All ECG Part 2 (DES Exam)

Cardiac Management Quiz
Test your knowledge and skills in the assessment and management of various cardiac conditions with our comprehensive quiz. This quiz features 26 challenging questions designed for medical professionals and students interested in cardiology.
Key features of the quiz:
- Realistic clinical scenarios
- Focused on ECG interpretation and cardiac management
- Designed to enhance your clinical decision-making skills
36/Manag/US/ 499) A 31-year-old kindergarten teacher presents to the ED complaining of acute-onset substernal chest pain that is sharp in nature and radiates to her back. The pain is worse when she is lying down on the stretcher and improves when she sits up. She smokes cigarettes occasionally and was told she has borderline diabetes. She denies any recent surgeries or long
travel. Her BP is 145/85 mmHg, HR is 99 beats per minute, RR is 18 breaths per minute, and temperature is 100.6°F. Examination of her chest reveals clear lungs and a friction rub. Her abdomen is soft and nontender to palpation. Her legs are not swollen. Chest radiography and echocardiography are unremarkable. Her ECG is shown below. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
travel. Her BP is 145/85 mmHg, HR is 99 beats per minute, RR is 18 breaths per minute, and temperature is 100.6°F. Examination of her chest reveals clear lungs and a friction rub. Her abdomen is soft and nontender to palpation. Her legs are not swollen. Chest radiography and echocardiography are unremarkable. Her ECG is shown below. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?

Anticoagulate and CT scan to evaluate for a PE
Prescribe a NSAID and discharge the patient
Aspirin, heparin, clopidogrel, and admit for ACS
Administer thrombolytics if the pain persists
Prescribe antibiotics and discharge the patient
37/Manag/US/ 797) A 43-year-old woman develops acute renal failure following an emergency resection of a leaking abdominal aortic aneurysm. One week after surgery, the following laboratory values are obtained:Serum electrolytes (mEq/L): Na+ 127, K+
5.9, Cl− 92, HCO3− 15Blood urea nitrogen: 82 mg/dLSerum creatinine: 6.7 mg/dLThe patient has gained 4 kg since surgery and is mildly dyspneic at rest. Eight hours after these values are reported, the following electrocardiogram is obtained. Which of the following is the most appropriate initial treatment in the management of this patient?
5.9, Cl− 92, HCO3− 15Blood urea nitrogen: 82 mg/dLSerum creatinine: 6.7 mg/dLThe patient has gained 4 kg since surgery and is mildly dyspneic at rest. Eight hours after these values are reported, the following electrocardiogram is obtained. Which of the following is the most appropriate initial treatment in the management of this patient?

10 mL of 10% calcium gluconate
0.25 mg digoxin every 3 hours for 3 doses
Oral Kayexalate
100 mg lidocaine
Emergent hemodialysis
38/Manag/US/ 1039) A 59-year-old male suffers a myocardial infarction. He is treated medically and is discharged home ten days later on aspirin, atorvastatin, metoprolol, lisinopril, and sublingual nitroglycerin. One month later, he presents to your office for a
follow-up visit. He denies chest pain, dyspnea or lightheadedness. His blood pressure is 120/75 mmHg. His EKG is pictured below. Echocardiogram reveals an ejection fraction of 45%. What is the best next step in his management?
follow-up visit. He denies chest pain, dyspnea or lightheadedness. His blood pressure is 120/75 mmHg. His EKG is pictured below. Echocardiogram reveals an ejection fraction of 45%. What is the best next step in his management?

Observation
Amiodarone
Digoxin
DC cardioversion
Verapamil
39/Manag/US/ 1137) A 63-year-old woman on digitalis for chronic atrial fibrillation experiences fatigue, nausea, and anorexia. Her pulse is regular at 50 beats/min, and the heart sounds, chest, and abdominal examinations are normal. On the ECG, no P waves are visible and the QRS complexes are narrow and regular. Which of the following is the most appropriate management step?

An increase in digitalis dose
Complete cessation of digitalis
Withdrawal of digitalis for one dose
Addition of a beta-blocker
Addition of a calcium channel blocker
40/Manag/US/ 1140) A 64-year -old male with a history of hypertension presents with general malaise and a 'funny' heart rhythm for the past 2 weeks. He had an echocardiogram done last year, which revealed mild left atrial dilatation and left ventricular hypertrophy. He has been taking hydrochlorothiazide for hypertension. His blood pressure at today's visit is 180/98 mmHg. An EKG is obtained and is shown below. Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment for this patient?

Immediate cardioversion
Lidocaine
Adenosine
Carotid massage
Diltiazem
41/Manag/US/ 1152) A 65-year -old Hispanic male is brought to the emergency room with severe substernal chest pain and diaphoresis that began suddenly 1 hour ago. He reports that his pain started while he was at rest and radiates to his left shoulder. The patient notes having vomited twice when the pain first began. Despite administration of 2 baby aspirins and 3 tablets of sublingual nitroglycerin, the pain persists. His initial EKG is shown below. On physical examination, the patient's temperature is 36.9°C (98.4°F), blood pressure is 110/80 mmHg, pulse is 60/min, and respirations are 18/min. S1 and S2 are normal, and an S4 is heard. The lungs are clear to auscultation. There is no jugular venous distension or pedal edema. Interventions to achieve which of the following goals would most improve this patient's long-term prognosis? 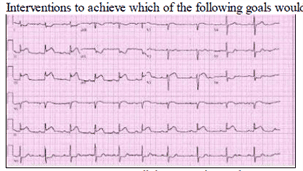

Decrease myocardial oxygen demand
Decrease blood coagulability
Restore coronary blood flow
Prevent ischemia-induced arrhythmias
Prevent reperfusin myocardial injury
42/Manag/US/ 1196) A 67-year-old male presents to the ER with chest pain. His medical history is significant for stable angina for which he takes aspirin and isosorbide dinitrate, as well as hypertension and bronchial asthma. Occasionally, he uses an albuterol inhaler. He is admitted to the hospital and five hours later, he begins to feel lightheaded and weak. His blood pressure is 100/60 mmHg. An EKG is obtained and is shown below. Which of the following is the best next step in managing this patient?

Cardiac catheterization
Pacemaker insertion
Adenosine
Digoxin
Metoprolol
43/Manag/US/ 1354) A patient has been in the coronary care unit for the past 24 hours with an acute anterior myocardial infarction. He develops the abnormal rhythm shown below, although blood pressure remains stable at 110/68 mmHg. Which of the following is the best next step in therapy?

Perform cardioversion
Arrange for pacemaker placement
Give digoxin.
Give propranolol
Give lidocaine
44/Manag/US/ 1447) An 82-year-old woman is brought to the ED by her daughter for worsening fatigue, dizziness, and light-headedness. The patient denies chest pain or shortness of breath. She has not started any new medications. Her BP is 140/70 mmHg, HR is 37 beats per minute, and RR is 15 breaths per minute. An IV is started and blood is drawn. An ECG is seen below. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?

Bed rest for the next 48 hours and follow-up with her primary-care physician
Administer aspirin, order a set of cardiac enzymes, and admit to the cardiac care unit (CCU)
Place a magnet on her chest to turn off her pacemaker
Admit for Holter monitoring and echocardiogram
Place on a cardiac monitor, place external pacing pads on the patient, and admit to the CCU
45/Manag/US/ 1471) An otherwise asymptomatic 65-year-old man with diabetes presents to the ER with a sports-related right shoulder injury. His heart rate is noted to be irregular, and this ECG is obtained. Which of the following is the best immediate therapy?

Atropine
Isoproterenol
Pacemaker placement
Electrical cardioversion
Observation
46/Emer/E/ 52) Un homme âgé de 82 ans consulte aux urgences pour une aggravation très récente d’une dyspnée d’effort. A l’examen, le patient présente une dyspnée avec des crépitants jusqu’à mi champ pulmonaire, il est pâle et des genoux sont marbrés. Ses constantes sont les suivantes : PA 95/50mmHg, pouls 90/min, T ˚37 ˚C, Sp02 91%. Vous réalisez un électrocardiogramme. Quelle étiologie grave est la plus probable concernant l’aggravation de l'insuffisance cardiaque de votre patient?

Un événement ischémique
Un trouble du rythme
Une atteinte valvulaire
Une cardiopathie dilatée
Une cardiopathie hypertrophique
46/Emer/E/ 53) Une femme de 69 ans est admise aux urgences pour dyspnée aiguë. Elle est atteinte d'un adénocarcinome gastrique métastatique avec compression médiastinale. Vous notez une PA à 105/60 même Hg, une SaO2 à 92% sous 6L. Elle n'a pas de signe de choc périphérique. Elle présente également un mollet droit rouge et douloureux. Vous suspectez une embolie pulmonaire sub-massive. Quel critère électrocardiographique est le plus spécifique de ce diagnostic ?

Tachycardie sinusale régulière
Bloc de branche droite incomplet
Sous décalage du segment ST en latéral
Onde S en DI et Q en DIII
Ondes T négatives de V1 à V3
47/Emer/US/ 124) A 3-month-old infant is brought to your office for pallor and listless- ness. Your physical examination reveals tachycardia that is constant and does not vary with crying. He has no hepatomegaly and the lungs are clear. His ECG is shown. Which of the following is the most appropriate initial management of this patient?

Rapid verapamil infusion
Transthoracic pacing of the heart
Carotid massage
DC cardioversion
Precordial thump
48/Emer/US/ 232) A 46-year-old man collapsed while getting out of his bed. He has been feeling weak over the last several days and has complained of vague chest
discomfort. He ascribed the symptoms to a recent respiratory infection and did not visit a doctor. His mother died of a stroke and his father suffered from recurrent myocardial infarctions. He eats a balanced diet and takes a multivitamin daily. His most recent blood cholesterol level was 200 mg/dl. An ECG strip taken by EMS is shown below. Which of the following is the best initial management of this patient?
discomfort. He ascribed the symptoms to a recent respiratory infection and did not visit a doctor. His mother died of a stroke and his father suffered from recurrent myocardial infarctions. He eats a balanced diet and takes a multivitamin daily. His most recent blood cholesterol level was 200 mg/dl. An ECG strip taken by EMS is shown below. Which of the following is the best initial management of this patient?

Procainamide
Synchronized DC cardioversion
Thrombolytic therapy
Beta-blockers and aspirin
Pericardiocentesis
49/Emer/US/ 252) A 51-year-old man with a long history of hypertension presents to the ED complaining of intermittent chest palpitations lasting for a week. He denies chest pain, shortness of breath, nausea, and vomiting. He recalls feeling similar episodes of palpitations a few months ago but they resolved. His blood pressure (BP) is 130/75 mmHg, heart rate (HR) is 130 beats per minute, respiratory rate (RR) is 16 breaths per minute, and oxygen saturation is 99% on room air. An ECG is seen below. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?

Sedate patient for immediate synchronized cardioversion with 100 J
Prepare patient for the cardiac catheterization laboratory
Administer warfarin
Administer amiodarone
Administer diltiazem
50/Emer/US/ 267) A 55-year-old man presents to the ED with worsening weakness, muscle cramps, and paresthesias. His past medical history is significant for hypertension and diabetes. He smokes one pack of cigarettes per day. On examination, the patient is alert and oriented and diffusely weak. An ECG is seen below. Which of the following is the most important next step in management?

Administer calcium gluconate
Administer insulin and dextrose
Administer aspirin and call the catheterization laboratory
Order an emergent head CT scan and get a neurology consult
Collect a sample of his urine to test for ketones
51/Emer/US/ 282) A 59-year-old man presents to the ED with left-sided chest pain and shortness of breath that began 1 hour ago. Initial vital signs are BP 85/45 mmHg, HR 105 beats per minute, RR 20 breaths per minute, and oxygen saturation 94% on room air. An ECG is seen below. Which of the following is the most appropriate definitive treatment?

Administer metoprolol or diltiazem
Electrical cardioversion
Administer calcium gluconate
Thrombolytic therapy
Percutaneous angioplasty
52/Emer/US/ 307) A 64-year-old male is admitted in ICU for acute myocardial infarction. He is on metoprolol, lisinopril, aspirin, furosemide, and potassium supplements. All of a sudden, the nurse mentions that the patient has a change in his tele monitoring. His blood pressure is 120/60 mmHg. His potassium level is 4.2. He is alert, awake and oriented time, place and person. Examination shows scattered bilateral crackles, peripheral pedal edema and elevated JVI. Which of the following is the next best step in the management of this patient?

IV amiodarone
IV digoxin
Cardioversion
IV diltiazem
Carotid massage
53/Emer/US/ 310) A 64-year-old man in the surgical intensive care unit goes into rapid atrial fibrillation on postoperative day one after a decortication for a loculated pulmonary empyema. He is given an appropriate loading dose of digoxin, but 4 hours after his second dose, the patient complains of increased palpitations and dizziness. The patient is conscious and hemodynamically stable. STAT serum blood tests show a potassium level of 5.0 mEq/L; all other electrolytes, including divalents, are in the normal range. The digitalis level is above the therapeutic range at 4 ng/mL (therapeutic range 0.5-2 ng/mL). Results of cardiac telemetry are shown in the image. Which of the following should be administered immediately?

Calcium
Furosemide
Magnesium
Potassium
Sodium polystyrene sulfonate
54/Emer/US/ 316) A 65-year-old man develops palpitations and dizziness. His blood pressure is 80/50 mm Hg and his pulse is regular at 150/min. His ECG shows a “saw-toothed” pattern of P waves. Which of the following procedures is most appropriate in converting him back to sinus rhythm?

Carotid sinus pressure
Gagging procedures
Valsalva maneuver
Eyeball compression
Electrical cardioversion
55/Emer/US/ 322) A 66-year-old male is rushed to the emergency department because he feels dizzy and light-headed. He denies chest pain or palpitations. He has a history of hypertension and diabetes. His blood pressure is 116/62 mmHg and his pulse is 35-40/min. He is alert, awake, and fully oriented. He is breathing comfortably and does not appear to be in any distress. His extremities are slightly cold and capillary refill is 3 seconds. His EKG is shown below. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?

Intravenous adenosine push
Intravenous atropine
Intravenous epinephrine
Intravenous amiodarone
Transcutaneous pacing
56/Emer/US/ 331) A 69-year-old male undergoes coronary artery bypass and aortic valve replacement surgery. The procedure goes well, and he is extubated and discharged to the step-down unit on postoperative day 2. That night, he complains of weakness, chest tightness and shortness of breath. His blood pressure is 70/30 mmHg, respiratory rate is 26/min, and heart rate is 148 beats per minute. Lung auscultation reveals bibasilar crackles. An EKG rhythm strip is obtained. Which of the following is the best next step in the management of this patient?

Amiodarone
Transcutaneous pacing
DC cardioversion
Lidocaine
Digoxin
57/Emer/US/ 336) A 70-year-old male with a history of mild chronic kidney disease, diabetes mellitus, and CHF is admitted to your inpatient service with decreased urine output, weakness, and shortness of breath. He takes several medications but cannot remember their names. Labs are pending; his ECG is shown below. Based on the information available, what is the best initial step in management?

Administration of intravenous insulin
Administration of intravenous sodium bicarbonate
Administration of intravenous 3% hypertonic saline
Administration of oral sodium polystyrene sulfonate
Administration of intravenous calcium gluconate
58/Emer/US/ 345) A 72-year-old female is admitted to the ICU with severe chest pain. The initial set of cardiac enzymes is positive and her EKG reveals an anterior wall myocardial infarction. She receives treatment with aspirin clopidogrel, metoprolol nitroglycerine drip, and morphine. Two hours later, her telemetry monitor displays the following rhythm. Which of the following is the best next step in managing this patient?

Lidocaine
Defibrillation
Digoxin
Amiodarone
Immediate echocardiogram
59/Emer/US/ 397) An 82-year-old white female is admitted to the hospital for observation after presenting to the emergency department with dizziness. After being
placed on a cardiac monitor in the ER, the rhythm strip below was recorded. There is no past history of cardiac disease, diabetes, or hypertension. With prompting, the patient discloses several prior episodes of transient dizziness and one episode of brief syncope in the past. Physical examination is unremarkable. Which of the following is the best plan of care?
placed on a cardiac monitor in the ER, the rhythm strip below was recorded. There is no past history of cardiac disease, diabetes, or hypertension. With prompting, the patient discloses several prior episodes of transient dizziness and one episode of brief syncope in the past. Physical examination is unremarkable. Which of the following is the best plan of care?

Reassurance. This is a benign condition, and no direct therapy is needed
Reassurance. The patient may not drive until she is symptom free, but otherwise no direct therapy is needed
Nuclear cardiac stress testing; treatment depending on results
Begin therapy with aspirin
Arrange placement of a permanent pacemaker
60/Emer/US/ 406) As you are examining the patient described in the previous question, he starts to complain of chest discomfort and shortness of breath and has another syncopal episode. His ECG is shown below. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?

Call cardiology consult
Cardiovert the patient
Administer metoprolol
Administer amiodarone
Apply transcutaneous pacemaker
{"name":"All ECG Part 2 (DES Exam)", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Test your knowledge and skills in the assessment and management of various cardiac conditions with our comprehensive quiz. This quiz features 26 challenging questions designed for medical professionals and students interested in cardiology.Key features of the quiz:Realistic clinical scenariosFocused on ECG interpretation and cardiac managementDesigned to enhance your clinical decision-making skills","img":"https:/images/course7.png"}
More Quizzes
Part 37
65320
ECG interpretation
740
100
August Quiz 2020
11624
Classification of Matter - Free Chemistry Practice
201017768
How to Know If Someone Likes You - Spot the Signs
201017768
How Picky Are You? - Free, Instant Results
201018501
How Will I Die? Free Online Personality
201016630
Guess the Soccer Player - Free to Play Online
201018658
Shark Tank: Which Judge Are You?
201016925
C1 English Vocabulary Test - Gap-Fill (Free)
201018348
Time Calculator - Free Hours & Minutes Practice
201017837