Quiz 2

Understanding Immunology Quiz
Test your knowledge on immunology with this comprehensive quiz designed for students and professionals alike. From the roles of antibodies to T cell development, challenge yourself with 30 questions that cover a range of immunological concepts.
Key Topics:
- Antibodies and their fun
ctions - MHC and antigen presentation
- Lymphocyte development and trafficking
- Immunological disorders and responses
Which one of the following people is more likely to develop HBV?
10-year-old girl with heterozygote for MHC alleles and prevalent alleles.
15-year-old boy with heterozygote for MHC alleles and rare alleles.
40-year-old man with homozygotes for MHC alleles and prevalent alleles.
35-year-old women with homozygotes for MHC alleles and rare alleles.
MHC refers to a large group of genes that code for proteins that play an essential role in which of the following?
Phagocytosis by Macrophages
Antigen presentation to T lymphocytes
Phagocytosis by neutrophils
Antigen presentation to B lymphocytes
A young person was infected with COVID-19, and recovered a few days later. This person has Antibodies against the virus. Then the doctor took Antibodies from the patient who recovered and injected it into the body of another infected person in order to recover from the virus. This an example respectively:
Artificial passive immunity, Natural passive immunity
Natural active immunity, Natural passive immunity
Natural active immunity, Artificial passive immunity
Artificial active immunity, Artificial passive immunity
Which antibody is produced at high levels in response to parasitic infection?
IgA
IgE
IgG
IgD
A 24 years old man presents with an extreme fever, fast weight lost, and a diarrhea that last for more than one week. After taking a blood sample; the lab report shows that the person is likely to have HIV. Which of the following must be true?
The patient is immunocompromised, and a high amount of cytokine will be released.
T cytotoxic cells and B cells get infected, but T helper cell is well functioning.
T helper cells get infected and patient will be severely compromised because of the loss of cytokines.
Patient will develop immune dysregulation and will be diagnosed with immunodeficiency
Two choices are correct.
Which of the following pairs is incorrect
T-progenitor cells - Bone marrow
Active Immunity – Monoclonal antibodies
Adaptive – Specific response
Surface pathogen – Arthropods
Which of the following is Correct:
Dendritic cells, macrophages, and T helper cells are all APCs
APCs are required in T-independent response.
B cells always need an APC to recognize antigens
MHC 2 can be found in macrophages.
A 1 –year-old has a history of immune deficiency. He presents to hospital with bone weakness. After taking a blood sample, the lab report shows that the person’s blood lacks of lymphocytes and calcium. The doctor diagnoses his case that is DiGeorge syndrome, what is the cause of this syndrome?
He has defection in the development of the bone marrow and thymus in the embryonic stages leads to lack of lymphocytes production.
He has defection in the development of the two third pharyngeal pouch, so he is born with an incomplete thymus gland and parathyroid gland.
He has defection in the development of the third pharyngeal pouch, so he is born without thymus gland and parathyroid gland. Therefore, severe immunocompromise.
He eats food that are not rich in calcium, he also has vitamin D deficiency.
A 24year old man started to suffer from enlarging in his mandible and it persist without any pain. What do you expect this to be?
Infection in the mandible lymph nodes.
Tumor in the mandible lymph nodes.
Tumor in the submandibular lymph nodes.
Infection in the mandible lymph nodes.
A 30 –year-old man attends your clinic complaining of lumps in his axillary for more than 10 days without feeling pain. On examination, your patient has enlargement lymph nodes in the axillary region, what is your diagnosis?
He has viral infection in the axillary and the treatment is not necessary.
He has chronic infection because lymphadenopathy persists for more than a few days.
He has lymphadenopathy due to bacterial infection.
He has lymphadenopathy due to cancer.
Which one of the following is mismatched according to anatomy of lymph nodes?
B cells → primary follicles of cortex
Memory B cells→ secondary follicles of cortex
T cells → paracortex
Macrophages, T cells and B cells → medulla
HEV→ cortex
According to B cells development, all the following is correct except: A) Stem cells in bone marrow develop to progenitors B cells then immature B cells.
If the immature B cells come out of the bone marrow without being exposed to antigens, we called them naïve B cells.
When IgD antibody attaches on the surface of B Cell ,we call it mature B cell.
When naïve B cells circulates in the primary lymphoid organs and meet its antigenic counterpart, we call it effector B
A 50 – year-old presents to emergency in shock with low blood pressure and high fever. He underwent an emergency splenectomy 3 years prior but has not been on antibiotics since then. A day later pneumococci is cultured from his blood sample, so the diagnosis is post-splenectomy invasive sepsis, why splenectomies patients are more susceptible to be infected ?
Pneumococci is an encapsulated bacterium and the spleen contains many of T-independent B cells that make antibodies against the polysaccharide capsule of these bacteria.
Spleen contains a few numbers of macrophages which phagocytose opsonized bacteria in the blood.
they take prophylactic antibiotics so that, they are immunocompromised.
More than two answers are correct.
A 44 years old women woke up in the morning and she feels that there is something unusual appeared on the left side of her body, and she decided to visit the hospital; the doctor asked for CT scan, after the CT scan the doctor decided for a lymphadenectomy, what will happen to the immune system?
The women will be immunocompromised, because it will be unable to produce T cells.
The women will be immunocompromised, because it will be unable to produce B cells.
The women will be immunocompromised, because the spleen will be affected, and there will be no more filtration for the blood.
The immune system will keep functioning will.
Two answers are correct.
The red pulp area in the spleen contains :
Lymphocyte tissue.
Only macrophages.
NK cells and destroyed RB cells.
There is no correct answer.
Which of the following is immunologically privileged?
Spinal cord
Bone marrow
Testes
Vagina
Positive selection is:
The ability of T cells to recognize non self-antigen and it takes place in thymic medulla.
The ability of T cells to recognize self-antigen and it takes place in thymic medulla.
The ability of T cells to recognize non self-antigen and it takes place in thymic cortex .
The ability of T cells to recognize self-antigen and it takes place in thymic cortex.
Read the following statements then order them according to the lymphatic trafficking: 1) T cells movement is stopped and express LFA-1 THEN BINDS TO ICAM-1 on the inflamed endothelium 2) T cells return to the blood 3) naïve T cells recognize HEVs in the lymph node by expressing L-selectin and binds to GLYCAM1 expressed on the lining of HEVs so that T cells roll along the endothelium. 4) inflammation occurs so macrophages release chemokines which activate lymphocytes 5) T cells trans-migration through the tight junctions 6) naïve T cells circulate via blood stream and lymphatics and to lymph nodes to meet its antigenic counterpart 7) synapse formation
6,3,4,1,5,7,2
6,3,1,4,5,7,2
2,7,5,4,3,1,6
3,2,6,7,1,4,5
2,7,5,4,6,3,1
Patients who are unable to secrete gastric acid have a high risk of :
Salmonella infection.
Gastritis.
Portal hypertensive gastropathy.
Stomach Flu.
All of the following are characteristics of acute phase response except :
Increase body temperature
Secrete IL-1,IL-6 and TNF
Increases metabolic rate
Weight gain
Type I interferons (IFNs) that are secreted by infected cells have these functions except:
Trigger neighboring cell
Promotes antigen presentation and natural killer cell functions while restraining pro-inflammatory pathways and cytokine production.
Activate the adaptive immune system
Increases the availability of peptides for binding to MHC class I and promote the effects of CD4+ T cells.
Which one of the following statements is correct :
C3 deficiency is associated with Neisseria
C5-c9(MAC) deficiency is associated with SLE
C1 deficiency Esterase leads to Angioedema
DAF(CD52) is responsible for the dissociation of c3 convertase
After the process of phagocytosis is completed , NADPH oxidase produces hypochlorus acid
Which one of the following statements is incorrect?
Neck stiffness is an indication for meningitides
Cationic protein in Eosinophils helps to damage parasite surface
After the process of phagocytosis , myeloperoxidase production lead to bleach
Eosinophils production is stimulated by IL-3 and IL-5
Two answers are incorrect
When you have a tissue that is infected, the lymphocytes or the defense cells have to go back to the same area that they originated from in order to provide it with protection.
True
False
A patient with high vascular tone, high cardiac output and low blood pressure, he was diagnosed with septic shock, the drug that he must take should increase the level of
Nitric oxide
Hydrogen peroxide
Hypochlorous acid
NADH oxidase.
One of the following is NOT a polyvalent antigen?
Cell surfaces which include proteins or polysaccharides
Cell surfaces which include proteins or polysaccharides
Nucleic acids polysaccharides
Macromolecules
Which of the following statements is / are correct?
IgG has a long half-life because it binds to FcRn which structurally resembles class II MHC.
Cell bound IgE have a very short half-life.
IgG3 is relatively short-lived because of its poor binding to FcRn.
Two answers are correct.
Which of the following statements is/are incorrect:
Serum is a mixture of plasma & coagulation factor.
3 fragments are produced from IgG cleavage by papain enzyme.
IgG has the longest half-life of all antibodies.
A and C
Which of the following sentences is mismatched:
The antigen binding site → VH/VL (variable region of the heavy & light chains).
C (constant) region of HV (heavy chain)→ effector function.
IgM is found in the monomer form when it is secreted.
IgA is involved in mucosal immunity.
Electrophoresis is a technique which is used to separate blood proteins based only on electric charges:
True
False
All of the following statements are false except:
Nuclear translocation of transcription factor is a step of the nuclear phase of signal transduction pathways.
The activation process of transcription factor refers to the changes in gene expression.
The activation of transcription factor leads to the activation of the target gene.
Nuclear phase is an essential phase for signal transduction pathways of all cells.
Choose the correct sentence:
Choose the correct sentence:
C – kit receptor IS an example of notch receptor.
Syk family kinases contain kinase domain \ unique domain \ ONLY one SH2 domain.
Unlike co-stimulatory receptors, co-receptors can identify the antigen-complex which bound to receptor complex and bind to it.
Regarding class 1 MHC pathway for processing and presentation of cytosolic Ag, which one of the following pairs is mismatched:
Ag presentation enhancement ---IFN-γ
Trimming of Ag peptides---proteasomes.
Ag tagging by covalent bonding---ubiquitin.
Regulating the assembly of the unstable trimer→(calnexin,calreticulin,tapasin).
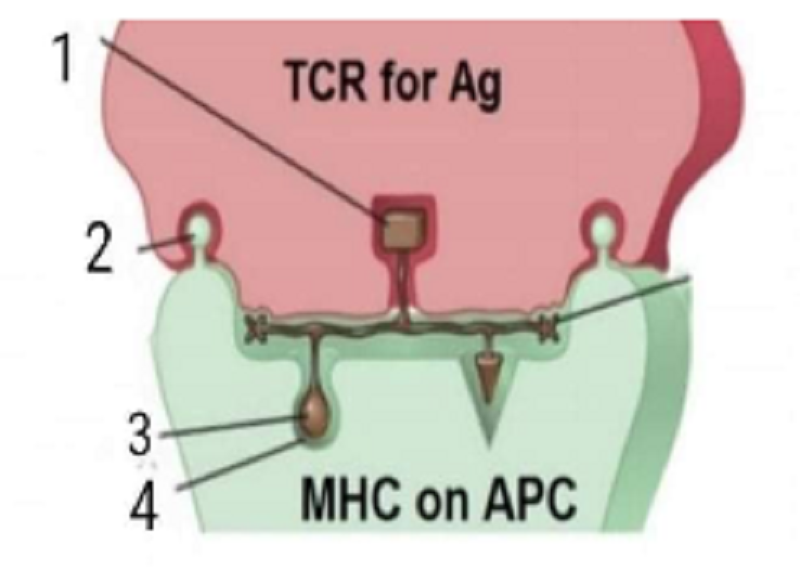
Which of the following structures is responsible for self-restriction:
1
2
3
4
All of the following is true about β2-mirogloulin except:
It’s non-polymorphic.
Maintain proper confirmation or shape of MHC l.
It’s MHC encoded.
Non-glycosylated.
Which one of the following is true about MHC genes:
Located at chromosome 17 in humans.
MHC locus in humans contains 2 major classes of genes.
MHC genes are expressed in an autosomal dominant manner.
None of the above.
Which one of the following statements is correct:
CD8 is A co-stimulator that consists of heterodimer, each chain with single extracellular domains.
CD8 is a single chain with 4 extracellular domains.
A key Adaptor activated by ZAP-70 in TCR complex is PLC gamma.
CD4 is a co-receptor that recognizes class II HLA antigen TCR complex.
Which one of the following cells has the strongest intracellular signal:
A cell that has inhibitory receptors, more ITIMs and more cross-linking.
A cell that has co-receptor, more ITIMs and less cross-linking.
A cell that has co-receptor, more ITEMs and more cross-linking.
A cell that has inhibitory receptors, more ITEMs and more cross-linking.
Regarding Conventional MHC pathways , which one of the following is correct:
Folding and assembly of unstable (class II dimers, class I dimers) in the Golgi complex , ER respectively.
DCs can express Both Ag associated with MHC I & MHC II to recognize by CD8+, CD4+ respectively.
In the class II pathway, the late endosomes contain proteolytic enzyme, calnexin, invariant chain and not polymorphic MHC-encoded.
In the class I pathway, TAP is a heterodimer protein that transports processing antigen to ER, located in ER lumen.
Most memory T cells express:
CD45RA
CD21
CD8
CD45RO
Which type of cells is similar to stem cells?
B cells
Macrophages
NK
Memory T cells
Which one of the following statements is incorrect?
NF-gamma secreted by TH1 cells respond to intracellular MOs that escape from phagosomes.
Survival of memory T cells is dependent on cytokines and Ag recognition.
Fully functional effector CTLs require both co-stimulation and cytokines.
None of the above.
Adaptive immune response to intracellular fungi is mediated by:
TH17
TH1
TH2
CTLs
Which of the following statements is incorrect regarding B-1 cells:
Originate from fetal spleen derived HSCs.
Carry CD5 on its surface.
Secrete natural antibodies.
Mostly found as self- renewing populations.
Which one of the following is correct?
In pre- B cell receptor the invariant surrogate light chain has two types V Pre-B and gamma 5.
In B Cell maturation, the positive selection is to enhance the function of BCR but the negative selection is to make sure that the cell has self-tolerance.
In the positive selection during T Cell maturation, the signal resulting from interaction between self-antigen and TCR is strong that it causes cell death.
In probabilistic model, Double positive cells interacts directly with MHCs that are present in APC to express one of the receptors and switch off other one.
In vitro, you get a random chain of a receptor from TLs. After you check it, you find that it is composed from 5 segments (L, V, J, D, C) and the gene that encodes the chain is located in chromosome 7. The type of chain will be :
Alpha
Beta
Gamma
Delta
The function of TdT enzyme in V(D)J recombination is:
Insertion of N region of nucleotides.
Insertion of P region of nucleotides.
Deletion of the nucleotides from P region.
It doesn’t have junctional function.
All of the following are key steps in T cell activation except:
APC must process & present peptides to T cells.
Accessory molecules are needed to stabilize binding.
T cells must receive co-stimulatory signal.
Signals from cell surface are transmitted to nucleus via 2nd messengers.
IL-17 drives cell division.
All of the following are functions of CLTA-4 except:
Binds B7 with a higher affinity than CD28
Inhibits access of CD28 to B7.
Removes B7 molecules from surface of APCs internalize them.
Delivers activating signals
Mediator of inhibitory function of Treg cells
Which of the following is true about naive TLs:
Express CD45RA isoform of the surface molecule CD45
Replaced by mature Ls and develop in the thymus.
Take 5-7 days to respond to Ag
All of the following are true
Which of the following is true about memory TLs:
Survive for prolonged period
Responsible for the secondary immune response
Take1-3 days to respond to Ag
All of the following are true
{"name":"Quiz 2", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Test your knowledge on immunology with this comprehensive quiz designed for students and professionals alike. From the roles of antibodies to T cell development, challenge yourself with 30 questions that cover a range of immunological concepts.Key Topics:Antibodies and their functionsMHC and antigen presentationLymphocyte development and traffickingImmunological disorders and responses","img":"https:/images/course1.png"}
More Quizzes
Microbiology
1368
Part 3 Immunology(100-149) prof. Keit vanseth
502544
Do you have any recommendations in new papers today?
100
MOV THE AMAZING RACE GIVEAWAYS
1160
Which Band Member Are You? Free Personality
201018969
How Tall Is Aishwarya Rai? Free Height
201018441
What Color Is Your Polyjuice Potion? Free
201020053
AP Stats Chapter 4 Practice - Free Online
201018192
Cashier Math Test - Free Aptitude Practice Questions
201024095
Percentage - Free Math Practice Questions
201019061
Ultimate DC Comics - Prove Your Knowledge
201021320
Word Wisdom Book - Test Your Vocabulary
201021196