Bones of the Foot Quiz: Name Every Bone
Quick, free foot bone quiz to test your anatomy knowledge. Instant results.
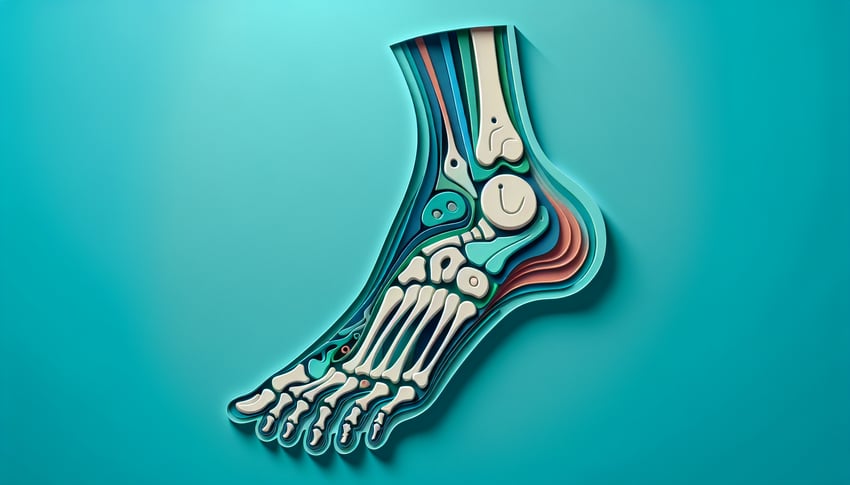
This bones of the foot quiz helps you name each tarsal, metatarsal, and phalanx by shape and position. Use it to check gaps before lab or exams, with quick feedback and clear images. When you finish, deepen your practice with our tarsal bones quiz, explore the whole limb in the lower limb bones quiz, or build labeling skills in the bone labeling quiz.
Study Outcomes
- Identify Key Foot Bones -
Use the bones of the foot quiz to accurately recognize and name tarsal, metatarsal, and phalangeal bones in the human foot.
- Distinguish Tarsal Structures -
Differentiate the seven tarsal bones using the tarsal bones quiz, reinforcing your grasp of their unique shapes and locations.
- Label Metatarsals and Phalanges -
Master the sequence and landmarks of metatarsals and phalanges through targeted foot bones quiz activities.
- Apply Anatomical Terminology -
Employ precise anatomical language from the foot anatomy quiz to describe bone positions, movements, and articulations.
- Analyze Clinical Foot Scenarios -
Interpret common injury or pathology cases by applying quiz insights to identify affected bones and suggest clinical considerations.
Cheat Sheet
- Tarsal Bone Landmarks -
The seven tarsal bones form the hind- and midfoot, including the calcaneus (heel) and talus (ankle). Recognize the navicular, cuboid, and three cuneiforms by recalling their positions: medial to lateral - medial, intermediate, lateral. Identifying these in a bones of foot quiz builds your foundation for more advanced foot anatomy quiz questions.
- Metatarsal Numbering & Clinical Pearls -
There are five metatarsals numbered I - V from the hallux (big toe) to the little toe; the second metatarsal acts as a keystone in the transverse arch. Palpate the dorsalis pedis pulse between metatarsals I and II to link anatomy with clinical exam skills. This detail often appears in foot bones quiz scenarios to test functional knowledge.
- Phalanges & Joint Classifications -
The toes contain 14 phalanges: two in the hallux and three in each lesser toe, connected by hinge (IP) and condyloid (MTP) synovial joints. Understanding these joint types helps you predict movement ranges like plantarflexion and dorsiflexion. Quizzing on these structures is standard in any bones of the foot quiz or foot anatomy quiz.
- Foot Arch Functional Anatomy -
The medial longitudinal arch (calcaneus to 1st metatarsal), lateral longitudinal arch, and transverse arch distribute weight and absorb shock during gait. Use the navicular drop test to assess arch integrity in practice questions or clinical scenarios. Recognizing arch mechanics boosts confidence in both tarsal bones quiz sections and dynamic anatomy reviews.
- Mnemonic Mastery: "Tiger Cubs Need MILC" -
Memorize "Tiger (Talus), Cubs (Calcaneus), Need (Navicular), M (Medial Cuneiform), I (Intermediate Cuneiform), L (Lateral Cuneiform), C (Cuboid)" to recall tarsal order quickly. Pair this with "Tom, Dick And Very Nervous Harry" for tarsal tunnel structures to reinforce neurovascular anatomy. These fun phrases will help you crush any bones of the foot quiz or tarsal bones quiz with ease!