Avionics - week 2 - practice quizzes

Avionics Navigation Principles Quiz
Enhance your understanding of avionics and navigation with this comprehensive quiz! Test your knowledge on key principles such as latitude, track, waypoints, and superheterodyne receivers. Designed for students and aviation enthusiasts alike, this quiz covers essential topics that every aviator should be familiar with.
Topics covered include:
- Navigation Techniques
- Aircraft Heading and Direction
- Superheterodyne Receiver Fun
ctions - Track and Angle Errors
L1 CLO 3. Explain Superheterodyne receivers
In a superheterodyne receiver the demodulator
IDC203087
The difference between the desired track and the actual track is the
IDC203058
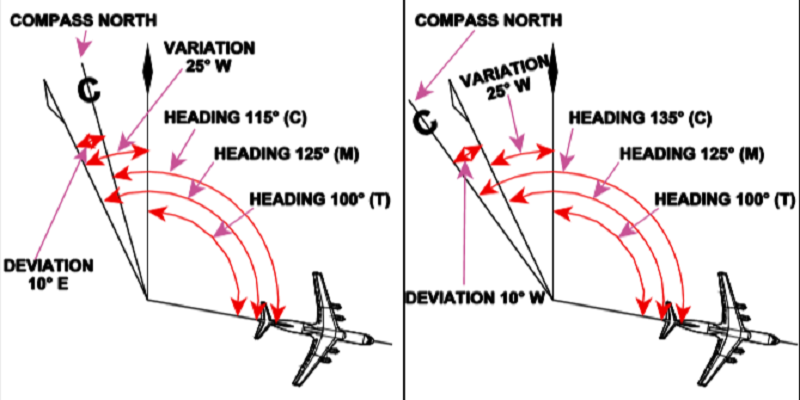
The Angle between Magnetic North and Compass North is called
IDC203061
The direction in which the nose of the aircraft is pointed is
IDC203059
L1 CLO 6. Explain principles of navigation
Relative bearing
IDC203078
L1 CLO 3. Explain Superheterodyne receivers
When two frequencies are mixed
IDC203064
L1 CLO 6. Explain principles of navigation
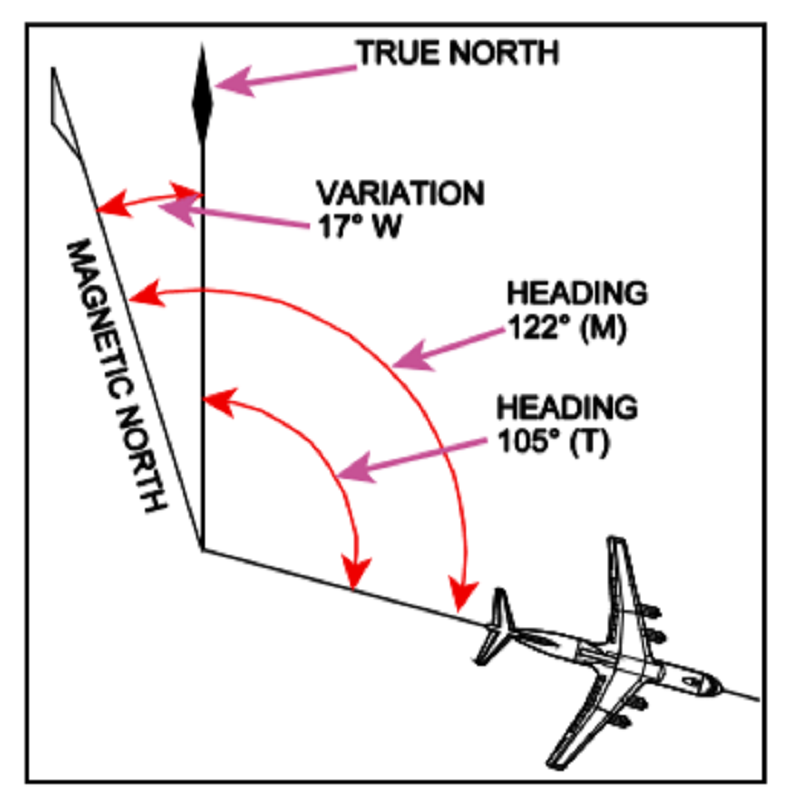
The difference between True North and Magnetic North is
IDC203073
L1 CLO 6. Explain principles of navigation
Declination
IDC203074
L1 CLO 3. Explain superheterodyne receivers
The antenna of a superheterodyne receiver
IDC203066
L1 CLO 3. Explain Superheterodyne receivers
Heterodyning is the process of
IDC203063
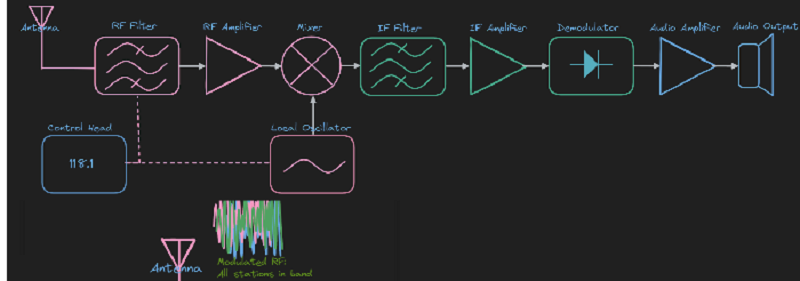
L1 CLO 3. Explain Superheterodyne receivers
An RF amplifier in a superheterodyne receiver
IDC203067
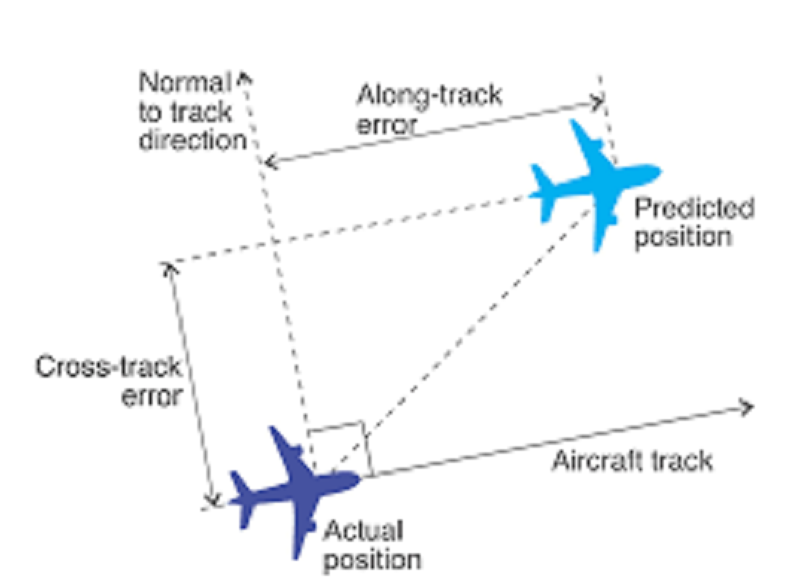
L1 CLO 6. Explain principles of navigation
Cross track
IDC203082
L1 CLO 6. Explain principles of navigation
An aircraft which is on a heading of 180° is facing which direction?
IDC203054
L1 CLO 3. Explain Superheterodyne receivers
The prefix “super” in superheterodyne
IDC203053
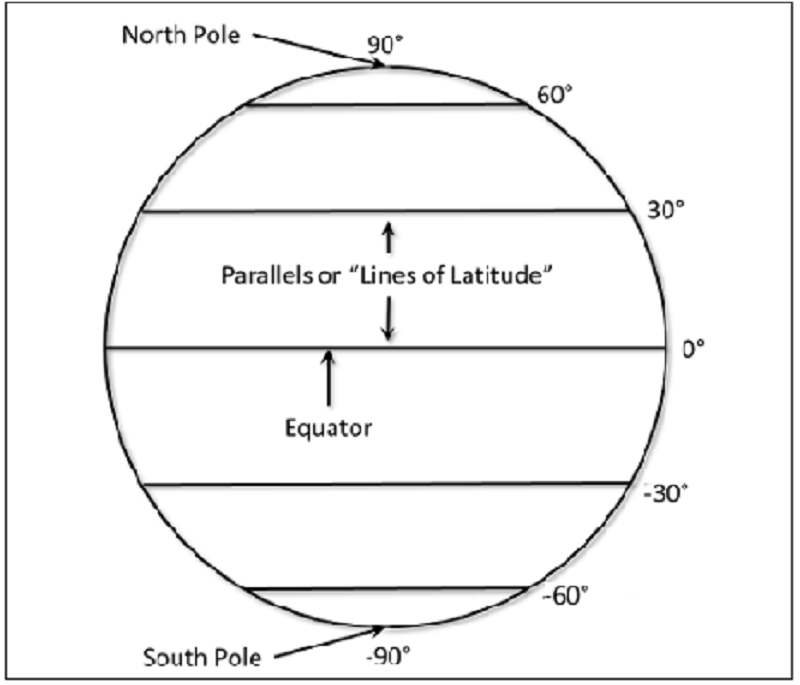
L1 CLO 6. Explain principles of navigation
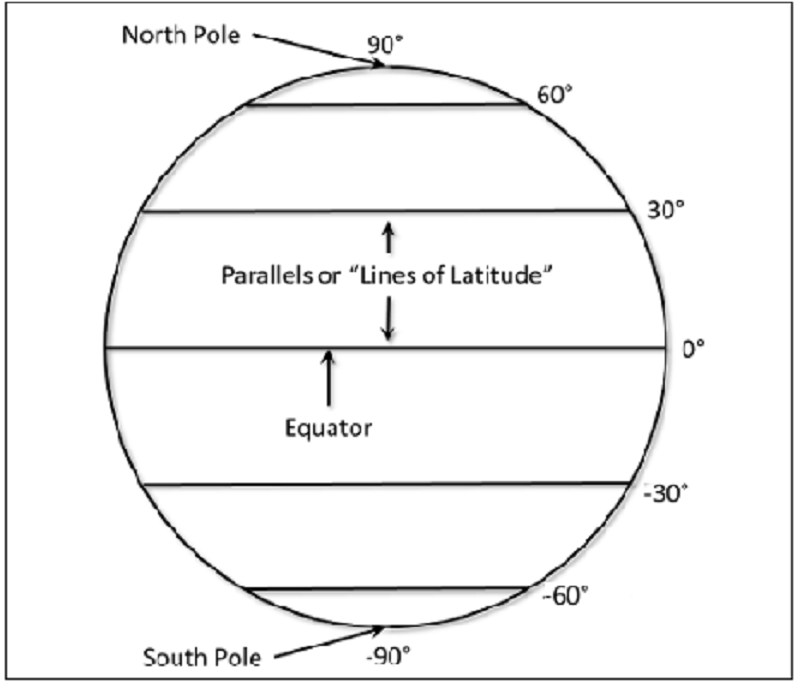
Lines running East-West parallel to the Equator are called.
IDC203060
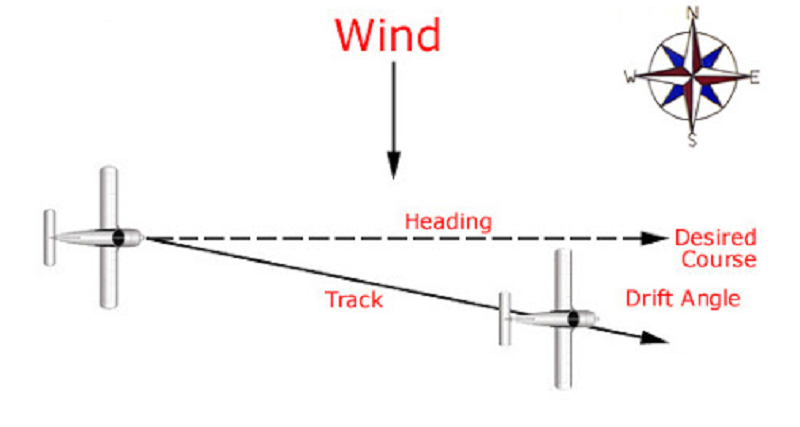
L1 CLO 6. Explain principles of navigation
Drift Angle
IDC203081
L1 CLO 6. Explain principles of navigation
An aircraft which is on a heading of 270° is facing which direction?
IDC203055
L1 CLO 6. Explain principles of navigation
A deviation card
IDC203075

L1 CLO 3. Explain Superheterodyne receivers
The first place we have audio in a superheterodyne receiver is after this block:
IDC203088
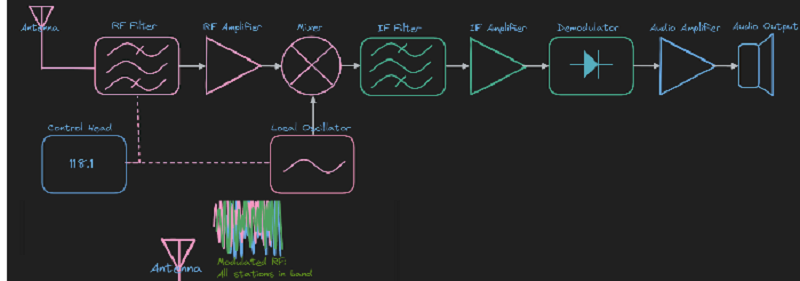
L1 CLO 3. Explain Superheterodyne receivers
In a superheterodyne receiver, the mixer block
(RF = Radio Frequency, LO = local oscillator)
IDC203086
L1 CLO 6. Explain principles of navigation
An aircraft which is on a heading of 0° is facing which direction?
IDC203056
L1 CLO 3. Explain Superheterodyne receivers
The difference between the incoming RF and the output of the oscillator is called the
IDC203062
L1 CLO 6. Explain principles of navigation
Track angle error is
IDC203083
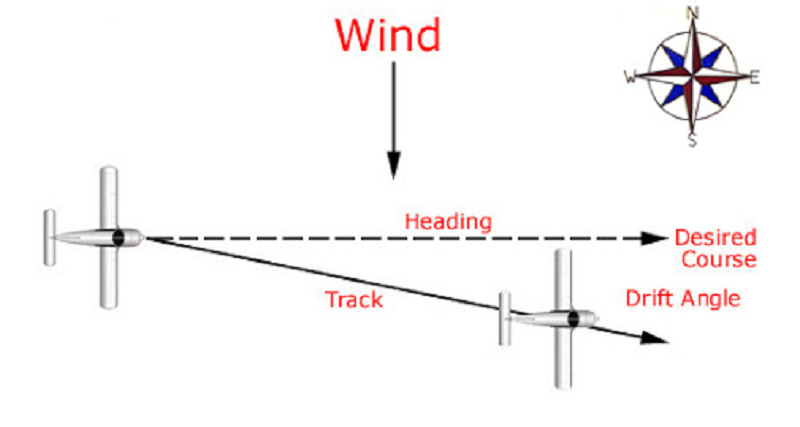
L1 CLO 6. Explain principles of navigation
The difference between the heading and track is the
IDC203085
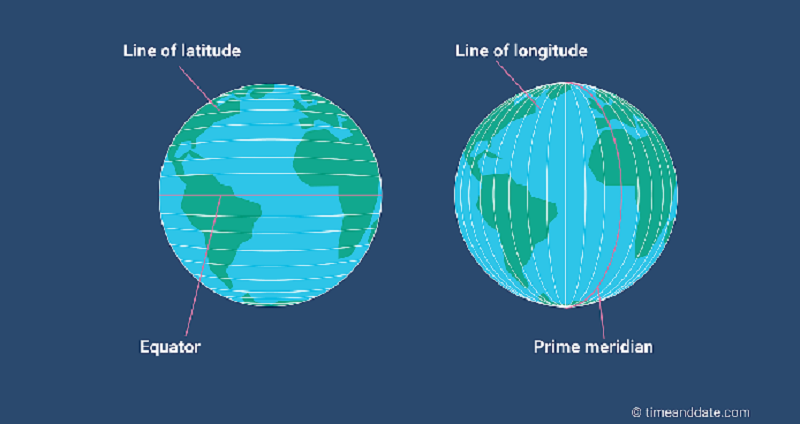
L1 CLO 6. Explain principles of navigation
The 0° reference for latitude is
IDC203068
L1 CLO 3. Explain Superheterodyne receivers
Beat Frequencies
IDC203065
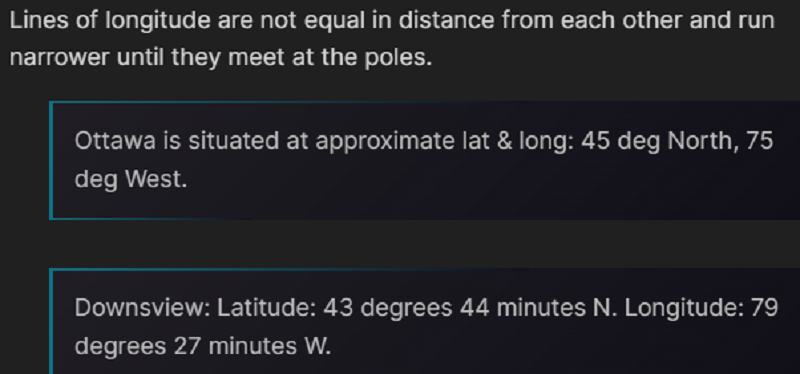
L1 CLO 6. Explain principles of navigation
Canada’s latitude would be expressed in “Degrees….”
IDC203057

L1 CLO 6. Explain principles of navigation
Bearing
IDC203076
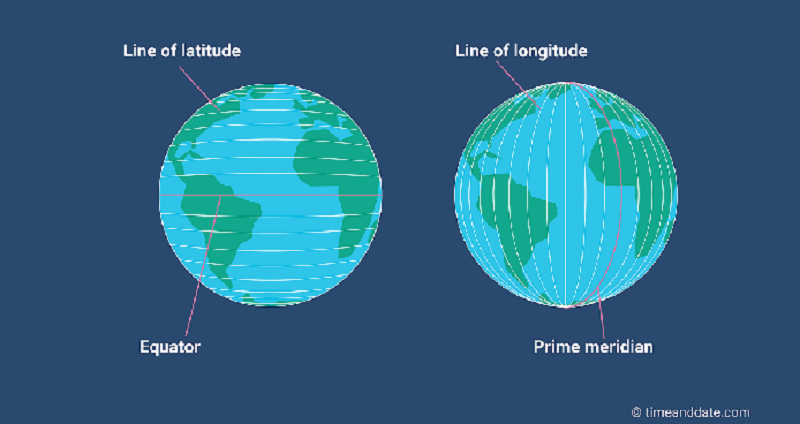
L1 CLO 6. Explain principles of navigation
Lines of longitude
IDC203071
L1 CLO 6. Explain principles of navigation
Magnetic bearing
IDC203077
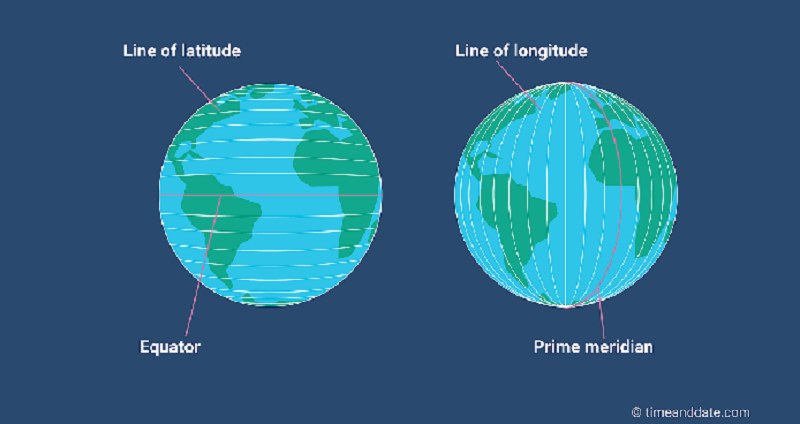
L1 CLO 6. Explain principles of navigation
The prime meridian
IDC203070
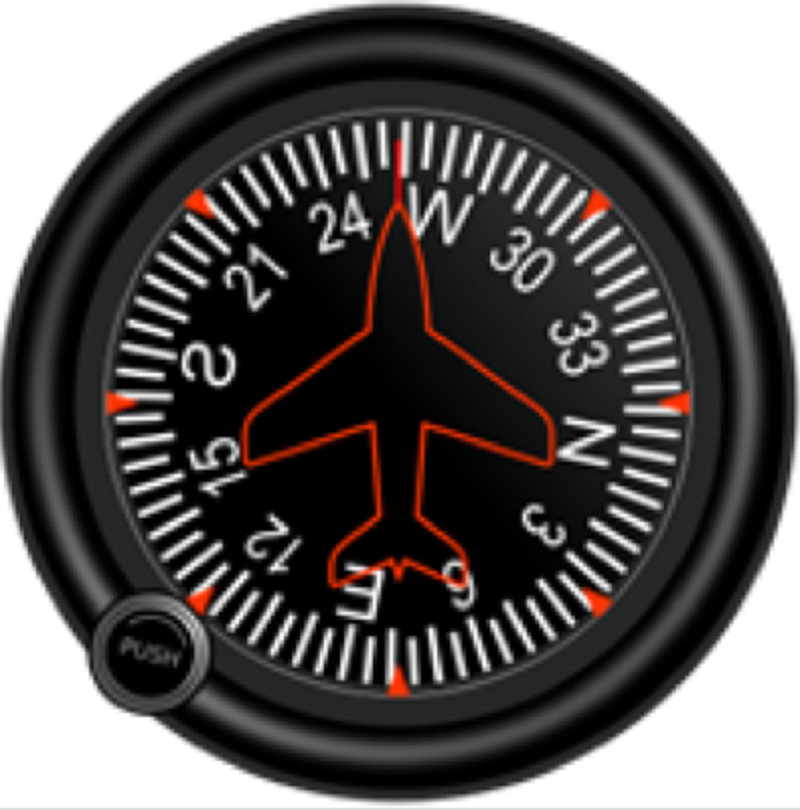

L1 CLO 6. Explain principles of navigation
A compass
IDC203072
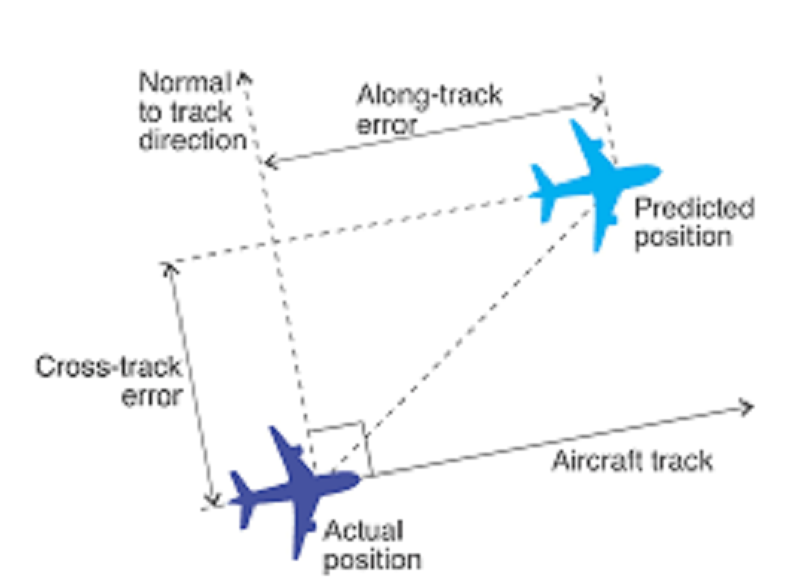
L1 CLO 6. Explain principles of navigation
The distance of the aircraft from the Desired Track is the
IDC203058