Vellus Hair Quiz: Which Hair Is Short, Fine, and Unpigmented?
Quick, free quiz to test your knowledge of short fine unpigmented hair. Instant results.

This quiz helps you identify vellus hair (the short, fine, unpigmented hair) and tell it from terminal hair in real photo examples. If you want a deeper foundation, try the hair anatomy quiz, and for broader texture checks and context, take the hair type quiz today.
Study Outcomes
- Identify Downy Hair -
Recognize the defining traits of short, fine, unpigmented downy hair and correctly answer what type of hair is short fine unpigmented and downy.
- Differentiate Hair Types -
Compare downy hair with vellus and terminal hair to distinguish between fine, unpigmented hairs and coarser, pigmented varieties.
- Analyze Electrolysis Methods -
Explain how an electrolysis hair removal system works and why it's considered the gold standard for permanent hair removal methods.
- Apply Quiz Insights -
Use quiz feedback to refine your understanding of hair removal systems and select the best approach for different hair types.
- Evaluate Removal Outcomes -
Assess the effectiveness of permanent hair removal methods, including electrolysis, based on hair type, skin considerations, and long-term results.
Cheat Sheet
- Identifying Vellus Hair -
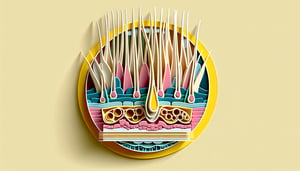
Vellus hair is the classic short, fine, unpigmented and downy hair covering most of the body; it's often described as "peach fuzz." According to the American Academy of Dermatology, these hairs measure less than 2 mm in length and lack a medulla, making them nearly invisible. Remember the mnemonic VELvet soft (Vellus = Very Extra Light) to recall its delicate nature.
- Vellus vs. Terminal Hair -
Terminal hairs are thicker, pigmented, and longer, while vellus hairs remain fine and non-pigmented; the ratio of terminal to vellus hair guides treatment planning. Studies in the Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology show that a high terminal-to-vellus ratio often correlates with hormonal influences. Use the simple formula TVR = Terminal ÷ Vellus to track changes over time during a hair removal quiz or treatment assessment.
- Why Electrolysis Is the Gold Standard -
Electrolysis hair removal system uses proven FDA-approved methods (galvanic, thermolysis, or blend) to permanently damage the hair follicle's bulb and matrix. Clinical trials in Dermatologic Surgery report success rates above 90% when performed by licensed electrologists. In a downy hair quiz context, emphasize that no other method guarantees absolute permanence like electrolysis.
- Core Components of an Electrolysis System -
An effective electrolysis setup includes a precision probe, power unit, grounding pad, and magnification tools; each plays a critical role in targeting vellus versus terminal hairs. The galvanic method uses chemical decomposition, while thermolysis relies on high-frequency heat - blend combines both for stubborn hairs. Always verify your device meets FCC and IEC safety standards to ensure client comfort and regulatory compliance.
- Comparing Permanent Hair Removal Methods -
Beyond electrolysis, laser and intense pulsed light (IPL) offer semi-permanent results by targeting melanin, making them less effective on unpigmented downy hair. The mnemonic LILPE (Laser, IPL, Light, Permanent?, Electrolysis) helps recall which methods work best depending on hair pigment and thickness. For complete coverage in a hair removal quiz, contrast each method's FDA-cleared indications, downtime, and efficacy for various skin types.