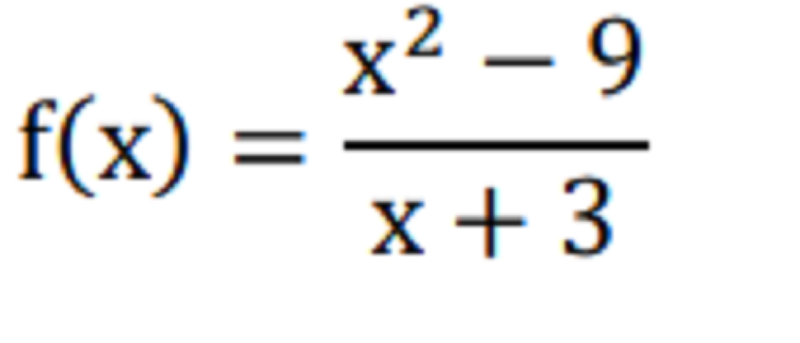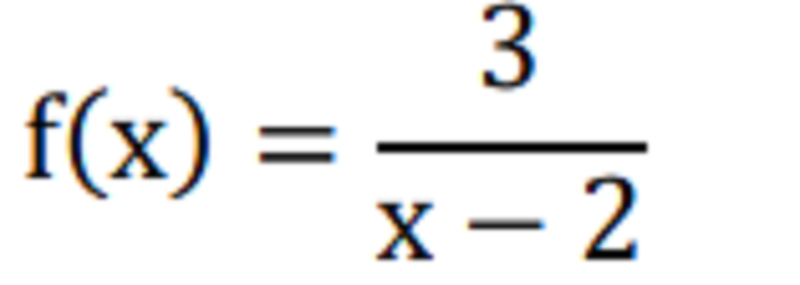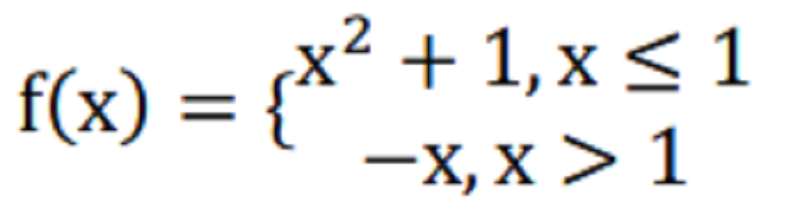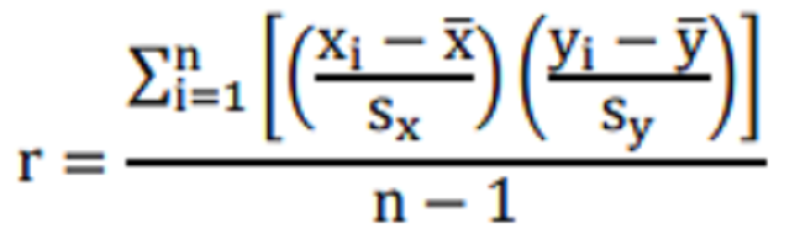MATH RHM TERMS
{"name":"MATH RHM TERMS", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Test your knowledge of functions, matrices, and logical reasoning with our comprehensive quiz designed for mathematics enthusiasts!Engage with 42 challenging questions covering:Monotonic functionsMatrix propertiesLogical propositionsHypothesis testing","img":"https:/images/course5.png"}
More Quizzes
Mathematics Concepts Quiz
8416
JEE Main Sets Relations And Functions: Quiz!
11615
Linear and Circular Economy
1260
Ramadan Quiz
1479
Realistic Zombie Survival - Can You Survive?
201021751
Citric Acid Cycle - Test Your Biochemistry Knowledge
201016528
Kids TV - How Well Do You Know Cartoons?
201023028
Which Avatar: The Last Airbender Character Are You?
201017181
Am I a Narcissist or an Empath? Take the Free
201018055
Which Zombie Monster Are You? Free Creature Personality
201018055
Free Compatibility Test for Couples: Discover Your Match
201016528
Qualitative Research MCQ - Free Practice Questions
201021992