DES C_Basic (4) Prepared : CHILLY
A 46-year-old woman undergoes an abdominal hysterectomy for a “fibroid” uterus. The surgeon requests a frozen section on the tumor, which is deferred because of the lesion’s degree of cellularity. Which of the following histologic criteria will be used by the pathologist to determine if this tumor is benign or malignant?
Mitotic rate
Cell pleomorphism
Cell necrosis
Nucleus-to-cytoplasm ratio
Tumor size
A 47-year-old male presents to your office with a two-month history of lethargy and decreased libido. His medical records reveal that he has been treated for joint pain and swelling over the last six months and was diagnosed with diabetes mellitus one year ago. Physical examination reveals hepatomegaly and testicular atrophy. Which of the following cardiac abnormalities is most likely to also be present in this patient?
Atrial septal defect
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Aortic stenosis
Cardiac conduction block
Endocardial fibroelastosis
A 47-year-old male was brought to the emergency room with chest pain of acute onset. The pain was associated with nausea, vomiting, and diaphoresis. He has a history of diabetes, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia. ECG reveals ST segment elevation in the anterolateral leads and ventricular premature beats (VPBs). The patient dies within the first hour after the arrival to emergency room. What is the most likely pathophysiologic mechanism responsible for this patient's death?
Electro-mechanic dissociation
Reentry
Full conduction block
Increased automaticity
Asystole
A 47-year-old man is found to have edema, ascites, and hepatosplenomegaly. The examination of his neck veins reveals elevated venous pressure with a deep y descent. Heart size on x-ray is normal. Which of the following etiologies is not a possible explanation for this syndrome?
Rheumatic fever
Unknown cause previous
Acute pericarditis
TB
Neoplastic involvement of the pericardium
A 47-year-old man presents to your office complaining of occasional daytime headaches, dizziness and nausea. He has no significant past medical history. He works as a traffic controller in an underground parking lot. He does not smoke cigarettes, and consumes alcohol only on weekends. He is sexually active in a monogamous relationship with his wife and uses condoms for contraception. His cardiac exam is unremarkable. His abdomen is soft and non-tender. The liver span is 8 cm and the spleen is not palpable. Laboratory findings are: Hematocrit 59%, WBC count 7,000/mm3, Platelets 200,000/mm3. Which of the following is most likely responsible for this patient's increased hematocrit?
Polycythemia vera
Pulmonary hypertension
Plasma volume loss
Arteriovenous shunting
Carboxyhemoglobinemia
A 47-year-old woman has new-onset transient right arm weakness and word finding difficulty symptoms lasting 3 hours. She is also experiencing exertional dyspnea, and had a syncopal event 1 month ago. Her echocardiogram reveals a cardiac tumor in the left atrium, it is pendunculated and attached to the endocardium. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this lesion?
Myxoma
Sarcoma
Rhabdomyoma
Fibroma
Lipoma
A 47-year-old woman loses consciousness for 2 minutes while shopping in a supermarket. In the emergency room, she recounts feeling nausea and warmth spreading over her body immediately before passing out. She has never had a similar episode before. She has not seen a doctor for several years and does not take any medications, nor does she use tobacco, alcohol or drug. Her family history is unremarkable. Which of the following most likely caused this episode?
Cardiac arrythmia
Seizure
Neurocardiogenic syncope
Heat valve disease
Orthostatic hypotension
A 47-year-old woman who is 2 weeks post triple bypass surgery presents to the emergency department with a chief complaint of sudden onset, sharp chest pain for several hours. She is fatigued and short of breath. On physical examination she has distended neck veins that grow more distended on inspiration. Muffled heart sounds are heard. Her temperature is 37.0°C (98.6°F), pulse is 133/min, blood pressure is 70/50 mmHg, respiratory rate is 30/ min, and oxygen saturation is 100% on room air. An echocardiogram shows a large pericardial effusion and chamber collapse; therefore, pericardiocentesis is performed. Although a large amount of blood is aspirated, the patient’s clinical picture acutely worsens. Her pain level increases substantially; pulse is 150/min, blood pressure is 60/41 mm Hg, respiratory rate is 30/ min, and oxygen saturation is 100%. Repeat echocardiography shows an even larger pericardial effusion with chamber collapse. Which complication of pericardiocentesis is most likely in this patient?
Acute left ventricular failure with pulmonary edema
Aspiration of 10 mL air into the pericardium
Laceration of a coronary vessel
Pneumothorax
Puncture of the left ventricle
A 48-year-old Caucasian male presents to your office complaining of progressive exertional dyspnea. It has become especially bothersome over the past two months. Presently, he becomes short of breath after climbing one flight of stairs. He denies any significant problems in the past. He is not taking any medications and he denies smoking or drinking alcohol. His temperature is 37.2°C (98.9°F), pulse is 78/min, blood pressure is 130/75 mmHg and respirations are 14/min. Chest examination reveals a harsh systolic murmur that is best heard at the right second intercostal space with radiation along the carotid arteries. An S4 is heard at the apex. Based on these findings, what is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Rheumatic heart disease
Myxomatous valve degeneration
Bicuspid aortic valve
Senile calcific aortic stenosis
A 48-year-old woman develops constipation postoperatively and self-medicates with milk of magnesia. She presents to clinic, at which time her serum electrolytes are checked, and she is noted to have an elevated serum magnesium level. Which of the following represents the earliest clinical indication of hypermagnesemia?
Loss of deep tendon reflexes
Flaccid paralysis
Respiratory arrest
Hypotension
Stupor
A 48-year-old woman notices a firm, fixed mass in her right breast but chooses to ignore it. The mass is then detected on her annual physical examination eight months later. By that point, the mass has increased greatly in size. When questioned as to why she did not report the mass when she first noticed it, the woman states that she was not concerned about the mass because she does not have a family history of breast cancer This response is an example of which of the following defense mechanisms?
Repression
Dissociation
Denial
Rationalization
Intellectualization
A 48-year-old woman presents to your office with the complaint of vaginal dryness during intercourse. She denies any medical problems or prior surgeries and does not take any medications. She still has regular menstrual cycles every 28 days. She denies any sexually transmitted diseases. She describes her sexual relationship with her husband as satisfying. Her physical examination is normal. Components of the natural lubrication produced by the female during sexual arousal and intercourse include which of the following?
Mucus produced by endocervical glands
Transudate-like material from the vaginal walls
Fluid from Skene glands
Viscous fluid from Bartholin glands
Uterotubal fluid
A 49-year-old woman presents to her physician with dysphagia, regurgitation of undigested food eaten hours earlier, and coughing over the last 6 months. She was hospitalized 1 month ago for aspiration pneumonia and successfully treated with antibiotics. Examination reveals a thin-appearing woman with normal vital signs and unremarkable chest, heart, and abdominal examination. A UGI contrast study is performed and reveals a pharyngoesophageal (Zenker’s) diverticulum. Which of the following statements is true regarding Zenker’s diverticula?
Cervical dysphagia is related to the size of the diverticulum
Pharyngoesophageal diverticula are of the pulsion type
Upper esophageal sphincter function is usually normal
Pharyngoesophageal diverticula are congenital in origin
Pharyngoesophageal diverticula are true diverticula
A 5-month-old boy is brought in for a routine check-up. He was born at 37 weeks' gestation and has had persistent wheezing since shortly after birth despite inhaled bronchodilator and oral corticosteroid therapy. His diet consists of 32 ounces of iron-fortified cow's milk-based formula daily. On physical examination, the child appears well-nourished and happy. You note moderate relief of his wheezing with neck extension. Which of the following is the most likely mechanism of this infant's wheezing?
Aspiration of a foreign body
Chronic upper respiratory tract infection
Allergic reaction to cow's milk
Asthma
Compression of the airway by a vascular ring
A 5-month-old infant is brought to the office for the evaluation of persistent vomiting, failure to thrive, and developmental delay. His antenatal and postnatal histories are not known to his Caucasian foster parents, who adopted him when he was 4 months old. The physical examination reveals an infant with blonde hair, fair skin and blue eyes. His urine has a peculiar musty odor. His plasma phenylalanine level is 40 mg/dl and tyrosine level is normal. His urinary phenylpyruvic and a-hydroxy phenylacetic acid levels are both increased. What is the most likely etiology of this child's symptoms?
Classic phenylketonuria
Transient hyperphenylalaninemia
Benign hyperphenylalaninemia
Tyrosinemia
Alcaptonuria
A 5-year-old boy suffers from a condition characterized by recurrent fungal and viral infections, thymic hypoplasia, tetany, and abnormal facies. Serum levels of immunoglobulins are mildly depressed, and lymph node biopsy shows lymphocyte depletion of T-dependent areas. Which of the following is the underlying pathogenetic mechanism?
Developmental defect of the third/fourth pharyngeal pouches
In utero infection by human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
Mutations of an X-linked gene coding for a tyrosine kinase
Mutations of an X-linked gene coding for a cytokine receptor subunit
Mutations of an autosomal gene encoding adenosine deaminase
A 5-year-old pedestrian is hit by a car in a mall parking lot and he is brought to the emergency department. There was loss of consciousness for less than 1 minute. On evaluation, the child has no neurologic deficits and a CT scan of the head reveals no intracranial abnormalities and no obvious skull fractures. The parents want to know what possible long-term problems there might be. You remember that problems after head trauma may include the development of seizures and that the risk of developing posttraumatic epilepsy is increased by which of the following?
A brief loss of consciousness
Retrograde amnesia
An acute intracranial hemorrhage
Posttraumatic vomiting
A small linear skull fracture
A 50-year-old man presents to the office with fatigue, malaise, and disabling joint pain in his fingers, wrists, shoulder, hips, knees, and ankles. His pain is severe and associated with a mild degree of morning stiffness for 10-15 minutes. He occasionally takes acetaminophen and ibuprofen for this pain. He has a 10-pack-year smoking history. He does not drink alcohol. Family history includes an uncle who died of liver cancer. On examination, there is grayish skin pigmentation, most prominent on the exposed parts. Abdominal examination is significant for liver enlargement 2 cm below the costal margin. Laboratory studies reveal the following: Hemoglobin 13.0 g/L, Leukocyte count 5,500/mm3, Serum creatinine 0.8 mg/dl, Blood glucose 218mg/dl, Aspartate aminotransferase (SGOT) 128 U/L, Alanine aminotransferase (SGPT) 155 U/L, Alkaline phosphatase 120 U/L , Serum iron 450 mol/L (50-170g/dL), Transferrin saturation of iron 62% (22-47%), Serum Ferritin 3000ng/L (15-200 ng/ml, males). X-ray of the joints shows narrowing of joint spaces and diffuses demineralization. This patient's condition makes him more vulnerable to which of the following infections?
Listeria monocytogenes
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Escherichia coli
Chlamydia psittaci
Epstein Barr virus
A 50-year-old man presents to your office complaining of pain and swelling of the right knee. He bumped his right knee into a pole 2 days ago while working. He had one episode of similar pain two years ago that resolved with over-the-counter analgesics. He denies any illicit drug use. He has no other medical problems and does not take any medications. His temperature is 37.2°C (98.9°F), and blood pressure is 126/76 mmHg. Examination reveals swelling, warmth and decreased range of motion of the right knee. All other joints are within normal limits. Synovial fluid analysis shows positive birefringent crystals and negative Gram stain. These crystals are most likely composed of?
Hydroxyapatite
Monosodium urate
Calcium pyrophosphate
Calcium oxalate
Ammonium phosphate
A 50-year-old man wants to talk to you about something, "absolutely confidential". After you assure him, he admits, "He is unable to get an erection and just can't have sex." He wants to figure it out quickly because "he simply can't live like this." He has never been diagnosed with diabetes and denies other complaints. He has a 2 pack/day history of smoking for 30 years. On examination, his BP: 158/90mm of Hg; Temperature: 37.1°C (98.8°F); RR 14/min; PR 82/min. There is upper body obesity, rounded face, increased fat around the neck, and thinning of arms and legs. You find his skin to be bruised, fragile and thin. Laboratory reveals the following results. Serum: Glucose 186 mg/dl, Sodium 142 mEq/L, Potassium 2.5 mEq/L, Bicarbonate 38 mEq/L. Chest X ray shows a large mass in left bronchus. What is the most likely cause of patient's condition?
Pituitary adenoma
Ectopic ACTH syndrome
Adrenal tumors
Familial cushing's syndrome
Exogenous steroid intake
A 50-year-old obese female is taking oral hypoglycemic agents. While being treated for an upper respiratory infection, she develops lethargy and is brought to the emergency room. Neurological examination is nonfocal; she does not have neck rigidity. Laboratory results are as follows: Na: 134 mEq/L, K: 4.0 mEq/L, HCO3: 25 mEq/L, Glucose: 900 mg/dL, BUN: 84 mg/dL, Creatinine: 3.0 mg/dL, HgA1c: 6.8%, BP: 120/80 mmHg lying down, 105/65 mmHg sitting. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient’s coma?
Diabetic ketoacidosis
Inappropriate ADH
Hyperosmolar coma
Noncompliance with medication
Bacterial meningitis
A 50-year-old white male comes into your office for a routine check-up. He has no present complaints. His past medical history is significant for hypertension controlled with a low-dose thiazide diuretic. His family history reveals non-fatal myocardial infarction in his father at the age of 47. The patient does not smoke or consume alcohol. His blood pressure is 130/75 mmHg and his heart rate is 70/min. His previous records show that his HDL level is persistently low in spite of acceptable total cholesterol and LDL levels. You prescribe niacin to raise HDL level. The patient returns in a week complaining of intensive generalized pruritis and flushing. What is the most probable cause of the patient's complaint?
Hypersensitivity reaction
Drug interaction
Prostaglandin-related reaction
Drug-induced vasoconstriction
Psychogenic reaction
A 50-year-old woman presents to your office complaining of lower extremity edema that stated several weeks ago, and slowly progressed thereafter. Her past medical history is significant for hypertension, treated with metoprolol for 2 years. Amlodipine was added recently because of inadequate control of BP with metoprolol alone. She does not smoke or consume alcohol. She has no known drug allergies. Her blood pressure is 130/80mmHg and her heart rate is 64/min. The physical examination reveals bilateral symmetric 3+ pitting edema of both lower extremities, without any skin changes or varicosities. Her neck vein pulsation is normal. Other physical findings are within normal limits. Her laboratory studies reveal the following: Serum albumin 4.5 g/dL, Total serum bilirubin 0.8 mg/dL, Serum sodium 140 mEq/L, Serum potassium 4.0 mEq/L, Serum creatinine 0.8 mg/dL. Urinalysis is within normal limite. What is the most likely cause of the edema in this patient?
Heart failure
Liver disease
Renal disease
Venous insufficiency
Side effect of her medications
A 51 -year-old man complains of difficulty walking and mild right-sided foot pain for the past several weeks. His medical history is significant for type 1 diabetes mellitus, hypertension and hypercholesterolemia. Physical examination reveals a significantly deformed right foot and a mildly deformed left foot. X-rays suggest effusions in several of the tarsometatarsal joints, large osteophytes, and several extra articular bone fragments. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's complaints?
Hyperuricemia
Poor vascular supply
Nerve damage
Rheumatoid arthritis
Bone demineralization
A 51 -year-old obese male presents to your office complaining of difficulty swallowing solids but not liquids. His medical history is significant for GERD. Six months ago he was diagnosed with Barrett's esophagus. He reports that three months after the diagnosis of Barrett's esophagus, his heartburn resolved. Barium swallow now reveals an area of symmetric, circumferential narrowing affecting the distal esophagus. Which of the following best explains this finding?
Esophageal adenocarcinoma
Hiatal hernia
Achalasia
Peptic stricture
Vascular ring
A 51-year-old female comes to the office for a routine visit. She is apparently healthy and does not have any complaints. Physical examination reveals a thyroid nodule. She is surprised to hear about the nodule and asks, "How often does this happen? What could have caused this?" Which of the following is the most common cause of thyroid nodules?
Follicular adenoma
Colloid nodule
Papillary carcinoma
Follicular carcinoma
Anaplastic carcinoma
A 51-year-old woman comes to your office for a routine health maintenance examination. She has no medical history but states that she has been having irregular menses and occasional hot flashes for the past eight months. Her husband has told her that she appears moody all the time. She has not had any surgeries in the past and currently takes no medications. She has a very stressful job and drinks two to three cups of coffee every morning. She does not smoke, but she does drink four to five twelve-ounce beers a day for the past 20 years to relieve her stress. She is a lacto-ovo vegetarian and walks two miles on a treadmill each day. Her temperature is 36.5C (97.7F), blood pressure is 120/70, heart rate is 84 beats/minute, and respirations are 12/minute. She is 5'4" and weighs 180 pounds (BMI is 30.9 kg/m2). Physical examination is unremarkable. You inform her that she is probably reaching menopause, and that she will be at an increased risk of developing osteoporosis. Which of the following is the most significant risk factor for the development of osteoporosis in this patient?
Caffeine use
Obesity
Excess alcohol use
Vegetarian diet
Excess walking
A 52-year-old African-American woman with type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM) presents to her physician’s office and states that she has been feeling lousy in the morning. She notes that she reliably checks her blood glucose levels, and is frustrated at the fact that she often has a blood sugar level in the 120s at night, followed by a level in the 170s to 180s the following morning. The patient’s primary care physician increased her nightly dose of neutral protamine Hagedorn insulin 1 month ago, but her morning glucose levels have only become more elevated. She has recently begun to limit her carbohydrate intake at night, with no effect. This patient’s morning hyperglycemia might most likely be alleviated by which of the following?
Decreasing neutral protamine Hagedorn insulin at night
Increasing neutral protamine Hagedorn insulin at night
Increasing regular insulin at night
Increasing regular insulin in the morning
Increasing neutral protamine Hagedorn insulin in the morning
A 52-year-old alcoholic man presents to the emergency department because of anxiety and tremors. His last drink of alcohol was 2 days ago. His initial electrolyte panel is: Sodium 132 mEq/L, Potassium 2.9 mEq/L, Chloride 100 mEq/L, Bicarbonate 25 mEq/L. He is treated for alcohol withdrawal, and given aggressive intravenous and oral potassium supplementation. Three days later, his electrolyte panel is: Sodium 135 mEq/L, Potassium 3.1 mEq/L, Chloride 102 mEq/L, Bicarbonate 28 mEq/L. Which of the following explains why this patient's potassium level is so difficult to correct?
Poor oral absorption
Hypophosphatemia
Alcohol withdrawal
Hypomagnesemia .
Thiamine deficiency
A 52-year-old female presents with a rash over her face for the past few weeks. She also complains of recent-onset difficulty with rising from a seated position and climbing stairs. On examination, you notice a dusky malar rash and a violaceous periorbital edema. Her vital signs are within normal limits. Examination shows symmetric proximal muscle weakness in legs. This patient's condition is most often associated with which of the following?
Aortic aneurysms
Renal failure
Alveolar hemorrhage
Malignancy
Carpal tunnel syndrome
A 52-year-old male is referred to the neurology clinic for the evaluation of EEG abnormalities. He presented with rapidly increasing memory impairment, and denied any history of seizures or head trauma. The physical examination revealed no abnormalities, except a myoclonus. An extensive work-up ruled out the presence of any medical illness; however, the EEG report revealed sharp, triphasic and synchronous discharges. Which of the following abnormalities is most likely in this patient?
Defect in an autosomal dominant gene on chromosome 4
Spongiform encephalopathy caused by a prion
Loss of nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurons
Neurodegeneration of frontal and temporal lobes
Histopathological findings of neurofibrillary tangles and amyloid plaques
A 52-year-old man has been impotent ever since he had an abdominoperineal resection for cancer of the rectum. The tumor was staged as T3, NO, MO. He gets no nocturnal erections, and his impotence extends to all situations, regardless of sexual partner, and includes inability to masturbate. His erectile dysfunction is most likely due to which of the following?
Arterial vascular insufficiency
Erectile nerve damage
Psychogenic factors
Tumor invasion of the urethra
Venous incompetence
A 52-year-old man with a family history of multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN1) has an elevated gastrin level and is suspected to have a gastrinoma. Which of the following is the most likely location for his tumor?
Fundus of the stomach
Antrum of the stomach
Within the triangle formed by the junction of the second and third portions of the duodenum, the junction of the neck and body of the pancreas, and the junction of the cystic and common bile duct Q
Tail of the pancreas
Within the triangle formed by the inferior edge of the liver, the cystic duct, and the common hepatic duct
A 52-year-old woman presents with hypertension, obesity, and new skin striae. You are concerned about possible Cushing syndrome. Which of the following is the most common cause of Cushing syndrome?
Adrenocortical hyperplasia
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)–producing pituitary tumor
Pharmacologic glucocorticoid use
Ectopic adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)–secreting carcinoid tumor
Primary adrenal neoplasms
A 53-year-old Caucasian man comes to the emergency department at 2 am because of severe pain in his right great toe for the past 2 hours. He complains that the pain began suddenly as a dull, aching pain, and has worsened over time to a severe throbbing pain, not relieved by acetaminophen. His other medical problems include hypertension, diabetes mellitus-type 2, hypercholesterolemia, and peptic ulcer disease. He has smoked 2 packs of cigarettes daily for 30 years. He drinks 5-6 ounces of alcohol daily. He eats a lot of junk food and exercises infrequently. Both his father and mother have diabetes and hypertension. His older brother died of a myocardial infarction 2 years ago. His medications include glyburide, lisinopril, atenolol, simvastatin and famotidine. His temperature is 37.8°C (100°F), blood pressure is 160/90 mm Hg, pulse is 88/min and respirations are 16/min. On examination, the right great toe appears markedly swollen, red, and is warm to touch. Aspiration of the joint fluid reveals negatively birefringent needle shaped crystals. Apart from prescribing oral indomethacin, what other intervention would be most important to prevent the development of further attacks?
Smoking cessation
Alcohol cessation
Stopping lisinopril
Stopping simvastatin
Stopping glyburide
A 53-year-old female presents to the clinic with an erythematous lesion on the dorsum of her right hand. The lesion has been present for the past 7 months and has not responded to corticosteroid treatment. She is concerned because the lesion occasionally bleeds and has grown in size during the past few months. On physical examination you notice an 11-mm erythematous plaque with a small central ulceration. The skin is also indurated with mild crusting on the surface. Which of the following is true about this process?
It is a malignant neoplasm of the keratinocytes with the potential to metastasize
It is an allergic reaction resulting from elevation of serum IgE
It is a chronic inflammatory condition, which can be complicated by arthritis of small and medium-sized joints
It is a malignant neoplasm of the melanocytes with the potential to metastasize
It is the most common skin cancer
A 53-year-old homosexual man comes to the ER with shortness of breath and dry cough over the past week. You note that he was hospitalized for Candida esophagitis one month ago, but left against medical advice. On physical examination, his blood pressure is 120/70 mmHg, heart rate is 120/min and regular, oxygen saturation is 89% on 2L/min of oxygen by nasal cannula, and temperature is 38.3°C (101°F). There are extensive white plaques over the oral mucosa and there is a soft 2/6 systolic murmur over the cardiac apex. Lung auscultation is remarkable for faint bilateral crackles. Which of the following is most likely responsible?
Alveolar hypoventilation
Increased lung compliance .
Increased pulmonary capillary wedge pressure
Pulmonary hypertension
Increased alveolar-arterial oxygen gradient
A 53-year-old male presents to your office with a two-day history of right calf pain and swelling. He describes the pain as constant and states that it is exacerbated by knee flexion. He has a history of past IV drug abuse, endocarditis, and stroke. He is currently wheelchair-bound secondary to stroke-related left-sided hemiparesis. On physical examination, his blood pressure is 140/90 mmHg and his heart rate is 100/min. There is no jugular venous distention or hepato-jugular reflux. His chest is clear to auscultation but his abdomen is enlarged with shifting dullness and a fluid wave, suggestive of ascites. His liver is palpable 3 cm below the right costal margin. His spleen is also palpable. On examination of his lower extremities, you note right-sided calf swelling and tenderness. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's ascites?
Right-sided heart failure
Pulmonary embolism
Protein C deficiency
Chronic liver disease
Paradoxical embolism
A 53-year-old man comes to the office because of difficulty reading fine print over the last year. He now has to hold books, menus, and magazines at an arm’s length in order to read them. He has never had visual problems before. Which of the following is most likely abnormal in this patient?
Corneal shape
Lens elasticity
Lens opacity
Macula
Peripheral retina
A 53-year-old man presents to the emergency room with squeezing chest pain that started two hours ago. He also complains of shortness of breath that is worse when lying down. He has never had pain like this before. He has no significant past medical history and he takes no medications. A routine health maintenance visit two weeks ago was normal. On physical examination in the ER, his blood pressure is 140/90 mmHg and his heart rate is 100/min. Chest auscultation reveals a grade II/VI blowing systolic murmur at the cardiac apex and bibasilar crackles in the lungs. ECG shows ST segment elevations in leads I, aVL, and v1-v3. Which of the following is most likely increased in this patient?
Left atrial pressure
Left ventricular ejection fraction
Left atrial size
Left ventricular compliance
Right ventricular preload
A 53-year-old man presents to your office complaining of weakness and exertional dyspnea over the last week. He denies chest pain and palpitations. He has no other past medical history. His father died of a myocardial infarction at age 55. On exam, his heart rate is 100/min and blood pressure is 90/60 mmHg. Internal jugular venous pulsation is observed 7 cm above the sternal angle. Lungs are clear to auscultation. Heart sounds are muffled. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's complaints?
Left ventricular outflow obstruction
Pulmonary hypertension
Decreased left ventricular preload
Decreased cardiac contractility
Increased right ventricular compliance
A 53-year-old woman has been intubated for several days after sustaining a right pulmonary contusion after a motor vehicle collision as well as multiple rib fractures. Which of the following is a reasonable indication to attempt extubation?
Negative inspiratory force (NIF) of –15 cm H2O
PO2 of 60 mm Hg while breathing 30% inspired FiO2 with a positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) of 10 cm H2O
A rapid shallow breathing index of 80
Minute ventilation of 18 L/min
Spontaneous respiratory rate of 35 breaths per minute
A 53-year-old woman presents to your office with right-sided abdominal pain that started two days ago. She describes the pain as constant and burning in nature. There is no associated nausea, vomiting or diarrhea. The patient reports taking over-the-counter antacids and ibuprofen, which brought no relief. Her medical history is significant for breast cancer diagnosed one year ago, for which she underwent a modified radical mastectomy and is receiving chemotherapy, the last course of which was completed two months ago. On physical examination, her temperature is 36.7°C (98°F), blood pressure is 120/70 mm Hg, pulse is 80/min, and respirations are 16/min. Her lung fields are clear to auscultation and her abdomen is soft and non-distended. The liver span is 10 cm and the spleen is not palpable. Lightly touching the skin to the right of the umbilicus elicits intense pain. In one week the patient is most likely to develop:
Intestinal obstruction
Skin lesions
Fever and jaundice
Ascites
Black stool
A 54 year-old male comes to the physician because of abdominal distention. He thinks his big belly is making it hard for him to breathe. He received radiation therapy for Hodgkin lymphoma several years ago and was told that he is cured. He drinks alcohol on a regular basis. His temperature is 36.7°C (98°F), blood pressure is 120/76 mm Hg, pulse is 80/min and respirations are 20/min. Examination shows a jugular venous pressure 7 cm above the sternal angle. Dullness to percussion and decreased breath sounds are noted in the right lung base. The abdomen is quite distended with an obvious fluid wave. Mild hepatomegaly is present. Extremities have 2+ lower extremity edema. Initial laboratory studies are shown below: Serum creatinine 0.8 mg/dL, Alburnin 4.0 mg/dL, Total bihrubin 1.0 mg/dl, Prothrombin time 11 sec. Urinalysis is within normal limits. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his condition?
Urinary protein loss
Portal vein compression
Portal vein thrombosis
Inelastic pericardium
Thoracic duct obstruction
A 54-year-old female complains of muscle weakness. She describes difficulty getting up from a chair and combing her hair. She does not use tobacco, alcohol or drugs. She takes no medication. Her vital signs are within normal limits. Physical examination reveals bilateral ptosis. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's complaints?
Ischemic stroke
Subdural hematoma
Epidural hematoma
Thyroid myopathy
Neuromuscular junction disease
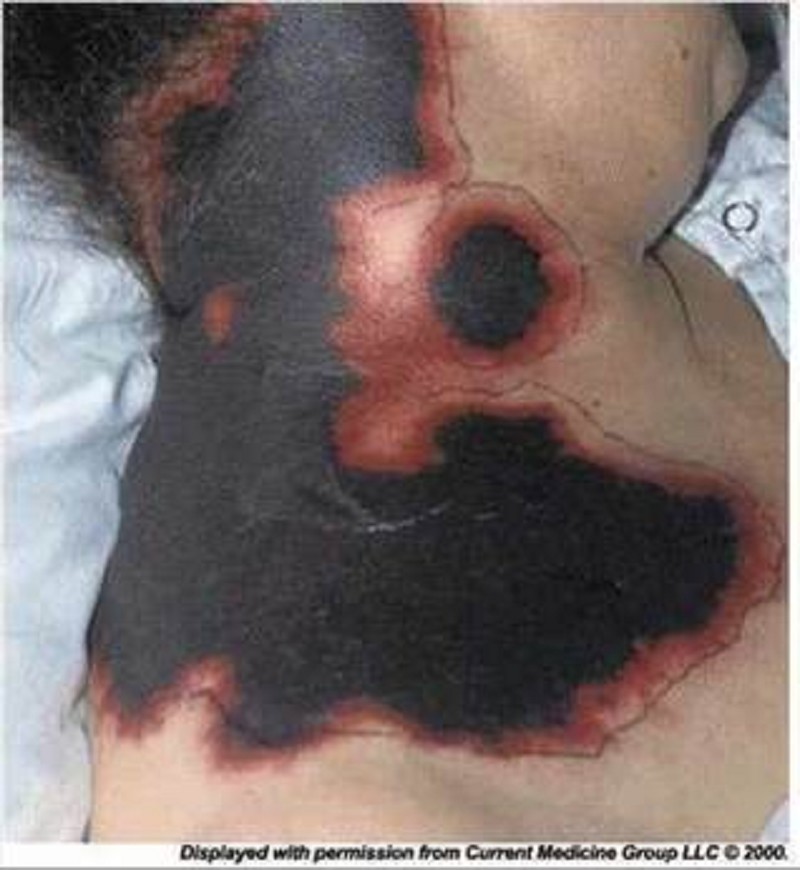
A 54-year-old female with a long history of hypertension and a recent hospitalization for atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response now returns to the hospital complaining of skin changes. Her medications include warfarin, hydrochlorothiazide and metoprolol. On physical examination, her temperature is 36.7°C (98°F), blood pressure is 130/80 mm Hg, pulse is 80/min and irregular, and respirations are 16/min. You observe the skin changes pictured below. Her exam is otherwise unremarkable. Which of the following is the primary cause of her condition?
Antithrombin III deficiency
Excessive platelet aggregation
Factor VII deficiency
Vitamin K deficiency
Protein C deficiency
A 54-year-old male with a history of chronic alcoholism is admitted to the hospital with hematemesis and abdominal distension. Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy reveals the presence of esophageal varices. Continued workup of his condition results in a diagnosis of cirrhosis of the liver. He is treated appropriately and strongly counseled about the need to abstain from alcohol. He is then discharged home. After discharge, he begins to work as a full-time volunteer for a non-profit organization that assists patients with alcoholic cirrhosis. Which of the following defense mechanisms is this man using?
Reaction formation
Denial
Sublimation
Altruism
Suppression
A 54-year-old man complains of burning epigastric pain that usually improves after a meal, and is occasionally relieved with antacids. On examination, he appears well and besides some epigastric tenderness on palpation, the rest of the examination is normal. Upper endoscopy confirms a duodenal ulcer. Which of the following statements concerning PUD is most likely correct?
Duodenal ulcer is seen more often in older people than is gastric ulcer
Clinically, gastric ulcers are more common than duodenal ulcers
Peptic gastric ulcers are usually quite proximal in the stomach
Infection can cause both types of peptic ulcer
Duodenal ulcers can frequently be malignant
A 54-year-old man with a 20-year history of chronic obstructive lung disease has a heave that is palpable at the lower left sternal border at the third, fourth, and fifth intercostal spaces. Which of the following best explains the etiology of the heave?
It means the patient has right ventricular hypertrophy
It means the patient has a pericardial effusion
It means that the patient has aortic stenosis
It means the patient has congestive heart failure
It is probably a displaced point of maximum impulse (PMI)
A 54-year-old woman presents to her physician for an opinion regarding additional therapy following curative resection of recently diagnosed colon cancer. She underwent uncomplicated sigmoid resection for invasive colon cancer 4 weeks ago. The pathology revealed carcinoma invading into, but not through, the muscularis propria, with one of eight positive mesenteric nodes. There was no evidence of liver metastases at the time of operation. Preoperative chest x-ray and CT scan of the abdomen showed no evidence of distant disease. Preoperative carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) level was normal. Past history is positive for diabetes and mild hypertension. Examination is unremarkable except for a healing abdominal incision. Which of the following is the correct stage of this patient’s colon cancer?
Stage 0
Stage II
Stage IV
Stage III
Stage I
A 54-year-old woman presents to your office complaining of difficulty walking. She describes severe weakness and occasional pain in her thigh muscles. She has stumbled and fallen several times over the last week. Her past medical history is significant for hypertension treated with hydrochlorothiazide and metoprolol. She consumes two to three cans of beer on weekends. Her younger brother died of a neurological disease when he was 20 years old. Her mother suffers from hypertension and diabetes mellitus. Her heart rate is 90/min and blood pressure is 170/100 mmHg. Chest examination is within normal limits. A bruit is heard over the left carotid artery. Neurologic examination reveals hyporeflexia and decreased strength in all muscle groups. Her ESR is 12 mm/hr. ECG shows flat and broad T waves with occasional premature ventricular contractions. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's current complaints?
Ischemic stroke
Subdural hematoma
Epidural hematoma
Lumbar spinal stenosis
Electrolyte disturbance
A 55-year-old Asian man with mitral stenosis secondary to rheumatic heart disease undergoes dental surgery for caries. Postoperatively, he does well and is discharged home. Two weeks later, he presents with fever, chills, fatigue, and feels "sick." Four out of four blood culture bottles are positive for gram-positive cocci. An echocardiogram is performed and shows mitral valve vegetations. Which of the following is the most likely causative organism of this patient's condition?
Groupe B streptococci
Streptococcus mutans
Streptococci bovis
Staphylococcus epidermis
Enterococci
A 55-year-old Caucasian male presents to the office for a routine check-up. He has no present complaints. His past medical history is significant for a long history of hypertension. He does not smoke or consume alcohol. His current medications are enalapril and hydrochlorothiazide. His blood pressure is 140/90 mmHg and heart rate is 80/min. Physical examination reveals a moderately overweight man (BMI = 27 kg/m2) with a waist circumference of 41 inches. The laboratory studies show: Fasting blood glucose 112 mg/dl, Total cholesterol 220 mg/dl, LDL cholesterol 140 mg/dl, Triglycerides 240 mg/dl. Which of the following is the most important pathogenic factor for this patient's condition?
Impaired secretion of insulin
Insulin resistance
Low absolute values of insulin
Sympathetic hyperactivity
Insulin-mediated vasodilatation
A 55-year-old Caucasian male presents to your office with muscle pain of recent onset. His past medical history is significant for hypertension and an acute myocardial infarction experienced 2 months ago. His current medications include metoprolol captopril, aspirin and simvastatin. His blood pressure is 130/80 mmHg and heat rate is 60/min. Liver function tests are slightly abnormal. Serum creatine kinase level is elevated. You suspect a drug-induced reaction. Which of the following is the most possible mechanism of drug-induced reaction in this patient?
Cell surface receptor blockage
Synthetic reaction inhibition
Immune-mediated reaction
Damage of membrane-bound lipids
Extracellular enzyme blockage
A 55-year-old homeless man presents to the emergency room complaining of muscle cramps and perioral numbing. The patient looks malnourished. He says that he consumed a lot of alcohol recently. His past medical history is significant for chronic and recurrent abdominal pain for which he was advised to quit drinking alcohol. His temperature is 36.7°C (98°F), blood pressure is 110/65 mmHg, pulse is 80/min, and respirations are 18/min. The laboratory values are: Hemoglobin 7.2 g/dl, MCV 105 fl, Leukocyte count 9,000/cmm, Platelets 200,000/cmm, ESR 20 mm/hr, Serum sodium 145 mEq/L, Serum potassium 4.0 mEq/L, Serum calcium 6.8 mg/dl, Serum phosphorus 2.5 mg/dl. What is the most probable cause of hypocalcemia observed in this patient?
Renal failure
Pseudohypoparathyroidism
Primary hypoparathyroidism
Hypoalbuminemia
Malabsorption
A 55-year-old man presents to the ED with chest pain and shortness of breath. His BP is 170/80 mmHg, HR is 89 beats per minute, and oxygen saturation is 90% on room air. Physical examination reveals crackles midway up both lung fields and a new holosystolic murmur that is loudest at the apex and radiates to the left axilla. ECG reveals ST elevations in the inferior leads. Chest radiograph shows pulmonary edema with a normal sized cardiac silhouette. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the cardiac murmur?
Critical aortic stenosis
Papillary muscle rupture
Pericardial effusion
CHF
Aortic dissection
A 55-year-old man presents with worsening cirrhosis. After evaluation by a hepatologist, he presents for evaluation for hepatic transplantation. He is informed that prioritization for transplantation is based on the Model of End-stage Liver Disease (MELD) score, and that patients with higher MELD scores have a greater benefit from transplantation. Which of the following contributes to the MELD score?
Platelet count
Total bilirubin
Albumin
Encephalopathy
Ascites
A 55-year-old woman has been hospitalized because of recurrent pancreatitis, ARDS, prolonged ileus, and need for parenteral nutrition. She demonstrates weakness, lassitude, orthostatic hypotension, nausea, and fever. Which of the following abnormalities is most likely to explain these symptoms?
Hypothermia
Hypokalemia
Hyperglycemia
Hyponatremia
Hypervolemia
A 55-year-old woman is in the intensive care unit on a ventilator for hypoxemia following “flash” pulmonary edema. Her PO2 on the blood gas prior to intubation was 44 mm Hg, and now while breathing 100% oxygen on the ventilator her repeat blood gas reveals a PO2 of 80 mm Hg. Hypoxemia while receiving 100% oxygen indicates which of the following problems?
Ventilation-perfusion ratio inequality
Right-to-left shunt
Hypoventilation
Impaired diffusion
Interstitial lung disease
A 55-year-old woman presents with a three-week history of low-grade fever, weight loss of 4.5kg (10 lb), and malaise. She is known to have mitral valve prolapse, but is otherwise healthy. She underwent a tooth extraction one month ago. She denies alcohol, tobacco, and illicit drug use. Her temperature is 38.5°C (101.3°F), pulse is 90/min, respirations are 18/min, and blood pressure is 145/76 mm Hg. Her chest is clear to auscultation and percussion. Cardiac examination reveals a III/IV holosystolic murmur at the apex that radiates to the axilla. Chest x-ray is normal. Urinalysis is unremarkable. Blood cultures are drawn and empiric antibiotics are started. Echocardiogram shows mitral regurgitation with vegetation on the mitral valve. Which of the following organisms is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
Staphylococcus aureus
Staphylococcus saprophyticus
Staphylococcus epidermidis
Viridans group streptococci
Enterococcus species
A 55-year-old woman who has end-stage liver disease is referred to a hepatologist for evaluation. Which of the following would prevent her from being a transplantation candidate?
Use of alcohol 3 months ago
Two 2-cm hepatocellular carcinomas (HCCs) in the right lobe of the liver
Development of hepatorenal syndrome requiring hemodialysis
A 4-cm hepatocellular carcinoma in the right lobe of the liver
History of breast cancer 5 years ago with no evidence of disease currently
A 55-year-old-woman of Asian descent goes to the emergency department because of vomiting and severe abdominal cramping of 3 days' duration. Her pain is centered on the umbilicus. She denies being exposed to a viral or bacterial illness. Her medical history includes a previous cholecystectomy and an appendectomy after which she developed an infection. Her abdomen is not tender, but hyperactive, high-pitched peristalsis with rushes coincides with palpable bowel cramping. Abdominal x-ray films taken in the supine and upright positions demonstrate a ladder-like series of distended small bowel loops. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for these findings?
Adhesions
Ascaris infection
Cancer
Volvulus
Intussusception
A 56-year-old male complains of occasional dizziness. He gets a brief spinning sensation while getting out of bed. He sometimes feels dizzy while turning in bed or looking up. He denies any nausea, diaphoresis, chest pain or tinnitus. His past medical history is significant for long-standing hypertension, which is being treated with hydrochlorothiazide, and hyperlipidemia, which is being treated with simvastatin. His father died of a stroke at the age of 62 years. His blood pressure is 130/80 mmHg while supine, and 135/85 mmHg while standing. His heart rate is 77/min. A grade II/VI ejection murmur is heard over the aortic area. ECG reveals left ventricular hypertrophy and premature ventricular contractions. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's complaints?
Transient ischemic attacks
Labyrinthine dysfunction
Aortic stenosis
Extracellular sodium loss
Cardiac arrhythmia
A 56-year-old male presents with progressively worsening dyspnea over a 4 month period. He denies fever, chest pain, cough or ankle swelling and does not use tobacco, alcohol or drugs. He works for a home insulation and plumbing company. He has never been abroad and does not own any pets. His only medications are hydrochlorothiazide and metoprolol for blood pressure control. On physical examination, his temperature is 36.8°C (98.2°F), pulse is 76/min, blood pressure is 130/78 mmHg, and respirations are 15/min. Examination shows digital clubbing and fine bibasilar end-inspiratory crackles. Jugular venous pressure is 7 cm and there is no peripheral edema. Which of the following additional findings is most likely in this patient?
Increased pulmonary capillary wedge pressure
Decreased diffusion lung capacity (DLCO)
Increased residual lung volume
Reduced FEV1/FVC ratio
Decreased pulmonary arterial pressure
A 56-year-old male with a long history of diabetes mellitus complains of nocturnal urinary frequency, occasional dribbling and difficulty completing his stream. His past medical history is significant for a myocardial infarction two years ago and moderately decreased visual acuity. On physical examination, his blood pressure is 160/100 mmHg and his heart rate is 70/min. There is a carotid bruit auscultated on the left side as well as trace ankle edema. Post-void bladder catheterization yields 60 ml of urine. Dipstick urinalysis reveals 2+ protein and 3-4 WBC/hpf. The patient's serum creatinine level is 2.4 mg/dl. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his renal dysfunction?
Ascending infection
Obstructive uropathy
Microangiopathy
Renal hypoperfusion
Cystic kidney disease
A 56-year-old man is having intermittent fevers and malaise for the past 2 weeks. He has no other localizing symptoms. Two months ago, he had valve replacement surgery for a bicuspid aortic valve. A mechanical valve was inserted and his postoperative course was uncomplicated. On examination, his temperature is 38°C, blood pressure 124/80 mm Hg, pulse 72/min, and head and neck are normal. There is a 3/6 systolic ejection murmur, the second heart sound is mechanical, and a 2/6 early diastolic murmur is heard. The lungs are clear and the skin examination is normal. Three sets of blood cultures are drawn and an urgent echocardiogram is ordered. Which of the following is the most likely causative organism?
S. epidermidis
Staphylococcus aureus
S. viridans
Enterococci
Candida
A 56-year-old woman becomes the chief financial officer of a large company and, several months thereafter, develops upper abdominal pain that she ascribes to stress. She takes an over-the-counter antacid with temporary benefit. She uses no other medications. One night she awakens with nausea and vomits a large volume of coffee grounds-like material; she becomes weak and diaphoretic. Upon hospitalization, she is found to have an actively bleeding duodenal ulcer. Which of the following statements is true?
The most likely etiology is adenocarcinoma of the duodenum
The etiology of duodenal ulcer is different in women than in men
The likelihood that she harbors Helicobacter pylori is greater than 50%
Lifetime residence in the United States makes H pylori unlikely as an etiologic agent
Organisms consistent with H pylori are rarely seen on biopsy in patients with duodenal ulcer
A 56-year-old woman is undergoing chemotherapy. She presents today with complaints of burning on urination and bloody urine. Which of the following agents causes hemorrhagic cystitis?
Bleomycin
5-fluorouracil
Cisplatin
Vincristine
Cyclophosphamide
A 56-year-old woman presents to the clinic for routine health screening. Her concern is the development of breast cancer. She has no current breast-related complaints. Past history is pertinent for fibrocystic changes with atypical ductal hyperplasia and a single fibroadenoma, both diagnosed by open biopsy 5 years ago. She smokes one pack per day and drinks one can of beer daily. Family history is positive for breast cancer in her mother, diagnosed at the age of 85. Current medications include a cholesterol-lowering agent, an antihypertensive, and HRT, which she has taken for 5 years. Physical examination is unremarkable. Mammograms show dense breasts, decreasing the accuracy of the study, but no suspicious findings were noted. Which of the following is the most common risk factor in evaluating women for breast cancer?
Fibrocystic changes with atypical ductal hyperplasia
Alcohol consumption
HRT
Age
Positive family history
A 56-year-old woman presents to your office for her routine wellwoman examination. She had a hysterectomy at age 44 for symptomatic uterine fibroids. She entered menopause at age 54 based on menopausal symptoms and an elevated FSH level. She started taking estrogen replacement therapy at that time for relief of her symptoms. She is fasting and would like to have her lipid panel checked while she is in the office today. You counsel the patient on the effects of estrogen therapy on her lipid panel. She should expect which of the following?
An increase in her LDL
A decrease in her triglycerides
An increase in her HDL
An increase in her total cholesterol
A decrease in her HDL
A 57-year-old Caucasian female is diagnosed with deep venous thrombosis of the right leg that was confirmed with Doppler ultrasonography. She was diagnosed with pneumonia and empyema one week earlier, and treated with chest tube, antibiotics and bed rest. On her 6th day of anticoagulation therapy, she develops right hemiparesis and slight motor aphasia. The laboratory findings are: Red blood cells 4.3 million/mm3, Hemoglobin 14.00 g/dL, White blood cells 7,000/cmm, Platelets 50,000/cmm, APTT 60 sec (N < 25-40 sec), Fibrin degradation products negative. The emergency head CT scan does not reveal blood in the subarachnoid space or brain parenchyma. Which of the following is the most probable cause of this patient's condition?
Non-immune platelet degradation
Venous thromboembolism
Antibody-mediated platelet activation
Platelet sequestration and redistribution
Disseminated intravascular coagulation
A 57-year-old Caucasian woman presents for a follow-up visit regarding her lower back pain. She originally presented with this complaint last month and was advised to limit activity and use ibuprofen as needed. When her pain persisted, she was scheduled for an MRI of her back. The MRI report returned today and describes the presence of metastatic deposits in her spine. The source of the primary neoplasm remains undetermined. The patient has not yet been told about the findings and will need to be informed today. Which of the following is the best means of initiating a conversation about her condition?
"You have cancer, and it has metastasized to your back."
"You should have come earlier for a medical checkup. It is now too late."
"We will try our best. However, once a tumor metastasizes, the prognosis is poor."
"How are you feeling today?"
"You do not have a simple back strain."
A 57-year-old female with a history of type 2 diabetes mellitus complains of fatigue, urinary frequency, increasingly blurred vision and worsening leg cramps over the past week. She reports that the symptoms all began following an upper respiratory infection 7 or 8 days ago. She does not take any medications, but adheres to a diet low in saturated fat and simple carbohydrates to manage her diabetes. On physical examination, her blood pressure is 160/90 mmHg and her heart rate is 90/min. Her mucous membranes are dry. Her urine is positive for glucose but negative for ketones. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's vision impairment?
Cataracts
Diabetic retinopathy
Arterial hypertension
Hyperosmolarity
Eye infection
A 57-year-old male is hospitalized for hyponatremia. Physical examination reveals no signs of fluid overload. Serum analysis reveals a sodium concentration of 125mEq/l, glucose level of 12mg/dl, BUN of 8mg/dl, and creatinine of 0.7mg/dl. The urine osmolarity is 330mOsm/l and urine sodium concentration is 45mEq/l. After a 2L normal saline infusion, the serum sodium is 126mEq/l and the urine sodium excretion is increased to 90 mEq/l. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's hyponatremia?
Inappropriate ADH secretion
Surreptitious diuretic use
Psychogenic polydipsia
Advanced liver disease
Interstitial renal disease
A 57-year-old male presents to your office with a two week history of fever, chills, and generalized weakness. His medical history is significant for a hospitalization for pyelonephritis requiring IV antibiotics six months ago. He also recently underwent cystoscopy for evaluation of persistent dysuria. His past medical history is also significant for an episode of rheumatic fever as a child and Hodgkin's lymphoma treated with chemotherapy 10 years ago. On examination, his temperature is 37.8°C (100°F), blood pressure is 150/86 mmHg, pulse is 98/min and regular, and respirations are 16/min. The patient appears slightly diaphoretic. You note a new II/VI systolic murmur and tender erythematous lesions affecting several fingertips. The remainder of the physical examination is unremarkable. Which of the following bacteria is most likely responsible for his present illness?
Streptococcus pyogenes
Staphylococcus epidermidis
Enterococci
Viridans streptococci
Coxiella burnetii
A 57-year-old man has end-stage heart failure due to atherosclerosis. His cardiologist refers him for evaluation for heart transplantation. Which of the following is an absolute contraindication for heart transplantation?
Cirrhosis
Diabetes without end-organ damage
Age over 65
Reversible high pulmonary vascular resistance
History of colon cancer resected 5 years ago with no evidence of recurrence
A 57-year-old man with a 40-pack-per-year history of smoking experiences symptoms of shortness of breath on exertion. He has bilateral wheezes on expiration and increased resonance to percussion of the chest. Pulmonary fun
It is caused by bronchial asthma
It is preceded by chronic bronchitis
It is airflow limitation that is not fully reversible
Is due to small airways disease only
It is due to destruction and dilatation of lung alveoli
A 58-year-old Caucasian woman comes in to your office for advice regarding her risk factors for developing osteoporosis. She is 5ft 1 in tall and weighs 195 lb. She stopped having periods at age 49. She is healthy but smokes one pack of cigarettes per day. She does not take any medications. She has never taken hormone replacement for menopause. Her mother died at age 71 after she suffered a spontaneous hip fracture. Which of the following will have the least effect on this patient’s risk for developing osteoporosis?
Her family history
Her race
Her history of smoking cigarettes
Her menopause status
Her obesity
A 58-year-old man presents with a one-year history of diarrhea. The stools are watery and accompanied by abdominal cramps. He denies any fever, blood per rectum, or foul-smelling stools. He has also experienced frequent episodes of dizziness, flushing, wheezing, and a feeling of warmth. He has taken herbal medicines, which failed to relieve his symptoms. He is depressed about his illness, and feels hopeless about diagnosis and treatment. He appears ill. Auscultation of the chest shows a 2/6 systolic murmur over the left lower sternal border. Abdominal examination shows hepatomegaly 3cm below the right costal margin, mild shifting dullness, and no abdominal tenderness. Laboratory studies show: Hb 13.0gm/dl, MCV 90fl, WBC 6,100/cmm, Platelets 210,000/cmm, AST101 U/L, ALT 99 U/L, Alkaline phosphatase 400 mg/dl. This patient is at risk of developing a deficiency of which vitamin or mineral?
Vitamin A
Iron
Niacin
Calcium
Vitamin C
A 59-year-old female is hospitalized due to lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Her past medical history includes diabetes mellitus, hypertension, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, cor pulmonale and recurrent urinary tract infections. Her condition initially stabilized with fluid resuscitation and blood transfusions, but she subsequently developed an acute renal failure. Her urine output has been between 300 and 400 ml per day for the last couple of days. On the 10th day of her hospitalization she is lethargic. Serum analysis reveals: Hemoglobin 10.2 g/dl, Hematocrit 30%, WBC 14,300/mm3, Blood glucose 93 mg/dl, BUN 141 mg/dl, Creatinine 4.1 mg/dl, Sodium 133 mEq/L, Potassium 5.0 mEq/L, pH 7.15, pO2 90 mmHg, pCO2 60 mmHg, HCO3 18 mEq/L. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her lethargy?
Low tubular ammonium production
Renal tubular chloride loss
Poor tubular bicarbonate reabsorption
Decreased anion gap
Hypoventilation
A 59-year-old male presents to the ER with diplopia that started several hours ago. He has no other complaints. His past medical history is significant for long-standing diabetes with poor glycemic control, right knee osteoarthritis, and peptic ulcer disease. Physical examination reveals right-sided ptosis with the right eye looking down and out. Pupils are equal and reactive to light. This patient's condition is most likely due to which of the following?
Nerve compression
Nerve ischemia
Nerve inflammation
Lacunar stroke
Muscle infiltration
A 59-year-old man comes to the physician because of dysuria, urinary urgency, and frequency. He also complains of hematuria, nocturia, decreased force of stream, and a feeling of incomplete voiding. These symptoms have been present for more than a month. For the past few days he has been experiencing dull, non-radiating suprapubic pain. He has also been having low-grade fever and malaise for the past couple of days. He has been taking analgesics for osteoarthritis of his right knee for more than 10 years. He has a 40-pack-years history of cigarette smoking and does not use alcohol or drugs. Rectal examination shows a smooth, firm enlargement of the prostate without induration or asymmetry. Neurological examination shows no abnormalities. Urinalysis shows hematuria with isomorphic red blood cells. Laboratory studies show a serum creatinine of 1.5 mg/dl, and a PSA of 2 ng/ml. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for this patient's symptoms?
Benign prostatic hyperplasia
Carcinoma of bladder
Carcinoma of prostate
Urethral stricture
Neurogenic bladder
A 6-day-old female neonate is admitted to the hospital for the evaluation of jaundice. She was born to a 17-year-old German mother at 39 weeks gestation. Her mother's blood type is B+, and was treated for newborn jaundice due to presumed ABO incompatibility. Her other family members also had neonatal jaundice. The infant's vital signs are normal. On examination, she is visibly jaundiced, and her spleen tip is palpable. Her total bilirubin level is 25mg/dl and direct bilirubin level is 0.4mg/dl. Her hemoglobin was initially 15.7g/dl, but is now 10.7g/dl. Her reticulocyte count is 4% and platelet count is 230,000/mm3. The peripheral smear shows moderate schistocytes with burr cells and moderate spherocytes. Her blood type is B+ and Coombs' test is negative. Her stools are negative for occult blood. Her mother's incubated red cell osmotic fragility study is abnormal. What is the most likely cause of this neonate's symptoms?
Normal physiologic changes occurring in red cells in the neonatal period
Hereditary spherocytosis
Hereditary elliptocytosis
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia due to warm antibodies
Isoimmune hemolytic disease of the newborn, due to ABO incompatibility
A 6-month-old infant has been exclusively fed a commercially available infant formula. Upon introduction of fruit juices, however, the child develops jaundice, hepatomegaly, vomiting, lethargy, irritability, and seizures. Tests for urine-reducing substances are positive. Which of the following is likely to explain this child’s condition?
Tyrosinemia
α1-Antitrypsin deficiency
Hereditary fructose intolerance
Galactosemia
Glucose-6-phosphatase deficiency
A 6-month-old male is brought to the office due to fussiness and tugging at his right ear for the past 2 days. He has had a fever of 39.4 C (103 F) for the past 2 days. His past medical history is significant for recurrent ear and lung infections, oral candidiasis, and persistent diarrhea by rotavirus. His temperature is 39.4 C (103F), pulse rate is 150/min, respirations are 28/min, and blood pressure is 80/60mm Hg. Physical examination reveals an erythematous, bulging right tympanic membrane with poor mobility on pneumatic otoscopy. His lymph nodes are not palpable, and his tonsils are not visualized. His B and T lymphocyte levels are markedly reduced. The chest x-ray reveals an absent thymic shadow. What is the most likely etiology of this patient's condition?
Common variable immunodeficiency
Wiskott-Aidrich syndrome
Severe combined immune deficiency
Bruton's agammaglobulinemia
Chronic granulomatous disease
A 6-week-old child arrives with a complaint of “breathing fast” and a cough. On examination you note the child to have no temperature elevation, a respiratory rate of 65 breaths per minute, and her oxygen saturation to be 94%. Physical examination also is significant for rales and rhonchi. The past medical history for the child is positive for an eye discharge at 3 weeks of age, which was treated with a topical antibiotic drug. Which of the following organisms is the most likely cause of this child’s condition?
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Staphylococcus aureus
Group B streptococcus
Chlamydia trachomatis
Herpesvirus
A 6-week-old male infant, who was born at 32 weeks' gestation with a birth weight of 1500 g, has had an average weight gain of 8 g/day since birth. He takes an iron-fortified formula that is 24kcal/oz. His calorie intake is about 125kcal/day. It is noted that his stool is poorly formed and bulky. Which of the following dietary modifications will most likely result in decreased steatorrhea and improved weight gain?
Add pancreatic enzymes to the formula
Change to a lactose-free formula
Increase calorie intake to 175 kcal/day by increasing volume per feed
Supplement with vitamins A and E
Substitute medium-chain triglycerides for long-chain triglycerides
A 6-year-old African-American child is brought in by his father for complaints of easy fatigability and pallor. These symptoms occurred after the son was treated with "some medication" for a recent diarrhea. Physical examination is normal except for pallor and multiple petechiae. Laboratory values are as follows: Hb 8.0 g/dL, WBC 12,000/cmm, Platelets 50,000/cmm, Blood glucose 118 mg/dL, Serum Na 135 mEq/L, Serum K 5.3 mEq/L, Chloride 110 mEq/L, Bicarbonate 18 mEq/L, BUN 38 mg/dL, Serum creatinine 2.5 mg/dL, Total bilirubin 3 mg/dL, Direct bilirubin 0.5 mg/dL, PT 12 seconds, APTT 30 seconds, LDH 900 IU/L, Reticulocyte count 6%. A peripheral blood smear reveals giant platelets and multiple schistocytes. What is the most likely underlying pathophysiology for this boy's pallor?
Sickle cell anemia
Vitamin B 12 deficiency
Thalassemia
Folate deficiency
Microangiopathic hemolytic anemia
A 6-year-old African-American child is brought in by his father for complaints of easy fatigability and pallor. These symptoms occurred after the son was treated with "some medication" for a recent diarrhea. Physical examination is normal except for pallor and multiple petechiae. Laboratory values are as follows: Hb 8.0 g/dL, WBC 12,000/mm3, Platelets 50,000/mm3, Blood glucose 118 mg/dL, Serum Na 135 mEq/L, Serum K 5.3 mEq/L, Chloride 110 mEq/L, Bicarbonate 18 mEq/L, BUN 38 mg/dL, Serum creatinine 2.5 mg/dL, Total bilirubin 3 mg/dL, Direct bilirubin 0.5 mg/dL, PT 12 seconds, APTT 30 seconds, LDH 900 IU/L, Reticulocyte count 6%. A peripheral blood smear reveals giant platelets and multiple schistocytes. What is the most likely underlying pathophysiology for this boy's pallor?
Sickle cell anemia
Thalassemia
Microangiopathic hemolytic anemia
Vitamin B12 deficiency
Folate deficiency
A 6-year-old Asian boy is brought by his parents to the office due to high-grade fever and rash for the last 9 days. A brick-red, maculopapular rash first appeared on his face and subsequently spread to his trunk and extremities. Prior to the outbreak of the rash, he had a non-productive cough, tearing of eyes, runny nose, sneezing, and intermittent nasal obstruction. Laboratory findings are as follows: Hct 46%, WBC 2,000/mm3, Platelets 160,000/mm3. Which of the following has been shown to reduce the morbidity and mortality rates of patients with this kind of infection?
Vitamin A
Vitamin B 6
Vitamin B 12
Vitamin E
Vitamin K
A 6-year-old boy had been in his normal state of good health until a few hours prior to presentation to the ER room. His mother reports that he began to have difficulty walking, and she noticed that he was falling and unable to maintain his balance. Which of the following is the most likely cause for his condition?
Drug intoxication
Ataxia telangiectasia
Muscular dystrophy
Agenesis of the corpus callosum
Friedreich ataxia
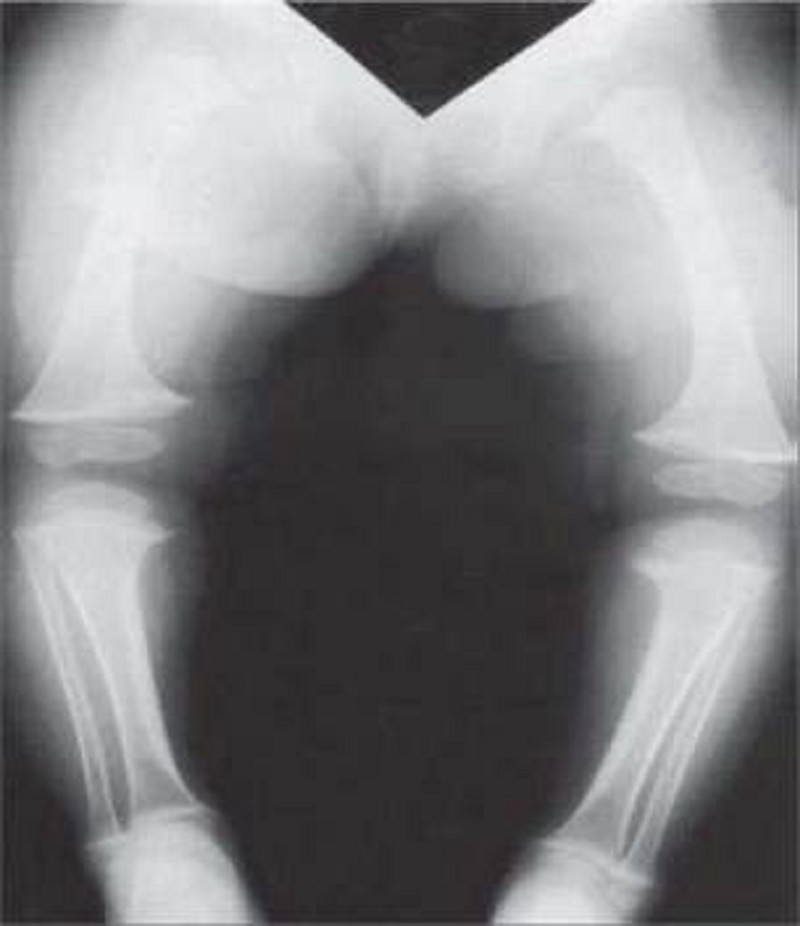
A 6-year-old boy is brought to his pediatrician for a routine check-up. He has not been seen by a physician for the past 3 years. Recently, he has developed some patchy areas of hair loss on his scalp. The mother also notes he has had many colds over the past year. She says he has developed normally, although he started walking later than her other two children. On physical examination his wrists appear enlarged, and he has bowing of the forearms and legs. X-ray of the boy’s legs is shown in the image. Laboratory tests show a calcium level of 7.1 mg/dL, phosphate of 1.8 mg/dL, and intact parathyroid hormone of 130 pg/mL (normal: 10–65 pg/mL). Vitamin D level is normal. Treatment with vitamin D does not correct the patient’s hypocalcemia. Which of the following disorders best explains this patient’s findings?
Dietary vitamin D deficiency
Vitamin D-resistant rickets
Primary hyperparathyroidism
Hypoalbuminemia
Pseudohypoparathyroidism
A 6-year-old boy is brought to the clinic for the evaluation of a large, red, circular rash on his left thigh which has been present since two weeks and has been enlarging. He has a mild headache and myalgia, but is afebrile. Three weeks ago, he and his family visited relatives at a rural farm in Connecticut and went hiking in the woods. His temperature is 37.2 C (99 F) and pulse is 90/min. He is alert, active, appears non-toxic, and not in distress. On the anterior surface of his left thigh, there is a red ring that is 7 cm in diameter with central clearing, and a central brownish-red macule that is 3 mm in diameter. Which of the following measures would have prevented this condition?
Childhood vaccinations as recommended by American Association of Pediatrics
Careful sanitary measures in food preparation
Avoiding water intake from streams
Wearing light-colored clothing. Long-sleeved shirts and tucking pants into socks or boot tops
No wearing light-colored clothing. Short-sleeved shirts and tucking pants into socks or boot tops
A 6-year-old boy is seen in the office for evaluation of polyuria. Further questioning reveals several months of headache with occasional emesis. Your physical examination reveals a child who is less than 5% for weight. He has mild papilledema. His glucose is normal, and his first urine void specific gravity after a night without liquids is 1.005 g/mL. Which of the following might also be expected to be seen in this patient?
Sixth nerve palsy
Unilateral pupillary dilatation
Unilateral cerebellar ataxia
Unilateral anosmia
Bitemporal hemianopsia
A 6-year-old Caucasian boy is hospitalized for acute sinusitis that was accompanied with intensive nasal bleeding. Past medical history is significant for recurrent pulmonary infections and several hospitalizations for parenteral antibiotic therapy. The sweat chloride test is positive. The blood tests reveal a prothrombin time (PT) of 20 seconds. Which of the following coagulation factors is most likely to be deficient in this patient?
Fibrinogen
Hageman factor
Factor VIII
Factor VII
Factor V
A 6-year-old child has had repeated episodes of otitis media. She undergoes an uneventful surgical placement of pressure-equalization (PE) tubes. In the recovery room she develops a fever of 40C (104F), rigidity of her muscles, and metabolic and respiratory acidosis. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for her condition?
Otitis media
Septicemia
Malignant hyperthermia
Dehydration
Febrile seizure
A 60-year-old Caucasian male is brought to the emergency department by his daughter due to a 2-day history of confusion and lethargy. According to his daughter, he had been complaining of fatigue, anorexia, polyuria and constipation for the last several weeks. He smokes two packs of cigarettes daily, and consumes alcohol occasionally. His blood pressure is 130/90 mmHg and heart rate is 90/min. Physical examination reveals a somnolent patient who is not oriented in time. His lab values are: Serum Na 140 mEq/L, Serum K 4.0 mEq/L, Serum chloride 100 mEq/L, Serum bicarbonate 22 mEq/L, Serum creatinine 1.6 mg/dl, Serum calcium 13.4 mg/dL, Serum phosphorus 2.2 mg/dL, Blood glucose 100 mg/dL, Alkaline phosphatase 80 U/L. Chest x-ray demonstrates a right middle lobe mass and perihilar adenopathy. What is the most probable cause of this patient's symptoms?
Elevated PTH
Metastatic osteolysis
Parathyroid hormone-like peptide
Increased vitamin D production
Local cytokine production
A 60-year-old Caucasian male presents to your office complaining of decreased hearing on the right side. He also feels that something is wrong with his head because his hat size had increased over the last two years. His past medical history is significant for hypertension and peptic ulcer disease. His current medications are hydrochlorothiazide and enalapril. He also takes ibuprofen for occasional headaches, and ranitidine for infrequent episodes of heartburn. Lab tests showed increased alkaline phosphatase levels. Which of the following is the most likely mechanism underlying this patient's condition?
Increased osteoid deposition
Fibrous replacement of the bone
Bone demineralization
Abnormal bone remodelling
Abundant mineralization of the periosteum
A 60-year-old diabetic man undergoes incision and drainage of an infected boil on his back. The wound is left open and packed daily. Week by week, the wound grows smaller and eventually heals. Which of the following terms describes the method of wound closure by the patient?
Primary intention
Tertiary intention
Secondary intention
Delayed primary closure
Delayed secondary closure
A 60-year-old male is brought to ER by his son because he had an episode of syncope. He was watching TV in an arm-chair when suddenly lost his consciousness without any warning sign. He had several clonic jerks while unconscious. He never had such an episode before. His past medical history is significant for acute myocardial infarction six months ago and well-controlled hypertension. His current medications include captopril metoprolol hydrochlorothiazide, clopidogrel and aspirin. His blood pressure is 130/85 mmHg and heat rate is 80/min with frequent ectopic beat. Physical examination revealed mild holosystolic apical murmur radiating to the axilla. Which of the following is the most probable pathophysiologic mechanism for his syncopal episode?
Vasovagal reaction
Arrhythmia
Autonomic dysfunction
Seizure
Postural hypotension
A 60-year-old male presents to the emergency room with the chief complaint of progressive exertional dyspnea and fatigue. He denies any chest pain, syncope, cough, or edema. He suffered an acute anterior wall myocardial infarction one month ago. Chest auscultation reveals bilateral crackles in his lower chest. Cardiac auscultation reveals a pansystolic murmur at the apex with radiation to the axilla. ECG shows previously present unchanged Q waves and a persistent ST segment elevation in the anterior leads. Based on these findings, what is the most likely underlying cause of his symptoms?
Interventricular wall rupture
Ventricular aneurysm
Ventricular free wall rupture
Recurrent ischemia
Right ventricular infarction
A 60-year-old man comes to the office with worsening shortness of breath over the last 5 months. He has had two episodes of bronchitis over the last 12 months. He now has a mild nonproductive cough. He denies any fever, chills, hemoptysis, chest pain, or difficulty breathing while lying on his back. His medications include an ipratropium inhaler, aspirin, and amlodipine. He was hospitalized twice in the last 3 years due to an exacerbation of his chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. He has been smoking 1 pack of cigarettes per day for the last 40 years. His temperature is 99°F (37.2°C), blood pressure is 130/86 mm Hg, pulse is 98/min, and respirations are 18/min. Examination shows a thin man in mild respiratory distress with increased anteroposterior chest diameter, diffuse expiratory wheeze and loud S2. Chest X-ray shows hyperinflation of bilateral lung fields with diaphragm flattening and small heart size. Which of the following is the most effective measure to decrease mortality in this patient?
Adding a short acting beta-agonist inhaler
Adding a long-acting beta agonist
Adding an inhaled corticosteroid
Adding systemic corticosteroids
Smoking cessation
A 60-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 2-day history of fever and left-sided scrotal pain. The pain has progressed in severity and it radiates to the flank. His has also had increased urinary frequency and urgency along with dysuria. His temperature is 38.1°C (100.8°F), blood pressure is 130/75mm Hg, pulse is 86/min, and respirations are 15/min. Physical examination shows left scrotal swelling and a tender scrotal mass; there is no urethral discharge. Rectal examination shows a tender prostate. Laboratory studies show a WBC count of 14,000/microl with a left shift. Urinalysis shows bacteriuria and pyuria. Which of the following is the most likely organism responsible for this patient's findings?
Escherichia coli
Pseudomonas
Chlamydia trachomatis
Gonococcus
Staphylococcus aureus
A 60-year-old man comes to the physician because of worsening fatigue and nausea. He had a carotid angiogram for the evaluation of symptomatic carotid artery stenosis 15 days ago, and was discharged home three days after the procedure. His medical problems are hypercholesterolemia, coronary artery disease, intermittent claudication, hypertension for 18 years, and diabetes mellitus for 15 years. Physical examination shows painless, reddish-blue mottling of the skin of the extremities. Laboratory studies show: Hb 10.5 g/dl, WBC 10,000/cmm with 12% eosinophils, BUN 46 mg/dl, Serum creatinine 3.0 mg/dl, Serum C3 level Decreased. Urinalysis:pH Normal,Esterase Negative, Nitrite Negative, Protein 1+, WBC Many eosinophils, RBC 1-2/HPF. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's findings?
Contrast nephropathy
Post streptococcal glomerulonephritis
Diabetic nephropathy
Cholesterol embolism
Acute allergic interstitial nephropathy
A 60-year-old man is brought to the ER by his wife because he lost consciousness in the bathroom at night. He says that he woke up, went to the bathroom to urinate, and fainted there. He rapidly recovered his consciousness without any indication of disorientation. He has never had such an episode before. He admits' problems with urination,' including difficulty with initiating urination and frequent awakening to void at night. He does not take any medication. His past medical history is insignificant. He smokes 2 packs of cigarettes per day and does not consume alcohol. His blood pressure is 130/80 mmHg while supine, and 132/80 mmHg while standing. His heart rate is 70/min. His physical examination is within normal limits. The ECG is normal. What is the most probable cause of the syncopal episode in this patient?
Arrhythmia
Postural hypotension
Situational syncope
Seizure
Transient ischemic attack (TIA)
A 60-year-old man presents to his primary care physician for routine medical care. He has no complaints, takes no medications, and has a family history of DM. Examination is unremarkable. A screening laboratory test reveals a fasting blood glucose level of 152 mg/dL. One week later the test is repeated and a value of 144 mg/dL is obtained. Which of the following is the most likely cause of these findings?
Autoimmune destruction of pancreatic islet cells
Pancreatitis
Patient’s findings represent normal laboratory values
Peripheral insulin resistance
Surreptitious insulin injection
A 60-year-old man presents with a 6-mm basal cell carcinoma on the tip of his nose. He is scheduled to undergo excision of the tumor in the operating room with repair of the defect using skin and subcutaneous tissue from his earlobe. Which of the following terms most appropriately describes this form of reconstructive surgery?
Split-thickness graft
Full-thickness graft
Composite graft
Pedicle flap
Free flap
A 60-year-old man presents with fever and malaise 6 weeks after mitral valve replacement. On examination, his temperature is 38°C, blood pressure 130/80 mm Hg, pulse 80/min, and a loud pansystolic murmur at the apex, which radiates to the axilla. He has no skin or neurologic findings. Which of the following is the most likely causative organism?
Staphylococcus aureus
Staphylococcus saprophyticus
A fungus
Staphylococcus epidermidis
Pneumococcus
A 60-year-old man with no past medical history undergoes upper endoscopy and biopsy for an upset stomach that is worsened by eating. He is found to have inflammation predominantly in the antrum of the stomach. Which of the following is the most likely etiology of this condition?
Alcohol abuse
Cigarette smoking
Iatrogenic
Infection
Spicy foods
A 60-year-old physician is admitted to the hospital for jaundice and weight loss. He denies other symptoms, including abdominal pain and alterations in bowel movements. His past medical history is noncontributory. He denies any history of significant alcohol intake but admits to a 30-pack-year smoking history. A detailed work-up eventually reveals the diagnosis of pancreatic carcinoma. Shortly after his discharge, he spends several hours per day on his laptop computer so that he can obtain the latest information on his illness. Which of the following psychological defense mechanisms is this physician most likely employing?
Intellectualization
Rationalization
Denial
Isolation
Resistance
A 60-year-old postmenopausal woman presents with the new onset of uterine bleeding. An endometrial biopsy is diagnosed as atypical hyperplasia. Which of the following histologic changes is most characteristic of this abnormality?
Crowding of endometrial glands with budding and epithelial atypia
Lymphatic invasion by interlacing bundles of atypical spindle-shaped cells
Menstrual-type endometrial glands with focal atypical cystic dilatation
Secretory-type endometrial glands with hyperplasia of atypical polygonal cells having clear cytoplasm
Stromal invasion by malignant glands with focal areas of atypical squamous differentiation
A 60-year-old white male presents to the Emergency Room with sudden onset of dyspnea. He is a truck driver and just returned from a long trip. His past medical history is insignificant. He is not taking any medications. His blood pressure is 110/70 mmHg and heart rate is 110/min. Physical examination reveals a moderately overweight man with tachypnea. Lungs are clear on auscultation. ECG shows right axis deviation. You order ventilation/perfusion scanning. Which of the following findings will help you the most to confirm the diagnosis?
An area of ventilation defect without perfusion defect
An area of perfusion defect without ventilation defect
Absence of ventilation and perfusion abnormalities
Several small perfusion and ventilation defects
An area of ventilation and perfusion defect
A 60-year-old white man comes into the Emergency Room with intensive retrosternal pain that began ten minutes ago. He has never had such pain before. His past medical history is significant for diabetes mellitus, type 2, controlled with diet. His blood pressure is 150/95 mmHg and HR is 80/min. You give him one chewable tablet of aspirin and two sublingual tablets of nitroglycerin with a 5-minute interval. After the second tablet of nitroglycerin, the pain is greatly relieved. What is the most important mechanism responsible for pain relief in this patient?
Increased cardiac contractility
Dilation of capacitance vessels
Increase in coronary blood flow
Change in the activity of baroreceptors
Dilation of resistance vessels
A 60-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 3-month history of worsening fatigue and back pain. She has had diabetes mellitus for the past three years, and hypertension for the past ten years. Laboratory studies show: Hb 9.0 mg/dL, Serum calcium 11.2 mg/dL, Serum phosphorus 3.5 mg/dL, BUN 38 mg/dL, Serum creatinine 2.0 mg/dL. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's renal failure?
Hypertension
Diabetes mellitus
Para protein
Primary hyperparathyroidism
Renal artery stenosis
A 60-year-old woman recently diagnosed with type 2 DM complains of daily headaches and double vision that have gradually worsened over the previous month. An MRI shows a large pituitary adenoma. Which of the following is most likely being secreted by this tumor?
ACTH
Growth hormone
Luteinizing hormone
Prolactin
Thyroid-stimulating hormone
A 60-year-old woman with heart failure and normal renal function is started on furosemide (Lasix) 80 mg/day. She notices a good diuretic response every time she takes the medication. A few weeks later, she is feeling unwell because of fatigue and muscle weakness, but her heart failure symptoms are better. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for her muscle weakness?
Hyponatremia
Hypernatremia
Hypokalemia
Hyperkalemia
Anemia
A 61-year-old man is being evaluated for progressive exertional dyspnea and decreased exercise tolerance. He has also noticed some ankle swelling. The patient has a 40 pack-year smoking history but denies illicit drug use or occupational exposures. His chest x-ray is shown below. The abnormal diaphragmatic contour seen here most likely results in which of the following?
Higher inspiratory flow
Increased thoracic wall recoil
Decreased lung compliance
Reduced expiratory effort
Increased work of breathing
A 62-year-old male comes to your office for a routine follow-up appointment. He has smoked one pack of cigarettes per day for the past 30 years and adamantly refuses to quit. He also drinks six to ten beers each weekend. His past medical history is significant for type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypertension. His last hemoglobinA1c was 8.3%. He is overweight with a current BMI of 27.5 kg/m2. While examining him, you notice a whitish patch over the anterior floor of his mouth. The lesion appears to have a granular texture and is not removed by scraping with a tongue depressor. Which of the following is most likely cause of his oral lesion?
Candidiasis
Leukoplakia
Herpes simplex virus infection
Melanoma
Squamous cell carcinoma
{"name":"DES C_Basic (4) Prepared : CHILLY", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"A 46-year-old woman undergoes an abdominal hysterectomy for a “fibroid” uterus. The surgeon requests a frozen section on the tumor, which is deferred because of the lesion’s degree of cellularity. Which of the following histologic criteria will be used by the pathologist to determine if this tumor is benign or malignant?, A 47-year-old male presents to your office with a two-month history of lethargy and decreased libido. His medical records reveal that he has been treated for joint pain and swelling over the last six months and was diagnosed with diabetes mellitus one year ago. Physical examination reveals hepatomegaly and testicular atrophy. Which of the following cardiac abnormalities is most likely to also be present in this patient?, A 47-year-old male was brought to the emergency room with chest pain of acute onset. The pain was associated with nausea, vomiting, and diaphoresis. He has a history of diabetes, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia. ECG reveals ST segment elevation in the anterolateral leads and ventricular premature beats (VPBs). The patient dies within the first hour after the arrival to emergency room. What is the most likely pathophysiologic mechanism responsible for this patient's death?","img":"https://cdn.poll-maker.com/17-718374/image.jpeg?sz=1200"}
More Quizzes
Discovering Africa
520
The Ultimate Friendship Quiz
8413
SIGN KT Assessment 3 - 24 April
4220
Do you know me well???
10510
Innocent or Guilty Questions - Judge Them Now
201023679
Test Your Knowledge: Licensed & Ordained Deacon
201027056
Free Contemporary Art Newsletter
201021490
Free Adult Learning Principles Assessment
201030786
Introduction to Computer Science II
15822433
Which Early Computing Device Did Charles Babbage Invent?
201043963
Popular Visual Culture
15821198
Which Male Naruto Character Are You? Personality
201033608