Ichigo USMLE Med Diagnosis P4
1) A 40-year-old man is brought to the emergency room because of altered mental status and gait instability. He has had two falls in the last two days. He drinks one pint of vodka daily and smokes one pack of cigarettes daily. His temperature is 35.0°C (95.0°F), blood pressure is 100/70 mm Hg, pulse is 90/min, and respirations are 14/min. He is disoriented, but not in acute distress. You note prominent horizontal nystagmus and conjugate gaze palsy in both eyes and absent ankle reflexes in both legs. His chest is clear to auscultation. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his symptoms?
. Viral encephalitis
. Thiamine deficiency
. Hypothyroidism
. Cerebellar infarction
. Opioid intoxication
2) A 16-year-old boy is recommended for admission to the neurology department for rapidly deteriorating clinical symptoms. He is a college student, living in a dormitory. During past week, he was sick. He did not recover fully and during last 3 days, his condition deteriorated. He started to have high fever, terrible headaches. His roommate said he talked about "some foolish happenings" during his high fever, and did not remember what he said later. This morning, he vomited repeatedly and his condition deteriorated rapidly. You examined him and found: febrile man in acute distress with cyanotic pallor, petechiae on his trunk and legs, purpura on his back bilaterally, with cold extremities. He is still alert, but has clammy skin, rapid pulse and labored respiration. His meningeal signs are positive. You diagnose this patient with meningococcal meningitis with systemic progression and you fear that he can develop the Waterhouse-Friderichsen syndrome. What characterizes this syndrome?
. Acute adrenal insufficiency
. Obstructive hydrocephalus
. Endocarditis and myocarditis
. Otitis media and sinusitis
. Brain abscess
3) A 67-year-old Caucasian female presents to your office three weeks after having an ischemic stroke. She complains of transient pain in the right upper and lower limbs that can be induced even by light touch. Her past medical history is significant for hypertension and diabetes mellitus, type 2. Her current medications include enalapril, amlodipine, aspirin, and glyburide. She has right hemianesthesia due to the stroke and mild athetosis of the right hand. The strength is preserved in all four extremities. Hypersensitivity to all kinds of stimuli that induce severe pain reaction is present over the right extremities. Which of the following is the most probable location of the stroke experienced by this patient three weeks ago?
. Internal capsule
. Thalamus
. Mid-brain
. Medulla
. Left post-central cortex
4) A 43-year-old man presents to your office complaining of periodic involuntary head turning and head fixation to the right side. Physical examination reveals a hypertrophied right sternocleidomastoid muscle. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Parkinson's disease
. Essential tremor
. Chorea
. Akathisia
. Dystonia
5) A 57-year-old man presents to the emergency department complaining of right arm weakness. He says that he first noticed the weakness two hours ago when he was unable to grip a pen. He is now unable to shake hands and walks with a mild limp. His past medical history is significant for hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and mild headaches over the past several days. He does not smoke or consume alcohol. His blood pressure is 180/100 mmHg, heart rate is 80/min and regular. There is mild asymmetry of the lower face, decreased muscle strength in the right arm, and an extensor plantar reflex on the right side. Sensory examination is normal. Blood glucose level is 210mg/dL. ECG shows sinus rhythm with occasional ventricular premature beats. His urine is negative for ketones and protein. Non-contrast CT scan of the head does not reveal any abnormalities. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
. Migraine-associated vascular spasm
. Carotid artery thrombosis
. Small vessel hyalinosis
. Brain tumor
. Cardiac embolism
6) A 30-year-old, HIV-positive male, presents with left-sided paralysis of recent onset. His temperature is 37.1°C (98.9°F), pulse is 78/min, blood pressure is 130/80, and respirations are 16/min. The neurological examination reveals loss of recent memory, expressive aphasia, hyperreflexia, hypertonia, and up going plantars on the left side. His current medications include zidovudine, didanosine, indinavir and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. His CD4 count is 70/dl and viral load is 90,000 copies/ml by PCR. The serology is positive for Toxoplasma. CT scan shows multiple, hypodense, non-enhancing lesions with no mass effect in the cerebral white matter. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Cerebral toxoplasmosis
. Primary CNS lymphoma
. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy
. AIDS dementia complex
. Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis
7) A 64-year-old Caucasian male presents to your office because he has had two falls within the last month. He states that he loses his balance when he tries to turn or stop suddenly while walking. Recently, he says, it has been taking him quite a while to get himself out of bed. He also complains of hand tremors that started last year in his left hand, but that now have been affecting both hands. Which of the following is the best tool to confirm his diagnosis?
. Physical examination
. Lumbar puncture
. CT scan of the head
. Electroencephalography
. Nerve conduction studies
8) A 60-year-old male presents to the office and complains of muscle weakness in his extremities. Other accompanying symptoms include progressive difficulty in performing weight-carrying tasks, and a 7 kg (15 lb) weight loss during the last three months. His past medical history is insignificant. He smokes 2 packs of cigarettes daily, and consumes alcohol occasionally. His muscle strength is 3/5 in the proximal muscle groups symmetrically. His reflexes are normal. No sensory abnormality is present. Chest x-ray reveals a right lower lobe ill-defined mass. Which of the following is the most likely localization of the pathologic process in this patient?
. Peripheral nerves
. Presynaptic membrane
. Postsynaptic membrane
. Muscle membrane
. Spinal cord
9) A 47-year-old obese female comes to the office for the evaluation of recent episodes of mood instability. Her mood varies between sad and irritable. She denies any other symptoms, except for some mild forgetfulness. She tearfully shares that she is convinced that she is going to die, as her father also developed similar symptoms around the same age and died subsequently. On physical examination, writhing movements of the extremities are prominent. This patient's clinical presentation is most consistent with:
. Alzheimer's disease
. Pseudodementia
. Huntington's disease
. Hypothyroidism
. Pick's disease
10) A 70-year-old Caucasian male is brought to the emergency department due to a sudden onset of right-sided weakness and urinary incontinence about ten hours ago. His past medical history is significant for type 2 diabetes for the last 20 years and hypertension for the last 28 years. On examination, there is 3/5 power in the right upper extremity and 1/5 power in the right lower extremity. Babinski's sign is positive on the right side. The sensations are decreased on the right side of the body, more so in the right lower limb than the right upper limb. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Lacunar stroke
. Anterior cerebral artery stroke
. Right middle cerebral artery stroke
. Left middle cerebral artery stroke
. Posterior cerebral artery stroke
11) A 32-year-old woman describes five episodes of intractable vomiting over the last year. The episodes last several hours and are associated with a sensation that the room is spinning or tilting. At these times, it is difficult for her to walk because she loses her balance. She cannot relate the timing of the episodes to any particular inciting event. Physical examination reveals stability in the Romberg position and during tandem walk. Proprioception is intact. Dysfunction of which of the following structures best explains this patient's symptoms?
. Posterior columns of the spinal cord
. Vagal nerve
. Optic tract
. Inner ear
. Cerebellum
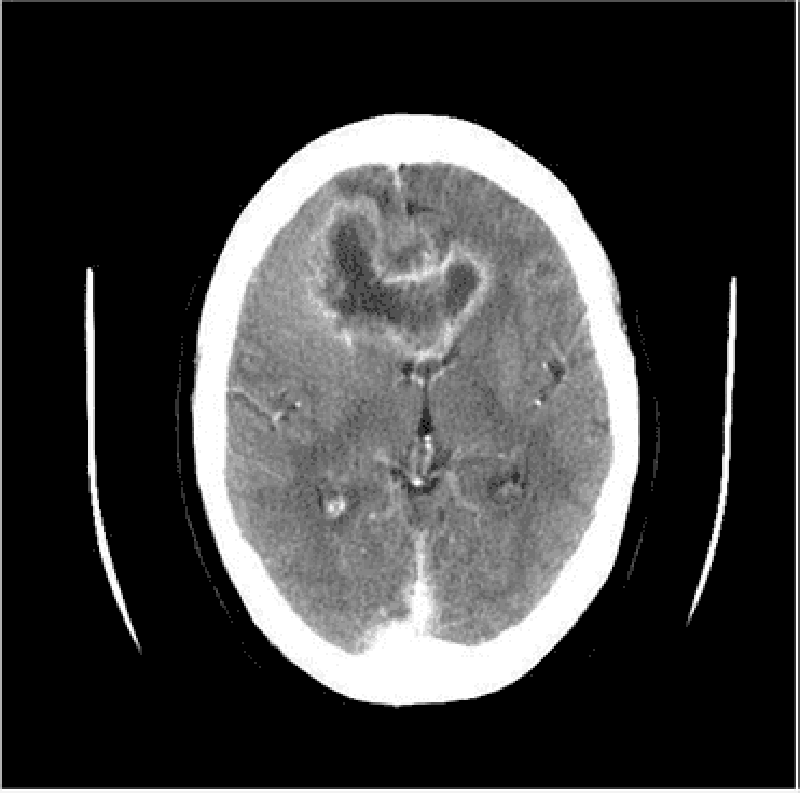
. Cerebellum 12) A 45-year-old white male presents with a 4-month history of headaches. The headache is generalized, dull, constant, and worsened by bending, coughing and sneezing. It is unresponsive to simple analgesics, and associated with nausea and vomiting. His wife says he has been acting strangely for the last few months, and she has noted a personality change. The neurological examination is non-focal. Fundoscopy reveals papilledema. His CT scan is shown below. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Brain abscess
. Metastatic brain tumor
. Glioblastoma multiforme
. Low-grade astrocytoma
. Cerebral infarction
13) A 35-year-old Caucasian man comes to the emergency department at 2 am because of severe pain 'behind the left eye' which woke him up in the middle of the night. The pain is intense and has a stabbing quality. He took ibuprofen at home but didn't get any relief. He denies fever, chills, decreased or blurred vision, cough, nausea or vomiting. He has no other medical problems. He drinks 3-4 bottles of beer daily. He has no known drug allergies. His temperature is 36.7°C (98°F), blood pressure is 120/80 mm Hg, pulse is 88/min and respirations are 14/min. The examination is unremarkable, except for left-sided ptosis and miosis. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Migraine headache without aura
. Migraine headache with aura
. Sinus headache
. Cluster headache
. Brain tumor
14) A 63-year-old Asian-American woman presents to the ER with a severe right-sided headache that started one hour ago. The pain is located "all around my eye." She has vomited once since the pain began. She also says that bright light aggravates the pain and she complains of seeing "halos" around light. She has never had a headache like this before. Her only medication is trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, which she has been taking for the last two days for a urinary tract infection. Her mother has a history of migraine headaches. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. On exam, she is afebrile with a pulse of 90/min. Physical exam reveals a non-reactive, dilated right pupil and erythematous right eye. There is lacrimation present. The remainder of examination is unremarkable. Laboratory studies reveal an ESR of 40 mm/hr. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Meningitis
. Subarachnoid bleeding
. Angle closure glaucoma
. Cluster headache
. Migraine without aura
15) A previously healthy 8-year-old boy is brought to the office by his mother because he has multiple staring episodes. During these episodes, he is unresponsive to verbal or tactile stimuli, and produces lip-smacking movements. Each episode lasts for a few minutes, after which he remains confused for some time. He has no family history of any seizure disorder. His neurological examination is unremarkable. EEG performed before and after hyperventilation is normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Complex partial seizure
. Typical absence seizure
. Atypical absence seizure
. Juvenile myoclonic epilepsy
. Lennox-Gastaut syndrome
16) A 1-year-old female infant is brought to the clinic by his 30-year-old mother due to feeding problems since birth. She still cannot walk nor speak. She began to sit when she was 8 months old. Her weight is in the 15th percentile, height is in the 20th percentile, and head circumference is in the 100th percentile for her age. She has multiple freckles in her armpit and groin area. She has cafe-au-lait spots on her skin, and the diameter of at least 20 of these spots is greater than 1 5mm. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Neurofibromatosis type 2
. Down syndrome
. Fetal alcoholic syndrome
. Normal development
. Neurofibromatosis type 1
17) A 33-year-old Caucasian female comes to the office and complains of occasional diplopia and ptosis. These symptoms become especially prominent when she looks above her head for some time. She also complains of fatigue in her hands and leg muscles after exercising, such as swimming. Her muscle strength and double vision returns to normal after resting for some time. On examination, lid lag is observed after she is asked to look above her head for some time. No pupillary involvement is seen. The rest of the examination is normal. What is the level of the lesion in the disease that is being described?
. Neuromuscular junction
. Nerve conduction
. Muscle contraction
. Corticospinal tract
. Autonomic nervous system
18) A 25-year-old, HIV-positive male presents to the office with an altered mental status. He is disoriented, lethargic, and has loss of recent memory. These symptoms have been present for the last month. His current medications include zidovudine, didanosine, indinavir, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole and azithromycin. His temperature is 37.7°C (99.8°F), pulse is 78/min, blood pressure is 130/80mm Hg, and respirations are 16/min. The neurological examination is non-focal. His CD4 count is 40/microl and viral load is 25,000 copies/ml by PCR. MRI scan reveals a solitary, irregular, weakly ring-enhancing mass in the periventricular area. The serology for Toxoplasma is positive. PCR of CSF shows EBV DNA. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Cerebral toxoplasmosis
. Primary CNS lymphoma
. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy
. AIDS dementia complex
. Bacterial abscess
19) A 33-year-old Canadian female presents to the office with severe, bilateral, lightning-like pain on her face. The pain is burning and sharp in nature, occurs 20-30 times a day, and each episode lasts a few seconds. She is completely incapacitated by this pain. Prior to this event, she had weakness in her left arm, which gradually improved. She denies any history of trauma or drug use. She has no other medical problems. She does not use tobacco, alcohol or drugs. Her blood pressure is 120/80 mmHg, pulse is 72/min, temperature is 36.7°C (98°F) and respirations are 14/min. Complete neurologic examination shows no focal deficits. This type of disorder is most commonly seen in which of the following?
. Parkinson disease
. Huntington chorea
. Multiple sclerosis
. Aseptic meningitis
. Transient ischemic attack
20) A 33-year-old white man with a 9-year-history of progressive-relapsing multiple sclerosis is brought to the emergency department (ED) due to a severe flare-up. He has had several attacks before, and has recovered every time with some residual damage. The last physical examination in his medical records revealed cerebellar symptomatology, a visual defect, and central hemiparesis on the right side. MRI showed multiple, bright, signal abnormalities in the white matter supratentorially on the left side, in the cerebellum, and the left optic nerve. CSF examination revealed an increased synthesis of oligoclonal bands. In the ED, the physical examination reveals paraplegia, bladder and fecal incontinency, and absent sensation from the nipples down. What is the most likely location of this patient's new plaque?
. Cerebellum
. Posterior columns
. Upper thoracic spinal cord
. Lower thoracic spinal cord
. Supratentorially
21) A 37-year-old homeless man complains of weakness in his right arm. He says that he was smoking a cigarette when the weakness developed, causing the cigarette to fall from his hand. He also reports having mild headaches, fatigue, and chills over the last week. He admits to regular intravenous heroin use and binge drinking. On physical examination, his blood pressure is 120/70 mmHg and his heart rate is 80/min. There is asymmetry of the lower face, decreased muscle strength in the right arm, and an extensor plantar reflex on the right side. He has multiple needle tracks on his arms. ECG shows sinus rhythm with occasional ventricular premature beats. Urinalysis shows 2+ proteins. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
. Migraine-associated vascular spasm
. Carotid artery thrombosis
. Small vessel hyalinosis
. Brain tumor
. Cerebral emboli
22) A 45-year-old man comes to the office for the evaluation of excessive wasting of his extremity muscles, which is more apparent on the extensor side. The weakness began distally and asymmetrically. He recently started to have difficulties with swallowing, chewing, and speaking. He feels some movements in his face and tongue. He also has muscle stiffness. His bowel, bladder, cognitive, and sensory functions are intact. The physical examination reveals excessive wasting of his muscles, which is more prominent in the lower extremities. Fasciculation and hyperreflexia of all extremities are noted. His bulbar reflexes are decreased. What neural pathway is most likely damaged?
. Pyramidal tract
. Lower motor neuron
. Upper motor neuron
. Lower and upper motor neuron
. Cerebral cortex
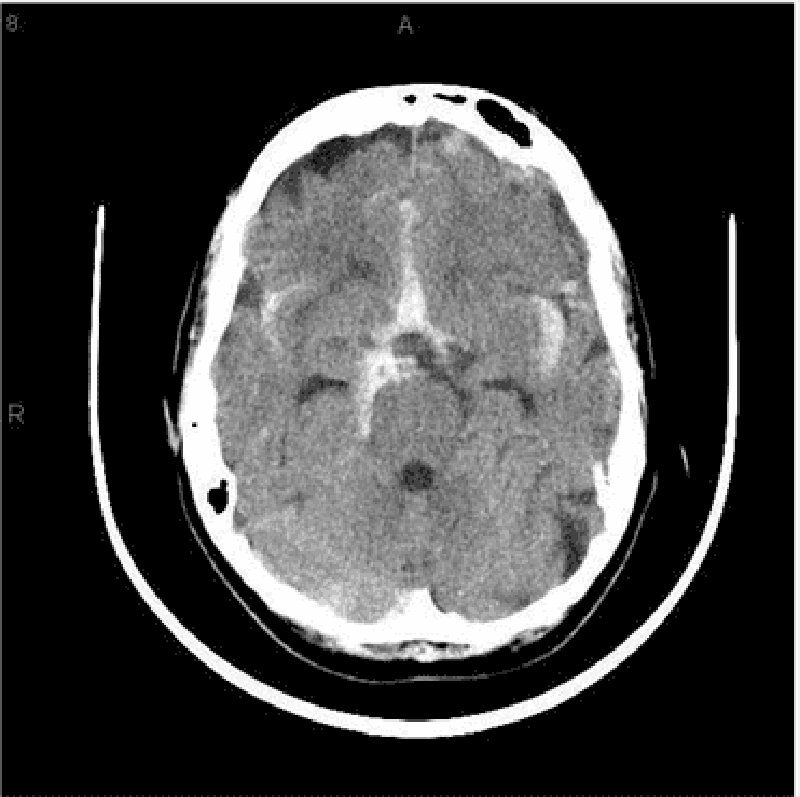
23) A 40-year-old Caucasian male comes to the emergency department because he is having "the worst headache" of his life. The headache is of sudden onset, and associated with nausea and vomiting. He denies any fever and trauma to head. He is not taking any medications. He has a history of migraine headaches. The neurological examination is non-focal. CT scan of the head without contrast is shown below. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's headache?
. Hypertension
. Rupture of saccular aneurysm
. Rupture of AV malformation
. Extension of primary intracerebral hemorrhage
. Amyloid angiopathy
24) A 67-year-old Asian male comes to the clinic for the first time. He walks very slowly as he enters the room. His chief complaint is "extreme forgetfulness" for the past 6 months. He tearfully shares that he has been "losing sleep." He used to be a very "bright and sharp" person, but is now unable to focus on his daily activities and feels "really extremely low and useless." His past medical history is significant for hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, diabetes, benign prostatic hyperplasia, and TIA. His family history is insignificant, except for Alzheimer's dementia in his father. He does not smoke, and drinks wine only occasionally. He has been living alone for the last 6 months, after his son moved out. His physical exam is normal, except for markedly slow movements. A CT scan of the head is normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Parkinson's disease
. Vascular dementia
. Alzheimer's dementia
. Pseudodementia
. Normal aging
25) A 54-year-old construction worker presents to your office complaining of a "funny sensation" in his right arm. He has no significant past medical history. His diet consists of mainly fast food and he drinks one to two litters of soda per day. He does not exercise regularly. He smokes 1½ pack of cigarettes per day. His BMI is 28.5 kg/m2. You ask the patient to stretch out his arms with the palms facing up and close his eyes. Five seconds later you observe the right palm turning inward and downward. Which of the following best explains the observed findings in this patient?
. Impaired proprioception
. Tactile sensation loss
. Cerebellar dysfunction
. Parietal lobe lesion
. Upper motor neuron lesion
26) A 53-year-old man complains of "shaking" of his right hand. He first noticed this shaking while resting in an armchair and watching TV. He reports that the shaking stopped when he reached for the remote to change the channel. On physical examination, his vital signs are within normal limits and all other organ systems appear normal. Which of the following is most likely responsible?
. Physiological tremor
. Essential tremor
. Cerebellar dysfunction
. Basal ganglia dysfunction
. Corticospinal tract lesion
27) A 60-year-old Hispanic female is brought to the emergency department due to a sudden onset of worsening, left-sided hemiplegia, which was followed by a headache and altered mental status. She was taking her regular morning walk when she developed these symptoms. Her past medical history is remarkable for uncontrolled essential hypertension. She has been a chronic smoker for the last 30 years. The neurological examination shows flaccid paralysis on the left side, and deviation of eyes towards the right side. The CT scan is consistent with a hemorrhagic stroke. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Putamen haemorrhage
. Cerebellar hemorrhage
. Pontine hemorrhage
. Subarachnoid haemorrhage
. Ventricular haemorrhage
28) A 70-year-old Caucasian male comes to your office four weeks after experiencing an ischemic stroke. His past medical history is significant for a long history of hypertension, diabetes, coronary artery disease, congestive heart failure, and atrial fibrillation. You noticed that the patient has shaved only the right side of his face. When you ask him to raise his left arm, he raises his right arm. You ask him to fill in the numbers of a clock, and he puts numbers only on the right side. Which of the following areas is most likely affected by the stroke in this patient?
. Left frontal cortex
. Left temporal cortex
. Right parietal cortex
. Right occipital cortex
. Right frontal cortex
29) A 10-year-old boy is brought to the office by his mother after having a seizure this morning. All he can recall before the episode is "seeing funny little lights." According to his mother, his body went stiff; he lost consciousness, and then had jerky movements of the entire body. He bit his tongue, and started to drool. The seizure lasted for about one minute. After the seizure, he appeared confused for several minutes, and passed urine. He has been complaining of a headache for the past two hours. The neurological examination is normal. What type of seizure did this patient experience?
. Childhood absence seizure
. Status epilepticus
. Simple partial seizures
. Complex partial seizures
. Tonic clonic seizure
30) A 56-year-old Hispanic male presents with right-sided arm weakness and speech difficulty. He expresses words slowly and with difficulty. His speech is agrammatic and the melody of speech is abnormal. He is able to comprehend words spoken to him. Which of the following is the most likely site of lesion in the above patient?
. Dominant parietal lobe
. Nondominant parietal lobe
. Dominant frontal lobe
. Nondominant frontal lobe
. Occipital lobe
31) A 69-year-old man presents to the emergency department with a severe occipital headache, nausea and vomiting for several hours. His medical history is significant for poorly controlled essential hypertension for the last 7 years. The neurologic examination shows ataxia, right-sided facial weakness and deviation of the eyes to the left side. His CT scan is consistent with a hemorrhagic stroke. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Putamen hemorrhage
. Cerebellar haemorrhage
. Pontine hemorrhage
. Subarachnoid haemorrhage
. Ventricular haemorrhage
32) A 76-year-old woman presents for a routine medical check-up. Her medical history is significant for hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and hypothyroidism that are controlled with oral agents. She had a stroke one year ago and has mild residual right arm weakness. Otherwise she has no physical complaints. She is widowed and lives alone. Regarding her memory, she sometimes forgets to return phone calls and take her blood pressure pills. Occasionally during conversations, she has difficulties finding the right word. She drives herself to the grocery market weekly to do her shopping, and has no difficulty managing her finances. She describes her mood as good. She visits her close friends on occasion and often has difficulty falling asleep. Her blood pressure is 135/76 mmHg and her heart rate is 65/min. Finger stick glucose and TSH levels are normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
. Alzheimer's dementia
. Depression
. Normal pressure hydrocephalus
. Frontotemporal dementia
. Normal aging
33) A 59-year-old man is brought to the office by his family due to attitude problems over the last year. He has a history of memory loss and word-finding problems. He has lost interest in golf, which used to be one of his favorite sports. Recently, he has become promiscuous and has started using "dirty language," which he has never used before. He is a non-smoker. He has no significant past medical or surgical history. His uncle had similar features, for which he was admitted into a nursing home, but died soon after admission. The physical examination reveals intact visuospatial functions, intact cranial nerves, and prominent snout and grasp reflexes. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Lewy body dementia
. Alzheimer's disease
. Multi-infarct dementia
. Neurosyphilis
. Pick's disease
34) A 65-year-old man comes to the physician's office because of frequent falls. For the past 2 months, he has been having increasing difficulty in maintaining balance when walking or standing. He tends to lose his balance on the left side, and feels that his "left body has become weak." He also complains of occasional headaches and nausea for the past 3 months. His other medical problems include hypertension, diabetes mellitus-type 2 and a myocardial infarction 10 years ago. He denies the use of tobacco, alcohol, or drugs. His medications include glyburide, aspirin and enalapril. His vital signs are within normal limits. When asked to get up from the chair and stand with his feet together, he tends to sway to the left, even with his eyes open. When asked to walk a few steps, he walks cautiously and lurches to the left. There is decreased resistance to passive flexion. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Major depression
. Huntington's disease
. Parkinsonism
. Cerebellar tumor
. Hemiparesis
35) A 26-year-old previously healthy white female is brought to the emergency department after having an episode of seizures one hour ago. She has a two-day history of fever and headaches, for which she has been taking acetaminophen and ibuprofen without much relief. She has no family history of seizures. Her temperature is 38.9°C (102°F), blood pressure is 120/70 mmHg, pulse is 110/min, and respirations are 18/min. Complete blood count and CT scan of the head are unremarkable. Her cerebral spinal fluid study shows: Opening pressure 220 mm H2O, Protein 200 mg/dl, Glucose 55 mg/dl, WBC 150/mm3, Lymphocytes 90%, Polymorphs 10%, RBC 200/cmm. What is the most likely diagnosis of this patient?
. Pneumococcal meningitis
. Meningococcal meningitis
. Hemophilus influenza meningitis
. Herpes simplex encephalitis
. Cryptococcal meningitis
36) A 64-year-old man presents to the ER with back pain and frequent falls. He also describes difficulty initiating urination. The symptoms started one week ago and have progressed gradually. He was diagnosed with prostate cancer one year ago and treated with radiation therapy. Physical examination reveals weakness of knee and hip extension that is more pronounced on the right. Knee and ankle reflexes are absent bilaterally. Babinski sign is negative. Perianal skin is insensitive to touch but sensation in the anterolateral thigh is preserved. Which of the following is the most likely lesion location in this patient?
. Peripheral nerves outside the spinal canal
. Spinal nerve roots
. Lumbar spinal cord
. Thoracic spinal cord
. Cervical spinal cord
37) A 62-year-old Caucasian woman complains of difficulty remembering important dates and appointments. She also describes poor concentration, daytime sleepiness and easy fatigability. She is concerned about her forgetfulness because her mother suffered from recurrent strokes and had severe memory loss. Her father died of chronic leukemia. Her daughter's recent job loss has caused her a lot of stress. She does not smoke or consume alcohol. Her appetite is decreased but she has gained 4 pounds over the last three months. She visited an otolaryngologist for hoarseness of recent onset. She takes over- the-counter laxatives for constipation and occasional aspirin for knee pain. She denies any other medication use. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
. Alzheimer's dementia
. Dementia with Lewy bodies
. Multiinfarct dementia
. Hypothyroidism
. Normal pressure hydrocephalus
38) A 46-year-old homeless man is being evaluated for frequent falls and a broad-based gait. A single tap on his patellar tendon elicits several to-and-fro leg movements. There is also nystagmus on physical examination. Which of the following additional findings would you expect most in this patient?
. Goiter
. Bradykinesia
. Intention tremor
. "Clasp knife" phenomenon
. Babinski sign
39) A 66-year-old female is brought to the office by her concerned son due to increasing confusion, loss of mobility and stiff limbs. She tends to cry out for no reason. She often screams and sees, "a lion roaring in the backyard." She often sees cats in her room, even though her son does not see any. She has significant memory loss. She never had "joint problems" before. She was previously treated with haloperidol, but this only aggravated her rigidity. She is a non-smoker. She has no significant past psychiatric history. In the office, she appears alert, but disoriented and quite agitated. Her blood pressure is 136/72 mm Hg, pulse is 98/min, and respirations are 16/min. Physical examination reveals impaired visuospatial abilities, increased tone, normal reflexes, and coarse resting tremors in the extremities. Her CBC, electrolytes, creatinine, glucose, LFTs, TSH and B 12 levels are within normal range. The serology for syphilis is negative. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Lewy body dementia
. Alzheimer's disease
. Multi infarct dementia
. Neurosyphilis
. Pick's disease
40) A 59-year-old obese man comes to the office "to make sure everything is okay." Yesterday after lunch, he experienced weakness in his right upper arm and right lower extremity. He was limping, and his right hand was not strong enough to hold some heavy things. His speech was "somewhat faulty”, and he had a light diffuse headache. By dinnertime, his symptoms were resolving, and when he woke up this morning, his weakness was gone. His past medical history is significant for hypertension, for which he takes atenolol. He has been smoking 1 pack of cigarettes a day for the past 40 yrs. His blood pressure is 150/95 mm of Hg and heart rate is 78/min. The neurological examination is normal. There is a mild carotid bruit on his left side. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Hemorrhagic stroke
. Completed ischemic stroke
. Transient ischemic attack
. Reversible ischemic neurologic deficit
. Cluster headache
41) A 68-year-old woman comes to the office due to the inability to move the right half of her face for the past 24 hours. Her blood pressure is 135/90 mm Hg and heart rate is 76/min. The physical examination is performed. Which of the following signs will exclude the diagnosis of central facial paresis?
. Dysarthria
. Absence of forehead furrows
. Normal sensations on the right side of the face
. Dropped right corner of the mouth
. Facial spasm on the right
42) A 32-year-old construction worker is brought to the emergency room after his co-workers found him confused, disoriented, and bleeding from the nose. His past medical history is unknown. According to his friends, he had been in his normal state of health this morning when he came to work. He then spent the morning moving heavy packages under direct sunlight for several hours. Presently, his blood pressure is 130/90 mmHg, heart rate is 120/min and regular, and temperature is 42°C (108°F). His skin is warm and dry and his neck is supple with no stiffness. His pupils are symmetric, mid-size and reactive to light. Deep tendon reflexes are symmetric and Babinski reflexes are downgoing bilaterally. He moves all four extremities but is unable to speak or follow simple commands. There is active bleeding from the right nostril. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Viral encephalitis
. Malignant hyperthermia
. Heat stroke
. Hypothalamic stroke
. Thyroid storm
43) A 65-year-old Caucasian male presents to the emergency department with sudden onset of weakness in his right arm and right leg. He has had episodes of transitory weakness and numbness in his right extremities over the last month, but those episodes used to resolve quickly. He denies headache, nausea, vomiting and loss of consciousness. His past medical history is significant for hypertension, diabetes mellitus, type 2 and myocardial infarction experienced 2 years ago. His current medications are aspirin, metoprolol, enalapril, simvastatin, and glyburide. He does not smoke or consume alcohol. His blood pressure is 160/80 mmHg, pulse is 65/min, temperature is 36.7°C (98°F) and respirations are 14/min. The physical examination reveals right-sided hemiplegia and facial paresis. His speech and praxis do not seem to be impaired. He correctly names his left and right arms. Bedside visual field testing is normal. Head CT without contrast shows no intracranial bleeding Where is the most likely location of the lesion responsible for this patient's condition?
. Middle cerebral artery occlusion
. Anterior cerebral artery occlusion
. Internal capsule involvement
. Pons lesion
. Midbrain lesion
44) A 20-year-old Caucasian male is on mechanical ventilation after sustaining a severe head trauma in a car accident. He is unresponsive to various stimuli. His blood pressure is 100/60mmHg and heart rate is 110/min. After monitoring the patient for six hours, the physician decides to do a bedside assessment of brain death. Which of the following can be observed in a patient with brain death?
. Pupillary light reaction
. Oculovestibular reaction
. Heart acceleration after atropine injection
. Spontaneous respiration at Pco2 = 60 mmHg
. Deep tendon reflexes
45) A 74-year-old woman comes to your office with her husband for a routine check-up. Her husband complains that she often forgets to take her blood pressure pills. He feels that her speech has changed because she occasionally struggles to find appropriate words. Two days ago, she drove to the nearby grocery store and did not find her way back. She has difficulty falling asleep and she always wakes up early in the morning. Her appetite is good. Which of the following is the best indicator of dementia in this patient?
. Memory impairment
. Language difficulty
. Sleep abnormalities
. Advanced age
. Impaired daily functioning
46) A 1-year-old boy is brought to the clinic by his 28-year-old Caucasian mother for the evaluation of his eyes. For the past several months, he has been bumping into objects. His perinatal history is unremarkable. Physical examination of the eyes reveals a bilateral white reflex. The retina cannot be visualized properly. Fundal reflection is absent, and the pupil is white. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Congenital glaucoma
. Congenital cataract
. Retinoblastoma
. Pterygium
. glaucoma
47) A 65-year-old white man is complaining of a sudden loss of vision in his left eye which resolved after 15 minutes. "It seemed like a curtain was falling down in my eye!" said the patient. He recalls having a similar episode 3 months ago. His past medical history is significant for hypertension, for which he takes lisinopril (20mg) and hydrochlorothiazide (25mg) daily. His pulse is 82/min, blood pressure is 140/90 mm Hg, respirations are 14/min, and temperature is normal. Fundoscopy reveals zones of whitened, edematous retina following the distribution of the retinal arterioles. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Central retinal artery occlusion
. Amaurosis fugax
. Central retinal vein occlusion
. Vitreous hemorrhage
. Hypertensive retinopathy
48) A 3-day-old female infant is noticed to have copious, purulent discharge from both eyes. Lid edema and chemosis are also noted. She was born by normal vaginal delivery. Her mother is a 20-year-old primigravida who had no prenatal care. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Chlamydia trachomatis
. Staphylococcus aureus conjunctivitis
. Chemical conjunctivitis
. Nasolacrimal duct obstruction
. Gonococcal conjunctivitis
49) A 22-year-old Caucasian female presents to the office with several months history of decreased visual acuity and decreased brightness sensation in the right eye. Slight exophthalmos of the right eye is present on physical examination, and ophthalmoscopy shows pallor of the right optic disk. Several cafe-au-lait spots and intensive axillary freckling are present. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's visual problems?
. Pigment retinitis
. Retinal hamartoma
. Optic glioma
. Pituitary adenoma
. Optic neuritis
50) A 65-year-old African American man comes to the emergency department due to a sudden loss of vision in his right eye. He has had diabetes, and has been treated with metformin and glyburide for the past 10 years. Visual acuity is reduced to light perception in his right eye, and normal in his left. His vital signs are normal. Ophthalmoscopy reveals loss of fundus details, floating debris and a dark red glow. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Retinal detachment
. Diabetic retinopathy
. Vitreous haemorrhage
. Central retinal vein occlusion
. Age related macular degeneration
51) A 60-year-old woman complains of decreasing vision and a dull ache over her left eye for the past 12 hours. She had a successful surgical cataract extraction in her left eye five days ago. Her blood pressure is 140/90 mmHg, pulse is 92/min, respirations are 14/min, and temperature is 38.1°C (101.7°F). Examination of the left eye reveals a swollen eyelid, edematous conjunctiva, and exudates in the anterior chamber. Testing with Snellen's chart demonstrates decreased visual acuity in her left eye. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Conjunctivitis
. Corneal ulceration
. Uveitis
. Postoperative endophthalmitis
. Cavernous sinus thrombosis
52) A 26-year-old male complains of itching and excessive watering of both eyes since this morning. He denies blurring of vision. He uses albuterol inhaler regularly for his bronchial asthma. His vital signs are normal. On examination, both eyes are noted to have conjunctival edema, hyperemia, swollen eyelids, and profuse watery discharge. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Atopic keratoconjunctivitis
. Allergic conjunctivitis
. Toxic conjunctivitis
. Blepharitis
. Dacryocystitis
53) A 4-year-old boy is brought by his mother to a Medical Camp for the Uninsured for the evaluation of his inflamed right eye. He has had a nasal discharge for the past 10 days. His brother has similar symptoms. His vital signs are stable. There are follicles and inflammatory changes in the conjunctiva of his right eye. The cornea shows neovascularization. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Herpes simplex keratitis
. Orbital cellulitis
. Trachoma
. Gonococcal conjunctivitis
. Viral conjunctivitis
54) A 60-year-old woman comes to the emergency department due to a sudden onset of severe pain in her left eye with blurred vision, nausea, and vomiting. The symptoms began a few minutes ago, while she was watching a movie in a nearby theatre. Her blood pressure is 140/90 mm Hg, pulse is 82/min, respirations are 14/min, and temperature is 98.4°F. Examination reveals decreased visual acuity. Her left eye appears red, with a hazy cornea, shallow anterior chamber, and dilated, fixed pupil. Her left eye is stony hard to touch. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Primary open angle glaucoma
. Conjunctivitis
. Acute angle closure glaucoma
. Anterior uveitis
. Corneal abrasion
55) A 32-year-old male construction worker presents with complaints of pain, watering, and redness in his left eye for the past 2 days. He reports having similar symptoms in the same eye a few months ago. Examination of his left eye reveals vesicles and dendritic ulcers in the cornea. His vital signs are stable. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Bacterial retinitis
. Herpes simplex keratitis
. Herpes zoster ophthalmicus
. Corneal abrasion
. Fungal keratitis
56) A 38-year-old man with AIDS (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome) is complaining of diminished vision in both eyes. His CD4 count last month was 50 cells/uL. He has been on highly active antiretroviral therapy for the past several months. He is afebrile, and his vital signs are stable. Ophthalmoscopic examination reveals yellow-white patches of retinal opacification and retinal hemorrhages. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Ocular toxoplasmosis
. Herpes simplex keratitis
. Herpes-zoster ophthalmicus
. CMV Retinitis
. HIV retinopathy
57) A 65-year-old man presents with complaints of decreased vision in both eyes. His visual impairment has been progressively worsening over the past five months. He was diagnosed with diabetes ten years ago. His current medications are metformin and glyburide. His blood pressure is 140/90 mm Hg, pulse is 82/min, respirations are 14/min, and temperature is 98.4°F (36.88°C). Examination shows decreased visual acuity in both eyes. Ophthalmoscopy reveals microaneurysms, dot and blot hemorrhages, hard exudates, and macular edema. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Central retinal vein occlusion
. Diabetic retinopathy
. Macular degeneration
. Retinal detachment
. Open angle glaucoma
58) A 69-year-old white male presents to your office complaining of progressive bilateral loss of vision over the past several months. He only has problems with his central vision. His peripheral field and navigational vision are not affected. He denies smoking and alcohol intake. He does not have any history of diabetes or hypertension Two years ago, he had cataracts removed from both eyes. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Open angle glaucoma
. Macular degeneration
. Recurrent cataracts
. Central retinal artery occlusion
. Retinal detachment
59) An 80-year-old white male comes to the emergency department due to a sudden loss of vision in his left eye that occurred this morning upon waking up. He has had hypertension for the past several years. Current medications include ramipril and atenolol. His blood pressure is 140/90 mm Hg, pulse is 86/min, respirations are 14/min, and temperature is 36.8°C (98.4°F). Examination of the left eye reveals no abnormalities. Funduscopic examination shows swelling of the optic disk, retinal hemorrhages, dilated and tortuous veins, and cotton wool spots. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Acute angle-closure glaucoma
. Central retinal vein occlusion
. Optic neuritis
. Amaurosis fugax
. Acute anterior uveitis
60) A 32-year-old woman comes to the office distraught because "the colors look washed out I" She has had this vision impairment since yesterday. She also complains of pain on eye movements. Her vital signs are stable, and she is afebrile. Examination reveals decreased visual acuity, sluggish afferent pupillary response to light, and changes in color perception. Fundoscopy reveals a swollen disc. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Orbital cellulitis
. Optic neuritis
. Acute anterior uveitis
. Open angle glaucoma
. Episcleritis
61) An 85-year-old man presents with a rash over his forehead, tip of nose and left eye. He also complains of pain and decreased vision. He has had fever, malaise, and a burning sensation around his left eye for the past 5 days. His blood pressure is 140/90 mm Hg, pulse is 92/min, respirations are 14/min, and temperature is 38.1°C (101°F). Physical examination reveals a vesicular rash on the periorbital region and lid margins. The left eye is red, with chemosis of the conjunctiva. Dendriform ulcers are seen on the cornea. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Herpes simplex keratitis
. Dacryocystitis
. Bacterial keratitis
. Trigeminal neuralgia
. Herpes zoster ophthalmicus
62) A 75-year-old African American man comes to your office for his annual check-up. He is a known diabetic and hypertensive. His medications include lisinopril and atenolol. His vital signs are normal. Examination of his fundus reveals cupping of the optic disc. Visual field examination reveals constricted peripheral vision. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Diabetic retinopathy
. Closed angle glaucoma
. Macular degeneration
. Primary open angle glaucoma
. Cataract
63) A 65-year-old female is complaining of seeing a sudden burst of flashing lights and blurred vision in her left eye. These symptoms started this morning. She now sees small spots in her field of vision. She felt "like a curtain came down" over her eye. She had a successful cataract extraction in her left eye 4 months ago. Her vital signs are stable. Examination shows a sluggish left pupil. Ophthalmoscopy reveals retinal tears and a grayish-appearing retina. What is the most probable diagnosis?
. Choroidal rupture
. Retinal detachment
. Central retinal artery occlusion
. Proliferative diabetic retinopathy
. Exudative macular degeneration
64) A 65-year-old woman presents with complaints of pain and swelling over the inner aspect of her right eye for the past two days. Examination of the eye reveals tenderness, edema, and redness over the medial canthus. Slight pressure over the area causes expression of purulent material. Visual acuity is normal. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Episcleritis
. Hordeolum
. Dacryocystitis
. Chalazion
. Orbital cellulitis
65) A 65-year-old man complains of gradual onset blurred vision for the past two months. He also has difficulty driving at night and reading fine print. He has diabetes and hypertension. His medications include ramipril and metoprolol. His vital signs are stable. His best corrected vision is OD (right eye) 20/80, OS (left eye) 20/100, with full fields. Ophthalmoscopic examination with good pupillary dilatation reveals a loss of transparency of lens in both eyes. The red fundal reflex is normal, but retinal details are difficult to visualize. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Open angle glaucoma
. Retinal detachment
. Macular degeneration
. Cataract
. Central retinal vein occlusion
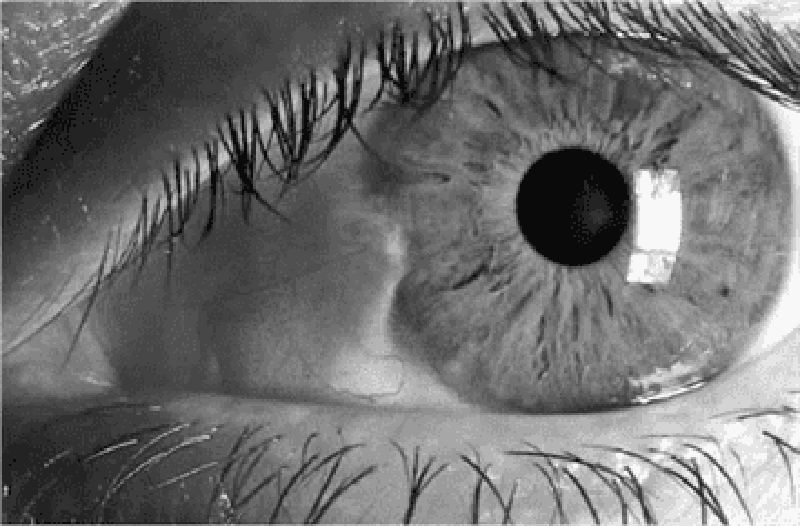
66) A 31-year-old nurse in your hospital has noticed a lesion in her left eye. She denies change in vision, pain, fevers, or discharge. A picture of her eye is shown below. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Hordeolum
. Chalazion
. Dacryocystitis
. Pinguecula
. Pterygium
67) A 35-year-old woman presents with a right-sided red eye for 3 days. She denies pain and notes that she has watery discharge from the eye. She has been coughing and congested for the past 5 days. On examination, the patient has a temperature of 98.4°F, HR of 72 beats per minute, BP of 110/70 mm Hg, and RR of 14 breaths per minute. Her visual acuity is 20/20. On inspection, the conjunctiva is erythematous with minimal chemosis and clear discharge. The slit-lamp, fluorescein, and funduscopic examinations are otherwise unremarkable. The patient has a nontender, preauricular lymph node and enlarged tonsils, without exudates. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Gonococcal conjunctivitis
. Bacterial conjunctivitis
. Viral conjunctivitis
. Allergic conjunctivitis
. Pseudomonal conjunctivitis
68) The local sorority house recently installed a sun-tanning station. Two days later three sorority girls present to the ED with bilateral eye pain, tearing, and photophobia. After ophthalmic anesthesia instillation, a complete eye examination is performed. Visual acuity is normal. Extraocular eye movements are intact and pupils are equal, round, and reactive to light. IOP is normal. Slit-lamp examination is normal, but fluorescein examination under cobalt blue light illuminates small dots throughout the cornea. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Ultraviolet keratitis
. Anterior uveitis
. Herpes simplex keratitis
. Allergic conjunctivitis
. Corneal ulcer
69) A 22-year-old man presents to the ED for left eye pain. He was in an altercation yesterday and was punched in the left eye. On examination, his left eye is ecchymotic and the eyelids are swollen shut. He has tenderness over the infraorbital rim but no step-offs. You use an eyelid speculum to examine his eye. His pupils are equal and reactive to light. His visual acuity is normal. On testing extraocular movements, you find he is unable to look upward with his left eye. He also complains of diplopia when looking upward. Funduscopic examination is normal. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Orbital blowout fracture
. Ruptured globe
. Retinal detachment
. Cranial nerve III palsy
. Traumatic retrobulbar hematoma
70) You are examining the pupils of a patient. On inspection, the pupils are 3 mm and equal bilaterally. You shine a flashlight into the right pupil and both pupils constrict to 1 mm. You then shine the flashlight into the left pupil and both pupils slightly dilate. What is this condition called?
. Anisocoria
. Argyll Robertson pupil
. Afferent pupillary defect
. Horner syndrome
. Normal pupil reaction
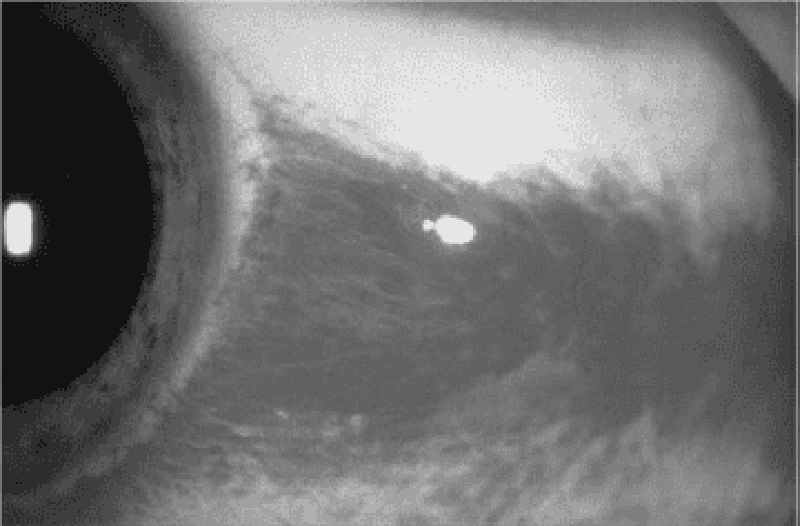
71) A 65-year-old man with a history of diabetes, hypertension, coronary artery disease, and atrial fibrillation presents with loss of vision in his left eye since he awoke 6 hours ago. The patient denies fever, eye pain, or eye discharge. On physical examination of the left eye, vision is limited to counting fingers. His pupil is 3 mm and reactive. Extraocular movements are intact. Slit-lamp examination is also normal. The dilated funduscopic examination is shown below. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Retinal detachment
. Central retinal artery occlusion
. Central retinal vein occlusion
. Vitreous hemorrhage
. Acute angle-closure glaucoma
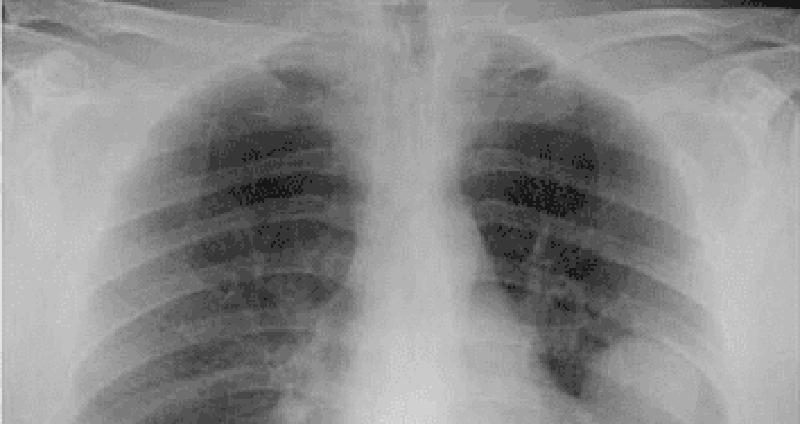
72) A 43-year-old man presents to your office complaint of nagging left-side chest pain that increases on deep inspiration, plus two weeks of non-productive cough. He denies chills, fever or weight loss. His medical history is significant for Hodgkin's disease treated 20 years ago with chemotherapy and radiation therapy. On physical examination today, his blood pressure is 140/90 mmHg and his heart rate is 90/min. His chest x-ray is shown below. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his chest pain?
. Radiation-induced fibrosis
. Recurrence of Hodgkin's disease
. Fungal pneumonia
. Pulmonary tuberculosis
. Secondary malignancy
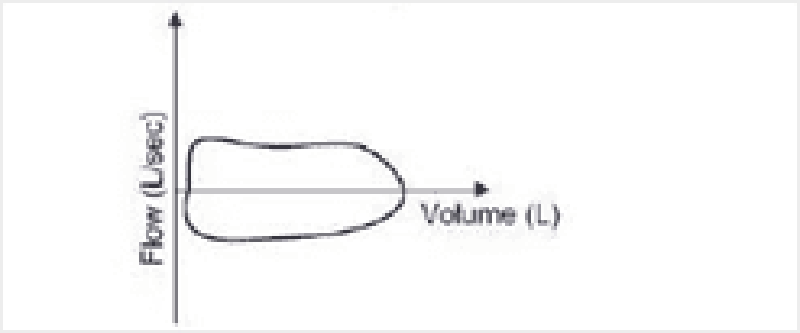
73) A 56-year-old woman is brought to the hospital from a local restaurant after suddenly becoming short of breath. Her flow-volume loop is shown below. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her symptoms?
. Asthma attack
. Pneumothorax
. Pulmonary edema
. Laryngeal edema
. Panic attack
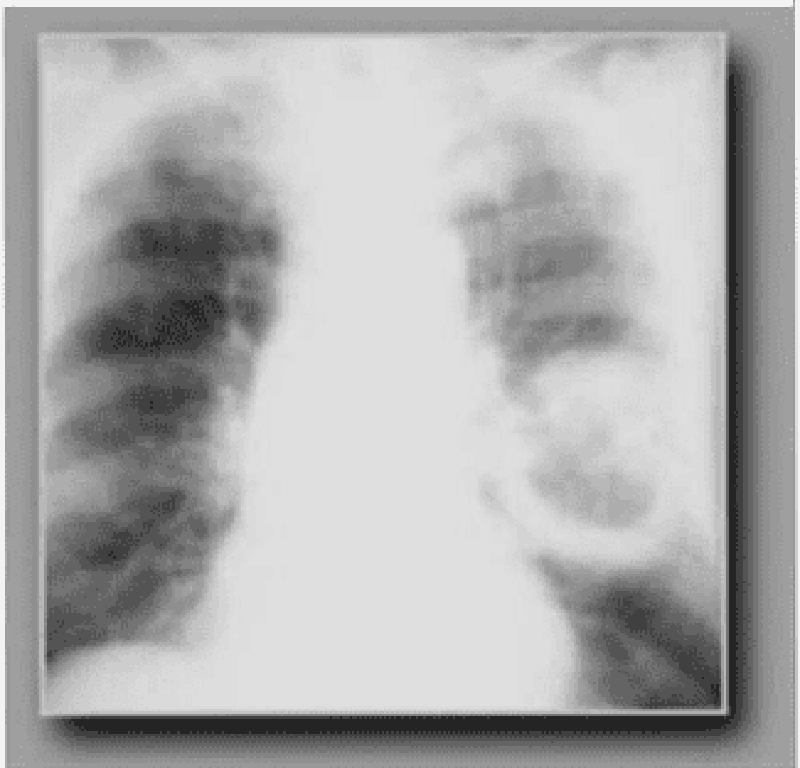
74) A 54-year-old black male from the southeast USA presents to you with complaints of generalized malaise, fever, and a cough. He claims that he has had intermittent hemoptysis for the past six months. He denies smoking and has never had tuberculosis. Examination is unremarkable and his chest x-ray is shown below. On changing position, you notice that the part of the lesion seen on x-ray also moves. The most likely diagnosis is?
. Lung abscess
. Pulmonary embolism
. Aspergilloma
. Histoplasmosis
. Bronchiectasis
75) A 66-year-old male presents to the emergency department with acute onset of severe chest pain and dyspnea. He localizes the pain to the right upper chest, and says that it is aggravated by deep breathing and coughing. On physical examination, his pulse is 116/min and regular, blood pressure is 110/70 mmHg, and respirations are 22/min. His lungs are clear to auscultation. Chest x-ray is unremarkable. EKG shows sinus tachycardia. CT angiogram of the chest shows a thrombus in the right pulmonary artery. Which of the following is the most likely source of his pulmonary thrombus?
. Clot in the right heart
. Upper extremity deep vein clot
. Renal vein clot
. Calf vein clot
. Iliofemoral vein clot
76) A 35-year-old male presents to the emergency room complaining of increasing shortness of breath, fever and malaise for several days. His past medical history is significant for two years of recurrent sinusitis. He is a former smoker and has an occasional glass of wine. His temperature today is 38.4°C (101.1°F), blood pressure is 110/65 mm Hg, pulse is 110/min, and respirations are 22/min. Examination reveals an illappearing male in mild respiratory distress. Patchy rales are appreciated on lung auscultation. Chest x-ray reveals multiple nodular densities bilaterally. His serum creatinine is 2.7 mg/dl and urinalysis shows red blood cell casts. Which of the following would be most helpful in diagnosing his condition?
. Serum alpha fetoprotein
. CT scan of the chest
. Serum antineutrophilic cytoplasmic antibody
. Sputum acid fast stain
. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
77) A 64-year-old male presents to the ER with a one-week history of progressive exertional dyspnea. Each of the past two nights he has awakened with a choking sensation and has had to sit up to catch his breath. His past medical history is significant for hypertension and a myocardial infarction two years ago. He takes a baby aspirin and lisinopril daily. His blood pressure is 140/90 mmHg, and his heart rate is 110/min, irregularly irregular. His temperature is 98°F (36.7°C) and his respiratory rate is 24/min. His oxygen saturation is 91% on room air. There is moderate jugular venous distention. Markedly reduced breath sounds are heard over the right lung base. Which of the following most likely underlies this patient's physical findings?
. Lung tissue consolidation
. Atelectasis
. Bronchoconstriction
. Pleural effusion
. Emphysema
78) A 62-year-old male is brought to the ER after passing out at work. He reports having had difficulty walking over the past couple of days due to an infected wound on his right foot. His past medical history is significant for diabetes mellitus. On physical examination, his blood pressure is 80/40 mm Hg and his heart rate is 120/min, regular. His skin is cold and clammy. Right heart catheterization is performed, and the following readings are obtained: Right atrial pressure 18 mmHg, Pulmonary artery pressure 40/20 mmHg, Pulmonary capillary wedge pressure 9 mmHg. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Aortic dissection
. Myocardial infarction
. Pulmonary embolism
. Hypovolemic shock
. Septic shock
79) You are asked to evaluate four different patients, all who have presented with cough and progressive dyspnea. Each has a chest x-ray showing diffuse pulmonary infiltrates. In which of the following patients would bronchoscopy with bronchoalveolar lavage be most likely to yield a diagnosis?
. 35-year-old female with suspected sarcoidosis
. 37-year-old female with positive rheumatoid factor
. 35-year-old HIV patient with CD4 count of 150
. 56-year -old female with suspected interstitial pulmonary fibrosis
. 50-year-old female with cardiopathy congestive
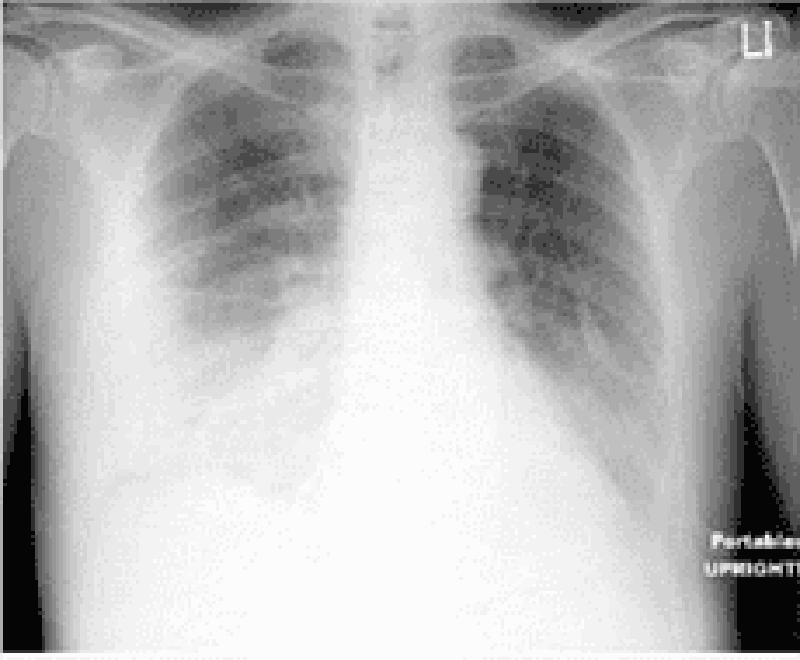
80) A 65-year-old male comes to the emergency department with severe shortness of breath. The symptoms started one week ago with fever and a non-productive cough. His past medical history is significant for coronary artery disease with bypass surgery two years ago, hypertension and diabetes mellitus. His temperature is 38.9°C (102°F), blood pressure is 160/70 mm Hg, pulse is 110/min, and respirations are 26/min. Physical examination reveals decreased breath sounds over the right lower lung base. His chest X-ray is shown on the slide below. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's current complaints?
. Bronchopleural fistula
. Lung abscess
. Empyema
. Pneumothorax
. Pulmonary infarction
81) A 54-year-old man is being evaluated for shortness of breath. Examination shows dullness to percussion and increased breath sounds, particularly during expiration, in the right lower lobe. Cardiac examination reveals regular rate and rhythm with normal S1 and S2. There is no murmur. Moderate peripheral edema is present. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his shortness of breath?
. Pleural effusion
. Pneumothorax
. Emphysema
. Interstitial lung disease
. Consolidation of the lung
82) A 15-year-old male comes to your office with a one-week history of fever, non-productive cough, sore throat and headaches. Today he noticed a skin rash. His temperature is 38.5°C (101.3°F), pulse is 90/min, blood pressure is 115/78 mm Hg and respirations are 16/min. His throat is hyperemic, but there is no cervical lymphadenopathy. Chest auscultation and percussion reveal no abnormalities. You note dusky red, target shaped skin lesions over all four extremities. Chest x-ray reveals interstitial infiltrates in the left lower lobe. Sputum gram stain reveals polymorphonuclear cells but no organisms. Which of the following organisms is most likely responsible for this presentation?
. Streptococcus pneumoniae
. Hemophilus influenzae
. Influenza virus
. Legionella pneumophila
. Mycoplasma pneumonia
83) A 53-year-old man presents with two episodes of hemoptysis over the last week. He describes a preceding two-year history of morning cough productive of approximately one tablespoon of yellowish sputum. During the last week his morning cough was accompanied by a small amount of blood on two occasions. He denies any dyspnea, fever, chest pain, or weight loss. He has been smoking for 30 years but has tried to cut down recently. He works in construction. His only medication is ranitidine for occasional heartburn. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his hemoptysis?
. Thrombocytopenia
. Pulmonary thromboembolism
. Bronchiectasis
. Chronic bronchitis
. Tuberculosis
84) A 60-year-old Caucasian man comes to the physician because of a productive cough and dyspnea on exertion. He denies hemoptysis, chest pain, and leg swelling. He has smoked one-and-a-half packs of cigarettes daily for 40 years and drinks 2-ounces of alcohol daily. He has worked in a shipyard for 10 years. His temperature is 37.2°C (99°F), blood pressure is 140/80 mmHg, pulse is 80/min, and respirations are 20/min. His chest x-ray shows prominent bronchovascular markings and mild diaphragmatic flattening. His pulmonary function testing shows decreased FEV1/FVC ratio and normal DLCO. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Emphysema
. Chronic bronchitis
. Sarcoidosis
. Silicosis
. Asbestosis
85) A 47-year-old smoker presents to the emergency room with a three-day history of shortness of breath and cough. His past medical history is significant for tuberculosis ten years ago, treated with six months of a multidrug regimen. On exam today, his blood pressure is 140/90 mmHg and his heart rate is 110/min. Breath sounds are decreased over the right lung base. Over the same area there is dullness to percussion and increased fremitus. The patient also has trace ankle edema. Which of the following most likely accounts for these findings?
. Pneumothorax
. Pleural effusion
. Emphysema
. Consolidation
. Asthma
86) A 51-year-old man develops acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) while hospitalized for acute pancreatitis. On his third day in the intensive care unit, he is sedated, intubated, and ventilated with a PEEP (positive end-expiratory pressure) of 15 cm water and Fi0 2 of 0.6 (60%). Suddenly his pulse increases from 100 to 140/min, systolic blood pressure drops from 120 to 90 mm Hg, and central venous pressure increases from 10 to 15 cm water. On chest auscultation, breath sounds are absent on the left side. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for this sudden deterioration?
. Endotracheal tube shift into the right main bronchus
. Pulmonary thromboembolism
. Myocardial infarction
. Tension pneumothorax
. Mucous plugging and atelectasis
87) A 27-year-old male presents to you with complaints of cough, chest discomfort and dyspnea on exertion. He says that he has lost 10 pounds over the past 2 months. He has been smoking 1 pack per day for the past 10 years. He drinks 2 beers every weekend. He denies illegal drug use and has not had multiple sexual partners. Physical examination is unremarkable. Chest x-ray reveals a large anterior mediastinal mass. Blood work reveals that he has elevated levels of HCG and alpha-fetoprotein (AFP). What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Benign teratoma
. Seminoma
. Nonseminomatous germ cell tumors
. Pericardial cysts
. Thymoma
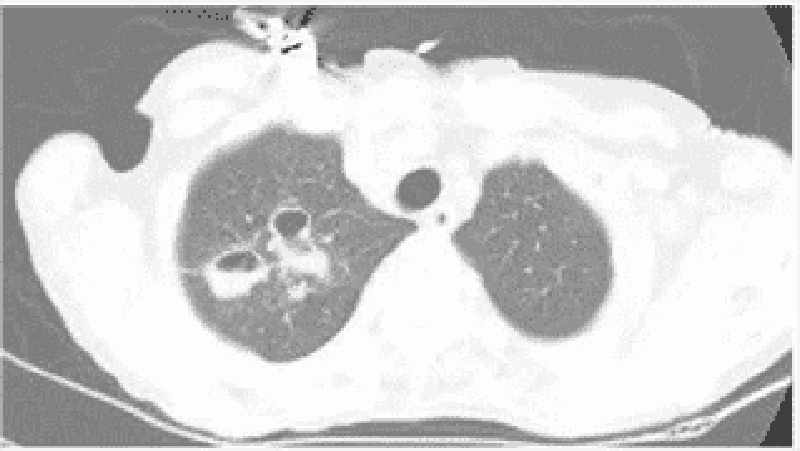
88) A 35-year-old man who recently emigrated from Mexico complains of persistent cough. He says that he coughs up yellowish sputum that is occasionally streaked with blood. He also notes occasional fevers and frequent nighttime awakenings with cough and choking. He has a 20 pack-year smoking history but does not use alcohol or drugs. CT of his chest is shown below. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Bronchiectasis
. Pulmonary tuberculosis
. Lung cancer
. Bronchopulmonary aspergillosis
. Sarcoidosis
89) A 42-year-old man presents to his primary care physician complaining of daytime sleepiness. He says that he often falls asleep during meetings, watching TV, and even while driving his car. He does not feel refreshed after his daytime naps, and has not experienced vivid hallucinations when falling asleep or upon awakening. He has occasional morning headaches and his wife complains that he sometimes keeps her up at night. Physical exam reveals a body mass index (BMI) of 31.3 kg/m2. An arterial blood gas is normal. What is this patient's most likely diagnosis?
. Narcolepsy
. Obesity hypoventilation syndrome
. Obstructive sleep apnea
. Central sleep apnea
. Primary insomnia
90) A 34-year-old male is rushed to the emergency room with severe respiratory distress. He is agitated and gasping for breath. He has been seen in the ER several times before for difficulty breathing, food intolerances and skin allergies. Physical examination is notable for excessive accessory respiratory muscle use, retraction of the subclavicular fossae during inspiration, and scattered urticaria over the upper body. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Upper airway obstruction
. Asthma exacerbation
. Pneumothorax
. Eosinophilic pneumonia
. Leukocytoclastic vasculitis
91) A healthy 36-year-old Caucasian woman comes to the physician because of dyspnea on exertion. She has no other medical problems. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or drugs. Her father has prostate cancer and her mother had a stroke. She takes no medication and has no known drug allergies. Her temperature is 36.7°C (98°F), blood pressure is 140/90 mmHg, pulse is 84/min, and respirations are 22/min. Examination shows clear lung fields. Her chest x-ray shows prominent pulmonary arteries and an enlarged right heart border. EKG shows right axis deviation. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Mitral stenosis
. Mitral valve prolapse
. Left ventricular failure
. Emphysema
. Pulmonary hypertension
92) A 65-year-old male comes to the physician because of fever, chills, and productive cough. The symptoms started four days ago. He also complains of chest pain, which increases with inspiration. He has smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for 45 years. He drinks 3-4 ounces of alcohol daily. His chest x-ray showed an infiltrate in the right upper lobe. The sputum examination of the patient reveals capsulated gram-negative bacilli. Sputum culture is growing mucoid colonies. Which of the following is the most likely causative organism in this patient?
. Escherichia coli
. Streptococcus pneumoniae
. Klebsiella pneumonia
. Legionella species
. Mycoplasma pneumonia
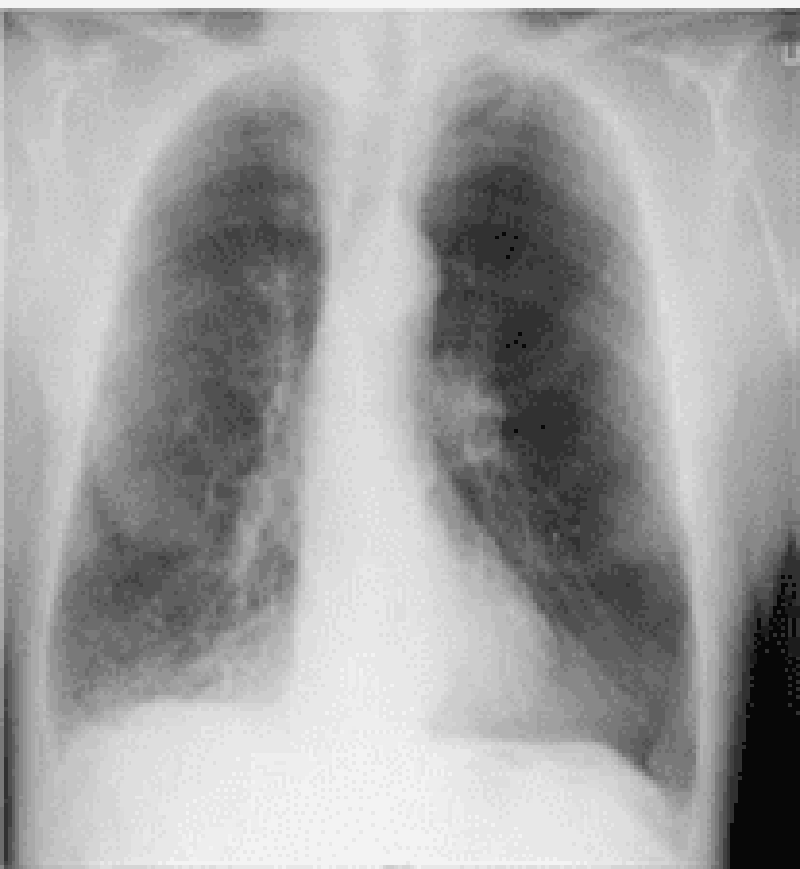
93) A 69-year -old Caucasian man presents with a two-day history of increasing shortness of breath and lower extremity edema. He is currently short of breath at rest and has an occasional cough. There is no past history of hypertension or ischemic heart disease. He reports drinking half a bottle of vodka daily and has smoked 1 pack of cigarettes per day for 45 years. His blood pressure is 160/90 mm Hg, pulse is 90/min, and oxygen saturation is 90% on room air. JVP is elevated and auscultation of his heart reveals faint heart sounds. The liver span is 18 cm and ascites is also present. No rales are heard in the lungs. There is 3+ lower extremity pitting edema up to the knees. The chest radiograph is shown below. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Alcoholic cirrhosis
. Coronary artery disease
. Cardiac tamponade
. Metastatic carcinoma of the liver
. Cor pulmonale
94) A 59-year-old male is brought to the emergency department with severe dyspnea and left-sided chest discomfort. He says that he was driving to work when he began to feel suddenly weak and short of breath. He has a long history of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, esophageal reflux and chronic pyelonephritis. He smokes one pack of cigarettes per day. His current medications include ranitidine and inhaled ipratropium and albuterol as needed. Physical examination reveals trace ankle edema, decreased breath sounds over the left chest and scattered wheezes over the right chest. ECG shows sinus tachycardia. Arterial blood gas analysis is given below: pH 7.42, pO2 59 mmHg, pCO2 41 mmHg. Which of the following most likely underlies this patient's current condition?
. Diffuse bronchial obstruction
. Inflammatory pulmonary infiltrates
. Interstitial pulmonary edema
. Dilated apical airspaces
. Pleural fluid transudation
95) A 32-year-old man with a known history of recreational drug abuse is found by a friend on the floor of his apartment. There is a pool of urine around him. He is confused, not oriented to time or place, and does not recall recent events. His blood pressure is 110/70 mmHg and his heart rate is 120/min. He talks and moves all his extremities. His laboratory findings are the following: Hemoglobin 15.2 mg/dl, WBC 12,500/mm3, Platelets 160,000/mm3, Sodium 136 mEq/L, Potassium 5.1 mEq/L, Creatinine 1.1 mg/dl, AST 35 units/L, AL T 40 units/L, Alkaline phosphatase 70 units/L, CPK 26,000 units/L. His urine toxicology screen is positive for cocaine and cannabinoids. The patient is at the greatest risk of which of the following?95) A 32-year-old man with a known history of recreational drug abuse is found by a friend on the floor of his apartment. There is a pool of urine around him. He is confused, not oriented to time or place, and does not recall recent events. His blood pressure is 110/70 mmHg and his heart rate is 120/min. He talks and moves all his extremities. His laboratory findings are the following: Hemoglobin 15.2 mg/dl, WBC 12,500/mm3, Platelets 160,000/mm3, Sodium 136 mEq/L, Potassium 5.1 mEq/L, Creatinine 1.1 mg/dl, AST 35 units/L, AL T 40 units/L, Alkaline phosphatase 70 units/L, CPK 26,000 units/L. His urine toxicology screen is positive for cocaine and cannabinoids. The patient is at the greatest risk of which of the following?
. Aseptic meningitis
. Acute renal failure
. Reye syndrome
. Dermatomyositis
. Splenic rupture
96) A 52-year-old nursing home worker presents with a four-week history of non-productive cough and night-time sweating. She also reports having unintentionally lost five pounds over the last month. Her medical history is significant for a mastectomy for left-sided breast cancer five years ago and hepatitis C for which she does not take treatment. She says she was last tested for HIV 6 months ago and the test was negative. She takes no medications currently. She emigrated from Mexico two years ago. She smokes one pack of cigarettes daily and consumes two bottles of beer every weekend. Chest x-ray shows a right upper lobe cavity with surrounding infiltration. Which of the following is the most important epidemiologic clue to the etiology of this patient's disease?
. Nursing home worker
. Foreign born individual
. Smoking history
. Previous breast cancer
. Hepatitis C
97) A 44-year-old obese Asian immigrant presents to the ER complaining of a persistent cough for about 3 months. He denies any fever, chills, runny nose or sputum production. He does complain of dyspnea on exertion, which also has been of a short duration. He says that over the last year, he has become progressively short of breath and is unable to sleep lying down. He denies any chest pain or diaphoresis, but has had palpitations in the past. He does not smoke or drink alcohol. On examination, he is alert and in mild distress. He has a BP of 110/70 mmHg, pulse 100/min and is afebrile. Auscultation is difficult. The chest-x ray reveals an enlarged cardiac silhouette. It appears that the left main stem bronchus is elevated. There is no other lung pathology visible. The ECG shows irregularly irregular rhythm. The pathophysiology of this condition is related to which of the following?
. Acute pericarditis
. Rheumatic fever
. Interstitial lung disease
. Malignancy
. Sarcoidosis
98) A 72-year-old white male with a past medical history of hypertension, hypothyroidism, and coronary artery disease presented to the physician's office because of fever, malaise, nonproductive cough, and shortness of breath. His temperature was 38.3°C (101°F). His chest x-ray showed a patchy right lower lobe infiltrate. He was sent home on oral amoxicillin. Four days later, the patient was brought to the emergency room because he was having continuous fevers, headache, pleuritic chest pain, and abdominal pain. He appears confused. His blood pressure is 120/70 mmHg, pulse rate is 100 per minute, respiratory rate is 24 per minute, and temperature is 38.9°C (102°F). His chest x-ray showed consolidation of the right lower lobe. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's pneumonia?
. Streptococcus pneumoniae
. Mycoplasma pneumoniae
. Mycobacterium tuberculosis
. Haemophilus influenzae
. Legionella pneumonia
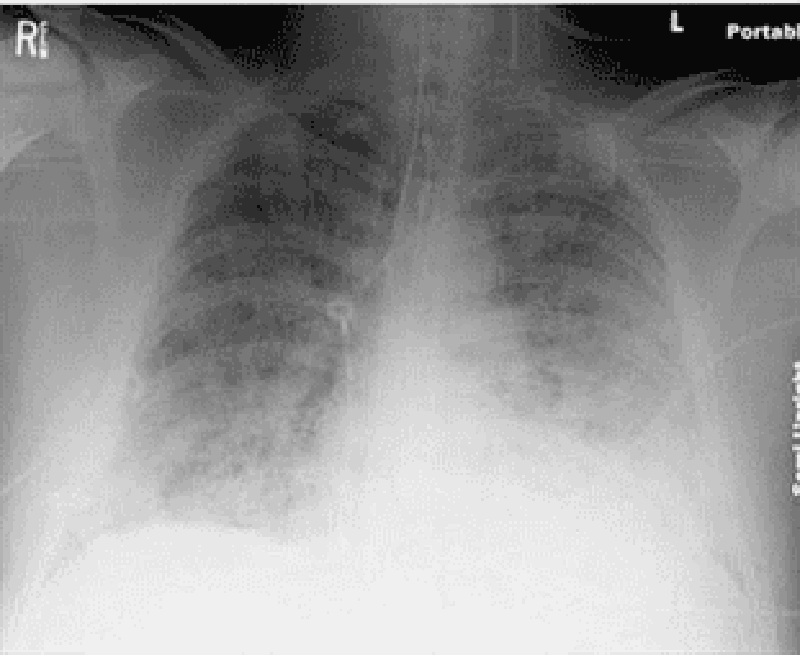
99) A 64-year-old male is admitted to the hospital with abdominal pain, abdominal distention, and confusion. Upon arrival his blood pressure is 90/60 mmHg and pulse is 120/min. On physical examination, his abdomen is tender, distended, and rigid with positive rebound tenderness. His past medical history is significant for rheumatic fever as a child, hypertension, coronary artery disease and atrial fibrillation. He receives a total of 6 liters of normal saline and undergoes emergent laparotomy. Postoperatively he complains of shortness of breath. His respiratory rate is 34/min. He is emergently intubated because of poor oxygenation. His chest x-ray is shown below. This film is compared to a chest x-ray performed one week earlier, which was within normal limits. Currently, the pulmonary capillary wedge pressure is 8 mmHg. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his current condition?
. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
. Mitral stenosis
. Acute respiratory distress syndrome
. Left ventricular systolic dysfunction
. Iatrogenic fluid overload
100) A 56-year-old woman is brought to the emergency room with shortness of breath, which she says began suddenly two hours ago while she was enjoying her favorite television show. She also reports the simultaneous onset of sharp, left-sided chest pain. Her previous medical history includes diabetes mellitus for the past 10 years and hypertension for the past 6 years. Her family history is significant for heart disease in her father, who died at age 40. Her medications include enteric-coated aspirin, captopril and glipizide. She has a 30 pack-year smoking history, but does not smoke currently. On physical examination, she is in acute distress and is sweating profusely. Her temperature is 38.0°C (100.5°F), pulse is 140/min and irregular, respiratory rate is 30/min, and blood pressure is 110/60 mm Hg. Her oxygen saturation is 84% on room air by pulse oximetry. Jugular venous pressure is within normal limits and her lungs are clear to auscultation. Serum analysis reveals the following: Hematocrit 40%, WBC count 11,600/mm3, Platelet count 190,000/mm3. Chest x-ray is unremarkable. ECG reveals irregular RR intervals, with no definite P waves and narrow QRS complexes. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her current symptoms?
. Myocardial infarction
. Mitral stenosis
. Cardiac tamponade
. Tension pneumothorax
. Pulmonary embolism
101) A 42-year-old white male presents to your office complaining of periodic breathing difficulty and wheezing. He visited an otolaryngologist for persistent nasal blockage recently. His past medical history is significant for unstable angina experienced five months ago. His current treatment includes aspirin, diltiazem, and pravastatin. He does not use tobacco, alcohol, or drugs. His vital signs are within limits. What is the most probable cause of this patient's respiratory complaints?
. IgE-mediated reaction
. Immune complex disease
. Cytotoxic antibodies
. Cell-mediated hypersensitivity
. Pseudo-allergic reaction
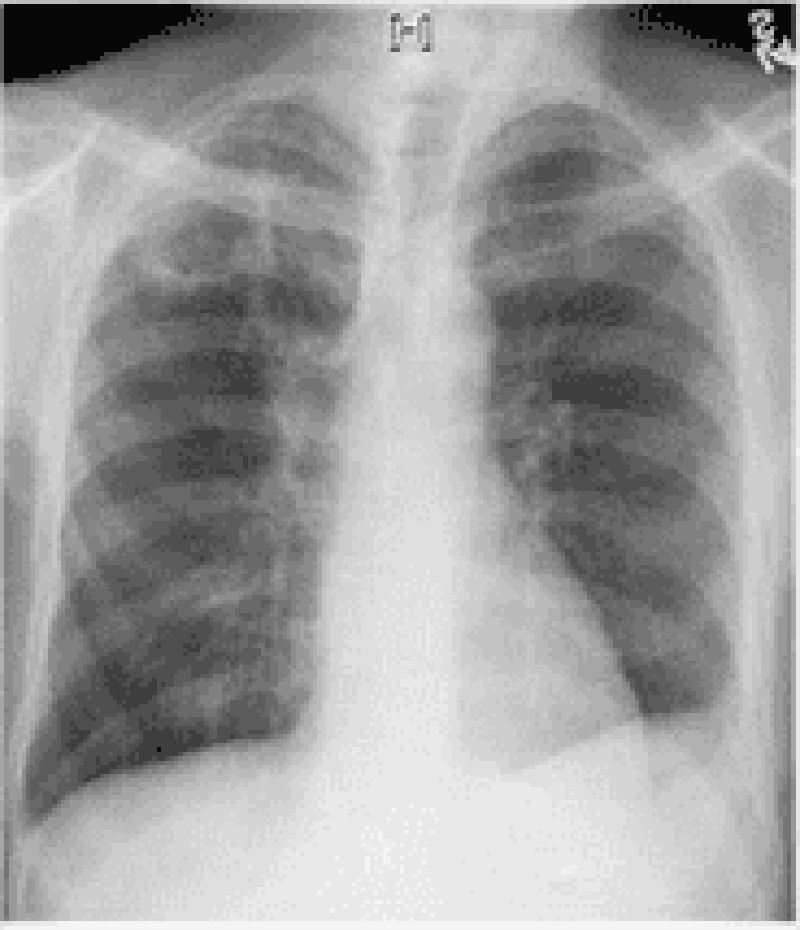
102) A 35-year-old male from Arizona presents to the physician's office with a low-grade fever and cough of two months duration. He also reports malaise and a weight loss of 7 1bs over this same period. He has a history of HIV infection diagnosed two years ago. He received a pneumococcal vaccine at the time his HIV was diagnosed. He also receives an annual influenza vaccine. He is not on any antiretroviral therapy. His temperature is 37.7°C (99.8°F), pulse is 75/min, blood pressure is 130/80 mm Hg and respirations are 14/min. Examination shows clear lungs to auscultation. His current CD4 count is 450cells/microl. His chest radiograph is shown below. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his cough?
. Bronchial asthma
. Gastroesophageal reflux disease
. Postnasal drip
. Mycobacterial infection
. Coccidioidomycosis
103) A 43-year-old moderately overweight woman presents to the emergency department complaining of two days of shortness of breath. Today, while climbing stairs, she had an episode of severe lightheadedness and near syncope. Her medical history is significant for a right calf deep venous thrombosis one year ago. She takes no medications currently. On physical examination, her blood pressure is 90/50 mmHg and her heart rate is 120/min and regular Imaging studies are most likely to reveal which of the following?
. Mitral stenosis
. Pericardial effusion
. Right ventricular dilation
. Bilateral pulmonary nodules
. Asymmetric hypertrophy of the intraventricular septum
104) A healthy 33-year-old man comes for a pre-employment examination. He has no complaints and has no medical problems. He does not use tobacco, alcohol, or drugs and takes no medications. He has no occupational exposures and has lived his entire life in suburban Mississippi. His temperature is 36.7°C (98.0°F), blood pressure is 120/80 mmHg, pulse is 78/min, and respirations are 16/min. Examination shows no abnormalities. His chest x-ray shows a 1 .5 cm nodule in his right mid-lung field. Other labs are unremarkable. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Coccidioidomycosis
. Histoplasmosis
. Tuberculosis
. HIV infection
. Pneumocystis jiroveci infection
105) A 30-year-old African American female presents with a two month history of shortness of breath and nonproductive cough. She has never had symptoms like these before. Her past medical history is significant for an episode of uveitis six months ago. She does not take any medications. She works as a secretary in a local office building. She does not use tobacco and drinks alcohol only on special occasions. She has no pets and has been monogamous with a single partner for the last three years. On physical examination, her temperature is 37.2°C (98.9°F), blood pressure is 126/76 mm Hg, pulse is 76/min and respirations are 16/min. Lung auscultation reveals patchy rales. The remainder of her examination is unremarkable. Chest x-ray shows diffuse interstitial infiltrates. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her shortness of breath?
. Pneumocystis pneumonia
. Congestive heart failure
. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
. Sarcoidosis
. Ankylosing spondylitis
106) A 63-year-old male complains of cough and nocturnal wheezing. The cough is mostly non-productive but can sometimes relieve chest tightness if a small amount of yellow sputum is produced. His past medical history is significant for a hospitalization for a 'chest infection' two years ago. His appetite is good but he lost 5 pounds over the last several months. He has smoked one pack of cigarettes per day for the past 40 years. He drinks 2-3 cans of beer per day on the weekends. His mother suffered from diabetes mellitus and his father died of a stroke. On physical examination, his blood pressure is 140/80 mmHg and his heart rate is 80/min. There is chest hyperinflation and scattered expiratory wheezes on auscultation. The patient expires through pursed lips. His fingers demonstrate prominent clubbing. This patient's clubbing is most likely related to:
. Lung hyperinflation
. Airflow obstruction
. Pulmonary hypertension
. Hypoxemia
. Occult malignancy
107) A 40-year-old Caucasian man comes to the emergency department because of fever, dry cough, and shortness of breath. Symptoms started 24 hours ago. He denies hemoptysis. He was recently discharged from the hospital after a second cycle of chemotherapy for acute myeloid leukemia. He does not use tobacco, alcohol, or drugs. His temperature is 38.9°C (102.0°F), blood pressure is 120/70 mmHg, pulse is 112/min and respirations are 28/min. The patient's pulse oximetry showed 86% at room air. Examination shows diffuse crackles all over the lung fields. His chest x-ray shows diffuse interstitial infiltrates. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his condition?
. Coccidioidomycosis
. Histoplasmosis
. Tuberculosis
. HIV infection
. Pneumocystis jiroveci
108) A 45-year-old woman comes to your office with a three-month history of fatigue, exertional dyspnea, and non-productive cough. She has also been having difficulty swallowing. Her only other medical problems are Raynaud's phenomenon, heartburn, and high blood pressure. On examination, diffuse thickening of the skin with telangiectasia is noted. Her current medications include amlodipine, enalapril, and ranitidine. What is the most probable pathologic mechanism of her pulmonary complaints?
. Pulmonary fibrosis
. Pulmonary vascular lesions
. Aspiration pneumonia
. Bronchogenic carcinoma
. Restriction of chest movement
109) A 65-year-old man with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, chronic atrial fibrillation, hypertension, and diabetes mellitus presents with a three-day history of shortness of breath. His condition began with runny nose, itchy eyes, and sore throat, but his symptoms progressed to productive cough, wheeze, and dyspnea. Physical examination reveals a mildly overweight man in moderate respiratory distress. His blood pressure is 150/90 mmHg and his heart rate is 110/min and irregular. On chest auscultation, expirations are prolonged and there are bilateral wheezes. You administer bronchodilators, facial mask oxygen, and lorazepam for agitation. Thirty minutes later, he is lethargic and confused. While you discuss the case with your attending, the patient experiences a generalized tonic-clonic seizure. Which of the following most likely underlies his neurologic symptoms?
. New-onset thromboembolic stroke
. Cerebral vasoconstriction
. Subarachnoid hemorrhage
. Carbon dioxide retention
. Metabolic acidosis
110) A 56-year-old Caucasian male complains of chronic exertional dyspnea for the past several years that has progressively worsened. He cannot remember the last time that he saw a doctor, and does not take any medications regularly. It is difficult for him to climb two flights of stairs without having to rest. His dyspnea has gotten so bad that it has severely limited his activity level, and he now spends most of his time on the couch. He also describes recurrent episodes of nocturnal dyspnea, during which he wakes up at around 2:00 AM with difficulty breathing, coughing, and wheezing that improve when he sits up. He usually coughs up some yellowish sputum before being able to go back to sleep. He has had no fever, chills, or chest pain. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's complaints?
. Left ventricular failure
. Bronchial asthma
. Chronic bronchitis
. Pulmonary thromboembolism
. Pulmonary fibrosis
111) A 62-year-old man presents to his primary care physician's office with progressive exertional dyspnea. His past medical history is significant for hypertension treated with hydrochlorothiazide and diabetes mellitus treated with metformin. He was an industrial worker for 30 years and retired one year ago. He smokes one pack of cigarettes per day and consumes alcohol occasionally. His blood pressure is 150/100 mmHg and his heart rate is 80/min. His BMI is 31 kg/m2. Chest x-ray reveals pleural calcifications. Pulmonary function studies show the following: FEV1 70% of predicted, FVC 65% of predicted, Residual volume 70% of predicted, DLCO decreased. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
. Impaired lung expansion due to pleural calcifications
. Emphysema from smoking
. Interstitial lung disease from occupational exposure
. Impaired lung expansion due to obesity
. Increased pulmonary capillary wedge pressure
112) A 47-year-old African American woman presents with two days of shortness of breath and left-sided chest pain. Her past medical history is significant for a mastectomy six months ago for breast cancer, for which she also received adjuvant chemotherapy. Her mobility has been limited recently due to progressive back pain. Her current medications include tamoxifen. On chest x-ray, there is an infiltrate obscuring the right heart border as well as a right-sided pleural effusion. Pleural fluid analysis reveals the following: pH 5.75, Nucleated cells 10,050/mm3, RBC 1,500/mm3, Protein 3.9 g/dl, LDH 620 units/L, Glucose 38 mg/dl. Her serum chemistries are notable for an LDH of 310 units/L and protein of 6.1 g/dl. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her effusion?
. Heart failure
. Pneumonia
. Drug-induced lupus
. Pulmonary embolism
. Hypoalbuminemia
113) A 64-year-old male presents to the ER with shortness of breath. The symptoms started one week ago with a dry cough and mild fever. His past medical history includes hypertension and exertional angina. He was hospitalized six months ago for pneumonia. He has a 35 pack-year smoking history. His blood pressure is 140/90 mmHg and heart rate is 90 and regular. On examination, the patient is in mild respiratory distress. He uses some accessory respiratory muscles for breathing, but he can speak in full sentences. Chest auscultation reveals bilateral wheezes and crackles at the left lung base. His ABG shows: pH 7.36, pO2 72mmHg, pCO2 51mmHg. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's current symptoms?
. Congestive heart failure ( CHF)
. COPD exacerbation
. Pulmonary embolism
. Pneumothorax
. Adult respiratory distress syndrome
114) A 37-year-old female with a long history of multiple sclerosis presents to her primary care physician complaining of dyspnea. She denies cough and fever but admits to right-sided chest pain. Her medical history is significant for an episode of atrial fibrillation diagnosed in the emergency department two weeks ago, which resolved spontaneously without intervention. She is wheelchair-bound due to spastic paraparesis and has saccadic speech. Her only allergy is to penicillin. On physical examination, her blood pressure is 120/70 mmHg and her heart rate is 110/min and regular. Chest x-ray demonstrates a right-sided pleural effusion. Therapeutic thoracocentesis is performed, and pleural fluid analysis reveals the following: Protein 3.1 g/L, RBC count 230/mm3, WBC count 150/mm3, LDH 220 IU/L, Glucose 100 mg/dl. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's pleural effusion?
. Congestive heart failure
. Hypoalbuminemia
. Pulmonary embolism
. Aspiration pneumonia
. Malignancy
115) A 35-year-old male from Wisconsin presents to his physician complaining of fever, night sweats, productive cough, and an unintentional 17-lb weight loss over the past 3 months. Several days ago, he also began to notice multiple skin lesions. He has no known medical problems and does not take any medications, nor does he use tobacco, alcohol or illicit drugs. He works outdoors in wood cutting and construction. Physical examination reveals a man of medium build in no apparent distress. His temperature is 38.4°C (101.1°F), blood pressure is 120/68 mm Hg, pulse is 86/min, and respirations are 14/min. Skin examination reveals multiple, well-circumscribed, verrucous, crusted lesions. Chest x-ray shows left upper lobe consolidation and two lytic lesions in the anterior ribs. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his current symptoms?
. Disseminated tuberculosis
. Sarcoidosis
. Metastatic osteosarcoma
. Blastomycosis
. Coccidioidomycosis
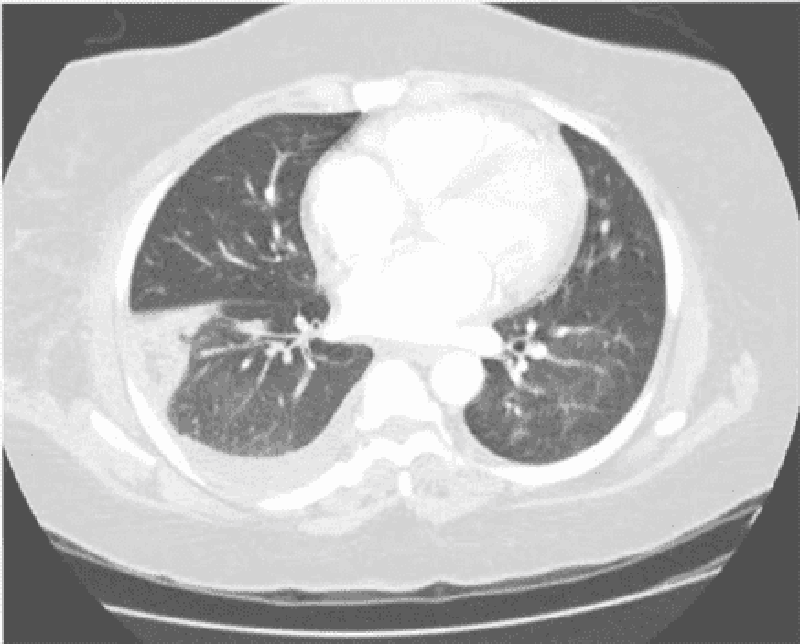
116) A 34-year-old woman presents with one week of low-grade fever, diarrhea, and lethargy plus two days of hemoptysis and severe pleuritic-type chest pain. In the past she abused heroin but is currently in a methadone program. She has a 20 pack-year cigarette smoking history. Her medical history is significant for HIV and hepatitis C infections. Her last CD4 count was 350/μl two months ago. PPD testing revealed 2 mm of induration at the same time. On physical examination today, her blood pressure is 130/80 mmHg, heart rate is 100/min, and temperature 38.1°C (100.6°F). Breath sounds are diminished at the base of the right lung. Chest CT is shown below. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Pulmonary tuberculosis
. Pulmonary thromboembolism
. Pneumocystis pneumonia
. Bacterial pneumonia
. Lung cancer
117) A 25-year-old man presents to the emergency room with shortness of breath and cough productive of blood tinged sputum for the past few days. He denies associated fever, arthralgias or weight loss. He has never had these symptoms before, and is extremely concerned. He has no history of recent travel or sick contacts. He smokes half a pack of cigarettes daily, and has had two sexual partners in the past six months. On physical examination, his temperature is 37.2°C (98.9°F), blood pressure is 120/70 mm Hg, pulse is 102/min, and respirations are 22/min. Lung auscultation reveals patchy bilateral rales. Chest x-ray demonstrates bilateral pulmonary infiltrates. His serum creatinine is 2.6 mg/dl and urinalysis shows dysmorphic red cells. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his current condition?
. Basement membrane antibodies
. Pneumocystis pneumonia
. Infection with acid fast bacilli
. Pulmonary thromboembolism
. Cardiac valve infection
118) A 32-year-old female complains of a 'nagging' dry cough over the last 4 weeks. She says that the cough is present during the day and also wakes her from sleep at night. There is no associated shortness of breath, chest pain or wheezing. Her past medical history is significant for chronic rhinorrhea and an occasional itching skin rash. She takes no medications. Chest x-ray shows no abnormalities. One week of treatment with chlorpheniramine significantly improves her symptoms. Decrease in which of the following is most likely responsible her symptom relief?
. Airway hyperreactivity
. Bronchial inflammation
. Acid aspiration
. Nasal secretions
. Bradykinin production
119) A 66-year-old male presents to the emergency room with shortness of breath. The symptoms started one week ago with a dry cough and exertional dyspnea. His past medical history includes hypertension and recent stenting for double-vessel coronary artery disease. He was hospitalized six months ago for pneumonia. He has a 35 pack-year smoking history. His temperature is 37.2°C (98.9°F), blood pressure is 160/90 mmHg, and heart rate is 90 and regular. On examination, the patient is in mild respiratory distress, but he can speak in full sentences. Chest auscultation reveals decreased breath sounds at the lung bases, bilateral crackles and occasional wheezes. His ABG shows: pH 7.46, pO2 73mmHg, pCO2 31mmHg. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for this patient's symptoms?
. Congestive heart failure
. COPD exacerbation
. Pulmonary embolism
. Pneumothorax
. Adult respiratory distress syndrome
120) A 55-year-old Caucasian man comes to the emergency department because of fever and productive cough, with foul-smelling sputum. He also complains of shortness of breath. His other medical problems include hypertension and hypercholesterolemia. In the past three months, he was admitted in the hospital two times for pneumonia. He has smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for 28 years and drinks 5-6 beers daily. Family history is not significant. His medications include hydrochlorothiazide and simvastatin. His temperature is 38.9°C (102°F), blood pressure is 120/70 mmHg, pulse is 112/min, and respirations are 24/min. The patient's pulse oximetry showed 89% at room air. Examination shows crackles at the right lung base. His chest x-ray shows right, lower lobe infiltrate. A CT scan of the chest shows no mass or obstruction. Which of the following is most likely responsible for this patient's symptoms?
. Excessive smoking
. Excessive alcohol intake
. Depressed humoral immunity
. Depressed cell-mediated immunity
. Underlying malignancy
121) A 45-year-old female presents to the emergency department because of increasing somnolence and shortness of breath. Her past medical history is significant for hyperlipidemia, hypertension and type2 diabetes. She has never smoked and does not use drugs or alcohol. Her temperature is 36.7°C (98°F), blood pressure is 160/80 mm Hg, pulse is 80/min, and respirations are 16/min. Her BMI is 55 kg/m2. On physical examination, she is drowsy but able to respond to commands. Jugular venous distention is difficult to visualize due to a thick neck. Lungs are clear to auscultation. Heart sounds are distant. Abdomen is obese and non-tender. Lower extremities have edema bilaterally. There are no obvious focal deficits on neurologic examination. Chest x-ray is poor in quality but no obvious abnormalities are noted. EKG shows low voltage QRS complexes but no significant ST-segment or T-wave abnormalities. Laboratory studies show: Complete blood count: Hemoglobin 16.0 g/L, Hematocrit 48%, Mean corpuscular volume 85 fl, Platelet count 224,000/mm3, Leukocyte count 6,600/mm3. Arterial blood gas: pH 7.30, pO2 60mmHg, pCO2 69mm Hg. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her condition?
. Venous thromboembolism
. Aspiration pneumonia
. Pneumocystis pneumonia
. Impaired chest wall compliance
. Pulmonary edema
122) A 60-year-old male with a history of hypertension, diabetes, coronary artery disease, asthma, and cigarette smoking undergoes emergent laparotomy for a perforated peptic ulcer. He receives 4 liters of intravenous normal saline intraoperatively. Following the procedure, he is extubated without complication, but subsequently develops respiratory distress. Immediate arterial blood gas analysis on room air shows: PaO2 60mmHg, pH 7.46, PaCO2 37mmHg, HCO3 22mmHg. His temperature is 37.2°C (98.9°F) and blood pressure is 126/76 mm Hg. Lung auscultation reveals bilateral rales. His arterial blood gas fails to improve with administration of 100% oxygen. What is the most likely cause of his respiratory distress?
. Excessive anesthesia
. Pulmonary edema
. Pulmonary embolism
. Aspiration pneumonia
. Exacerbation of bronchial asthma
123) A 40-year-old man presents to the emergency room with shortness of breath, cough and hemoptysis for the past two days. He says he has never had symptoms like these before. His medical history is significant for a non-healing leg ulcer and chronic purulent nasal discharge. He has smoked a pack of cigarettes daily for the past 20 years. On physical examination, his temperature is 37.6°C (99.7°F), blood pressure is 130/90 mm Hg, pulse is 94/min and respiratory rate is 18/min. Lung auscultation reveals patchy rales bilaterally. Heart sounds are regular. A 2x3cm ulcer with rolled, undermined borders is noted on the right lower leg. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for his hemoptysis?
. Pulmonary tuberculosis
. Bronchogenic carcinoma
. Wegener's granulomatosis
. Mitral stenosis
. Pulmonary embolism
124) A 62-year-old Caucasian male presents to your office because of a non-productive cough that is 'quite disturbing.' The cough has been present for several weeks. He visited your office two times before for poorly controlled hypertension, and was started on lisinopril. He usually takes aspirin, amlodipine, and metoprolol. He does not smoke or consume alcohol. His blood pressure is 130/90 mmHg and heart rate is 60/min. Physical examination reveals a bruit over the right carotid artery, but is otherwise normal. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's complaint?
. Inhibition of beta-adrenoreceptors
. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis
. Increased serum renin level
. Low level of circulating catecholamines
. High kinin level
125) A 26-year-old white female comes to the Emergency Room with severe shortness of breath. She has a long history of asthma with periodic exacerbations. She is taking an inhaled albuterol, inhaled steroid, salmeterol and cromolyn. Her temperature is 37.2°C (99°F), blood pressure is 150/90 mmHg, pulse is 110/min, and respirations are 24/min. On examination, she has moderate respiratory distress, prolonged expiratory phase, and significant wheezing all over the lung fields. Patient is admitted and is given nebulized albuterol, intravenous methyl prednisone, and oxygen. The next day her respiratory status improved. Her vital signs did not change much, except normalization of respiratory rate. Still scattered bilateral wheezes are heard on lung auscultation. The next day her laboratory values are: Hemoglobin 14 g/dL, MCV 95 fL, Leukocyte count 19,000/cmm, Segmented Neutrophils 80%, Bands 5%, Lymphocytes 13%, Eosinophils 0%, Basophils 0%, Monocytes 2%. Chest x-ray obtained at the time of admission is normal, except for hyperinflated lung fields. What is the most probable cause of the abnormal lab findings in this patient?
. Pneumonia
. Hypersensitivity reaction
. Myeloproliferative state
. Metabolic disorder
. Drug reaction
126) A 32-year-old male presents to your office complaining of daytime sleepiness and frequent night-time awakenings. He says that his sleep gets disrupted by a choking sensation, sometimes accompanied by cough and dyspnea. After such episodes he typically has trouble falling back to sleep. The patient notes that his symptoms are somewhat improved when he sleeps with multiple pillows. Physical examination is unremarkable except for a BMI of 29 Kg/m2. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Restless leg syndrome
. Asthma
. Left ventricular failure
. Obstructive sleep apnea
. Gastroesophageal reflux disease
127) A 20-year-old African American woman presents with mild dyspnea on exertion and joint discomfort in her knees, wrists, and ankles. She also has a fever and red tender rash on her shins. Physical examination reveals hepatosplenomegaly, generalized lymphadenopathy, corneal opacities, and tender erythematous nodules on her legs. CXR shows bilateral symmetric hilar adenopathy. Transbronchial biopsy reveals noncaseating granulomas. Which of the following is the most likely cause for the eye lesion?
Uveitis
Diabetic complications
Steroids
Congenital origin
Infectious infiltration
128) A 74-year-old man with a history of smoking notices blood in his chronic daily sputum production. He has no fever or chills, but has lost 10 lb in the past 6 months. On examination, he has bilateral expiratory wheezes, and his fingers are clubbed. There are no lymph nodes and the remaining examination is normal. CXR reveals a left hilar mass. Which of the following suggests that the tumor is a small cell lung cancer?
Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH) secretion
Acanthosis nigricans
Cushing’s syndrome
Leukemoid reaction
Stevens-Johnson syndrome
129) A 35-year-old HIV-positive man (CD4+ cell count 150/mm³) is seen in the emergency department with right-sided chest pain. The patient has become progressively dyspneic over the past few days. Suddenly, 30 minutes ago he noticed a sharp pain in his chest associated with shortness of breath. His temperature is 37.7°C (99.9°F), blood pressure is 128/84 mm Hg, pulse is 102/min and regular, respiratory rate is 25/min, and oxygen saturation is 90% on room air. Physical examination reveals diminished right-sided breath sounds and hyperresonance. Jugular venous distention is 5 cm and there is no tracheal deviation. ECG shows sinus tachycardia. X-ray of the chest shows a right-sided pneumothorax occupying approximately 10% of the right thoracic cavity. Which of the following most likely caused this patient’s presentation?
Intravenous drug use
Kaposi’s sarcoma
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia
Toxoplasmosis
130) A 74-year-old man presents to his primary care physician complaining of dyspnea and cough with blood-tinged sputum for the past several weeks. He has diabetes and elevated cholesterol. Medications include a sulfonylurea and a statin. The patient has a 50-pack-year smoking history and a family history of hypertension. His vital signs are within normal limits. Physical examination reveals abdominal striae and moon facies, along with a truncal fat distribution. X-ray of the chest reveals a single central nodule, and follow-up CT again demonstrates the nodule and multiple solid hepatic masses. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Adenocarcinoma of the lung
Carcinoma metastatic to the lung
Large cell carcinoma of the lung
Small cell carcinoma of the lung
Squamous cell carcinoma of the lung
131) A 5-month-old infant has failed to gain weight despite a good appetite. The child’s mother reports that the baby has up to eight bulky, foul-smelling, oily stools per day. A sweat chloride test reveals a chloride level of 78 mEq/L (normal: <60 mEq/L). Which of the following sequelae is most likely to occur as a result of this patient’s disease?
Cirrhosis and subsequent hepatic failure
Dehydration, electrolyte abnormalities, and acute hypotension
Esophageal ulceration or strictures and upper gastrointestinal bleeding
Purple lines on the gums, red-brown discoloration of the urine, and renal tubular acidosis
Recurrent airway disease with eventual respiratory insufficiency associated with bronchiectasis
132) A 33-year-old farmer complains of recurrent episodes of wheezing after working in a barn where hay is stored. On auscultation, there are bibasilar crackles and heart sounds are normal. His laboratory work is normal with no increase in eosinophils and the chest x-ray (CXR) reveals patchy lower lobe infiltrates. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Asthma
Chronic obstructive lung disease
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis
Bronchiectasis
Sarcoidosis
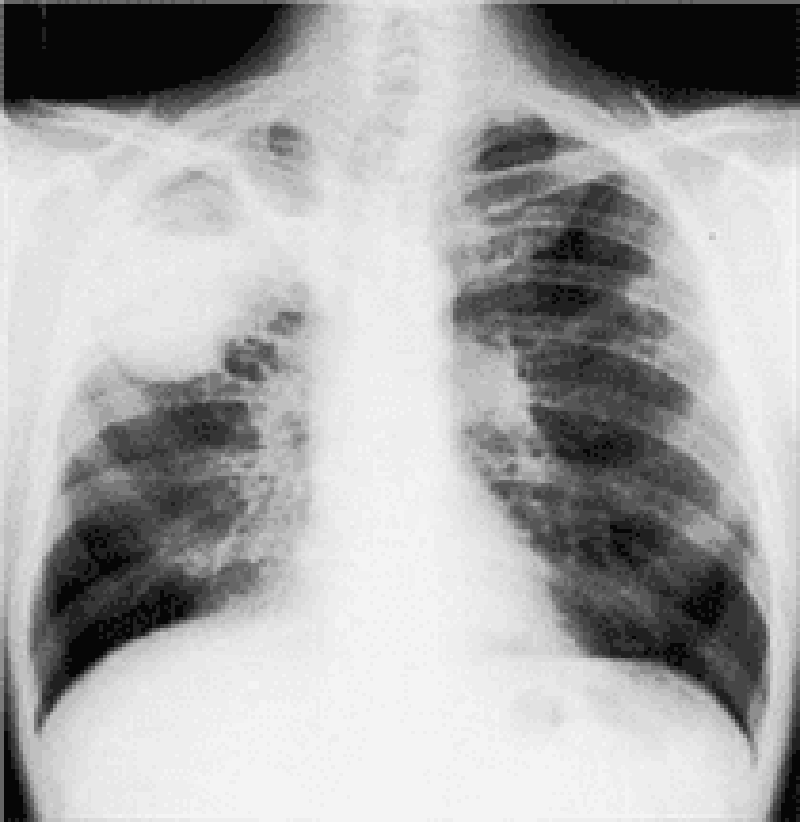
133) A 21-year-old nonsmoking college student comes to the local emergency department because pf cough, weight loss, and low-grade fever. Occasionally his sputum is tinged with blood. X-ray of the chest is shown in the image. He reports traveling to Haiti on a “medical mission” trip several years ago. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Aspergillosis
Klebsiella infection
Lung cancer
Sarcoidosis
Tuberculosis
134) A 53-year-old man presents to the clinic with complaints of increasing shortness of breath, a nagging cough, and weight loss over several months. He reports no history of cigarette smoking but has worked underground in the New York City subway system for the past 20 years. Spirometry demonstrates an FEV1: FVC ratio of 0.7 and an FEV1 value that is 60% of expected. The FEV1 improves to 70% of expected with bronchodilator treatment. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Asthma
Chronic aspiration
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Histoplasmosis
Tuberculosis
135) A 78-year-old woman is seen in the emergency department for difficulty breathing and cough over the past 4 hours. She has a history of congestive heart failure for which she takes hydrochlorothiazide, metoprolol, and enalapril. Her oxygen saturation is 92% on room air. On examination there is a high-pitched systolic crescendodecrescendo murmur best heard at the right upper sternal border with radiation to the carotids, and rales are present in both lung fields on inspiration. There is 2+ symmetrical pitting edema bilaterally in the lower extremities. X-ray of the chest shows an enlarged heart and prominent pulmonary vasculature. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the patient’s pulmonary edema?
Decreased capillary fluid oncotic pressure
Decreased interstitial fluid hydrostatic pressure
Increased capillary fluid hydrostatic pressure
Increased capillary permeability
Increased interstitial fluid oncotic pressure
136) A 56-year-old man is evaluated for chronic cough. It is present most of the time and is progressively getting worse over the past 3 years. With the cough he usually has white to yellow sputum that he has to expectorate. There is no history of wheezing, asthma, congestive heart failure (CHF), or acid reflux disease. He currently smokes one pack a day for the past 25 years. On examination, his chest is clear. CXR is normal and his forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) and forced vital capacity (FVC) on spirometry are normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
Early cor pulmonale
Chronic bronchitis
Asthma
Emphysema
137) A 35-year-old man is evaluated for symptoms of shortness of breath. He reports no other lung or heart disease. He smokes half pack a day for the past 10 years. On examination, his JVP is 2 cm, heart sounds normal, and lungs are clear. A CXR shows hyperinflation and increased lucency of the lung fields. A chest CT reveals bullae and emphysematous changes, while pulmonary function tests show an FEV1/FVC ratio of <70%. Evaluation of his family reveals other affected individuals. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Alpha1-antitrypsin deficiency
Beta-glycosidase deficiency
Glucose-6-phosphatase deficiency
Glucocerebrosides deficiency
Growth hormone deficiency
138) A 23-year-old man notices a gradual but progressive increase in breathing difficulty. He has a long history of back pain with prolonged morning stiffness. He has also had an episode of iritis in the past. On examination, there is reduced range of motion in the lumbar spine with forward flexion and pain on palpation of the sacroiliac joint and surrounding soft tissue. X-rays of the pelvis show erosions and sclerosis of the sacroiliac joint. Which of the following is the most likely pulmonary complication of this condition?
Fibrocavitary disease
Airflow obstruction
Bilateral lower lobe involvement
Pleural effusions
Hilar adenopathy
139) A 45-year-old Haitian immigrant presents to the emergency department with a chief complaint of productive, blood-tinged cough for 2 months. He has been in the United States for 1 month. His temperature is 40.1°C (104.2°F) and heart rate is 105/min. On physical examination he appears cachectic, and pulmonary rales are heard throughout his lung fields. X-ray of the chest reveals multiple bilateral upper lobe cavitary lesions with associated intrathoracic adenopathy. Results of sputum culture are pending. Which of the following tuberculosis medications can potentially cause optic neuritis?
Ethambutol
Isoniazid
Levofloxacin
Pyrazinamide
Rifampin
140) A 44-year-old woman has been complaining of a 4-year history of increasing dyspnea and fatigue. Physical examination reveals increased JVP and a reduced carotid pulse. Precordial examination reveals a left parasternal lift, loud P2, and right-sided S3 and S4. There are no audible murmurs. CXR reveals clear lung fields and an ECG shows evidence of right ventricular hypertrophy. Pulmonary function tests show a slight restrictive pattern. A diagnosis of primary pulmonary hypertension is made. Which of the following is the most likely cause of death in this condition?
Intractable left ventricular failure
Intractable respiratory failure
Massive PE
Intractable right ventricular failure or sudden death
Myocardial infarction
141) After an uncomplicated pregnancy and cesarean section for breech presentation, twins are born at 32 weeks’ gestation to a 24-year-old primigravida mother. Twin A weighs 1610 g (3.5 lb) and has Apgar scores of 8 and 9 at 1 and 5 minutes, respectively. Twin B weighs 1600 g (3.5 lb) and has Apgar scores of 7 and 8 at 1 and 5 minutes, respectively. Within minutes of birth, twin B becomes mildly cyanotic and tachypneic with subcostal retractions, expiratory grunting, and nasal flaring. Twin B’s blood pressure is 58/39 mm Hg, heart rate is 130/min, respiratory rate is 100/min, and temperature is 37.0°C (98.6°F). Twin B is intubated and given 70% fraction of inspired oxygen. Compared to twin A, what is twin B at greater risk of developing?
Apnea of prematurity
Gastroesophageal reflux disease
Hyperbilirubinemia
No difference because they are both pre- mature
Retinopathy of prematurity
142) A 32-year-old white man with HIV and a re- cent CD4+ cell count of 400/mm³ presents to the emergency department with a 3-day history of fever, anorexia, cough, and night sweats. He recently returned from a camping vacation in Arizona, approximately 1 month prior to presentation. He also describes diffuse joint pains. His temperature is 38.9°C (102°F), oxygen saturation is 99% on room air, and there is a rash on his arms and hands. There is dullness to percussion at the right lung base. X-ray of the chest reveals a small right-sided infiltrate and hilar lymphadenopathy. Sputum analysis does not reveal any organisms. He reportedly had a negative purified protein derivative test 2 months ago. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Coccidioidomycosis
Histoplasmosis
Lung carcinoma
Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia
Sarcoidosis
143) A 55-year-old man was admitted to the hospital 2 weeks ago for rapid onset of cough, fatigue, and pleuritic chest pain. He has worked as a sandblaster for the past year. When first seen in the hospital, he denied hemoptysis and smoking. Currently, the patient is intubated and on assist-control ventilation. His temperature is 36.7°C (98°F), pulse is 96/min, blood pressure is 138/85 mm Hg, and respiratory rate is 18/ min. A recent arterial blood gas study showed a pH 7.42, arterial carbon dioxide pressure of 36 mm Hg, and arterial oxygen pressure of 110 mm Hg while on 100% oxygen. Physical examination is significant for diffuse crackles throughout both lung fields, a loud pulmonic component of the second heart sound, and jugular venous distention of 9 cm with a prominent A wave, a left parasternal heave, and symmetric 3+ lower extremity pitting edema. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Asbestosis
Berylliosis
Byssinosis
Coal worker’s pneumoconiosis
Silicosis
144) A 30-year-old woman presents to her physician’s office because of 3 months of nonproductive cough, exertional dyspnea, fatigue, malaise, and blurred vision. She denies weight loss, fever, chills, sweats, recent travel, or sick contacts. She works on the assembly line of an electronics plant. Vital signs are unremarkable. Physical examination reveals she has tender red papules over her shins. The patient said she first noticed the bumps when she changed oral contraceptive pills (her only medication), but assumed they would disappear. X-ray of the chest shows bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy with pulmonary infiltrates. Laboratory findings are: WBC count: 5600/mm3, Hemoglobin: 14.3 g/dL, Platelet count: 300,000/mm3, Na+: 140 mEq/L, K+: 4.2 mEq/L, Cl−: 108 mEq/L, Ca2+: 16 mg/dL, CO2: 24 mmol/L, Blood urea nitrogen: 10 mg/dL, Creatinine: 1.0 mg/dL. Culture of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid is neg- ative. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Berylliosis
Fungal infection
Lymphoma
Sarcoidosis
Tuberculosis
145) A 58-year-old man presents to the emergency department complaining of fever and chills. The fever started last night and has not subsided, even though he took acetaminophen. He had a successful appendectomy 3 days ago and was discharged from the hospital 2 days ago. His only medication is ibuprofen, which is adequately controlling his pain. He is a 30-pack-year smoker with a chronic cough productive of white sputum. He has noticed increased sputum production, which has become yellowish-green. He denies dysuria, urgency, or frequency. His temperature is 38.4°C (101.1°F), heart rate is 88/min, respiratory rate is 16/min, and blood pressure is 126/74 mm Hg. On examination he appears to be tired but not in acute distress. Pulmonary examination is limited because deep inhalation causes coughing and slight abdominal pain. There is no tactile fremitus or dullness to percussion. He has a slightly erythematous, appropriately tender healing incision in the right lower quadrant without exudates and normal active bowel sounds. Extremities are warm and well perfused without erythema or edema. Pulses are intact. Which of the following most likely could have prevented this condition?
Aggressive incentive spirometry
Early removal of the Foley catheter
Early removal of the intravenous catheter
Pre- and postoperative antibiotic prophylaxis
Use of compression stockings and subcutaneous heparin
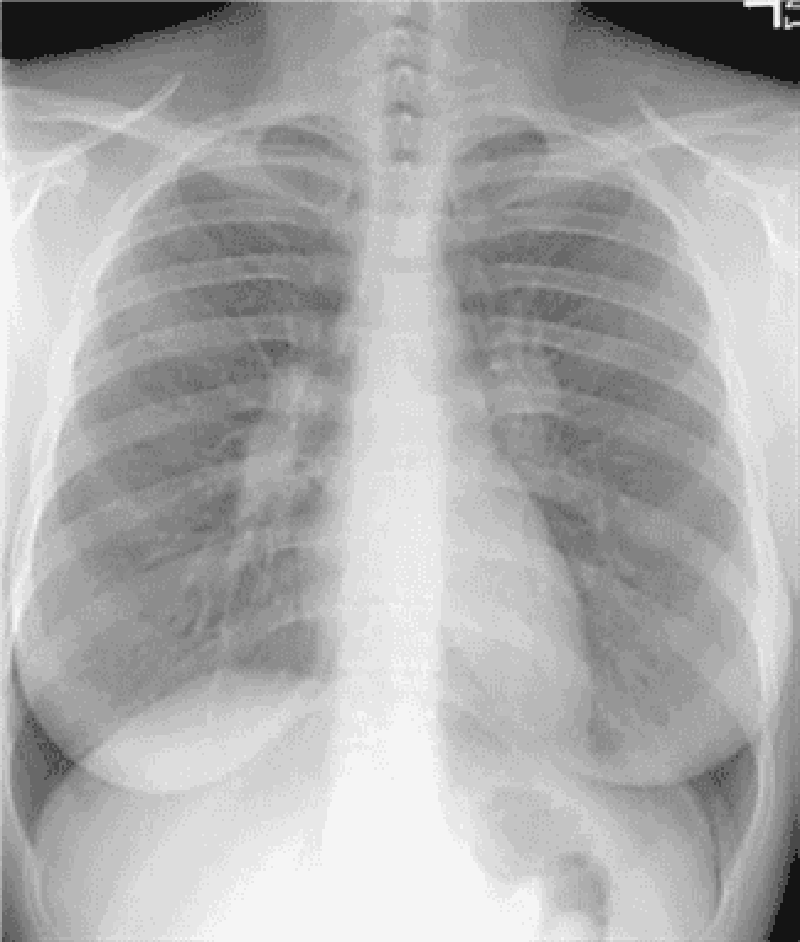
146) A 24-year-old African American woman presents with mild dyspnea on exertion, fever, and a rash on her legs. Her symptoms have come on gradually and she reports no pleuritic chest pain, hemoptysis or sputum production. She has no significant past medical history, smokes 10 cigarettes/day and is not taking any medications. Physical examination reveals generalized lymphadenopathy and tender erythematous nodules on her legs. CXR shows bilateral symmetric hilar adenopathy and reticulonodular changes in both lungs. She has a restrictive lung disease pattern on pulmonary function testing. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Hodgkin’s disease
Tuberculosis
Rheumatic fever
Sarcoidosis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
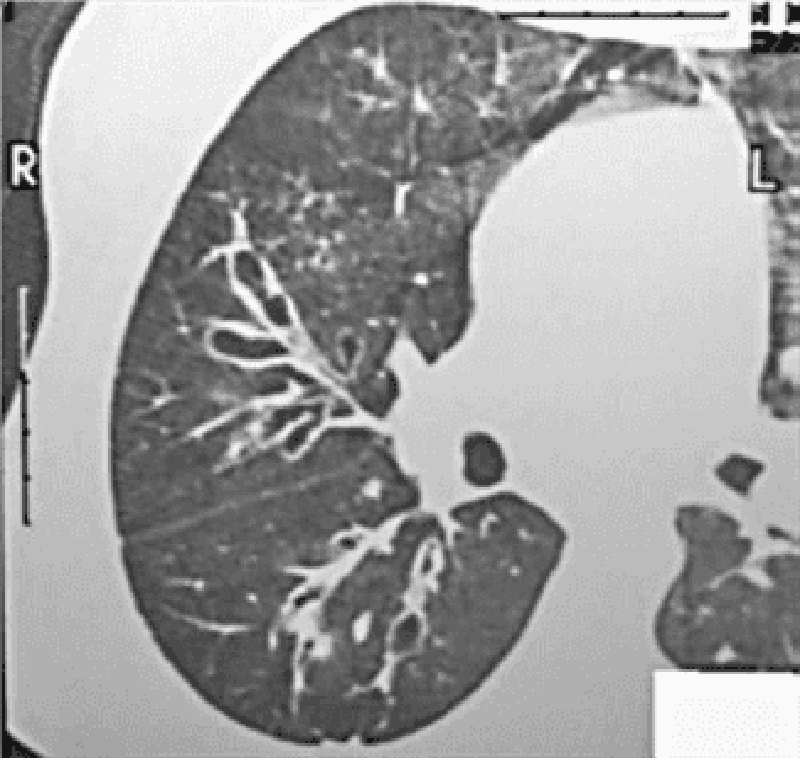
147) A 30-year-old man presents with coughing up blood and sputum. There is no associated dyspnea, fever, or pleuritic chest pain. His past medical history is significant for recurrent pneumonias and a chronic cough productive of foul-smelling purulent sputum. The sputum production is usually worse when lying down and in the morning. He quit smoking 5 years ago and started when he was 18 years old. On physical examination, he appears chronically ill with clubbing of the fingers. Wet inspiratory crackles are heard at the lung bases posteriorly. CXR shows scaring in the right lower lobe, which on chest CT scan is identified as airway dilatation, bronchial wall thickening, and grapelike cysts. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Bronchiectasis
Chronic bronchitis
Disseminated pulmonary tuberculosis
Pulmonary neoplasm
Chronic obstructive emphysema
148) A 23-year-old man is experiencing a flare of his asthma. He is using his salbutamol inhaler more frequently than usual and despite increasing his inhaled steroids he is still short of breath. Previously his asthma was considered mild with no severe exacerbations requiring oral steroids or hospitalization. With his flare, he has recurrent episodes of bronchial obstruction, fever, malaise, and expectoration of brownish mucous plugs. On examination, there is bilateral wheezing. The heart, abdomen, neurologic, and skin exams are normal. CXR reveals upper lobe pulmonary infiltrates; the eosinophil count is 3000/mL, and serum precipitating antibodies to Aspergillus are positive. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Ascaris infestation
Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis
Churg-Strauss allergic granulomatosis
Löeffler’s syndrome
Hypereosinophilic syndrome
149) A 55-year-old woman presents with coughing up blood and sputum. She gives a history of recurrent pneumonias and a chronic cough productive of foul-smelling purulent sputum. The sputum production is worse on lying down and in the morning. On physical examination, she appears chronically ill with clubbing of the fingers. Wet inspiratory crackles are heard at the lung bases posteriorly. There are no hepatosplenomegaly or any palpable lymph nodes. CXR shows scaring in the right lower lobe, which on chest CT scan is identified as airway dilatation, bronchial wall thickening, and grapelike cysts. Which of the following is a recognized precursor to this patient’s condition?
Bronchial asthma
Cigarette smoking
Lung infection and impairment of drainage
Lung cancer
Silicosis
150) A 50-year-old man presents with excessive day- time sleepiness and a history of snoring. One week ago, he fell asleep while driving his car and got into a minor accident. On examination, he is obese (body mass index [BMI] >30) and his blood pressure is 160/90 mm Hg. His lungs are clear and heart sounds are distant. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for the symptoms associated with this condition?
Related to cardiac dysfunction
Neuropsychiatric and behavioral
Pulmonary
Gastrointestinal (GI)
Musculoskeletal
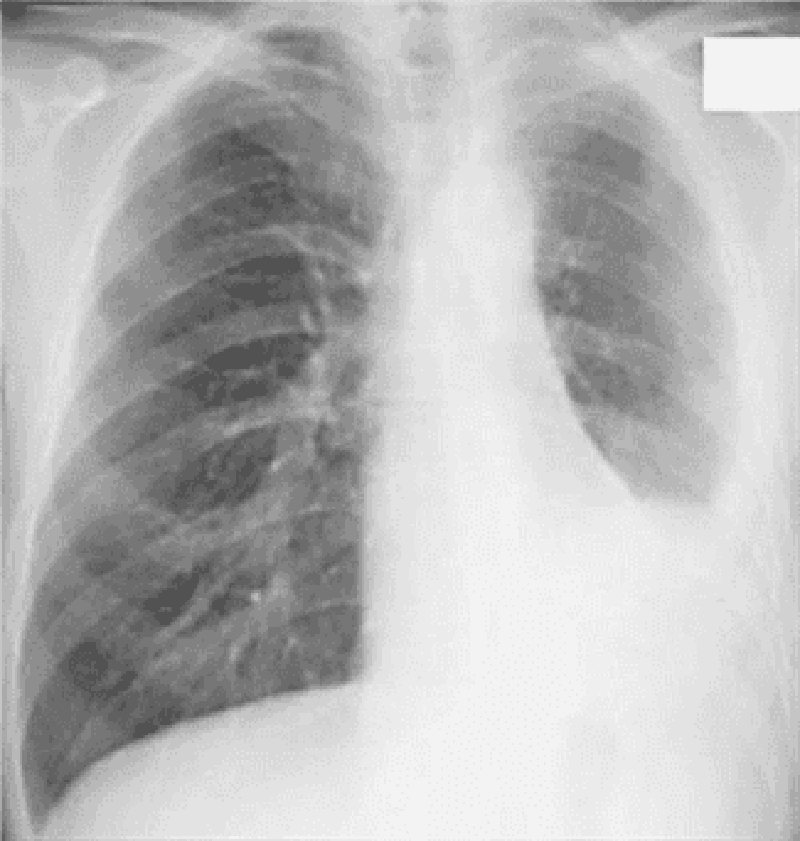
151) A 58-year-old steam pipe worker presents with a vague ache in the left chest and mild dyspnea of several months’ duration. There is dullness on percussion of the left chest associated with diminished breath sounds. His CXR is shown in Fig. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Pleural metastases
Paget’s disease
Mesothelioma and asbestosis
Pleural effusion
Multiple myeloma
152) A 23-year-old man presents with coughing up blood and sputum. He gives a history of recurrent pneumonias and a chronic cough productive of foul-smelling purulent sputum. The sputum production is worse when lying down and in the morning. On physical examination, he appears chronically ill with clubbing of the fingers. Wet inspiratory crackles are heard at the lung bases posteriorly. There are no hepatosplenomegaly or any palpable lymph nodes. CXR shows scaring in the right lower lobe, which on chest CT scan is identified as airway dilatation, bronchial wall thickening, and grapelike cysts. Which of the following is sometimes seen in this condition?
Lung cancer
Dextrocardia
Fungal infection
Carcinoid syndrome
Hodgkin’s disease
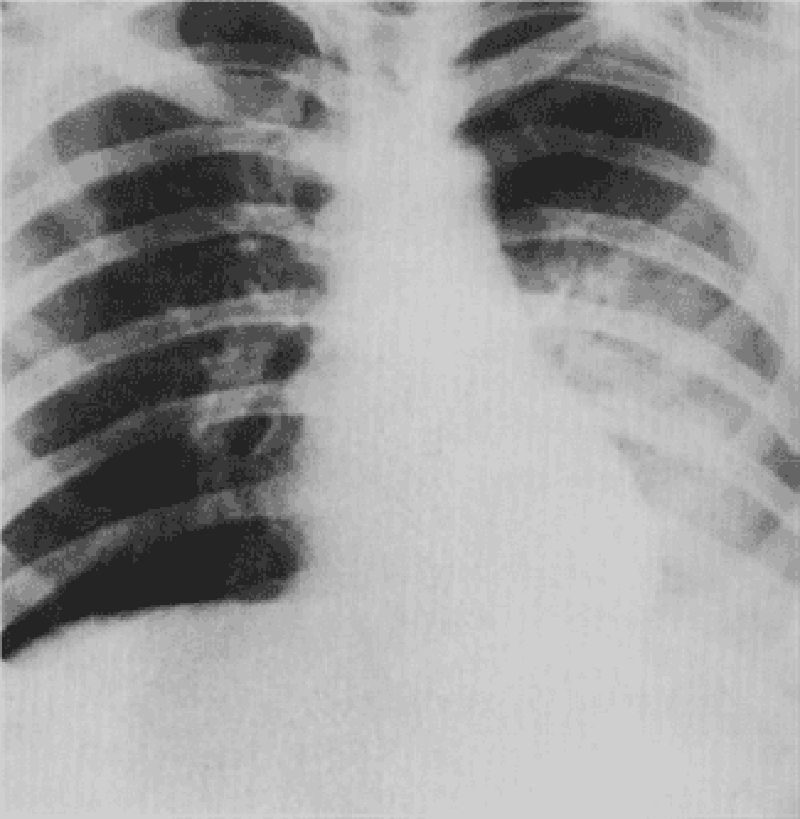
153) A 27-year-old man presents with chest pain and feeling unwell. He describes cough with blood-tinged sputum, chills, and fever of 2 days’ duration. Physical findings reveal dullness and moist rales in the left lower chest. His CXR is shown in Fig. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Pneumonia, left lower lobe
Atelectasis, left lower lobe
PE
Tuberculosis
Sarcoidosis
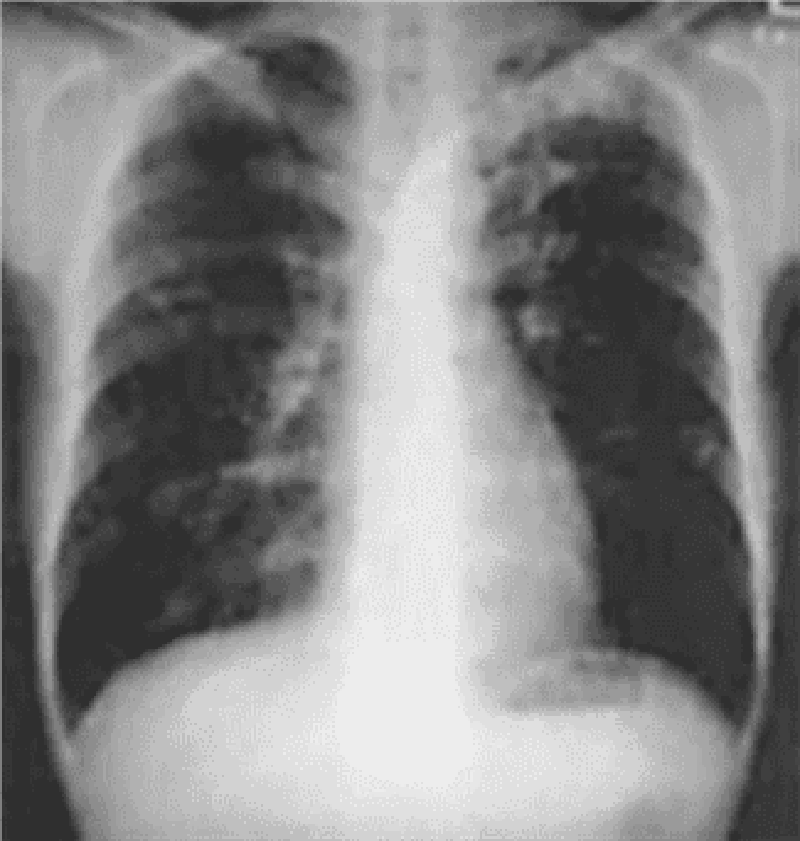
154) A 40-year-old man is seen for an insurance assessment. He has no past medical history and feels well. His compete physical examination is normal. His biochemistry, complete blood count (CBC), ECG, and urinalysis are also normal. His CXR is abnormal and presented in Fig. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Hamartoma of the lung
Tuberculous granuloma of the left apex
Osteochondroma of the left 4th rib
Bronchogenic carcinoma
Pulmonary metastases
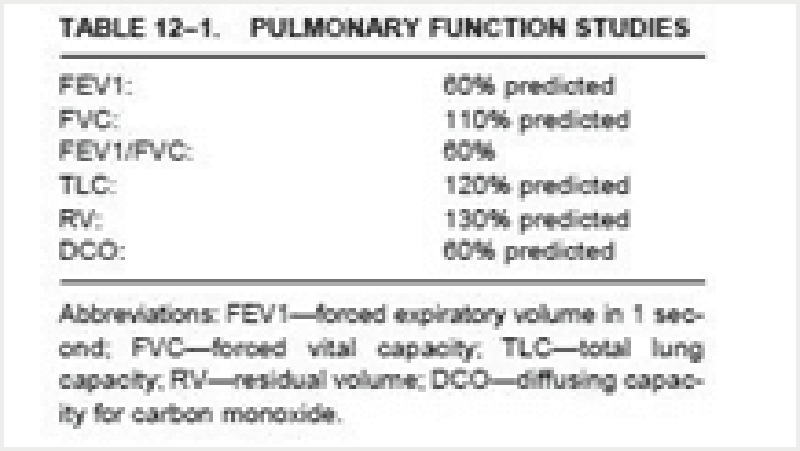
155) The pulmonary function studies shown in Table 12–1 are of a 65-year-old man with severe dyspnea and cough. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Emphysema
Lobar pneumonia
Chronic bronchitis
Acute bronchitis
CHF
156) A 34-year-old woman is complaining of progressive and worsening shortness of breath. Her symptoms first started 3 years ago, and she now gets dyspneic and fatigued while doing her activities of daily living. Her past medical history is not significant and she not taking any medications. Physical examination reveals increased JVP and a reduced carotid pulse. Precordial examination reveals a left parasternal lift, loud P2, and right-sided S3 and S4. There are no audible murmurs. CXR reveals clear lung fields and an ECG shows evidence of right ventricular hypertrophy. Pulmonary function tests are normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Asthma (without wheezing)
Primary pulmonary hypertension
Pulmonary veno-occlusive disease
Pulmonary leiomyomatosis
Silent tricuspid valve disease
157) A 45-year-old woman has severe symptoms of epigastric and abdominal pain after eating. A trial of acid suppression therapy with proton pump inhibitors (PPI) only partially improved her symptoms. She undergoes elective outpatient upper endoscopy, which is positive for a small duodenal ulcer. Two hours later, she is short of breath and complaining of severe anterior chest pain, which is made worse with deep inspiration. On examination, she looks unwell, blood pressure is 150/90 mm Hg, pulse 110/min, and lungs are clear. Heart sounds are normal but an “extra crunching” type sound is intermittently heard. CXR demonstrates air surrounding the heart. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Acute pericarditis
Acute cardiac ischemia
Acute mediastinitis
Aortic dissection
Pneumothorax
158) A 31-year-old G4P3 woman gave birth via repeat cesarean section to a full-term, 3700-gm (8.2-lb) baby girl. There were no complications during the pregnancy or delivery. Two hours after the birth the resident is called to evaluate the baby girl. She is afebrile but is breathing rapidly with mild subcostal retractions. Breath sounds are equal and clear bilaterally. S1 and S2 are normal and the point of maximal intensity is not displaced. X-ray of the chest reveals flattened diaphragms, prominent vascular markings, and fluid lines in the fissures. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Diaphragmatic hernia
Neonatal respiratory distress syndrome
Pulmonary hemorrhage
Pulmonary interstitial emphysema
Transient tachypnea of the newborn
159) A 67-year-old man presents to his primary care physician with complaints of dyspnea on exertion over the past 6 months that has progressively worsened to dyspnea at rest. He denies cough and wheezing and has had no fevers, night sweats, or unintentional weight loss. The man has never smoked and worked as a ship-builder for >30 years. Which of the following findings on x-ray of the chest would confirm the most likely diagnosis?
Bilateral diffuse infiltrates
Bilateral hilar adenopathy
Consolidation of lung tissue
Focal mass with air bronchograms
Multiple pleural plaques with patchy parenchymal opacities
160) A 16-year-old girl is brought to clinic by her mother, who complains that the girl is "difficult to get along with lately." The mother says her daughter can no longer concentrate for prolonged periods and is easily fatigued. She has found her tossing in her sleep at night. She says that her daughter is generally considered by friends and family to be "high strung." Upon inquiry, the girl admits to feeling extremely apprehensive when taking tests at school. She feels this stems from her naturally competitive nature and her desire to be class valedictorian. She worries about being accepted to a good university and then business school. She says that she is unable to control her thoughts and sometimes takes a day off from school to "escape all the stress that comes with it” Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Panic disorder
. Generalized anxiety disorder
. Obsessive-compulsive disorder
. Avoidant personality disorder
. Simple phobia
161) A 30-year-old man presents to his primary care physician and describes a sense of generalized fatigue. He reports having been very energetic and healthy during his college days but says that "everything has seemed to be go wrong" for at least the last 6 years. He eats poorly and has lost 8 pounds over the last three years. He sleeps 12 hours per night and says that he has difficulty concentrating on most tasks. His past medical history is otherwise unremarkable, and he does not abuse drugs or alcohol. The patient says that he is not suicidal and still enjoys watching baseball with his friends. Based on the above presentation, what is the most likely diagnosis?
. Adjustment disorder
. Dysthymia
. Major depressive disorder
. Generalized anxiety disorder
. Substance-induced mood disorder
162) A single mother brings her 10-year-old son to see the pediatrician. The mother says that she is "absolutely fed up" with her son's behavior and is unable to control him. The boy frequently gets into fights with his siblings, neighbors, and classmates at school. When asked to help with household chores, he refuses. He is very short-tempered and argues frequently with his parents and teachers. A few days ago, he got into an argument with the elderly woman who lives next door, and in a fit of anger he "grabbed a marker and wrote an obscenity on her front door." What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Conduct disorder
. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
. Tourette's disorder
. Oppositional defiant disorder
. Antisocial personality disorder
163) A middle-aged, divorced woman brings her 18-year-old daughter to the physician with the complaint that her daughter "seems abnormal." She is concerned because her daughter has no close friends, does not date, and shows no interest in the activities that are popular with young adults. The girl prefers solitude and keeps to her room for most of the day. When she does go out, she hikes in the woods alone for hours at a time. She attends a local university where she studies engineering and performs well academically. During the office visit, the daughter avoids eye contact. In response to questioning about her reasons for being aloof, she replies, "I just don't enjoy being in the company of others. People do not interest me much and I would rather keep to myself." Her thought process appears devoid of delusions or hallucinations. Which of the following personality disorders is demonstrated by her behavior?
. Schizotypal personality disorder
. Dependent personality disorder
. Schizoid personality disorder
. Avoidant personality disorder
. Borderline personality disorder
164) A middle-aged, divorced mother brings her 19-year -old daughter in for an evaluation. She says that her daughter has "a serious problem." The woman is concerned because her daughter always keeps to herself, does not date, has no close friends, and refuses to participate in activities popular with women of her age. The daughter is extremely fascinated by witchcraft, spending countless hours in her room gazing into a crystal ball and muttering under her breath. When confronted about her behavior, she says, "I have some supernatural powers that I am not willing to discuss." She attends college regularly and earns good grades. Which one of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Avoidant personality disorder
. Dependent personality disorder
. Schizoid personality disorder
. Schizotypal personality disorder
. Schizophrenia
165) A Hispanic married couple brings in their 17-year-old son because his behavior has been abnormal for the past two weeks. Normally, the boy is polite and soft spoken but he has recently become irritable and rude. His parents dismissed his behavior as a "phase" with the expectation that he would grow out of it, but they became very concerned upon discovering that he had been spending large sums of money from his college fund without their consent. When questioned by his father about his strange behavior, the boy responded, "I'm on a secret mission. The king of Norway has sent me here to spy on the U.S. government." His vital signs include temperature of 36.6°C (98.0°F), blood pressure of 132/94 mm Hg, pulse of 105/min, and respirations of 18/min. On physical examination, the boy appears to be in no distress. His pupils are dilated. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Brief psychotic episode
. Manic episode
. Heroin intoxication
. Schizophrenia
. Amphetamine intoxication
166) A 32-year-old woman is brought in to clinic by her husband of four years because she has been "restless and hyperactive" for the past two weeks. The husband describes her as unusually talkative, and says she speaks so quickly that others have difficulty understanding her. She has spent large sums of money on new clothing, makeup, and perfumes. When asked about her purchases, she says that she needs to look elegant since she is "a member of the royal family." She stays up very late each night to thoroughly clean the house, often sleeping only an hour or two. The husband has never observed these symptoms before in his wife. Physical examination of her is unremarkable. Which of the following is this woman most likely suffering from?
. Manic episode
. Hypomanic episode
. Bipolar II disorder
. Dysthymic disorder
. Brief psychotic disorder
167) A 74-year-old woman is brought to the clinic by her daughter-in-law. The woman is a regular patient and has a long history of hypertension and ischemic heart disease. She lives with her son and daughter in-law, who are concerned that she has become increasingly forgetful over the past year. Initially, they attributed her forgetfulness to normal aging but her memory impairment has progressively worsened over the past several months. Of late, she has also developed some difficulty with speech and now is no longer able to perform the activities of daily living. Which one of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Pick disease
. Pseudodementia
. Multi-infarct dementia
. Alzheimer's dementia
. Normal pressure hydrocephalus
168) A 4-year-old boy is brought to his pediatrician by his mother for "multiple fainting spells." Although physical examination reveals no abnormalities, the boy is admitted to the hospital for an extensive diagnostic workup. Laboratory evaluation reveals no abnormalities except for low serum glucose, high serum insulin, and low levels of serum C-peptide. The test results are revealed to the boy's mother, who works as a nurse in the hospital. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Factitious disorder
. Malingering
. Child abuse
. Hypoglycemia
. Munchausen syndrome by proxy
169) An 18-year-old college freshman is brought to the emergency department by his friends. They say that he is normally happy and good-natured, but became unusually withdrawn and aloof a few hours after a football game. He complains of a dry mouth. Physical examination reveals injected conjunctivae and tachycardia. Which of the following is most consistent with this patient's presentation?
. Opioid overdose
. Adrenal crisis
. Alcohol intoxication
. Cocaine withdrawal
. Cannabis abuse
170) A 34-year-old male presents to the emergency department complaining of severe lower back pain. He rates the pain as 10/10 in severity and describes it as non-radiating, sudden in onset, and aggravated by movement. He refuses to be examined, insisting that any examination will worsen his pain. He denies any history of trauma or lifting of heavy weights. He says, "Doc, the only thing that can relieve my pain is morphine ... You've got to have mercy on me." The patient has a long history of opioid dependence and has been admitted to the hospital multiple times while intoxicated. His last admission was two weeks ago and he was referred to a drug rehabilitation program upon discharge. Given the clinical presentation, what is the most likely diagnosis?
. Factitious disorder
. Hypochondriasis
. Malingering
. Conversion disorder
. Disc herniation
171) A young Caucasian mother brings her 5-year-old daughter to the pediatrician two months after the girl first began attending kindergarten. She says that earlier this week, her daughter's teacher called to say that the girl persistently refuses to answer questions or to speak to others in class. The teacher added that the girl also does not smile at, play with, or otherwise engage her fellow students. The mother finds this very surprising because her daughter is very verbal and talkative at home, plays happily with her siblings, and is an affectionate child. Further questioning reveals that the girl is "a little shy" at social gatherings. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Separation anxiety disorder
. Social phobia
. Selective mutism
. Autism
. Stranger anxiety
172) A 12-year-old boy is accused of setting his neighbor's house on fire. His parents describe him as a hyperactive, talkative child. He earns excellent grades in school but frequently gets into fights with schoolmates and siblings. Two years ago, he was caught setting the interior of his father's car on fire. He has also been linked to several suspicious fires in the neighborhood, though no criminal charges were brought against him Based on this information, what is the most likely diagnosis?
. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
. Pyromania
. Oppositional defiant disorder
. Antisocial personality disorder
. Conduct disorder
173) A 39-year-old agitated female with an unknown medical history is brought to the emergency department by police after she was found assaulting an innocent pedestrian on the street. She tells the attending physician that she has unusual powers and has been sent on a special mission by God. She is proud of frequently communicating with God, both telepathically and verbally, and says that he assists her in "punishing all of the wicked people in the world” Which of the following is most demonstrated in her thought content?
. Magical thinking
. Ideas of reference
. Grandiose delusion
.Illusion
. Hallucination
174) A 28-year-old female presents to her family doctor with her mother, who complains that her daughter has been behaving eccentrically and has been socially withdrawn for the past year. The mother says that her daughter used to be very lively and friendly, but that she abruptly quit her job as a data analyst one year ago and now prefers to stay home in her bedroom most of the time. The patient is thoroughly evaluated by a psychiatrist. During that interview, she reveals to the psychiatrist that she constantly hears "so many voices" in her head. The voices tell her various things of a critical and suspicious nature. She also adds that she feels very sad and has had numerous severe crying spells after her pet dog's death four months ago. She prefers to be alone and does not enjoy interacting with others. She has poor sleep and little appetite. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this woman?
. Schizophrenia
. Schizoaffective disorder
. Major depression with psychotic features
. Dysthymia
. Cyclothymia
175) A 10-year old girl is brought to the office by her mother for the evaluation of recent changes in behavior. She has been sleeping poorly at night and has started wetting her bed. Her school grades have dropped significantly, and she has become irritable and cranky. She refuses to sleep at night until her father returns home and goes to bed. Her father works as a taxi driver, and is an alcoholic. Her mother is a close friend of yours, and appears very concerned. Prior to this office visit, you have known this girl to be cheerful and lively; however, as you attempt to talk to the young girl in the office, she suddenly bursts into tears. Which of the following should you consider at this point?
. Major depression with melancholic features
. Physical abuse
. Anxiety disorder
. Panic disorder
. Specific phobia
176) A 19-year-old woman makes an appointment to see her primary care physician about a "personal concern." When she comes in for her visit, she says that she has been "deeply depressed" for the past several months because of her "enormous nose." She proceeds to describe in detail the numerous cosmetic aspects of her nose that prove troubling. She says that she is now so embarrassed that she is unwilling to go out with friends because "everyone just stares at my nose." She finds it difficult to concentrate on her studies because she is preoccupied with thoughts about undergoing corrective surgery. On examination, her nose appears completely normal. She pleads for a referral to a good plastic surgeon. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Hypochondriasis
. Body dysmorphic disorder
. Major depression
. Somatization disorder
. Delusional disorder, somatic type
177) You are an internist making your rounds at a local nursing home. While you are reviewing a medical chart, one of the nurses approaches you to complain about a 62-year-old male patient who frequently masturbates in front of the staff and other nursing home residents. He has been taking olanzapine for years for schizophrenia. Upon interviewing him, you find the patient's thought processes to be devoid of hallucinations or delusions. There are several times when he laughs inappropriately during the interview. His speech is rambling and unpredictably shifts from one topic to another. Based on his clinical presentation, how should his illness be classified?
. Schizophrenia, catatonic type
. Schizophrenia, undifferentiated type
. Schizophrenia, disorganized type
. Schizophrenia, paranoid type
. Schizophrenia, residual type
178) A 27-year-old male presents to clinic complaining of "marital problems." He says that for the past year that he has been married, he and his wife have not successfully had sexual intercourse on even one occasion. He strongly feels that she either finds him physically unattractive or is having an affair with another man. He adds that he is extremely frustrated with his wife "contracting herself," which prevents any kind of vaginal penetration. After several failed attempts, his wife now avoids any sexual intimacy with him. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Hypoactive sexual desire
. Sexual aversion disorder
. Female sexual arousal disorder
. Female orgasmic disorder
. Vaginismus
179) A 19-year-old student is referred to the university health center for inability to complete his assignments. He has always been a good student, and was valedictorian of his high school class. However, since starting college, he has found it difficult to keep up with all the work. He audio-records every class, playing the tapes back later in the day to transcribe each entire lecture word for word. He admits to sometimes needing to go over certain sections multiple times to be sure he has heard correctly. He also takes a long time to complete assignments, as he always checks his work multiple times prior to handing it in. Because of this, he has had to ask for many extensions on his assignments. He is sure to complete all his assignments, even after they have been reviewed in class and even though they are not graded. He spends all his time doing his classwork, and is not involved in social activities. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Asperger's disorder
. Generalized anxiety disorder
. Obsessive-compulsive disorder
. Obsessive-compulsive personality disorder
. Schizoid personality disorder
180) A 46-year-old man with a history of medication-controlled hypertension sees his doctor for a routine check-up. His blood pressure is 115/80 mm Hg and an electrocardiogram shows a normal sinus rhythm. The doctor notes that the man seems more down than usual. The man admits that he has been "stressed out" for the past two weeks, as a few people at work recently quit and he has had to take on more work while management finds replacements. He has been sleeping poorly at night, feels tired during the day, and states that he hates his job right now, but has no other choice. He continues to get his work done and enjoys social activities, remarking that he "can still golf on the weekends." What is the patient's most likely diagnosis?
. Adjustment disorder with depressed mood
. Acute stress disorder
. Major depressive disorder
. Primary insomnia
. Normal human experience
181) An anxious mother brings her 4-year-old son to clinic for a new patient visit. She says that her son was progressing well developmentally and meeting all milestones until three months ago. Since then, she and her husband have noticed a marked restriction in the boy's activities. He keeps to himself, refuses to play with his siblings, speaks only when spoken to, and appears indifferent to the presence of others. Attempts to engage the child in conversation are unsuccessful. He seems disinterested and refuses to make eye contact. While in the examination room, he starts banging his head against the wall. Given this clinical presentation, which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Autism
. Rett disorder
. Childhood disintegrative disorder
. Asperger syndrome
. Oppositional defiant disorder
182) A 59-year-old Caucasian female presents to the emergency department with sudden onset paralysis of her bilateral lower extremities. She has no other symptoms. Physical examination reveals normal tone, normal deep tendon reflexes, and no Babinski sign. Her motor strength is 3/5 in both lower extremities. The remainder of her examination is unremarkable. The patient dramatically improves after she is injected with sodium amytal. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Histrionic personality disorder
. Malingering
. Munchausen syndrome by proxy
. Conversion disorder
. Factitious disorder
183) A mother brings in her 3-year-old son to the pediatrician because she is concerned about his "poor development." She says that she thinks her son's behavior is "very different from that of other children his age." She says that ever since he was a toddler, he has seemed indifferent to her presence. She previously attributed this to her son being "unique" compared to his two older sisters. However, she is increasingly worried about her son because he does not play with his siblings or the neighborhood children who come to visit, and she suspects that his speech development is limited. Upon examination, the child is spinning continuously in a circle. When questions are asked of him, he makes no eye contact and responds with "A house for the mouse." His physical appearance is otherwise normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Tourette's disorder
. Schizotypal disorder
. Avoidant personality disorder
. Schizoid personality disorder
. Autism
184) A 36-year-old known patient of yours presents for a routine annual examination. Toward the end of the visit, she glumly mentions that she intends to file for a divorce from her husband. She says that he is always in an irritable or depressed mood, and that she is "sick and tired of him spending huge sums of money on gambling." Although she was aware of his placing the occasional bet before they got married, she says his passion for gambling has increased significantly since his mother's death two months ago. He was recently fired from his job as an insurance agent after he was caught forging signatures in an attempt to finance some gambling trips to Las Vegas. She has confronted him about his behavior on many occasions in the past, but he has always denied that it was a problem. Now he admits that he finds it hard to control himself and that he is in debt to several creditors. Although he has lost a considerable amount of money, he is convinced that he could win it all back if he could just borrow enough from friends. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Bipolar disorder, manic episode
. Obsessive-compulsive disorder
. Antisocial personality disorder
. Pathological gambling
. Adjustment disorder
185) An anxious mother brings in her 12-year-old daughter to your clinic for "severe hair loss". On examination, you find several alopecic patches on her head. While taking a detailed history, you find out that the young girl has been pulling out her hair when stressed. Although she has been indulging in this behavior periodically since childhood, she finds a recent increase in the same. She reveals to you that she is "really nervous" about her upcoming exams, and has disturbed sleep. She also adds that she feels so stressed that she has been avoiding going out with her friends and keeps to her books all the time. She denies any alterations in weight, but does admit to a decreased appetite. What do you think is the underlying diagnosis in this case?
. Alopecia areata
. Lupus erythematosus
. Trichotillomania
. Generalized anxiety disorder
. Major depressive disorder
186) A 21-year-old woman presents to the physician at her mother's urging because she has been experiencing significant sleep disturbances. Three months ago, she was the victim of a sexual assault in the parking lot of her workplace. Since then, she has had recurrent nightmares about the assault, and dreads falling asleep at night. During the day, she has flashbacks about the assault. She has become very withdrawn, quit her job, and avoids other people. The woman is very distressed about the flashbacks and says that they "dominate her life." She has difficulty concentrating and startles easily when others speak to her. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Acute stress disorder
. Post-traumatic stress disorder
. Major depressive disorder
. Adjustment disorder
. Acute psychosis
187) A 32-year-old married woman presents with lower back pain that has persisted for the past week. She says she developed the pain after lifting some heavy furniture. She denies any other symptoms. A thorough physical examination reveals mild paraspinal muscle spasm. There is no significant pain with a straight leg raise on either side. Multiple bruises on her abdomen, back, and chest are also evident. When the topic of the bruises is raised, the woman becomes tearful and begins to cry. Which of the following is the most appropriate response?
. "Is someone physically abusing you?"
. "It would seem that someone is physically abusing you."
. "Would you like to tell me a little more about these bruises?"
. "Physical abuse is against the law. I recommend you file a report with the police if you have been a victim of an assault."
. "I will give you a muscle relaxant to resolve your back pain."
188) A 31-year-old Caucasian female with a chronic history of schizophrenia presents for a prescription refill at her local mental health clinic. She has been treated with olanzapine for the last six months. The psychiatrist notes at this visit that the woman appears less agitated and complains of fewer auditory hallucinations. When asked questions, the woman gives detailed but irrelevant responses. Her answers drift away from the subject but eventually return. Which of the following is she demonstrating?
. Flight of ideas
. Circumstantiality
. Tangentiality
. Lose associations
. Perseveration
189) A 27-year-old female is brought to the emergency department by her husband after she fainted at home. The patient admits that she has been fasting and exercising vigorously for the past two days to compensate for the excessive amount of food she ate three days ago. She admits to a similar pattern of eating large amounts of food followed by a period of fasting since she lost her job a few months ago. She is very distressed by these "uncontrollable eating episodes" because she feels awful afterward. Periodically, she breaks down in tears while telling her story. Review of systems is otherwise unremarkable. Her menstrual periods are regular. Vital signs are temperature 37°C (98.6°F), blood pressure 98/62 mmHg, pulse 96/min, and respiratory rate 14/min. Her height is 5'4" (163 cm) and weight is 120 lbs (54 kg). Physical examination is unremarkable. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Anorexia nervosa
. Borderline personality disorder
. Bulimia nervosa
. Histrionic personality disorder
. Major depression
190) A 42-year-old man comes to the emergency room with the chief complaint that “the men are following me.” He also complains of hearing a voice telling him to hurt others. He tells the examiner that the news anchorman gives him special messages about the state of the world every night through the TV. Which of the following psychiatric findings best describes this last belief of the patient?
. Grandiose delusion
. Illusion
. Loose association
. Idea of reference
. Clouding of consciousness
191) A 32-year-old woman is seen in an outpatient psychiatric clinic for the chief complaint of a depressed mood for 4 months. During the interview, she gives very long, complicated explanations and many unnecessary details before finally answering the original questions. Which of the following psychiatric findings best describes this style of train of thought?
. Loose association
. Circumstantiality
. Neologism
. Perseveration
. Flight of ideas
192) An 18-year-old man is seen by a psychiatrist in the emergency room. During the history, the patient is asked to describe his mood. He answers the following, “My mood is flextitating, I am up and down.” The patient is exhibiting which of the following thought disorders?
. Clang association
. Thought blocking
. No thought disorder is apparent
. Tangentiality
. Neologism
193) A 56-year-old man has been hospitalized for a myocardial infarction. Two days after admission, he awakens in the middle of the night and screams that there is a man standing by the window in his room. When the nurse enters the room and turns on a light, the patient is relieved to learn that the “man” was actually a drape by the window. This misperception of reality is best described by which of the following psychiatric terms?
. Delusion
. Hallucination
. Illusion
. Projection
. Dementia
194) A 22-year-old woman is seen by a psychiatrist in the emergency room after she is found walking in the middle of a busy street with no shoes on. During her interview she is asked to count backwards from 100 by 7’s. Which of the following best describes the cognitive functions being tested by this request?
. Orientation
. Immediate memory
. Fund of knowledge
. Concentration
. Abstract reasoning
195) A 72-year-old woman is admitted to the burn unit with second- and third-degree burns covering 35% of her body, which she received in a house fire. At 8 pm on the fourth day of her hospital stay, she pulls out her IV and begins screaming that people are trying to hurt her. Several hours later she is found to be difficult to arouse and disoriented. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Emergence of an underlying dementia
. Brief reactive psychosis
. Acute manic episode
. Delirium
. Acute stress disorder
196) A psychiatric resident is called to consult on the case of a 75-year-old woman who had undergone a hip replacement 2 days before. On examination, the resident notes that the patient states the date as 1956, and she thinks she is at her son’s house. These impairments best illustrate which aspect of the mental status examination?
. Concentration
. Memory
. Thought process
. Orientation
. Level of consciousness
197) A 52-year-old man is sent to see a psychiatrist after he is disciplined at his job because he consistently turns in his assignments late. He insists that he is not about to turn in anything until it is “perfect, unlike all of my colleagues.” He has few friends because he annoys them with his demands for “precise timeliness” and because of his lack of emotional warmth. This has been a lifelong pattern for the patient, though he refuses to believe the problems have anything to do with his personal behavior. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis for this patient?
. Obsessive-compulsive disorder
. Obsessive-compulsive personality disorder
. Borderline personality disorder
. Bipolar disorder, mixed state
. Anxiety disorder not otherwise specified
198) A 23-year-old woman comes to the psychiatrist because she “cannot get out of the shower.” She tells the psychiatrist that she has been unable to go to her job as a secretary for the past 3 weeks because it takes her at least 4 hours to shower. She describes an elaborate ritual in which she must make sure that each part of her body has been scrubbed three times, in exactly the same order each time. She notes that her hands are raw and bloody from all the scrubbing. She states that she hates what she is doing to herself but becomes unbearably anxious each time she tries to stop. She notes that she has always taken long showers, but the problem has been worsening steadily for the past 5 months. She denies problems with friends or at work, other than the problems that currently are keeping her from going to work. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder
. Obsessive-compulsive disorder
. Obsessive-compulsive personality disorder
. Separation anxiety disorder
. Brief psychotic disorder
199) A 23-year-old woman comes to the emergency room with the chief complaint that she has been hearing voices for 7 months. Besides the hallucinations, she has the idea that the radio is giving her special messages. When asked the meaning of the proverb “People in glass houses should not throw stones,” the patient replies, “Because the windows would break.” Which of the following mental status findings does this patient display?
. Poverty of content
. Concrete thinking
. Flight of ideas
. Loose associations
. Delirium
200) A 69-year-old man is brought to see his physician by his wife. She notes that over the past year he has experienced a slow, stepwise decline in his cognitive functioning. One year ago she felt his thinking was “as good as it always had been,” but now he gets lost around the house and can’t remember simple directions. The patient insists that he feels fine, though he is depressed about his loss of memory. He is eating and sleeping well. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Multi-infarct dementia
. Mood disorder secondary to a general medical condition
. Schizoaffective disorder
. Delirium
. Major depression
201) A psychiatrist is seeing a patient in his outpatient practice. The patient treats the psychiatrist as if he were unreliable and punitive, though he had not been either. The patient’s father was an alcoholic who often did not show up to pick her up from school and frequently hit her. The psychiatrist begins to feel as if he must overprotect the patient and treat her gingerly. Which of the following psychological mechanisms best describes the psychiatrist’s behavior?
. Reaction formation
. Projection
. Countertransference
. Identification with the aggressor
. Illusion
202) A patient is able to appreciate subtle nuances in thinking and can use metaphors and understand them. This patient’s thinking can be best defined by which of the following terms?
. Intellectualization
. Abstract
. Rationalization
. Concrete
. Isolation of affect
203) A 65-year-old man, who had been hospitalized for an acute pneumonia 3 days previously, begins screaming for his nurse, stating that “there are people in the room out to get me.” He then gets out of bed and begins pulling out his IV line. On examination, he alternates between agitation and somnolence. He is not oriented to time or place. His vital signs are as follows: pulse, 126 beats per minute; respiration, 32 breaths per minute; blood pressure (BP), 80/58; temperature, 39.2°C (102.5°F). Which of the following diagnoses best fits this patient’s clinical picture?
. Dementia
. Schizophreniform disorder
. Fugue state
. Delirium
. Brief psychotic episode
204) A 59-year-old man goes to a psychiatrist for a 3-month history of panic attacks. He notes for the past 3 months he has experienced “out of the blue,” extreme episodes of fearfulness that last about 20 minutes. During that time he experiences palpitations, sweating, shortness of breath, and trembling. He denies any substance abuse, and has never had symptoms like this before these past 3 months. Which of the following signs or symptoms would likely lead the physicians to expect a diagnosis of anxiety secondary to a general medical condition in this case?
. The patient’s age
. History of palpitations
. History of sweating
. History of shortness of breath
. History of trembling
205) A 19-year-old woman presents to the emergency room with the chief complaint of a depressed mood for 2 weeks. She notes that since her therapist went on vacation she has experienced suicidal ideation, crying spells, and an increased appetite. She states that she has left 40 messages on the therapist’s answering machine telling him that she is going to kill herself and that it would serve him right for leaving her. Physical examination reveals multiple well-healed scars and cigarette burns on the anterior aspect of both forearms. Which of the following diagnoses best fits this patient’s clinical presentation?
. Dysthymic disorder
. Bipolar disorder
. Panic disorder
. Borderline personality disorder
. Schizoaffective disorder
206) A 29-year-old man is brought to the emergency room by his wife after he woke up with paralysis of his right arm. The patient reports that the day before, he had gotten into a verbal altercation with his mother over her intrusiveness in his life. The patient notes that he has always had mixed feelings about his mother, but that people should always respect their mothers above all else. Which of the following diagnoses best fits this patient’s clinical picture?
. Major depression
. Conversion disorder
. Histrionic personality disorder
. Fugue state
. Adjustment disorder
207) A 28-year-old business executive sees her physician because she is having difficulty in her new position, as it requires her to do frequent public speaking. She states that she is terrified she will do or say something that will cause her extreme embarrassment. The patient says that when she must speak in public, she becomes extremely anxious and her heart beats uncontrollably. Based on this clinical picture, which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Panic disorder
. Avoidant personality disorder
. Specific phobia
. Agoraphobia
. Social phobia
208) A 56-year-old man is brought to the physician’s office by his wife because she has noted a personality change during the past 3 months. While the patient is being interviewed, he answers every question with the same three words. Which of the following symptoms best fits this patient’s behavior?
. Negative symptoms
. Disorientation
. Concrete thinking
. Perseveration
. Circumstantiality
209) A 32-year-old patient is being interviewed in his physician’s office. He eventually answers each question, but he gives long answers with a great deal of tedious and unnecessary detail before doing so. Which of the following symptoms best describes this patient’s presentation?
. Blocking
. Tangentiality
. Circumstantiality
. Looseness of associations
. Flight of ideas
210) An 18-year-old man is brought to the emergency room by the police after he is found walking along the edge of a high building. In the emergency room, he mumbles to himself and appears to be responding to internal stimuli. When asked open-ended questions, he suddenly stops his answer in the middle of a sentence, as if he has forgotten what to say. Which of the following symptoms best describes this last behavior?
. Incongruent affect
. Blocking
. Perseveration
. Tangentiality
. Thought insertion
211) A 26-year-old woman with panic disorder notes that during the middle of one of her attacks she feels as if she is disconnected from the world, as though it were unreal or distant. Which of the following terms best describes this symptom?
. Mental status change
. Illusion
. Retardation of thought
. Depersonalization
. Derealization
212) A patient with a chronic psychotic disorder is convinced that she has caused a recent earthquake because she was bored and wishing for something exciting to occur. Which of the following symptoms most closely describes this patient’s thoughts?
. Thought broadcasting
. Magical thinking
. Echolalia
. Nihilism
. Obsession
213) A 45-year-old man with a chronic psychotic disorder is interviewed after being admitted to a psychiatric unit. He mimics the examiner’s body posture and movements during the interview. Which of the following terms best characterizes this patient’s symptom?
. Folie á deux
. Dereistic thinking
. Echolalia
. Echopraxia
. Fugue
214) A 54-year-old man with a chronic mental illness seems to be constantly chewing. He does not wear dentures. His tongue darts in and out of his mouth, and he occasionally smacks his lips. He also grimaces, frowns, and blinks excessively. Which of the following disorders is most likely in this patient?
. Tourette syndrome
. Akathisia
. Tardive dyskinesia
. Parkinson disease
. Huntington disease
215) A 58-year-old woman with a chronic mental disorder comes to the physician with irregular choreoathetoid movements of her hands and trunk. She states that the movements get worse under stressful conditions. Which of the following medications is most likely to have caused this disorder?
. Fluoxetine
. Clozapine
. Perphenazine
. Diazepam
. Phenobarbitol
216) A 24-year-old woman comes to the emergency room with the chief complaint that “my stomach is rotting out from the inside.” She states that for the last 6 months she has been crying on a daily basis and that she has decreased concentration, energy, and interest in her usual hobbies. She has lost 25 lb during that time. She cannot get to sleep, and when she does, she wakes up early in the morning. For the past 3 weeks, she has become convinced that she is dying of cancer and is rotting on the inside of her body. Also, in the past 2 weeks she has been hearing a voice calling her name when no one is around. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Delusional disorder
. Schizoaffective disorder
. Schizophreniform disorder
. Schizophrenia
. Major depression with psychotic features
217) A 19-year-old man is brought to the physician by his parents after he called them from college, terrified that the Mafia was after him. He reports that he has eaten nothing for the past 6 weeks other than canned beans because “they are into everything––I can’t be too careful.” He is convinced that the Mafia has put cameras in his dormitory room and that they are watching his every move. He occasionally hears the voices of two men talking about him when no one is around. His roommate states that for the past 2 months the patient has been increasingly withdrawn and suspicious. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Delusional disorder
. Schizoaffective disorder
. Schizophreniform disorder
. Schizophrenia
. Phencyclidine (PCP) intoxication
218) A 36-year-old woman is brought to the psychiatrist by her husband because for the past 8 months she has refused to go out of the house, believing that the neighbors are trying to harm her. She is afraid that if they see her they will hurt her, and she finds many small bits of evidence to support this. This evidence includes the neighbors’ leaving their garbage cans out on the street to try to trip her, parking their cars in their driveways so they can hide behind them and spy on her, and walking by her house to try to get a look into where she is hiding. She states that her mood is fine and would be “better if they would leave me alone.” She denies hearing the neighbors or anyone else talks to her, but is sure that they are out to “cause her death and mayhem.” Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Delusional disorder
. Schizophreniform disorder
. Schizoaffective disorder
. Schizophrenia
. Major depression with psychotic features
219) A 35-year-old woman has lived in a state psychiatric hospital for the past 10 years. She spends most of her day rocking, muttering softly to herself, or looking at her reflection in a small mirror. She needs help with dressing and showering, and she often giggles and laughs for no apparent reason. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Schizophrenia
. Delusional disorder
. Bipolar disorder, manic phase
. Schizoaffective disorder
. Schizophreniform disorder
220) A 20-year-old woman is brought to the emergency room by her family because they have been unable to get her to eat or drink anything for the past 2 days. The patient, although awake, is completely unresponsive both vocally and nonverbally. She actively resists any attempt to be moved. Her family reports that during the previous 7 months she became increasingly withdrawn, socially isolated, and bizarre; often speaking to people no one else could see. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Schizoaffective disorder
. Delusional disorder
. Schizophreniform disorder
. Catatonia
. PCP intoxication
221) A 21-year-old man is brought to the emergency room by his parents because he has not slept, bathed, or eaten in the past 3 days. The parents report that for the past 6 months their son has been acting strangely and “not himself.” They state that he has been locking himself in his room, talking to himself, and writing on the walls. Six weeks prior to the emergency room visit, their son became convinced that a fellow student was stealing his thoughts and making him unable to learn his school material. In the past 2 weeks, they have noticed that their son has become depressed and has stopped taking care of himself, including bathing, eating, and getting dressed. On examination, the patient is dirty, disheveled, and crying. He complains of not being able to concentrate, a low energy level, and feeling suicidal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis for this patient?
. Schizoaffective disorder
. Schizophrenia
. Bipolar I disorder
. Schizoid personality disorder
. Delusional disorder
222) A 47-year-old woman is brought to the emergency room after she jumped off an overpass in a suicide attempt. In the emergency room she states that she wanted to kill herself because the devil had been tormenting her for many years. After stabilization of her fractures, she is admitted to the psychiatric unit, where she is treated with risperidone and sertraline. After 2 weeks she is no longer suicidal and her mood is euthymic. However, she still believes that the devil is recruiting people to try to persecute her. In the past 10 years, the patient has had three similar episodes prior to this one. Throughout this time, she has never stopped believing that the devil is persecuting her. Which of the following is the most appropriate diagnosis for this patient?
. Delusional disorder
. Schizoaffective disorder
. Schizophrenia, paranoid type
. Schizophreniform disorder
. Major depression with psychotic features
223) A 40-year-old woman is arrested by the police after she is found crawling through the window of a movie star’s home. She states that the movie star invited her into his home because the two are secretly married and “it just wouldn’t be good for his career if everyone knew.” The movie star denies the two have ever met, but notes that the woman has sent him hundreds of letters over the past 2 years. The woman has never been in trouble before and lives an otherwise isolated and unremarkable life. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Delusional disorder
. Schizoaffective disorder
. Bipolar I disorder
. Cyclothymia
. Schizophreniform disorder
224) A 26-year-old woman is brought to the emergency room by her husband after she begins screaming that her children are calling to her and becomes hysterical. The husband states that 2 weeks previously, the couple’s two children were killed in a car accident, and since that time the patient has been agitated, disorganized, and incoherent. He states that she will not eat because she believes he has been poisoning her food, and she has not slept for the past 2 days. The patient believes that the nurses in the emergency room are going to cause her harm as well. The patient is sedated and later sent home. One week later, all her symptoms remit spontaneously. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis for this patient?
. Delirium
. Schizophreniform disorder
. Major depression with psychotic features
. Brief psychotic disorder
. Posttraumatic stress disorder
225) A 25-year-old woman is diagnosed with schizophrenia when, after the sudden death of her mother, she begins complaining about hearing the voice of the devil and is suddenly afraid that other people are out to hurt her. Her history indicates that she has also experienced a 3-year period of slowly worsening social withdrawal, apathy, and bizarre behavior. Her family history includes major depression in her father. Which of the following details of her history leads the physician to suspect that her outcome may be poor?
. She is female
. She was age 25 at diagnosis
. She had an acute precipitating factor before she began hearing voices
. She had an insidious onset of her illness
. There is a history of affective disorder in her family
226) A 22-year-old man is brought to the emergency room after he became exceedingly anxious in his college dormitory room, stating that he was sure the college administration was sending a “hit squad” to kill him. He also notes that he can see “visions” of men dressed in black who are carrying guns and stalking him. His thought process is relatively intact, without thought blocking or loose associations. His urine toxicology screen is positive for one of the following drugs. Which drug is the most likely cause of these symptoms?
. Barbiturates
. Heroin
. Benzodiazepines
. Amphetamines
. MDMA (Ecstasy)
227) A 72-year-old woman is brought to the emergency room by her daughter after she found her mother rummaging in the garbage cans outside her home. The daughter states that the patient has never had any behavior like this previously. On interview, the patient states she sees “martians hiding around her home, and on occasion, hears them too.” She also demonstrates a constructional apraxia, with difficulty drawing a clock and intersecting pentagons. All of these symptoms point to a medical cause for this patient’s behavior except one. Which symptom is common in patients with a psychiatric cause for their behavior (ie, not a medical cause)?
. Patient’s age
. No previous history of this behavior
. Visual hallucinations
. Auditory hallucinations
. Constructional apraxia
228) A 62-year-old man with chronic schizophrenia is brought to the emergency room after he is found wandering around his halfway house, confused and disoriented. His serum sodium concentration is 123 meq/L and urine sodium concentration is 5 meq/L. The patient has been treated with risperidone 4 mg/day for the past 3 years with good symptom control. His roommate reports that the patient often complains of feeling thirsty. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient’s symptoms?
. Renal failure
. Inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (ADH) secretion
. Addison disease
. Psychogenic polydipsia
. Nephrotic syndrome
229) A 75-year-old man is being cared for in a hospice setting. He has widely spread prostatic carcinoma and is considered terminal. Which of the following psychiatric symptoms are seen in 90% of all terminal patients?
. Delusions
. Hallucinations
. Flight of ideas
. Anxiety
. Depression
230) A 52-year-old man is seen by a psychiatrist in the emergency room because he is complaining about hearing and seeing miniature people who tell him to kill everyone in sight. He states that these symptoms developed suddenly during the past 48 hours, but that he has had them “on and off” for years. He states that he has never previously sought treatment for the symptoms, but that this episode is particularly bad. He denies the use of any illicit substances. The patient is alert and oriented to person, place, and time. His mental status examination is normal except for his auditory and visual hallucinations. His thought process is normal. His drug toxicology screen is positive for marijuana. He is quite insistent that he needs to be “put away” in the hospital for the symptoms he is experiencing. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Substance-induced psychosis
. Schizophrenia
. Schizoaffective disorder
. Schizophreniform disorder
. Malingering
231) A 25-year-old man is brought to the physician after complaining about a visual hallucination of a transparent phantom of his own body. Which of the following specific syndromes is this patient most likely to be displaying?
. Capgras syndrome
. Lycanthropy
. Cotard syndrome
. Autoscopic psychosis
. Folie á deux
232) A 26-year-old man comes to the physician with the chief complaint of a depressed mood for the past 5 weeks. He has been feeling down, with decreased concentration, energy, and interest in his usual hobbies. Six weeks prior to this office visit, he had been to the emergency room for an acute asthma attack and was started on prednisone. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Mood disorder secondary to a general medical condition
. Substance-induced mood disorder
. Major depression
. Adjustment disorder
. Dysthymia
233) A 24-year-old woman, 5 days after delivery of a normal, full-term infant, is brought to the obstetrician because she is so tearful. She states that her mood is quite labile, often changing within minutes. She has trouble sleeping, both falling asleep and awakening early. She notes anhedonia, stating she doesn’t enjoy “much of anything” right now. Which of this patient’s symptoms point preferentially to a postpartum depression?
. Time that is, 5 days post-delivery
. Tearfulness
. Labile mood
. Insomnia
. Anhedonia
234) A 28-year-old woman sees her physician with the chief complaint of a depressed mood. She also notes that she is sleeping more than usual––up to 14 hours per night––but does not feel rested and that she feels tired and fatigued all the time. She has gained 14 lb in the last month, something that she is very unhappy about, but she says that she seems to have such a craving for sweets that the weight gain seemed inevitable. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Mood disorder secondary to a general medical conditi
. Substance-induced mood disorder
. Cyclothymia
. Seasonal affective disorder
. Dysthymic disorder
235) A 27-year-old woman has been feeling blue for the past 2 weeks. She has little energy and has trouble concentrating. She states that 6 weeks ago she had been feeling very good, with lots of energy and no need for sleep. She says that this pattern has been occurring for at least the past 3 years, though the episodes have never been so severe that she couldn’t work. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Borderline personality disorder
. Seasonal affective disorder
. Cyclothymic disorder
. Major depression, recurrent
. Bipolar disorder, depressed
236) A 19-year-old woman comes to the psychiatrist for a history of anger and irritability, which occurs on monthly on an average. During this time the patient also reports feeling anxious and “about to explode,” which alternates rapidly with crying spells and angry outbursts. The patient notes during this time she can’t concentrate and sleeps much more than she usually needs to do. During the several days these symptoms last, the patient must skip most of her classes because she cannot function. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Adjustment disorder with depressed mood
. Major depression
. Premenstrual dysphoric disorder
. Dysthymic disorder
. Depressive personality disorder
237) A 64-year-old man is admitted to the psychiatric unit after an unsuccessful suicide attempt. Following admission, he attempts to cut his wrists three times in the next 24 hours and refuses to eat or drink anything. He is scheduled to have electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) because he is so severely depressed that an antidepressant is deemed too slow acting. Which of the following side effects should the patient be informed is most common after ECT?
. Headache
. Palpitations
. Deep venous thromboses
. Interictal confusion
. Worsening of the suicidal ideation
238) A 14-year-old boy is brought to the psychiatrist because for the past 15 months he has been irritable and depressed almost constantly. The boy notes that he has difficulty concentrating, and he has lost 5 lb during that time period without trying. He states that he feels as if he has always been depressed, and he feels hopeless about ever feeling better. He denies suicidal ideation or hallucinations. He is sleeping well and doing well in school, though his teachers have noticed that he does not seem to be able to concentrate as well as he had previously. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Major depression
. Dysthymic disorder
. Mood disorder secondary to a general medical condition
. Normal adolescence
. Cyclothymia
239) A 45-year-old woman comes to her physician for help with her insomnia. She states “ever since my husband died, I just can’t sleep.” The patient states her 57-year-old husband died suddenly of a heart attack 9 weeks ago. Since that time, the patient has had a very depressed mood, had been crying, has lost interest in activities, is fatigued, and has insomnia. Which of the following symptoms, if present, should make the physician think this patient has a major depression instead of bereavement?
. The patient feels that she would be better off dead
. The patient has marked functional impairment
. The patient has lots of guilt about not recognizing that the chest pain her husband was having was the start of a heart attack
. The patient has mild psychomotor retardation
. The patient reports hearing the voice of her dead husband calling her name twice
240) A 32-year-old man is being treated for a severe major depression. Which of the following symptoms, if present, is one of the most accurate indicators of long-term suicidal risk?
. Revenge fantasies
. Presence of rage in the patient
. Hopelessness
. Presence of guilt
. The patient has a need for punishment
241) A 44-year-old white male presents with a long history of joint pains in several joints. He has seen a physician before but no diagnosis was made. He has been taking ibuprofen with partial relief. He has now developed fever, diarrhea and weight loss. He denies any genitourinary or eye symptoms. He does not use tobacco, alcohol or drugs. He is a farmer. On examination, he has generalized lymphadenopathy and non-deforming arthritis. Small intestinal biopsy reveals periodic Acid-Schiff (PAS)-positive macrophages. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Reactive arthritis
. Sarcoidosis
. Inflammatory bowel disease
. Whipple's disease
. Celiac disease
242) A 33-year-old tennis player comes to you with a complaint of pain in his right shoulder. He says that the pain is absent at rest but present when he lifts his arm over his head. The pain is compromising his play. On examination, active motion at right shoulder is limited due to pain. Pain is most severe on passive internal rotation and flexion at the right shoulder. No atrophy of the shoulder muscle is seen. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
. Tear of long head of bicep tendon
. Tennis elbow
. Subacromial bursitis
. Anterior dislocation of shoulder
. Axillary nerve palsy
243) A 75-year-old white male comes to the physician's office for his routine health maintenance examination. He has no symptoms. He has a past medical history significant for hypertension and hyperlipidemia. He takes aspirin, hydrochlorothiazide and simvastatin. He does not smoke and consumes 1-2 beers on weekends. He walks 2 miles every morning and eats a balanced diet. His vital signs are within normal limits. His chest is clear to auscultation, and his abdomen is soft and nontender. Rectal examination shows a diffusely enlarged, firm prostate without nodules. Stool for occult blood is negative. The distal interphalangeal joints are enlarged, and his gait is normal. His labs are as follows: Total bilirubin 1.0 mg/dl, Alkaline phosphatase 420 U/L, Aspartate aminotransferase (SGOT) 20 U/L, Alanine aminotransferase (SGPT) 25 U/L, Serum creatinine 0.8 mg/dl, Calcium 8.8 mg/dl, Serum PSA 2.1 ng/ml. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the elevated alkaline phosphatase in this patient?
. Metastatic bone disease
. Plasma cell neoplasia
. Simvastatin
. Paget's disease of bone
. Alcohol use
244) A 21-year-old Caucasian female presents with a one-week history of low-grade fever and joint pain. She describes symmetric swelling of the small hand joints. Her rheumatoid factor tests positive, and antinuclear antibodies are weakly positive at a 1:40 dilution. She is treated with NSAIDs. Four weeks later, the patient reports not taking the prescribed drugs since she feels no pain. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Septic arthritis
. Rheumatoid arthritis
. Crystalline arthritis
. Systemic lupus erythematosus
. Viral arthritis
245) A 64-year-old male comes to the physician's office because of increasing pain in his right groin for the past several months. The pain increases with activity and is relieved with rest. He also has difficulty moving after a period of rest. He denies any trauma or falls. He has no fever, weight loss or loss of appetite. He has had lumbar disk herniation in the past but denies any current back pain. He has no other active medical problems. His vital signs are within normal limits. He weighs 95 kg (210 lb) and is 168 cm (66 in) tall. Examination shows pain on passive internal rotation of right hip joint. Direct pressure over the groin did not increase the pain. His reflexes are 2+, and there are no sensory deficits. Muscle bulk, tone and power are within normal limits. Pulses are 2+ in both legs. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his hip pain?
. Cutaneous nerve compression
. Inflammation of the trochanteric bursa
. Degenerative joint disease
. Disruption of bone vasculature
. Referred pain from the lumbosacral area
246) A 36-year-old female who is currently having regular menstrual periods comes to the emergency room because of malaise and a high-grade fever with chills. She also complains of pain in multiple joints. She always uses highly absorbent tampons during her menses. She uses intravenous heroin and cocaine and works as a prostitute. Her temperature is 39.3°C (103.4°F), pulse is 102/min, blood pressure is 120/80mmHg and respirations are 14/min. Examination shows multiple pustules on the extensor surfaces of her forearms. Joint examination does not show redness, swelling or tenderness. Three sets of blood cultures are negative Based on these findings, which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
. Infective endocarditis
. Disseminated gonococcal infection
. Toxic shock syndrome
. Acute HIV infection
. Secondary syphilis
247) A 54-year-old retired schoolteacher comes to the physician's office because of worsening low back pain. The pain started three weeks ago. It is continuous and is worse at night. He has had little relief with over-the-counter nonsteroidal analgesics. He has no other symptoms. He had a surgical resection of a lung tumor one year ago for non-small cell carcinoma of the lung. Preoperative positron emission tomography (PET) scanning did not reveal any evidence of metastasis. His vital signs are within normal limits. Examination shows local spinal tenderness at the L4-L5 level. What is the most likely cause of his back pain?
. Lumbar strain
. Central spinal canal stenosis
. Disc herniation
. Vertebral compression fracture
. Metastatic disease
248) A 60-year-old man presents to the emergency department after being awoken from sleep by severe pain in his right great toe. He reports that his toe is suddenly swollen and very tender to touch. On review of systems, the patient also describes occasional headaches and pruritus that can be "unbearable" after a hot bath. He does not smoke or drink alcohol. On physical examination, his lungs are normal. The liver span is 10 cm and the spleen is palpable 2 cm below the costal margin. Aspiration of the affected toe joint reveals negatively birefringent crystals. Which of the following is most likely responsible for this patient's symptoms?
. Chronic kidney disease
. Myeloproliferative disorder
. Hemochromatosis
. Inherited enzyme deficiency
. Hyperparathyroidism
249) A 29-year-old woman presents to your office complaining of easy fatigability over the last several months. She tires easily after walking short distances. She also has difficulties combing her hair due to an inability to hold her hands over her head for a long time. She reports a weight loss of two or three pounds over the last two months. She denies fever or loss of appetite. She does not smoke or consume alcohol. On family history, her father died of a stroke when he was 54 years old and her mother has diabetes mellitus. On examination, she is afebrile with a pulse of 105/min. Cardiac exam reveals regular rhythm with no murmur. Her gait is normal but, when asked to sit down slowly, she drops into the chair. A fine finger tremor is evident when she extends her arms. Her muscles are non-tender to palpation. She appears to have decreased muscle mass in her shoulders. Deep tendon reflexes are normal. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
. Upper motor neuron disease
. Polyneuropathy
. Inflammatory muscle disease
. Thyroid disease
. Cerebellar dysfunction
250) A 62-year-old male treated for hypertension and hyperlipidemia complains of nagging right knee pain that is worse in the evening. The pain has been present for several months and it seems to limit his physical activities. His blood pressure is 160/100 mmHg and his heart rate is 70/min. His BMI is 32 kg/m2, and palpation of the knee reveals a cool joint with bony tenderness. His blood cholesterol level is 200 mg/dl and his serum uric acid level is 9.0 mg/dl. Which of the following additional findings is likely on further examination of the right knee?
. Soft tissue swelling
. Painful tibial tuberosity
. Palpable popliteal mass
. Bony crepitus
. Subcutaneous nodules
251) A 34-year-old man complains of back tightness and persistent low back pain. The pain has a dull and aching quality. It is worse during the night and in the morning but improves gradually during the day. He has no significant past medical history. He does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. He is married and lives with his wife. His pulse is 80/min, respirations are 14/min, and blood pressure is 120/76 mmHg. Which of the following most likely accounts for this patient's symptoms?
. Ligamentous sprain
. Lumbar disk degeneration
. Apophyseal joint arthritis
. Nerve root demyelinization
. Abnormal bone mineralization
252) A 34-year-old woman with a skin rash, joint pains, and oral ulcers is diagnosed with systemic lupus erythematosus. She has no renal or central nervous system involvement, and her past medical history and review of systems are otherwise negative. Therapy with hydroxychloroquine is started. Which of the following screening tests is most important in this patient?
. Complete blood count
. Liver function panel
. Urinalysis
. Audiometry
. Eye examination
253) A 68-year-old man with hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and diabetes is hospitalized for an acute myocardial infarction. It is complicated by pulmonary edema and he undergoes angiography of the left anterior descending artery. On post-operative day 3, he complains of abdominal pain and discoloration of his toes. His vital signs are stable. Examination shows bluish discoloration of his right great toe and of all the toes on his left foot. The skin over the toes is cold and clammy. Bilateral pedal pulses are present and full. His abdomen is soft and mildly tender at the center. Chest auscultation is clear. Laboratory studies show a rise in creatinine to 2.3 g/dl from his baseline of 1.2 g/dl. An EKG shows sinus rhythm and Q waves in anterior leads. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his toe discoloration?
. Ketoacidosis
. Vasospasm
. Right to left shunt
. Autoimmune vasculitis
. Cholesterol embolism
254) A 32-year-old man presents to the clinic with one week of escalating lower back pain. He describes the pain as dull and aching. It increases with motion and it is not completely relieved by rest. He has no significant past medical history. He smokes one pack of cigarettes per day and consumes alcohol occasionally. He admits to being "under a lot of stress" and has recently used injectable drugs. His family history is significant for prostate cancer in his father. His temperature is 36.7°C (98°F), pulse is 90/min, respirations are 16/min, and blood pressure is 120/80 mmHg. Gentle percussion over the lumbar vertebrae elicits pain. A full neurologic exam including straight leg raise is normal. Laboratory results are shown below: Complete blood count: Leukocyte count 6,500/mm3, Hematocrit 46%, Platelets 400,000/mm3. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Ankylosing spondylitis
. Lumbar disk herniation
. Lumbar spinal stenosis
. Vertebral osteomyelitis
. Vertebral compression fracture
255) A 35-year-old African-American woman comes to the physician's office complaining of blurred vision, cough and shortness of breath. For the past few days she has had mild fevers, malaise and easy fatigability. She has never had these symptoms before and is anxious to uncover a diagnosis. She was recently incarcerated for two months. She practices unprotected sex with her new boyfriend. Her temperature is 37.2°C (98.9°F) and her blood pressure is 116/80 mmHg. On exam, her right eye is red and slit lamp examination shows leukocytes in the anterior chamber. Lungs have patchy rales. Chest x-ray shows bilateral reticulonodular infiltrates and hilar adenopathy. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
. Acute HIV infection
. Disseminated tuberculosis
. Sarcoidosis
. Histoplasmosis
. Ankylosing spondylitis
256) A 60-year-old Caucasian woman comes to the physician because of joint pains in both hands. Her other medical problems include obesity and gastroesophageal reflux disease. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or drugs. Family history is not significant. Her medications include omeprazole and acetaminophen. Her vital signs are within limits. X-ray of the joints is shown below. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Rheumatoid arthritis
. Systemic lupus erythematosus
. Osteoarthritis
. Reactive arthritis
. Gouty arthritis
257) A 67-year-old male hospitalized after elective hernia repair complains of severe right knee pain. Physical examination reveals redness and swelling of the right knee with limited motion due to pain. His temperature is 38.9°C (102°F), blood pressure is 160/110 mm Hg, pulse is 80/min, and respirations are 16/min. Synovial fluid analysis reveals the following findings: WBC count 30,000mm3, Neutrophils 90%, Crystals rhomboid-shaped, positively birefringent, Gram stain negative. Which of the following is most likely associated with this patient's current condition?
. Tophi
. Transient bacteremia
. Chondrocalcinosis
. Rheumatoid factor
. Heberden nodes
258) A 43-year-old Caucasian female presents to your office complaining of joint pain and swelling in her hand. On history, she endorses easy fatigability and loss of energy that has been worsening insidiously. It is especially difficult for her to do daily activities in the morning due to prolonged stiffness. She also describes frequent knee pain accompanied by a low-grade fever. She takes ibuprofen and naproxen to relieve her symptoms. Her hematocrit is 33%. The patient is at the greatest risk of which of the following?
. Osteitis fibrosis cystica
. Osteitis deformans
. Avascular bone necrosis
. Osteomalacia
. Osteoporosis
259) A 32-year-old Caucasian male complains of inability to grip his cup of coffee and hold a pen in the morning. He says that he is 'fully functional' in the afternoon. His ESR is 45 mml hr. Which of the following is most likely to be affected by this patient's disease?
. Sacral spine
. Sacroiliac joints
. Lumbar spine
. Thoracic spine
. Cervical spine
260) A 21-year-old woman presents with 4 months of slowly progressive low back pain. Her back pain is associated with early morning stiffness that improves as the day progresses. She has no fever or gastrointestinal complains. She denies any recent illness. On examination, there is limited range of motion of her back. Other examination is unremarkable. Plain X-ray films show bilateral sacroiliitis. Which of the following conditions is this patient at greatest risk of developing?
. Aortic coarctation
. Thoracic aortic aneurysm
. Renal failure
. Oral ulcers
. Anterior uveitis
261) A 30-year-old female comes to your office with a complaint of pain over the lateral side of her wrist for the last four days. She is two months postpartum and notes that her pain is most severe when she lifts her infant from a crib. On examination, there is tenderness over the radial side of wrist and first dorsal compartment. Passive stretching of the thumb tendons over the radial styloid while the thumb is held in flexion aggravates the pain. She denies any recent trauma over the tender area. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
. Osteoarthritis of first metacarpophalangeal joint
. Trigger thumb
. De Quervain tenosynovitis
. Scaphoid fracture
. Flexor carpi radialis tenosynovitis
262) A 44-year-old female complains of generalized weakness, low-grade fever and joint pain. Her daily activities are limited due to joint stiffness, especially in the morning. Her hand joints are swollen symmetrically. The inferior pole of the spleen is palpable on physical examination. Her hematocrit is 34%. Liver and renal function tests are normal. Two months after the initial visit, the patient develops painful oral ulcers. Her laboratory values are: Hematocrit 33%, AST 120 U/L, ALT 90 U/L, Alkaline phosphatase 90 U/L, Bilirubin 1.1 mg/dl, Creatinine 0.8 mg/dl, BUN 16 mg/dl. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's current complaints?
. Viral hepatitis
. Felty syndrome
. Lymphoid cell proliferation
. Antimetabolite agent
. Corticosteroid treatment
263) A 35-year-old woman presents with complaints of aching pain and stiffness over her entire body for the past 3 months. She also reports, easy fatigability, poor sleep and frequent headaches. She has been using over the counter pain medications with no relief. While examining her, she complains of extreme pain to gentle palpation over her neck, shoulders and back. Her vital signs are stable. What is your diagnosis?
. Chronic fatigue syndrome
. Polymyalgia rheumatica
. Rheumatoid arthritis
. Polymyositis
. Fibromyalgia.
264) A 25-year-old immigrant from Eastern Europe is being evaluated for right shoulder pain and swelling. He also complains of heel pain while walking. Palpation over the heels, iliac crests and tibial tuberosities elicits tenderness. Which of the following additional findings is most likely in this patient?
. Positive rheumatoid factor
. Proteinuria
. Limited spine mobility
. Subcutaneous nodules
. Hand joint deformities
265) A 9-year-old Caucasian male complains of fever, sore throat and difficulty swallowing. Small tender lymph nodes are palpated in the cervical region. The symptoms subside quickly on penicillin therapy. Ten days later, the patient presents again with fever, skin rash and fleeting joint pain in the lower extremities. Physical examination reveals scattered urticaria and palpable lymph nodes in the cervical, axillary and inguinal regions. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's current complaints?
. Rheumatic fever
. Drug-induced reaction
. Lymphoproliferative disorder
. Henoch-Schonlein purpura
. Infective endocarditis
266) A 66-year-old man comes to the physician's office complaining of progressive lower back pain. Over-the-counter ibuprofen has provided him with moderate relief. The back pain is associated with bilateral leg pain that is precipitated by walking. The pain improves upon lying down or sitting. He has no pain at night, and no problems with bowel and bladder function. He underwent coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) 6 years ago for a 3-vessel coronary artery disease. His medications include aspirin, enalapril, atenolol, and lovastatin. Physical examination shows normal strength, reflexes and sensation in his legs. A straight leg raise test fails to reproduce pain. His femoral, popliteal and pedal pulses are full bilaterally and he has no bruits. Plain films of the lumbosacral spine show degenerative changes of the vertebrae. Ankle brachial index measurement is within normal limits. Which of the following is most likely responsible for his current condition?
. Atherosclerosis
. Spinal canal narrowing
. Bulging disc
. Vertebral metastasis
. Spinal cord compression
267) A 35-year-old female presents with a complaint of oral ulcers that are extremely painful. She had a similar presentation three months ago and the ulcers healed without any scarring. Her medical history includes a recent visit to the ophthalmologist with complaints of blurred vision and she is now being treated for anterior uveitis. She has also had recurrent painful ulcers in her genital area for which she has regular follow-up with her gynecologist. On examination, you notice many hyper-pigmented areas over her extremities and few painful, nodular lesions. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Sarcoidosis
. Reiter's Syndrome
. Herpes simplex infection
. Behcet's syndrome
. Systemic lupus erythematosus
268) A 71-year-old female is brought to your clinic by her daughter with a complaint of severe pain in her fingers. Her daughter says, "Mom has horrible problems with her joints and she has never tried to get help". The patient adds that her fingers have been swollen and painful for a few weeks. She claims that she had a similar condition in her foot last year. She was given a pain pill, but it was ineffective. She takes a water pill for her blood pressure. What is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
. Rheumatoid nodules
. Gouty arthritis
. Severe osteoarthritis
. Bone tumor
. Severe psoriatic arthritis
269) A 52-year-old male presents with a long history of joint pain. He describes pain and stiffness of the small joints of his hand that is worse in the morning and can last several hours. He also complains of occasional digit swelling. A picture of the patient's hands is shown on the slide below. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Enteropathic arthritis
. Rheumatoid arthritis
. Psoriatic arthritis
. Crystalline arthritis
. Sarcoidosis
270) A 30-year-old white male presented to your office with low back pain and stiffness. His pain is worse in the morning and is improved with activity. He has also been having bloody diarrhea for the past few days. On examination, he has painful erythematous nodules over his shins. Pain and stiffness is present in his lower back. Plain radiographs show sacroiliac joint inflammation. Stool cultures are negative. Laboratory studies show anemia and thrombocytosis. P-ANCA is positive in high titers. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his symptoms?
. Reactive arthritis from diarrhea
. Inflammatory bowel disease
. Infection with T ropheryma whippelii
. Gluten-sensitive enteropathy
. Infection with Giardia Iamblia
271) A 42-year-old male presents to your office complaining of back pain that started two days ago after carrying heavy packages. He denies any weakness or sensory changes in his legs. His past medical history is insignificant. He is not taking any medications and denies drug abuse. His temperature is 36.7°C (98°F), blood pressure is 120/76 mmHg, pulse is 80/min, and respirations are 16/min. Physical examination reveals paravertebral tenderness. Lower extremity power is 5/5 and the deep tendon reflexes are 2+. Babinski's sign is negative. Straight-leg raising test is negative at 90 degrees. What is the most probable diagnosis in this patient?
. Multiple myeloma
. Ankylosing spondylitis
. Compression fracture of the vertebrae
. Lumbosacral strain
. Herniated disk
272) A 30-year-old obese woman comes to the emergency department complaining of four days of progressive pain, swelling and redness of her right leg. She has no obvious trauma or insect bites. She does not use tobacco, alcohol or illicit drugs. Her temperature is 38.7°C (103.0°F), pulse is 106/min, and blood pressure is 130/80 mmHg. Her right calf is swollen, erythematous, and extremely tender and warm to the touch over a 6 x 3 cm region. There is a tender, palpable mass in her right groin. There is no overlying crepitus and no bullae are seen. The toe webs are fissured and macerated. Laboratory studies show: Complete blood count: Hemoglobin 14.0 g/L, Platelets 222,000/mm3, Leukocyte count 14,500/mm3, Neutrophils 86%, Lymphocytes 14%, Which of the following is the most likely cause of her current leg condition?
. Cellulitis
. Arterial thrombosis
. Deep venous thrombosis
. Necrotizing fascitis
. Ruptured Baker's cyst
273) A 27-year-old African-American woman presents with several complaints. She has had pain and swelling of her hands and wrists for the past few days. She also complains of easy fatigability and frequent mouth ulcers. She has no significant past medical history and does not take any medications. Her temperature is 37.1°C (98.9°F), blood pressure is 140/90mmHg, and pulse is 76/min. Examination reveals swollen, tender metacarpophalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joints. There are superficial ulcers on her buccal mucosa. X-ray of hands and wrists shows no bony erosions. Laboratory studies show: Hemoglobin 11.0 g/L, Platelets 90,000/mm3, Leukocyte count 4,500/mm3. Urinalysis shows 2+ protein and red blood cell casts. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her joint pains?
. Systemic lupus erythematosus
. Dermatomyositis
. Sarcoidosis
. Neuropathic joint disease
. Systemic iron overload
274) A 63-year-old painter presents with pain in his right shoulder for the past few weeks. He experiences pain when he tries to reach for objects and he is unable to lift his arm above his head. He denies trauma to the shoulder, fevers, chills and weight loss. Vital signs are within normal limits. On exam, the physician raises the patient's arm while asking him to relax the shoulder. At 60 degrees, the patient begins to shrug his shoulder and complain of pain. In spite of the pain, his range of motion is normal. A lidocaine injection into the shoulder leads to a significant decrease in pain upon lifting the arm. Which of the following is most likely responsible for his current condition?
. Rotator cuff tear
. Adhesive capsulitis
. Rotator cuff impingement
. Crystal arthritis
. Bacterial infection
275) A 22-year-old Caucasian female comes to your office complaining of difficulty swallowing. She says that solid food sticks in the middle of her chest, and that's why she prefers liquids. She has lost 10 pounds over the last 3 months. She also complains of recent severe heartburn that does not respond well to over-the-counter antacids. On review of systems, she denies cough, shortness of breath and palpitations. She has noticed occasional swelling and pain in her small finger joints. Her fingers turn blue upon cold exposure, and she always wears gloves to keep them warm. She does not smoke or drink alcohol. She denies illegal drug use. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. CREST syndrome
. Esophageal neoplasm
. Esophageal neoplasm . Achalasia
. Diffuse esophageal spasm
. Rheumatoid arthritis
276) A 28-year-old woman presents to her physician's office because of pain in her left knee joint. She reports having mild discomfort and pain in right wrist 4 days ago and left ankle pain two days ago. She denies any recent respiratory illness, diarrhea, or urinary symptoms. She has no vaginal discharge. She has no previous medical problems and does not take any medications. She drinks half a pint of vodka daily but denies intravenous drug abuse. She is single and sexually active. Her last menstrual period was one week ago. Her temperature is 38.5°C (101.3°F), blood pressure is 120/80 mmHg, pulse is 98/min, and respirations are 15/min. Examination of the knee reveals warmth, tenderness, decreased range of motion, and an effusion. No skin lesions are present and her pelvic examination is unremarkable. Synovial fluid analysis shows a white blood cell count of 75,000/microl. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her symptoms?
. Non-gonococcal septic arthritis
. Gonococcal septic arthritis
. Acute rheumatic fever
. Acute HIV infection
. Crystal induced arthritis
277) A 45-year-old tennis player comes to your office with a complaint of pain over the lateral side of the right elbow. He has been a professional tennis player for 15 years but has never had this kind of pain before. Range of motion at both elbows is normal. There is point tenderness over the lateral side of the distal end of right humerus. Pain is exacerbated by extension of wrist against resistance. The rest of the physical examination is normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
. Lateral epicondylitis
. Rotator cuff injury
. Radial tunnel syndrome
. Posterior interosseous nerve entrapment
. Rupture of long head of biceps tendon
278) A 65-year-old man complains of periodic back pain radiating to his thigh and buttock. The pain is related to walking or climbing the stairs but is promptly relieved by leaning forward. He also has noticed tingling and numbness in both lower extremities. He has a history of hypertension and takes hydrochlorothiazide. He does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. His pulse is 76/min, respirations are 14/min, and blood pressure is 140/80 mmHg. Lumbar extension reproduces the pain and tingling, while lumbar flexion relieves the symptoms. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
. Iliac artery atherosclerosis
. Abdominal aortic aneurysm
. Degenerative central canal stenosis
. Lumbar disk herniation
. Spina bifida occulta
279) A 51-year-old Caucasian female complains of low-back pain radiating to the buttocks. She also complains of persistent muscle pain that gets worse with exercise. Physical examination reveals normal muscle strength. Her joints are not swollen, but palpation over the outer upper quadrants of the buttocks and the medial aspect of the knees elicits tenderness. Her ESR is 12mm/hr. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Seronegative spondyloarthropathy
. Polymyalgia rheumatica
. Polymyositis
. Rheumatoid arthritis
. Fibromyalgia
280) A 27-year-old male presents to the physician's office because of pain on the medial side of the tibia just below the knee. The pain does not radiate and is continuous. He relates the onset of his pain to falling on the ground while playing football two weeks ago. He denies fever, malaise and weight loss. His past medical history is not significant. On examination, a well-defined area of tenderness is present on the upper tibia below the medial knee joint. There is no redness, warmth or swelling. His gait is normal. A valgus stress test has no effect on his pain. X-ray of the knee and tibia shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his current symptoms?
. Anserine bursitis
. Prepatellar bursitis
. Medial collateral ligament strain
. Medial compartment osteoarthritis
. Patellofemoral syndrome
281) A 16-year-old boy presents with a seven-month history of intermittent right knee pain and swelling. He states that his discomfort first began after a baseball injury. This injury was associated with pain, swelling, and restriction of movement in his right knee. He has had three subsequent episodes of pain and swelling in his right knee, not precipitated by trauma. The last episode occurred three days ago. He denies history of fevers or chills. There is no history of recent travel, other than a camping trip with his friends to Long Island, New York a few months ago. On physical examination, he has a marked effusion of his right knee and is unable to fully flex or extend his leg. X-ray reveals no bony abnormalities. What is the most probable diagnosis?
. Rheumatoid arthritis
. Septic arthritis
. Lyme arthritis
. Reactive arthritis
. Osteomyelitis
282) A 75-year-old female comes to the emergency room with acute onset of severe back pain. The pain started while lifting a turkey from the freezer. She had no obvious trauma preceding the pain. She denies weakness or sensory loss in the legs. Her past medical history is significant for temporal arteritis diagnosed several months ago and has been taking prednisone. She does not smoke or consume alcohol. Her temperature is 36.7°C (98°F), blood pressure is 140/70 mmHg, pulse is 80/min, and respirations are 16/min. Physical examination reveals local tenderness of the lumbar spine area. Bilateral ankle reflex is absent. Knee reflex is 2+ in both legs. Babinski's sign is absent bilaterally. Muscle power is 5/5 in both legs. Bilateral straight-leg raising to 90 degrees does not increase the pain What is the most probable diagnosis in this patient?
. Multiple myeloma
. Ankylosing spondylitis
. Compression fracture of the vertebrae
. Lumbosacral strain
. Herniated disk
283) A 66-year-old man complains of a 1-year history of low-back and buttock pain that worsens with walking and is relieved by sitting or bending forward. He has hypertension and takes hydrochlorothiazide but has otherwise been healthy. There is no history of back trauma, fever, or weight loss. On examination, the patient has a slightly stooped posture, pain on lumbar extension, and has a slightly wide base gait. Pedal pulses are normal and there are no femoral bruits. Examination of peripheral joints and skin is normal. What is the most likely cause for this patient’s back and buttock pain?
. Lumbar spinal stenosis
. Herniated nucleus pulposus
. Atherosclerotic peripheral vascular disease
. Facet joint arthritis
. Prostate cancer
284) A 22-year-old man develops the insidious onset of low-back pain improved with exercise and worsened by rest. There is no history of diarrhea, conjunctivitis, urethritis, rash, or nail changes. On examination, the patient has loss of mobility with respect to lumbar flexion and extension. He has a kyphotic posture. A plain film of the spine shows sclerosis of the sacroiliac joints. Calcification is noted in the anterior spinal ligament. Which of the following best characterizes this patient’s disease process?
. He is most likely to have acute lumbosacral back strain and requires bed rest.
. The patient has a spondyloarthropathy, most likely ankylosing spondylitis.
. The patient is likely to die from pulmonary fibrosis and extrathoracic restrictive lung disease.
. A rheumatoid factor is likely to be positive.
. A colonoscopy is likely to show Crohn disease.
285) A 20-year-old man complains of arthritis and eye irritation. He has a history of burning on urination. On examination, there is a joint effusion of the right knee and a rash of the glans penis. Which of the following is correct?
. Neisseria gonorrhoeae is likely to be cultured from the glans penis.
. The patient is likely to be rheumatoid factor—positive.
. An infectious process of the GI tract may precipitate this disease.
. An ANA is very likely to be positive.
. CPK will be elevated.
286) Last week a 20-year-old college student developed acute wrist pain and swelling. This resolved in four days. Yesterday, he developed pain and swelling in his left knee. Two months ago he went on a backpacking trip in Rhode Island. A week or so later he developed an enlarging circular red spot that persisted for 2 weeks and then resolved. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Acute rheumatoid arthritis
. Parvovirus infection
. Psoriatic arthritis
. Lyme disease
. Inflammatory bowel disease
287) A 38-year-old man has pain and stiffness of his right knee. This began 2-weeks ago after he fell while skiing. On two occasions he had the sense that his knee was locked in a semiflexed position for a few seconds. He has noted a popping sensation when he bends his knee. On examination there is tenderness over the medial joint line of the knee. Marked flexion and extension of the knee are painful. The Lachman test (anterior displacement of the lower leg with the knee at 20°of flexion) and the anterior drawer test are negative. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Medial meniscus tear
. Osteoarthritis
. Anterior cruciate ligament tear
. Chondromalacia patella
. Lumbosacral radiculopathy
288) A 63-year-old painter complains of severe right shoulder pain. The pain is located posteriorly over the scapula. These symptoms began after he fell from a ladder 2 weeks ago. The pain is especially bad at night and makes it difficult for him to sleep. In addition, he has had some pain in the right upper arm. Treatment with acetaminophen and ibuprofen has been unsuccessful in controlling his pain. On examination the patient appears uncomfortable. The right shoulder has full range of motion. Movement of the shoulder is not painful. There is no tenderness to palpation of the scapula. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Subdeltoid bursitis
. Rotator cuff tendonitis
. Adhesive capsulitis
. Osteoarthritis
. Cervical radiculopathy
289) A 50-year-old woman with rheumatoid arthritis has been treated with meloxicam (Mobic). You add hydroxychloroquine. Six weeks later her arthritis is mildly improved. The same joints are still involved but she now reports only 1-hour morning stiffness. She has, however, developed epigastric burning and melena for the past 3 days. Stool is strongly positive for occult blood. Which of the following is the most likely cause for the melena in this case?
. Emotional stress over her illness resulting in acid peptic disease
. Hydroxychloroquine-induced acid peptic disease
. Gastric lymphoma associated with autoimmune disease
. NSAID gastropathy
. Meckel diverticulum
290) A 55-year-old woman with long-standing rheumatoid arthritis is on prednisone 5 mg daily and etanercept (Enbrel) 50 mg subcutaneously once a week. Her arthritis is well-controlled. However, she complains of a 2-day history of headaches, chills, and spiking fevers to 39.4°C (103°F). You suspect which of the following?
. An allergic febrile reaction to etanercept
. Fever related to her underlying autoimmune disease
. A serious infection
. A viral syndrome
. An occult malignancy
291) A 32-year-old Japanese woman has a long history of recurrent aphthous oral ulcers. In the last 2 months she has had recurrent genital ulcers. She now presents with a red painful eye that was diagnosed as anterior uveitis. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Herpes simplex
. HIV infection
. Behçet disease
. Diabetes mellitus
. Systemic lupus erythematosus
292) A 53-year-old man presents with arthritis and bloody nasal discharge. Urinalysis reveals 4+proteinuria, RBCs, and RBC casts. ANCA is positive in a cytoplasmic pattern. Antiproteinase 3 (PR3) antibodies are present, but antimyeloperoxidase (MPO) antibodies are absent. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Behçet syndrome
. Sarcoidosis
. Wegener granulomatosis
. Henoch-Schönlein purpura
. Classic polyarteritis nodosa
293) A 35-year-old right-handed construction worker presents with complaints of nocturnal numbness and pain involving the right hand. Symptoms wake him and are then relieved by shaking his hand. There is some atrophy of the thenar eminence. Tinel sign is positive. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Carpal tunnel syndrome
. De Quervain tenosynovitis
. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
. Rheumatoid arthritis of the wrist joint
. Guillain-Barré syndrome
294) A 50-year-old white woman presents with aching and stiffness in the trunk, hip, and shoulders. There is widespread muscle pain after mild exertion. Symptoms are worse in the morning and improve during the day. They are also worsened by stress. The patient is always tired and exhausted. She has trouble sleeping at night. On examination, joints are normal. ESR is normal, and Lyme antibody and HIV test are negative. A diagnosis is best made by which of the following?
. Trial of glucocorticoid
. Muscle biopsy
. Demonstration of 11 tender points
. Psychiatric evaluation
. Trial of an NSAID
{"name":"Ichigo USMLE Med Diagnosis P4", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"1) A 40-year-old man is brought to the emergency room because of altered mental status and gait instability. He has had two falls in the last two days. He drinks one pint of vodka daily and smokes one pack of cigarettes daily. His temperature is 35.0°C (95.0°F), blood pressure is 100\/70 mm Hg, pulse is 90\/min, and respirations are 14\/min. He is disoriented, but not in acute distress. You note prominent horizontal nystagmus and conjugate gaze palsy in both eyes and absent ankle reflexes in both legs. His chest is clear to auscultation. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his symptoms?","img":"https://cdn.poll-maker.com/14-620852/dp4-12.png?sz=1200"}
More Quizzes
Which Durarara Character Are You?
271424
Who knows me best?
520
Do you really know me?
10512
Cafe survey
740
Discover Your Clan with Our Warrior Cats Clan
201025904
Free 2.07 Water Cycle
201021842
Free Civics Examlet Review
201021842
Free Insurance Sales Fundamentals
201023189
Free Employee HSE Knowledge Assessment
201022490
Gender Relations & Intl Dev
15828926
Death & Dying
15821241
Free Dentin Bonding Agent Knowledge
201030974