1. Which of the following is NOT part of the normal process of cloning recombinant DNA in bacteria?
A- Restriction endonuclease digestion of cellular and plasmid DNA
B- Production of recombinant DNA using DNA ligase and a mixture of digested cellular and plasmid DNA
C- Separation of recombinant DNA by electrophoresis and use of Southern Blotting to determine where the desired recombinant DNA migrates
D- Transformation of bacteria by recombinant DNA plasmids and selection using antibiotics
2. Which of the following statements about electrophoresis is INCORRECT
A- Electrophoresis is the movement of charged molecules in an electrical field
B- Negatively charged molecules will move towards the positively charged electrode (anode)
C- All proteins are positively charged therefore they will move towards the cathode
D- In gel electrophoresis molecules are separated by charge and size
3. The PCR technique involves the use of:
Synthesized oligonucleotide primers
B- DNA template
C- DNA polymerase
D- All of the above
4. In one form of familial isolated growth hormone deficiency, deletion of an exon of a gene on chromosome 17 alters the protein product. In heterozygotes, this protein product then binds with the normal protein product encoded by the normal copy of the gene on chromosome 17, disabling the normal growth hormone molecule. This is best described as an example of:
A- Dominant-negative effect
B- Haploinsufficiency
C- Gain-of-function mutation
D- Nonsense mutation
5. The major cause of small-scale mutations in human cells is:
A- Failure to repair DNA damage
B- Errors arising during DNA replication
C- Chromosomal translocations
D- Reverse transcription of mRNA to cDNA
6. Phenotype is:
A- One of the alternate forms of a gene
B- The genetic make-up of a cell or organism
C- The observed attributes of a cell /individual which are a result of the interaction of genotype and environment
D- The precise allelic composition of a cell or organism
7. Failure of a chromosome in the segregation process during cell division is known as:
A- Chromosomal replication
B- Chromosomal location
C- Chromosomal condensation
D- Chromosomal non-disjunction
8. Which of the following does NOT play a role in the regulation of transcription
A- Transcription factors
B- Silencer sequences
C- Promoter
D- Spliceosome
9. PAX6 is an important gene for the development of the:
A- Antenna
B- Leg
C- Segments
D- Eye
10. Unaffected parents of a child with cystic fibrosis attend a genetic counseling clinic when trying to decide whether they should have another baby. The likelihood of them having another child with cystic fibrosis is:
A- 1 in2
B- 1 in 4
C- 1 in 6
D- 2 in 8
11. Trisomy 21 means…
A- Extra chromosome 21
B- Missing chromosome 21
C- Section of chromosome 21 missing
D- Inversion in chromosome 21
12. Which of the following is NOT part of maternal blood screen known as Triple Test
A- Alpha foetal protein (AFP)
B- Estriol
C- Human chorionic gonadotrophin (HCG)
D- Progesterone
13. Which of the following genotypes causes Turner syndrome?
A- XO
B- XX
C- XXY
D- XYY
14. Which of the following are transcription factors involved with tumorigenesis?
A- Bcl-2 and Bax
B- fos and jun
C- VEGF and tie2
D- Hela and PC3
15. Which of the following is NOT a hallmark of cancer?
A- Sensitivity to apoptosis
B- Ability to invade and form metastases
C- Evasion of growth inhibitory signals
D- Unlimited replicative potential
16. Which of the following factors are NOT part of the regulatory process that helps
A- Signal transduction molecules
B- Growth factor receptors
C- Nuclear transcription factors
D- DNA polymerase
17. The process of extravasation is:
A- The process of forming new blood vessels from pre-existing ones
B- The death of tumour cells by chemotherapy
C- The escape of a tumour cell from a blood or lymphatic vessel
D- The penetration of a cell into a blood or lymphatic vessel
Following 3 questions are based on the following information. In humans, 3 alleles (alleles IA, IB , i) determine blood group type. IA and IB are co-dominant while I is recessive to both IA and IB 18. A man with blood type A and a woman with blood type B could NEVER produce a child with blood type
A- O
B- A
C- B
D- AB
E- None of teh above
19. A person with type B blood could have which genotype type
A- IB/IB
B- IB/I
C- i/I
D- IB/IB or IB/I
E- IA/i
20. Which of the following outcomes is possible
A- An O child from the marriage of two A individuals
B- An AB child from the marriage of an A to an O?
C- An O child from the marriage of an AB to an A
D- Answers a and b
E- Answers a and c
F- Answers a, b and c
21. Central Dogma in genetics describes
A- Pattern of information flow in the cell
B- Pattern of chromosomal inheritance in populations
C- Role of mutations in disease
D- Role of promoters
22. Complete the following sentence: Transcription factors…
A- Promote the synthesis of mRNA in the expression of a gene
B- Inhibit the translation of mRNA in the expression of a gene
C- Promote the synthesis of DNA
D- Inhibit DNA synthesis
23. Which phase of Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is routinely carried out at 72C?
A- Annealing of primers to the separated DNA strands
B- Extension/Polymerisation adding on nucleotide bases
C- Denaturation of the double-stranded DNA
D- Both annealing and extension phases
24. Which of the following allows identification and selection of cloned DNA in a bacterial plasmid?
A- Multiple cloning site
B- Origin of replication site
C- Restriction enzyme site
D- Antibiotic resistance gene
25. Automated Sanger sequencing is based on:
A- Utilization of a DNA template
B- Utilization of 4 types of fluorescently labelled dideoxynucleosides
C- Utilization of DNA polymerases
D- A, B and C
26. Random inactivation of most of the genes on one or other of the x chromosomes in each of the cells of a human female early in embryonic development is known as:
A- Heterozygosity
B- Lyonization
C- Dominance
D- Autosomal mosaicism
27. Piebaldism is caused by mutations in which gene?
A- KIT
B- PAX6
C- SRY
D- HOXD13
28. Which of these gene classes is highest up the hierarchy?
A- Pair-rule
B- Gap
C- Segment-polarity
D- Homeotic
29. Which enzyme is the last to act in the process of Base Excision Repair (BER) by repairing the sugar-phosphate backbone?
A- Deaminase
B- AP endonuclease
C- DNA glycosylase
D- DNA ligase
30. Caspases are a group of protein proteases which cleave/cut proteins at:
A- Arginine residues
B- Asparagine residues
C- Alanin residues
D- Aspartic acid residues
31. Complete the following statement “A highly ionized drug…”
A- Excreted mainly by the kidney
B- Can cross the placental barrier
C- Well absorbed from the intestine
D- Accumulates in the cellular lipids
32. Three babies were mixed up in a hospital. After consideration of the data below, which of the following represent the correct baby and parent combinations?
Couple# Blood Groups Baby # Blood Groups
I A and A 1 B
II A and B 2 O
III B and O 3 AB
A- I-3, II-1, III-2
B- I-1, II-3, III-2
C- I-2, II-3, III-1
D- I-2, II-1, III-3
E-I-3, II-2, III-1
33. A man with type AB blood is married to a woman with type A blood. No other information about couple is known. What are possible blood types of their children
A- A, B, AB, or O
B- AB only
C- A or B only
D- A or AB only
E- None of the above
34- X, Y and Z are linked genes. Based on test-cross data, the frequency of recombination between genes X and Z was determined to be 33.1 map units; between genes X and Y the distance was 11.8 mu; and between Y and Z the distance was 21.3 mu. What is the order of these three genes on the chromosome?
A- X-Y-Z
B- X-Z-Y
C- Y-Z-X
D- Y-X-Z
35. Which of the following primers would allow copying of the following DNA sequence 5’-GCCTAATAAATGCCTAGGTC-3’?
A- 5’-ATGCC-3’
B- 5’-CTGGA-3’
C- 5’-GACCT-3’
D- 5’-GGCAT-3’
36. Microarray analysis can be used to:
A- Determine the intron-exon organization of a cell
B- Determine the concentration of a protein in the cell
C- Determine the stage or time-specific expression of a gene
D- Determine the presence of a DNA sequence in a cell
37. Which one of the following is NOT a step in the processing of pre-messenger RNA to form (primary transcript) messenger RNA?
A- Additional of a Poly-A tail
B- Splicing of the exons
C- Initiation of transcription
D- Capping at the 5’ end
38. Which of the following is the most common type of polymorphism in human genome
A- Variable number of tandem repeats (VNTRs)
B- Insertion/deletion polymorphisms (I/Ds)
C- Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs)
D- All of the above occur in equal frequencies
39. An allele is ___.
A- one of the bases in DNA
B- An alternate form of a gene
C- Present only in males and is responsible for sex determination
D- Found in mitochondria but not in nuclei
40. A nonsense mutation is:
A- A mutation that substitutes an incorrect amino acid
B- A mutation that does not result in any change in amino acid sequence
C- A mutation that deletes a multiple of 3 bases from the sequence
D- A mutation that changes a codon for an amino acid into a termination codon
41. Which of the following is NOT a feature of autosomal dominant inheritance?
A- Manifest in the heterozygous state
B- Each affected person usually has an affected parent
C- If affected individuals are able to reproduce the disorder is likely to be manifest in 50% of the children
D- Carriers are unaffected
42. In which of the following diseases are dominant-negative effects seen
A- Haemophilia
B- Cystic fibrosis
C- Retinoblastoma
D- Marfan syndrome
43. Loss of Bicoid protein in fly causes:
A- Failure for the segments to form
B- Absence of head structures
C- Half the normal number of segments to form
D- Every segment to be affected
44. The normal genes that are found in the genome of an organism and that have the potential to transform a cell to a cancerous cell if they are activated are called
A- Proto-oncogenes
B- Anti-oncogenes
C- Retro-genes
D- Fragile site genes
45. What structural domain of p53 that is the most common place to get a mutation:
A- Activation domain
B- DNA binding domain
C- Oligomerization domain
D- Regulatory domain
46. The sequence of one strand of DNA is 5’-TCGATC-3’. The sequence of the complementary strand would be ___.
A- 5’ AGCTAG 3’
B- 5’ TCGATC 3’
C- 5’ CTAGCT 3’
D- 5’ GATCGA 3’
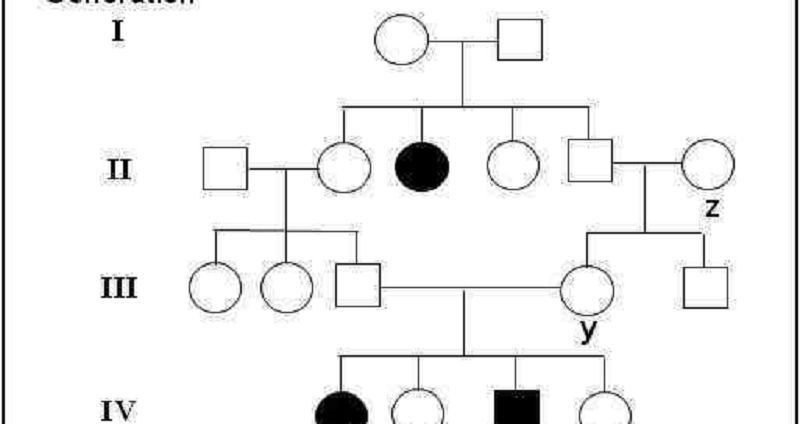
The following 3 questions are based on the pedigree above. 47. What is the most likely mode of inheritance for trait?
A- Autosomal recessive
B- Autosomal dominant
C- Y-linked
D- X-linked recessive
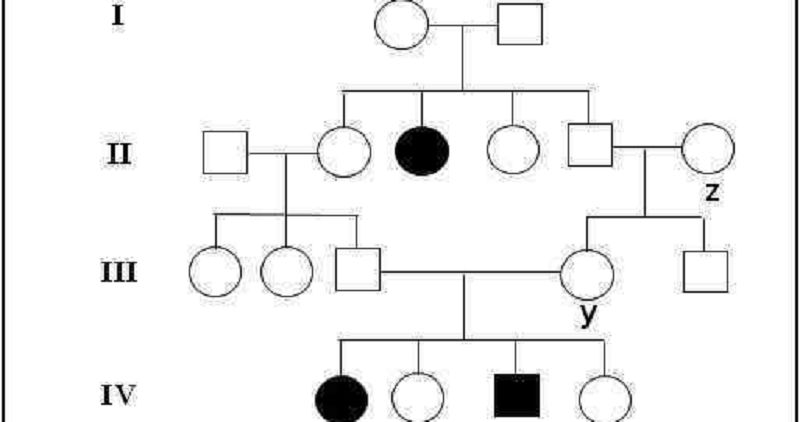
48. Assuming that the dominant allele for the trait is (A) and the recessive allele (a), what is the correct genotype of individual X in generation IV?
A- aa
B- Aa
C- AA
D- XAY
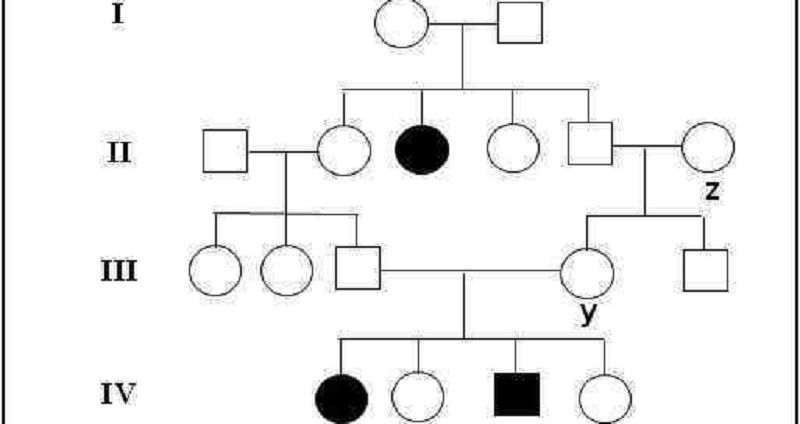
49. Assuming the dominant allele for the trait is (A) and the recessive allele (a), what is the correct genotype of individual y in generation III
A- aa
B- XAY
C- AA
D- Aa
50. Which of the following tools of recombinant DNA technology is INCORRECTLY paired with one of its uses?
A- DNA ligase – enzyme that cuts DNA creating sticky ends
B- DNA polymerase – copies DNA sequences in PCR
C- Reverse transcriptase – produces cDNA from Mrna
D- Electrophoresis – RFLP analysis
51. Automated sequencing is based on:
A- Utilization of fluorescent labeling
B-Utilization of four types of dideoxynucleosides
C- Utilization of DNA polymerases
D- A, B and C
52. The position of DNA in a gel after electrophoresis is dependent on?
A- Size of the DNA fragment
B- Overall charge of the DNA molecules
C- Presence of ethidium bromide
D- Thickness of the gel
53. The mutation that causes Huntington disease is best described as:
A- CAG repeat expansion that occurs in the 3’ untranslated region of the gene
B- CAG repeat expansion that produces a protein that tends to form aggregates in nucleus of cell.
C- CAG repeat expansion that leads to haploinsufficiency & thus neuronal cell death
D- CAG repeat expansion that causes earlier onset of disease in males than females
54. Which of the following mechanisms is known to cause Prader-Will syndrome?
A- Uniparental disomy
B- Chromosome duplication
C- Translocation
D-Autosomal trisomy
55. With respect to genetic mutation, mosaicism means…
A- The absence of a chromosome from the karyotype of an organism
B- Possession, by an organism, of a mixture of both normal and mutated cells
C- Exchange of segments between non-homologous chromosomes
D- Having a more severe form of the mutation
56. Which enzyme is the first to act in the process of Base Excision Repair (BER)?
A- Deaminase
B- AP endonuclease
C- DNA glycosylase
D- DNA ligase
57. A karyotype is:
A- The sex chromosome ratio of somatic cells of an organism
B- The autosomal ratio of the gamete cells of an organism
C- The size, number and shape of the chromosomes in a somatic cell
D- The size, number and shape of the chromosomes in a gamete cell
58. Which of the following is an upstream activator of p53?
A- DNA repair
B- DNA damage
C- Inhibition of angiogenesis
D- Apoptosis
{"name":"applied genetics", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"1. Which of the following is NOT part of the normal process of cloning recombinant DNA in bacteria?, 2. Which of the following statements about electrophoresis is INCORRECT, 3. The PCR technique involves the use of:","img":"https://cdn.poll-maker.com/49-1654766/vbnm.jpg?sz=1200-00000008951000005300"}
More Quizzes
740
Ege Quizi
1368
Sophomore Class Officers
320
Annie Lennox discography quiz
105294
Am I Manipulative? Uncover Hidden Behaviors
201023989
Test My Ethics IQ: Are You Ethically Intelligent?
201033969
Ultimate Singing in the Rain Trivia - Test Your Film IQ
201037604
The Happy Prince: Ultimate Prince Trivia Challenge
201024817
Ultimate South American Countries & Capitals
201028086
Free Dangerous Goods Knowledge
201021720
Ultimate Benchwarmers Gus Trivia - Test Your Movie IQ
201025258
Free Memorize Unit Circle Game
201024603