Chir Diagnosis P2 Q 1 to 50
1) A 25-year-old previously healthy man is scheduled for elective inguinal hernia repair under general anesthesia. After induction of anesthesia and initial inguinal incision, the patient develops tachycardia, muscle rigidity, fever of 38.5°C, and elevated end-tidal carbon dioxide. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. pneumonia
. atelectasis
. Urinary tract infection
. Myocardial infarction
. Malignant hyperthermia
2) A 55-year-old man presents to the emergency department with left lower quadrant abdominal pain. The pain has been present for 1 week, but has increased in intensity over the last 2 days associated with nausea, constipation, and dysuria. Past history is unremarkable. Examination reveals a temperature of 101°F, pulse rate of 95/min, BP of 130/70 mmHg, and normal heart and lung examinations. Abdominal examination reveals fullness and marked tenderness in the left lower quadrant, with voluntary guarding and decreased bowel sounds. Laboratory tests reveal a WBC count of 18,000 with a left shift and 20–50 WBCs in the urinalysis. A CT scan of the abdomen reveals a thickened sigmoid colon with pericolonic inflammation. He is admitted to the hospital for treatment. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Colon cancer with contained perforation
. Ischemic colitis
. Pseudomembranous colitis
. diverticulitis
. pyelonephritis
3) A 56-year-old woman has been treated for 3 years for wheezing on exertion, which was diagnosed as asthma. Chest radiograph, shown here, reveals a midline mass compressing the trachea. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Lymphoma
. Neurogenic tumor
. Lung carcinoma
. Goiter
. Pericardial cyst
5) A 25-year-old man was admitted to the ICU with severe head injury with a basal skull fracture. Eighteen hours after the injury, he developed polyuria. Urine osmolality was 150 mOsm/Land serum osmolality was 350 mOsm/L. IV fluids were stopped, and 1 hour later urine output and urine osmolality remained unchanged. Five units of vasopressin were administered intravenously, and urine osmolality increased to 300mOsm/L. Select the most likely diagnosis of the patients with polyuria?
. Central diabetes insipidus (DI)
. nephrogenic DI
. Water intoxication
. Solute overload
. Diabetes mellitus
6) A 70-year-old man was admitted to the ICU with severe pancreatitis. During his ICU course, he underwent several CT scans with IV contrast and was also treated with an aminoglycoside for a urinary tract infection. The patient required a prolonged course of TPN, and developed Candida sepsis treated with amphotericin. He subsequently developed polyuria with urine osmolality of 250mOsm/L and serum osmolality of 350 mOsm/L. After receiving 5 units of vasopressin intravenously, there is no change in urine osmolality or urine output. Select the most likely diagnosis of the patients with polyuria?
. Central diabetes insipidus (DI)
. nephrogenic DI
. Water intoxication
. Solute overload
. Diabetes mellitus
7) A 42-year-old man describes intermittent episodes of severe, crushing chest pain that extends to the back and the jaw and last anywhere from a few seconds to several minutes. Many times the pain is accompanied by dysphagia and triggered by the ingestion of very cold or very hot liquids. However, sometimes the pain occurs for no apparent reason. There is no history of regurgitation, and, although the problem has been present for many years, there has been no progression of the symptoms. Repeated ECGs and cardiac enzymes have always been negative. Barium swallow shows an area of "corkscrew" appearance. Manometry shows that about one half of wet swallows produce repetitive simultaneous esophageal contractions of the esophageal body, and that the lower esophageal sphincter has normal pressures and exhibits normal relaxation. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Achalasia of the esophagus
. Cancer of the lower esophagus
. Diffuse esophageal spasm
. Nutcracker esophagus
. Zenker's diverticulum
8) A 29-year-old man presents to the ER with persistent vomiting and abdominal pain for the last 24 hours. The pain is crampy, diffuse, and has been getting worse. He had a normal bowel movement two days ago and denies diarrhea. The emesis appears green without blood or coffee grounds. He has not eaten since the onset of the pain due to nausea. On exam, his temperature is 36.8° C (98.2° F}, pulse is 91/min, and blood pressure is 116/75 mmHg while sitting and 94/65 mmHg while standing. His abdomen is distended with hyperactive bowel sounds. Percussion reveals tympany and he is diffusely tender to palpation. There is no rebound tenderness or guarding. Laboratory studies reveal:WBC count 9,600/mm3Hematocrit 45%Sodium 147 mEq/LPotassium 3.1 mEq/LCreatinine 1.0 mg/dLAST 20 U/LALT 12 U/LBilirubin 0.8 mg/dLWhich of the following historical findings would you most expect in this patient?
. High alcohol consumption
. Occasional black or tarry stool
. Appendectomy six months ago
. Fatty food intolerance
. Recent weight loss
9) A 63-year-old obese female undergoes an elective cholecystectomy after two episodes of acute calculous cholecystitis. Three days after surgery, her blood pressure is 150/100 mmHg, her heart rate is 90/min, and her arterial oxygen saturation is 91 % on room air. She is afebrile. Which of the following would most likely increase her functional residual lung capacity?
. Inhaled albuterol
. Sequential compression devices to her lower extremities
. Elevation of the head of the bed
. Decreasing the dose of her postoperative opioids
. Postoperative benzodiazepines
10) A 62-year-old woman had an abdominal hysterectomy and salpingo-oophorectomy 3 days ago. She had an indwelling bladder catheter during the procedure, which was removed in the recovery room. She has been voiding at will since then. She also had compression pneumatic stockings on both lower extremities during the operation. She began ambulation on the 1st postoperative day, and has been as active as possible under the circumstances, including faithful adherence to a prescribed program of incentive spirometry. On the evening of the 3rd postoperative day, she spikes a fever, with a temperature to 39.4C (103F). Which of the following is the most likely source of the fever?
. Atelectasis
. Deep thrombophlebitis
. Intra-abdominal abscess
. Urinary tract infection
. Wound infection
11) A 44-year-old male is found unresponsive and hypotensive at the scene of a high-speed motor vehicle accident. He is intubated and immediately rushed to the emergency department. The passenger in his car is pronounced dead at the scene. Physical examination in the ED shows large bruises over the entire chest wall and collapsed neck veins bilaterally. Lung exam reveals decreased breath sounds on the left side. Chest x-ray shows a large left hemothorax and a widened, rightward deviating mediastinum. The most likely diagnosis is?
. Esophageal rupture
. Aortic injury
. Myocardial rupture
. Myocardial contusion
. Diaphragm rupture
12) An 85-year-old male is placed on mechanical ventilation after a complicated elective hernia repair. After five days of endotracheal intubation with mechanical ventilation, the ratio of the rate of carbon dioxide produced to the rate of oxygen uptake is 1.05. What is the best explanation for these findings?
. Sepsis
. High-protein tube feeding
. Carbohydrate excess in the diet
. High inspired oxygen fraction
. Pulmonary atelectasis
13) A 75-year-old woman is admitted to the hospital from a nursing home for abdominal pain and pneumonia. She was noted to be short of breath with increasing cough for 2 days before admission. Treatment, consisting of supplemental oxygen, IV antibiotics, and pulmonary toilet, is instituted, with improvement within 2 days. On the third hospital day, her abdominal pain worsens. Examination reveals a mildly distended abdomen with bowel sounds but no signs of peritonitis. Remainder of examination reveals a tender bulge in the medial left thigh below the inguinal ligament. Gentle pressure causes more pain but does not change the size or shape of the bulge. Abdominal films show a nonspecific bowel gas pattern. Laboratory analysis shows a WBC of 13,000, decreased from 18,000 at the time of admission. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Incarcerated direct inguinal hernia
. Lymph node with abscess
. Femoral artery aneurysm
. Incarcerated indirect inguinal hernia
. Incarcerated femoral hernia
14) A 66-year-old woman picks up a bag of groceries out of the supermarket cart to place it in the trunk of her car. As she does so, she feels sharp, sudden pain in the middle of her arm, and her humerus suddenly breaks. She arrives at the emergency department cradling her arm; the deformity leaves no doubt that the bone is broken. Which of the following is the most likely reason for the fracture?
. Bony metastasis to the humerus from breast cancer
. Osteitis fibrosa cystica from parathyroid disease
. Osteomalacia from nutritional deficiency
. Osteoporosis
. Primary malignant bone tumor
15) An 18-year-old male comes to the physician's office because of dull aching and fullness of the scrotum. Examination shows soft left-sided scrotal swelling; transillumination testing is negative. The scrotal swelling increases when the patient performs the Valsalva maneuver. The physical examination is otherwise unremarkable. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his condition?
. Hypoalbuminemia
. Dilatation of pampiniform plexus
. Fluid in the tunica vaginalis
. Testicular neoplasia
. Cystic dilations of the efferent ductules
16) A 72-year-old man underwent surgical repair of an aneurysm of the infrarenal aorta. He received perioperative prophylaxis with a second-generation cephalosporin antibiotic. On the first postoperative day he complains of progressive abdominal pain and bloody diarrhea. His temperature is 38.5° C (101° F), blood pressure is 110/65 mm Hg, pulse is 110/min and respirations are 22/min. His abdomen is mildly distended and tender to palpation. The tenderness is mostly in the left lower quadrant without rebound. Femoral pulses are full and symmetric. His white blood cell count is 12,000/mm3. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Pseudomembranous colitis
. Invasive infectious diarrhea
. Aortoenteric fistula
. Ischemia of the bowel
. Perforation of the colon
17) A 32-year-old male comes to the emergency department because of a 3 day history of increasing lower abdominal pain, mild diarrhea and rectal pain on defecation. Ten days ago he had right lower quadrant (RLQ) pain for about 24 hours that resolved spontaneously. Since then, he has had malaise and low-grade fever. His temperature is 38.7°C (101.6°F), blood pressure is 150/90 mm Hg, pulse is 11 0/min and respirations are 15/min. Examination shows lower abdominal tenderness without rebound. No masses are palpable, and bowel sounds are decreased. Rectal examination shows a very tender, boggy and fluctuant bulging mass on palpation with the tip of the finger anteriorly. Laboratory studies show:Complete blood count Hemoglobin14.0 g/LPlatelets270,000/mm3Leukocyte count15,500/mm3His current condition is most likely a complication of?
. Anorectal abscess
. Invasive diarrhea
. Acute appendicitis
. Acute diverticulitis
. Colon cancer
18) A 44-year-old man complains of vague right upper abdominal discomfort that he has had for about 1 month. He describes no other symptoms, and, except for enucleation of one eye at age 21 "for a tumor," he has been in excellent health all his life. He exercises regularly and neither smoke nor drinks. The only findings on physical examination include the artificial eye and a tender, enlarged, and nodular liver. CT scan of the upper abdomen demonstrates multiple masses within the liver. Which of the following will most likely be found on biopsy of these masses?
. Metastatic malignant melanoma
. Metastatic prostatic cancer
. Metastatic retinoblastoma
. Metastatic sarcoma
. Primary hepatocellular carcinoma
19) A previously healthy, intoxicated, 19-year-old man is driving a car without using a seat belt. He crashes the car into the back of a parked truck. In the process he slams his abdomen into the steering wheel and ruptures his spleen. Which of the following is the most important problem associated with this type of injury?
. Bacteremia
. Electrolyte abnormalities
. External blood loss
. Internal blood loss
. Peritonitis
20) A 27-year-old immigrant from El Salvador has a 14 × 12 × 9 cm mass in her left breast. It has been present for 7 years and has slowly grown to its present size. The mass is firm, nontender, rubbery, and completely movable, and it is not attached to the overlying skin or the chest wall. There are no palpable axillary nodes or skin ulceration. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Breast cancer
. Chronic cystic mastitis
. Cystosarcoma phyllodes
. Intraductal papilloma
. Mammary dysplasia
21) A 63-year-old man, who weighs 65 kg, is in his 2nd postoperative day after an abdominoperineal resection for cancer of the rectum. An indwelling Foley catheter was left in place after surgery. The nurses are concerned because, even though his vital signs have been stable, his urinary output in the past 2 hours has been zero. In the preceding 3 hours, they had collected 56 mL, 73 mL, and 61 mL. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Acute renal failure
. Damage to the bladder during the operation
. Damage to the ureters during the operation
. Dehydration
. Plugged or kinked catheter
22) A 55-year-old woman falls in the shower and hurts her right shoulder. She shows up in the emergency department with her arm held close to her body, but the forearm rotated outward as if she were going to shake hands. She is in pain and will not move the arm from that position. Her shoulder looks "square" in comparison with the rounded unhurt opposite side, and there is numbness in a small area of her shoulder over the deltoid muscle. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Acromioclavicular separation
. Anterior dislocation of the shoulder
. Fracture of the upper end of the humeral shaft
. Posterior dislocation of the shoulder
. Scapular fracture
23) A 68-year-old man is brought to the emergency department with excruciating back pain that began suddenly 45 minutes ago. The pain is constant and is not exacerbated by sneezing or coughing. He is diaphoretic and has a systolic blood pressure of 90 mm Hg. There is an 8 cm pulsatile mass deep in his epigastrium, above the umbilicus. A chest x-ray film is unremarkable. Two years ago, he was diagnosed with prostatic cancer and was treated with orchiectomy and radiation. At that time, his blood pressure was normal, and he had a 6-cm, asymptomatic abdominal aortic aneurysm for which he declined treatment. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Dissecting thoracic aortic aneurysm
. Fracture of lumbar pedicles with cord compression
. Herniated disc
. Metastatic tumor to the lumbar spine
. Rupturing abdominal aortic aneurysm
An out-of-shape, recently divorced, 42-year-old man is trying to impress a young woman by challenging her to a game of tennis. In the middle of the game, a loud "pop" (like a gunshot) is heard, and the man falls to the ground clutching his ankle. He limps off the court with pain and swelling in the back of the lower leg. Although he can still weakly plantar-flex his foot, he seeks medical help the next day because of persistent pain, swelling, and limping. He can put weight on that foot with no exacerbation of the pain, but the motion of taking a step is painful. Which of the following would be the most likely finding on physical examination?
. Tapping on the calcaneus is extremely painful
. The ankle joint can be abducted farther out than the normal contralateral side
. The ankle joint can be adducted farther in than the normal contralateral side
. There is a gap in the Achilles tendon easily felt by palpation
. There is crepitation and grating by direct palpation over either malleoli
25) A 27-year-old man sustained penetrating injuries of the chest and abdomen when he was repeatedly stabbed with a long ice-pick. At the time of admission, he had a right pneumothorax, for which a chest tube was placed prior to undergoing a general anesthetic for exploratory laparotomy. The operation revealed no intraabdominal injuries and was terminated sooner than had been anticipated. The patient remained intubated, waiting for the anesthetic to wear off. Because he was not moving enough air, he was placed on a respirator. Then, he suddenly went into cardiac arrest and died. All through this time he had been hemodynamically stable, and never had any signs of hypotension or arrhythmias. Which of the following was the most likely cause of the cardiac arrest?
. Air embolism
. Fat embolism
. Myocardial infarction
. Pulmonary embolus
. Tension pneumothorax
26) A 13-year-old, obese boy complains of persistent knee pain for several weeks. The family brings him in because he has been limping. He sits in the examining table with the sole of the foot on the affected side pointing to the other leg. Physical examination is normal for the knee, but shows limited hip motion. As the hip is flexed, the leg goes into external rotation and cannot be rotated internally. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Avascular necrosis of the femoral head
. Developmental dysplasia of the hip
. Osteogenic sarcoma of the lower femur
. Slipped capital femoral epiphysis
. Tibial torsion with foot inversion Chir Diagnosis P2
27) A 72-year-old man comes in complaining of persistent and nagging low back pain that he has had for several weeks. The pain seems to be increasing in intensity, is worse at night, is unrelieved by rest or positional changes, and is not exacerbated by coughing, sneezing, or straining to have a bowel movement. He is a chronic smoker, and for the past 3 months has had persistent cough with occasional bloody streaked sputum, as well as a 20-pound weight loss. On physical examination, he is distinctly tender to palpation at a particular spot over his lower thoracic spine. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Ankylosing spondylitis
. Herniated disk
. Metastatic tumor to the thoracic spine
. Multiple myeloma
. Primary malignant bone tumor
28) The unrestrained front-seat passenger in a car that crashed at high speed arrives at the emergency department with signs of moderate respiratory distress. Physical examination shows no breath sounds at all on the left hemithorax. Percussion is unremarkable, and his vital signs are normal. A chest x-ray film shows a collapsed left lung and multiple air-fluid levels filling the left pleural cavity. A nasogastric tube that had been placed prior to taking the film shows the tube reaching the upper abdomen and then curling up into the left chest. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Blow out of pulmonary blebs
. Esophageal rupture or perforation
. Left diaphragmatic rupture
. Left hemopneumothorax
. Major injury to the tracheobronchial tree
29) A 67-year-old man shows up in the emergency department because he has not been able to void for the past 12 hours. He feels the need to, but he cannot do it. He gives a history that, for several years now, he has been getting up four or five times a night to urinate. It would take him a considerable time to get the urinary stream going, and the stream lacked force and often ended in a dribble. Because of a cold, 2 days ago he began taking an antihistamine, taking a decongestant, and drinking plenty of fluids. Physical examination shows a palpable, smooth, round mass arising from the pubis and reaching about half way toward the umbilicus. The mass is dull to percussion, and pushing on it accentuates the feeling of needing to void. Rectal examination reveals a large, boggy, non-tender prostate gland without nodules. This a classic presentation for which of the following acute conditions?
. Bacterial prostatitis
. Cystitis in a patient with bladder cancer
. Renal failure
. Urinary retention in a patient with benign prostatic hypertrophy
. Urinary retention in a patient with prostatic cancer
30) Several months after sustaining a crushing injury to his arm, a patient complains bitterly about constant, burning, agonizing pain in that arm, that does not respond to the usual analgesic medications. The pain in his arm is aggravated by the slightest stimulation of the area, such as rubbing from the shirt sleeves. The arm is cold, cyanotic, and moist, but it is not swollen. Pulses at the wrist are normal, and neurologic function of the three major nerves is intact. Which of the following is most appropriate to provide diagnostic confirmation of the nature of the problem and eventual therapy?
Angiogram and subclavian vein bypass
. Cervical spine x-rays and cervical rib resection
. Doppler studies and arterial reconstruction
. Doppler studies and fasciotomy
. Sympathetic block and surgical sympathectomy
31) A 57-year-old alcoholic man is being treated for acute hemorrhagic pancreatitis. He was in the intensive care unit for 1 week, where he required chest tubes for pleural effusions and was on a respirator for several days. Eventually, he improved sufficiently to be transferred to the floor. Three days after leaving the unit, and about 2 weeks after the onset of the disease, he spikes a fever and develops leukocytosis. Which of the following developments do these recent findings most likely suggest?
. Chronic pancreatitis
. Pancreatic abscess
. Pancreatic pseudocyst
. Pelvic abscess
. Subphrenic abscess
32) A 33-year-old woman is involved in a high-speed automobile collision. She arrives at the emergency department gasping for breath. Her lips are cyanotic and she has flaring nostrils. There are bruises over both sides of the chest, and tenderness suggestive of multiple rib fractures. Her blood pressure is 60/45 mm Hg, pulse is 160/min and feeble and central venous pressure is 25 cm H2O. Her neck and forehead veins are distended. She is diaphoretic and has a hint of subcutaneous emphysema in the lower neck and upper chest. Her left hemithorax has no breath sounds and is hyper resonant to percussion. The trachea is deviated to the right, as are the heart sounds. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Air embolism from tracheobronchial injuries
. Flail chest due to multiple rib fractures
. Massive intrapleural bleeding from torn intercostal vessels
. Massive mediastinal bleeding from ruptured aorta
. Tension pneumothorax caused by lung punctured by broken ribs
33) A 32-year-old male is rushed to the emergency room after a motor vehicle accident. He was driving 55 mph when he suddenly lost control of his vehicle and hit a tree. He was wearing a seat belt. On physical examination, the patient appears scared and complains of moderate chest and abdominal discomfort. His voice is soft. His blood pressure is 190/ 100 mmHg and his heart rate is 100/min. The pupils are symmetric and reactive to light and the trachea is midline. You note bruising over the chest and upper abdomen. No penetrating injuries are evident. Which of the following injuries is most likely in this patient?
. Esophageal rupture
. Tracheobronchial disruption
. Vagus nerve disruption
. Aortic rupture
. Pulmonary contusion
34) A 23-year-old male is brought to the emergency department following a motor vehicle accident (MVA) where he was the unrestrained driver. The patient was found unresponsive at the scene and was intubated by paramedics. He receives 2.5L of normal saline over the 20 minutes before he reaches the ED. His blood pressure there is 70/30 mmHg and his heart rate is 120/min. On physical examination, he responds to strong vocal and tactile stimuli by opening his eyes. His pupils are equal and reactive to light. There are multiple bruises over the anterior chest and upper abdomen. His neck veins are flat, trachea is midline and extremities are cold. Cardiac monitoring shows sinus tachycardia. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's current condition?
. Impaired myocardial contractility
. Ventricular filling restriction
. Loss of intravascular volume
. Air embolism
. Loss of vascular tone
35) A 33-year-old male falls while riding his bicycle in the park, and presents to the emergency department. Physical examination reveals upper abdominal bruises. His abdomen is non-distended, soft, and mildly tender in the epigastrium. Abdominal CT scan does not reveal any abnormalities. The patient is sent home with analgesic medications. He returns one week later with fever, shaking chills, poor appetite and deep abdominal pain Which of the following is most likely related to this patient's symptoms?
. Spleen rupture
. Stomach perforation
. Pancreatic laceration
. Small bowel necrosis
. Meckel diverticulitis
36) A 36-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with severe epigastric pain and right shoulder pain of about two hours duration. She also reports having one episode of emesis. When asked about her diet, she explains that she unintentionally fasted yesterday and had a large meal two hours ago. Her past medical history is significant for frequent heartburn for which she takes ranitidine. Several hours after presenting, the patient's pain resolves completely. Which of the following best explains this episode?
. Viscus distention
. Acid hypersecretion
. Peritoneal irritation
. Mucosal inflammation
. Vascular obstruction
37) A 74-year-old male is undergoing elective abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. He is given two units of packed red blood cells during the surgery. He develops fever and chills one hour after finishing the surgery and transfusion. He received one dose of prophylactic antibiotics before surgery. He had coronary bypass grafting two months ago. His temperature is 38.5C (101.3F), blood pressure is 130/76 mm Hg, pulse is 90/min and respirations are 16/min. Physical examination shows a mildly tender wound; there is no redness. The lungs are clearto auscultation. He has a Foley catheter and right subclavian central venous access, each placed at the time of surgery. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his fever?
. Nosocomial pneumonia
. Drug fever
. Transfusion reaction
. Urinary tract infection
. Catheter associated infection
38) A 55-year-old male comes to the physician's office because of chronic pain in his buttock, hip and thigh muscles. The aching pain is present in both legs and usually is associated with walking. He has multiple medical problems and takes several medications. He has a 30 pack year smoking history. His temperature is 36.7C (98F), blood pressure is 150/88 mm Hg, pulse is 80/min and respirations are 16/min. Examination shows decreased femoral, popliteal and dorsalis pedis pulses in both legs. Which of the following additional complaints is most likely in this patient?
. Snoring
. Headache
. Anorexia
. Ankle swelling
. Impotence
39) A 23-year-old male is brought to the emergency department after a motor vehicle accident. He was an unrestrained driver. He was found unresponsive at the scene of the accident, and was intubated by the paramedics. He has received 2L of normal saline over the last 20 minutes. His blood pressure is 80/40 mmHg, and heart rate is 120/min. He responds to strong vocal and tactile stimuli by opening his eyes. His pupils are equal and reactive to light. His neck veins are distended. There are multiple bruises involving the anterior chest and upper abdomen. His chest x-ray shows a small, left-sided pleural effusion and normal cardiac contours. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Lung contusion
. Aortic rupture
. Esophageal rupture
. Pericardial tamponade
. Bronchial rupture
40) A 65-year-old male comes to the ER because of sudden onset severe pain in his right leg. He says he has never previously had pain in his leg and denies any recent trauma, fever or chills. He recently suffered an acute anterior wall myocardial infarction that resulted in cardiogenic shock and is currently undergoing cardiac rehabilitation. His other medical problems include hypertension, diabetes and hyperlipidemia. His temperature is 36.7C (98F), blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg, pulse is 90/min (regular) and respirations are 16/min. His lungs are clear to auscultation. His heart rate is regular with no murmurs. Below the knee the right leg is cool to touch and appears pale. The dorsalis pedis pulse is not palpable while the popliteal pulses are full. Pulses are normal in the contralateral extremity. Neurologic examination shows numbness over the dorsum of the leg and foot. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his symptoms?
. Nerve compression
. Arterial thrombosis
. Arterial embolism
. Venous thrombosis
. Arterial vasculitis
41) An 88-year-old male complains of severe right calf pain several hours after undergoing a right femoral artery embolectomy. He also complains of a burning sensation in his posterior right leg. He has a long history of atrial fibrillation and hypertension. His past medical history also includes stroke, bleeding duodenal ulcer, diabetes mellitus and diabetic nephropathy. On physical examination, his blood pressure is 160/70 mm Hg and his heart rate is 100 per minute and irregular. His right calf is swollen, tense and exquisitely tender; the pain is worsened by passive extension of the right knee. Dorsalis pedis and posterior tibial pulses are palpable in the bilateral lower extremities. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
. Recurrent embolism
. Venous thrombosis
. Soft tissue swelling
. Bone infarction
. Anaerobic infection
42) A 62-year-old man is brought to the emergency department after being involved in a motor vehicle collision where he suffered serious burns. On physical examination there are second degree burns covering both upper extremities and third degree burns over the anterior aspects of both lower extremities. On day three of his hospitalization, the patient develops tachycardia and decreased urine output. His blood pressure is 90/60 mmHg, pulse is 120/min, temperature is 95°F (35°C), and respirations are 26/min. Laboratory analysis reveals: Blood glucose 230 mg/dL, WBC 16,000/mm3, Platelets 80,000/mm3. Which of the following is the best explanation for this patient's current condition?
. Myocardial injury
. Extensive protein breakdown
. Immune reaction to heterologous proteins
. Bacterial infection
. Renal glomerular injury
43) A 36-year-old male presents with firm, non-tender swelling of his right cheek. He tells you that he had similar swelling at that site two years ago and was diagnosed with a tumor, which was subsequently removed without complication. Examination reveals fullness of the parapharyngeal space on the right side. Repeat surgery in this patient is most likely to result in which of the following complications?
. Hoarseness
. Tic douloureux
. Facial droop
. Tongue palsy
. Jaw asymmetry
44) A 43-year-old male complains of right shoulder pain and weakness after falling on his outstretched hands two days ago. He denies any swelling or shoulder deformity. You passively abduct both his arms above his head and then ask him to bring his arms down slowly in an adducting motion. The right arm drops rapidly at the midpoint of its descent. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Biceps tendon tear
. Long thoracic nerve injury
. Lower brachial trunk injury
. Rotator cuff tear
. Humoral neck fracture
45) A 32-year-old female presents with intermittent blood staining of her bra from her left breast. She has not felt any lumps on either breast. Physical examination shows no breast mass or axillary lymphadenopathy. Ultrasonogram of the breast is within normal limits. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Fibrocystic changes
. Fibroadenoma
. Intraductal papilloma
. Ductal carcinoma in situ
. Hyperprolactinemia
46) A 31-year-old male presents to your office with pain and swelling over his coccyx. He has never had symptoms like this before. His past medical history is significant for an appendectomy two years ago and acute pyelonephritis one year ago. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Perianal abscess
. Pilonidal disease
. Crohn's disease
. Suppurative hidradenitis
. Bowen's disease
47) An 18-year-old male comes to the physician's office because of dull aching and fullness of the scrotum. Examination shows soft testicular swelling; transillumination testing is negative. The scrotal swelling increases when the patient performs the Valsalva maneuver. The physical examination is otherwise unremarkable. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his condition?
. Hypoalbuminemia
. Dilatation of pampiniform plexus
. Fluid in the tunica vaginalis
. Testicular neoplasia
. Cystic dilations of the efferent ductules
48) A 12-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department after being involved in a motor vehicle collision. He is in no distress and is admitted for observation. Two hours after admission, he develops tachypnea and tachycardia. His temperature is 36.7C (98F), blood pressure is 110/66 mm Hg, pulse is 110/min, and respirations are 22/min. Examination shows bruises on the right side of the chest, but palpation of the ribs does not elicit pain or suspicion for rib fractures. Breath sounds are decreased on the right side. ABG on 6 liters of oxygen shows PO2 of 60 mm Hg, PCO2 of 32 mm Hg, and pH of 7.42. An x-ray film of the chest shows a patchy irregular alveolar infiltrate in the right middle and lower lobes. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Adult respiratory distress syndrome
. Aspiration pneumonia
. Fat embolism
. Hemothorax
. Pulmonary contusion
49) A 31-year-old male is brought to the emergency department after being involved in a motor vehicle collision as an unrestrained passenger. He was given 3L of normal saline in the ambulance on his way to the hospital and has been receiving 5 L/min of oxygen by nasal cannula. He is agitated and moves all four extremities spontaneously. His blood pressure is 85/55 mmHg and his heart rate is 120/min. His respiratory rate is 30/min. His pupils are symmetric and reactive to light. His neck veins are flat and his trachea is shifted slightly to the right. Over the left hemithorax, breath sounds are absent and there is dullness to percussion. Which of the following diagnoses is most likely?
. Tension pneumothorax
. Lung contusion
. Lung atelectasis
. Hemothorax
. Diaphragmatic rupture
50) A 45-year-old policeman presents to your office complaining of tiredness and sleepiness. He says that his job seems tiring to him recently. It is difficult for him to get up in the morning and go to work. He goes to bed early because he feels tired and sleepy. Two months ago, he was investigating a case of massive murder. He slipped on the blood on the floor, fell and hit his head. He also describes recent abdominal pain that is constant and gnawing, interfering with his sleep. His appetite is poor, and he lost 15 pounds over the last month. Physical examination is significant only for tenderness and fullness in the epigastrium. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Duodenal ulcer
. Major depressive episode
. Pancreatic cancer
. Post-traumatic stress disorder
. Chronic subdural hematoma
4) A 62-year-old woman presents to the physician’s office with complaints of constipation. She has had constipation for the last 6 months, which has worsened over the last month, associated with mild bloating. She noted that her stool has become “pencil thin” in the last month, with occasional blood, but she continues to have bowel movements daily. Past history is unremarkable. Examination reveals normal vital signs and heart and lung examination. Abdominal examination reveals mild fullness, especially in the lower quadrants. Rectal examination shows no rectal masses, but the stool is hematest positive. A barium xray is obtained, and one view is shown in Figure 6-11. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
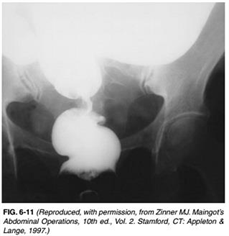
USMLE Surgery

. Crohn’s disease
. Ischemia with stricture
. Rectal carcinoma
. Sigmoid volvulus
. Diverticulitis with colovesical fistula
{"name":"Chir Diagnosis P2 Q 1 to 50", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"How a u?.","img":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/3012/images/ogquiz.png"}
More Quizzes
PSYC 101 TRIAL QUIZ
40202190
What Tyler are You?
126130
Efectul Mandela
840
Drzavni
251295
What Is Your Color Aura? Take the Free to Find Out
201030975
Free MMPI-2 Online Test - Uncover Your Personality Today
201030610
Fun Facts About Chemical Changes - Test Your Skills
201054091
Introduction to Design Thinking
15826911
Free "Am I Full of Myself?": Discover Your True Self
201027178
Free Storage Classification Knowledge Test
201022160
Free Civics and Government Knowledge
201027732
Ace Your Rational Functions Test: Graphing Challenge
201056890