USMLE pediatry basic 2
107) An 18-month-old male infant is brought to the office by his parents for a follow-up visit. He has a congenital condition that started at the age of 6 months with repeated vomiting and hypotonia, and progressively evolved into choreoathetosis, spasticity and dystonia. Over the past month, he has started biting his hands and arms, pinching himself and banging his limbs against the wall. His family history is unremarkable. On examination, he has several scars, cuts and bruises over his arms and hands. His uric acid levels are elevated. What is the most likely deficient enzyme in this patient?
Glutamine-phosphorylase pyrophosphate aminotransferase
Xanthine oxidase
Hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase
Adenyl succinate synthase
Purine nucleoside phosphorylase
108) A 16-day-old infant presents with fever, irritability, poor feeding, and a bulging fontanelle. Spinal fluid demonstrates gram-positive cocci. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Listeria monocytogenes
Group A streptococci
Group B streptococci
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Staphylococcus aureus
109) A 16-year-old boy presents to the emergency center with a 2-day history of an abscess with spreading cellulitis. While in the emergency center, he develops a high fever, hypotension, and vomiting with diarrhea. On examination you note a diffuse erythematous macular rash, injected conjunctiva and oral mucosa, and a strawberry tongue. He is not as alert as when he first arrived. This rapidly progressive symptom constellation is likely caused by which of the following disease processes?
Kawasaki disease
TSST-1–secreting S aureus
Shiga toxin–secreting Escherichia coli
α-Toxin–secreting Clostridium perfringens
Neurotoxin-secreting Clostridium tetani
110) An 18-month-old child presents to the emergency center having had a brief, generalized tonic-clonic seizure. He is now postictal and has a temperature of 40C (104F). During the lumbar puncture (which ultimately proves to be normal), he has a large, watery stool that has both blood and mucus in it. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
Salmonella
Enterovirus
Rotavirus
Campylobacter
Shigella
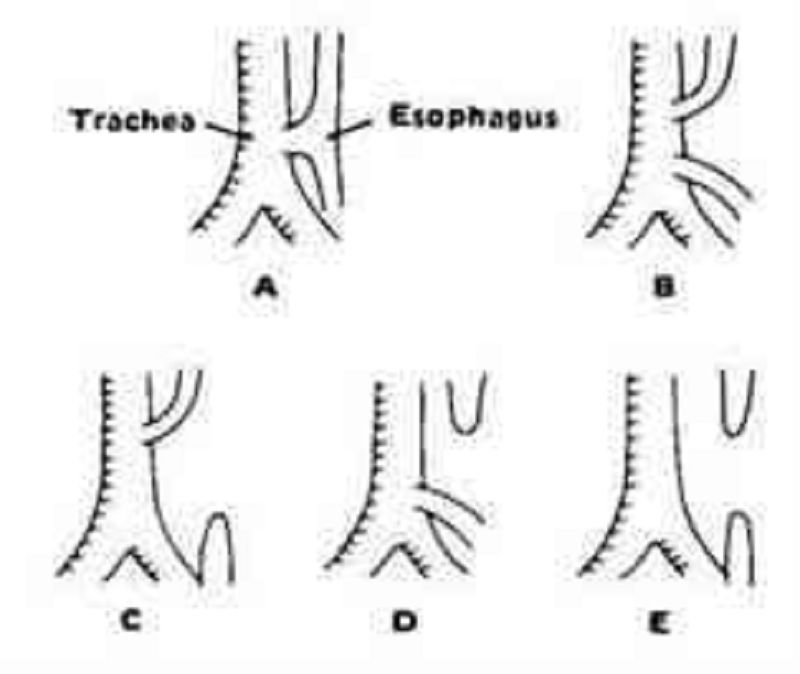
111) Shortly after birth, an infant develops abdominal distention and begins to drool. When she is given her first feeding, it runs out the side of her mouth, and she coughs and chokes. Physical examination reveals tachypnea, inter- costal retractions, and bilateral pulmonary rales. The esophageal anomaly that most commonly causes these signs and symptoms is illustrated by which of the following?
Figure A
Figure B
Figure C
Figure D
Figure E
112) The mother and father of a newborn come in for the 2-week check-up. The mother complains of “colic” and asks if she can switch to goat’s milk instead of breast milk. Which of the following should be your main concern about using goat’s milk instead of breast milk or cow’s milk?
It has insufficient calories
It has insufficient folate
It has insufficient whey
It has insufficient casein
It has insufficient fat
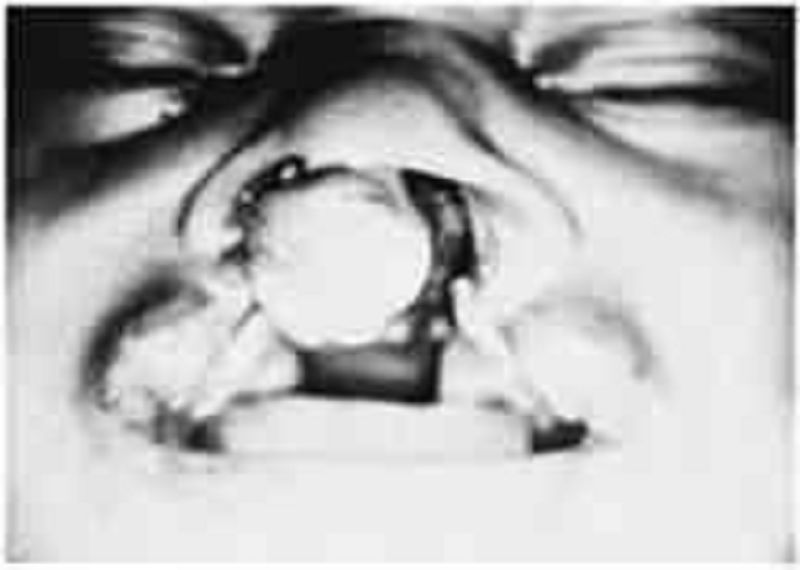
113) You see the newborn baby shown below for the first time in the nursery. You consult plastic and reconstructive surgeon as well as the hospital’s speech therapist. Understandably, the parents have many questions. Which of the following statements is appropriate anticipatory guidance for this family?
Parenteral alimentation is recommended to prevent aspiration
Surgical closure of the palatal defect should be done before 3 months of age
Good anatomic closure will preclude the development of speech defects
Recurrent otitis media and hearing loss are likely complications
The chance that a sibling also would be affected is 1 in 1000
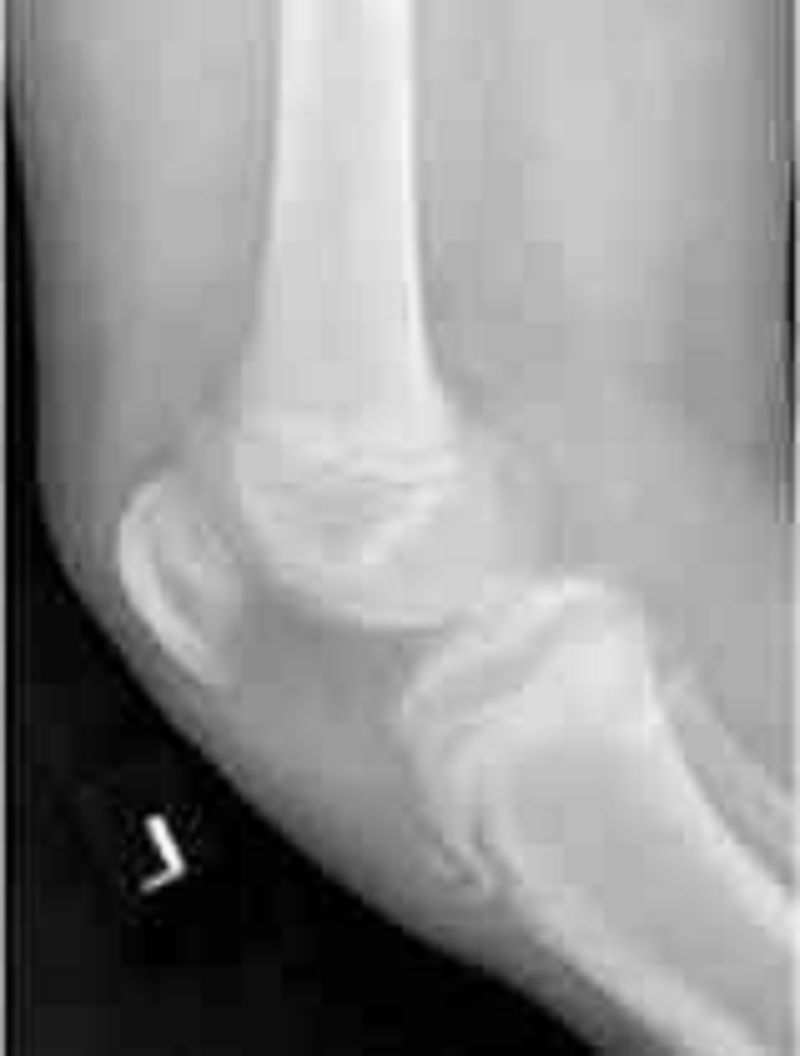
114) A 13-year-old male is brought to the physician for evaluation of intermittent left knee pain that arose three months ago. He does not remember any trauma to his knee. The pain worsens after basketball games, but improves some with rest. He has been taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications with some relief. On physical examination, he has edema and tenderness over the proximal tibia at the site of the patellar tendon insertion. Examination of the knee joint is normal and no effusion is present. His knee pain is reproducible by extending the knee against resistance. A lateral radiograph of his knee is shown below. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's knee pain?
Prepatellar bursitis
Traction apophysitis
Patellar tendonitis
Tibial osteomyelitis
Patellofemoral stress syndrome
115) A 4-day-old infant is brought to the physician for an outpatient follow-up visit. The mother's pregnancy and delivery were uncomplicated. The infant weighed 3.4kg (7 .5 lb) and was 19 in (48.2 cm) long at birth. He did well in the newborn nursery and was discharged from the hospital on day 2 of life. Today his mother reports that he is exclusively breastfed, and nurses for 10 minutes every 3 hours. He has 3-4 wet diapers a day, and has not had a bowel movement for two days. On examination, he weighs 2.95 kg (6.5 lb) and is 19 in (48.2 cm) long. He appears jaundiced on the face and chest. The remainder of the physical examination is unremarkable. Laboratory values are shown below. Total bilirubin 15 mg/dl, direct bilirubin 1 mg/dl, Infant's blood type O positive, Mother's blood type A positive. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this infant's hyperbilirubinemia?
Biliary atresia
Breast milk jaundice
Breastfeeding jaundice
Galactosemia
ABO incompatibility
116) A 10-year-old presents with 2 months history of heavy menstrual-like bleeding. Menarche occurred 6 months ago and this first menses consisted of spotting for 3-4 days without cramps. Subsequent periods were light in flow but lasted 6 to 8 days. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her bleeding?
Von Willebrand disease
Ovarian tumor
Thyroid disease
Dysfunctional uterine bleeding
Pregnancy
117) A 25-year-old woman comes to your office for counseling. She says that her husband has cystic fibrosis, and that she has no family history of this disease. They are planning to have a child. She wonders what the probability is for their baby to have cystic fibrosis. Which of the following is your best response in this situation?
Cystic fibrosis is an autosomal dominant disease, so the child will have the disease
Cystic fibrosis is an autosomal recessive disease, so the child has 25% probability of getting the disease
Cystic fibrosis is an autosomal recessive disease, so the child has 50% probability of getting the disease
The probability cannot be determined because her carrier status is unknown
The probability cannot be determined because cystic fibrosis does not follow Mendelian transmission
118) An awake, alert infant with a 2-day history of diarrhea presents with a depressed fontanelle, tachycardia, sunken eyes, and the loss of skin elasticity. Which of the following is the correct percentage of dehydration?
Less than 1%
1% to 5%
5% to 9%
10% to 15%
More than 20%
119) A newborn infant is brought to the nursery for evaluation after delivery. The mother reports that the pregnancy was uncomplicated, but she had only two prenatal visits. The infant was born via normal spontaneous vaginal delivery and required no resuscitation. The infant has hepatosplenomegaly on examination. While in the hospital, the infant requires treatment for anemia and hyperbilirubinemia. On subsequent examinations, the infant has clear rhinorrhea and ulcerative lesions on his feet. Which of the following congenital infections is most likely in this patient?
Toxoplasmosis
Syphilis
Rubella
Cytomegalovirus infection
Human immunodeficiency virus infection
120) A 17 -year-old boy is brought to the emergency department by his father after the boy began threatening him at home. Over the last several months, the father reports, the boy has been increasingly abusive. He was recently involved in a fist fight at school. The boy states that there is nothing wrong. He is otherwise healthy. He denies alcohol use, but does admit to occasional marijuana use. On examination he has acne on his forehead and back and his hairline is receding. There is palpable tissue underneath his nipples bilaterally Heart and lung exams are normal. What substance is this boy most likely abusing?
Anabolic steroids
Cocaine
Heroin
Methamphetamine
Phencyclidine
121) A 16-year-old African American male with sickle cell anemia presents complaining of a 1-week history of exertional dyspnea, fatigue, and generalized weakness. He denies fevers, chills, night sweats, or cough. His only medication is oxycodone for chronic pain. On physical examination, he weighs 68 kg (150 lbs) and is 168cm (66 in) tall His temperature is 36.7C (98F), blood pressure is 120/70 mm Hg, pulse is 76/min, and respirations are 18/min. All organ systems appear normal Laboratory studies show: Hematocrit 20%, Mean corpuscular volume 110 fl, Reticulocyte count 1.0%. Which of the following is the most likely mechanism underlying these findings?
Adverse drug reaction
Gastric mucosal atrophy
Bacterial overgrowth in the small intestine
Increased demand for folic acid
Increased demand for vitamin B 12
122) In the 2nd week of life, a previously healthy newborn develops diarrhea. The stools are watery and voluminous and continue even when the infant is fasting. Which of the following is the most likely pathogen?
Campylobacter jejuni
Enteroinvasive Escherichia coli
Rotavirus
Salmonella species
Shigella species
123) A 17-year-old girl presents to the office with a 5-day history of a malodorous vaginal discharge. She is sexually active and uses condoms for sexual intercourse. On examination, a thin, white discharge is seen. A "fishy" odor is produced when KOH is added to the discharge. The vaginal fluid has a pH of 5. Which of the following is the most likely finding on a microscopic examination of the vaginal fluid?
Clue cells
Gram-negative diplococci
Lactobacilli
Pseudohyphae
Trichomonads
124) A 20-month-old male is brought to ER with high fever, confusion and a skin rash suggestive of measles. He has a history of recurrent respiratory infections over the last 6 months. The patient's family has recently emigrated from a rural Russian province. Which of the following forms of vitamin supplementation should be considered in this patient?
Vitamin A
Vitamin K
Vitamin D
Vitamin E
Vitamin B 12
125) A 3-year-old male is brought to the emergency department for evaluation of right neck swelling. His parents noticed a lump on his right neck yesterday, which has since increased in size and is now erythematous and tender. He has been previously healthy except for mild upper respiratory tract symptoms last week. His temperature is 38C (100.4F), pulse is 90/min, and respiratory rate is 25/min. On examination, he is nontoxic appearing. A 5-cm anterior cervical lymph node is palpated on the right side. It is poorly mobile, warm, erythematous, and tender to palpation. There is no fluctuance or induration. What is the most likely organism causing these symptoms?
Staphylococcus aureus
Francisella tularensis
Peptostreptococcus
Nontuberculous mycobacteria
Epstein-Barr virus
126) A 5-month-old infant is brought to the office for the evaluation of persistent vomiting, failure to thrive, and developmental delay. His antenatal and postnatal histories are not known to his Caucasian foster parents, who adopted him when he was 4 months old. The physical examination reveals an infant with blonde hair, fair skin and blue eyes. His urine has a peculiar musty odor. His plasma phenylalanine level is 40 mg/dl and tyrosine level is normal. His urinary phenylpyruvic and a-hydroxy phenylacetic acid levels are both increased. What is the most likely etiology of this child's symptoms?
Classic phenylketonuria
Benign hyperphenylalaninemia
Transient hyperphenylalaninemia
Tyrosinemia
Alcaptonuria
127) A 2 1/2-year-old child is evaluated by a neurologist because of difficulty walking. Neurological examination documents ataxia and mental retardation. The neurologist notes the presence of multiple telangiectasias involving the conjunctiva, ears, and antecubital fossae. The child also has a history of multiple respiratory tract infections. Immunoglobulin studies on the child would most likely demonstrate an absence of which of the following?
IgA and IgE
IgA and IgG
IgE and IgG
IgE and IgM
IgM and IgG
128) A premature neonate with respiratory distress syndrome is maintained on mechanical ventilation in a neonatal intensive care unit. Two weeks after delivery, the nurses in the intensive care unit notice that higher ventilation settings are needed and that more secretions are being suctioned from the endotracheal tube. A chest x-ray film shows questionable new infiltrates. Which of the following is the most likely pathogen?
Coagulase-negative oxacillin-resistant Staphylococcus
Coagulase-negative oxacjllin-sensitive Staphylococcus
Group B Streptococcus
Methkillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus
129) A 3-year-old boy is brought by his father to the Emergency Department with fever, headache and neck pain that developed over the past several hours. The father states he is not the birth father, and that he and his wife adopted the boy at 18 months of age after his birth mother abandoned him. Physical examination reveals a lethargic male with a temperature of 39.7 C (103.5 F). There is photophobia, and mildly injected conjunctiva are appreciated. Pupils are equal and reactive and funduscopic examination is unremarkable. The patient has neck stiffness with a positive Kernig's sign. A complete blood count reveals a leukocyte count of 24,000/mm3 with 64 segmented neutrophils and 25 bands. A lumbar puncture is performed that reveals elevated CSF pressure, decreased glucose, and elevated protein. A Gram's stain shows gram-negative pleomorphic rods. There is no growth on blood agar. Growth on chocolate agar reveals white colonies. Which of the following is the most likely pathogen?
Haemophilus ducreyi
Haemophilus influenzae type b
Neisseria meningitidis
Listeria monocytogenes
Streptococcus pneumoniae
130) A 2-week-old boy in the neonatal intensive care unit had a birth weight of 1200 g. Ultrasound of the head reveals grade II intraventricular hemorrhage and periventricular leukomalacia. An ophthalmologic examination reveals retinopathy of prematurity of both eyes. In addition, a hearing screen demonstrates bilateral hearing deficits. Which of the following is the most important determinant of this child's neurodevelopmental outcome?
Length of gestation
Maternal education
Outcome of the mother's previous pregnancies
Quality of prenatal care
Socioeconomic status of the family
131) A 9-year-old boy is brought to the pediatric clinic by his mother, who noticed that the left side of his mouth has started to droop over the past several days. In addition, he is unable to close his left eye completely and complains of it burning. Review of systems reveals a cold approximately two weeks ago and recent decreased taste sensation. Physical examination reveals a well-nourished male with normal vital signs. There is left eye ptosis and mild erythema of the left conjunctiva. His smile is asymmetrical on the left. Laboratory evaluation, including a complete blood count and chemistry profile, are normal. Which of the following infections is most closely associated with this patient's condition?
Epstein-Barr Virus
Group A Streptococcus
Human Immunodeficiency Virus
Influenza
Measles
132) A 6-week-old child arrives with a complaint of “breathing fast” and a cough. On examination you note the child to have no temperature elevation, a respiratory rate of 65 breaths per minute, and her oxygen saturation to be 94%. Physical examination also is significant for rales and rhonchi. The past medical history for the child is positive for an eye discharge at 3 weeks of age, which was treated with a topical antibiotic drug. Which of the following organisms is the most likely cause of this child’s condition?
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Staphylococcus aureus
Group B streptococcus
Chlamydia trachomatis
Herpesvirus
133) A 12-year-old girl comes to the physician for an annual examination. She has been in good health for the past year and has no complaints. She began having menses this year and, after a few irregular cycles, is now having a monthly period. Past medical history is significant for multiple episodes of otitis media as a child. Past surgical history is unremarkable. She takes no medications and has no known drug allergies. Physical examination is unremarkable. If not currently immune, which of the following immunizations should this patient most likely receive?
Hepatitis B virus immunization
HIV immunization
Japanese encephalitis virus immunization
Rabies virus immunization
Salmonella typhi immunization
134) An infant is brought to the office for health maintenance visit. On examination, the infant turns when her name is called. She is able to say "mama." Her mother mentions that she also says "dada" at home. She is able to look for her mother when she gets frightened. She also waves bye-bye to the doctor when the doctor steps out of the examination room. What age of this child is most consistent with these developmental milestones?
3 months
5 months
7 months
9 months
11 months
135) A 4-year-old male is brought to the physician with fever and headache. His symptoms began two days ago with low-grade fever, cough, and congestion. Last night, he developed a temperature of 102 F (38.9 C) and became fussy and less active. Today, he is crying and complaining of a headache. His parents report that he has vomited twice today. In the office, his temperature is 102.5 F (39 C), pulse is 110/min, and respiratory rate is 20/min. On examination, he is irritable and shows signs of photophobia. His oropharynx is erythematous. Nuchal rigidity is present and when the neck is flexed, the patient flexes his lower extremities. The remainder of the physical examination is normal. Lumbar puncture is performed and the results are shown below. CSF: Glucose 60 mg/dL, Protein 80 mg/dL, RBC 10/mm3, WBC 100/mm3, Neutrophils 10%, Lymphocytes 70%, Monocytes 20%, Gram stain negative. Which of the following organisms is most likely responsible for this patient's presentation?
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Epstein-Barr virus
Neisseria meningitidis
Echovirus
136) A 12-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department with a temperature of 39.1 C (102.4 F) at home, difficulty speaking, and odynophagia for 2 days, Physical examination reveals marked erythema of the right tonsil pillar and edema of the uvula with deviation to the left. In addition to anaerobic bacteria, which of the following organisms is most likely to be isolated from a tonsillar pillar aspirate?
Beta-hemolytic Streptococcus
Enterococcus
Haemophilus influenzae type b
Staphylococcus aureus
Streptococcus pneumonia
137) A neonate is noted to have many abnormalities, a number of which are located in the midline. The infant has cleft lip and cleft palate. His eyes are very small and have fissures of the iris, shallow supraorbital ridges, and slanted palpebral fissures. He is deaf, and the ears are low set and malformed. Each hand has six fingers and a simian crease. Which of the following congenital abnormalities of the brain is particularly likely to be present in this infant?
Anencephaly
Encephalocele
Hydranencephaly
Holoprosencephaly
Porencephaly
138) A 4196 g (9 lb 4 oz) infant is delivered via vaginal delivery to a 31-year-old mother with gestational diabetes. The delivery was complicated by shoulder dystocia. He is taken to the newborn nursery where his initial plasma glucose level is 20 mg/dL. The initial spun hematocrit is 65%. Which of the following congenital anomalies is this baby most likely to have?
Aniridia
Cleft palate
Macroglossia
Omphalocele
Small left colon
139) A 24-month-old girl is brought to the pediatrician's office for evaluation because her mother noticed a yellowish discharge on the girl's underwear for the past 3 days. She had no fever, but her mother said she has been fussier recently. On physical examination, the girl is appears excessively anxious about contact with the physician. Her introitus is inflamed, and the hymeneal edge is jagged at the 8 o'clock position. A vaginal culture is taken. Which of the following organisms, if isolated from the vaginal vault, would constitute the most definitive evidence of sexual abuse?
Candida albicans
Chlamydia trachomatis
Gardnerella vaginalis
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
140) An 8-month-old previously preterm infant with bronchopulmonary dysplasia presents to the emergency department with lethargy. His regular medications include furosemide and spironolactone. His temperature is 37.4 C (99.3 F), blood pressure is 68/32 mm Hg, pulse is 110/min, and respirations are 10/min. He has poor skin turgor and dry mucous membranes. Laboratory chemistry evaluation reveals: sodium, 131 mEq/L; potassium, 3.0 mEq/L; chloride, 84 mEq/L; bicarbonate, 38 mEq/L; blood urea nitrogen, 36 mg/dL; and creatinine, 0.4 mg/dL. An arterial blood gas shows pH, 7.52; PaCO2: 49 mm Hg; and PaO2: 92 mm Hg. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for these findings?
Bartter syndrome
Primary hyperaldosteronism
Primary respiratory acidosis with metabolic compensation
Pseudohyperaldosteronism
Volume depletion
141) An 8-year-old boy with sickle cell disease presents with left leg pain and a high fever. He has been refusing to walk since yesterday. On physical examination, his temperature is 39.8 C (103.6 F), blood pressure is 122/68 mm Hg, pulse is 102/min, and respirations are 20/min. His left femur is tender to palpation 3 cm above the left knee, and there is marked soft tissue swelling. A plain film of his left leg is normal. A bone scan shows increased uptake around the metaphysis of the left femur. Which of the following is the most likely pathogen?
Escherichia coli
Haemophilus influenzae
Salmonella
Staphylococcus aureus
Streptococcus pneumoniae
142) A 10-year-old male fell while riding his scooter down a steep hill. In the Emergency Department, his injuries included a fractured wrist and a lacerated spleen, which required surgical removal. Two years later he is diagnosed with bacterial pneumonia. Which of the following bacterial agents is the most likely pathogen for this patient's pneumonia?
Escherichia coli
Klebsiella pneumoniae
Neisseria meningitidis
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Staphylococcus aureus
143) A 10-year-old boy was healthy until about 10 days ago when he developed 7 days of fever, chills, severe muscle pain, pharyngitis, headache, scleral injection, photophobia, and cervical adenopathy. After 7 days of symptoms he seemed to get better, but yesterday he developed fever, nausea, emesis, headache and mild nuchal rigidity. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) shows 200 white blood cells (WBC) per microliter (all monocytes) and an elevated protein. Correct statements about this infection include which of the following?
The condition is obtained from arthropod vectors
CNS involvement is uncommon
Most cases are mild or subclinical
Appropriate treatment includes intravenous (IV) immune globulin (IVIG) and aspirin
Hepatic and renal involvement occurs in the majority of cases
144) A 12-year-old African American boy is brought to the office due to a 2-day history of high-grade fever and chills. He was apparently well before the onset of fever. He has no bone pain. He has sickle cell disease and has had 4 hospitalizations for painful crises and one episode of osteomyelitis. His blood pressure is 90/60 mm Hg, pulse is 100/min, respirations are 22/min and temperature is 38.9 C (102F). He appears drowsy. His laboratory report shows a total WBC count of 16,000/mm3 with 12% bands and Hb of 9.0 g/dl. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Staphylococcus aureus
Salmonella
Escherichia coli
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
145) A 13-year-old comes to your office expressing concern about his height. He had first seen you a year prior for his routine checkup and a preparticipation sports physical for soccer (see growth curve). Now in the eighth grade, all of his friends are taller than he is, and he is at a disadvantage on the soccer field playing against much larger boys. After obtaining height information from his parents shown here, you order a skeletal bone age radiograph. Which of the following results would allow you to assure him of an excellent prognosis for normal adult height?
A bone age of 9 years
A bone age of 13 years
A bone age of 15 years
Being at the 50th percentile for weight
Being at the 3rd percentile for weight
146) A 16-year-old girl with an incomplete vaccination record received one dose of the measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine during a doctor's visit. One month later, she learns that she is 9 weeks pregnant, and she is concerned about potential birth defects resulting from the MMR vaccine. Which of the following most closely approximates the risk of birth defects secondary to MMR vaccine exposure during the first trimester?
<1%
3%
5%
8%
10%
147) A 6-week-old male infant, who was born at 32 weeks' gestation with a birth weight of 1500 g, has had an average weight gain of 8 g/day since birth. He takes an iron-fortified formula that is 24kcal/oz. His calorie intake is about 125kcal/day. It is noted that his stool is poorly formed and bulky. Which of the following dietary modifications will most likely result in decreased steatorrhea and improved weight gain?
Add pancreatic enzymes to the formula
Change to a lactose-free formula
Increase calorie intake to 175 kcal/day by increasing volume per feed
Substitute medium-chain triglycerides for long-chain triglycerides
Supplement with vitamins A and E
148) An 8-year-old sickle-cell patient arrives at the emergency room (ER) in respiratory distress. Over the previous several days, the child has become progressively tired and pale. The child’s hemoglobin concentration in the ER is 3.1 mg/dL. Which of the following viruses commonly causes such a clinical picture?
Roseola
Parvovirus B19
Coxsackie A16
Echovirus11
Cytomegalovirus
149) A 7 -year-old boy is rushed to the emergency department after falling on his outstretched hand. He immediately complained of right arm pain after the accident, and he currently cannot move his arm due to the pain. He is crying and holding his right arm in flexion. There is ecchymosis just above his elbow. He cries out in pain when his arm is moved. An x-ray reveals a supracondylar fracture. What secondary injury is most commonly associated with this patient's fracture?
Median nerve injury
Axillary nerve injury
Ulnar artery injury
Brachial artery injury
Brachial plexus injury
150) A 6-year-old Asian boy is brought by his parents to the office due to high-grade fever and rash for the last 9 days. A brick-red, maculopapular rash first appeared on his face and subsequently spread to his trunk and extremities. Prior to the outbreak of the rash, he had a non-productive cough, tearing of eyes, runny nose, sneezing, and intermittent nasal obstruction. Laboratory findings are as follows: Hct 46%, WBC 2,000/mm3, Platelets 160,000/mm3. Which of the following has been shown to reduce the morbidity and mortality rates of patients with this kind of infection?
Vitamin A
Vitamin B 6
Vitamin B 12
Vitamin E
Vitamin K
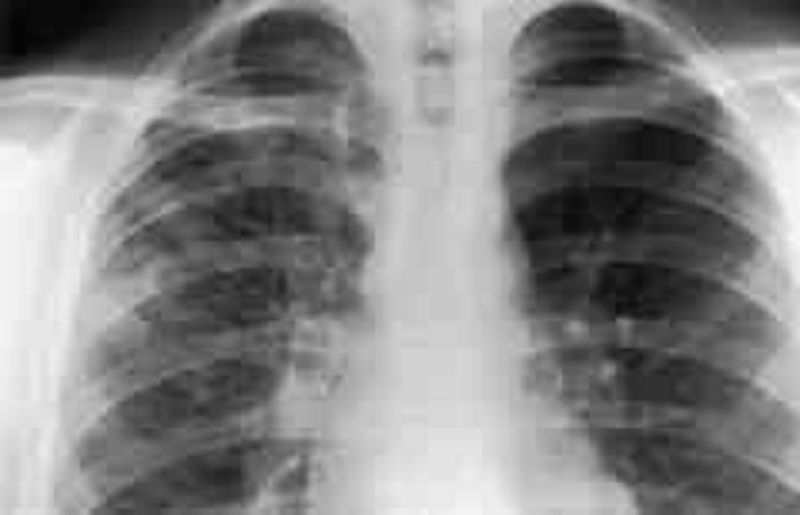
151) A 13-year-old develops fever, malaise, sore throat, and a dry, hacking cough over several days. He does not appear to be particularly sick, but his chest examination is significant for diffuse rales and rhonchi. The chest radio- graph is shown below. Which of the following is the most likely pathogen?
Staphylococcus aureus
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Haemophilus influenzae
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Mycoplasma pneumoniae
152) A 4-month-old infant boy has gained only 10 ounces since birth. He has failed to gain weight with multiple formula preparations. His stools have been loose and fatty. An older sister had similar symptoms and has been repeatedly hospitalized for failure to thrive and recurrent pulmonary infections. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's gastrointestinal symptoms?
Achlorhydria
Bacterial overgrowth
Colonic inertia
Gastric hypersecretion
Pancreatic exocrine insufficiency
153) A term newborn is delivered vaginally following a breech presentation. On physical examination, the Barlow test is positive for bilateral subluxation of the hips. There is decreased abduction of both hips. Besides breech presentation, which of the following infants are most at risk for developmental dysplasia of the hip?
African American infants
Female infants
Second-born infants
Infants of mothers with preeclampsia
Premature infants
154) A 4-year-old boy, who has a ventriculoperitoneal shunt for congenital hydrocephalus, develops fever, headache, irritability, lethargy, photophobia, and vomiting. His temperature is 39.6 C (103.2 F). He is noted to have nuchal rigidity, with the presence of both Kernig's and Brudzinski's signs. The shunt tract is erythematous on the surface. A lumbar puncture is performed and shows a WBC of 40,000/mm3 with 85% neutrophils, a glucose concentration of 48 mg/dL, and a protein concentration of 169 mg/dL. Which of the following is the most likely pathogen?
Haemophilus influenzae
Neisseria meningitidis
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Staphylococcus epidermidis
Streptococcus pneumoniae
155) A 6-month-old male is brought to the office due to fussiness and tugging at his right ear for the past 2 days. He has had a fever of 39.4 C (103 F) for the past 2 days. His past medical history is significant for recurrent ear and lung infections, oral candidiasis, and persistent diarrhea by rotavirus. His temperature is 39.4 C (103F), pulse rate is 150/min, respirations are 28/min, and blood pressure is 80/60mm Hg. Physical examination reveals an erythematous, bulging right tympanic membrane with poor mobility on pneumatic otoscopy. His lymph nodes are not palpable, and his tonsils are not visualized. His B and T lymphocyte levels are markedly reduced. The chest x-ray reveals an absent thymic shadow. What is the most likely etiology of this patient's condition?
Severe combined immune deficiency
Common variable immunodeficiency
Bruton's agammaglobulinemia
Wiskott-Aidrich syndrome
Chronic granulomatous disease
156) A 2-year-old child is admitted to your hospital team. The child’s primary care doctor has been following the child for several days and has noted her to have had high fever, peeling skin, abdominal pain, and a bright red throat. You are concerned because two common pediatric problems that could explain this child’s condition have overlapping presenting signs and symptoms. Which of the following statements comparing these two diseases in your differential is true?
Neither has cardiac complications
Serologic tests are helpful in diagnosing both
Only one of the diseases has mucocutaneous and lymph node involvement
Pharyngeal culture aids in the diagnosis of one of the conditions
A specific antibiotic therapy is recommended for one of the conditions, but only supportive care is recommended for the other
157) Two new mothers are discussing their infants outside the neonatal intensive care unit. Both were born at 36 weeks’ gestation. One infant weighs 2600 g (5 lb, 12 oz) while the other infant weighs 1600 g (3 lb, 8 oz). The mother of the second infant should be told that her child is more likely to have which of the following conditions?
Congenital malformations
Low hematocrit
Hyperglycemia
Surfactant deficiency
Rapid catch-up growth
158) A 2-day-old male infant is jaundiced. He was born at term from an uncomplicated pregnancy, and was normal at birth. He otherwise appears healthy and is feeding well. Vital signs are stable. Physical examination shows jaundice. There is no organomegaly. Laboratory investigations show: Hemoglobin 17.0 g/L, MCV 88 fl, Platelets 220,000/mm3, Leukocyte count 4,500/mm3, Total bilirubin 7.5 mg/dL, Indirect bilirubin 6.0 mg/dL. What is the most likely cause of this patient's jaundice?
Physiologic jaundice
Bacterial infection
Breast milk jaundice
Biliary atresia
Erythroblastosis fetalis
159) An infant in brought to the clinic for a routine healthy visit and vaccinations. She is the product of an uncomplicated pregnancy and has been meeting development mileposts. She is feeding well, and her mother reports that the baby seems to be growing well as well. On physical examination, the infant is afebrile with stable vital signs. She can lift her head to 90 degrees, her eyes follow past the midline, she laughs, regards her own hand and has slight awareness of her mother. Which of the following is the most likely age of this infant?
2 months
4 months
6 months
12 months
18 months
160) A two-day old infant develops seizures, bulging fontanel, and focal neurologic signs. His temperature is 37 C (98F), pulse is 180/min, and capillary refill is> 2 seconds. The initial work-up reveals a hemoglobin level of 12g/dl. Transfontanel ultrasonography demonstrates a hemorrhage involving the germinal matrix, lateral ventricles, and brain parenchyma. Which of the following is the most significant risk factor for this newborn's condition?
Prematurity
Pelvic dystocia
Prenatal infection
Congenital anomaly
Macrosomia
161) A 16-year-old girl, accompanied by her mother, is in your office for a well-adolescent visit. The mother asks about drug and alcohol abuse. You explain that the warning signs of abuse include which of the following?
Excessive concern for weight and body configuration
Improved school performance
Recent changes from age-appropriate, acceptable friends to younger associates
Deterioration in personal habits, hygiene, dress, grooming, speech patterns, and fluency of expression
Improvement in relationships with adults, siblings, and authority figures
162) A 3-month-old male infant is brought to the emergency department by his mother because of difficulty in breathing. His mother was admitted in the hospital ten days ago due to a urinary tract infection, and he was cared for by his grandmother during that period. His mother had just been discharged from the hospital yesterday, and noticed that he was constipated and having difficulty with breastfeeding. On examination, he is afebrile. His pulse rate is 110/min, respirations are 36/min with shallow breathing efforts, and blood pressure is 90/50mm Hg. His weight is at the 35th percentile. Examination shows ptosis, dilated pupils with sluggish reaction to light, diminished deep tendon reflexes and decreased muscle tone. What is the most likely mechanism of his illness?
Bacterial infection of the meninges
Autoimmune disease against acetylcholine receptors
Clostridium difficile toxin in the intestinal tract
Clostridium botulinum in the intestinal tract
Clostridium botulinum toxin intake
163) A 16-year-old College student presents to the physician's office because of a generalized malaise, sore throat and fever for the past 2 to 3 days. She is given amoxicillin prescription. Twenty-four hours later, she develops a polymorphous rash over her entire body. She has taken amoxicillin in the past for sinus disease and never had any problem. What is the most likely organism that is responsible for her symptoms?
Group B streptococcus
Epstein-Barr virus
Coxsackie virus
Escherichia coli
Nocardia
164) 16 An 18-month-old child is brought to the emergency department by his mother due to a one-day history of lethargy and anorexia. He had a fever the whole day yesterday, which responded to Tylenol (Acetaminophen). He then developed a petechial rash over his entire body, which worsened in the last few hours. He is up-to-date with his immunizations, and is an otherwise healthy baby. On examination, he is drowsy and lethargic. He has neck stiffness and appears septic. He flexes his hips when his neck is flexed. What is the most likely organism responsible for the patient's symptoms?
Meningococcus
Haemophilus influenza
Cytomegalo virus
Borrelia burgdorferi
Listeria monocytogenes
165) A child can walk well holding on to furniture but is slightly wobbly when walking alone. She uses a neat pincer grasp to pick up a pellet, and she can release a cube into a cup after it has been demonstrated to her. She tries to build a tower of two cubes with variable success. She is most likely at which of the following age?
2 months
4 months
6 months
9 months
1 year
166) A 3-week-old female is brought into the emergency department with a fever and irritability. She was born after a normal pregnancy and delivery. Her mother had routine prenatal care and has no history of sexually transmitted infections. The infant's mother is 14 years old and the father is 17 years old. They are not married, and the father is not involved in the care of the infant. The infant lives with her mother and maternal grandparents at the maternal grandparents' home. You are concerned about meningitis and decide to do a lumbar puncture. The mother and maternal grandparents are present in the emergency department. Informed consent should be obtained from which of the following individuals?
Mother
Maternal grandparents since the mother is a minor
Mother and father must both provide consent
Mother and grandparents since the mother is a minor
Informed consent is not necessary because the mother is a minor
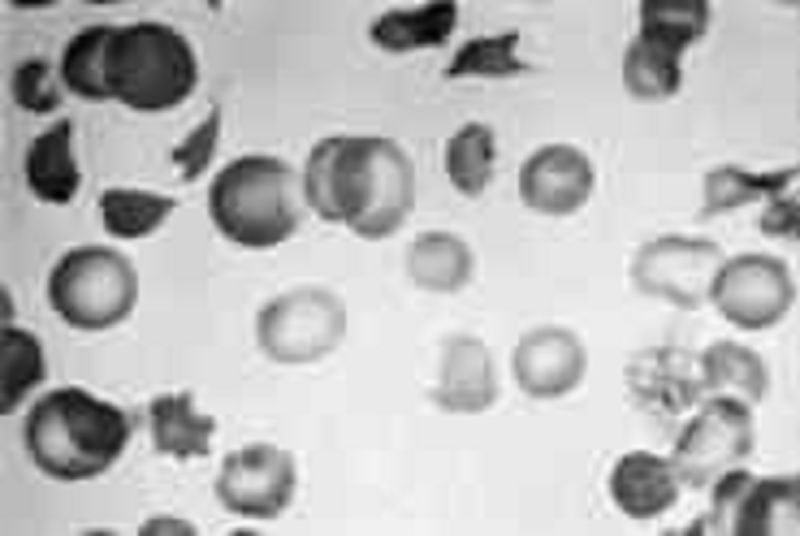
167) A 2-year-old child in shock has multiple nonblanching purple lesions of various sizes scattered about on the trunk and extremities; petechiae are noted, and oozing from the venipuncture site has been observed. The child’s peripheral blood smear is shown below. Clotting studies are likely to show which of the following?
Increased levels of factor V and VIII
A decreased prothrombin level
An increased fibrinogen level
The presence of fibrin split products
Normal partial thromboplastin time (PTT)
168) A 10-year-old boy is admitted to the hospital because of bleeding. Pertinent laboratory findings include a platelet count of 50,000/μL, prothrombin time (PT) of 15 seconds (control 11.5 seconds), activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) of 51 seconds (control 36 seconds), thrombin time (TT) of 13.7 seconds (control 10.5 seconds), and factor VIII level of 14% (normal 38%-178%). Which of the following is the most likely cause of his bleeding?
Immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP)
Vitamin K deficiency
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)
Hemophilia A
Hemophilia B
169) Varicella vaccination is a live virus vaccine. It is generally not recommended in immunocompromised patients. Which of the following is an exception to this rule?
Children on high doses of corticosteroids
Leukemia in inducton therapy
Lymphoma
Congenital T-cell abnormalities
Leukemia in remission for >1 year and a normal lymphocyte count
170) The signs and symptoms of meningitis in an infant can be different than those in an adult. Which of the following signs and symptoms of meningitis is more helpful in an adult patient than in a 4-month-old?
Lethargy
Jaundice
Vomiting
Brudzinski sign
Hypothermia
171) A woman gives birth to twins at 38 weeks’ gestation. The first twin weighs 2800 g (6 lb, 3 oz) and has a hematocrit of 70%; the second twin weighs 2100 g (4 lb, 10 oz) and has a hematocrit of 40%. Which of the following statements is correct?
The second twin is at risk for developing respiratory distress, cyanosis, and congestive heart failure
The first twin is more likely to have hyperbilirubinemia and convulsions
The second twin is at risk for renal vein thrombosis
The second twin probably has hydramnios of the amniotic sac
The second twin is likely to be pale, tachycardic, and hypotensive
172) A 9-month-old African American boy is brought to the office by his parents due to swelling of the feet and hands for the past two days, accompanied by poor feeding and fussiness. His vital signs are stable, except for a temperature of 38.3C (101 F). He appears pale. On examination, the dorsal surface of his hands and feet on both sides are swollen and tender, with restricted range of movement. He is an adopted child, and his family history is not available. Radiography of the feet and hands reveal soft tissue swelling. What is the pathophysiology of this patient's presentation?
Salmonella osteomyelitis
Vasa-occlusive phenomena
Hypertrophic osteoarthropathy
Staphylococcus osteomyelitis
Autoimmune phenomena
173) A 4-year-old child presents in the clinic with an illness notable for swelling in front of and in back of the ear on the affected side, as well as altered taste sensation. Correct statements about this condition include which of the following?
Arthritis is a common presenting complaint in children
The disease could have been prevented by prior immunization with killed whole cell vaccine
Involvement of the central nervous system (CNS) may occur 10 days after the resolution of the swelling
Orchitis can occur and is almost exclusively seen in prepubertal males
Subendocardial fibroelastosis is a common complication in a child of this age
174) A 3-year-old boy is brought to the office by his 27-year-old white mother for the evaluation of recurrent bone fractures. His first fracture was that of the femur, and occured when he was 6 months old. He had a fracture of the wrist 4 months ago. His mother also has a history of multiple fractures since childhood. She lost all her teeth at a very early age and is complaining of deafness. Her husband has a history of severe alcohol abuse. On examination, both mother and son have blue sclerae. What is the most likely involved disease process?
Mutations in type 1 collagen
Mutations in fibrillin 1 gene
Child abuse
Vitamin-D deficiency
Congenital syphilis
175) A mother brings her infant into the clinic for a routine visit. Examination reveals nothing abnormal. Developmental assessment shows that the infant sits well unsupported, enjoys looking around, babbles, and has a raking grasp. What is the most likely age of this infant?
4 months
6 months
8 months
10 months
12 months
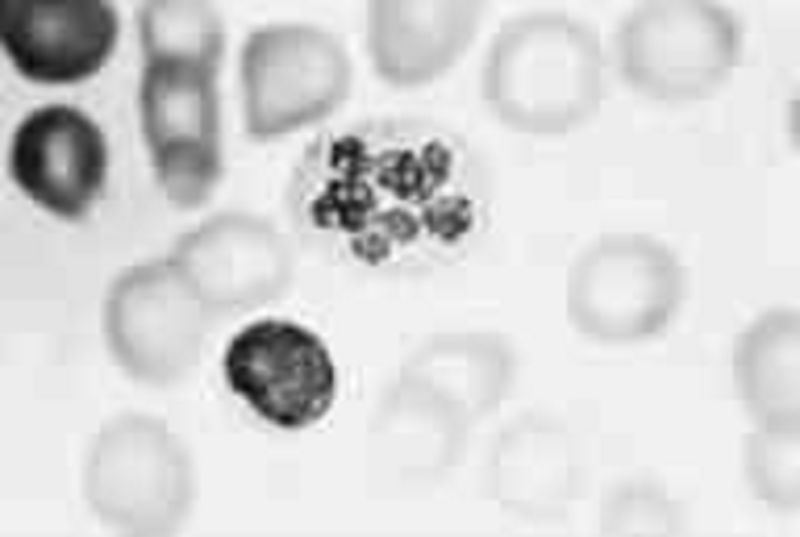
176) An otherwise healthy child has on his 1-year-old routine CBC the polymorphonuclear neutrophil shown below. This child likely has which of the following?
Malignancy
Iron deficiency
Folic acid deficiency
Döhle inclusion bodies
The Pelger-Huët nuclear anomaly
177) A 6-month-old infant has been exclusively fed a commercially available infant formula. Upon introduction of fruit juices, however, the child develops jaundice, hepatomegaly, vomiting, lethargy, irritability, and seizures. Tests for urine-reducing substances are positive. Which of the following is likely to explain this child’s condition?
Tyrosinemia
Galactosemia
Hereditary fructose intolerance
α1-Antitrypsin deficiency
Glucose-6-phosphatase deficiency
178) A term newborn infant from an uncomplicated pregnancy is being examined. He is pink, except for his extremities, which are blue. His heart rate is 150/min, and his respirations are irregular and slow at 40/min. He coughs on nasal stimulation and has some flexion of the extremities. What is his Apgar score?
6/ 10
7/10
8/ 10
9/ 10
10/ 10
179) A 2-year-old child is brought to the emergency department because of generalized convulsions that last 15 minutes. He has had a fever for 24 hours, and his current temperature is 39.5 C (103 F). He also has a sore throat, but otherwise looks healthy. His father also had several episodes of febrile seizures in his childhood. Which of the following is the most important factor that will increase the risk of recurrence of febrile seizures?
Age older than 18 months
Duration of seizure longer than 5 minutes
Family history of febrile seizures
Fever of long duration before onset of seizure
Temperature higher than 39.0 C
180) An 8-year-old immigrant from rural Central America presents with complaints of weakness, facial swelling, muscle pain, and fever. A CBC reveals marked eosinophilia. Which of the following parasites is most likely to be responsible?
Cryptosporidium parvum
Sporothrix schenckii
Giardia lambila
Enterobius vermicularis
Trichinella spiralis
181) The mother of a 4-year-old child takes her daughter to a pediatrician because she is "scratching all the time." Physical examination demonstrates multiple areas of excoriation, which are worst on the shoulders, buttocks, and abdomen. In the areas where the scratching has occurred, scattered tiny red punctate lesions are also seen. Careful examination of the clothing reveals small, ovoid, grayish-white structures attached to threads on the seams. Which of the following is the most likely causative agent?
Ancylostoma braziliense
Corynebacterium minutissimum
Pediculus humanus corporis
Sarcoptes scabiei
Trichophyton rubrum
182) A previously healthy 6-year-old girl is brought to the office due to a 10-day history of persistent, thick, nasal discharge, nasal congestion, cough, and intermittent low-grade fever. She has had no vomiting, headache, earache, or rash. Her temperature is 37.2 C (98.9 F), blood pressure is 88/50 mmHg, pulse is 90/min, and respirations are 15/min. Physical examination shows clear tympanic membranes, congested posterior nasopharynx with thick, yellow and purulent mucus, and red, swollen nasal turbinates. Transillumination of the sinuses is equivocal. Palpation of the maxillary sinuses shows mild tenderness. Lungs are clearto auscultation. Which of the following organisms is the most common etiologic agent of this condition?
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Streptococcus pneumonia
Moraxella catarrhalis
Staphylococcus aureus
Anaerobes
183) A one-month-old infant is brought to the physician for evaluation. His mother reports that for the past two weeks, he has been crying inconsolably for several hours every evening. His mother has tried multiple methods to calm the infant down, but nothing seems to work. The infant was born full term without complications. He takes two ounces of cow's milk-based formula every two hours and is growing well. His mother reports that he is happy and alert the rest of the day. The child's physical examination is unremarkable. Which of the following is a true statement about the child's condition?
The infant should be started on ranitidine for gastroesophageal reflux
The infant should be changed to a lactose-free formula
Bloody stools are often present
The child will likely develop an anxiety disorder during childhood
This condition usually resolves by four months of age
184) An 18-month-old male is brought to the hospital because of fever, dyspnea, and productive cough of two days duration. His mother reports that he just recovered from prolonged diarrhea due to Giardia infection. His past medical history is also significant for pneumonia and recurrent ear infections since 6 months of age. On physical examination, his temperature is 38.7°C (101.7°F), pulse is 140/min, and respirations are 40/min. Examination reveals a young child in mild respiratory distress and bronchial breath sounds in the right lower lung lobe. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his recurrent infections?
Impaired oxidative metabolism
Complement deficiency
Thymic hypoplasia
Adenosine deaminase deficiency
Abnormal B-lymphocyte maturation
185) You are called to the nursery to evaluate a newborn infant. The mother is a 24-year-old primigravida. Her pregnancy was complicated by preeclampsia. The infant was delivered at 39-weeks’ gestation via emergent cesarean section due to maternal hypertension and non-reassuring fetal heart tones. On examination, the infant's weight is 2.6 kg (5 lb 11 oz) placing him in the 5th percentile, height is 18 inches (46 em) placing him in the 5th percentile, and head circumference is 13 inches (33 cm) placing him in the 1oth percentile. The infant's head seems large for her body. There is a paucity of subcutaneous fat. The remainder of the physical examination is unremarkable. This infant is at risk for developing which of the following?
Hip subluxation
Polycythemia
Hyperglycemia
Hyperthermia
Hypercalcemia
186) A 16-year-old girl comes to the physician with headache and vision changes for the past month. The headaches are worse in the morning and are associated with nausea. She takes oral isotretinoin for severe acne. Her temperature is 36.7 C, BP is 130/80 mmHg, Pulse is 70/min, and respirations are 15/min. Eye examination shows papilledema and decreased visual acuity. There is no neck stiffness. Motor examination shows 5/5 strength, 2+ deep-tendon reflexes, and a normal plantar response. Sensory examination is unremarkable. Computed tomography scan of the head is within normal limits. Lumbar puncture shows the following: Opening pressure 280 mm H2O, Cerebrospinal fluid glucose 40 mg/dL, Cerebrospinal fluid protein 40 mg/dL, White blood cell 3/mm3. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient’s symptoms?
Classic migraine
Cluster headaches
Medication side effect
Multiple sclerosis
Normal-pressure hydrocephalus
187) A 3-month-old infant without significant past history was brought to the emergency center by her mother with a generalized tonic-clonic seizure. She is found to have glucose of 5 mg/dL. After correction of her hypoglycemia, she is admitted to your service for further evaluation. Several hours later, her nurse calls to tell you that her bedside glucose check was now 10 mg/dL. You order laboratory work suggested by the pediatric endocrinology team and again correct the infant’s hypoglycemia. The results of the laboratory tests you drew include an elevated serum insulin level of 50 μU/mL, and a low IGFBP-1 (plasma insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1). C-peptide levels are not detectable. Which of the following is the likely cause of this child’s recurrent hypoglycemia?
Nesidioblastosis
Pancreatitis
Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome
Galactosemia
Factitious hypoglycemia
188) A 10-year-old African American boy is brought to the office for the evaluation of worsening fatigue for the past few weeks. He has sickle cell anemia, and has had several hospitalizations for painful crises. His vital signs are stable. He appears pale. He has a hemoglobin level of 7. 7 g/dl and hematocrit of 22.5%. Which is the most likely type of anemia of this patient?
Iron deficiency anemia
Anemia of chronic disease
Megaloblastic anemia
Hemolytic anemia
Sideroblastic anemia
189) A 6-year-old child has had repeated episodes of otitis media. She undergoes an uneventful surgical placement of pressure-equalization (PE) tubes. In the recovery room she develops a fever of 40C (104F), rigidity of her muscles, and metabolic and respiratory acidosis. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for her condition?
Otitis media
Septicemia
Malignant hyperthermia
Dehydration
Febrile seizure
190) A 3-year-old-boy ingests 40 of his older sister's chewable vitamin tablets, as well as 3 tablets of 250 mg of acetaminophen. The ingredients in the multivitamin tablets are as follows: Vitamin A 3000 IU, Thiamine 1 mg, Vitamin C 75 mg, Vitamin B6 1 mg, Vitamin D 400 IU, Iron 12 mg, Fluoride 1 mg. The child is brought to the emergency department in no acute distress. Which of the following complications may occur if appropriate therapy is not undertaken?
Acute renal failure from vitamin D toxicity
Hepatic failure from acetaminophen toxicity
Hepatic failure from iron toxicity
Increased intracranial pressure from vitamin A toxicity
Intestinal ischemia from fluoride toxicity
191) A 7-year-old boy presents with tenderness and erythema of one knee joint. He has had troubles with infections since about 3 months of age. A brother and a maternal uncle both died of infectious disease at an early age. A detailed immunologic evaluation performed at 2 years of age demonstrated plasma IgG less than 50 mg/100 mL. Normal numbers of circulating T cells and normal cellular immunity were found. The boy had been treated monthly since then with IV immunoglobulin. This therapy had markedly reduced, but not eliminated, the boy's infection rate. Which of the following is the most likely pathogen to cause infectious arthritis in this patient?
Aspergillus
Herpes
Mycobacteria
Mycoplasma
Toxoplasma
192) A 3-week-old African American boy is brought to the Emergency Department because of a generalized seizure 2 hours ago. The infant is highly irritable with incessant high pitched crying. The infant's weight is 2.5 kg (250 gm below birth weight), blood pressure is 70 /40 mm Hg, pulse is 145/min and respirations are 50/min. Laboratory results show: Blood glucose 120 mg/dL, Urea nitrogen 50 mg/dL, Serum sodium 170 mEq/L, Serum calcium 8.5 mg/dL, Serum magnesium 1.5 mg/dL. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this infant’s seizure?
Hypocalcemia
Hypoglycemia
Hypomagnesemia
Intracranial hemorrhage
Meningitis
193) A neonate born at term is found to have webbed neck and swollen hands and feet. Ultrasonogram of the abdomen shows a horseshoe kidney. Which of the following is the most likely cause of edema?
Immune mediated red cell destruction
Dysgenesis of the lymphatic network
Decreased synthesis of albumin
Increased urinary loss of protein
Severe intrauterine hypoxia
194) An 8-year-old girl is being evaluated for short stature. She is at 8th percentile for height and 30th percentile for weight. Vital signs are within normal limits. Examination shows a high arched palate and inverted, widely spaced nipples Karyotyping shows 45 XO. Which of the following is she most at risk of developing?
Osteoporosis
Mitral valve prolapse
Mental retardation
Bipolar disorder
Breast cancer
195) A premature infant has a difficult delivery with episodes of arrhythmia and suspected hypoxiaischemia. After the delivery, the infant is lethargic and has periods of apnea. Intracranial hemorrhage is suspected. No obvious head trauma is noted. Cranial ultrasound identifies blood within the ventricles. Which of the following structures is the most likely source of the hemorrhage?
Bridging veins of the skull
Cerebral cortex
Germinal matrix
Thalamus
Vessels of the circle of Willis
196) A 16-year-old girl is in your office for a preparticipation sports examination. She plans to play soccer in the fall, and needs her form filled out. Which of the following history or physical examination findings is usually considered a contraindication to playing contact sports?
Congenital heart disease, repaired
Obesity
Absence of a single ovary
Absence of a single eye
Diabetes mellitus
197) A 15-year-old boy is in the office for a preparticipation sports physical examination before he begins playing with the varsity football team at his school. Although he is a skilled receiver, he will be one of the smallest players on the field and is concerned about the potential for injury. He asks how to bulk up. Appropriate advice to increase muscle mass includes which of the following?
Taking extra vitamins
Doubling protein intake
Using anabolic steroids
Increasing muscle work
Taking ergogenic medication
198) A 3-week-old boy presents to the physician's office with a 1-week history of forceful, projectile vomiting. He has been vomiting after almost every feeding. The vomitus contains mostly undigested formula and is non-bilious. On examination, his oral mucosa is dry, his anterior fontanel appears to be depressed, and his capillary refill is 3-4 seconds. An abdominal examination reveals an olive-sized mass in the epigastrium. Which of the following electrolyte findings will most likely be seen?
Hypochloremic metabolic acidosis
Hypochloremic metabolic alkalosis
Normal electrolytes
Respiratory acidosis with metabolic compensation
Respiratory alkalosis
199) A 3-month-old infant is taken to the emergency department with constipation and behavioral changes. Physical examination demonstrates ptosis and an absence of facial expression. The child appears conscious but has trouble following a toy with her gaze. The crying is very weak, and saliva is pooling in her mouth. She is also developing a generalized hypotonia, and breathing is becoming more shallow. This child's condition is most likely related to ingestion of which of the following food products?
Canned carrots
Canned green beans
Canned peaches
Formula
Honey
200) A blood type B infant born to a blood type O mother has clinically significant fetal-maternal blood group incompatibility with mild anemia and a weakly positive Coombs test. The infant develops jaundice a few hours after birth, with a bilirubin (measured at 12 hours after birth) of 12 mg/dL (predominately unconjugated) compared with 3.5 mg/dL in cord blood. The physician is concerned that the rising bilirubin levels will damage the infant's nervous system. Which of the following sites is most vulnerable to this injury?
Basal ganglia
Cerebellum
Cerebral cortex
Peripheral nerve
Spinal cord
201) A 15-year-old girl is brought to the pediatrician's office because of sudden deterioration of school performance. Over the past month, her mother has noticed an occasional paint stain on the girl's hands. Her mother also noticed six bottles of typewriter correction fluid in her bedroom about a week ago. She raised the concern of inhalant abuse. Which of the following is the most likely consequence of chronic inhalant abuse?
Arrhythmia
Bronchial asthma
Cerebral hemorrhage
Encephalopathy
Respiratory depression
202) A 4-year-old child comes in for a health maintenance visit. His mother is concerned that he is not doing some things that other kids in his preschool do. Which of the following skills would be expected of a 4-year-old?
Building a 10-cube staircase
Drawing a square
Drawing a triangle
Drawing a person with six parts
Repeating five digits
203) A mother brings her 3-year-old son to the pediatrician because he has had 7 days of fever and a painful swollen lymph node in his right groin. This is the boy's sixth episode of lymph node swelling; previous episodes resolved after drainage and prolonged antibiotic therapy. The child also has a past medical history significant for pneumonia at 12 months of age that required chest tube placement for drainage. His maternal uncle died in childhood from recurrent infections. On examination, the boy is at the 5th percentile for both height and weight His temperature is 38.5 c (101.3 F). There is an enlarged, tender lymph node in the right inguinal area with erythema and warmth of the overlying skin. There are several healed incisions in the inguinal regions bilaterally, as well as around the neck from old drainage sites. Laboratory analyses reveal the following: Hematocrit 35%, Platelet count 350,000/mm3, Leukocyte count 17000/mm3, Segmented neutrophils 65%, Bands 10%, Lymphocytes 25%. Gram stain of fluid aspirated from the affected lymph node reveals numerous bacteria-filled segmented neutrophils. Cultures grow S. aureus. What is the most likely mechanism underlying these findings?
Adenosine deaminase deficiency
Complement consumption
Defective opsonization
Destruction of CD4+ lymphocytes
Impaired oxidative metabolism within phagocytes
204) A 7-year-old boy has cramping abdominal pain and a rash mainly on the back of his legs and buttocks as well as on the extensor surfaces of his forearms. Laboratory analysis reveals proteinuria and microhematuria. You diagnose Henoch-Schönlein, or anaphylactoid, purpura. In addition to his rash and abdominal pain, what other finding is he likely to have?
Chronic renal failure
Arthritis or arthralgia
Seizures
Unilateral lymphadenopathy
Bulbar nonpurulent conjunctivitis
205) An infant is brought to a hospital because her wet diapers turn black when they are exposed to air. Physical examination is normal. Urine is positive both for reducing substance and when tested with ferric chloride. This disorder is caused by a deficiency of which of the following?
Homogentisic acid oxidase
Phenylalanine hydroxylase
L-histidineammonia-lyase
Ketoacid decarboxylase
Isovaleryl-CoA dehydrogenase
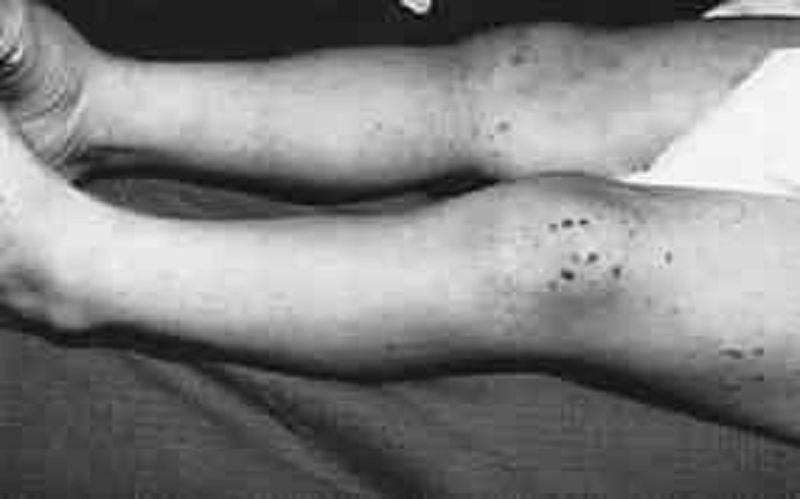
206) A previously healthy 5-year-old boy has a 1-day history of low-grade fever, colicky abdominal pain, and a rash. He is well-appearing and alert. His vital signs, other than a temperature of 38°C (100.5°F) are completely normal. A diffuse, erythematous, maculopapular, and petechial rash is present on his buttocks and lower extremities, as shown in the photograph. He has no localized abdominal tenderness or rebound; bowel sounds are active. Laboratory data demonstrate Urinalysis: 30 red blood cells (RBCs) per high-powered field, 2+ protein. Stool: Guaiac positive Platelet count: 135,000/μL. These findings are most consistent with which of the following?
Anaphylactoid purpura
Meningococcemia
Child abuse
Leukemia
Hemophilia B
207) A 23-year-old primigravida comes to the physician for a prenatal visit. She is considering breastfeeding her infant, and the physician discusses the benefits of breastfeeding for both the mother and the infant. She asks if there are any reasons that she should not breastfeed. Which of the following maternal conditions is a contraindication to breastfeeding?
Tobacco smoking
Hepatitis C
Mastitis
Active tuberculosis
Alcohol use
208) A 1-year-old patient is in the office for a health maintenance visit and is ready for immunizations. The child has a mild upper respiratory infection and a low-grade fever. The mother does not want the child to receive vaccine because she has been told that the vaccine could make the illness worse. You tell her the only true contraindication to vaccination is which of the following?
If the child has a skin rash
If there is an immunosuppressed adult in the household
If the child has hypersensitivity to a vaccine component
If a pregnant woman is in the household
If the mother is breast-feeding
209) An infant comes to the office for his 1-year check-up. His father states that he is worried that his son is smaller than he should be. The child's weight is 8.6 kg (19 lb), and his length is 71 cm (28 in). He appears to be growing appropriately on his growth curve. Which of the following is the most appropriate explanation about growth to be given to the father?
Infants usually double their birth weight by 1 year
Infants usually triple their birth weight by 1 year
Infants usually quadruple their birth weight by 1 year
Infants usually double their length by 1 year
Infants usually triple their length by 1 year
210) A 15-year-old Ashkenazi Jewish boy comes to the office because of pain in his right knee. He gives a history of easy bruising and chronic fatigue. His height and weight are in the 40th percentile mark for his age. The physical examination reveals tenderness over the lower end of the right femur, mildly enlarged liver, and moderately enlarged spleen. X-rays of the right femur reveal an Erlenmeyer flask deformity of the distal femur. Significant lab findings are anemia and thrombocytopenia. A bone marrow examination reveals cells with a wrinkled paper appearance. What is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
Deficiency of the enzyme acid beta-glucosidase
Deficient activity of sphingomyelinase
Deficient activity of beta-galactosidase
Deficiency of hexosaminidase activity
Deficiency of the lysosomal enzyme, ceramidase
211) A 7-year-old girl is brought to the office by her mother. The mother is worried because she noticed some axillary hair development in her daughter. The girl appears calm, and denies the presence of headaches, visual disturbances or abdominal pain. There has been no change in her behavior. Her medical history is unremarkable. Her older sister's pubertal changes began at age 11. Physical examination reveals scarce and dark axillary hair, absent breast development and absent pubic hair. The rest of the examination is unremarkable. Activation of which of the following structures is most likely responsible for this patient's symptomatology?
Hypothalamus
Pituitary gland
Adrenal glands
Ovaries
Liver
212) An 8-year-old boy is seen in the pediatrician's office for a routine health supervision visit. The mother states that he has Duchenne muscular dystrophy. On examination, he is found to have hip waddle and enlargement of both calves. He is ambulatory, but his muscle strength is diminished symmetrically. Which of the following signs is most consistent with Duchenne muscular dystrophy?
"Foot drop" gait
Gower sign
Increased deep tendon reflex
Myotonia
Positive Babinski sign
{"name":"USMLE pediatry basic 2", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"107) An 18-month-old male infant is brought to the office by his parents for a follow-up visit. He has a congenital condition that started at the age of 6 months with repeated vomiting and hypotonia, and progressively evolved into choreoathetosis, spasticity and dystonia. Over the past month, he has started biting his hands and arms, pinching himself and banging his limbs against the wall. His family history is unremarkable. On examination, he has several scars, cuts and bruises over his arms and hands. His uric acid levels are elevated. What is the most likely deficient enzyme in this patient?, 108) A 16-day-old infant presents with fever, irritability, poor feeding, and a bulging fontanelle. Spinal fluid demonstrates gram-positive cocci. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?, 109) A 16-year-old boy presents to the emergency center with a 2-day history of an abscess with spreading cellulitis. While in the emergency center, he develops a high fever, hypotension, and vomiting with diarrhea. On examination you note a diffuse erythematous macular rash, injected conjunctiva and oral mucosa, and a strawberry tongue. He is not as alert as when he first arrived. This rapidly progressive symptom constellation is likely caused by which of the following disease processes?","img":"https://cdn.poll-maker.com/12-549518/5.jpg?sz=1200"}
More Quizzes
Which House Do You Belong To?
740
MBI Exam #1 Review
21100
Saviours of the train
11616
100
Best Hair Colour for Me - Find Your Ideal Shade
201017117
Am I Communist or Capitalist? - Find Your Alignment
201017981
What's Your Spirit Animal? Free to Reveal Yours
201018198
How Long Will My Dog Live? Free Lifespan Calculator
201016527
Big Picture vs Detail-Oriented - What's Your Focus?
201018500
Spanish Alphabet - Free Practice for Letters & Sounds
201016815
Fast and Furious Characters - How Many Can You Name?
201016527
Coupleszes to Take Together - Strengthen Your Bond
201016583