What Is Trichoptilosis? A Split Ends Basics Quiz
Quick, free trichoptilosis quiz to test your split ends knowledge. Instant results.

Use this trichoptilosis quiz to check your understanding of split ends, from causes to care, and spot any gaps before class or client work. Build context with what is trichology, then go deeper with our hair follicle anatomy quiz. For a lighter challenge across topics, try hair trivia questions.
Study Outcomes
- Definition of Trichoptilosis -
Understand that trichoptilosis is the technical term for split ends, reinforcing your ability to fill in the blank for "trichoptilosis is the technical term for ____."
- Lanugo Hair Identification -
Identify the hair type described by the question "what type of hair is short fine unpigmented and downy" as lanugo hair, boosting your classification skills.
- Comparison of Hair Types -
Differentiate between various hair types and scalp properties, such as vellus, terminal, and lanugo, to deepen your cosmetology knowledge.
- Practical Scalp Assessment Skills -
Apply key hair and scalp concepts to real-world scenarios, sharpening your ability to perform accurate assessments as a cosmetology pro on ProProfs.
- Quiz-Based Skill Enhancement -
Evaluate and sharpen your cosmetology skills through targeted ProProfs quiz scenarios, gaining confidence and professional insight.
Cheat Sheet
- Trichoptilosis Defined -
Trichoptilosis is the technical term for split ends, describing the fraying of the hair shaft's distal end due to mechanical or chemical damage. Simple routines like gentle detangling, bi-monthly trims, and protein-rich conditioners can boost shine and minimize damage (Milady's Standard Cosmetology).
- Lanugo Hair Identification -
The question "what type of hair is short fine unpigmented and downy" refers to lanugo, the soft fetal hair that may persist on newborns or between vellus hairs in adults. A handy mnemonic is "Lanugo = Little Airy Nuzzle Underneath Grainy Outline" (American Academy of Dermatology).
- Hair Growth Cycle Phases -
Hair grows in three stages: anagen (active, 2 - 6 years), catagen (brief transition, ~2 weeks), and telogen (resting, ~3 months), according to the Journal of Cosmetic Science. Understanding these phases empowers cosmetology proprofs to confidently plan treatments and predict regrowth patterns.
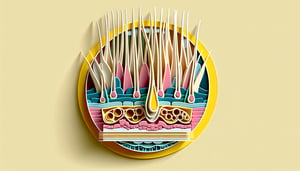
- Hair Shaft Structure -
The hair shaft has three layers: the protective cuticle, the fibrous cortex, and sometimes a medulla. Think "CCM" (Cuticle, Cortex, Medulla) and visualize an onion to remember these concentric layers (American Hair Research Society).
- Common Scalp Conditions -
Key scalp issues include dandruff (seborrheic dermatitis), folliculitis, and psoriasis, each requiring protocols like medicated shampoos or topical corticosteroids. Refer to the American Academy of Dermatology for evidence-based treatment guidelines to keep clients comfortable and confident.