Oral Pathology Identification Review

Oral Pathology Identification Quiz
Test your knowledge on oral pathology with this comprehensive quiz designed for students, professionals, and enthusiasts. With 80 challenging questions, this quiz covers a wide range of topics including lesions, oral conditions, and tissue responses.
Key Features:
- 80 detailed questions
- Multiple choice format
- Learning opportunity for dental students and practitioners
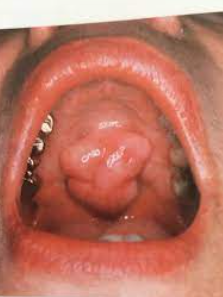
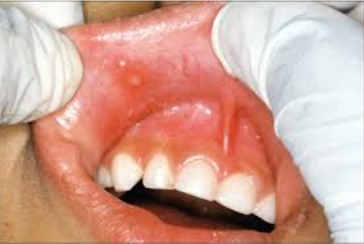
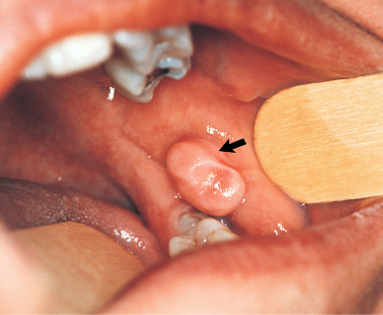
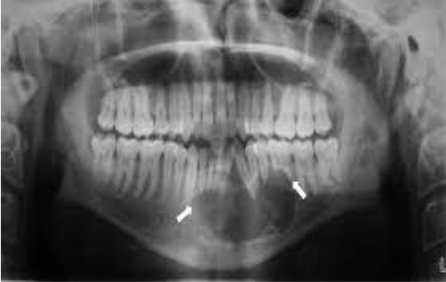
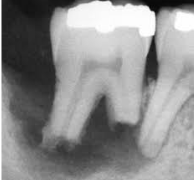
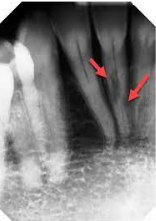
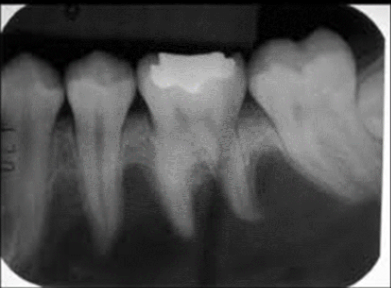
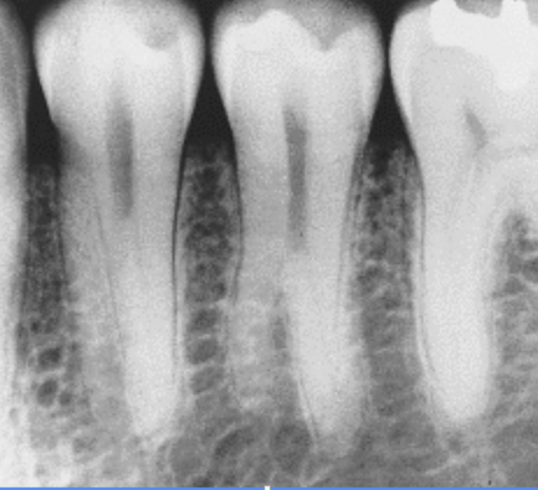
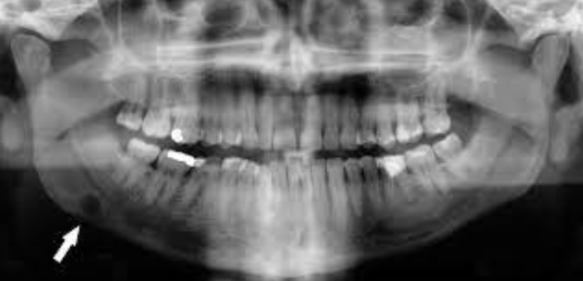
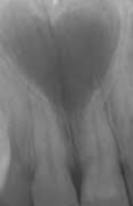
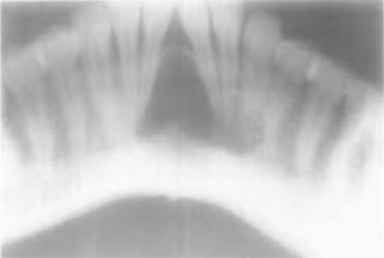
Cannot be diagnosed through clinical appearance, this lesion is diagnosed with radiographs
Defined as a odontogenic tumor that consists of a collection of numerous small teeth. They do not exhibit unlimited growth potential therefor are classified more as a developmental abnormality more than true tumors
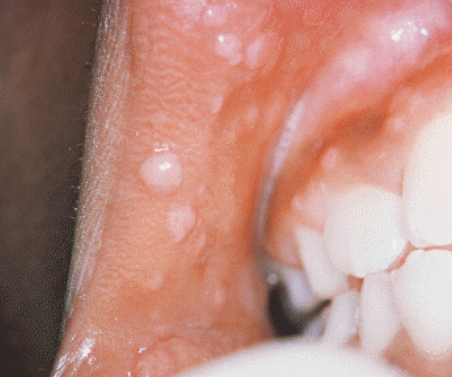
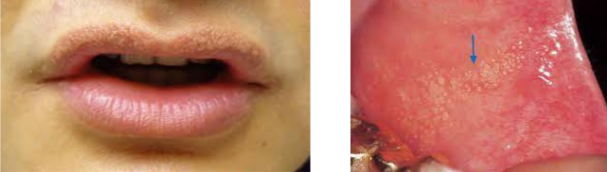
Clusters of ectopic sebaceous glands
Diagnosed through clinical appearance
Appear as yellow lobules in clusters
Commonly observed on vermilion border of lips and buccal mucosa
No treatment
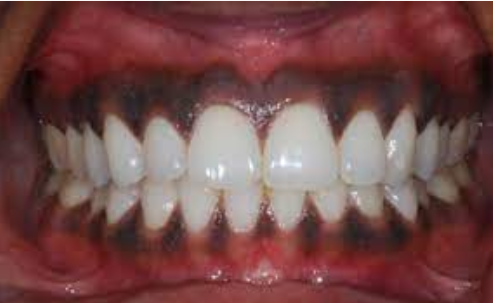
The pigment that gives color to skin, eyes, hair, mucosa, and gingiva
Most commonly observed in dark-skinned individuals
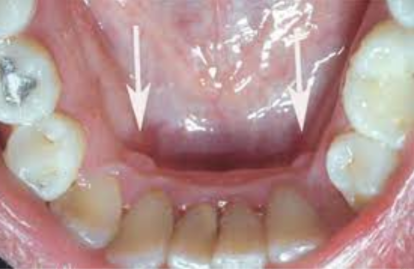
Clinical appearance
Red-to-purple enlarged vessels or clusters
Usually observed on the ventral and lateral surfaces of the tongue
Most commonly observed in individuals older than 60 years
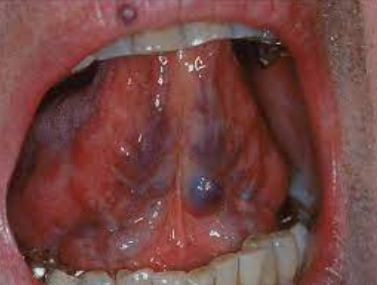
A “white line” extends anteroposteriorly on the buccal mucosa along the occlusal plane
May be bilateral
May be more prominent in patients who have a clenching or bruxing habit
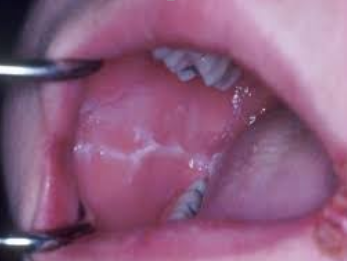
A generalized opalescence on the buccal mucosa
Most commonly observed in black adults
If the mucosa is stretched, the opalescence becomes less prominent
No treatment
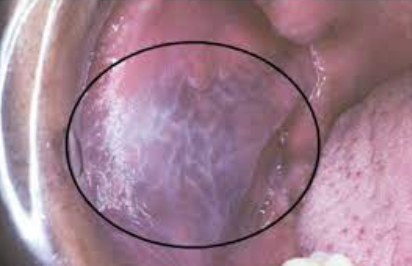
Clinical appearance:
Flat or slightly raised oval or rectangular erythematous area in center of tongue
May be associated with a chronic infection with Candida albicans
No treatment necessary, but antifungal treatment may be used
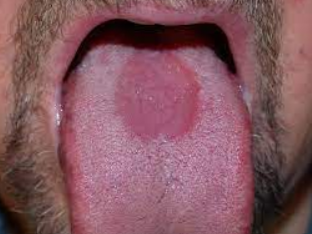
Clinical appearance:
Erythematous patches surrounded by a white or yellow border
Diffuse areas devoid of filiform papillae
Distinct presence of fungiform papillae
There appear to be remission and changes in the depapillated areas
NOT a variant of normal- can be associated with other issues.
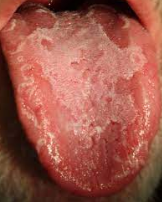
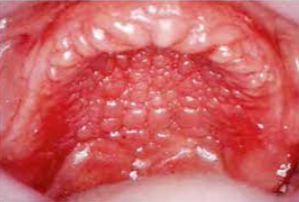
Clinical appearance: The dorsal surface of the tongue appears to have deep fissures or grooves
Cause: Unknown
Probably involves genetic factors
Seen in about 5% of the population
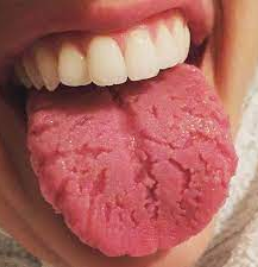
Clinical appearance: Elongated filiform papillae are white- know what papillae are involved
Result of an increase in keratin production or a decrease in normal desquamation
Home care: Direct the patient to brush the tongue gently with a toothbrush to remove debris
Tooth-to-tooth wear
May be observed in both primary and permanent dentition
Cause: Microfracture of tooth structure in areas of concentration of stress. May be related to fatigue, flexure, fracture, and deformation of tooth structure. May occur in combination with abrasion
Appearance: Typically appears as wedge-shaped lesions at the cervical areas of teeth
Preventive treatment: Fabricating an acrylic splint
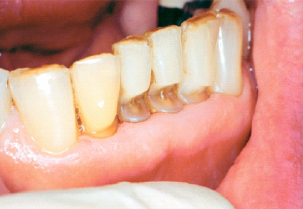
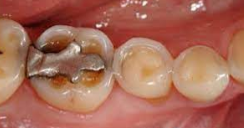
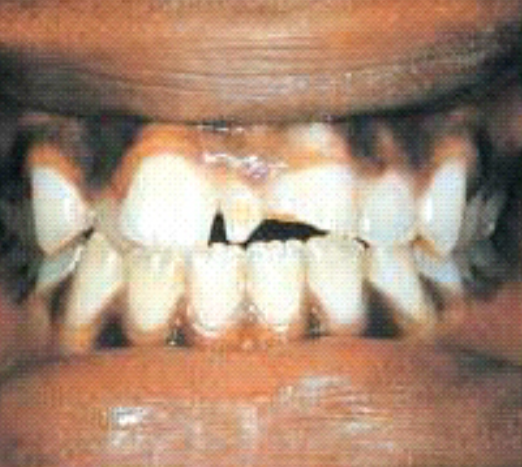
Rapid destruction of teeth as a result of:
Methamphetamine acid content
Decreased salivary flow
Cravings for high-sugar beverages
Lack of oral hygiene
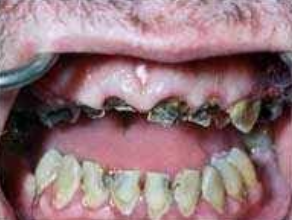
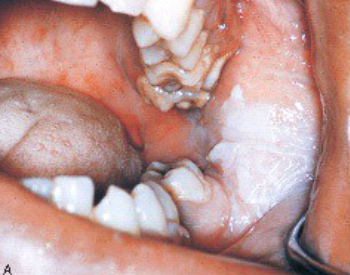
Used in dentistry as a cavity-sterilizing agent and a cauterizing agent
Will cause whitening and sloughing of the area as a result of tissue destruction
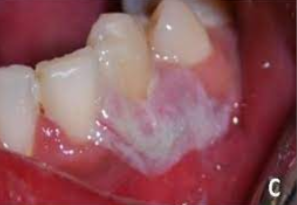
May be quite extensive, damaging oral tissue and even tooth buds
May cause permanent disfigurement and scarring
Treatment: Plastic surgery, Oral surgery, or Orthodontic therapy
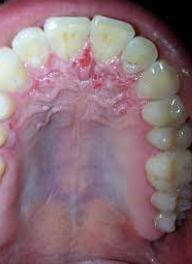
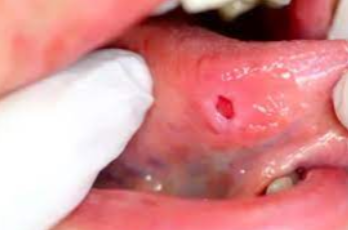
Accumulation of blood within tissue as a result of trauma
Appears as a red to purple to bluish-gray mass
Frequently seen on labial or buccal mucosa
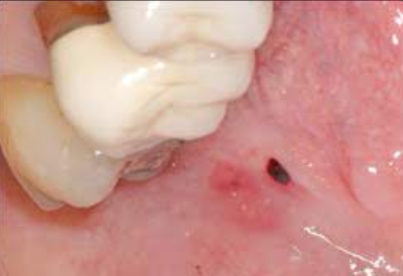
A form of hyperkeratosis
Cause: Chronic rubbing or friction against an oral mucosal surface; resembles a callus on skin
Appearance: Opaque white
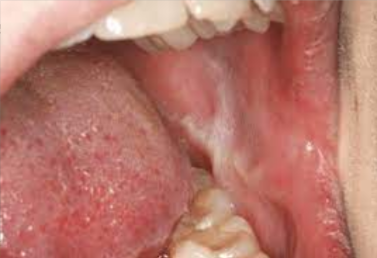
A benign lesion typically associated with pipe and/or cigar smoking; may also occur with cigarette smoking
Raised red areas occur at the openings of ducts of inflamed minor salivary glands
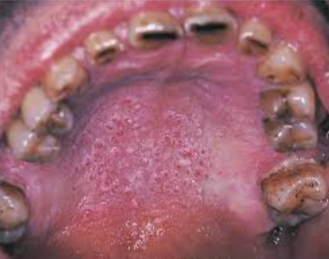
A white lesion located where chewing tobacco is placed, most often in the mucobuccal fold
Early lesions may have a granular or wrinkled appearance
Long-standing lesions may be more opaquely white and have a corrugated surface
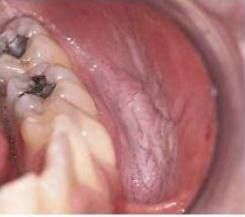
A degeneration of the tissue of the lips
Appearance:
Lips appear dry and cracked
The vermilion appears pale pink and mottled
The interface between lips and skin is indistinct
Microscopically: Epithelium is thinner than normal; degenerative CT changes
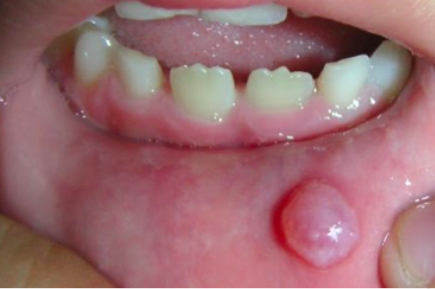
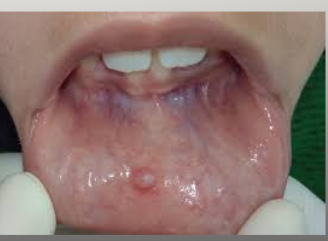
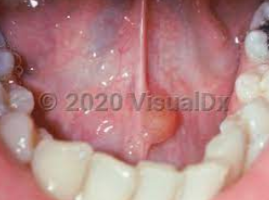
A lesion formed when a salivary gland duct is severed and the mucous salivary gland secretion spills into the adjacent connective tissue
Not a true cyst because it is not lined with epithelium
A result of trauma to a minor salivary duct
A salivary gland stone
May be found in both minor and major salivary glands
Formed by precipitation of calcium salts around a central core
May often be seen on radiographs
Treatment
Sometimes the calcification can be “milked” from the duct
It may require surgical removal; this may damage the duct
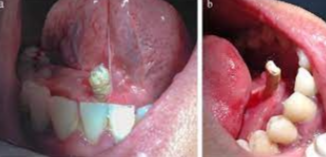
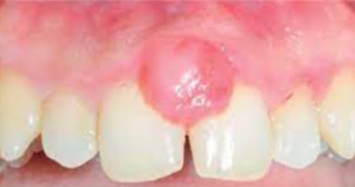
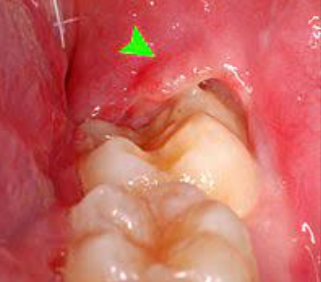
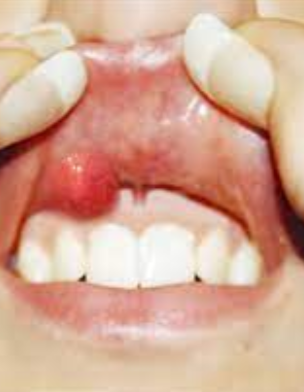
Recently defined lesion that clinically resembles a pyogenic granuloma
Thought to arise from improper exteriorization of junctional epithelium
Seen most commonly in younger patients, with a slight female predilection reported
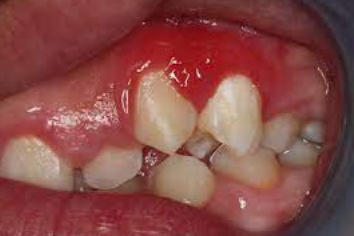
The most common mass on the gingiva
Caused by trauma
(Select all that apply)
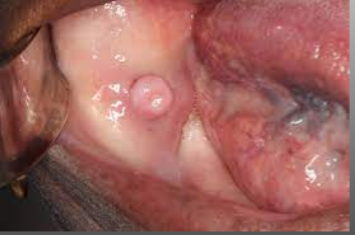
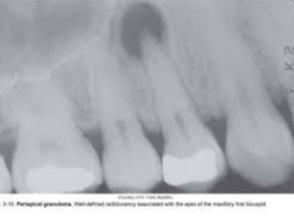
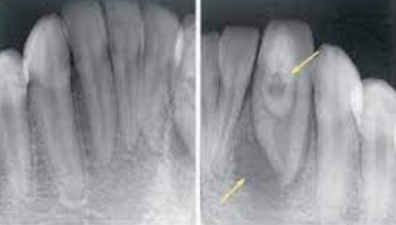
A true epithelium-lined cyst
Associated with the root of a nonvital tooth
The most commonly occurring cyst in the oral region
Usually asymptomatic and discovered on radiograph
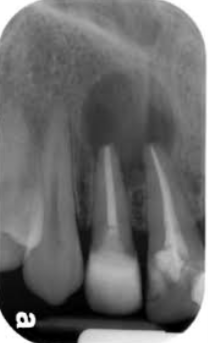
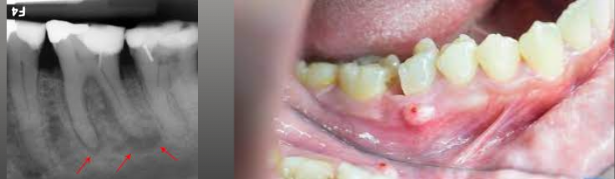
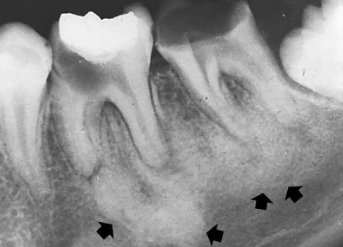
A change in the bone near the apices of teeth
Thought to be a reaction to low-grade infection
Generally asymptomatic
If painful, may be associated with pulpal inflammatory disease
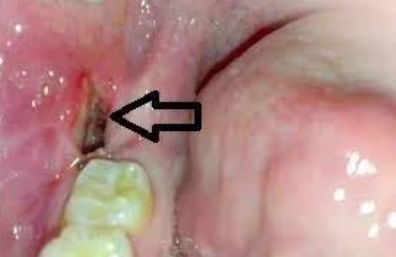
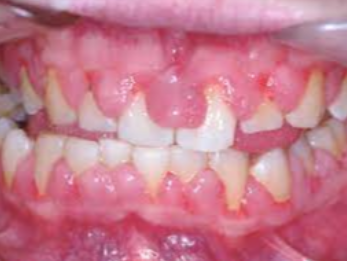
Acute, self-limited disease that affects skin and mucous membranes
Cause: Not clear; may be a hypersensitivity reaction
Target, iris or bull’s-eye lesions
Concentric erythematous rings alternating with normal skin color
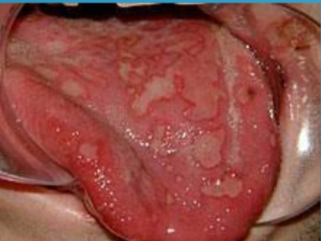
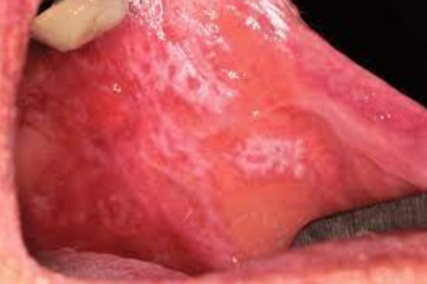
A benign, chronic disease affecting the skin and oral mucosa
Unknown cause
Lesions have characteristic Wickham’s striae (lacelike)
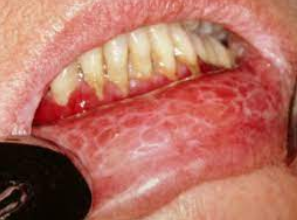
When diagnosed, this vascular lesion meets the criteria for the diagnosis of acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS)
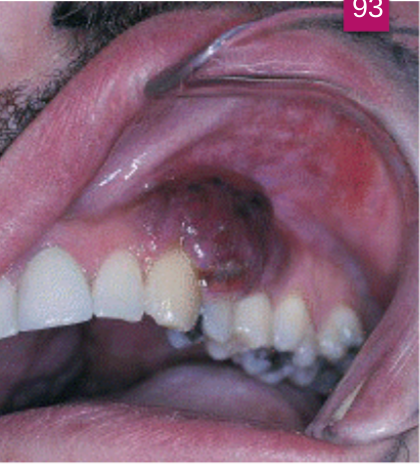
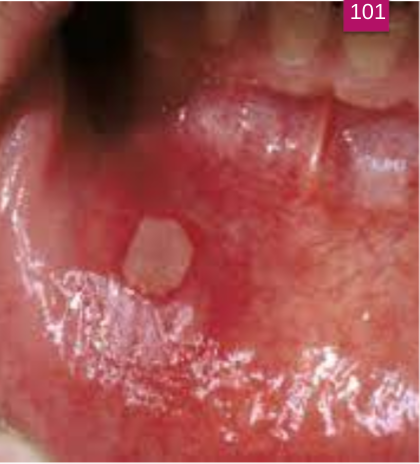
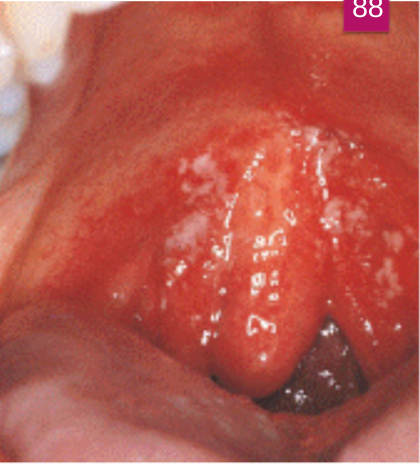
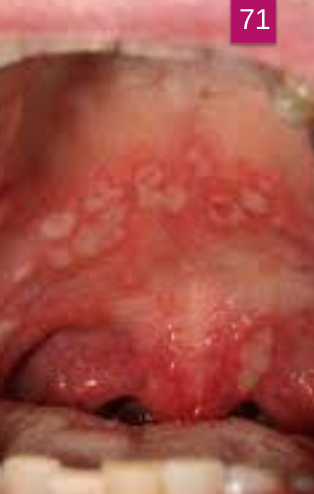
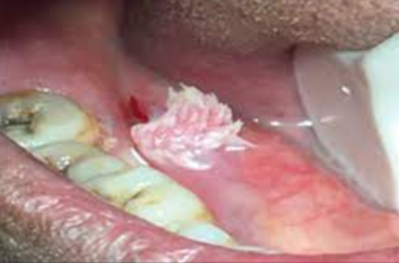
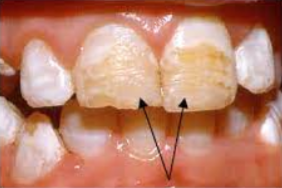
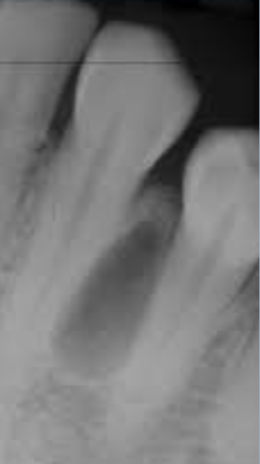
An abnormal curve or bend in the root of a tooth
Usually discovered on radiograph
May cause a problem if the tooth must be removed or a root canal performed
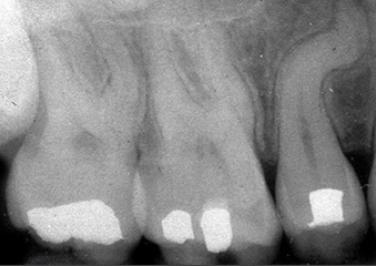
Appears as two crowns joined together by a notched incisal area
Radiographically, usually one single root and one common pulp canal exist
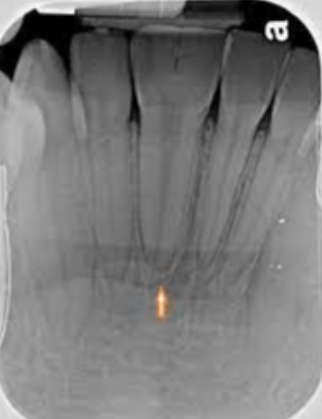
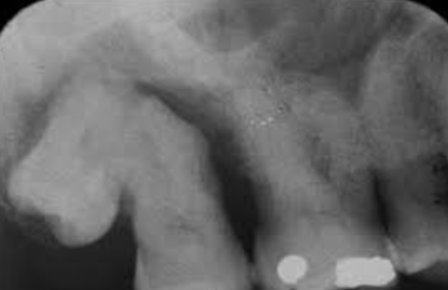
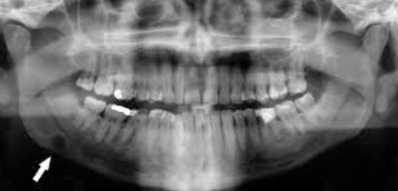
Develops in place of a tooth
Most commonly in place of a third molar
Most often seen in young adults and discovered on radiographic examination
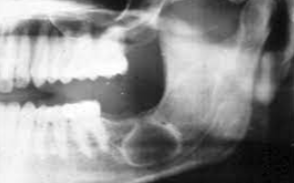
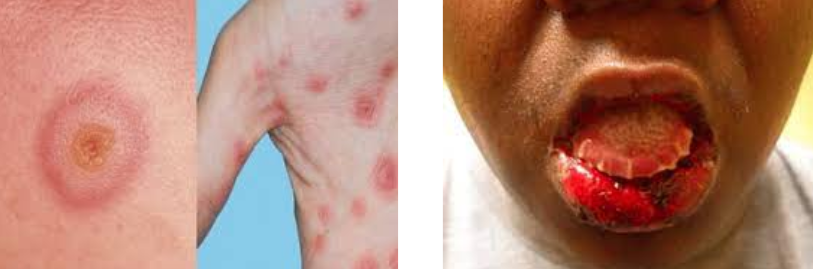
This condition is 8 times more likely to be seen in women than in men
Usually seen in women of childbearing age
3 times more likely to be seen in black women
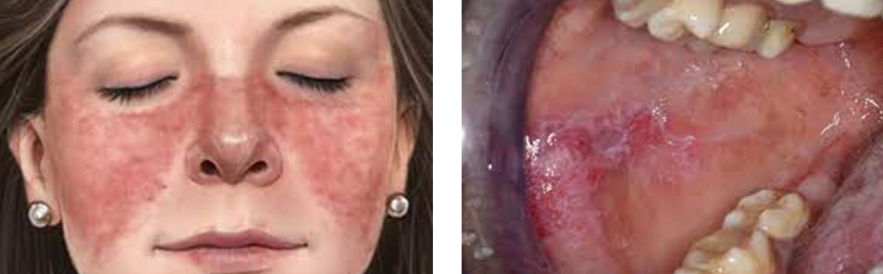
Characterized extraorally by a butterfly rash
Characterized intraorally by erythematous plaques or erosions that may have white striae that radiate from the center of the lesion
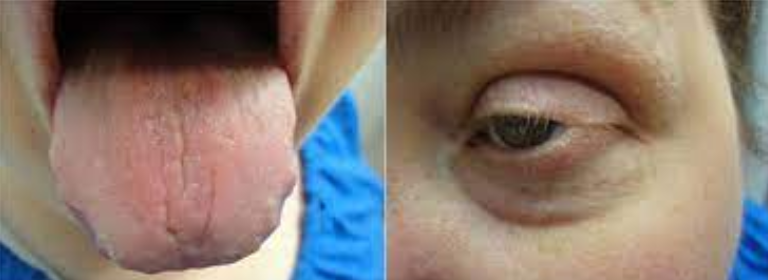
Patients who suffer from this syndrome will have xerostomia, dry eyes, and a very high probability of having rheumatoid arthritis.
May also have Raynaud Phenomenon
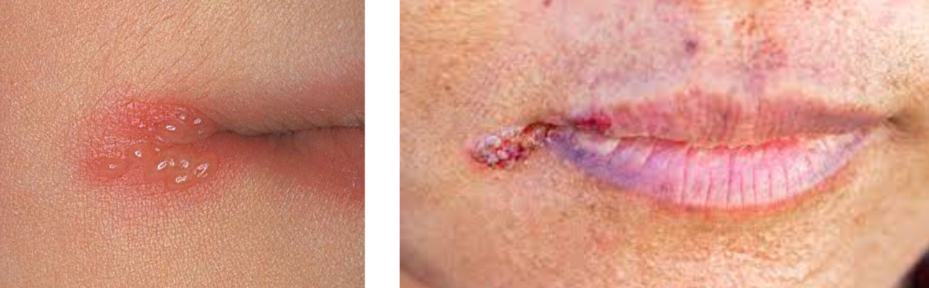
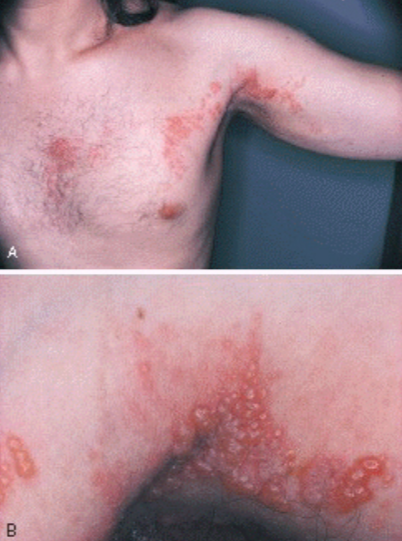
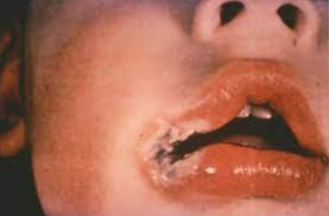
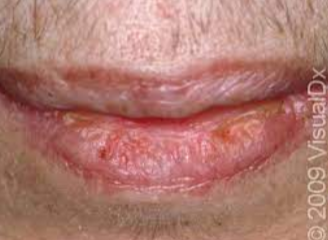
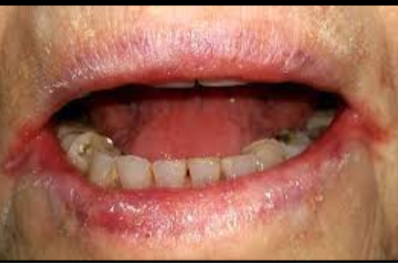
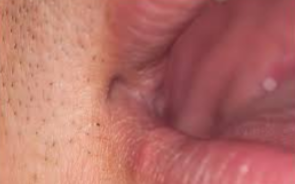
Patient presents with crusted lesion on the corner of the lips and states she gets cold sores a lot.
Stages of “cold sore” starts with fluid filled vesicle, followed by a “wet” stage where lesion leaks clear fluid. She states that the last stage is the crusted stage it is currently in and lesion will go away soon.
What is the same of this lesion?