Suppose the cost of flying a 200-seat plane for an airline is $100,000 and there are 10 empty seats on a flight, The airline should sell a ticket to a standby passenger only if the passenger is willing to pay
A. More than $500.
B. This cannot be determined from the information given.
C. More than $300.
D. More than $200
The opportunity cost of an item is
A. The dollar value of the item
B. The number of hours needed to earn money to buy the item.
C. What you give up to get that item.
D. Usually less than the dollar value of the item
In a market economy, economic activity is guided by
A. The government
B. self-interest and prices
C. Central planners
D. corporations
The mainstream view among economists is that
A. Society faces a tradeoff between unemployment and inflation, but only in the short run.
B. Society faces a tradeoff between unemployment and inflation, both in the short run and in the long run.
C. No tradeoff exists between unemployment and inflation, either in the short run or in the long run.
D. Society faces a tradeoff between unemployment and inflation, but only in the long run
Consider Mandy's decision to go to college. If she goes to college, she will spend $20,000 on tuition, $10,000 on room and board, and $2,000 on books. If she does not go to college, she will earn $18,000 working in a store and spend $8,000 on room and board. Mandy's cost of going to college is
A. $50,000
B. $58,000
C. $42,000
D. $32,000
A construction company has built 30 houses so far this year at a total cost to the company of $7.5 million. If the company builds a 31st house, its total cost will increase to $7.76 million. Which of the following statements is correct?
A. For the first 30 houses, the average cost per house was $250,000.
B. The marginal cost of the 31st house, if it is built, will be $260,000.
C. If the company can experience a marginal benefit of $275,000 by building the 31st house, then the company should build it.
D. All of the above are correct.
When the government implements programs such as progressive income tax rates, which of the following is likely to occur?
A. Equality is decreased and efficiency is increased.
B. Equality is increased and efficiency is increased
C. Equality is increased and efficiency is decreased
D. Equality is decreased and efficiency is decreased
If the government were to intervene and set the price of a dozen eggs above the market price, then we would expect, relative to the market outcome.
A. A decrease in the number of eggs people want to buy and a decrease in the number of eggs farmers want to sell.
B. A decrease in the number of eggs people want to buy and an increase in the number of eggs farmers want to sell.
C. An increase in the number of eggs people want to buy and a decrease in the number of eggs farmers want to sell.
D. An increase in the number of eggs people want to buy and an increase in the number of eggs farmers want to sell.
The invisible hand's ability to coordinate the decisions of the firms and households in the economy can be hindered by
A. Enforcement of property rights.
B. Too much attention paid to efficiency.
C. Increased competition in markets.
D. Government actions that distort prices
Betty's Bakery bakes fresh bread every morning. Any bread not sold by the end of the day is thrown away. A loaf of bread costs Betty $2.00 to produce, and she prices loaves of bread at $3.50 per loaf. Suppose near the end of one day Betty still has 12 loaves of bread on hand. Which of the following is correct?
A. Betty should only sell the remaining bread for $2.00 per loaf or more since that is what the bread costs to make.
B. Betty should be willing to sell the remaining bread for any price above $0 per loaf since she will have to throw it away if she does not sell it for something.
C. Betty should just throw the bread away and change the price of her bread starting tomorrow to make sure she sells all of her bread each day.
D. Betty should only sell the remaining bread for $3.50 per loaf since that is the regular price.
The word "economy" comes from the Greek word oikonomos, which means
A. "environment"
B. "one who makes decisions"
C. "one who manages a household"
D. "production"
Suppose the cost of operating a 75 room hotel for a night is $6,000 and there are 5 empty rooms for tonight. If the marginal cost of operation one room for one night is $40, the hotel manager should rent one of the empty rooms only if a customer is willing to pay
A. More than $40, as the average benefit will exceed the marginal cost.
B. More than $80, as the marginal benefit will exceed the marginal cost.
C. More than $80, as the average benefit will exceed the marginal cost.
D. More than $40, as the marginal benefit will exceed the marginal cost.
One advantage market economies have over centrally-planned economies is that market economies
A. Provide an equal distribution of goods and services to households.
B. Solve the problem of scarcity.
C. Are more efficient.
D. Establish a signficant role for government in the allocation of resources.
In most societies, resources are allocated by
A. A single central planner
B. The combined actions of millions of households and firms.
C. Those firms that use resorces to provide goods and services.
D. A small number of central planners.
To increase the living standards, public policy should
A. Ensure a greater degree of equality, taking all income-earners into account.
B. Move workers into jobs directly from high school.
C. Make unemployment benefits more generous.
D. Ensure that workers are well educated and have the necessary tools and technology.
During the early 1920s in Germany, prices
A. Tripled monthly
B. Doubled monthly
C. Doubled annually.
D. Tripled annually.
In 2011, the average American earned about $48,000 while the average Nigerian earned about $1,200. Which of the following statements is likely?
A. The average american purchases more televisions than the average Nigerian.
B. The average american has better nutrition and healthcare than the average Nigerian.
C. The average American has a longer life expectancy than the average Nigerian
D. All of the above are correct
The economy of the former Soviet Union is best described as a
A. Market economy
B. centrally-planned economy
C. Primitive economy
D. Hybrid economy
Making rational decisions "at the margin" means that people
A. Always calculate the dollar costs for each decision.
B. Evaluate how easily a decision can be reversed if problems arise.
C. Make those decisions that do not impose a marginal cost.
D. Compare the marginal costs and marginal benefits of each decision.
Most economists believe that an increase in the quantity of money results in
A. An increase in the demand for goods and services.
B. Lower unemployment in the short run.
C. Higher inflation in the long run.
D. All of the above are correct.
Government policies designed to equalize the distribution of economic well-being include (i) the welfare system (ii) unemployment insurance (iii) progressive income tax
A. (i), (ii), and (iii)
B. (i) only
C. (ii) only
D. (i) and (ii) only
People are willing to pay more for a diamond than for a bottle of water because
A. The marginal benefit of an extra diamond far exceeds the marginal benefit of an extra bottle of water
B. Producers of diamonds have a much greater ability to manipulate diamond prices than produces of the water have to manipulate water prices
C. The marginal cost of producing an extra diamond far exceeds the marginal cost of producing an extra bottle of water.
D. Water prices are held artificially low by governments, since water is necessary for life.
Central planning refers to
A. Markets guiding economic activity. Today many countries that had this system have abandoned it.
B. Markets guiding economic activity. Today many countries that did not have this system have implemented it.
C. Government guiding economic activity. Today many countries that did not have this system have implemented it.
D. Government guiding economic activity. Today many countries that had this system have abandoned it.
When a society cannot produce all the goods and services people wish to have, it is said that the economy is experiencing
A. scarcuty
B. inefficiencies
C. surpluses
D. inequalities
A certain state legislature is considering an increase in the state gasoline tax. Representative Campbell argues that an increase in the gasoline tax would harm low-income drivers disproportionately. Representative Richards responds by saying that low-income drivers own smaller cars that use less gasoline, and that low-income drivers therefore would not be harmed disproportionately.
A. Representative Campbell's arguments are based primarily on equality, while Representative Richards' argument is based primarily on efficiency.
B. Both representatives' arguments are based primarily on equality.
C. Both representatives' arguments are based primarily on efficiency.
D. Representative Campbell's argument is based primarily on efficiency, while Representative Richards' argument is based primary on equality.
President Gerald Ford referred to inflation as
A. A fly in the ointment.
B. A necessary evil to combat high unemployment
C. A blight on our nation's economy
D. Public enemy number one
One effect of the government-imposed seat belt law in the U.S. Has been
A. An increase in the number of accidents
B. A dramatic decrease in the number of driver deaths.
C. A dramatic decrease in the number of pedestrian deaths.
D. Safer driving.
When the government redistributes income from the wealthy to the poor
A. Both efficiency and equality are improved
B. Neither efficiency nor equality are improved
C. Efficiency is improved, but equality is not.
D. Equality is improved, but efficiency is not
When the government prevents prices from adjusting naturally to supply and demand,
A. It improves efficiency but reduces equality.
B. It adversely affects the allocation of resources.
C. It improves equality and efficiency.
D. It equates the amount buyers want to buy with the amount sellers want to sell.
For which of the following individuals would the opportunity cost of going to college be the highest?
A. A student who is the best player on his college basketball team, but who lacks the skills necessary to play professional basketball
B. A famous, highly-paid actor who wants to take time away from show business to finish college and earn a degree
C. A student with average grades who has never held a job
D. A promising young mathematician who will command a high salary once she earns her college degree
Benefits from trade would not include
A. A greater variety of goods and services becoming available
B. Less competition
C. Lower prices
D. The ability of people and nations to specialize
The fact that different countries experience different standards of living is largely explained by differences in those countries'
A. populations
B. Productivity levels
C. locations
D. None of the above is correct. Economists are puzzled by differences in standards of living around the world.
Which of the following is not generally regarded by economists as a legitimate reason for the government to intervene in a market?
A. To promote equality
B. To promote efficiency
C. To protect an industry from foreign competition
D. To enforce property rights
Rick buys a 1966 Mustang for $3,000, planning to restore and sell the car. He goes on to spend $9,000 restoring the car. At this point he can sell the car for $10,000. As an alternative, he can spend an additional $3,000 replacing the engine. With a new engine the car would sell for $13,000. Rick should
A. Sell the car now for $10,000
B. Never try such an expensive project again.
C. Complete the repairs and sell the car for $13,000
D. Be indifferent between (i) selling the car now and (ii) replacing the engine and then selling it
The term market failure refers to
A. A firm which is forced out of business because of losses.
B. An unsuccessful advertising campaign which reduces demand for a product.
C. A situation in which the market on its own fails to allocate resources efficiently
D. A situation in which competition among firms becomes ruthless
In the United States, incomes historically have grown about 2 percent per year. At this rate, average income doubles every
A. 25 years
B. 15 years
C. 45 years
D. 35 years
Suppose that a country that has a high level of output per person agrees to trade with a country that has a low level of output per person. Which country can benefit?
A. Only the one with a high level of output per person
B. both
C. Only the one with a low level of output per person.
D. neither
The business cycle is the
A. Irregular fluctuations in economic activity
B. Positive relationship between the quantity of money in an economy and inflation.
C. Relationship between unemployment and inflation.
D. Predictable changes in economic activity due to changes in government spending and taxes.
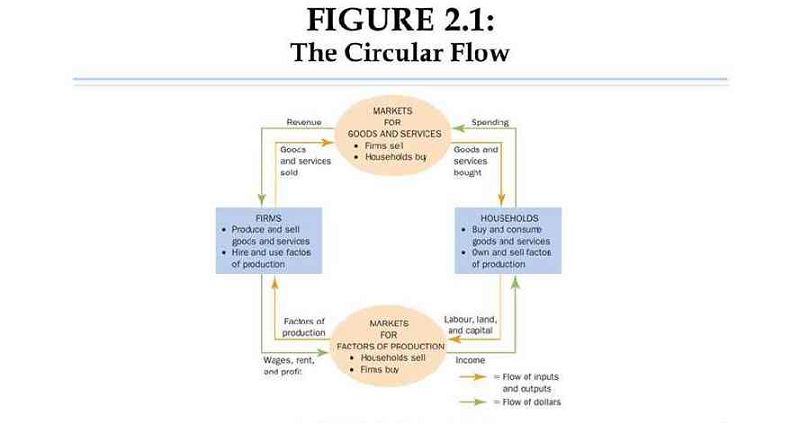
Refer to Figure 2-3. Which of the following is an activity undertaken by the actors in rectangle 2?
A. Produce and sell goods and services
B. Exchange goods and services between firms and households
C. Hire and use factors of production
D. Own and sell factors of production
Which of the following is an example of a normative - as opposed to a positive - statement?
The US employment rate is increased to 10 percent in 2009.
B. The US income tax rate increases with the amount of income earned.
C. The discount rate is the interest rate the Federal Reserve charges banks to borrow funds.
D. The government should increase the tax on gasoline.

Refer to Figure 2-2. If the flow of goods and services is part of what is represented by the inner loop of this circular-flow diagram, then
A. The flow of income paid to households is also part of what is represented by the inner loop
B. The flow of revenue to firms is also part of what is represented by the inner loop
C. The flow of factors of production is also part of what is represented by the inner loop
Households must be sellers of output
John Maynard Keynes described economics as an easy subject at which very few excel. Which of the following is not one of the reasons Keynes gave for why so few people excel at the study of economics?
A. An economist must also be a mathematician, historian, statesman, and philosopher in some degree.
B. An economist must be purposeful and disinterested in a simultaneous mood.
C. An economist must understand environmental science, regulation, and political science.
D. An economist must understand symbols and speak in words.
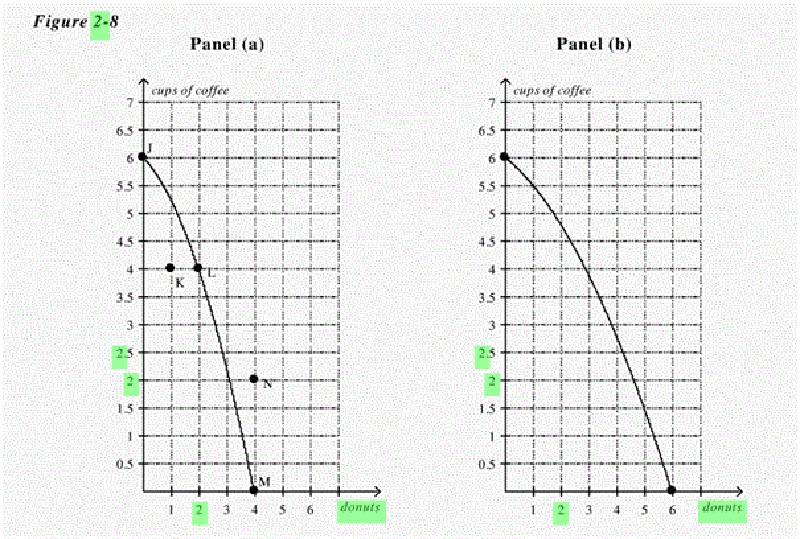
Refer to Figure 2-9, Panel (a). To gain 2 donuts by moving from point L to point M, society must sacrifice
A. efficiency
B. employment.
C. 4 cups of coffee
D. More than one of the above is correct
Which of the following is correct?
A. A horizontal line has a zero slope, and a vertical line has an infinite slope.
B. A horizontal line has a slope of 1, and a vertical line has a slope of -1.
C. A horizontal line has an infinite slope, and a vertical line has a zero slope.
D. A horizontal line has a slope of -1, and a vertical line has a slope of 1.
Economic models are built with
A. Facts about the legal system
B. Statistical forecasts
C. Recommendations concerning public policies
Assumptions
Which types of models are built with assumptions?
A. Economic models, but not models in other disciplines such as physics and biology
B. Economic models as well as models in other disciplines such as physics and biology
C. Models that are built for teaching purposes but not for research purposes
D. Bad models
An assumption an economist might make while studying international trade is
There are only two countries
Countries only produce two goods
C. Technology does not change
All of the above are possible assumptions
Suppose price is measured along the vertical axis on a graph. When price changes, there will be a
A. Movement along the curve
B. Change in the slope of the curve.
C. Rotation of the curve
D. Shift of the curve.
Which of the following would likely be studied by a macroeconomist rather than a microeconomist?
A. The effect of an increase in the alcohol tax on the market for beer
B. The effect of a price war in the airline industry
C. The effect of an increase in the minimum wage on an economy's overall rate of unemployment
D. The effect of foreign competition on the domestic auto industry
| Hotdogs | Burgers |
| 1800 | 0 |
| 1350 | 450 |
| 900 | 750 |
| 450 | 975 |
| 0 | 1125 |
What is the opportunity cost to Picnicland of increasing the production of hotdogs from 450 to 900?
A. 225 burgers
B. 300 burgers
C. 150 burgers
D. 450 burgers
Almost all economists agree that local and state governments should
A. Eliminate subsidies to professional sports franchises
B. Copy economic policy from Washington, D.C.
C. Increase subsidies to professional sports franchises
D. Prevent companies from outsourcing work
The Council of Economic Advisers
A. Was created in 1776 and consists of three members and a staff of several dozen economists.
B. Was created in 1946 and consists of thirty members and a staff of a dozen economists
C. Was created in 1776 and consists of thirty members and a staff of a dozen economists
D. Was created in 1946 and consists of three members and a staff of several dozen economists.
Suppose you like to make, from scratch, pies filled with banana cream and vanilla pudding. You notice that the price of bananas has increased. As a result, your demand for vanilla pudding would
A. decrease
B. increase
C. Be unaffected
D. There is insufficient information given to answer the question.
Good X and good Y are substitutes. If the price of good Y increases, then the
A. Demand for good X will decrease
B. Quantity demanded of good X will increase
C. Quantity demanded of good X will decrease
D. Demand for good X will increase
If a study by medical researchers finds that eating brown rice causes weight loss while eating white rice causes weight gain, then we likely would see
A. No change in demand for either type of rice because weight loss is not a determinant of demand
B. A decrease in demand for brown rice and an increase in demand for white rice
C. An increase in demand for both brown and white rice
D. An increase in demand for brown rice and a decrease in demand for white rice.
When a shortage exists in a market, sellers
A. Raise price, which decreases quantity demanded and increases quantity supplied until the shortage is eliminated
B. Lower price, which decreases quantity demanded and increases quantity supplied until the shortage is eliminated
C. Raise price, which increases quantity demanded and decreases quantity supplied until the shortage is eliminated.
D. Lower price, which increases quantity demanded and decreases quantity supplied until the shortage is eliminated
If the supply of a product increases, then we would expect equilibrium price
A. And equilibrium quantity to both increase
B. To decrease and equilibrium quantity to increase
C. To increase and equilibrium quantity to decrease
D. And equilibrium quantity to both decrease
Workers at a bicycle assembly plant currently earn the mandatory minimum wage. If the federal government increases the minimum wage by $1.00 per hour, then it is likely that the
A. Firm must increase output to maintain profit levels.
B. Supply of bicycles will shift to the left
C. Demand for bicycle assembly workers will increase
D. Supply of bicycles will shift to the right.
Suppose that Amanda receives a pay increase. We would expect
A. To observe Amanda moving down and to the right along her given demand curve.
B. Amanda's demand for each of two goods that are complements to increase
C. Amanda's demand for inferior goods to decrease
D. Amanda's demand for normal goods to decrease
Assume Diana buys computers in a competitive market. It follows that
A. Diana has a limited number of sellers to turn to when she buys a computer
B. Diana will find herself negotiating with sellers whenever she buys a computer.
C. if Diana buys a large number of computers, the price of computers will rise noticeably.
D. None of the above is correct.
A competitive market is one in which there
A. Are many sellers, and they compete with one another in such a way that some sellers are always being forced out of the market
B. Are many sellers, and each seller has the ability to set the price of his product.
C. Are so many buyers and so many sellers that each has a negligible impact on the price of the product.
D. Is only one seller, but there are many buyers
Which of the following events would cause both the equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity of number two grade potatoes to increase if number two grade potatoes are an inferior good?
A. A decrease in consumer income
B. Greater government restrictions on agricultural chemicals
C. An increase in consumer income
D. Fewer government restrictions on agricultural chemicals
What would happen to the equilibrium price and quantity of lattes if consumers' incomes rise and lattes are a normal good?
A. The equilibrium price would decrease, and the equilibrium quantity would increase
B. Both the equilibrium price and quantity would decrease.
C. Both the equilibrium price and quantity would increase
D. The equilibrium price would increase, and the equilibrium quantity would decrease
In markets, prices move toward equilibrium because of
A. Government regulations placed on market participants
B. Buyers' ability to affect market outcomes.
C. The actions of buyers and sellers.
D. Increased competition among sellers.
Which of the following is not a determinant of demand?
A. The price of a resource that is used to produce the good
B. The price of a complementary good
C. The price of a substitute good
D. The price of the good next month
An example of a perfectly competitive market would be the
A. Shampoo market
B. cable TV market
C. Breakfast cereal market
D. Soybean market
Which of the following events must cause equilibrium quantity to rise?
A. Demand increases and supply decreases
B. Demand and supply both decrease
C. Demand decreases and supply increases
D. Demand and supply both increase
Equilibrium price must increase when demand
A. Decreases and supply does not change, when demand does not change and supply increases, and when demand decreases and supply increases simultaneously
B. Increases and supply does not change, when demand does not change and supply decreases, and when demand increases and supply decreases simultaneously
C. Increases and supply does not change, when demand does not change and supply decreases, and when demand decreases and supply increases simultaneously
D. Decreases and supply does not change, when demand does not change and supply increases, and when demand increases and supply decreases simultaneously
A tax imposed on a buyers of a good will
A. Raise the prices buyers pay and lower the effective prices sellers receive.
B. Lower the price buyers pay and raise the effective price sellers receive
C. Raise both the price buyers pay and the effective price sellers receive
D. Lower both the prices buyers pay and the effective price sellers receive
An outcome that can result from either a price ceiling or a price floor is
A. A shortage in the market
B. Long lines of frustrated buyers
C. A nonbinding price control
D. A surplus in the market
The incidence of a tax falls more heavily on
A. Consumers than producers if demand is more inelastic than supply
B. Producers than consumers if supply is more inelastic than demand
C. Consumers than producers if supply is more elastic than demand
D. All of the above are correct
If a price ceiling is not binding, then
A. The equilibrium price is above the price ceiling
B. The equilibrium price is below the price ceiling
C. It has no legal enforcement mechanism
D. None of the above is correct because all price ceilings must be binding.
After a binding price floor becomes effective, a
A smaller quantity of the good is bought and sold
B. A larger quantity of the good is demanded
C. A smaller quantity of the good is supplied
D. All of the above are correct
A tax on the sellers of coffee mugs
A. Has no effect on the size of the coffee mug market.
B. Increases the size of the coffee mug market.
C. Decreases the size of the coffee mug market
D. May increase, decrease, or have no effect on the size of the coffee mug market.
A price floor is binding when it is set
A. Below the equilibrium price, causing a surplus
B. Above the equilibrium price, causing a surplus
C. Below the equilibrium price, causing a shortage.
D. Above the equilibrium price, causing a shortage
Which of the following causes a shortage of a good?
A. A binding price floor
B. A binding price ceiling
C. A tax on the good
D. None of the above is correct
The imposition of a binding price ceiling on a market causes
A. Quantity demanded to be greater than quantity supplied
B. Quantity demanded to be less than quantity supplied
C. Quantity demanded to be equal to quantity supplied
D. The price of the good to be greater than its equilibrium price
Consider the market for gasoline. Buyers
A. And sellers would lobby for a price ceiling
B. Would lobby for a price floor, whereas sellers would lobby for a price ceiling
C. Would lobby for a price ceiling, whereas sellers would lobby for a price floor
And sellers would lobby for a price floor.
Economists blame the long lines at gasoline stations in the U.S. In the 1970s on
A. Consumers who bought gasoline frequently, even when their cars' gasoline tanks were nearly full.
B. Major oil companies operating in the U.S.
C. the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC)
D. U.S. Government regulations pertaining to the price of gasoline.
In "Venezuela Versus the Market," the price control placed on coffee
A. Resulted in higher profits for coffee growers.
B. Created a shortage of coffee.
C. Increased coffee exports to other countries
D. Increased the amount of land and coffee used in production
If the government removes a binding price ceiling from a market, then the price received by sellers will
A. decrease, and the quantity sold in the market will decrease
B. increase, and the quantity sold in the market will decrease
C. increase, and the quantity sold in the market will increase.
D. decrease, and the quantity sold in the market will increase.
The price paid by buyers in a market will increase if the government (i) increases a binding price floor in that market. (ii) increases a binding price ceiling in that market (iii) decreases a tax on the good sold in that market
A. (ii) only
B. (i), (ii), and (iii)
C. (iii) only
D. (i) and (ii) only
A key lesson from the payroll tax is that the
A. True burden of a tax cannot be legislated.
B. Tax is a tax solely on firms that hire workers
C. Tax is a tax solely on workers
D. Tax eliminates any wedge that might exist between the wage that firms pay and the wage that workers receive
A result of welfare economics is that the equilibrium price of a product is considered to be the best price because it
A. Maximizes both the total revenue for firms and the quantity supplied of the product
B. Minimizes the level of welfare payments
C. Maximizes the combined welfare of buyers and sellers
D. Minimizes costs and maximizes output
Bob purchases a book for $6, and his consumer surplus is $2. How much is Bob willing to pay for the book?
A. $8
B. $2
C. $4
D. $6
Moving production from a high-cost producer to a low-cost producer will
A. Raise total surplus
B. Raise producer surplus but lower consumer surplus
C. Lower producer surplus
D. Lower total surplus
Suppose your own demand curve for tomatoes slopes downward. Suppose also that, for the last tomato you bought this week, you paid a price exactly equal to your willingness to pay. Then
A. You already have bought too many tomatoes this week.
B. You should buy more tomatoes before the end of the week.
C. Your consumer surplus on all of the tomatoes you have bought this week is zero.
D. Your consumer surplus on the last tomato you bought is zero.
If a market is allowed to adjust freely to its equilibrium price and quantity, then an increase in demand will
A. Increase producer surplus
B. Reduce producer surplus
C. Not affect producer surplus
D. Any of the above are possible
In a market, the marginal buyer is the buyer
Who would be the first to leave the market if the price were any higher
B. Who is willing to buy exactly one unit of the good
C. Whose willingness to pay higher than that of all other buyers and potential buyers.
D. Whose willingness to pay is lower than that of all other buyers and potential buyers.
Denise values a stainless steel dishwasher for her new house at $500, but she succeeds in buying one for $350. Denise's consumer surplus is
A.$350
B. $850
C. $500
D. $150
| Seller | Cost |
| Abby | $1,600 |
| Bobby | $1,300 |
| Dianne | $1,100 |
| Evaline | $900 |
| Carlos | $800 |
A. $100
B. $500
C. $800
D. $400
When markets fail, public policy can
A. Always remedy the problem and increase economic efficiency.
B. Do nothing to improve the situation
C. Potentially remedy the problem and increase economic efficiency
D. In theory, remedy the problem, but in practice, public policy has proven to be ineffective.
When the supply of a good decreases and the demand for the good remains unchanged, consumer surplus
A. Is unchanged
B. May increase, decrease, or remain unchanged.
C. increases.
D. decreases.
In which of the following instances would the deadweight loss of the tax on cartons of cigarettes increase by a factor of 9?
A. The tax on cartons of cigarettes increases from $10 to $20.
B. The tax on cartons of cigarettes increases from $10 to $11.11.
C. The tax on cartons of cigarettes increases from $10 to $90
D. The tax on cartons of cigarettes increases from $10 to $30
Anger over British taxes played a significant role in bringing about the
A. Election of John Adams as the second American president.
B. War of 1812.
C. American Revolution
D. "no new taxes" clause in the U.S. Constitution
In a 2012 Wall Street Journal column, economists Edward Prescott and Lee Ohanian claimed that in order to promote faster economic growth, the government should
A. Increase tax rates on individuals with high incomes, and leave tax rates on other individuals unchanged
B. Equalize tax rates on all individuals, regardless of how much they earn
C. Decrease tax rates on income and increase tax rates on consumption
D. Increase the after-tax benefits to successful entrepeneurship and risk-taking
Which of the following scenarios is not consistent with the Laffer curve?
A. The tax rate is very high, and tax revenue is very high.
B. The tax rate is very low, and tax revenue is very low.
C. The tax rate is very high, and tax revenue is very high.
D. The tax rate is moderate (between very high and very low), and tax revenue is relatively high.
Suppose the government increases the size of a tax by 20 percent. The deadweight loss from that tax
A. Increases by 20 percent
B. Increases by more than 20 percent
C. Decreases by 20 percent
D. Increases but by less than 20 percent
As the size of a tax rises, the deadweight loss
A. rises, and tax revenue first rises, then falls.
B. falls, and tax revenue first rises, then falls.
C. Rises as does tax revenue
D. Falls as does tax revenue
Who once said that taxes are the price we pay for civilized society
A. George Washington
B. Aristotle
C. Oliver Wendell Holmes, Jr.
D. Ronald Reagan
The higher a country's tax rates, the more likely that country will be
A. Experiencing small deadweight losses
B. On the positively sloped part of the Laffer curve
C. On the negatively sloped part of the Laffer curve
D. At the top of the Laffer curve
In which of the following cases is it most likely than an increase in the size of a tax will decrease tax revenue?
A. The price elasticity of demand and the price elasticity of supply are both large.
B. The price elasticity of demand is large, and the price elasticity of supply is small.
C. The price elasticity of demand and the price elasticity of supply are both small.
D. The price elasticity of demand is small, and the price elasticity of supply is large.
In 2012, in The Wall Street Journal, economists Peter Diamond and Emmanuel Saez wrote that, according to their analysis, the federal government's tax revenue would be maximized if the marginal income tax rate on individuals with the highest earnings were in or near the range of
A. 10 percent to 30 percent
B. 30 percent to 50 percent
C. 50 percent to 70 percent
D. 70 percent to 90 percent
Ronald Reagan believed that reducing income tax rates would
A. Do little, if anything, to encourage hard work.
B. Result in large increases in deadweight losses.
C. Raise economic well-being and perhaps even tax revenue
D. Lower economic well-being, even though tax revenue could possibly increase
In which of the following instances would the deadweight loss of the tax on airline tickets increase by a factor of 9?
A. The tax on airline tickets increases from $20 per ticket to $90 per ticket.
B. The tax on airline tickets increases from $15 per ticket to $135 per ticket
C.The tax on airline tickets increases from $20 per ticket to $60 per ticket
D. The tax on airline tickets increases from $15 per ticket to $60 per ticket.
Supply-side economics is a term associated with the views of
A. Ronald Reagan and Arthur Laffer
B. Bill Clinton and Greg Mankiw
C. Milton Friedman.
D. Karl Marx
As the tax on a good increases from $1 per unit to $2 per unit to $3 per unit and so on, the
A. Tax revenue increases at first, but it eventually peaks and then decreases
B. Tax revenue always decreases, and the deadweight loss always increases
C. Tax revenue increases, and the deadweight loss always increases
D. Deadweight loss increases at first, but it eventually peaks and then decreases.
{"name":"Suppose the cost of flying a 200-seat plane for an airline is $100,000 and there are 10 empty seats on a flight, The airline should sell a ticket to a standby passenger only if the passenger is willing to pay", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Suppose the cost of flying a 200-seat plane for an airline is $100,000 and there are 10 empty seats on a flight, The airline should sell a ticket to a standby passenger only if the passenger is willing to pay, The opportunity cost of an item is, In a market economy, economic activity is guided by","img":"https://cdn.poll-maker.com/10-458132/slide-9.jpg?sz=1200-000000100053"}
More Quizzes
Can you guess the emoji country
9417
Test tester
210
Rrrrr
320
Atopic Skin Challenge with Dr. Eman Altantawy
940
Karen Fraction Trivia: Test Your seaQuest DSV Knowledge
201029681
Qualitative Methods
15822372
Annoy Squidward Day: Test Your Mischief Mastery
201060650
Free Confluent Kafka Knowledge Assessment
201029029
Free Homeostasis: Practice & Review
201026475
Am I a Christian: Unveil Your True Faith
201025277
Test Your Saola Knowledge: What Is a Saola
201038877
Test Your Skills: Multiplying and Dividing Monomials
201068413