Animal Cell Labeling Quiz: cell label game on the Golgi apparatus
Quick, free animal cell labeling quiz to check your organelle knowledge. Instant results.
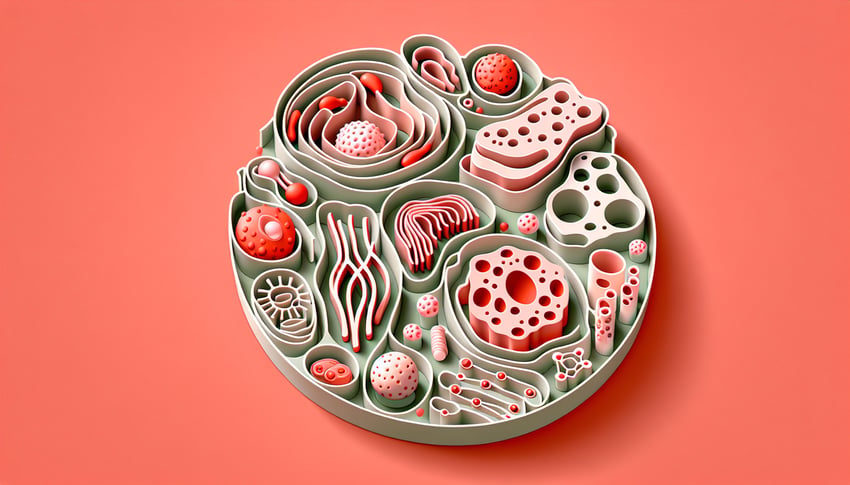
This quiz helps you label an animal cell diagram and spot key parts, with a focus on the Golgi apparatus. Check what you know before a test, then keep learning with cell labeling practice , review shapes on the animal cell diagram, or explore functions in the animal cell organelles quiz .
Study Outcomes
- Identify Major Organelles -
Recognize and name structures such as the nucleus and mitochondria in an animal cell diagram, strengthening your understanding of cellular components.
- Label Cellular Structures -
Apply learned labeling techniques to accurately label an animal cell diagram, improving your proficiency in cell labeling quiz scenarios.
- Describe Organelle Functions -
Explain the primary functions of each organelle, reinforcing why each part is essential to the life of an animal cell.
- Differentiate Cell Components -
Distinguish between similar organelles based on structure and function, enhancing your ability to complete cell labeling activities with confidence.
- Apply Knowledge in a Quiz Setting -
Use your understanding of labeling animal cell parts to tackle timed cell labeling quiz challenges and animal cell labeling games effectively.
- Self-Assess Learning Progress -
Evaluate your mastery of animal cell structure through interactive practice, identifying areas for further study and improvement.
Cheat Sheet
- Cell Membrane - The Selective Barrier -
The phospholipid bilayer controls the passage of ions and molecules, acting like a security gate (Alberts et al., Molecular Biology of the Cell). When you practice labeling animal cell diagrams in our cell labeling quiz, look for its thin, flexible outline to distinguish it from plant cell walls. Remember the mnemonic "FLIP-FLOP" for the fluid and flexible phospholipids.
- Nucleus - The Control Center -
The nucleus houses DNA and directs cellular activities, making it the most prominent organelle (Campbell Biology, 11th Edition). In your animal cell labeling game, spot the dark-stained sphere at the center and label the nuclear envelope, nucleolus, and chromatin. Try the phrase "NEC" (Nucleolus, Envelope, Chromatin) to remember its major parts.
- Mitochondria - The Powerhouse -
Mitochondria generate ATP through cellular respiration, supplying energy for the cell (National Institutes of Health). In a label parts of a cell quiz, look for the bean-shaped organelle with inner folds called cristae. Use the rhyme "Mighty Mite Makes Energy Right" to recall its powerhouse role.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum - Rough vs. Smooth -
The rough ER is studded with ribosomes for protein synthesis, while the smooth ER handles lipid production and detoxification (Khan Academy). When labeling an animal cell diagram, identify the rough ER by its dotted texture and the smooth ER by its tubular network. Think "R-ER for Ribosomes, S-ER for Soaps" to keep their functions straight.
- Golgi Apparatus & Lysosomes - Packaging and Recycling -
The Golgi apparatus modifies, sorts, and ships proteins, while lysosomes contain enzymes for waste breakdown (University of California, Berkeley). In a cell labeling quiz, the Golgi looks like a stack of flattened pancakes, and lysosomes are small round vesicles. Remember "Golf Bags & Little Bins" to map Golgi and Lysosomes correctly.