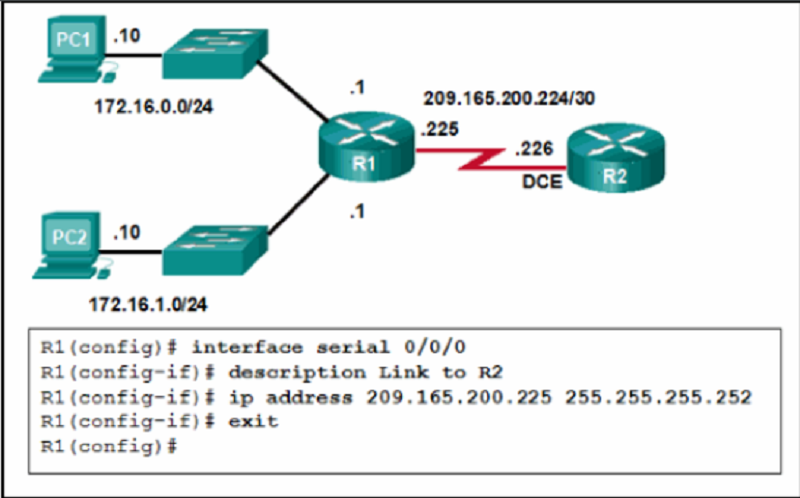
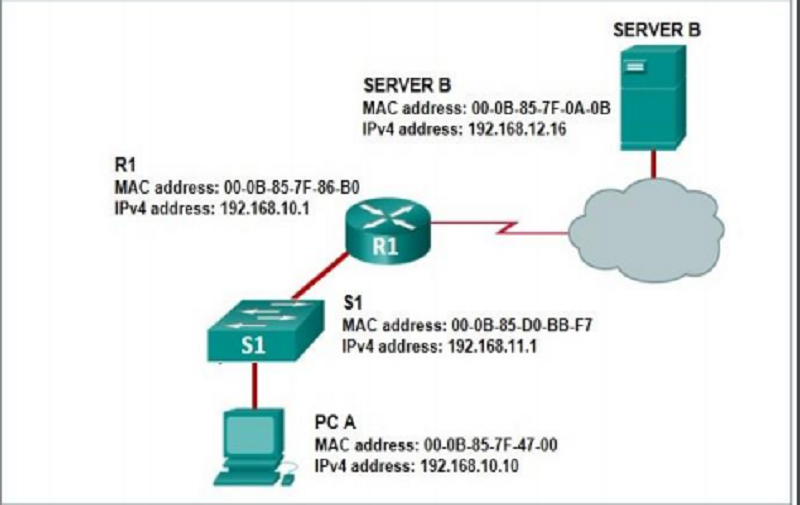
Mrezni Uredjaji 1 Pitanja za Proveru
{"name":"Mrezni Uredjaji 1 Pitanja za Proveru", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Test your knowledge on dynamic routing protocols and related networking concepts with this comprehensive quiz. Designed for network administrators and students, this quiz covers essential topics and practical applications.22 engaging questionsMultiple-choice formatIdeal for both beginners and experienced professionals","img":"https:/images/course5.png"}
More Quizzes
Data
101500
Networking
5221
Pride Month Awareness Trivia
10517
Descubra sua idade mental
1050
Macronutrients: Identify Carbs, Protein & Fat
201016237
Ruler - Free Fractional Inch Reading Practice
201018109
Nutrition Trivia - Free Diet & Health Knowledge
201016798
IT Support Technician Knowledge - Free Online
201017354
Zakat Calculation (Maliki Fiqh) - Free Practice
201016078
Dry Sense of Humor Personality - Free Online
201016567
Exam Passing Score & Pass Rate Calculation - Free
201016290
Constitution Test: 50 Questions (Free Practice)
201016455