DES C_Diagnosis (6) Prepared : CHILLY
A 34-year-old woman with a skin rash, joint pains, and oral ulcers is diagnosed with systemic lupus erythematosus. She has no renal or central nervous system involvement, and her past medical history and review of systems are otherwise negative. Therapy with hydroxychloroquine is started. Which of the following screening tests is most important in this patient?
Complete blood count
Liver function panel
Audiometry
Urinalysis
Eye examination
A 34-year-old woman, gravida 1, para 0, at 18 weeks’ gestation with severe hyperemesis has a blood pressure of 150/95 mm Hg and 2 proteinuria. Pelvic examination reveals bilateral adnexal masses that are 8–10 cm in diameter and appear multiloculated on a sonogram. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Follicular cyst
Corpus luteum cyst
Theca-lutein cyst
Luteoma of pregnancy
Endometrioma
A 35-week-term infant presents with cyanosis shortly after birth. His arterial oxygen saturation is only 30%. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Patent ductus arteriosus
Atrial septal defect
Coarctation of the aorta
Ventricular septal defect
Transposition of the great vessels
A 35-year-old African-American marathon runner presents to the gynecologist complaining of secondary amenorrhea that developed three months ago. Her cycles are normally 28 days long, and her menses last three to five days with moderate flow. One year ago, the woman adopted a vigorous exercise regimen that lasted between three and five hours every day. Since then, her BMI has declined from 23.4 to 16.5 Kg/m2. She has been winning many local races and is considering increasing the difficulty of her exercise regimen, but would like to address the issue of her amenorrhea first. Physical examination reveals a thin woman with well-defined musculature but is otherwise unremarkable. Pregnancy test is negative. What is the most likely etiology of her amenorrhea?
Kwashiorkor
Estrogen deficiency
Testosterone deficiency
Progesterone deficiency
Prolactin excess
A 35-year-old African-American marathon runner presents to the gynecologist complaining of secondary amenorrhea that developed three months ago. Her cycles are normally 28 days long, and her menses last three to five days with moderate flow. One year ago, the woman adopted a vigorous exercise regimen that lasted between three and five hours every day. Since then, her BMI has declined from 23.4 to 16.5. She has been winning many local races and is considering increasing the difficulty of her exercise regimen, but would like to address the issue of her amenorrhea first. Physical examination reveals a thin woman with well-defined musculature but is otherwise unremarkable. Pregnancy test is negative. What is the most likely etiology of her amenorrhea?
Kwashiorkor
Estrogen deficiency
Testosterone deficiency
Progesterone deficiency
Prolactin excess
A 35-year-old African-American woman comes to the physician's office complaining of blurred vision, cough and shortness of breath. For the past few days she has had mild fevers, malaise and easy fatigability. She has never had these symptoms before and is anxious to uncover a diagnosis. She was recently incarcerated for two months. She practices unprotected sex with her new boyfriend. Her temperature is 37.2°C (98.9°F) and her blood pressure is 116/80 mmHg. On exam, her right eye is red and slit lamp examination shows leukocytes in the anterior chamber. Lungs have patchy rales. Chest x-ray shows bilateral reticulonodular infiltrates and hilar adenopathy. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
Acute HIV infection
Disseminated tuberculosis
Sarcoidosis
Histoplasmosis
Ankylosing spondylitis
A 35-year-old black man is brought to the emergency department after a motorcycle accident. He hit the street with the side of his head. He was found unconscious when the emergency medical team arrived. However, on the way to the emergency department he regains consciousness. Upon arrival he is confused and complains of a headache. His temperature is 36.9C (98.5F), blood pressure is 100/60 mm Hg, pulse is 110/min, and respirations are 22/min. Examination shows a dilated pupil on the right side, with some weakness of the left arm and leg. CT scan of the head shows a biconvex hematoma on the right side of the head. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Acute subdural hematoma
Basilar fracture of skull
Acute epidural hematoma
Intracerebral bleeding
Subarachnoid hemorrhage
A 35-year-old Caucasian female presents to your office with several months history of heartburn. She also describes a periodic 'sticking sensation' in her throat during the meal. Her past medical history is significant for asthma that is controlled with inhaled steroids, and acoustic neuroma that was removed 2 years ago. She does not smoke or consume alcohol. She denies any recreational drug use. She is not allergic to any medications. She works as a secretary at a private firm, and considers her work moderately stressful. Her family history is significant for breast cancer in her mother and prostate cancer in her father. Endoscopic evaluation shows mild hyperemia in the distal esophagus. Esophageal manometry reveals absent peristaltic waves in the lower two-thirds of the esophagus and a significant decrease in lower esophageal sphincter tone. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's complaints?
Achalasia
Scleroderma
GERD with or without hiatal hernia
Non-ulcer dyspepsia
Diffuse esophageal spasm
A 35-year-old Caucasian man comes to the emergency department at 2 am because of severe pain 'behind the left eye' which woke him up in the middle of the night. The pain is intense and has a stabbing quality. He took ibuprofen at home but didn't get any relief. He denies fever, chills, decreased or blurred vision, cough, nausea or vomiting. He has no other medical problems. He drinks 3-4 bottles of beer daily. He has no known drug allergies. His temperature is 36.7°C (98°F), blood pressure is 120/80 mm Hg, pulse is 88/min and respirations are 14/min. The examination is unremarkable, except for left-sided ptosis and miosis. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Migraine headache without aura
Migraine headache with aura
Sinus headache
Cluster headache
Brain tumor
A 35-year-old female presents with a complaint of oral ulcers that are extremely painful. She had a similar presentation three months ago and the ulcers healed without any scarring. Her medical history includes a recent visit to the ophthalmologist with complaints of blurred vision and she is now being treated for anterior uveitis. She has also had recurrent painful ulcers in her genital area for which she has regular follow-up with her gynecologist. On examination, you notice many hyper-pigmented areas over her extremities and few painful, nodular lesions. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Sarcoidosis
Herpes simplex infection
Reiter's Syndrome
Behcet's syndrome
Systemic lupus erythematosus
A 35-year-old HIV-positive man (CD4+ cell count 150/mm³) is seen in the emergency department with right-sided chest pain. The patient has become progressively dyspneic over the past few days. Suddenly, 30 minutes ago he noticed a sharp pain in his chest associated with shortness of breath. His temperature is 37.7°C (99.9°F), blood pressure is 128/84 mm Hg, pulse is 102/min and regular, respiratory rate is 25/min, and oxygen saturation is 90% on room air. Physical examination reveals diminished right-sided breath sounds and hyperresonance. Jugular venous distention is 5 cm and there is no tracheal deviation. ECG shows sinus tachycardia. X-ray of the chest shows a right-sided pneumothorax occupying approximately 10% of the right thoracic cavity. Which of the following most likely caused this patient’s presentation?
Intravenous drug use
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia
Toxoplasmosis
Kaposi’s sarcoma
A 35-year-old male complains of inability to close his right eye. Examination shows facial nerve weakness of the upper and lower halves of the face. There are no other cranial nerve abnormalities, and the rest of the neurological examination is normal. Examination of the heart, chest, abdomen, and skin show no additional abnormalities. There is no lymphadenopathy. About one month ago the patient was seen by a dermatologist for a bull’s-eye skin rash. The patient lives in upstate New York and returned from a camping trip a few weeks before noting the rash. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Sarcoidosis
Lacunar infarct
Idiopathic Bell palsy
Lyme disease
Syphilis
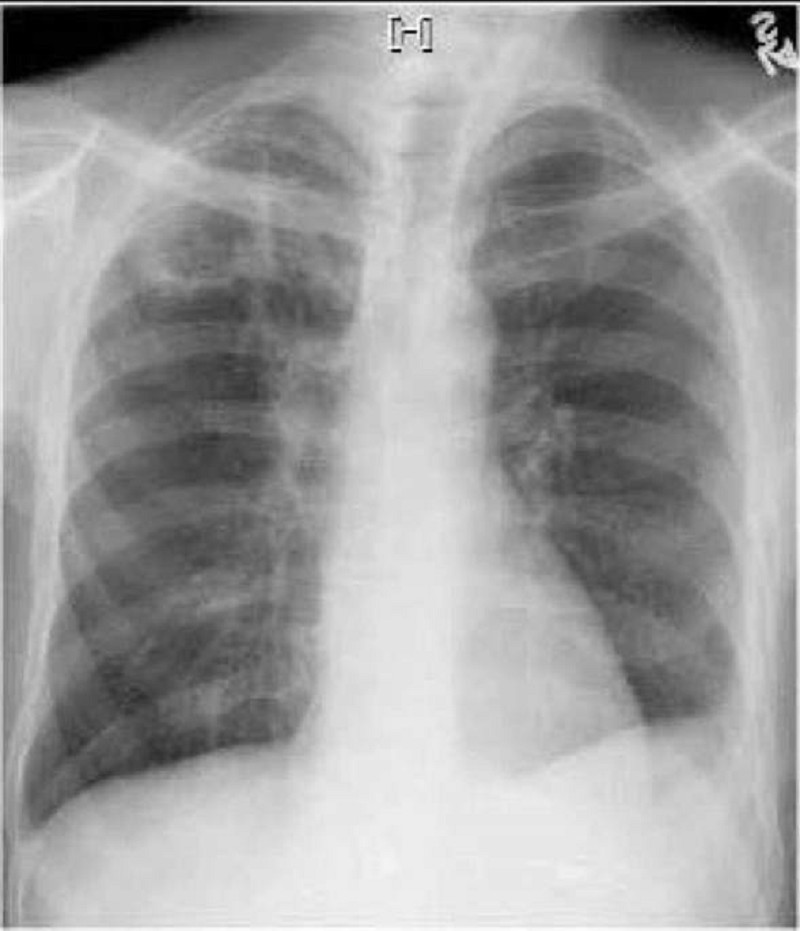
A 35-year-old male from Arizona presents to the physician's office with a low-grade fever and cough of two months duration. He also reports malaise and a weight loss of 7 lbs over this same period. He has a history of HIV infection diagnosed two years ago. He received a pneumococcal vaccine at the time his HIV was diagnosed. He also receives an annual influenza vaccine. He is not on any antiretroviral therapy. His temperature is 37.7°C (99.8°F), pulse is 75/min, blood pressure is 130/80 mm Hg and respirations are 14/min. Examination shows clear lungs to auscultation. His current CD4 count is 450cells/microl. His chest radiograph is shown below. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his cough?
Bronchial asthma
Postnasal drip
Mycobacterial infection
Coccidioidomycosis
Gastroesophageal reflux disease
A 35-year-old male from Wisconsin presents to his physician complaining of fever, night sweats, productive cough, and an unintentional 17-lb weight loss over the past 3 months. Several days ago, he also began to notice multiple skin lesions. He has no known medical problems and does not take any medications, nor does he use tobacco, alcohol or illicit drugs. He works outdoors in wood cutting and construction. Physical examination reveals a man of medium build in no apparent distress. His temperature is 38.4°C (101.1°F), blood pressure is 120/68 mm Hg, pulse is 86/min, and respirations are 14/min. Skin examination reveals multiple, well-circumscribed, verrucous, crusted lesions. Chest x-ray shows left upper lobe consolidation and two lytic lesions in the anterior ribs. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his current symptoms?
Disseminated tuberculosis
Sarcoidosis
Metastatic osteosarcoma
Blastomycosis
Coccidioidomycosis
A 35-year-old male presents to the emergency room complaining of increasing shortness of breath, fever and malaise for several days. His past medical history is significant for two years of recurrent sinusitis. He is a former smoker and has an occasional glass of wine. His temperature today is 38.4°C (101.1°F), blood pressure is 110/65 mm Hg, pulse is 110/min, and respirations are 22/min. Examination reveals an illappearing male in mild respiratory distress. Patchy rales are appreciated on lung auscultation. Chest x-ray reveals multiple nodular densities bilaterally. His serum creatinine is 2.7 mg/dl and urinalysis shows red blood cell casts. Which of the following would be most helpful in diagnosing his condition?
CT scan of the chest
Sputum acid fast stain
Serum alpha fetoprotein
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
Serum antineutrophilic cytoplasmic antibody
A 35-year-old male presents to the family physician for bilateral gynecomastia. He observed a progressive increase in his breast size starting 6 months ago. He is sexually active and denies any drug use. Physical examination reveals bilateral gynecomastia and tenderness. The genito-urinary examination shows a 1 cm nodule in the right testis. Otherwise, the examination is within normal limits. The laboratory report shows: LH 3 U/L, FSH 2 U/L, testosterone 270 ng/dL (Normal 3-10 ng/dL), estradiol 115 pg/mL (Normal 20-60 pg/mL), beta HCG undetectable, AFP undetectable. Which is the most likely diagnosis?
Leydig cell tumor
Choriocarcinoma
Teratoma
Seminoma
Endodermal sinus tumor
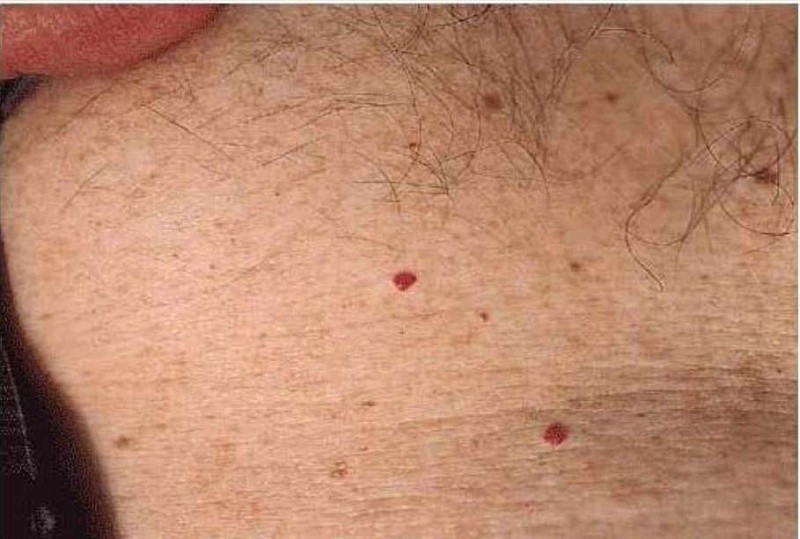
A 35-year-old male presents to your office with red skin lesions on his back that were first noticed by his wife. His past medical history is not significant. Physical examination reveals the following findings (see the slide below). Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
Strawberry (capillary) hemangioma
Cherry hemangioma
Spider angioma
Cavernous hemangioma
Cystic hygroma
A 35-year-old male presents with complaints of muscle weakness and sensory loss in his upper extremities. His medical history is significant for involvement in a motor vehicle accident seven years ago in which he sustained a whiplash cervical spine injury. Physical examination today reveals moderate wasting of the small hand muscles and impaired pain and temperature sensation in the bilateral upper extremities. Light touch, vibration, and position senses are all intact. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Syringomyelia
Cervical spondylosis
Intervertebral disk prolapse
Multiple sclerosis
A 35-year-old male presents with complaints of weakness and fatigue of one year's duration. He is anorexic and has lost interest in all his activities. He also complains of cold intolerance and constipation. His blood pressure is 98/72 mmHg, temperature is 37.1°C (99°F), respirations are 14/min, and pulse is 50/min. His skin is dry and rough, nails are brittle, and hair is thin. There is no hyperpigmentation of the skin. Delayed deep tendon reflexes are noted on neurological examination. Lab studies show: Hemoglobin 10.2 g/dL, WBC count 5,000/micro-L, Neutrophils 45%, Monocytes 5%, Eosinophils 10%, Basophils 1%, Lymphocytes 40%, Serum sodium 135 mEq/L, Serum potassium 4.0 mEq/L. Which of the following is most consistent with this patient's findings?
Autoimmune destruction of adrenal glands
Adrenal CMV infection
Adrenal tuberculosis
Adrenoleukodystrophy
Pituitary tumor
A 35-year-old man comes to the physician because of persistent dull perineal pain and dysuria for 6 months. The patient denies urinary tract infections or urethral discharge. His temperature is 37 C (98.6 F). On digital rectal examination, the prostate is slightly tender and boggy but not enlarged or indurated. Urinalysis is normal. Expressed prostatic secretions show the following: Leukocytes 30 cells/high power field Bacteria None Cultures of prostatic secretion and urine are negative for bacteria. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Acute cystitis
Chronic bacterial prostatitis
Acute prostatitis
Chronic nonbacterial prostatitis
Prostatodynia
A 35-year-old man complains of increasing shortness of breath with exercise. These symptoms have been ongoing for the last year. Previously he has been healthy. He denies any fever, chills, shakes, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, chest pain, palpitations, hemoptysis, or weight loss. He denies any occupational exposure. He also reports a dry cough. He does not take any medications and has no known drug allergies. He denies a smoking history. His oxygen saturation is 93% on room air. Lungs have a fine crackle pattern. Heart is regular. Examination of the extremities shows clubbing. Chest x-ray reveals diffuse linear capacities. Pulmonary fun
Acute interstitial pneumonia
Idiopathic cardiomyopathy
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Sarcoidosis
Asbestosis
A 35-year-old man had a splenectomy 8 days ago, following a motor vehicle accident. He is now complaining of left shoulder pain. His temperature is 39.0C (102.2F), blood pressure is 110/80 mm Hg, pulse is 110/min, and respirations are 30 min and shallow, Physical examination shows clear lungs with equal breath sounds bilaterally and mild tenderness to palpation in the left upper quadrant with a well-healing midline laparotomy incision. Laboratory studies show: Hemoglobin 15 g/dL, Hematocrit 45%, Leukocyte counts 15,000/mm3.A chest x-ray film shows no infiltrates or effusions. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Left clavicle fracture
Post-splenectomy sepsis
Left lower lobe pneumonia
Subphrenic abscess
Subphrenic hematoma
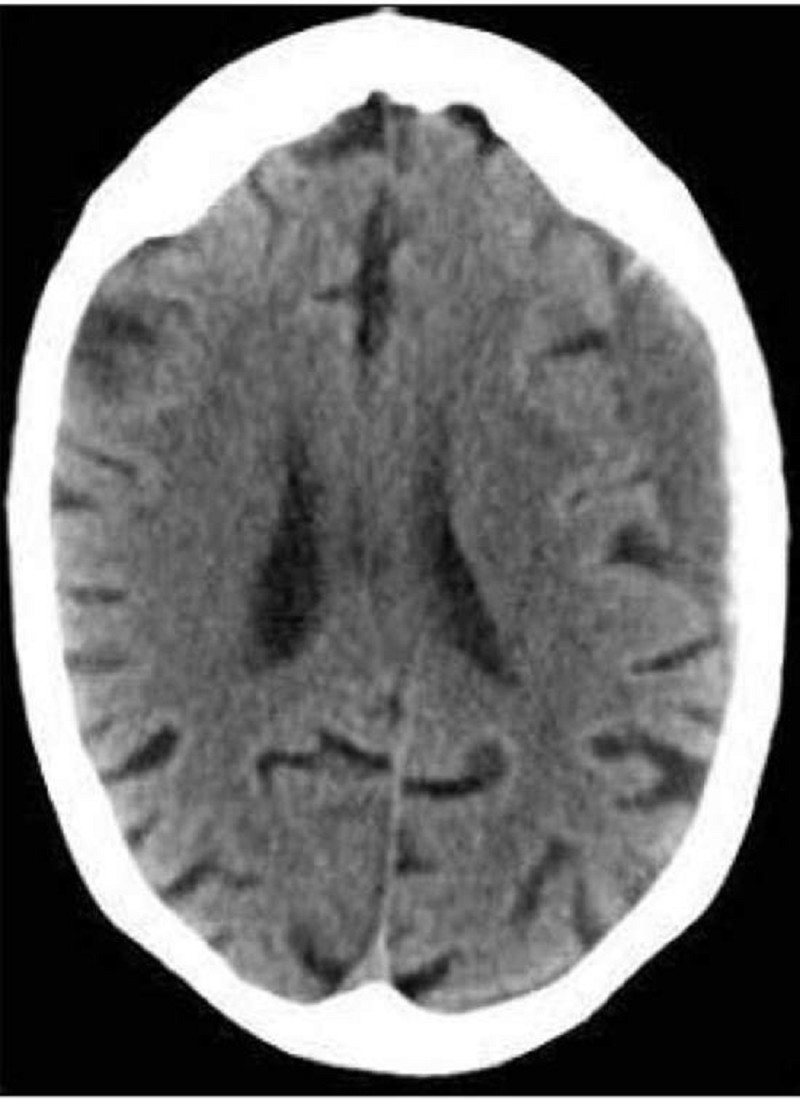
A 35-year-old man is brought to the emergency department after a motorcycle accident. He is unconscious when the emergency medical team arrived. He regains consciousness on the way to the emergency department. Upon arrival, he is mildly confused and complains of headache and nausea. His temperature is 36.9° C (98.5° F), blood pressure is 102/60 mm Hg, pulse is 116/min, and respirations are 22/min. Pupils are equal and reactive to light. He moves all extremities on command, and deep tendon reflexes are symmetric. Head CT scan shows: Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Acute epidural hematoma
Concussion
Diffuse axonal injury
Intracerebral bleeding
Acute subdural hematoma
A 35-year-old man is brought to the emergency department after being involved in a motor vehicle collision. He is unconscious. His blood pressure is 100/50 mm Hg, pulse is 100/min, and respirations are 19/min. Examination shows bilaterally reactive and non-dilated pupils. He does not follow commands and makes inappropriate sounds. A CT scan of the head shows numerous minute punctuate hemorrhages with blurring of the gray-white matter interface. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Epidural hematoma
Diffuse axonal injury
Subdural hematoma
Subarachnoid hemorrhage
Multiple sclerosis
A 35-year-old man is brought to the emergency department after he jumped from the fourth floor of a burning building. His temperature is 36.9° C (98.5° F), blood pressure is 90/40, pulse is 90/min, and respirations are 20/min. Examination shows a fracture of the right tibia. He is conscious and his pupils are bilaterally equal and reactive to light and accommodation. His neurological examination shows paraplegia, with loss of pain and temperature in both legs but normal proprioception. Upper extremities do not show any neurological deficits. Passive straight leg raising test is negative. A CT scan of the spine shows a burst fracture at the level of the fourth thoracic vertebra. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Central cord syndrome
Brown Sequard syndrome
Anterior cord syndrome
Acute disk prolapse
Cauda equine syndrome
A 35-year-old man is evaluated for symptoms of shortness of breath. He reports no other lung or heart disease. He smokes half pack a day for the past 10 years. On examination, his JVP is 2 cm, heart sounds normal, and lungs are clear. A CXR shows hyperinflation and increased lucency of the lung fields. A chest CT reveals bullae and emphysematous changes, while pulmonary fun
Alpha1-antitrypsin deficiency
Glucocerebrosides deficiency
Glucose-6-phosphatase deficiency
Beta-glycosidase deficiency
Growth hormone deficiency
A 35-year-old man presents to the office with a two-week history of low-grade fever and progressive weakness. He has "a heart murmur detected a long time ago." He denies illicit drug use. Physical examination reveals splinter hemorrhages, small petechiae on the palatal mucosa, and an audible murmur. His ESR is 60/min. Urinalysis reveals microscopic hematuria and 1 +proteinuria. Which of the following valvular dysfun
Aortic regurgitation
Mitral regurgitation
Tricuspid regurgitation
Pulmonic stenosis
Mitral stenosis
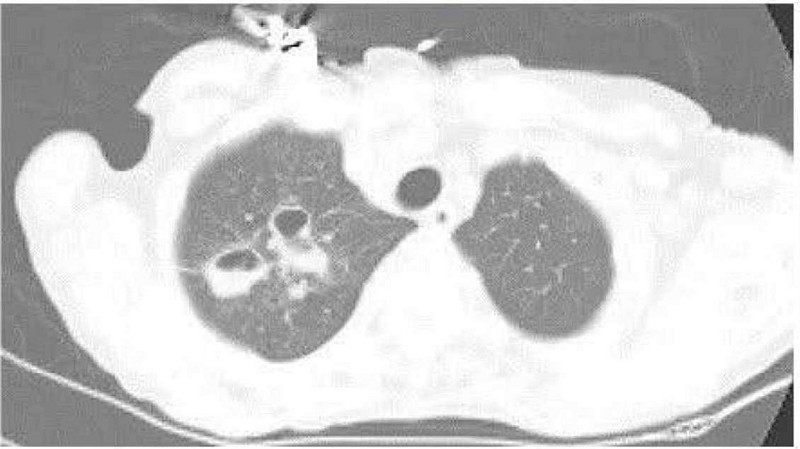
A 35-year-old man who recently emigrated from Mexico complains of persistent cough. He says that he coughs up yellowish sputum that is occasionally streaked with blood. He also notes occasional fevers and frequent nighttime awakenings with cough and choking. He has a 20 pack-year smoking history but does not use alcohol or drugs. CT of his chest is shown below. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Bronchiectasis
Lung cancer
Bronchopulmonary aspergillosis
Sarcoidosis
Pulmonary tuberculosis
A 35-year-old right-handed construction worker presents with complaints of nocturnal numbness and pain involving the right hand. Symptoms wake him and are then relieved by shaking his hand. There is some atrophy of the thenar eminence. Tinel sign is positive. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Carpal tunnel syndrome
Rheumatoid arthritis of the wrist joint
De Quervain tenosynovitis
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Guillain-Barré syndrome
A 35-year-old white male presents with fatigue, decreased appetite, weight gain, constipation and cold intolerance. He cannot recall any stressful event. He does not take any medications. He is a non-smoker and non-alcoholic. His pulse is 47/min and blood pressure is 145/91 mmHg. Physical examination reveals cool, pale skin, coarse hair, and brittle nails. There is delayed relaxation of deep tendon reflexes. The thyroid gland is normal on palpation. Laboratory studies reveal increased serum free T3 and T4 levels, and normal serum TSH level. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Primary hypothyroidism
Generalized resistance to thyroid hormones
Secondary hypothyroidism
Subclinical hypothyroidism
Graves' disease
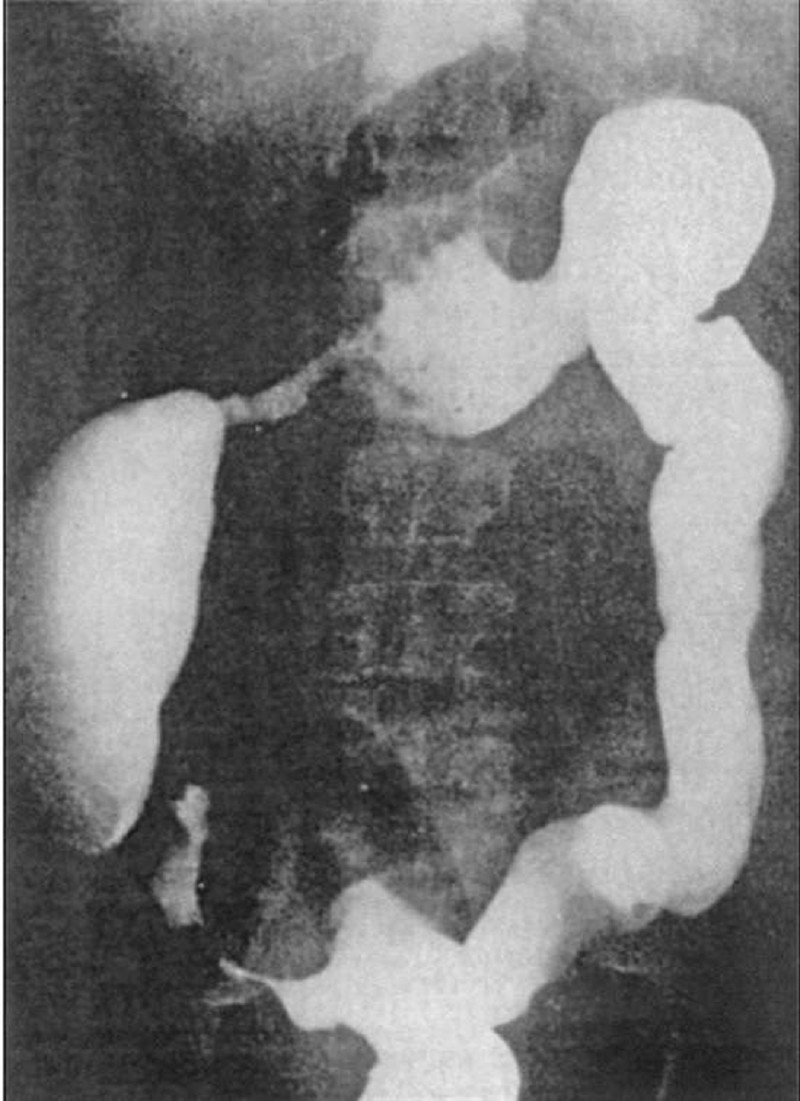
A 35-year-old White man has a long past history of diarrhea, rectal bleeding, crampy abdominal pain, and the passage of mucus. He now presents with a worsening of his symptoms despite taking his medications. A barium enema is performed and is shown in Fig. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis of this new complication?
Toxic megacolon
Amoebic colitis
Appendicitis
Ischemic colitis
Annular carcinoma
A 35-year-old woman has lived in a state psychiatric hospital for the past 10 years. She spends most of her day rocking, muttering softly to herself, or looking at her reflection in a small mirror. She needs help with dressing and showering, and she often giggles and laughs for no apparent reason. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Schizophrenia
Bipolar disorder, manic phase
Delusional disorder
Schizoaffective disorder
Schizophreniform disorder
A 35-year-old woman is involved in a motor vehicle crash, sustaining a severe pelvic fracture, with disruption of the pelvic ring. In the trauma resuscitation room, she is confused and tachypneic, with a blood pressure of 90 mmHg systolic and a heart rate of 130/min. Laboratory investigations include serum electrolyte analysis, revealing a sodium of 139, a chloride of 103, and a bicarbonate of 14 meq/L. This patient demonstrates which of the following?
Nonanion gap metabolic acidosis
Metabolic alkalosis
Anion gap metabolic acidosis
Respiratory acidosis
Normal serum electrolytes
A 35-year-old woman presents to the clinic because of visual problems. She states that she has always had difficulty looking up, and over the past few years her overall vision has become blurry. Review of symptoms is notable for several recent episodes of “near fainting.” She takes no medication and has no other medical history, and has not seen a physician for 7 years. Because she was adopted as a child, she does not know her family history, but her son has required special tutoring at school. The patient also remarks that her son seems to have been dropping objects lately. Physical examination reveals bilateral ptosis. Her extraocular movements are intact and the pupils are equal, round, and reactive. Her corrected visual acuity is 20/100 in the right eye and 20/120 in the left eye. The view of the fundus is obscured. On ambulation she raises her knees and makes a slapping sound on the floor as she walks. ECG indicates heart block. What is the pathogenesis of this patient’s disorder?
Deletion mutation in dystrophin
Trinucleotide repeat expansion
Borrelia burgdorferi infection
X-linked emerin deficiency
Frameshift mutation in dystrophin
A 35-year-old woman presents to the physician’s office for evaluation of a left neck mass discovered 1 month ago on a routine physical examination. On examination, the mass measures 2 cm and is located anterolateral to the larynx and trachea. It is nontender and moves with swallowing. Past history is pertinent for a 15 pack-year smoking history and occasional alcohol intake. Which one is the most likely diagnosis?
Thyroid carcinoma
Cystic hygroma
Acute suppurative lymphadenitis
Thyroglossal duct cyst
Lipoma
A 35-year-old woman presents with a right-sided red eye for 3 days. She denies pain and notes that she has watery discharge from the eye. She has been coughing and congested for the past 5 days. On examination, the patient has a temperature of 98.4°F, HR of 72 beats per minute, BP of 110/70 mm Hg, and RR of 14 breaths per minute. Her visual acuity is 20/20. On inspection, the conjunctiva is erythematous with minimal chemosis and clear discharge. The slit-lamp, fluorescein, and funduscopic examinations are otherwise unremarkable. The patient has a nontender, preauricular lymph node and enlarged tonsils, without exudates. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Gonococcal conjunctivitis
Viral conjunctivitis
Bacterial conjunctivitis
Allergic conjunctivitis
Pseudomonal conjunctivitis
A 35-year-old woman presents with complaints of aching pain and stiffness over her entire body for the past 3 months. She also reports, easy fatigability, poor sleep and frequent headaches. She has been using over the counter pain medications with no relief. While examining her, she complains of extreme pain to gentle palpation over her neck, shoulders and back. Her vital signs are stable. What is your diagnosis?
Chronic fatigue syndrome
Polymyalgia rheumatica
Rheumatoid arthritis
Polymyositis
Fibromyalgia
A 35-year-old woman who recently emigrated from Russia comes to the physician because of hematuria. She has a history of frequent headaches. Extensive evaluation did not reveal the cause of her headaches. They occur almost every day, and she tried various analgesics to relieve them. Her family history is significant for hypertension and diabetes mellitus. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or drugs. Her blood pressure is 120/70 mm Hg and heart rate is 80/min. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. Urinalysis shows numerous unchanged red blood cells/hpf. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
Malignancy
Glomerular injury
Papillary necrosis
Infection
Nephrolithiasis
A 36-year-old female presents with headaches and visual problems. She also complains of palpitations, heat intolerance and weight loss. Her past medical history is unremarkable. She is currently on no medications. Her blood pressure is 130/60 mmHg, heart rate is 100/min and regular, and weight is 152 lb (weight one year ago was 170 lb). Physical examination reveals a symmetrically enlarged thyroid gland without any tenderness. Auscultation of the chest reveals tachycardia. She has bitemporal hemianopsia on confrontation. The rest of the physical examination is unremarkable. Her lab investigations show: Serum T3 222 ng/mL, Serum T4 13.9 mcg/dL, Serum TSH 7.9 IU/mL, Alpha subunit level elevated. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
TSH-secreting pituitary adenoma
Primary hypothyroidism
Generalized resistance to thyroid hormone
Graves' disease
Toxic multinodular goiter
A 36-year-old female who is currently having regular menstrual periods comes to the emergency room because of malaise and a high-grade fever with chills. She also complains of pain in multiple joints. She always uses highly absorbent tampons during her menses. She uses intravenous heroin and cocaine and works as a prostitute. Her temperature is 39.3°C (103.4°F), pulse is 102/min, blood pressure is 120/80mmHg and respirations are 14/min. Examination shows multiple pustules on the extensor surfaces of her forearms. Joint examination does not show redness, swelling or tenderness. Three sets of blood cultures are negative Based on these findings, which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
Infective endocarditis
Toxic shock syndrome
Disseminated gonococcal infection
Acute HIV infection
Secondary syphilis
A 36-year-old G1P0 at 35 weeks gestation presents to labor and delivery complaining of a several-day history of generalized malaise, anorexia, nausea, and emesis. She denies any headache or visual changes. Her fetal movement has been good, and she denies any regular uterine contractions, vaginal bleeding, or rupture of membranes. On physical examination, you notice that she is mildly jaundiced and appears to be a little confused. Her vital signs indicate a temperature of 37.7C (99.9F), pulse of 70 beats per minute, and blood pressure of 100/62 mm Hg. Blood is drawn and the following results are obtained: WBC = 25,000, Hct = 42.0, platelets = 51,000, SGOT/PT= 287/350, glucose = 43, creatinine = 2.0, fibrinogen = 135, PT/PTT = 16/50 s, serum ammonia level = 90 mmol/L (nl = 11-35). Urinalysis is positive for 3+ protein and large ketones. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Hepatitis B
Severe preeclampsia
Acute fatty liver of pregnancy
Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy
Hyperemesis gravidarum
A 36-year-old G2P2 presents for her well-woman examination. She has had two spontaneous vaginal deliveries without complications. Her largest child weighed 3500 g at birth. She uses oral contraceptive pills and denies any history of an abnormal Pap smear. She does not smoke, but drinks about four times per week. Her weight is 70 kg. Her vital signs are normal. After placement of the speculum, you note a clear cyst approximately 2.5 cm in size on the lateral wall of the vagina on the right side. The cyst is nontender and does not cause the patient any dyspareunia or discomfort. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis of this mass?
Bartholin duct cyst
Gartner duct cyst
Lipoma
Hematoma
Inclusion cyst
A 36-year-old known patient of yours presents for a routine annual examination. Toward the end of the visit, she glumly mentions that she intends to file for a divorce from her husband. She says that he is always in an irritable or depressed mood, and that she is "sick and tired of him spending huge sums of money on gambling." Although she was aware of his placing the occasional bet before they got married, she says his passion for gambling has increased significantly since his mother's death two months ago. He was recently fired from his job as an insurance agent after he was caught forging signatures in an attempt to finance some gambling trips to Las Vegas. She has confronted him about his behavior on many occasions in the past, but he has always denied that it was a problem. Now he admits that he finds it hard to control himself and that he is in debt to several creditors. Although he has lost a considerable amount of money, he is convinced that he could win it all back if he could just borrow enough from friends. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Bipolar disorder, manic episode
Antisocial personality disorder
Obsessive-compulsive disorder
Pathological gambling
Adjustment disorder
A 36-year-old male comes to the office for the evaluation of a skin lesion. For the past two months, he noticed darkening and thickening of the skin over his neck and groin area. These areas occasionally feel itchy. His pulse is 82/min, blood pressure is 130/80 mmHg, respirations are 14/min, and temperature is 36.8°C (98.4°F). Physical examination reveals symmetrical, hyperpigmented, velvety plaques on the axilla, groin and posterior neck. This patient's condition should alert the physician to check for which of the following?
Gastrointestinal malignancy
Diabetes mellitus
Addison's disease
Pellagra
Hemochromatosis
A 36-year-old male comes to the office for the evaluation of fatigue and weakness for the last several weeks. He denies any change in appetite, change in weight, heat or cold intolerance, nausea, vomiting and constipation. He cannot recall any recent stressful events. His past medical and family histories are unremarkable. He does not have any medications. His pulse is 76/min, blood pressure is 120/70 mmHg, respirations are 14/min, and temperature is 36.7°C (98°F). He is well-oriented to time, place and person. His neurological examination is nonfocal; the deep tendon reflexes are normal. Lab tests show: Hematocrit 43%, WBC count 6,000/microl, Platelet count 200,000/microl, Serum calcium 11 mg/dL, Serum albumin 4.5 g/dL, 24-hour urinary calcium 200 mg. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his symptoms?
Primary hyperparathyroidism
Increased calcium intake
Malignancy
Familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia
Milk alkali syndrome
A 36-year-old male is brought to the emergency department due to confusion, nausea and decreased arousal. He is unable to answer questions and no other history is available. His temperature is 36.7ׄ°C (98.2°F), respirations are 22/min and pulse is 86/min. His ABG and serum electrolyte levels are shown below: pH 7.21, PaO2 96 mmHg, PaCO2 28 mmHg, Serum sodium 140 mEq/L, Serum potassium 3.6 mEq/L, Chloride 90 mEq/L, Bicarbonate 12 mEq/L, Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) 30 mg/dl, Serum creatinine 1.2 mg/dl. What is the most likely primary acid-base disorder in this patient?
Non-anion gap metabolic acidosis
Metabolic alkalosis
Anion gap metabolic acidosis
Respiratory alkalosis
Respiratory acidosis
A 36-year-old male presents to clinic complaining of a pruritic eruption on his forearms. He denies fever, chills and malaise. Physical examination reveals an erythematous rash with occasional vesicles affecting both forearms. No lymphadenopathy is appreciated. Vesicular fluid grows coagulase-negative staphylococci. His only relevant history is recent work in the woods behind his home chopping and transporting firewood. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Herpes simplex infection
S. Epidermidis cellulitis
S. Aureus cellulitis
Suppurative hidradenitis
Contact dermatitis
A 36-year-old male presents with firm, non-tender swelling of his right cheek. He tells you that he had similar swelling at that site two years ago and was diagnosed with a tumor, which was subsequently removed without complication. Examination reveals fullness of the parapharyngeal space on the right side. Repeat surgery in this patient is most likely to result in which of the following complications?
Hoarseness
Tic douloureux
Facial droop
Tongue palsy
Jaw asymmetry
A 36-year-old man comes to the emergency department because of excruciating flank pain. The pain radiates to the groin. His temperature is 36.9°C (98.5°F), blood pressure is 115/75 mm Hg, pulse is 85/min, and respirations are 14/min. Urinalysis shows six RBCs/HPF. Laboratory studies show BUN of 12mg/dl and serum creatinine of 0.9mg/dl. X-ray film of the abdomen shows nephrocalcinosis and IVP shows multiple contrast filled cysts. Ultrasonogram of the kidneys is unremarkable. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Hydronephrosis
Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease
Medullary cystic kidney
Acquired cystic kidney disease
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease
A 36-year-old man comes to the physician because of fatigue and generalized edema. He was recently diagnosed with Hodgkin's lymphoma. Laboratory studies show: Serum sodium 145 mEq/L, Serum potassium 3.8 mEq/L, Serum albumin 2.0 g/dl, Serum globulin 7.0 g/dl, Total serum bilirubin 0.9 mg/dl, Serum creatinine 1.2 mg/dl. Urinalysis shows proteinuria 4+. Which of the following glomerulopathies is more likely to be present in this patient?
Membranous glomerulonephritis
Minimal change disease
Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis
Crescentic glomerulonephritis
Diffuse proliferative glomerulonephritis
A 36-year-old man from Ohio presents with fever, malaise, fatigue, and skin lesions on his right forearm. His fever is low-grade, without any rigors or chills. His temperature is 38.4°C (101°F), pulse is 87/min, and blood pressure is 124/74mm Hg. Examination shows 1-2cm warty, heaped-up skin lesions with a violaceous hue and sharply demarcated border. Some of these lesions are crusted. Wet preparation of purulent material from skin lesions shows yeast Based on these findings, what is the most likely diagnosis?
Histoplasmosis
Blastomycosis
Coccidioidomycosis
Aspergillosis
Sporotrichosis
A 36-year-old man is seen because of palpitations. He admits to precordial discomfort, weakness, and anxiety. His pulse is 150/min, and his blood pressure is 124/70 mmHg. Heart sounds are normal. Carotid sinus pressure gradually changes the rate to 75/min, but when released, the pulse rate returns to 150/min. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Atrial flutter with 2:1 block paroxysmal
Atrial tachycardia with 2:1 block
Sinus arrhythmia
Atrial fibrillation
Nodal tachycardia
A 36-year-old man presents to the clinic with complaints of a genital sore. The patient is a sexually active heterosexual involved with three partners and practices unprotected intercourse. Four days ago he noted a painless sore on his penis. He is afebrile, with a heart rate of 80/min and blood pressure of 120/77 mmHg. Physical examination reveals a solitary ulcerated lesion located on the lateral aspect of his penis. The lesion is nontender and associated with bilateral inguinal lymphadenopathy. Physical examination is otherwise normal. If left untreated, this man is at increased risk for which of the following?
Ascending aortic aneurysm
Endocarditis
Coronary artery aneurysm
Mitral valve stenosis
Rupture of ventricular free wall
A 36-year-old man who was hit by a car presents to the ER with hypotension. On examination, he has tenderness and bruising over his left lateral chest below the nipple. An ultrasound examination is performed and reveals free fluid in the abdomen. What is the most likely organ to have been injured in this patient?
Kidney
Liver
Spleen
Intestine
Pancreas
A 36-year-old migrant farm worker comes to a community outreach health clinic complaining of hemoptysis. For the past 2 months, while she has traveled from Tijuana, Mexico, up through California’s central agricultural valley, she has suffered from intermittent episodes of a hacking cough, as well as intermittent joint pain. Physical exam reveals some faint crackles in her left upper lobe, and three small, tender, violaceous subcutaneous nodules on her right pretibial region. Laboratory studies are unremarkable, but a chest radiograph reveals a 3-cm thin-walled cavity in the left upper lobe with no surrounding infiltrate. A PPD skin test shows 4 cm of induration 72 hours after placement. On the basis of this patient’s history and findings, which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Blastomycosis
Coccidioidomycosis
Histoplasmosis
Paragonimiasis
Tuberculosis
A 36-year-old primigravid woman at 36 weeks' gestation comes to the physician for a prenatal visit. She is experiencing good fetal movement and has had no loss of fluid, bleeding from the vagina, or contractions. She has no complaints. Her past medical history is significant for mitral stenosis, which she developed after an episode of rheumatic fever as a child. She also has asthma for which she uses an albuterol inhaler daily. She has herpes outbreaks approximately once a year. At her last visit she was found to be positive for Group B Streptococcus colonization. For which of the following disease processes would this patient benefit by having a forceps-assisted vaginal delivery at the time of delivery?
This patient would not benefit from a forceps-assisted vaginal delivery
Asthma
Group B Streptococcus (GBS) colonization
Herpes
Mitral stenosis
A 36-year-old woman comes to your office because of back pain. She states that the pain started around the time of her cesarean delivery 8 weeks ago. The pain is located in the lower back and does not radiate. It improves with rest and worsens with prolonged standing. She cannot stand for more than 30 minutes without what she describes as debilitating pain. She has no significant past medical history. She had a cesarean delivery 8 weeks ago for arrest of dilation during labor. She had epidural anesthesia for labor and surgery. Otherwise she has never had surgery. She takes ibuprofen for the pain. She is allergic to sulfa drugs. Physical examination is within normal limits, including a normal neurologic examination. The patient is most interested in knowing what caused her to start having this back pain. Which of the following is the most appropriate response?
�Your back pain is normal in the postpartum period.”
�Your back pain was likely caused by the cesarean delivery.”
�Your back pain was likely caused by the arrest of dilation.”
�Your back pain is most likely caused by breastfeeding.”
�Epidurals have not been shown to be associated with back pain.”
A 36-year-old woman is brought to the psychiatrist by her husband because for the past 8 months she has refused to go out of the house, believing that the neighbors are trying to harm her. She is afraid that if they see her they will hurt her, and she finds many small bits of evidence to support this. This evidence includes the neighbors’ leaving their garbage cans out on the street to try to trip her, parking their cars in their driveways so they can hide behind them and spy on her, and walking by her house to try to get a look into where she is hiding. She states that her mood is fine and would be “better if they would leave me alone.” She denies hearing the neighbors or anyone else talks to her, but is sure that they are out to “cause her death and mayhem.” Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Delusional disorder
Schizoaffective disorder
Schizophreniform disorder
Schizophrenia
Major depression with psychotic features
A 36-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with severe epigastric pain and right shoulder pain of about two hours duration. She also reports having one episode of emesis. When asked about her diet, she explains that she unintentionally fasted yesterday and had a large meal two hours ago. Her past medical history is significant for frequent heartburn for which she takes ranitidine. Several hours after presenting, the patient's pain resolves completely. Which of the following best explains this episode?
Viscus distention
Peritoneal irritation
Acid hypersecretion
Mucosal inflammation
Vascular obstruction
A 36-year-old woman presents to your office with complaints of worsening throat pain for the past six days. She also has pain in her ears and neck as well as difficulty swallowing. On examination, she has excessive salivation and difficulty opening her mouth. Her temperature is 39°C (102.2°F), blood pressure is 130/80 mmHg, pulse is 100/min, and respiratory rate is 18/min. Which of the following neck space infections carries the highest risk of mediastinal involvement?
Submandibular space
Sublingual space
Parapharyngeal space
Retropharyngeal space
Retro-obital
A 36-year-old woman, gravida 3, para 2, at 33 weeks' gestation comes to the physician for a prenatal visit. She has some fatigue but no other complaints. Her current pregnancy has been complicated by a Group B Streptococcus urine infection at 16 weeks. Her past obstetric history is significant for a primary, classic cesarean delivery 5 years ago for a non-reassuring fetal tracing. Two years ago, she had a repeat cesarean delivery. Past surgical history is significant for an appendectomy 10 years ago. Which of the following is the major contraindication to a vaginal birth after cesarean (VBAC) in this patient?
Previous appendectomy
Two prior cesarean deliveries
Classic uterine scar
Group B Streptococcus urine infection
Prior cesarean delivery for non-reassuring fetal tracing
A 36-year-old woman, gravida 3, para 2, comes to the physician for a prenatal checkup. According to her last menstrual period and an ultrasonography performed at 16 weeks gestation, she is at 30 weeks gestation. She missed two antenatal appointments. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or drugs. Examination shows a fundal height of 26 cm (9.8 in). Fetal heart tones are heard by Doppler. Repeat ultrasound shows a fetal biparietal diameter consistent with 30 weeks and an abdominal circumference below the 10th percentile. Which of the following could most likely be responsible for the observed fetal findings?
Chromosomal abnormalities
Intrauterine infection
Hypertension
Fetal anomalies
Inaccurate dates
A 36-year-old woman, gravida 3, para 2, comes to the physician for a prenatal checkup. According to the last menstrual period and an ultrasonography performed at 16 weeks gestation, she is at 30 weeks gestation. She missed two antenatal appointments. She does not use tobacco, alcohol or drugs. Examination shows a fundal height of 26cm (9.8in). Fetal heart tones are heard by Doppler. Repeat ultrasonogram shows a biparietal diameter consistent with dates and an abdominal circumference below the 10th percentile. Which of the following could most likely be responsible for the observed fetal findings?
Chromosomal abnormalities
Intrauterine infection
Hypertension
Gross fetal anomalies
Inaccurate dates
A 37-year-old Cambodian woman presents to the emergency room with acute onset of left-sided weakness. She has been experiencing progressive exertional dyspnea, nocturnal cough and occasional hemoptysis over the past six months. She also describes frequent episodes of palpitations and irregular heartbeats. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Mitral stenosis
Wolf-Parkinson-White syndrome
Aortic insufficiency
Primary pulmonary hypertension
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
A 37-year-old female presents to your clinic complaining of lower abdominal discomfort. On bimanual examination the uterus is enlarged. Biopsy reveals normal appearing endometrial glands within the myometrium. The most likely diagnosis is:
Leiomyoma
Endometrial carcinoma
Adenomyosis
Endometriosis
Ectopic pregnancy
A 37-year-old female with a long history of multiple sclerosis presents to her primary care physician complaining of dyspnea. She denies cough and fever but admits to right-sided chest pain. Her medical history is significant for an episode of atrial fibrillation diagnosed in the emergency department two weeks ago, which resolved spontaneously without intervention. She is wheelchair-bound due to spastic paraparesis and has saccadic speech. Her only allergy is to penicillin. On physical examination, her blood pressure is 120/70 mmHg and her heart rate is 110/min and regular. Chest x-ray demonstrates a right-sided pleural effusion. Therapeutic thoracocentesis is performed, and pleural fluid analysis reveals the following: Protein 3.1 g/L, RBC count 230/mm3, WBC count 150/mm3, LDH 220 IU/L, Glucose 100 mg/dl. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's pleural effusion?
Congestive heart failure
Hypoalbuminemia
Pulmonary embolism
Aspiration pneumonia
Malignancy
A 37-year-old homeless man complains of weakness in his right arm. He says that he was smoking a cigarette when the weakness developed, causing the cigarette to fall from his hand. He also reports having mild headaches, fatigue, and chills over the last week. He admits to regular intravenous heroin use and binge drinking. On physical examination, his blood pressure is 120/70 mmHg and his heart rate is 80/min. There is asymmetry of the lower face, decreased muscle strength in the right arm, and an extensor plantar reflex on the right side. He has multiple needle tracks on his arms. ECG shows sinus rhythm with occasional ventricular premature beats. Urinalysis shows 2+ proteins. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
Migraine-associated vascular spasm
Carotid artery thrombosis
Small vessel hyalinosis
Brain tumor
Cerebral emboli
A 37-year-old male prisoner has been complaining of fever, chills and abdominal pain over the last week. He vomited once before reaching the emergency room. On physical examination, his blood pressure is 112/63 mmHg and his heart rate is 115/min. Breath sounds are diminished at the left lung base and there is marked left upper quadrant tenderness. Laboratory values are given below:WBC count 23,500/mm3, Neutrophils 65%, Bands 11%, Hemoglobin 12.5 mg/dL, Platelets 250,000/mm3, Total bilirubin 3.1 mg/dL, AST 46 units/L, AL T 70 units/L, Alkaline phosphatase 120 units/L. CT scan of the abdomen reveals a fluid collection within the spleen. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Functional asplenia
Inflammatory bowel disease
Infectious endocarditis
Portal hypertension
Infectious mononucleosis
A 37-year-old woman comes to the physician for evaluation of infertility. She and her 39-year-old husband have not been able to conceive after 13 months of unprotected and frequent intercourse. She has 28-day regular menstrual cycles. The patient had a pregnancy with her husband at age 31. She has no other genitourinary complaints such as menorrhagia, dyspareunia or pelvic pain. She has no previous history of sexually transmitted diseases or abdominal surgery. The patient does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. She is an aerobics instructor and teaches 230-minute classes daily. Her blood pressure is 130/80 mm Hg and pulse is 84/min. Her body mass index is 23 kg/m2. Complete physical examination is unremarkable. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her condition?
Adrenal hyperplasia
Intense exercise
Decreased ovarian reserve
Premature ovarian failure
Uterine leiomyomas
A 37-year-old woman presents for evaluation of infertility. She and her 39-year-old husband have not been able to conceive after 9 months of unprotected and frequent intercourse. She had one pregnancy with her husband when she was 31. She has 28-day regular menstrual cycles and enjoys frequent sexual intercourse. She has no other complaints. She denies any previous history of sexually transmitted diseases or abdominal surgery. She does not use tobacco, alcohol or drugs. She has been working as an aerobic teacher and teaches two 30 minute classes every day. Her blood pressure is 130/80 mmHg and her pulse is 84/min. Her BMI is 23 Kg/m2. Complete physical examination is unremarkable. Which of the following is most likely cause of her condition?
Intense exercise
Hypothyroidism
Premature ovarian failure
Adrenal hyperplasia
Oocyte aging
A 37-year-old woman with sarcoidosis presents to her primary care physician complaining of progressive fatigue and shortness of breath over the past 3 months. She also reports that her socks and shoes do not fit the way they used to and that she fainted a few weeks ago for the first time in many years. She denies any recent illness and only takes medications to control her sarcoid. She states that she is more comfortable sitting than lying down. She has jugular venous distension, which increases with inspiration. Her blood pressure is 134/87 mmHg, respiratory rate is 17/min, pulse is 96/min, and temperature is 37.2°C (98.9°F). She also has decreased breath sounds bilaterally at the bases. ECG shows decreased QRS voltage. An echocardiogram shows a thick left ventricle. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Aortic stenosis
Hypertensive heart disease
Cardiac tamponade
Pericarditis
Restrictive cardiomyopathy
A 38-year-old Caucasian female presents to the office complaining of lethargy, weight gain and fatigue. She denies headaches, pruritus or urine discoloration. She just gave birth 2 months ago via vaginal delivery; her baby is in good health and receives formula nutrition. Her delivery was complicated by vaginal bleeding that required blood transfusion, and postpartum endometritis that rapidly responded to antibiotics. She has not had any menstrual periods following delivery. Physical examination shows sparse pubic hair, dry skin and delayed tendon reflexes. Urinalysis shows no glucose or ketones. Which of the following is most likely to be responsible for this patient's condition?
Infiltrative disorder
Autoimmune tissue destruction
Ischemic necrosis
Drug effect
Neoplasia
A 38-year-old G1P0 presents to the obstetrician’s office at 37 weeks gestational age complaining of a rash on her abdomen that is becoming increasingly pruritic. The rash started on her abdomen, and the patient notes that it is starting to spread downward to her thighs. The patient reports no previous history of any skin disorders or problems. She denies any malaise or fever. On physical examination, she is afebrile and her physician notes that her abdomen, and most notably her stretch marks, is covered with red papules and plaques. No excoriations or bullae are present. The patient’s face, arms, and legs are unaffected by the rash. Which of the following is this patient’s most likely diagnosis?
Herpes gestationis
Prurigo gravidarum
Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy
Impetigo herpetiformis
Pruritic urticarial papules and plaques of pregnancy
A 38-year-old man has pain and stiffness of his right knee. This began 2-weeks ago after he fell while skiing. On two occasions he had the sense that his knee was locked in a semiflexed position for a few seconds. He has noted a popping sensation when he bends his knee. On examination there is tenderness over the medial joint line of the knee. Marked flexion and extension of the knee are painful. The Lachman test (anterior displacement of the lower leg with the knee at 20°of flexion) and the anterior drawer test are negative. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Medial meniscus tear
Anterior cruciate ligament tear
Osteoarthritis
Chondromalacia patella
Lumbosacral radiculopathy
A 38-year-old man with AIDS (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome) is complaining of diminished vision in both eyes. His CD4 count last month was 50 cells/uL. He has been on highly active antiretroviral therapy for the past several months. He is afebrile, and his vital signs are stable. Ophthalmoscopic examination reveals yellow-white patches of retinal opacification and retinal hemorrhages. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Ocular toxoplasmosis
Herpes-zoster ophthalmicus
Herpes simplex keratitis
CMV Retinitis
HIV retinopathy
A 38-year-old woman comes to the physician because of burning with urination. She states that the burning started about 2 days ago and has been growing worse since. She has no frequency or urgency. She had one episode of pyelonephritis in the past but no other medical problems. On examination there is no costovertebral angle or abdominal tenderness. The examination is significant for a thick, white vaginal discharge with erythema and excoriations of the labia. Urinalysis is negative. KOH/Normal saline smear demonstrates pseudohyphae. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Candida vaginitis
Pelvic inflammatory disease
Hemorrhagic ovarian cyst
Pyelonephritis
Urinary tract infection
A 38-year-old woman presents to the emergency room complaining of chest pain for the past several hours. She describes it as sharp, centrally located and non-radiation. The pain worsens somewhat with inspiration and movement. The patient denies having fevers, chills, dyspnea, swelling, or difficulty breathing at night. She says she first noticed the pain while exercising three weeks ago, but has experienced it at rest as well. She says that she has been exercising heavily in an attempt to lose weight. Her BMI is currently 34kg/m2. Her father had a myocardial infarction at age 60. Her medical history is significant for two normal vaginal deliveries. She smokes a half-pack of cigarettes daily. On physical examination, her blood pressure is 112/69 mmHg and her heat rate is 72/min. Cardiac exam reveals a regular S1 and S2 without extra sounds or murmurs. There is tenderness to palpation over the sternum. What is the most likely cause of her chest pain?
Gastroesophageal reflux disease
Pulmonary embolism
Unstable angina
Pericarditis
Costochondritis
A 38-year-old woman who underwent a cadaveric renal transplant 8 years ago presents with fevers, fatigue, and weight loss. Evaluation included CT scans of the head, neck, chest, abdomen, and pelvis; she is noted to have diffuse lymphadenopathy and pulmonary nodules. A biopsy and histologic examination of a lymph node is performed. Which of the following viruses is most likely to be present in the lymph node?
Cytomegalovirus
Human papillomavirus
Human herpesvirus 8
Epstein-Barr virus
Coxsackie virus
A 38-year-woman at 39 weeks delivers a 7-lb infant female without complications. At 2 weeks of life, the infant develops fulminant liver failure and dies. What is the most likely causative virus?
Cytomegalovirus
Hepatitis B
Herpes simplex
Parvovirus
Rubeola
A 39-year-old agitated female with an unknown medical history is brought to the emergency department by police after she was found assaulting an innocent pedestrian on the street. She tells the attending physician that she has unusual powers and has been sent on a special mission by God. She is proud of frequently communicating with God, both telepathically and verbally, and says that he assists her in "punishing all of the wicked people in the world” Which of the following is most demonstrated in her thought content?
Magical thinking
Ideas of reference
Hallucination
Grandiose delusion
Illusion
A 39-year-old Caucasian female presents to your office with a palpable nodularity in the right breast. Pathologically, the lesion is composed of ducts distended by pleomorphic cells with prominent central necrosis. The lesion does not extend beyond the ductal basal membrane. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
Paget disease
Medullary carcinoma
Comedocarcinoma
Sclerosing adenosis
Mammary duct ectasia
A 39-year-old G1P0 at 39 weeks gestational age is sent to labor and delivery from her obstetrician’s office because of a blood pressure reading of 150/100 mm Hg obtained during a routine OB visit. Her baseline blood pressures during the pregnancy were 100 to 120/60 to 70. On arrival to labor and delivery, the patient denies any headache, visual changes, nausea, vomiting, or abdominal pain. The heart rate strip is reactive and the tocodynamometer indicates irregular uterine contractions. The patient’s cervix is 3 cm dilated. Her repeat blood pressure is 160/90 mm Hg. Hematocrit is 34.0, platelets are 160,000, SGOT is 22, SGPT is 15, and urinalysis is negative for protein. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Chronic hypertension
Eclampsia
Preeclampsia
Gestational hypertension
Chronic hypertension with superimposed preeclampsia
A 39-year-old G3P3 complains of severe, progressive secondary dysmenorrhea and menorrhagia. Pelvic examination demonstrates a tender, diffusely enlarged uterus with no adnexal tenderness. Results of endometrial biopsy are normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Endometriosis
Endometritis
Adenomyosis
Uterine sarcoma
Leiomyoma
A 39-year-old G5P5 woman delivered a 4.1-kg (9-lb) healthy male infant 20 minutes ago. She is now experiencing heavy vaginal bleeding, with the passage of large blood clots. She had an uncomplicated pregnancy, with a 15.9-kg (35-lb) weight gain. The patient had spontaneous onset of labor and spontaneous rupture of the membranes at 5 cm dilation. Labor lasted 3 hours, including 10 minutes of pushing. She did not have an episiotomy. The placenta delivered spontaneously 5 minutes after the infant, was normal in appearance, and was intact with a 3-vessel cord. The patient's previous 4 pregnancies and deliveries were normal. Her blood pressure is 110/60 mm Hg, pulse is 106/min, and respirations are 20/min. The uterine fundus is soft and at the level of the umbilicus. The patient's peri-pad is saturated with blood, and there are clots extruding from the vagina. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
Cervical/vaginal laceration
Clotting disorder
Inverted uterus
Retained placental tissue
Uterine atony
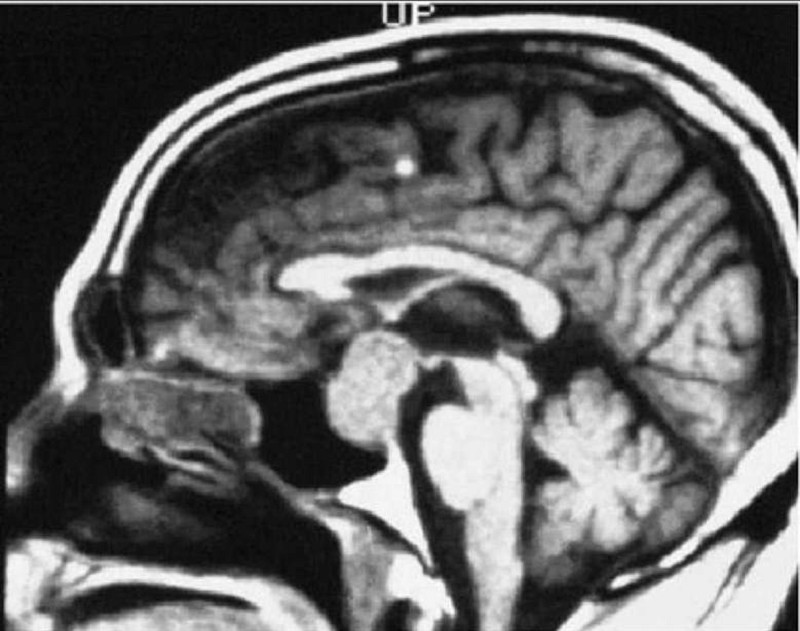
A 39-year-old man presents to his physician with the complaint of loss of peripheral vision. Which of the following findings are demonstrated by the subsequent magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan, shown here?
Cerebral atrophy
Pituitary adenoma
Optic glioma
Pontine hemorrhage
Multiple sclerosis plaque
A 39-year-old multiparous woman complains of intermittent vaginal bleeding between normal menstrual periods that has been going on for the past 4 months. The bleeding is painless and occurs after sexual intercourse. She has had three cesarean sections, along with a tubal sterilization with her last delivery. She has a 30 pack-year history of cigarette smoking. She is currently in a monogamous sexual relationship but has had multiple sexual partners in the past. She has not been regular in her annual examinations. Her last Pap smear was 5 years ago. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Submucous leiomyoma
Cervical carcinoma
Molar pregnancy
Simple hyperplasia without atypia
Sarcoma botryoides
A 39-year-old paleontologist complains of right-sided hip pain that makes it very difficult for him to lie on his right side while sleeping. He localizes the pain to the outer surface of his thigh. He was recently diagnosed with hypertension and hyperlipidemia. He takes hydrochlorothiazide and atorvastatin. He has smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for 15 years. He does not use alcohol or illicit drugs. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his pain?
Slipped femoral epiphysis
Peripheral vascular disease
Paget's disease
Trochanteric bursitis
Hip osteoarthritis
A 39-year-old woman at 16 weeks’ gestation complains of headaches, blurred vision, and epigastric pain. Her blood pressure is now 156/104 mmHg. Her uterine fundus is palpable 22 cm above her symphysis pubis. Fetal heart tones could not be heard with a handheld Doppler. She has 3+proteinuria. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Anencephaly
Twin gestation
Hydatidiform mole
Gestational diabetes mellitus
Maternal renal disease
A 39-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a "pins and needles" sensation around her mouth for the last 2-3 weeks. She gets similar sensations in her feet sometimes, along with muscle cramps, especially at the end of the day. She has no similar episodes in the past and has always been healthy. She works as a waitress and has "clean habits." Her family history is not significant. She is currently not taking any medications, and is allergic to penicillin. Her vital signs are normal. Examination is unremarkable. The patient's labs reveal: CBC: Hb 12.4 g/dl, WBC 6,000/cmm. Serum: Serum Na 140 mEq/L, Serum K 4.0 mEq/L, Chloride 100 mEq/L, Bicarbonate 24 mEq/L, BUN 10 mg/dl, Serum creatinine 0.8 mg/dl, Glucose 100 mg/dl, Calcium 6.5 mg/dl, Phosphorus, inorganic 5.8 mg/dl. Protein: Total 7.0 g/dl, Albumin 3.8 g/dl, Globulins 3.0 g/dl. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her condition?
Osteoporosis
Familial hypocalciuria
Osteomalacia
Primary hyperparathyroidism
Primary hypoparathyroidism
A 39-year-old woman presents with new onset of a bloody discharge from her right nipple. Physical examination reveals a 1-cm freely movable mass that is located directly beneath the nipple. Sections from this mass reveal multiple fibrovascular cores lined by several layers of epithelial cells. Atypia is minimal. The lesion is completely contained within the duct and no invasion into underlying tissue is seen. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Benign phyllodes tumor
Ductal papilloma
Intraductal carcinoma
Paget disease
Papillary carcinoma
A 39-year-old woman presents with severe menorrhagia and colicky dysmenorrhea. A hysterectomy including resection of the fallopian tubes and ovaries is performed. Examination by the pathologist finds a right adnexal cyst measuring approximately 2.3 cm in diameter and filled with clotted blood. Microscopic examination reveals the presence in the wall of the cyst of endometrial glands, stroma, and hemosiderin pigment. What is the best diagnosis?
Adenomyosis
Endometriosis
Hydatid cyst
Hydatidiform mole
Luteal cyst
A 39-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, at 30-weeks gestation comes to the physician for a prenatal visit. The patient's due date was determined by a 7-week ultrasound. Her prenatal course has been unremarkable. She has no complaints of contractions, loss of fluid, or bleeding from the vagina, and her baby is moving well. Examination demonstrates a fetal heart rate of 150 and a fundal height of 27 centimeters, which is the same measurement as that determined 4 weeks ago. This patient's fundal height measurement is most suggestive of which of the following?
Inaccurate estimated date of delivery (due date)
Intrauterine growth restriction
Premature labor
Twin gestation
Uterine cancer
A 4-day old pre term male neonate is being managed in the neonatal intensive care unit. He was born in the 34th week of gestation via lower segment caesarian section. On the first day of life, he developed tachypnea, grunting and nasal flaring. Chest x-rays showed a ground glass appearance of both lungs. He underwent endotracheal intubation and therapy with intravenous fluids, positive pressure ventilation, and intravenous antibiotics. He consequently showed remarkable improvement; however, he is currently beginning to have increased gastric residues. What is the most likely cause for this child's increased gastric residues?
Tracheo-esophageal fistula
Duodenal atresia
Necrotizing enterocolitis
Meconium aspiration syndrome
Pyloric stenosis
A 4-day-old female infant presents to the emergency department with vomiting and abdominal distention. The mother states that the vomitus was green. The infant also has had difficulty feeding and has been hard to console. The mother had an uncomplicated pregnancy. The infant passed meconium within 12 hours after birth. She also had several small, seedy, yellowish stools each day since birth. On physical examination, she is very irritable, her anterior fontanelle is slightly depressed. Her abdomen is distended. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Allergic reaction to formula
Hirschsprung disease
Gastroesophageal reflux disease
Meconium ileus
Midgut volvulus
A 4-day-old infant presents with yellow discoloration of the skin and sclera. The baby was born at term by a normal vaginal delivery. Pregnancy was uncomplicated; there were no risk factors for sepsis and no history of maternal alcohol or drug use. The baby is breast-fed and has been nursing every 2 hours, about 10 minutes at each breast. The bilirubin level is 15 mg/dL (all unconjugated), the hematocrit is 45%, and the Coombs test is negative. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Congenital biliary atresia
Crigler-Najjar syndrome
Isoimmune hemolytic disease
Breast milk jaundice
Breast-feeding jaundice
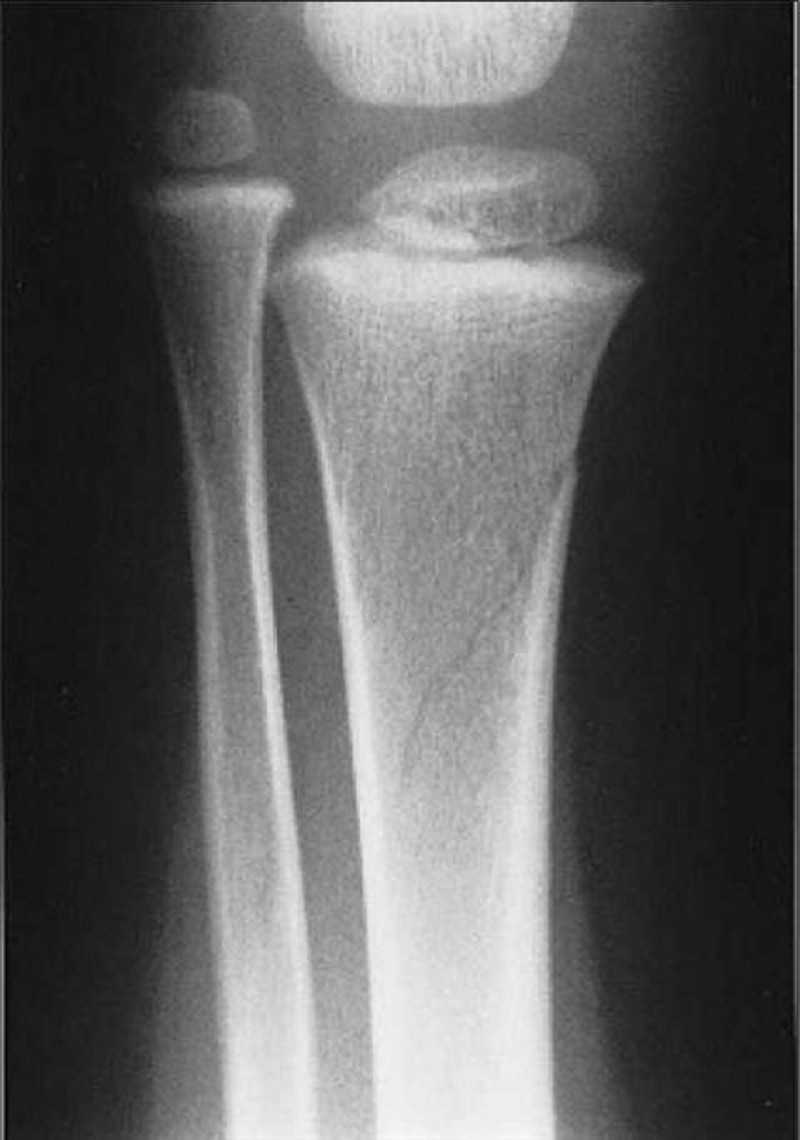
A 4-month-old baby boy arrives to the ER cold and stiff. The parents report that he had been healthy and that they put him to bed as usual for the night at the regular time. When they next saw him, in the morning, he was dead. Physical examination is uninformative. A film from a routine skeletal survey is shown below. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Scurvy
Sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS)
Osteogenesis imperfecta
Abuse
Congenital syphilis
A 4-month-old child presents with a 2-day history of vomiting and intermittent irritability. On examination, “currant jelly” stool is noted in the diaper, and a sausage-shaped mass is palpated in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen. Which of the following conditions is most likely to cause this?
Appendicitis
Diaphragmatic hernia
Giardiasis
Intussusception
Rotavirus gastroenteritis
A 4-month-old infant is evaluated by a dermatologist because of thick, erythematous skin with fine scaling, principally involving his face. The mother reports that the infant is "always scratching his face." An older brother and a maternal uncle had a similar condition. Screening hematologic studies show the following: Erythrocyte count 5.1 million/mm3, Leukocyte count 12,000/mm3, Segmented neutrophils 80%, Bands 5%, Eosinophils 3%, Basophils 1%, Lymphocytes 5%, Monocytes 6%, Platelet count 35,000/mm3 , with the comment that the platelets are smaller than normal. Serum immunoglobulin studies demonstrate the following: IgA 120 mg/dL, IgE 2300 IU/mL, IgG 900 mg/dL, IgM 15 mg/dL. Patients with this condition have a significantly increased incidence of which of the following?
Basal cell carcinoma
Melanoma
Hodgkin lymphoma
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma
Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin
A 4-month-old male infant is brought to the office by his parents due to progressive lethargy, poor feeding, fatigue and increasing pallor for the past four weeks. His antenatal and birth histories are unremarkable. His diet consists mainly of breast milk. His immunizations are up-to-date. His mother's blood type is 0 +. Physical examination reveals a webbed neck, cleft lip, shielded chest, triphalangeal thumbs, and pale mucous membranes and conjunctivae. Cardiac auscultation reveals mild tachycardia and a systolic ejection murmur over the left upper sternal border. The initial investigations reveal the following: Hb 8 g/dl, Ht 26%, WBCs 7,000/mm3, Platelets 300,000 /mm3, Reticulocytes 04%, MCV 104 fl, Blood type A -, Bilirubin direct 0.1 mg/dl, Bilirubin total 1.0 mg/dl. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Wiskott-Aidrich syndrome
Idiopathic aplastic anemia
Transient erythroblastopenia of childhood
Fanconi's anemia
Diamond-Biackfan anemia
A 4-year-old boy and his family have recently visited a local amusement park. Several of the family members developed “gastroenteritis” with fever and diarrhea, but the 4-year-old’s stool was slightly different, as it contained blood. His mother reports that in the past 24 hours he developed pallor and lethargy; she relates that his face looks swollen and that he has been urinating very little. Laboratory evaluation reveals a hematocrit of 28% and a platelet count of 72,000/µL. He has blood and protein in the urine. Which of the following diagnoses is most likely to explain these symptoms?
Henoch-Schönlein purpura
Intussusception
Meckel diverticulum
Hemolytic-uremic syndrome
IgA nephropathy
A 4-year-old boy is being evaluated for short stature. He has a history of multiple bone fractures in the past. He requires a wheelchair to ambulate and has hearing difficulty. On physical examination, his height is below the 5th percentile. His sclerae are blue in color. There is marked deformity of his lower extremities. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Achondroplasia
Developmental dysplasia of the hip
Constitutional delay of growth
Familial short stature
Osteogenesis imperfecta
A 4-year-old boy is brought by his mother to a Medical Camp for the Uninsured for the evaluation of his inflamed right eye. He has had a nasal discharge for the past 10 days. His brother has similar symptoms. His vital signs are stable. There are follicles and inflammatory changes in the conjunctiva of his right eye. The cornea shows neovascularization. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Herpes simplex keratitis
Orbital cellulitis
Trachoma
Gonococcal conjunctivitis
Viral conjunctivitis
A 4-year-old boy is brought to his pediatrician by his mother for "multiple fainting spells." Although physical examination reveals no abnormalities, the boy is admitted to the hospital for an extensive diagnostic workup. Laboratory evaluation reveals no abnormalities except for low serum glucose, high serum insulin, and low levels of serum C-peptide. The test results are revealed to the boy's mother, who works as a nurse in the hospital. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Factitious disorder
Malingering
Child abuse
Hypoglycemia
Munchausen syndrome by proxy
A 4-year-old boy is brought to the office because his school teacher thinks that his dusky blue appearance may have something to do with his inability to participate in regular school activities. His mother says that he has always appeared slightly out of breath. He has no history of any trauma, past surgery or medical conditions. His birth history is unremarkable. Physical examination reveals perioral cyanosis and a systolic murmur along the left sternal border. When the child squats, the murmur disappears and the cyanosis slightly improves. What is the most likely diagnosis of this patient?
Ventricular septal defect
Atrial septal defect
Coarctation of aorta
Tetralogy of Fallot
Eisenmenger syndrome
A 4-year-old boy is brought to the office for a routine exam. He has a small face, upslanting palpebral fissures, a speckled iris, and a simian crease. Auscultation reveals a loud P2. His mother informs you that he has trisomy. What is the most likely congenital heart disorder in this patient?
Tetralogy of F allot
Atrial septal defect
Endocardial cushion defect
Coarctation
Patent ductus arteriosus
A 4-year-old boy is seen in the office for a general check-up. The child appears well nourished and has normal developmental milestones. His temperature is 36.6 C (98 F), pulse rate is 80/min, and blood pressure is 110/70 mmHg. On abdominal palpation, there is a lobular right-sided flank mass, and the kidneys are palpable bilaterally. What is the most likely cause of the flank mass in this child?
Malignancy of neural crest cells
Renal cell carcinoma, embryonal variant
Tumor originating from the metanephros
Acquired renal cystic disease
Polycystic kidney disease, infantile type
A 4-year-old boy presents to the emergency department with generalized tonic-clonic seizures. On physical examination, the child is noted to be lethargic. His temperature is 37.4 C (99.3 F), blood pressure is 100/60 mm Hg, pulse is 72/min, and respirations are 16/min. His oral mucosa is moist, and there is no peripheral edema. Laboratory tests show: Blood: Sodium 120 mEq/L, Potassium 4.2 mEq/L, Chloride 96 mEq/L, Bicarbonate 20 mEq/L, Blood urea nitrogen 9.6 mg/dL, Creatinine 0.4 mg/dL, Glucose 88 mg/dL, Urine: Sodium 55 mEq/L, Potassium 16 mEq/L, Osmolality 530 mOsmol/kg. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Addison disease
Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH)
Acute renal failure
Congestive heart failure
Hyponatreraic dehydration
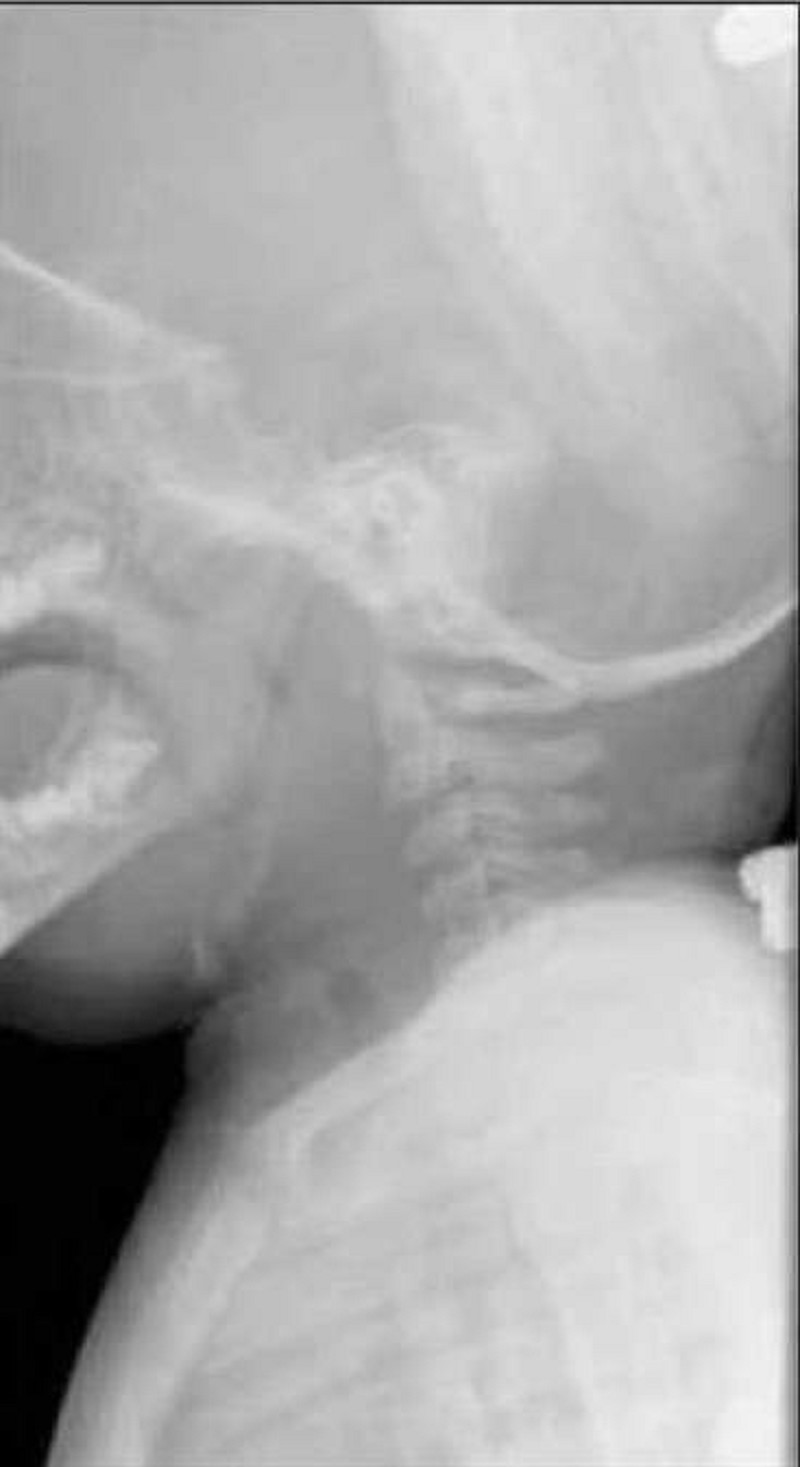
A 4-year-old boy presents to the physician with fever and a sore throat. His illness began with rhinorrhea, cough, and congestion one week ago, but in the last 24 hours he has developed fever, a sore throat, and neck pain. His mother also reports that he sounds hoarse. His appetite is decreased and he complains of dysphagia. His temperature is 39.7 C (103.5F), pulse is 100/min, and respiratory rate is 25/min. On examination, the child appears sick. He has cervical lymphadenopathy on the right and decreased range of motion of his neck. His voice is muffled and sounds hoarse. His oropharynx is erythematous and a bulge is noted in the posterior pharyngeal wall. A lateral radiograph of the neck is shown below. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Diphtheria
Epiglottitis
Infectious mononucleosis
Retropharyngeal abscess
Viral pharyngitis
A 4-year-old boy presents with severe pains in both of his legs. On physical examination, his temperature is 37.7 C (99.8 F), blood pressure is 108/68 mm Hg, pulse is 96/min, and respirations are 17/min. He is noted to have marked pallor on his lips and palpebral conjunctiva. Numerous purpura and petechiae are noted on his skin. His spleen is palpable 3 cm below his left costal margin. Laboratory evaluation reveals a white blood cell count of 1600/mm3; hemoglobin, 6.1 g/dL; and platelets, 36,000/mm3. Which of the following diagnoses is most consistent with these findings?
Acute lymphocytic leukemia
Immune thrombocytopenic purpura
Aplastic anemia
Henoch-Schönlein purpura
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura
A 4-year-old boy, whose past medical history is positive for three urinary tract infections, presents with a blood pressure of 135/90 mm Hg. He is likely to exhibit which of the following symptoms or signs?
Multiple cranial nerve palsy
Headache
Hyporeflexia
Increased urine output
Right ventricular hypertrophy
A 4-year-old Caucasian boy is brought to his physician's office for a health maintenance exam. He will be starting preschool soon, and his parents want to make sure that he is in optimal health. The child has no complaints, and is generally happy. His medical history is significant for pneumonia as a newborn, and three episodes of otitis media since birth. He does not take any medications on a regular basis. His newborn screening test results are normal. His developmental milestones are at par with his age. He lives with his parents in a middle-class, suburban house built in 1981. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step for this child's primary care?
Screen him for inguinal hernias
Meningococcal vaccine
Vision exam
Rotavirus vaccine
Serum lead level
{"name":"DES C_Diagnosis (6) Prepared : CHILLY", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"A 34-year-old woman with a skin rash, joint pains, and oral ulcers is diagnosed with systemic lupus erythematosus. She has no renal or central nervous system involvement, and her past medical history and review of systems are otherwise negative. Therapy with hydroxychloroquine is started. Which of the following screening tests is most important in this patient?","img":"https://cdn.poll-maker.com/18-738655/image.jpeg?sz=1200"}
More Quizzes
Primary 4 English F1W2 (Day 1 CBT 2) (tklesson)
1050
Genres and Literary Movements
1580
Rack your brains
10522
First Nations Quiz - "Be You, Belong" 2023
10514
Employment Law for HR Managers: Separations, Worker's Compensation & Safety
15828414
Free US History Final Exam Study Guide
201022048
Descubre qué personaje de South Park eres tú
201025509
Emotional Health: Assess Your Well-Being Now
201032278
Pediatric NCLEX Questions: Test Your Peds RN Knowledge
201024008
Ancient Mesopotamia: Fertile Crescent Map Challenge
201024008
Fetal Development: Test Your Prenatal Growth Knowledge
201034976
Ultimate Filing Tests: Master Rules & Standards
201038266