20 Fire

In coal and firecrackers, a chemical reaction takes place in which carbon is oxidized to carbon dioxide (CO2). Coal reacts with the oxygen in the air, while firecrackers contain oxygen rich compounds like potassium nitrate (KNO3) to ensure a quick reaction. A combustion reaction is a redox reaction between a fuel and an oxidizer, usually oxygen.
Our sun consists of 73,5 % hydrogen. This hydrogen does not combust in a chemical reaction, but it is transformed into helium in a nuclear fusion.
In coal and firecrackers, a chemical reaction takes place in which carbon is oxidized to carbon dioxide (CO2). Coal reacts with the oxygen in the air, while firecrackers contain oxygen rich compounds like potassium nitrate (KNO3) to ensure a quick reaction. A combustion reaction is a redox reaction between a fuel and an oxidizer, usually oxygen.
Our sun consists of 73,5 % hydrogen. This hydrogen does not combust in a chemical reaction, but it is transformed into helium in a nuclear fusion.

A fire is extinguished by taking away either oxygen, heat or fuel.
The extinguisher suffocates the fire by displacing the oxygen with carbon dioxide (CO2). However, it can reignite as soon as oxygen comes into contact with the hot oil again.
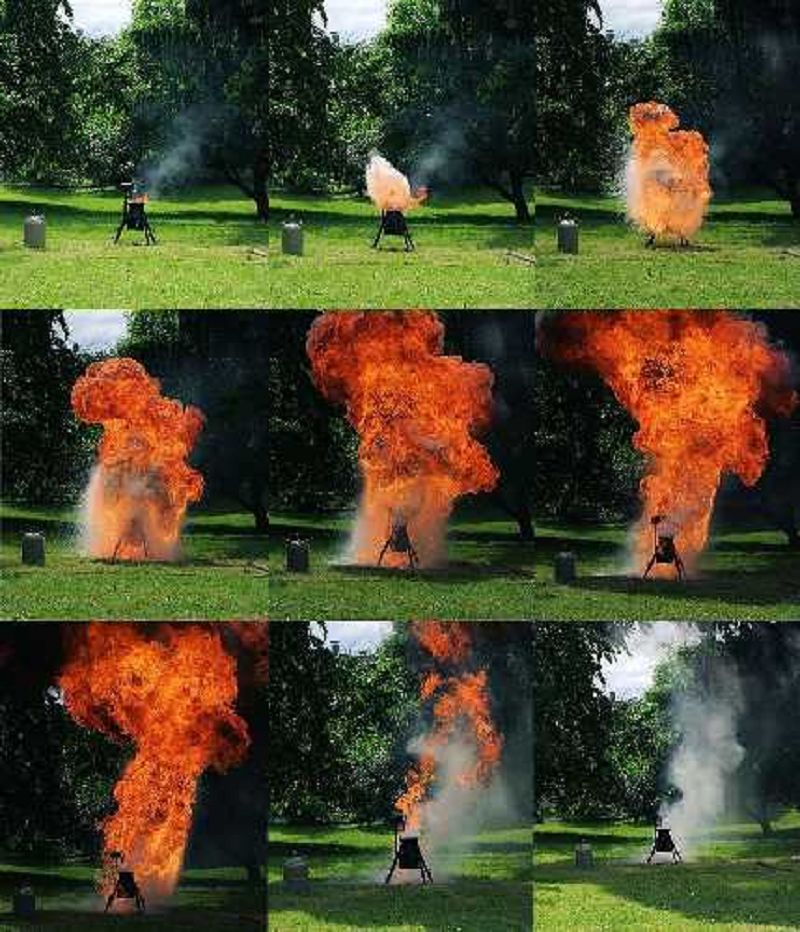
Water and oil do not mix, and since water is denser than oil it settles under the oil. The high temperature brings the water to boil and the expanding steam sprays the burning oil, causing a violent flame.
Covering the fire also separates the fire from oxygen thereby suffocating it. Additionally, it allows the oil to cool down enough.
A fire is extinguished by taking away either oxygen, heat or fuel.
The extinguisher suffocates the fire by displacing the oxygen with carbon dioxide (CO2). However, it can reignite as soon as oxygen comes into contact with the hot oil again.
Water and oil do not mix, and since water is denser than oil it settles under the oil. The high temperature brings the water to boil and the expanding steam sprays the burning oil, causing a violent flame.
Covering the fire also separates the fire from oxygen thereby suffocating it. Additionally, it allows the oil to cool down enough.
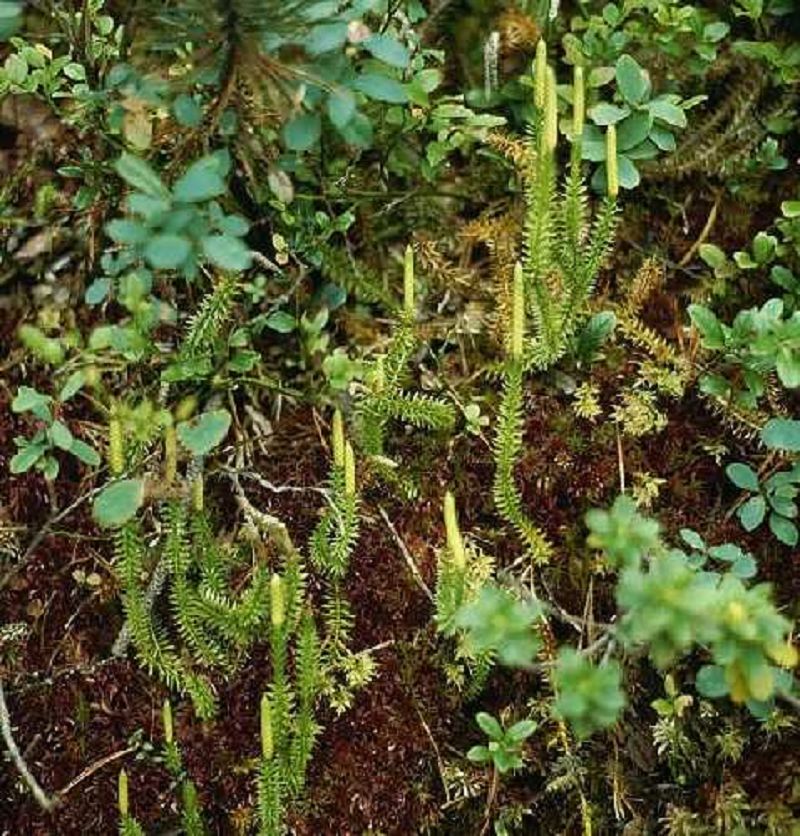

The diameter of a single dried lycopodium spore is about 33 micrometres. They are rich in oil and, because of their small size, they have a large surface area when sprayed in the air, which allows them to burn easily. These spores were already used as pyrotechnic effect in the Middle Ages and offer a less dangerous alternative to conventional fire spitting, using flammable liquids.

The diameter of a single dried lycopodium spore is about 33 micrometres. They are rich in oil and, because of their small size, they have a large surface area when sprayed in the air, which allows them to burn easily. These spores were already used as pyrotechnic effect in the Middle Ages and offer a less dangerous alternative to conventional fire spitting, using flammable liquids.


The iron in the burning wool is oxidized by the oxygen. The iron oxide that is formed is a solid containing both iron and oxygen atoms. The oxygen atoms that bind to the iron are responsible for the higher mass of the burned wool.
Organic substances like wood or wax get lighter when burning, because the products, CO2 and H2O (steam), are gases.
The iron in the burning wool is oxidized by the oxygen. The iron oxide that is formed is a solid containing both iron and oxygen atoms. The oxygen atoms that bind to the iron are responsible for the higher mass of the burned wool.
Organic substances like wood or wax get lighter when burning, because the products, CO2 and H2O (steam), are gases.
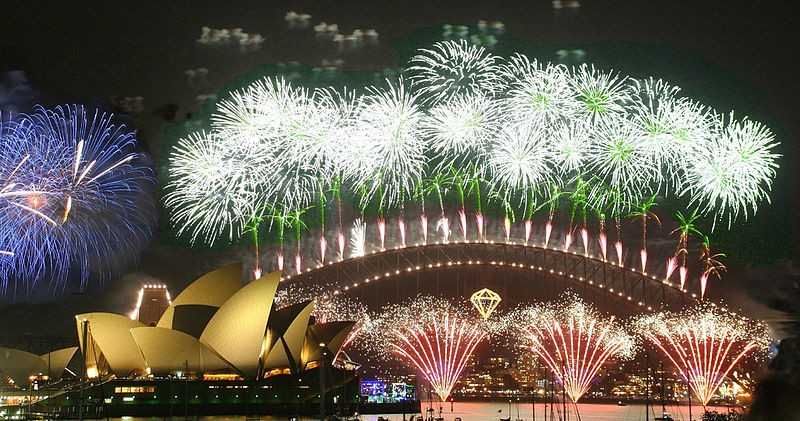

A firework glows green by adding a white salt. We are not talking about regular table salt, NaCl, but barium or copper salts. When the fireworks explode, the electrons of the barium and copper atoms become excited. This means that the electrons jump to a higher energy level. From there the electrons fall back down to their original level, releasing light. In the case of barium and copper this emitted light is green.

A firework glows green by adding a white salt. We are not talking about regular table salt, NaCl, but barium or copper salts. When the fireworks explode, the electrons of the barium and copper atoms become excited. This means that the electrons jump to a higher energy level. From there the electrons fall back down to their original level, releasing light. In the case of barium and copper this emitted light is green.

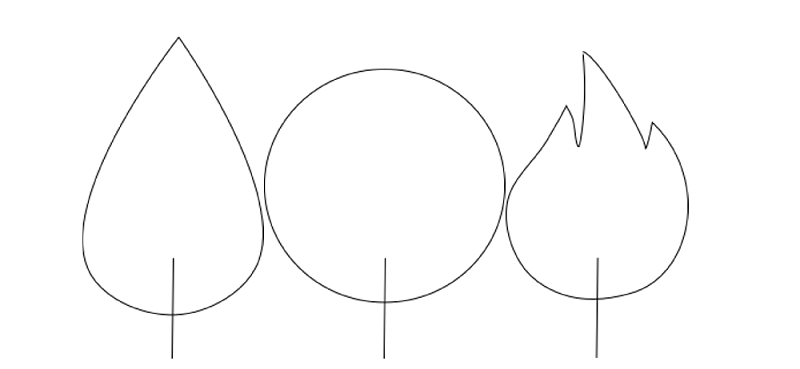
On earth, a flame has a teardrop shape. However, a flame on the International Space Station (ISS) has a round, spherical shape. On Earth, warm air rises as it has a lower density than cold air. Meanwhile, cool, oxygen-rich air is sucked into the flame from below. This gives the flame its drop-like shape. There is no gravity on the ISS, and therefore no direction in which light gases rise. This allows the burning gases of the candle to spread evenly around the wick and thus, create a spherical flame.

On earth, a flame has a teardrop shape. However, a flame on the International Space Station (ISS) has a round, spherical shape. On Earth, warm air rises as it has a lower density than cold air. Meanwhile, cool, oxygen-rich air is sucked into the flame from below. This gives the flame its drop-like shape. There is no gravity on the ISS, and therefore no direction in which light gases rise. This allows the burning gases of the candle to spread evenly around the wick and thus, create a spherical flame.


Phlogiston comes from the Greek and means "burned". It is a hypothetical substance that was introduced in the 17th century by Georg Ernst Stahl to explain combustions. At that time, it was thought that the phlogiston was found in all combustible materials and would escape when burned. Only after almost a century did the chemist Antoine de Lavoisier disprove this theory and prove that oxygen plays a decisive role in combustion.
Phlogiston comes from the Greek and means "burned". It is a hypothetical substance that was introduced in the 17th century by Georg Ernst Stahl to explain combustions. At that time, it was thought that the phlogiston was found in all combustible materials and would escape when burned. Only after almost a century did the chemist Antoine de Lavoisier disprove this theory and prove that oxygen plays a decisive role in combustion.

Our body has so-called heat receptors that signal heat to the brain when the temperature exceeds 42 °C. If we drink alcohol, also called ethanol, it interacts with these heat receptors. This interaction lowers the activation temperature of these receptors to about 34 °C. However, since the body temperature of a human being is around 37 °C, the body temperature is sufficient to trigger a feeling of heat.
Our body has so-called heat receptors that signal heat to the brain when the temperature exceeds 42 °C. If we drink alcohol, also called ethanol, it interacts with these heat receptors. This interaction lowers the activation temperature of these receptors to about 34 °C. However, since the body temperature of a human being is around 37 °C, the body temperature is sufficient to trigger a feeling of heat.

This quiz was written by the Luxembourg Science Center in Differdange. Visit the Centre to learn more about fire and other scientific topics!
This quiz was written by the Luxembourg Science Center in Differdange. Visit the Centre to learn more about fire and other scientific topics!
Before you discover your result, please leave us your e-mail address if you would like to be drawn amongst the highest scorers and thereby win free entrances to the Luxembourg Science Center!