29, PaO2 of 60 mm Hg, and PaCO2 of 54 mm Hg. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient’s problem?
Carbon dioxide (CO2) absorption from induced pneumoperitoneum
Alveolar hypoventilation
Acute pulmonary embolism
Pulmonary edema
Atelectasis from a high diaphragm
An older, overweight man complains of disabling, sharp heel pain every time his foot strikes the ground. The pain is worse in the mornings, preventing him from putting any weight on the heel. X-ray films show a bony spur matching the location of his pain, and physical examination shows exquisite tenderness to direct palpation right over that heel spur. Furthermore, when the ankle is dorsiflexed, the entire inner border of the fascia is tender to palpation. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Epiphysitis of the calcaneus
Plantar fasciitis
Fracture of the posterolateral talar tubercle
Posterior Achilles tendon bursitis
Posterior tibial nerve neuralgia
An otherwise healthy 7-year-old child is brought to you to be evaluated because he is the shortest child in his class. Careful measurements of his upper and lower body segments demonstrate normal body proportions for his age. Which of the following disorders of growth should remain in your differential?
Achondroplasia
Morquio disease
Hypothyroidism
Growth hormone deficiency
Marfan syndrome
An out-of-shape, recently divorced, 42-year-old man is trying to impress a young woman by challenging her to a game of tennis. In the middle of the game, a loud "pop" (like a gunshot) is heard, and the man falls to the ground clutching his ankle. He limps off the court with pain and swelling in the back of the lower leg. Although he can still weakly plantar-flex his foot, he seeks medical help the next day because of persistent pain, swelling, and limping. He can put weight on that foot with no exacerbation of the pain, but the motion of taking a step is painful. Which of the following would be the most likely finding on physical examination?
The ankle joint can be abducted farther out than the normal contralateral side
There is crepitation and grating by direct palpation over either malleoli
The ankle joint can be adducted farther in than the normal contralateral side
There is a gap in the Achilles tendon easily felt by palpation
Tapping on the calcaneus is extremely painful
An overweight 12-year-old boy presents with left knee pain that has been going on intermittently for the past three months. Physical activity, especially stair climbing, exacerbates the pain. The boy's mother also points out that he has been limping recently. On physical examination, his anterior left hip is moderately tender to palpation, and when he is asked to stand on his left leg, the right half of his pelvis tilts downward. Which of the following best explains this finding?
Psoas muscle weakness
Quadriceps muscle weakness
Tensor fascia lata weakness
Gluteus muscle weakness
Quadratus lumborum weakness
An ultrasound is performed on a patient with right upper quadrant pain. It demonstrates a large gallstone in the cystic duct but also a polypoid mass in the fundus. Which of the following is an indication for cholecystectomy for a polypoid gallbladder lesion?
Presence of clinical symptoms
Presence of multiple small lesions
Size greater than 0.5 cm
Absence of shadowing on ultrasound
Patient age of older than 25 years
Approximately 6 weeks following a kidney transplant, a 59-year-old woman develops fever, malaise, and myalgias and is found to have a cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection. Which of the following is a potential sequela of CMV infection?
Pyelonephritis
Cholecystitis
Gastrointestinal (GI) ulceration and haemorrhage
Intra-abdominal abscess
Parotitis
At 38 weeks’ gestation, a 4030-g (8.9-lb) boy is delivered by spontaneous vaginal delivery. During the first minute of life he is limp, cyanotic, lacks respiratory effort, has a heart rate of 95/min, flexes his extremities, and grimaces to nasal suctioning. By 5 minutes, he continues to grimace to nasal suctioning, has a weak cry, is well perfused with a heart rate of 160/min, and is kicking both legs. Based on his Apgar scores, when will the child need to be resuscitated?
Indicated at 5 minutes and not at 1 minute
Not enough information to determine
Indicated at 1 and 5 minutes
Indicated at 1 minute and not at 5 minutes
Not indicated at 1 or 5 minutes
At a follow-up routine prenatal visit, the uterine fundus of a healthy 23-year-old pregnant woman is palpated halfway between her symphysis pubis and umbilicus. Which of the following is the most appropriate test to order at this stage of her pregnancy?
Maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein (MSAFP)
Cervical culture for group B Streptoccus (GBS)
Serum human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) titer
Glucose tolerance test
Amniocentesis
At the time of annual examination, a patient expresses concern regarding possible exposure to sexually transmitted diseases. During your pelvic examination, a single, indurated, nontender ulcer is noted on the vulva. Venereal Disease Research Laboratory (VDRL) and fluorescent treponemal antibody (FTA) tests are positive. Without treatment, the next stage of this disease is clinically characterized by which of the following?
Optic nerve atrophy and generalized paresis
Tabes dorsalis
Gummas
Macular rash over the hands and feet
Aortic aneurysm
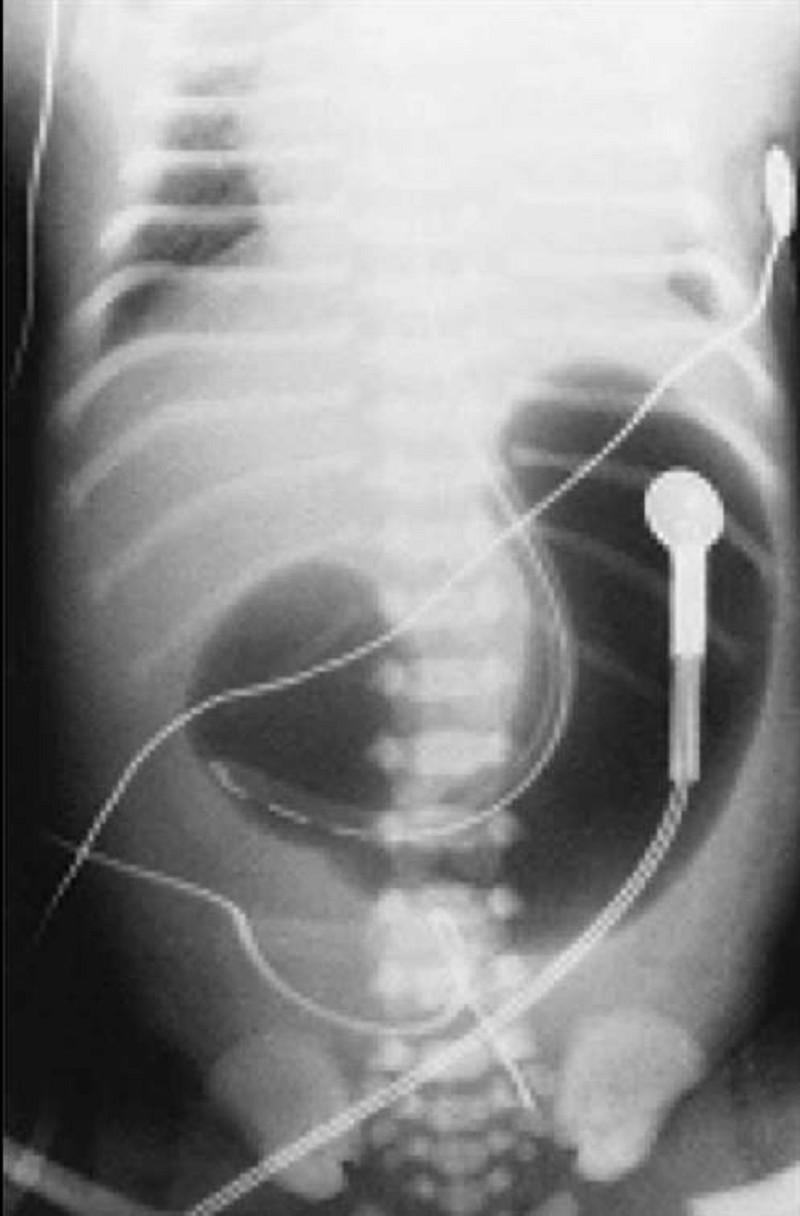
At the time of delivery, a woman is noted to have a large volume of amniotic fluid. At 6 hours of age, her baby begins regurgitating small amounts of mucus and bile-stained fluid. Physical examination of the infant is normal, and an abdominal x-ray is obtained (see below). Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis of this infant’s disorder?
Gastric duplication
Pyloric stenosis
Esophageal atresia
Duodenal atresia
Midgut volvulus
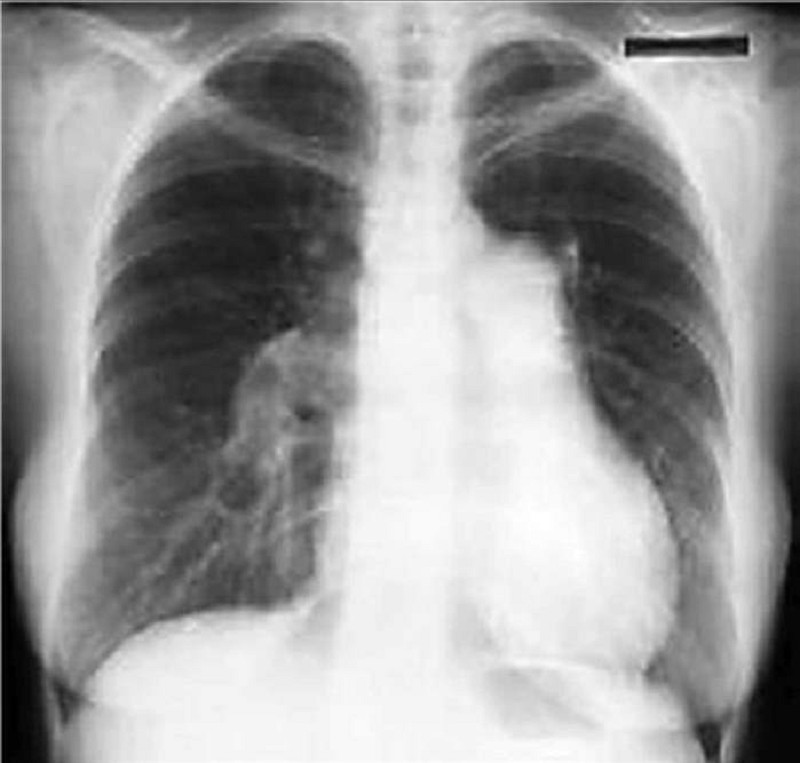
Auscultation of the heart of a 17-year-old boy reveals an increased intensity of the pulmonary component of the second heart sound. He complains of dyspnea on exertion but no other cardiac or pulmonary symptoms. Which of the following explanations is the most likely cause of his dyspnea?
Pulmonary stenosis
Aortic stenosis
MI
Pulmonary hypertension
Systemic hypertension
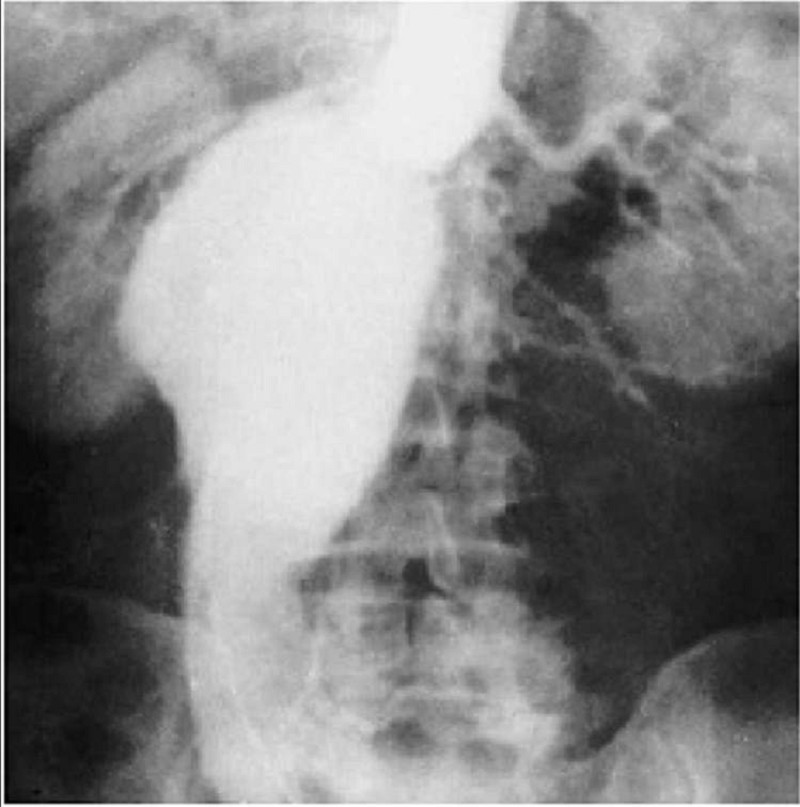
An 80-year-old man is found to have an asymptomatic pulsatile abdominal mass. An arteriogram is obtained (shown below). Which of the following is the most frequent and lethal complication of this condition?
Rupture
Dissection
Acute thromboembolism
High-output congestive heart failure
Myocardial infarction
{"name":"DES C_Diagnosis (13) Prepared : CHILLY", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"A previously healthy 8-year-old boy has a 3-week history of low-grade fever of unknown source, fatigue, weight loss, myalgia, and headaches. On repeated examinations during this time, he is found to have developed a heart murmur, petechiae, and mild splenomegaly. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?","img":"https://cdn.poll-maker.com/18-747524/image.jpeg?sz=1200"}
More Quizzes
Which ctd writer ru?
10514
Find Your Perfect Production
420
100
630
Free Scenic Viewpoints Trivia
201021560
Free Counseling Theory Practice Exam
201021560
Polyatomic Compounds - Test Your Ion Knowledge!
201038640
Find Your Stand: JJBA Guess the Stand Personality
201023773
Free Employee Company Knowledge
201021560
Religion & Society in West II
15822513
Arrhythmia Test Online: Can You Master Heart Rhythm Drugs?
201025455
What Car Best Fits You? Free to Find Your Ride
201025455