Control

Master Your Control Systems Knowledge
Test your understanding of control systems with this comprehensive quiz covering various concepts, advantages, and applications of open and closed loop systems. Whether you're a student or a professional, this quiz will help solidify your knowledge and prepare you for real-world applications.
Key features of the quiz:
- 30 carefully curated questions
- Multiple-choice format for simplicity
- Immediate feedback on your answers
1. A disadvantage of closed loop system is that it is…………
A. More complicated to design
B. cheap
C. More accurate
D. None of the above
2. An example of closed loop system can be………..
A. Washer
B. microwave
C. Electrical water heater
D. None of the ab
3. Operation to reduce the difference O/P of the system and the desired (reference) I/P is called……….
A. Advantage
B. disadvantage
C. Feedback
D. feedforward
4. A system that has no feedback is called………. system.
A. One loop
B. Closed loop
C. Open loop
D. Small loop
5. A disadvantage of open loop system is that it is…………
A. More complicated to design
B. cheap
C. More accurate
D. None of the above
6. An example of open loop system can be………..
A. Fan
B. Air-conditioning
C. Refrigerator
D. None of the above
7. Some of closed loop system advantages are that it is………….
A. Simple
B. cheap
D. Both a & b
D. Not in the choices
8. The Laplace transform of a unit impulse fun
A. 1/s
B. 1/s²
C. 1
D. S
9. The response of an initially relaxed system to a unit ramp excitation is (𝑡 + 𝑒−𝑡). Its response will be
A. 1/2 t2- e-t
B. 1 - e-t
C. e-t
D. t
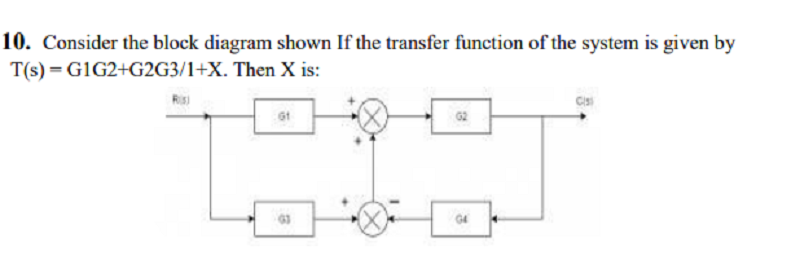
A. 𝝺2𝝺4
B. 𝝺2𝝺3
C. 𝝺3𝝺4
D. 𝝺2𝝺1
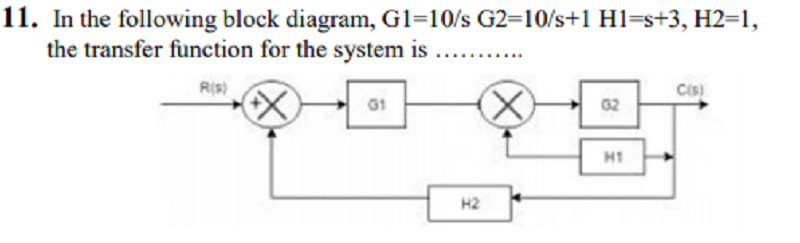
A. 𝝺1𝝺2 / 1+𝝺1𝝻2+𝝺1𝝺2
B. 𝝺1𝝺2 / 1+𝝺2𝝻2
C. 𝝺2 / 1+𝝺2𝝻2
D. 𝝺1𝝺2 / 1+𝝺2𝝻1+𝝺1𝝺2
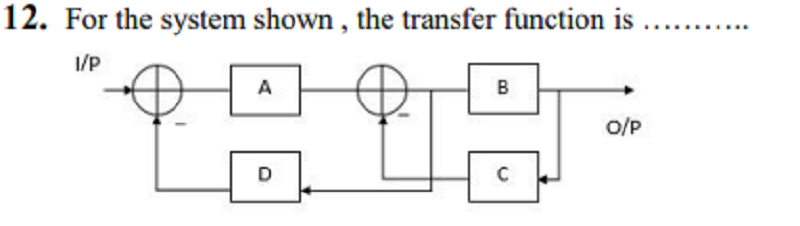
A. 𝝴𝝵 / 1+𝝴𝝶+𝝷
B. 𝝴𝝵 / 1+𝝷𝝴𝝶
C. 𝝴𝝵 / 1+𝝴𝝶+𝝵𝝷
D. 𝝴𝝵 / 1+𝝵𝝶+𝝴D
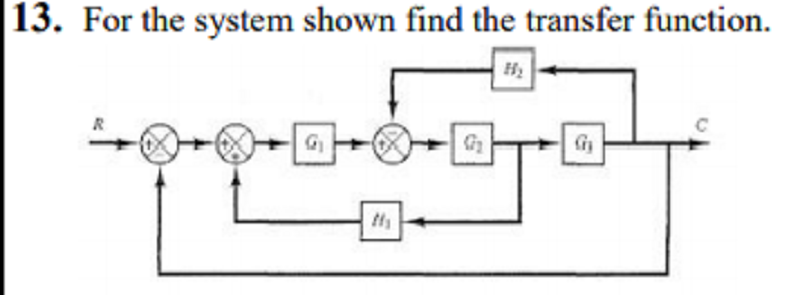
A. 𝝺1𝝺2𝝺3 / 1+𝝺2𝝺3𝝻2+𝝺1𝝺2𝝺3−𝝺1𝝺2𝝻1
B. 𝝺1𝝺3 / 1+𝝺3𝝻2+𝝺1𝝺2−𝝺1𝝺2𝝻1
C. 𝝺1𝝺2𝝺3 / 1+𝝺1𝝺3𝝻2+𝝺1𝝺2𝝺3−𝝺2𝝻1
D. 𝝺1𝝺2 / 1+𝝺2𝝺3𝝻1+𝝺2𝝺3−𝝺1𝝺2𝝻2
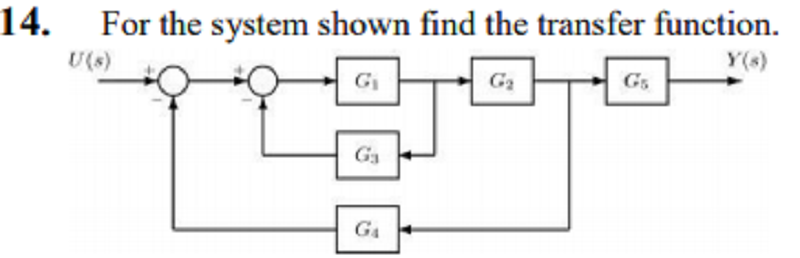
A. 𝝺1𝝺2𝝺5 / 1+𝝺1𝝺3−𝝺1𝝺2𝝺4
B. 𝝺1𝝺2𝝺5 / 1+𝝺1𝝺2−𝝺1𝝺2𝝺4
C. 𝝺1𝝺2𝝺5 / 1+𝝺1𝝺4−𝝺1𝝺2𝝺5
D. 𝝺1𝝺2𝝺5 / 1+𝝺1𝝺3−𝝺1𝝺5𝝺4
15. From which of the following transfer function can be obtained?
A. Signal flow graph.
B. Analogous table.
C. Output-input ratio.
D. Standard block system.
16. With feedback _____ increases.
A. System stability.
B. Sensitivity.
C. Gain.
D. Effects of disturbing signals.
17. In a system zero initial condition means that
A. The system is at rest and no energy is stored in any of its components.
B. The system is working with zero stored energy.
C. The system is working with zero reference signal.
D. None of the above
18. Static error co-efficient are used as a measure of the effectiveness of closed loop systems for specified ________ input signal.
A. Acceleration.
B. Velocity.
C. Position.
D. All of the above.
19. The type 0 system has ______ at the origin.
A. No pole.
B. Net pole.
C. Simple pole.
D. Two poles.
20. The type 1 system has ______ at the origin.
A. No pole.
B. Net pole.
C. Simple pole.
D. Two poles.
21. Transfer function of a system is defined as the ratio of output to input in
A. Fourier transform
B. Laplace transform
C. Z-transformer
D. All of these
22.___ Signal will become zero when the feedback signal and reference signs are equal.
A. Input.
B. Error.
C. Feedback.
D. Reference.
23. What is the Kp equation?
A. lim𝑠→0 𝝺(𝑆)
B. lim𝑠→0 𝑆 𝝺(𝑆)
C. lim𝑠→0 𝑠2𝝺(𝑆)
D. Not in the choices
24. What is the Kv equation?
A. lim𝑠→0 𝝺(𝑆)
B. lim𝑠→0 𝑆𝝺(𝑆)
C. lim𝑠→0 𝑠2𝝺(𝑆)
D. Not in the choices ices
25. What is the Ka equation?
A. lim𝑠→0 𝝺(𝑆)
B. lim𝑠→0 𝑆𝝺(𝑆)
C. lim𝑠→0 𝑠2𝝺(𝑆)
D. Not in the choices ices
26. Some of open loop system advantages are that it is………….
A. Simple
B. cheap
C. Both a & b
D. Not in the choices
27. A control system in which the control action is somehow dependent on the output is known as……………..
A. Closed loop system
B. Semi closed loop system.
C. Open system.
D. None of the above
28. In open loop system
A. The control action depends on the size of the system.
B. The control action depends on system variables.
C. The control action depends on the input signal.
D. The control action is independent of the output.
29. A good control system has all the following features except
A. Good stability.
B. Slow response.
C. Good accuracy.
D. Sufficient power handling capacity.
30. An automatic toaster is a ______ loop control system.
A. Open.
B. Closed.
C. Partially closed.
D. Any of the above
31. The steady state error for a unity feedback system for the input r(t) to the system G(s) = K(s+2)/s(s3+7s2+12s) is 6R/K. The input r (t) is _______
A. Rt2/2
B. Rt3/2
C. Rt5/2
D. Rt7/2
32. The initial response when output is not equal to input is ….
A. Error response
B. Transient response
C. Dynamic response
D. Static response
33. The steady state error for unit step input is …..
A. 1/kp
B. 1/1+kp
C. 1/1-kp
D. 1/3kp
34. The steady state error for unit ramp input is …...
A. 1/kp
B. 1/kv
C. 1/1-kv
D. 1/ka
35. The output is said to be zero state response because ______conditions are made equal to zero.
A. Initial
B. Final
C. Steady state
D. Impulse response
36. Consider the assertions related to block diagram. Which among them represents the precise condition? A. Block diagram is used for analysis & design of control system. B. Block diagram also provides the information regarding the physical construction of the system.
A. A is true, B is false
B. A is false, B is true
C. Both A & B are true
D. Both A & B are false
37. What is the value of parabolic input in Laplace domain?
A. 1
B. A/s
C. A/s2
D. A/s3
38. What is the definition of the peak time?
A. The time required for the response to reach the first peak of the overshoot.
B. The time required to rise to 90%.
C. The time required for the response to remain within a desired percentage (2%or 5%) of the final value.
D. The time required to reach the half of the final value.
39. What is the definition of the rise time?
A. The time required for the response to reach the first peak of the overshoot.
B. The time required to rise to 90%.
C. The time required for the response to remain within a desired percentage (2%or 5%) of the final value.
D. The time required to reach the half of the final value.
40. What is the definition of the delay time?
A. The time required for the response to reach the first peak of the overshoot.
B. The time required to rise to 90%.
C. The time required for the response to remain within a desired percentage (2%or 5%) of the final value.
D. The time required to reach the half of the final value.
41. In the field controlled motor the entire damping comes from
A. Armature resistance
B. Back emf
C. Motor friction and load
D. Field resistance
42. In control systems the output of sensor usually, is
A. Analog electrical signal
B. Digital electrical signal
C. Mechanical signal
D. Analog or Digital electrical signal
43. A unit step is applied at t=0 to a first order system without time delay. The response has the value of 1.264 units at t=10 mins, and 2 units at steady state. The transfer function of the system is_____________
A. 3/(1+600s)
B. 2/(1+500s)
C. 5/(1+220s)
D. 2/(1+600s)
44. The transfer function of the system is G(s) =100/(s+1) (s+100). For a unit step input to the system the approximate settling time for 2% criterion is:
A. 100 sec
B. 4 sec
C. 1 sec
D. 0.01 sec
45. Match the following notations with their meanings:
A. G(s) ---------- 1) Laplace of error signal
B. H(s) ---------- 2) Laplace of output signal
C. C(s) ---------- 3) Forward transfer function
D. E(s) ---------- 4) Feedback transfer function
A. G(s) ---------- 1) Laplace of error signal
B. H(s) ---------- 2) Laplace of output signal
C. C(s) ---------- 3) Forward transfer fun
D. E(s) ---------- 4) Feedback transfer fun
A. A- 2, B- 3, C- 1, D- 4
B. A- 3, B- 4, C- 2, D- 1
C. A- 2, B- 3, C- 4, D- 1
D. A- 1, B- 2, C- 3, D- 4
46. If two blocks having gains A and B respectively are in series connection, find the resultant gain using block diagram reduction technique?
A. A+B
B. A*B
C. A/B
D. A-B
47. When writing a transfer function which of the following loops are not valid loops?
A. Self loops at input node.
B. Self loops at output node.
C. Both 1 and 2.
D. Neither 1 nor 2.
48. If two blocks having gains A and B respectively are in parallel connection, find the resultant gain using block diagram reduction technique?
A. A+B
B. A*B
C. A/B
D. A-B
49. Which of the following combinations is/are correct electrical analogous elements in force-current analogy?
A. Velocity (v) ----------------- Voltage(V)
B. Force (f) --------------------- Current (i)
C. Spring element (K) --------- Inverse inductance (1/L)
D. All of the above
50. Transient state analysis deals with -------------
A. Magnitude of error
B. Nature of response
C. both 1 and 2
D. None of the above
51. Given the transfer function 121 / 𝑠2+13.2𝑠+121 of a system. Which of the following characteristics does it have?
A. Over damped
B. Critical damped
C. Under damped
D. Any of the above
52. Which of the following transfer functions represent under damped second order systems?
A. 1/(s² + s + 1)
B. 4/(s² + s + 4)
C. 2/(s² + s + 2)
D. All of the above
53. The open loop transfer function of a unity feedback control system is given byG(s) = k/s(s+1). If gain k is increased to infinity, then damping ratio will tend to become
A. Infinite
B. 0.707
C. Unity
D. Zero
54. Consider a network function H(s) = 2(s+3)/{(s+2)(s+4)}. What is the steady state response due to step input?
A. 4/3
B. 1/2
C. 1
D. 3/4
55. Given a unity feedback system with G(s) = k/s(s+4), the value of k for damping ratio of 0.5 is
A. 16
B. 1
C. 4
D. 64
56. The type number of the control system with G(s) = k(s+2)/(s(s²+2s+3) is
A. 1
B. 0
C. 2
D. 3
57. For type 1 system with parabolic input, the steady state error is
A. zero.
B. Finite constant.
C. infinite.
D. indeterminate.
58. What is the laplace transform of a function δ(t-2)?
A. 2
B. e-2s
C. 2s
D. 0
59. The impulse response of a linear system is e-t, (t > 0). The corresponding transfer function is
A. 1/s(s+1)
B. 1/(s+1)
C. 1/s
D. s/(s+1)
60. Time taken for the response to rise from zero to 100 % for very first time is called
A. Rise time
B. Settling time
C. Delay time
D. Peak time
61. Type and order of transfer function G (s) = K / {s(s + 2)}
A. 1,2
B. 2,1
C. 0,2
D. 1,1
62. Name test signals used in time response analysis?
A. Unit step
B. Unit ramp
C. Impulse
D. All of the above
63. The second order system defined by 25/ (s2 + 5s + 25) is given a step input. The time taken for the output to settle within 2 % of input is
A. 1.6 sec
B. 1.2 sec
C. sec
D. 0.4 sec
64. Given the transfer function 100 / 𝑠2+20𝑠+100 of a system. Which of the following characteristics does it have?
A. Over damped
B. Critical damped
C. Under damped
D. Any of the above
65. Find the order of a system given by s+6 / s(s−2)(s−4)
A. 2
B. 3
C. 4
D. 1
66. The root locus is the part of roots of the characteristic equation traced out in the S plane. Which one of the following is correct?
A. As the input of the system is changed
B. As the output of the system is changed
C. As a system parameter is changed
D. As the sensitivity is changed
67. A control system has G (s) H (s) = K / [ s (s + 4) (s2 + 4s + 20) (0 < K)< ∞) What is the number of breakaway points in the root locus diagram ?
A. One
B. Two
C. Three
D. Zero
68. For root loci which of the following are the starting points?
A. Open loop zeros
B. Closed loop zeros
C. Closed loop poles
D. Open loop poles
69. Which one of the following open-loop transfer functions has root locus parallel to imaginary axis?
A. k / ( s + 1 )
B. k / ( s + 1 ) / ( s + 1 )2
C. k / ( s + 1 )2
D. k / ( s + 12) / ( s + 1 )2
70. If poles are added to the system, where will the system tend to shift the root locus?
A. To the left of an imaginary axis
B. To the right of an imaginary axis
C. At the center
D. No shifting takes place
71. If the system is specified by open loop transfer function G(s)H(s) = k / s(s+3) (s + 2), how many root loci proceed to end at infinity?
A. 2
B. 3
C. 5
D. 6
72. What should be the nature of root locus about the real axis?
A. Assymetric
B. Symmetric
C. Exponential
D. Decaying
73. Routh test_________________?
A. Criterion provides information about the actual location of roots
B. Cannot be used to test the stability of a control system containing transportation lag
C. Criterion is not applicable to systems with polynomial characteristic equation
D. Cannot determine as to how many roots of the characteristics equation have positive real roots
74. Select the correct statement from the following?
A. The frequency response of a pure capacity process is unbounded
B. The phase lag of a pure time delay system decreases with increasing frequency
C. The amplitude ratio of a pure capacity process is inversely proportional to frequency
D. The amplitude ratio of a pure time delay system increases with frequency
75. Consider the loop transfer function K(s+6)/(s+3) (s+5) In the root locus diagram the centroid will be located at:
A. -4
B. -1
C. -2
D. -3
1. For a stable system having two or more gain crossover frequencies the phase margin is measured at the highest crossover frequency
A. True
B. False
2. In bode plots the frequency at which two asymptotes meet is called corner frequency
A. True
B. False
3. Gain margin and phase margin can be determined from bode plots as well as nyquist plot
A. True
B. False
4. Nyquist stability criterion uses open loop frequency response characteristics.
A. True
B. False
5. An Open-loop control system uses a measurement of the output and feed-back of the signal to compare it with the desired input.
A. True
B. False
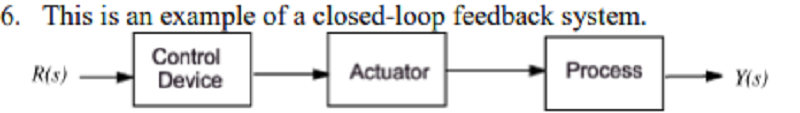
A. True
B. False
7. The rise time, is defined as the time required for the system to settle within a certain percentage of the input amplitude.
A. True
B. False
8. A type 1 system has a zero steady-state tracking error to a ramp input.
A. True
B. False
9. For a second-order system with no zeros, the percent overshoot to a unit step is a function of the damping ratio.
A. True
B. False
10. First order system is Total number of poles and order of equation
A. True
B. False
11. Time response during steady state the output velocity matches with the input velocity but lags behind the input by T.
A. True
B. False
12. In control systems the output of sensor usually, is Analog electrical signal
A. True
B. False
13. A system zero initial condition is working with zero stored energy.
A. True
B. False
14. The steady state error due to ramp input for a type two system is equal to Zero
A. True
B. False
15. Differentiation of parabolic response is a parabolic response?
A. True
B. False
16. Weighting function is in terms of Laplace transform of the step response
A. True
B. False
17. Lead compensator is used to improve transient response
A. True
B. False
18. The steady state error due to ramp input for a type two system is equal to Two
A. True
B. False
19. In control systems the output of sensor usually, is Digital electrical signal
A. True
B. False
20.Steady-state error is a property of the input/output response for a linear system.
A. True
B. False
21. The amplitude ratio of a pure capacity process is inversely proportional to frequency
A. True
B. False
22. The frequency response of a pure capacity process is unbounded
A. True
B. False
23. The amplitude ratio of a pure time delay system increases with frequency
A. True
B. False
24. The root-locus is the path the roots of the characteristic equation (given by 1 + KG(s) =0) trace out on the s-plane as the system parameter K varies.
A. True
B. False
25. On the root locus plot, the number of separate loci is equal to the number of poles of G(s).
A. True
B. False
26. The root locus provides the control system designer with a measure of the sensitivity of the poles of the system to variations of a parameter of interest.
A. True
B. False
27. The root locus provides valuable insight into the response of a system to various test inputs.
A. True
B. False
28. The root-locus always starts at the zeros and ends at the poles of G(s).
A. True
B. False
29. The breakaway point calculated mathematically must always lie on the root locus."
A. True
B. False
{"name":"Control", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Test your understanding of control systems with this comprehensive quiz covering various concepts, advantages, and applications of open and closed loop systems. Whether you're a student or a professional, this quiz will help solidify your knowledge and prepare you for real-world applications.Key features of the quiz:30 carefully curated questionsMultiple-choice format for simplicityImmediate feedback on your answers","img":"https:/images/course7.png"}
More Quizzes
Control Systems
12462115
Control Theory & it's applications
221121
How well do you know Jordan?
10522
Unsaturated Soil Mechanics Quiz
67340
Free Art Praxis Practice Test - PRAXIS II Exam Prep
201018674
Adam Sandler Movie Trivia - Can You Ace It?
201022429
Mpox - Test Your Knowledge Free Online
201016998
The Black Phone - Which Character Are You?
201016641
Classical Conditioning CLEP Practice - Free Intro Psych
201020683
Stroop Test Online - Free Color-Word Interference
201018139
Should I Kiss My Best Friend? - Get Your Answer
201018213
Greek Alphabet - Can You Name All 24 Letters?
201018835